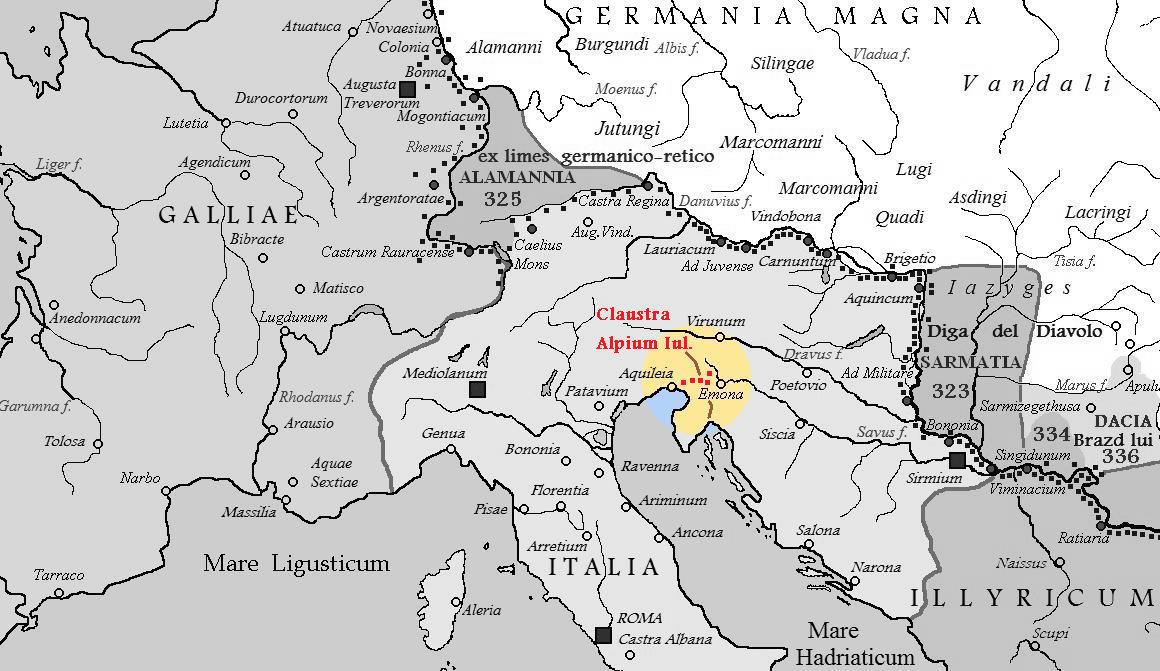
Claustra Alpium Iuliarum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 (
(
Claustra.org
Website dedicated to Claustra Alpium Iuliarum. * {{Coord, 45, 51, 49, N, 14, 6, 42, E, type:landmark_region:SI_dim:140km, display=title Roman walls Roman fortifications in Slovenia Linear earthworks
 (
(Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for 'Barrier of the Julian Alps'; hereby, the term Julian Alps refers to the wider mountainous and hilly region from the Julian Alps
The Julian Alps ( sl, Julijske Alpe, it, Alpi Giulie, , ) are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps that stretch from northeastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2,864 m at Mount Triglav, the highest peak in Slovenia. A large pa ...
to the Kvarner Gulf
The Kvarner Gulf (, or , la, Sinus Flanaticus or ), sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal wa ...
) was a defense system within the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
between Italia
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
that protected Italy from possible invasions from the East. It secured the Postojna Gate
The Postojna Gate, less often the Postojna Gap ( sl, Postojnska vrata), named after the local town of Postojna, is a major mountain pass of the Dinaric Alps. It lies in southwestern Slovenia, between the Hrušica Plateau to the north and the Javo ...
, the land link between the eastern and western part of the empire, and thus the Claustra represented an inner border defense of the empire. Unlike a linear rampart, the Claustra consisted of a series of interconnected fortifications with its center at Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum
(Latin for 'Fortress by the Cold River'), also simply ( sl, Kastra), referred to as (Castra relay station) in , was a Late-Roman fortress (''castrum'') which constituted the centre of ''Claustra Alpium Iuliarum'', an Ancient Roman defensive s ...
(in the area of today's town of Ajdovščina
Ajdovščina (; it, Aidussina,trilingual name "Haidenschaft, Aidussina, Ajdovščina" inGemeindelexikon, der im Reichsrate Vertretenen Königreiche und Länder. Bearbeit auf Grund der Ergebnisse der Volkszählung vom 31. Dezember 1900. Herausgege ...
, the Vipava Valley
The Vipava Valley (; sl, Vipavska dolina, german: Wippachtal, it, Valle del Vipacco) is a valley in the Slovenian Littoral, roughly between the village of Podnanos to the east and the border with Italy to the west. The main towns are Ajdovš ...
); other important fortresses were ''Ad Pirum
''Ad Pirum'' was a Roman fortress active during the time of the late Roman Empire. It is located on the Hrušica Plateau in southwestern Slovenia, in the hamlet of Hrušica in Podkraj. It was built in the 320s.
