
Classical Anatolia is
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
during
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
. Early in that period, Anatolia was divided into several
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
kingdoms, most notably
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
in the west,
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
in the center and
Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
in the east. Anatolia fell under
Achaemenid Persian rule c. 550 BC. In the aftermath of the
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of th ...
, all of Anatolia remained under Persian control except for the Aegean coast, which was incorporated in the
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
in the 470s BC.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
finally wrested control of the whole region from Persia in the 330s BC. After Alexander's death, his conquests were split amongst several of his trusted generals, but were under constant threat of invasion from both the
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
and other powerful rulers in
Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
,
Pontus, and
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
.
The
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, the largest of Alexander's territories, and which included Anatolia, became involved in a disastrous war with
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
culminating in the battles of
Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
and
Magnesia. The resulting
Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
in (188 BC) saw the Seleucids retreat from Anatolia. The
Kingdom of Pergamum and the
Republic of Rhodes, Rome's allies in the war, were granted the former Seleucid lands in Anatolia. Anatolia subsequently became contested between the neighboring rivalling Romans and the
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
, which frequently culminated in the
Roman-Parthian Wars.
Anatolia came under
Roman rule entirely following the
Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
of 88–63 BC. Roman control of Anatolia was strengthened by a 'hands off' approach by Rome, allowing local control to govern effectively and providing military protection. In the early 4th century,
Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
established a new administrative centre at
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, and by the end of the 4th century a new
eastern empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
was established with
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
as its capital, referred to by historians as the Byzantine Empire from the original name,
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
.
In the subsequent centuries up to including the advent of the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the Parthians were succeeded by the
Sassanid Persians
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, who would continue the centuries long rivalry between Rome and Persia, which again culminated
in frequent wars on the eastern fringes of Anatolia.
Byzantine Anatolia
Byzantine Anatolia refers to the peninsula of Anatolia (modern day Turkey) during the rule of the Byzantine Empire. Anatolia would prove to be of vital importance to the empire following the Arabic conquest of the Levant and of Egypt during t ...
came under pressure of the
Muslim invasion
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
in the southeast, but most of Anatolia remained under Byzantine control until the
Turkish invasion of the 11th century.
Early antiquity

Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
had become the predominant power in western Anatolia by the 7th century BC, although often subject to
Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyri ...
control. The Lydian empire gained independence from Assyria by the end of the 7th century. The flourishing of Lydia during the first half of the 6th century BC is also dubbed the
Lydian Empire
Lydian may refer to:
* Lydians, an ancient people of Anatolia
* Lydian language, an ancient Anatolian language
* Lydian alphabet
** Lydian (Unicode block)
* Lydian (typeface), a decorative typeface
* Lydian dominant scale or acoustic scale, a m ...
period. Although the
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
peoples had existed in the area south of the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
(
Iranian Plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros ...
) from pre-historic times, their major influence began when the
Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
united them in 625 BC allowing them to sweep away the
Assyrian Empire
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyr ...
shortly after, when
Cyaxares
Cyaxares (Median language, Median: ; Old Persian: ; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ; Phrygian language, Old Phrygian: ; grc, wikt:Κυαξάρης, Κυαξαρης, Kuaxarēs; Latin: ; reigned 625–585 BCE) was the third king of the Medes.
C ...
(625–585 BC) led the invasion in 612 BC. Lydian king
Sadyattes (ruled c. 624/1–610/609 BC) joined forces with Cyaxares the Mede to drive the
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
out of Anatolia. This alliance was short lived, since his successor
Alyattes (ruled c. 605–560 BC) found himself being attacked by Cyaxares, although the neighbouring king of
Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
intervened, negotiating a peace in 585 BC, whereby the
Halys River Halys may refer to:
* Health-adjusted life years (HALYs), a type of disability-adjusted life year which are used in attempts to quantify the burden of disease or disability in populations
* Halys River, a western name for the Kızılırmak River (T ...
in north central Anatolia was established as the Medes' frontier with Lydia.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
writes:
:"On the refusal of Alyattes to give up his supplicants when Cyaxares sent to demand them of him, war broke out between the Lydians and the Medes, and continued for five years, with various success. In the course of it the Medes gained many victories over the Lydians, and the Lydians also gained many victories over the Medes."
Alyattes issued minted electrum coins, and his successor
Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was r ...
, ruling c. 560–546 BC, became known for being the first to issue
gold coin
A gold coin is a coin that is made mostly or entirely of gold. Most gold coins minted since 1800 are 90–92% gold (22karat), while most of today's gold bullion coins are pure gold, such as the Britannia, Canadian Maple Leaf, and American Buf ...
s.
The southeast of Anatolia was ruled by the
Assyrian Empire
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyr ...
.
Tabal was a
Luwian
The Luwians were a group of Anatolian peoples who lived in central, western, and southern Anatolia, in present-day Turkey, during the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. They spoke the Luwian language, an Indo-European language of the Anatolian sub-fam ...
speaking
Neo-Hittite
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwester ...
kingdom of South Central Anatolia which fell under Assyrian rule in 713 BC.
Persian rule

The Medean Empire turned out to be short lived (c. 625 – 549 BC). By 550 BC, the
Median Empire
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
of eastern Anatolia, which had existed for barely a hundred years, was suddenly torn apart by a Persian rebellion in 553 BC under Cyrus II (
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
c. 600 BC or 576–530 BC), overthrowing his grandfather
Astyages
Astyages ( Median: ; Akkadian: ; Ancient Greek: grc, Αστυαγης, Astuagēs, , romanized: , , romanized: ; la, Astyages, , ; reigned 585–550 BC) was the last king of the Median Empire. The son of Cyaxares; he was dethroned in 550 BC by ...
(585–550 BC) in 550 BC. The Medes then became subject to the Persians.
The Persians, who had scant resources for governing their vast empire, ruled relatively benignly as conquerors, attempting to obtain the cooperation of the local elite in governance. They ruled their vassal states by appointing local rulers, or
satraps
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
with responsibility for their satrapies (Greek: Satrapeia). However, the Greeks referred to these satraps as 'tyrants', meaning they were neither democratically elected or derived authority from
dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
. The
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
Persian Empire, continued its expansion under
Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
(521–486 BC). The
satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
system of local governors continued to be used and upgraded and other governmental upgrades were carried out.
[
Anatolia was carved up under Persian ]hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
into regional administrations (Satrapies or provinces, depending on sources) which replaced the hegemonic kingdoms prior to the conquest. Kings were replaced by Satraps. ''Satrap'' and ''Satrapy'' corresponding to Governor and Province respectively. The administration was hierarchical, often referred to as Great, Main and Minor Satrapies. The main administrative units in Anatolia were the Great Satrapy of Sardis (Sparda/Lydia) in the west, Main satrapy of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
centrally, Main Satrapy of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
in the north-east and Main Satrapy of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
in the south-east. These correspond to Herodotus's Districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
I-IV. However, the number of satrapies and their boundaries varied over time.
Within the hierarchical system, Sparda was a Great Satrapy consisting of the Major Satrapies of Sarda (including minor satrapies of Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of ...
, Greater Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
, Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
, and Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek D ...
) and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
. Note that Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
and Aeolis
Aeolis (; grc, Αἰολίς, Aiolís), or Aeolia (; grc, Αἰολία, Aiolía, link=no), was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islan ...
were not considered separate entities by the Persians, while Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
was included in semi-autonomous Caria, and Sparda included the offshore islands. Greater Phrygia included Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west b ...
, Pisidia
Pisidia (; grc-gre, Πισιδία, ; tr, Pisidya) was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Pamphylia, northeast of Lycia, west of Isauria and Cilicia, and south of Phrygia, corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Ant ...
, and Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
. Cappadocia initially included Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, also known as Cappadocia-beside-the-Taurus, and Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
.
Assyria was a Main Satrapy of the Great Satrapy of Babylon, and included Cilicia, while Armenia was a Main Satrapy within the Great Satrapy of Media.[Encyclopaedia Iranica: Achaemanid Satrapies]
/ref>
Anatolia remained one of the most principal regions of the empire during its entire existence. During the reign of Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
, the Royal Road
The Royal Road was an ancient highway reorganized and rebuilt by the Persian king Darius the Great (Darius I) of the first (Achaemenid) Persian Empire in the 5th century BC. Darius built the road to facilitate rapid communication on the western ...
, which directly linked the city of Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
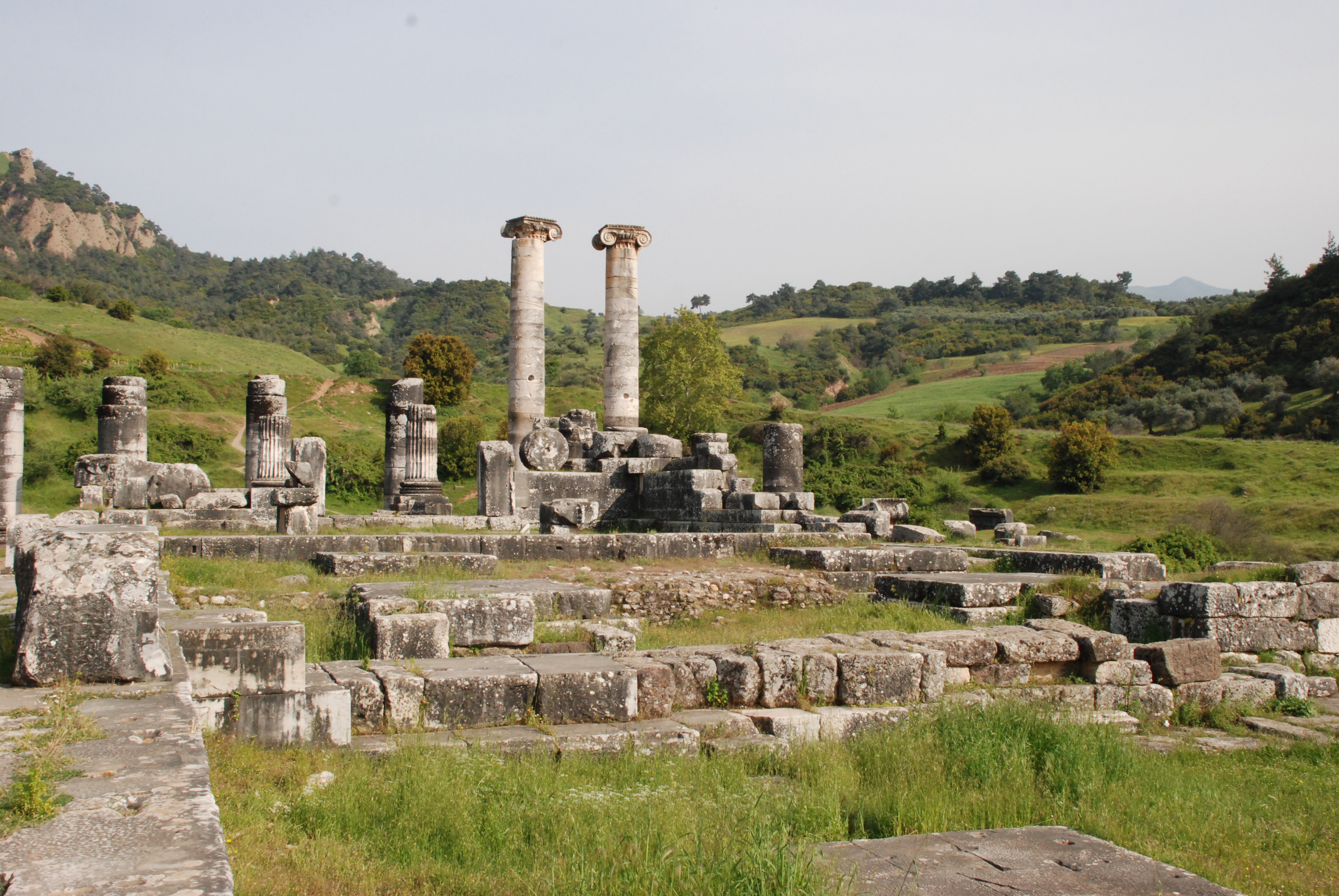
with the western Anatolian city of Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
.
The fall of Lydia (546 BC) and the Lydian revolt
 By 550 BC Lydia controlled the Greek coastal cities, who paid tribute, and most of Anatolia, except
By 550 BC Lydia controlled the Greek coastal cities, who paid tribute, and most of Anatolia, except Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
, Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
. In 547 BC, King Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was r ...
, who had amassed great wealth and military power, but concerned by the growing Persian power and obvious intent, took advantage of the instability of the Persian revolt and besieged and captured the Persian city of Pteria in Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
.[
]Cyrus The Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
then marched with his army against the Lydians. Although the Battle of Pteria
The Battle of Pteria ( grc, Πτερία) was fought in 547 BC between the Persian forces of Cyrus the Great and the Lydian forces of Croesus. Both armies suffered heavy casualties in this indecisive battle.
Background
Croesus learned of the su ...
led to a stalemate, the Lydians were forced to retreat to their capital city of Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
. Some months later the Persian and Lydian kings met at the Battle of Thymbra
The Battle of Thymbra was the decisive battle in the war between Croesus of the Lydian Kingdom and Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire. Cyrus, after he had pursued Croesus into Lydia after the drawn Battle of Pteria, met the remains of Cr ...
. Cyrus won, capturing Sardis after a 14-day siege, Croesus giving himself up to Cyrus. According to the Greek author Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
, Cyrus treated Croesus well and with respect after the battle, but this is contradicted by the Nabonidus Chronicle, one of the Babylonian Chronicles (although whether or not the text refers to Lydia's king or prince is unclear).Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
, also known as the Satrapy of Lydia and Ionia, although there was an unsuccessful rebellion led by Pactyas
Pactyes was the Lydian put in charge of civil administration and gathering Croesus's gold when Lydia was conquered by Cyrus the Great of Persia around 546 BC:
He led a revolt against Cyrus and Tabalus, the Persian military commander or satrap w ...
(Pactyes), the leader of the civil administration, against Tabalus, the Persian military commander (satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
) (546–545 BC), shortly thereafter. Once Lydia had been subdued, Cyrus returned to deal with problems in the East leaving a garrison to assist in the governing of his new acquisition. Almost immediately Pactyas, who had been given the responsibility of raising tributes, raised a mercenary army from neighboring Greek cities and besieged Tabulus in the citadel. Herodotus' account that Cyrus intended to enslave the Lydians seems unsubstantiated. Pactyas soon found that he had no allies and furthermore that Cyrus was acting swiftly to put down the rebellion, sending Mazares
Mazares (Median: ''Mazdara'', grc, Μαζάρης) was a Median general who defected to Cyrus the Great when the latter overthrew his grandfather, Astyages and formed the Persian Empire. Mazares is mentioned by Herodotus as a Median general in th ...
(545–544 BC), one of his generals to restore order. Pactyas subsequently fled to the coast and took refuge in the Aeolian city of Cyme. Mazares demanded that Cyme release Pactyas to him. Fearing retribution, the Cymeans sent him to Mytilene
Mytilene (; el, Μυτιλήνη, Mytilíni ; tr, Midilli) is the capital of the Greek island of Lesbos, and its port. It is also the capital and administrative center of the North Aegean Region, and hosts the headquarters of the University o ...
on the island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, Λέσβος, Lésvos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the nar ...
. On hearing that the Mytilenians were negotiating a price for Pactyas, the destination was changed to Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mast ...
, but they too handed him over to the Persians.[''From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire'']
Pierre Briant
Pierre Briant (born 30 September 1940 in Angers) is a French Iranologist, Professor of History and Civilisation of the Achaemenid World and the Empire of Alexander the Great at the Collège de France (1999 onwards), Doctor Honoris Causa at the Uni ...
, Eisenbrauns: 2002, [Aristodicus of Cyme and the Branchidae. Truesdell S. Brown. The American Journal of Philology Vol. 99, No. 1 (Spring, 1978), pp. 64–78]
/ref>
Mazares was followed by Harpagus
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus ( Ancient Greek Ἅρπαγος; Akkadian: ''Arbaku''), was a Median general from the 6th century BC, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during th ...
(544–530 BC) on his death, and then Oroetus (530–520 BC). Oroetus became the first satrap recorded as demonstrating insubordination with respect to the central power of Persia. When Cambyses Cambyses may refer to:
* Cambyses I, King of Anshan 600 to 559 BCE
* Cambyses II, King of Persia 530 to 522 BCE
* Cambyses, ancient name of the Iori river in the South Caucasus
* ''Cambyses'', a tragedy (published 1569) by Thomas Preston (writer)
...
(530–522 BC), who succeeded his father Cyrus, died, the Persian Empire was in chaos prior to Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
(522–486 BC) finally securing control. Oroetus defied Darius' orders to assist him, whereupon Bagaeus
Bagaeus ( Old Iranian: ''Bagaya'') (fl. circa 520-517 BCE), son of Artontes, was an Achaemenid nobleman, who was ordered by Darius I to kill the rebellious satrap of Lydia, Oroetes. Oroetes was accused of having killed Mitrobates, the satrap of ...
(520–517 BC) was sent by Darius to arrange his murder.
The subjugation of Ionia and the Ionian Revolt (500–493 BC)
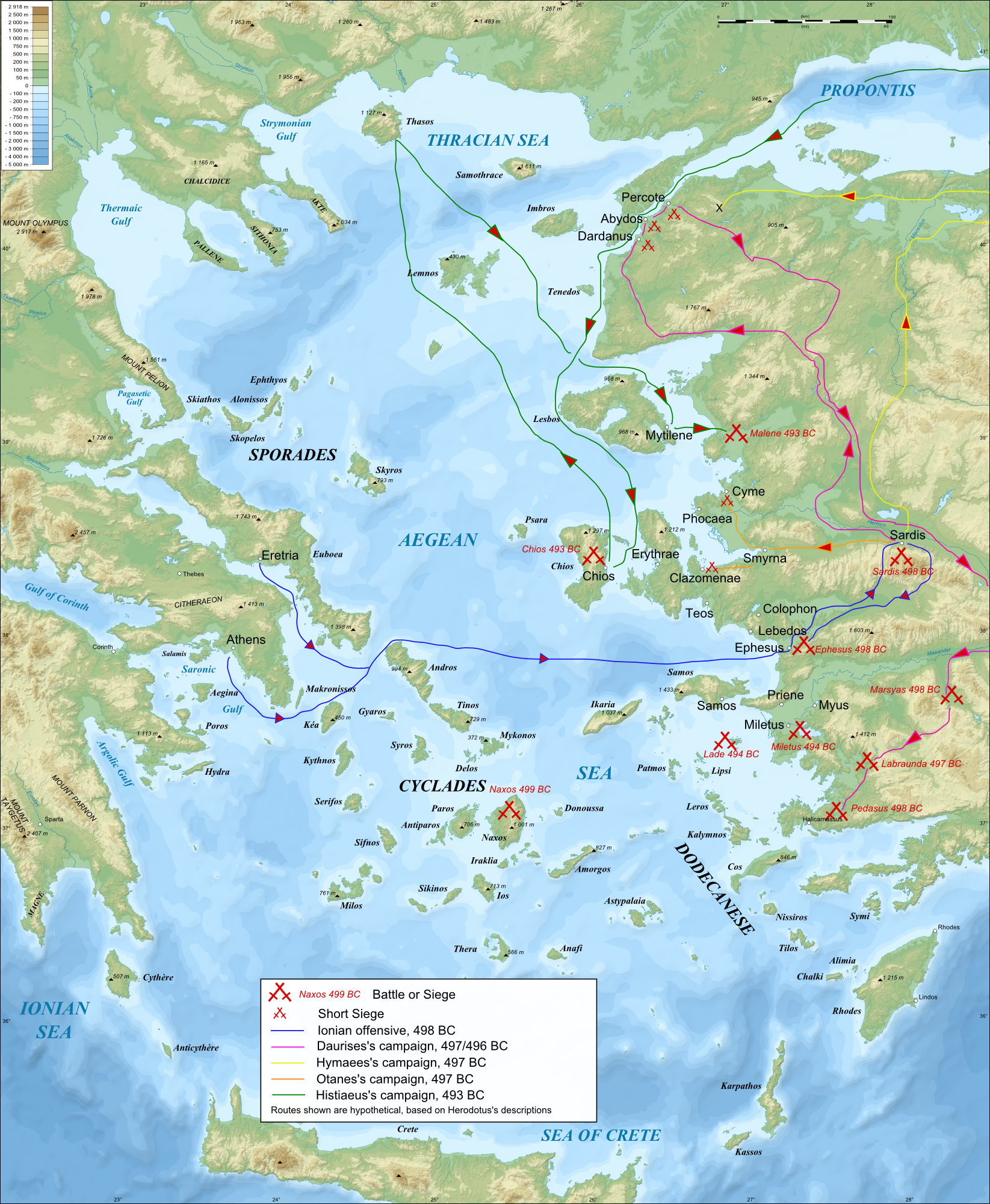
Cyrus
Cyrus (Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus ...
had initially unsuccessfully tried to persuade the Aeolian and Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
n cities to rebel against Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
. At the time of the fall of Sardis, only one city, Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' ( exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ...