Structure and function
Excavati ...
'' on today's Hrušica Plateau and '' Tarsatica'', now a part of the city of Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
. They had been governed from the town of Aquileia
Aquileia / / / / ;Bilingual name of ''Aquileja – Oglej'' in: vec, Aquiłeja / ; Slovenian: ''Oglej''), group=pron is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river N ...
.
Development
In the year 6 AD theGreat Illyrian Revolt
The (Latin for 'War of the Batos') was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Roma ...
took place threatening the Roman heartland. Subsequently, in order to protect Italy, a series of walls and fortifications were gradually erected around the area of the strategic Postojna Gate. Most of the construction was done after 284 under Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
and Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
. Although this development was done subsequent to a major invasion of Northern Italy by the Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
in 271, Whittaker indicates that inner fortification lines were primarily aimed to secure the internal stability of the empire rather than keeping barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by som ...
s out. The fortification system included Forum Iulii (in the area of today's Cividale del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli ( fur, Cividât (locally ); german: Östrich; sl, Čedad) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Udine, part of the North-Italian Friuli Venezia Giulia ''regione''. The town lies above sea-level in the foothills of the e ...
), Tarsatica (in the area of today's Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
) and followed the valley of the Idrijca
The Juridical is a river flowing through the Idrija Hills and Cerkno Hills. It is long. It rises near Vojsko, flows towards northeast and after passing through Idrija turns to the northwest. After passing through Spodnja Idrija and Cerkno it jo ...
river. It stretched over the Postojna Gate to the hills south of Emona
Emona (early gkm, Ἤμονα) or Aemona (short for ) was a Roman castrum, located in the area where the navigable Ljubljanica river came closest to Castle Hill,
(in the area of today's Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
). In-depth fortifications along the Roman road Via Gemina
Via Gemina was the Roman road linking Aquileia and Emona (the modern Ljubljana). It was built in 14 AD by the legio XIII Gemina,. In spite of the name given by its constructors it was said it took its name, the "twin road", from the circumstance ...
started at the fortress of Castra ad Fluvio Frigido (the remains of which are today still visible in Ajdovščina
Ajdovščina (; it, Aidussina,trilingual name "Haidenschaft, Aidussina, Ajdovščina" inGemeindelexikon, der im Reichsrate Vertretenen Königreiche und Länder. Bearbeit auf Grund der Ergebnisse der Volkszählung vom 31. Dezember 1900. Herausgege ...
), which was the centre of the system, and ended at Nauportus
Nauportus ''(Navport, Navportus)'' ( grc, Ναύπορτον), was an ancient Roman town in Pannonia Superior (later 10th Italian region) on the road from Aquileia to Emona with a port at the Nauportus river, now the Ljubljanica River.
Strabo ...
(in the area of today's Vrhnika
Vrhnika (; german: Oberlaibach;''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 120. la, Nauportus) is a town in Slovenia. It is the seat of the Muni ...
). The hill fortress of Ad Pirum
''Ad Pirum'' was a Roman fortress active during the time of the late Roman Empire. It is located on the Hrušica Plateau in southwestern Slovenia, in the hamlet of Hrušica in Podkraj. It was built in the 320s.
Structure and function
Excavati ...
was typically manned with 500 soldiers but could keep up to 100,000 soldiers. Ad Pirum’s walls were unearthed by Austrian and Italian archeologists and shown to be at a height of 8 m and a thickness of 2 m; the wall towers were 10 m high.
Battles
Castra Alpium Iuliarum saw a number of battles. Early fortifications may have been useful in 169 when the Marcomanni attempted to enter Italy but proved inadequate when the Alemanni invaded Italy in 271. In 351Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germani ...
took Ad Pirum during his fight against his challenger Magnentius
Magnus Magnentius ( 303 – 11 August 353) was a Roman general and usurper against Constantius II from 350 to 353. Of Germanic descent, Magnentius served with distinction in Gaul under the Western emperor Constans. On 18 January 350 Magnentius ...
. Most importantly, the Battle of the Frigidus
The Battle of the Frigidus, also called the Battle of the Frigid River, was fought between 5 and 6 September 394 between the army of the Roman emperor Theodosius the Great and the army of the rebel ''augustus'' Eugenius (), in the eastern bor ...
took place in 394 between Castra and Ad Pirum. In this battle the eastern emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
prevailed over his western rival Eugenius
Eugenius (died 6 September 394) was a usurper in the Western Roman Empire (392–394) against Emperor Theodosius I. While Christian himself, Eugenius capitalized on the discontent in the West caused by Theodosius' religious policies targeting p ...
and by his victory secured Christianity as the main religion of the empire.
After the 5th century the Roman fortifications fell into disrepair. Today selected sections have been restored by archeologists.
Further reading
*References
External links
Claustra.org
Website dedicated to Claustra Alpium Iuliarum. * {{Coord, 45, 51, 49, N, 14, 6, 42, E, type:landmark_region:SI_dim:140km, display=title Roman walls Roman fortifications in Slovenia Linear earthworks