, had made terms with Cyrus. According to Herodotus, when Lydia fell to Cyrus, the Greek cities begged him to allow them to exist within the former Lydian territories on similar terms to those they had earlier enjoyed, Cyrus pointed out that they were too late, and they started building defensive structures. They appealed to Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
for help, but Sparta refused, instead warning Cyrus not to threaten the Greeks. Cyrus was unimpressed, but nevertheless headed east without bothering them further. This account seems somewhat conjectural.[
Following the defeat of the Lydian revolt, Mazares began to reduce the other cities in the Lydian lands one by one, starting with ]Priene
Priene ( grc, Πριήνη, Priēnē; tr, Prien) was an ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called th ...
and Magnesia. However, Mazares died, and was replaced by another Mede, Harpagus
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus ( Ancient Greek Ἅρπαγος; Akkadian: ''Arbaku''), was a Median general from the 6th century BC, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during th ...
(544–530 BC), who completed the subduing of Asia Minor. Some communities, rather than face a siege, chose exile, including Phocaea
Phocaea or Phokaia (Ancient Greek: Φώκαια, ''Phókaia''; modern-day Foça in Turkey) was an ancient Ionian Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Greek colonists from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, in ...
to Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
and Teos
Teos ( grc, Τέως) or Teo was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus. It was founded by Minyans from Orchomenus, Ionians and Boeotians, but the date of its foundation is unknown. Teos was ...
to Abdera in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
. Although our principal source for this period, Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
of Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was locate ...
, implies this was a swift process, it is more likely that it took four years to subdue the region completely, and the Ionian colonies on the coastal islands remained largely untouched.Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
(Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), ...
V, VI) around 500 BC Aristagoras, tyrant of Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' ( exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ...
approached Artaphernes
Artaphernes ( el, Ἀρταφέρνης, Old Persian: Artafarna, from Median ''Rtafarnah''), flourished circa 513–492 BC, was a brother of the Achaemenid king of Persia, Darius I, satrap of Lydia from the capital of Sardis, and a Persian gener ...
, satrap of Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
(c. 492 – 480), for assistance in aiding some citizens of Naxos
Naxos (; el, Νάξος, ) is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best ab ...
who had been forced to flee (C. 502 BC) and seek his help. He planned to annex not only Naxos but also the Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name ...
and Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest poi ...
. With the permission of Darius he gathered a force to invade Naxos, but the expedition was a failure. Motivated by fear of the wrath of Darius he prevailed upon those in the expedition to mount an insurrection and subsequently went to Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
(unsuccessfully) and Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
(successfully) for help. The Ionians attacked Sardis in approximately 499 BC, but Artarphernes managed to hold the acropolis, although the lower city was burnt. The Ionians retreated but were defeated by pursuing Persians at Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
in 498 BC, whereupon the Athenian ships withdrew. However, over the next two years open rebellion broke out from Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
to Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
. Eventually Aristagoras realized the futility of the exercise, as Artaphernes won a number of victories, and fled. Miletus fell to the Persian forces in 494 BC, following the Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade ( grc, Ναυμαχία τῆς Λάδης, translit=Naumachia tēs Ladēs) was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities (joined by the Lesbi ...
, who wreaked vengeance. The last pockets of resistance were obliterated by 493 BC. Herodotus depicts these events as the catalyst to the Graeco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
(499–449 BC).[
However, Herodotus, as is so often our only source, had an agenda in his imprecise accounts, which do not fit well with what is known of the period. It is likely that the affair in Naxos represented a democratic revolt against the tyrants.][
]
Other satrapies
Hellespontine Phrygia

Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of ...
lay to the north of the Lydia/Sardis satrapy, incorporating Troad
The Troad ( or ; el, Τρωάδα, ''Troáda'') or Troas (; grc, Τρῳάς, ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula ( Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the � ...
, semi-autonomous Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
, and Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
with its capital at Dascylium
Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion ( grc, Δασκύλιον, Δασκυλεῖον), also known as Dascylus, was a town in Anatolia some inland from the coast of the Propontis, at modern Ergili, Turkey. Its site was rediscovered in 1952 and ...
(modern day Ergili) on the south of the Hellespont
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
. Previously it was part of the Kingdom of Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
. Mitrobates
Mitrobates (Old Persian: , Ancient Greek: ); (fl.c. 525 - 520 BC) was an Achaemenid satrap of Daskyleion (Hellespontine Phrygia) under the reigns of Cyrus the Great, who nominated him for the role, and Cambyses. After Cambyses died, and dur ...
was a satrap, and one of the officials killed by Oroetes
Oroetus, or Oroetes (Old Iranian: ''Arvita'', Ancient Greek: ''Ὀροίτης''), was a Persian Satrap of Lydia (c. 530-520 BC), during the reigns of Cyrus the Great, Cambyses and Darius the Great, succeeding Harpagus, and being followed by ...
(Oroetus), satrap of Sparda (Sardis), in the 520s. Because of its strategic position between Europe and Asia it was the launching pad for expeditions to subdue Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and Macedonia. Arsites was the last Achaemenid satrap of Dascylium (350–334 BC) according to Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual pr ...
, committing suicide after the Persian defeat at the battle of Granicus in 334 BC at the hands of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.[
]
Greater Phrygia
Greater Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
was a minor satrapy of Sparda, with its capital at Celaenae. It concluded Lycaonia, Pisidia, and Pamphylia.
Semi-autonomous jurisdictions
Cilicia
Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
remained a semi-independent minor satrapy under both Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was r ...
of Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
, and under Persian rule, although paying tribute. Similarly Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
remained under petty local dynasts, with allegiance to Persia.
Mysia
Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
was ruled by its own dynasty within the minor satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of ...
.
Caria
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
was a satrap of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
which included Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
as well as the islands of Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mast ...
, Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
, and Cos
Cos, COS, CoS, coS or Cos. may refer to:
Mathematics, science and technology
* Carbonyl sulfide
* Class of service (CoS or COS), a network header field defined by the IEEE 802.1p task group
* Class of service (COS), a parameter in telephone syst ...
at times. The appointed local ruler Hecatomnus
Hecatomnus of Mylasa or Hekatomnos ( el, Ἑκατόμνος, Carian: 𐊴𐊭𐊪𐊵𐊫 ''k̂tmno'' “under-son, descendant(?)”) was an early 4th-century BC ruler of Caria. He was the satrap (governor) of Caria for the Persian Achaemenid k ...
took advantage of his position. He gained for his family an autonomous hand in control of the province by providing the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
with regular tribute, avoiding the look of deception. His son Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by ...
continued in this manner, and expanded upon the groundwork laid by his father. He first removed the official capital of the satrap from Mylasa
Milas ( grc, Μύλασα, Mylasa) is an ancient city and the seat of the district of the same name in Muğla Province in southwestern Turkey. The city commands a region with an active economy and very rich in history and ancient remains, the ter ...
to Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was locate ...
, gaining a strategic naval advantage as the new capital was on the ocean. On this land he built a strong fortress and built up a strong navy. He shrewdly used this power to guarantee protection for the citizens of Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mast ...
, Kos
Kos or Cos (; el, Κως ) is a Greek island, part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 36,986 (2021 census), ...
, and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
as they proclaimed independence from Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
Greece. Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by ...
did not live to see his plans realized fully, and his position went to his widow Artemisia. The local control over Caria remained in Hecatomnus
Hecatomnus of Mylasa or Hekatomnos ( el, Ἑκατόμνος, Carian: 𐊴𐊭𐊪𐊵𐊫 ''k̂tmno'' “under-son, descendant(?)”) was an early 4th-century BC ruler of Caria. He was the satrap (governor) of Caria for the Persian Achaemenid k ...
's family for another 20 years before the arrival of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.
Greco-Persian Wars 499–449 BC
 The preceding events of the
The preceding events of the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
marked the beginning of half a century of conflict between the superpowers that faced each other across the Aegean. The Persians were already in Europe, with a presence in both Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and Macedonia, a position they consolidated following the suppression of the revolt between 492 and 486 BC under Mardonius and later by Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
.
 From the Greek perspective the first war was when Darius assembled a fleet in
From the Greek perspective the first war was when Darius assembled a fleet in Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
and Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a sepa ...
under Datis
Datis or Datus ( el, Δάτης, Old Iranian: *Dātiya-, Achaemenid Elamite: Da-ti-ya), was a Median noble and admiral who served the Persian Empire during the reign of Darius the Great. He was familiar with Greek affairs and maintained connecti ...
and Artaphernes
Artaphernes ( el, Ἀρταφέρνης, Old Persian: Artafarna, from Median ''Rtafarnah''), flourished circa 513–492 BC, was a brother of the Achaemenid king of Persia, Darius I, satrap of Lydia from the capital of Sardis, and a Persian gener ...
(son of the satrap Artaphernes
Artaphernes ( el, Ἀρταφέρνης, Old Persian: Artafarna, from Median ''Rtafarnah''), flourished circa 513–492 BC, was a brother of the Achaemenid king of Persia, Darius I, satrap of Lydia from the capital of Sardis, and a Persian gener ...
) and sailed for Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopi ...
in 490 BC, first taking islands such as Naxos which it had failed to capture in 500, in addition to disembarking at Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
where they were soundly defeated. Greek (Herodotus) and Persian sources (for instance see Dio Chrysostom
Dio Chrysostom (; el, Δίων Χρυσόστομος ''Dion Chrysostomos''), Dion of Prusa or Cocceianus Dio (c. 40 – c. 115 AD), was a Greek orator, writer, philosopher and historian of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. Eighty of hi ...
XI 148) differ in terms of the significance of Marathon, great victory or minor skirmish.
Greece was spared further invasions when an unplanned interbellum (490–480 BC) occurred due to an insurrection in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
in 486 BC and Darius' illness and death that year. By 480 BC, Darius' successor, his son Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of D ...
(485–465 BC) had amassed a huge army, and marched into Europe by crossing the Hellespont by means of pontoon bridges
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, uses floats or shallow- draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the supports limits the maximum load that they can carry. ...
, meeting and defeating the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lastin ...
later that year and razing Athens. However, the loss of the Persian fleet at the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
gave command of the sea to the Greeks, and Xerxes retreated back to Asia. The following year (479 BC) the Greeks won a decisive land victory at Platea in which Mardonius was also killed, followed by another naval victory at Mycale
Mycale (). also Mykale and Mykali ( grc, Μυκάλη, ''Mykálē''), called Samsun Dağı and Dilek Dağı (Dilek Peninsula) in modern Turkey, is a mountain on the west coast of central Anatolia in Turkey, north of the mouth of the Maeander an ...
. Greece then went on the offensive, capturing Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
and Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
and thus controlling the Hellespont
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
.[
Following these Persian reverses, the Greek cities of Asia Minor again rebelled. The focus of the war now moved to the Aegean islands with the formation of the ]Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
in 477 BC. Over the next 30 years Greek forces continued to harass Persian garrisons, invading Asia Minor in the 460s with an important victory at the Battle of the Eurymedon
The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth ...
c. 469. The wars effectively ended in 449 BC with the Battle of Salamis-in-Cyprus, a peace being declared, which Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
refers to as the Peace of Callias, although this is debated.
Skirmishes continued, and the Greek cities of Asia Minor continued to be pawns in the struggles.

Final years: the invasion of the Macedonians 358–330 BC
 The later years of the Empire were beset by internal turmoil.
The later years of the Empire were beset by internal turmoil. Artaxerxes III
Ochus ( grc-gre, Ὦχος ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
(358–338 BC) achieved the throne by violent means and was rumored to have been murdered himself. His successor Artaxerxes IV Arses
Arses ( peo, *R̥šā; grc-gre, Ἀρσής), also known by his regnal name Artaxerxes IV (; peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was the twelfth Achaemenid King of Kings from 338 to 336 BC.
Arses ascended ...
(338–336 BC) also met a violent end, paving the way for the accession of his nephew Darius III
Darius III ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; c. 380 – 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC.
Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Dariu ...
(336–330), then Satrap of Armenia. Darius proved to be the last king to rule since in the same year Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
became king of neighboring Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
. Within a year Alexander was in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, putting down rebellions and securing his northern frontiers. Alexander then turned his attention to the east, landing on the shores of Anatolia near Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
on the Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles s ...
peninsula in 334 BC, and soon crossing the Hellespont
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
into Asia (335 BC). Initially the Persians offered little resistance and Alexander began to liberate Greek city states.
 Advancing on
Advancing on Dascylium
Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion ( grc, Δασκύλιον, Δασκυλεῖον), also known as Dascylus, was a town in Anatolia some inland from the coast of the Propontis, at modern Ergili, Turkey. Its site was rediscovered in 1952 and ...
he first encountered Persian troops at the Battle of Granicus
The Battle of the Granicus in May 334 BC was the first of three major battles fought between Alexander the Great of Macedon and the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The battle took place on the road from Abydus to Dascylium, at the crossing of the ...
in 334 BC. This battle occurred on the Granicus (Biga Çayı) river near modern-day Biga
Biga may refer to:
Places
* Biga, Çanakkale, a town and district of Çanakkale Province in Turkey
* Sanjak of Biga, an Ottoman province
* Biga Çayı, a river in Çanakkale Province
* Biga Peninsula, a peninsula in Turkey, in the northwest par ...
in Çanakkale, on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via t ...
. The Persians were routed and the Greeks moved down the Aegean coast, taking Sardis, and besieging many cities. From the Aegean they moved east along the Mediterranean coast as far as Side
Side or Sides may refer to:
Geometry
* Edge (geometry) of a polygon (two-dimensional shape)
* Face (geometry) of a polyhedron (three-dimensional shape)
Places
* Side (Ainis), a town of Ainis, ancient Thessaly, Greece
* Side (Caria), a town of a ...
in Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
(333 BC), securing all of the Anatolian naval bases. From Side they moved north into the interior of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
before returning through the Cilician Gates
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates ha ...
to the Cilician coast, and then east towards the Gulf of Issus
The Gulf of Alexandretta or İskenderun ( tr, İskenderun Körfezi) is a gulf of the eastern Mediterranean or Levantine Sea. It lies beside the southern Turkish provinces of Adana and Hatay.
Names
The gulf is named for the nearby Turkish city ...
. It was there they encountered and defeated Darius at the Battle of Issus
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on November 5, 333 BC between the Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III. It was the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of ...
(333 BC).
On reaching Mount Amanus
The Nur Mountains ( tr, Nur Dağları, "Mountains of Holy Light"), formerly known as Alma-Dağ, the ancient Amanus ( grc, Ἁμανός), medieval Black Mountain, or Jabal al-Lukkam in Arabic, is a mountain range in the Hatay Province of south ...
, scouts found the Persians advancing through the plains of Issus. Realizing that the terrain at this point favored his smaller army, Alexander attacked the Persians, who were effectively squeezed by the Macedonians. Although Darius escaped, back across the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
river, leaving the rest of his family in Alexander's hands, the battle marked the end of Persian hegemony in Anatolia. Alexander then turned his attention to Syria, the eastern Mediterranean coast and Egypt.
Hellenistic period
Alexander the Great
Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
(336–323 BC) succeeded his father King Philip of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
(359 BC – 336 BC) on his assassination in 336 BC. Alexander invaded Asia Minor in 335 BC with a combined land and naval force, and by 333 BC had effectively vanquished the Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ns in the Anatolian lands, and ending the Achaemenid Empire by 330 BC. However, he devoted the rest of his life to military conquests further east, dying in 323 BC. Thus he fulfilled his father's ambition of liberating the Greeks of Asia Minor.
Administratively he continued the satrapy system, his strategy being to respect and win support from the conquered (or liberated) people's, respecting their traditions. he also positioned himself as a crusader for pan-hellenism, rescuing the Greek people of Anatolia from tyrants and oligarchs. In addition he colonised the lands he captured with Greek settlers, spreading Greek culture. One of the controversies is the extent to which the Macedonian Empire represented either rupture or continuity. The ascendancy of Greek, and by extension European culture in an area predominantly influenced by Asia to date was to leave a lasting legacy.[Encyclopaedia Iranica: Alexander the Great]
/ref>
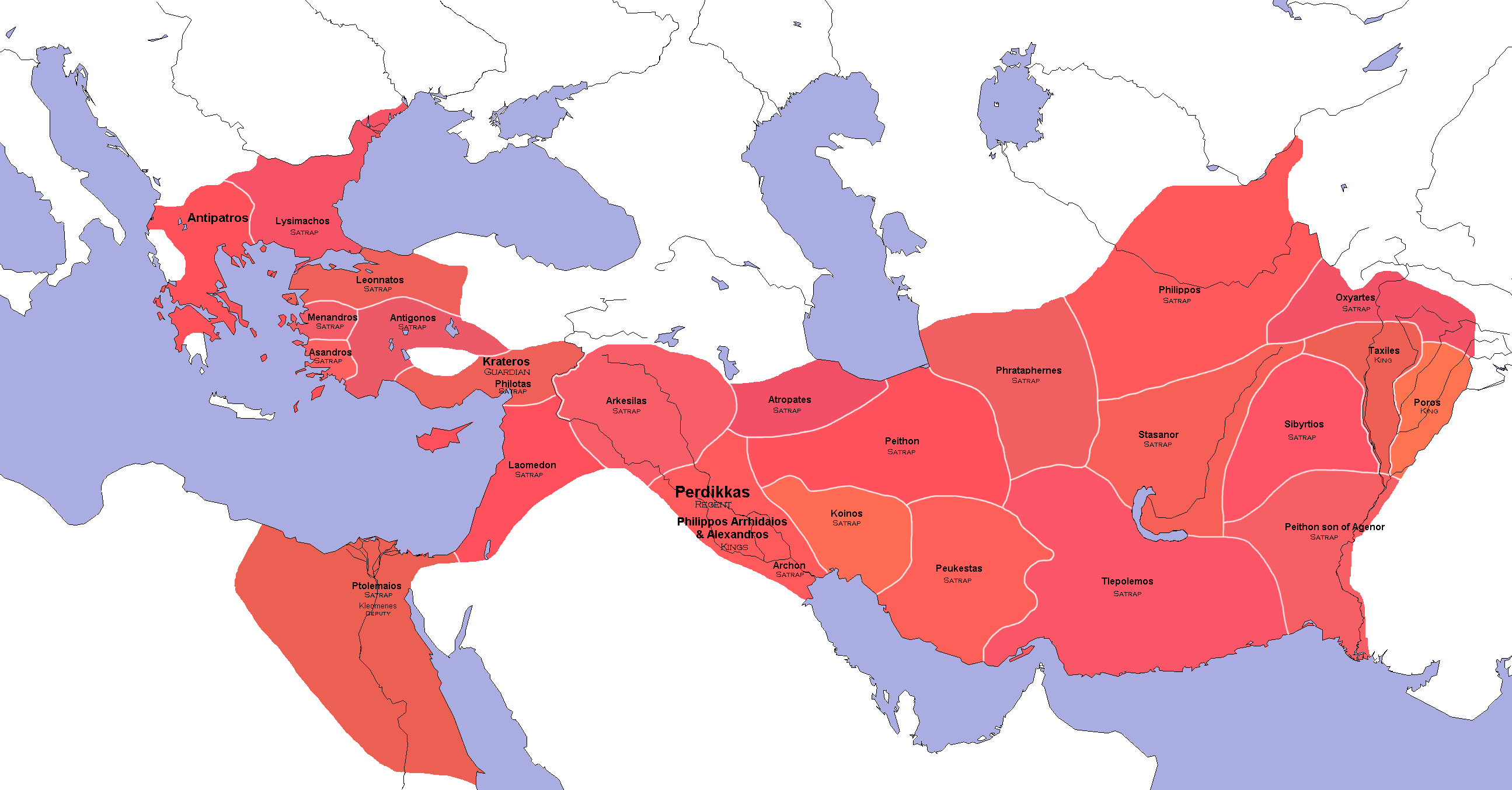
Wars of the Diadochi and division of Alexander's empire

 In June 323 BC,
In June 323 BC, Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
died suddenly and unexpectedly in Babylon at the age of 32, leaving a power vacuum in Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
, putting all he had worked for at risk. His vision of a unified empire proved short lived. He had no heir, and had not made apparent plans for succession. Some classical writers state he wished Perdiccas
Perdiccas ( el, Περδίκκας, ''Perdikkas''; 355 BC – 321/320 BC) was a general of Alexander the Great. He took part in the Macedonian campaign against the Achaemenid Empire, and, following Alexander's death in 323 BC, rose to becom ...
one of his generals, to take charge, and that Perdiccas envisioned sharing power, as regent, with his then unborn son, Alexander IV (323–309 BC). This was not universally accepted, and his half-brother Arrhidaeus
Arrhidaeus or Arrhidaios ( el, Ἀρριδαῖoς lived 4th century BC), one of Alexander the Great's generals, was entrusted by Ptolemy to bring Alexander's body to Egypt in 323 BC, contrary to the wishes of Perdiccas who wanted the body sent t ...
(323–317 BC) was advanced as a candidate by Meleager. Eventually Alexander and Philip were made joint monarchs and responsibility for regional administration divided up at the Partition of Babylon
The Partition of Babylon was the first of the conferences and ensuing agreements that divided the territories of Alexander the Great. It was held at Babylon in June 323 BC.
Alexander’s death at the age of 32 had left an empire that stretched fro ...
(323 BC).[Shipley, Graham (2000) ''The Greek World After Alexander''. Routledge History of the Ancient World. (Routledge, New York)]
/ref> Philip was unable to rule effectively due to a serious disability, and both he and Alexander were soon murdered. Perdiccas himself was assassinated in 321 BC.[Freeman (1999).]
Power often lay with the Satraps, usually generals. In Anatolia, this initial division of power at Babylon was as follows;
Western Anatolia: Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of ...
by Leonnatus
Leonnatus ( el, Λεοννάτος; 356 BC – 322 BC) was a Macedonian officer of Alexander the Great and one of the ''diadochi.''
He was a member of the royal house of Lyncestis, a small Greek kingdom that had been included in Macedonia by Kin ...
, Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
by Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, Μένανδρος ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His ...
, Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
by Asander
Central Anatolia: Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
, Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
and Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
by Antigonus, Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
by Eumenes of Cardia
Eumenes (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης; c. 362316 BC) was a Greek general and satrap. He participated in the Wars of Alexander the Great, serving as both Alexander's personal secretary and as a battlefield commander. He later was a participant in th ...
, Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
by Philotas
Philotas ( el, Φιλώτας; 365 BC – October 330 BC) was the eldest son of Parmenion, one of Alexander the Great's most experienced and talented generals. He rose to command the Companion Cavalry, but was accused of conspiring against Alex ...
Eastern Anatolia: Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
by Neoptolemus
In Greek mythology, Neoptolemus (; ), also called Pyrrhus (; ), was the son of the warrior Achilles and the princess Deidamia, and the brother of Oneiros. He became the mythical progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Molossians of ancient Ep ...
However, dissent was endemic, and almost continuous war ensued amongst the Macedonian generals, lasting over 40 years; these wars were referred to as the wars of the successors (Διάδοχοι, Diadokhoi, or Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
) (323–276 BC). Although Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
had been allocated to Eumenes, it had not yet been subdued and had to be put down in 322 BC, in the course of which Antigonus fell out with Perdiccas and fled to Europe from Phrygia, where he initiated a conspiracy (First War of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule ...
). Perdiccas' murder necessitated a further partitioning and appointment of a new regent, Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
, at Triparadisus
Triparadeisos or Triparadisus ( el, Τριπαράδεισος) was a settlement in Lebanon near the sources of the Orontes. A paradeisos was a hunting reserve or pleasure-ground for the nobility of the Achaemenid (Persian) Empire, normally a w ...
in 321 BC. Eumenes was condemned and control of Cappadocia passed to Nicanor, while Lydia was given to Cleitus and Hellespontine Phrygia to Arrhidaeus
Arrhidaeus or Arrhidaios ( el, Ἀρριδαῖoς lived 4th century BC), one of Alexander the Great's generals, was entrusted by Ptolemy to bring Alexander's body to Egypt in 323 BC, contrary to the wishes of Perdiccas who wanted the body sent t ...
.
The second partitioning did little to quell the continuing scheming and jockeying for power. Antipater's illness in 320 BC led him to appoint Polyperchon Polyperchon (sometimes written Polysperchon; el, Πολυπέρχων; b. between 390–380 BCafter 382 BC according to Billows, R., 'Antigonos the One-Eyed and the Creation of the Hellenistic State' (1990), p. 172, n. 20 – d. after 304 BC,Heckel ...
as regent, passing over his own son Cassander
Cassander ( el, Κάσσανδρος ; c. 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and ''de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
A son of Antipater and a conte ...
, who now conspired with Antigonus. The result was civil war ( Second War of the Diadochi) with Cassander declaring himself regent in 317 BC and King in 305 BC, having had Alexander IV murdered in 309 BC.
Meanwhile, Antigonus in Phrygia was expanding east forcing Seleucus, Satrap of Babylon, to flee to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, Satrap of Egypt and Libya in 315 BC (Third War of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule h ...
). This aggression brought pressure to bear on Antigonus, who soon found himself under attack in Thrace, Caria and Palestine. As a result, Seleucus was reinstated in 312 BC, and a treaty was arranged in 311 BC between Cassander, Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus wa ...
Satrap of Thrace, Antigonus, Seleucus and Ptolemy which divided the Empire into four spheres of influence. By 304 BC all of these had proclaimed themselves 'kings' (Basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean " monarch", referring to either a " king" or an "emperor" and ...
: Βασιλεύς), effectively ending the concept of a Macedonian Empire, although it was unclear as to whether all saw themselves as the legitimate heir of the entire empire. It was Antigonus and his son Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
who continued to wage war ( Fourth War of the Diadochi). The Fourth War culminated in the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his ...
, Phrygia in 301 BC, in which Antigonus now in his 80s faced the combined forces of Cassander, Lysimachus and Seleucus. Antigonus was killed, and Demetrius fled, allowing his enemies to carry out a third partition, dividing his possessions between them.
In post-Ipsus Anatolia, Lysimachus held the west and north, Seleucus the east, and Ptolemy the south east. For a while Pleistarchus
Pleistarchus ( grc-gre, Πλείσταρχος ; died c. 458 BC) was the Agiad King of Sparta from 480 to 458 BC.
Biography
Pleistarchus was born as a prince, likely the only son of King Leonidas I and Queen Gorgo. His grandparents were King ...
, Antipater's son and Cassander's brother ruled Cilicia, before being driven out the following year (300 BC) by Demetrius. The other exception was Pontus which under Mithridates I managed to gain independence.
The third partition of 301 BC was no more effective at bringing stability to the region than its predecessors. Demetrius, who eventually became King of Macedon (294 BC – 288 BC), was still at large controlling a significant naval force, raiding Lysimachus' territory in Asia Minor. Nor did the Ipsus alliance between the three kings last.
Lysimachian Empire 301–281 BC
Of the three empires carved out of Alexander's possessions following the battle of Ipsus, the Lysimachian of Thrace, Western (including Lydia, Ionia, Phrygia) and Northern Asia Minor, was the shortest lived. Lysimachus attempted unsuccessfully to extend his possessions in Europe and Greece. Some of Lysimachus' cruelty, such as the murder of his son Agathocles Agathocles ( Greek: ) is a Greek name, the most famous of which is Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from , ''agathos'', i.e. "good" and , ''kleos'', i.e. "glory".
Other personalities named Agathocles:
*Agathocles ...
in 284 BC engendered both revulsion and revolt. Distrusting Seleucus, Lysimachus had now allied himself with Ptolemy. Seleucus invaded the Lysimachian lands and in the ensuing Battle of Corupedium, near Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
in 281 BC, Lysimachus was killed and Seleucus seized control over western Asia Minor.
Ptolemaic Empire 301–30 BC
Of all the major satraps appointed on the death of Alexander the Great (323 BC), Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
(323–283 BC) settled into his new province of Egypt and Libya with the least difficulty, controlling much of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and at times south-eastern Anatolia. This was confirmed following the third partition following the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his ...
in 301 BC. However, a series of Syrian Wars
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of t ...
(274–168 BC) between the Ptolomies and the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
varied the degree of control they had in Anatolia. The First Syrian War
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of t ...
(274–271 BC) fought by Ptolemy I's son and successor Ptolemy II Philadelphus
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gold ...
(283–246 BC) resulted in extending these possessions to include Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
, Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
, Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, and Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
, as well as the Aegean islands, only to lose some of them in the second war (260–253 BC). The territorial extent of the Ptolemies reached its zenith under Ptolemy III Euergetes
, predecessor = Ptolemy II
, successor = Ptolemy IV
, nebty = ''ḳn nḏtj-nṯrw jnb-mnḫ-n-tꜢmrj'Qen nedjtinetjeru inebmenekhentamery''The brave one who has protected the gods, a potent wall for The Beloved Land
, nebty_hiero ...
(246–222 BC) and the third (Laodicean) war (246–241 BC).
Thereafter the Ptolemaic powers declined. Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon a ...
(221–179 BC) seized territory in Caria, and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
influence steadily increased as it progressively absorbed much of the Greek world. Egypt formed a pact with Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and the dynasty eventually came to an end in 30 BC with the death of Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
(51–30 BC).
Seleucid Empire 301–64 BC
 On the death of
On the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 323 BC Seleucus (321–281 BC) was appointed to head the elite cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
(ἑταῖροι, hetairoi) and a Chiliarch Chiliarch is a military rank dating back to antiquity. Originally denoting the commander of a unit of about one thousand men (a chiliarchy) in the Macedonian army, it was subsequently used as a Greek translation of a Persian officer who functioned ...
. At the Partition of Triparadisus
The Partition of Triparadisus was a power-sharing agreement passed at Triparadisus in 321 BC between the generals ('' Diadochi'') of Alexander the Great, in which they named a new regent and arranged the repartition of the satrapies of Alexander's ...
in 321 BC he was appointed Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
of Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
, but soon found himself involved in the Wars of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule ...
. In particular this involved conflict with Antigonus, Satrap of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
, to his west, who progressively enlarged his possessions to include all of Asia Minor. Eventually, at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC Antigonus was overthrown and killed, and his lands partitioned. This gave Seleucus control of south eastern Anatolia. In the ensuing years he was in conflict with Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
, Antigonus' son gaining and then losing Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
in 294 and 286 BC respectively, but then regained it shortly thereafter. His next problem was to deal with Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus wa ...
who now controlled Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and western Asia Minor. In the ensuing Battle of Corupedium, near Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
in 281 BC, Lysimachus was killed and Seleucus seized control over the remaining lands of Asia Minor. Now reigning over all of Alexander's empire except the Ptolemaic lands in Egypt, his victory was short lived. Immediately moving to take commands of the new lands in Europe, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
ia he crossed into Thracian Chersonese
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
when he was assassinated near Lysimachia
''Lysimachia'' () is a genus consisting of 193 accepted species of flowering plants traditionally classified in the family Primulaceae. Based on a molecular phylogenetic study it was transferred to the family Myrsinaceae, before this family wa ...
by Ptolemy Keraunos
Ptolemy Ceraunus ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Κεραυνός ; c. 319 BC – January/February 279 BC) was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and briefly king of Macedon. As the son of Ptolemy I Soter, he was originally heir to the thron ...
, future king of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
. Seleucus was noted for his founding of cities, such as Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
(one of many cities with that name), named after his father Antiochus, and which became the capital of Syria.Syrian Wars
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of t ...
with the Seleucids southern neighbours, the Ptolomies. He was unable to fulfill his father's ambitions of incorporating Thrace and Macedonia and nor was he able to subdue Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
in Asia Minor. A new threat was incursions by the Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
from the north west but they were repelled in 278 BC. Within Asia Minor, the power of Pergamon on the Aegean coast, a remnant
Remnant or remnants may refer to:
Religion
* Remnant (Bible), a recurring theme in the Bible
* Remnant (Seventh-day Adventist belief), the remnant theme in the Seventh-day Adventist Church
* ''The Remnant'' (newspaper), a traditional Catholic n ...
of the Lysimachean Empire, was growing. Eumenes I
Eumenes I ( grc-gre, Εὐμένης) was dynast (ruler) of the city of Pergamon in Asia Minor from 263 BC until his death in 241 BC. He was the son of Eumenes, the brother of Philetaerus, the founder of the Attalid dynasty, and Satyra, daug ...
, dynast of Pergamon, revolted against Seleucid rule and defeated Antiochus near Sardis in 262 BC, guaranteeing Pergamon's independence. Antiochus died the following year,
Antiochus I Soter was succeeded by his son Antiochus II (261–246 BC) named Theos, or "divine", who conducted the Second Syrian War (260–253 BC). Eventually he was poisoned by his first wife, Laodice I
Laodice I ( el, Λαοδίκη; flourished 3rd century BC, died before 236 BC) was a Greek noblewoman of Anatolia who was a close relative of the early Seleucid dynasty and was the first wife of the Seleucid Greek King Antiochus II Theos.
Family ...
who also poisoned his second wife Berenice Phernophorus, daughter of Ptolemy II Philadelphus
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gold ...
and her infant son. Antiochus II's son by Laodice from his first wife, Seleucus II Callinicus
Seleucus II Callinicus Pogon ( el, ; ''Kallinikos'' means "beautifully triumphant"; ''Pogon'' means "the Beard"; July/August 265 BC – December 225 BC),, . was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, who reigned from 246 BC to 225 BC. Faced ...
(246–225 BC), was proclaimed by his mother.
Seleucus II oversaw the Third Syrian War (246–241 BC) with Berenice's brother, Ptolemy III Euergetes
, predecessor = Ptolemy II
, successor = Ptolemy IV
, nebty = ''ḳn nḏtj-nṯrw jnb-mnḫ-n-tꜢmrj'Qen nedjtinetjeru inebmenekhentamery''The brave one who has protected the gods, a potent wall for The Beloved Land
, nebty_hiero ...
. In Asia Minor a rebellion by his younger brother Antiochus Hierax led to Seleucus II leaving the lands beyond the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
to him following a defeat at Ancyra in 236 BC, although the latter was eventually driven out of Anatolia by Pergamon in 227 BC.
Seleucus' sister Laodice married Mithridates II in 245 BC and brought with her the lands of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
as a dowry.
Despite this Mithridates joined Antiochus Hierax against Seleucus.
 After the brief reign of Seleucus II's son
After the brief reign of Seleucus II's son Seleucus III Ceraunus
Seleucus III Soter, called Seleucus Ceraunus (Greek: ; c. 243 BC – April/June 223 BC, ruled December 225 – April/June 223 BC), was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Kingdom, the eldest son of Seleucus II Callinicus and Laodice II.
Biograph ...
( 226–223 BC), his brother Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the res ...
(223–187 BC) ascended the throne. By the time Antiochus III became king, the empire had already reached a low point. In the east provinces were breaking away, while in Asia Minor, subject states were becoming increasingly independent, including Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
, Pontus, Pergamum
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
(traditionally difficult to subjugate). A new presence was Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
, a 3rd-century settlement of Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
from Thrace in central Anatolia. Antiochus III set about restoring the former glories of the empire, initially campaigning in the east and subduing the independent provinces, before turning his attention to the west. His ambition to fulfill the thwarted dreams of his great great grandfather Seleucus I proved to be his undoing. His initial attempts to regain control of Asia Minor drew the attention of the growing Mediterranean power of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
when Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prom ...
appealed to it for help. He then crossed into Europe in 196 BC and Greece in 192 BC but by 191 BC came up against the Roman legions at the Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lastin ...
where his defeat forced his retreat from Greece. The following year the Romans pursued him into Anatolia inflicting another major victory at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
in Lydia. Antiochus was forced to sue for peace and by the terms of the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
in 188 BC retreated beyond the Taurus Mountains, dying the following year. Anatolia now lay largely in the hands of the Romans and their allies, at least in the west. Those states that had allied themselves with the Romans were freed while Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
south of the River Maeander and Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
were granted to Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. The balance of Antiochus' lands, the largest share, were granted to Eumenes II of Pergamum. These settlements were made on the understanding that they would all keep the peace in a manner satisfactory to Rome.

 While the Seleucids continued to maintain lands in south eastern Anatolia the empire was progressively weakened on all fronts, and became progressively unstable, torn by civil war in the 2nd century BC. After the death of
While the Seleucids continued to maintain lands in south eastern Anatolia the empire was progressively weakened on all fronts, and became progressively unstable, torn by civil war in the 2nd century BC. After the death of Antiochus VII Sidetes
Antiochus VII Euergetes ( el, Ἀντίοχος Ευεργέτης; c. 164/160 BC129 BC), nicknamed Sidetes ( el, Σιδήτης) (from Side, a city in Asia Minor), also known as Antiochus the Pious, was ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empir ...
(138–129) BC the empire became increasingly diminished and by the reign of Antiochus IX Cyzicenus (116–96 BC) there was little left outside Antioch and Syria. The invasion of Syria by Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
(95–55 BC) in 83 BC virtually extinguished the empire, a process completed when Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
made Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
a Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
in 64 BC.
Independent, semi-independent and client states
Pontus 291–63 BC
 The
The Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus (region), Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian people, Persian origin), which possibly may have been di ...
lay on the north west Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast, stretching from Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
to Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
and bordered to the south by Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
. Its mountain ranges were divided by river valleys including the Halys, Iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
, and Lycus, parallel to the coast. Its main centres were on the Lycus and Iris rivers including the royal centre of Amaseia.
Pontus was founded by Mithridates I (302 – 266 BC) in 291 BC, who assumed the title of king in 281 BC. Its capital was Sinope, now the Turkish town of Sinop Sinop can refer to:
* Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea
** Sinop Nuclear Power Plant, was planned in 2013, but cancelled in 2018
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*** Russian ship ''Sinop'', Russian ships named after the ...
. Originally he had inherited Cius
Cius (; grc-gre, Kίος or Κῖος ''Kios''), later renamed Prusias on the Sea (; la, Prusias ad Mare) after king Prusias I of Bithynia, was an ancient Greek city bordering the Propontis (now known as the Sea of Marmara), in Bithynia and i ...
to the west in Bithynia, but fled from Antigonus Monophthalmos to form a new dynasty in nearby Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
. Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
states that he was directly descended from the Persian Satrap of Pontus. he consolidated his kingdom seeking alliances from neighbouring peoples, including the Gauls, as protection form the larger powers of the region.
His grandson, Mithridates II (c. 250–210 BC) married into the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
line, acquiring Phrygia as a dowry from Laodice, sister of Seleucus II
Seleucus II Callinicus Pogon ( el, ; ''Kallinikos'' means "beautifully triumphant"; ''Pogon'' means "the Beard"; July/August 265 BC – December 225 BC),, . was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, who reigned from 246 BC to 225 BC. Faced ...
. Later he was part of an alliance that defeated Seleucus at Ancyra
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, mak ...
in 239 BC. However, the alliance between the dynasties was further consolidated when he gave his daughter, Laodice III in marriage to Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
, and another daughter to Antiochus'cousin, Achaeus.
Mithridates II's grandson, Pharnaces I
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblin ...
(c. 190 – c. 155 BC) waged war on many of his neighbours including Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
of Pergamon and Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
(220 BC – 163 BC) as well as Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
in 181 BC. Ultimately he gained little, although the Romans attempted to intercede. He also continued alliances with the Seleucids, marrying Nysa who was the daughter of his cousins Laodice IV and crown prince Antiochus. He was succeeded by his brother Mithridates IV (c. 155 – c. 150 BC) who allied himself with Rome and her allies, including Pergamon.
Mithridates IV was succeeded by his nephew, Mithridates V (c. 150 – 120 BC), son of Pharnaces I. He assisted the Romans in suppressing the revolt by the pretender of Pergamon, Eumenes III. In exchange he received Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
from the Romans. He allied himself with Cappadocia by marrying his daughter Laodice to Ariarathes VI of Cappadocia
Ariarathes VI Epiphanes Philopator ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Ἐπιφανής Φιλοπάτωρ), was the Ariarathid king of Cappadocia from 130 BC to 116 BC. He was the youngest son of Ariarathes V of Cappadocia and Nysa of Cappadocia.
Nam ...
.
His son, Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
(120 – 63 BC) reversed earlier policies of friendship with the growing power of Rome, engaging in a series of wars that now bear his name, the Mithradatic wars (88–63 BC), and which ultimately led to the end of his kingdom and dynasty. Mithridates was ambitious and planned to conquer the litoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal area ...
of the Black Sea. His first campaign was against Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
on the eastern shore of the Black Sea, and then extended as far north as Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
.
= Mithridatic wars 88–63 BC
=
He next turned his attention to Anatolia where he sought to partition Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
and Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
with King Nicomedes III of Bithynia (127 – 94 BC) in 108 BC also acquiring Galatia and Armenia Minor but soon fell out with him over control of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and by extension his ally Rome setting the scene for the subsequent series of Mithridatic Wars (88–63 BC). Relations between the adjacent states of Pontus, Bithynia, Cappadocia and Armenia were complex. Mithridates' sister, Laodice was queen of Cappadocia, being married to Ariarathes VI
Ariarathes VI Epiphanes Philopator ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Ἐπιφανής Φιλοπάτωρ), was the Ariarathid king of Cappadocia from 130 BC to 116 BC. He was the youngest son of Ariarathes V of Cappadocia and Nysa of Cappadocia.
Nam ...
(130 – 116 BC). Mithridates had his brother in law Ariarathes murdered, whereupon Laodice married Nicomedes III of Bithynia. Pontus and Bithynia then went to war over Cappadocia, and Mithridates had his nephew and new king, Ariarathes VII (116 – 101 BC) killed. Ariarethes' brother Ariarathes VIII
Ariarathes VIII Epiphanes ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Ἐπιφανής, Ariaráthēs Epiphanḗs; reigned c. 101–c. 96 BC and in 95), King of Cappadocia, was the second son of Ariarathes VI of Cappadocia and wife Laodice of Cappadocia. Ariarat ...
(101 – 96 BC) ruled for a brief period before being replaced by Mithridates with his own son Ariarathes IX (101 – 96 BC). The Roman Senate then had Ariarathes replaced by Ariobarzanes I (95 – c. 63 BC). Mithrodates then dragged his eastern neighbour Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
into the fray, since Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
(95–55 BC) was his son in law.
Nicomedes IV of Bithynia
Nicomedes IV Philopator ( grc-gre, Νικομήδης Φιλοπάτωρ) was the king of Bithynia from c. 94 BC to 74 BC. (''numbered as III. not IV.'') He was the first son and successor of Nicomedes III of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wro ...
(94 – 74 BC) declared war on Pontus aided by Roman legions in 89 BC launching the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridat ...
(89–84 BC). During this period, Mithridates swept through Asia Minor occupying most of it except Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
by 88 BC, before Roman retaliation forced his retreat and abandonment of all the occupied territory. Mithridates still controlled his own Pontine lands and a second war by Rome (83–81 BC) was rather inconclusive and failed to dislodge him. In the meantime the Roman presence in Anatolia was steadily growing. As with Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
Nicomedes who had no heirs, bequeathed Bithynia to Rome. This provided the opportunity for Mithridates to invade Bithynia and precipitated the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of th ...
(74–63 BC). Mithridates' position was considerably weakened following the fall of Armenia to Rome in 66 BC. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
had dislodged Mithridates from Pontus by 65 BC, who now retreated to his northern domains but was defeated by rebellion in his own family and died, possibly by suicide, ending the Pontine Kingdom as it then existed.
= Aftermath
=
The lands were divided with the western part including the capital being absorbed into the Roman province of Bithynia et Pontus, while the east was divided into client kingdoms including Pontus, with Mithridates' son Pharnaces II
Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithrida ...
(63–47 BC) as king. However, he attempted to take advantage of the Roman civil war between Caesar and Pompey (49–45 BC) but was driven back by Caesar at Zela in 47 BC. Many of the centres brought into the Roman province reverted under Mark Anthony, but were eventually returned to the provincial fold, forming part of the province of Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
as the districts of Pontus Galaticus
Pontus or Pontos (; el, Πόντος, translit=Póntos, "Sea") is a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in the modern-day eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region and its mountainous ...
and Pontus Polemoniacus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
.[ Pontus continued under client kings, initially descended from Pharnaces. Polemon I ruled from 38 to 8 BC, followed by his widow Pythodorida (8 BC – 38 AD), and after her death her son Polemon II (38–62 AD). Pythidora joined her kingdom to ]Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
by marrying Archelaus until his he was deposed in 17 BC by the Emperor Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
(54–68 AD), while Polemon II was also king of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
where he continued as king after losing Pontus which then also became a Roman province.
Bithynia 326–74 BC
Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
was an area in north west Anatolia, south of the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via t ...
. It was originally just part of the Chalcedon peninsula but was extended to include Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
and Prusa and the cities of the coast, east towards Heraclea and Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
, and south across the Propontis to Mysian Olympus.
Bithynians were of Thracian origin. There is some evidence that even before the invasion of Alexander the Great, Bithynia enjoyed some independence.[ After Alexander's death, Zipoetes I (326–278 BC) had himself proclaimed king in 297 BC, waging war against both ]Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus wa ...
and the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
. Zipoetes was succeeded by his son Nicomedes I
Nicomedes I ( grc, Νικομήδης; lived c. 300 BC – c. 255 BC, ruled 278 BC – c. 255 BC), second king of Bithynia, was the eldest son of Zipoetes I, whom he succeeded on the throne in 278 BC.
Life
He commenced his reign by putting t ...
(278 – 255 BC) who was instrumental in inviting aid from the Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
, who having entered Anatolia settled in Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
were to prove a source of problems in Bithynian affairs. Like the other Anatolian states Bithynia was torn by disputes within the ruling family and civil war. They formed various judicious alliances and marriages against the Seleucids and Heraclea and were often at war with neighbouring states.
Prusias II (156–154 BC) joined Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
in a war against Pharnaces I
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblin ...
of Pontus (181–179 BC) but then attacked Pergamon (156–154 BC) with disastrous consequences. His son Nicomedes II
Nicomedes II Epiphanes (Greek: Νικομήδης ὁ Ἐπιφανής "Nicomedes God-Manifest") was the king of Bithynia from 149 to c. 127 BC. He was fourth in descent from Nicomedes I. Nicomedes II was the son and successor of Prusias II and ...
(149 – 127 BC) sided with Rome in putting down the revolt by Eumenes III (133–129 BC), the pretender of Pergamon. His son Nicomedes III
Nicomedes III Euergetes ("the Benefactor", grc-gre, Νικομήδης Εὐεργέτης) was the king of Bithynia, from c. 127 BC to c. 94 BC. He was the son and successor of Nicomedes II of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wrote that Nico ...
(127 – 94 BC) became entangled in the complex intermarriages of Pontus and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
, attempted to annex Paphlagonia and claim Cappadocia. He was succeeded by his son Nicomedes IV (94 – 74 BC) who bequeathed the kingdom to Rome, precipitating the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
between Rome and Pontus who claimed Bithynia.
Galatia 276–64 BC

Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
was an area in central Anatolia, situated in northern and eastern Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
, east and west of Ancyra
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, mak ...
(Ankara). It was settled by Gauls who were originally invited to Anatolia by Nicomedes I of Bithynia
Nicomedes I ( grc, Νικομήδης; lived c. 300 BC – c. 255 BC, ruled 278 BC – c. 255 BC), second king of Bithynia, was the eldest son of Zipoetes I, whom he succeeded on the throne in 278 BC.
Life
He commenced his reign by putting t ...
around 278 BC to aid his campaigns but remained and settled in an adjacent area over the next decade, with Ancyra as its capital city. They frequently raided surrounding lands and were hired as mercenaries in the continuing struggles between the Anatolian states. They were defeated by Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the fi ...
of Pergamon c. 230 BC. Subsequently, the theme of the Dying Gaul
Dying is the final stage of life which will eventually lead to death. Diagnosing dying is a complex process of clinical decision-making, and most practice checklists facilitating this diagnosis are based on cancer diagnoses.
Signs of dying ...
, a statue displayed in Pergamon, was a favorite in Hellenistic art. Rome launched a campaign against them in 189 BC, defeating them in the Galatian War
The Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey.
The Romans had just defeated the Seleucid ...
. At times part of Pontus, they became independent again in the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
. They controlled territory from the Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
n coast to Trapezus.
The Gauls retained traditional Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
models of governance with tribes and cantons, whose rulers were described by the Greeks as Tetrachs. The territory was divided between three tribes, the Tolistobogii
Tolistobogii (in other sources Tolistobogioi, Tolistobōgioi, Tolistoboioi, Tolistobioi, Toligistobogioi or Tolistoagioi) is the name used by the Roman historian, Livy, for one of the three ancient Gallic tribes of Galatia in central Asia Minor ...
in the west, the Tectosages around Ancyra, and the Trocmi The Trocmii or Trocmi were one of the three ancient tribes of Galatia in central Asia Minor, together with the Tolistobogii and Tectosages,Livy, xxxviii. 16 part of the possible Gallic group who moved from Macedonia into Asia Minor
Anatolia ...
in the east around Tavium
Tavium, or Tavia ( grc, Τάουιον, translit=Taouion; la, Taouion or Tavium), was the chief city of the Galatian tribe of Trocmi, one of the three Celtic tribes which migrated from the Danube Valley to Galatia in present-day central Turkey in ...
. Of these we know more about Deiotarus (c. 105 – 42 BC) than many others. As chief tetrach of the Tolistobogii he was eventually granted the title of King of Galatia by Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, having allied himself with Rome against Pontus in the Mithridatic Wars. The title came with part of the Pontic lands, specifically Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
in the east. Deiotarus was adroit at manoeuvering between the various internal struggles of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
surviving to an advanced age. He formed a political alliance with Pergamon by marrying Berenice, daughter of Attalus III (138–133 BC) the last king of Pergamon.
In 64 BC Galatia became a client state of Rome and a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
in 25 BC following the reign of Amyntas (36–25 BC).[
]
Pergamon 281–133 BC
Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
an Ionian city state close to the Aegean coast, in Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
was a remnant
Remnant or remnants may refer to:
Religion
* Remnant (Bible), a recurring theme in the Bible
* Remnant (Seventh-day Adventist belief), the remnant theme in the Seventh-day Adventist Church
* ''The Remnant'' (newspaper), a traditional Catholic n ...
of the Lysimachean Empire, which was destroyed in 281 BC. Today it is at the modern town of Bergama
Bergama is a populous district, as well as the center city of the same district, in İzmir Province in western Turkey. By excluding İzmir's metropolitan area, it is one of the prominent districts of the province in terms of population and is l ...
. The site formed a natural fortress of strategic importance, guarding the Caïcus plains. Capital of the Attalid dynasty, it was one of the three major cities of Asia Minor.[
]Philetaerus
Philetaerus (; grc, Φιλέταιρος, ''Philétairos'', c. 343 –263 BC) was the founder of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon in Anatolia.
Early life and career under Lysimachus
Philetaerus was born in Tieium (Greek: ''Tieion''), a smal ...
who had served under Lysimachus was the ruler of Pergamon, Lysimachus' treasury, at that time, exercised some autonomy under the Seleucids who seized Lysimachus' lands, ruling from 282–263 BC. The subsequent dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
was named Attalid, in honour of Philetaerus'father Attalis. On his death he was succeeded by his nephew Eumenes I
Eumenes I ( grc-gre, Εὐμένης) was dynast (ruler) of the city of Pergamon in Asia Minor from 263 BC until his death in 241 BC. He was the son of Eumenes, the brother of Philetaerus, the founder of the Attalid dynasty, and Satyra, daug ...
(263–241 BC), who revolted against Seleucid rule and defeated Antiochus near Sardis in 262 BC, guaranteeing Pergamon's independence. Eumenes enlarged Pergamon to include parts of Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
and Aeolis
Aeolis (; grc, Αἰολίς, Aiolís), or Aeolia (; grc, Αἰολία, Aiolía, link=no), was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islan ...
, and held tightly onto the ports of Elaia and Pitane. Eumenes was succeeded by his nephew Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the fi ...
(241–197 BC) who was the first dynast of Pergamon to assume the title of 'king'. He succeeded in defeating the plundering Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
n Gauls, who had become an increasing problem in Anatolia, in 230 BC. Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of v ...
Nikephorus's (The Victory Bearer) temple was decorated with Epigonus
Epigonus ( el, Ἐπίγονος) of Pergamum was the chief among the court sculptors to the Attalid dynasty at Pergamum in the late third century BCE. Biography
Pliny the Elder, who offers the only surviving list of the sculptors of this inf ...
' famous statues of the defeated Galatians. Attalus protected the Greek cities of Anatolia but harassed the Macedonians on the mainland, allying himself with Rome during the Macedonian Wars. A series of wars against Antiochus Hierax
Antiochus (; el, Ἀντίoχoς; killed c. 226 BC), called Hierax (, Ἱέραξ, "Hawk") for his grasping and ambitious character, was the younger son of Antiochus II and Laodice I and separatist leader in the Hellenistic Seleucid kingdom, who r ...
gave Pergamon control over much of Seleucid territory north of the Taurus Mountains, only to lose it under Antiochus III.Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
had any meaningful success in Anatolia as the Roman Empire lay on the horizon. After that victory, Seleucus's heirs would never again expand their empire.Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
, under King Prusias (228 – 182 BC).
Attalus' son, Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
(197–159 BC) also collaborated with Rome to defeat Antiochus the Great at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
in 190 BC. In the subsequent Peace of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae ...
two years later he received Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
, Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
, Pisidia
Pisidia (; grc-gre, Πισιδία, ; tr, Pisidya) was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Pamphylia, northeast of Lycia, west of Isauria and Cilicia, and south of Phrygia, corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Ant ...
, Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
, and parts of Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
from the former Seleucid possessions. He subsequently enlarged and adorned the city, building amongst other things the Great Altar. His brother Attalus II Philadelphus
Attalus II Philadelphus (Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antalya) ...
(c. 160–138 BC) fought with the Romans against Galatia and Bithynia and founded the cities of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
and Attalia.
The last of the Attalid kings was Attalus III (138–133 BC), son of Eumenes II, who bequeathed his kingdom to the Roman Republic. However, a pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term is often used to suggest that a claim is not legitimate.Curley Jr., Walter J. P. ''Monarchs-in-Waiting'' ...
, calling himself Eumenes III briefly seized the throne until captured by the Romans in 129 BC. The lands occupied by Pergamon were divided up between Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and Pontus while the rest came directly under Rome. Pergamon had acted as a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
to Rome after Apamea, but after the death of Attalus III became the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
(Asiana).[
]
Cappadocia 323–17 BC
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
is a mountainous district in central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
, and west of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
and the Armenian Highlands. It was bordered by Pontus in the North and Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west b ...
to the west. At one time it included the area from Lake Tatta
Lake Tuz ( tr, Tuz Gölü meaning 'Salt Lake'; anciently Tatta — grc, ἡ Τάττα, la, Tatta Lacus) was the second largest lake in Turkey with its
surface area and one of the largest hypersaline lakes in the world. It is located in the C ...
to the Euphrates and from the Black Sea to Cilicia. The northern portion, known as Cappadocia Pontus, became Pontus, while the centre and south was known as Greater Cappadocia, predominated by a plateau. At times the northern section constituted Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
. It was strategically situated on the overland route between Syria and the Seleucid territories in western Asia Minor, and hence important to maintain access. Even as a Persian satrapy it had retained a degree of autonomy.[
At the time of the conquest by Alexander the Great, the Persian satrap was Ariarathes I of Cappadocia (331–322 BC), and had himself proclaimed king. Ariarathes I refused to submit to ]Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and remained unsubdued by the time of Alexander's death. Cappadocia was then given to Eumenes (323–321 BC) to govern, who had Ariarthes killed. Eumenes was replaced in 321 BC by Nicanor (321–316 BC). However, despite these Greek appointments Cappadocia continued to be governed by local rulers. Ariarthes had adopted his nephew Ariarthes II (301 – 280 BC), who fled to Armenia but then reconquered Cappadocia killing the local Macedonian satrap Amyntas in 301 BC. Nevertheless, he was permitted to continue to reign as a vassal of the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
. Ariarthes's son Ariamnes
Ariamnes I ( grc, Ἀριάμνης ''Ariámnēs''; fl. 4th century BC; ruled 362–350 BC) was satrap of Cappadocia under Persian suzerainty. Son of Datames and father of Ariarathes I and his brother Orophernes (Holophernes), Diodorus states ...
(280 – 230 BC) continued the policy of increasing independence. His son in turn, Ariarathes III (255 – 220 BC) adopted the title of king, and sided with Antiochus Hierax
Antiochus (; el, Ἀντίoχoς; killed c. 226 BC), called Hierax (, Ἱέραξ, "Hawk") for his grasping and ambitious character, was the younger son of Antiochus II and Laodice I and separatist leader in the Hellenistic Seleucid kingdom, who r ...
against the Seleucid Empire and expanded his frontiers to include Cataonia
Cataonia ( grc, Kαταoνία) was one of the divisions of ancient Cappadocia.
It is described by Strabo, who had visited it, as a level plain surrounded by mountains: on the south by the Amanus, and on the west by the Antitaurus, which bra ...
.[
Ariarathes III's son, Ariarathes IV (220 – 163 BC) consolidated his power by marrying into the Seleucid dynasty, taking ]Antiochis The name Antiochis ( grc, Ἀντιoχίς) is the female name of Antiochus.
Women Seleucid Princesses & Hellenistic Queen Consorts
*Antiochis, a daughter of Achaeus and granddaughter of Seleucus I Nicator. She married Attalus and became the moth ...
, daughter of Antiochus the Great (222–187 BC) as his wife, and assisting him against the Romans. Although the Romans proved victorious at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
(190 BC) Ariarathes had another alliance which spared Cappadocia following the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
(188 BC). His daughter Stratonice married Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
of Pergamon (197–159 BC), a Roman ally. In this role he joined Eumenes in his struggle against Pontus. His son, Ariarathes V
Ariarathes V Eusebes Philopator ( grc-gre, Ἀριαράθης Εὐσεβής Φιλοπάτωρ; reigned 163–130 BC) was a son of the preceding king Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia and queen Antiochis. He was distinguished by his contemporaries ...
(163 – 130 BC) found himself in conflict with the Seleucid Emperor, Demetrius I Soter
Demetrius I ( Greek: ''Δημήτριος Α`'', 185 – June 150 BC), surnamed Soter ( Greek: ''Σωτήρ'' - "Savior"), reigned as king (basileus) of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire from November 162 – June 150 BC. Demetrius grew up in Ro ...
(161–150 BC) who attempted to replace him with his brother Orophernes forcing him to flee to Rome. The Romans restored him as a joint king with Orophernes in 157 BC by dividing the kingdom. Orophernes was reluctant to cede territory and with the support of Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus ( Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antal ...
of Pergamon (160–138 BC) Ariarathes was victorious in 156 BC. He then allied himself with Attalus II against Prusias II of Bithynia (182–149 BC). He died in 130 BC assisting the Romans in putting down the pretender Eumenes III of Pergamon. His efforts were rewarded by the granting of Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west b ...
and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
to his family.
The Cappadocian monarchy then fell victim to the ambitions of Pontus. Ariarathes' son, Ariarathes VI
Ariarathes VI Epiphanes Philopator ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Ἐπιφανής Φιλοπάτωρ), was the Ariarathid king of Cappadocia from 130 BC to 116 BC. He was the youngest son of Ariarathes V of Cappadocia and Nysa of Cappadocia.
Nam ...
(130–116 BC) was related to the Pontine monarchy through his mother Nysa of Cappadocia
Nysa or Nyssa ( el, Νύσ(σ)α, flourished 150s BC-126 BC) was a princess from the Kingdom of Pontus and was a Queen of Cappadocia. She was the ruler of Cappadocia on behalf of her minor son in 130-126 BC.
Biography
Nysa was of Greek Macedon ...
. His uncle, Mithridates V of Pontus (150–120 BC) had the young king married to his daughter Laodice in order to bring Cappadocia under his control. Mithridates V's son, Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
(120–63 BC) then had Ariarathes murdered. Cappadocia was then briefly ruled by Nicomedes III
Nicomedes III Euergetes ("the Benefactor", grc-gre, Νικομήδης Εὐεργέτης) was the king of Bithynia, from c. 127 BC to c. 94 BC. He was the son and successor of Nicomedes II of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wrote that Nico ...
of Bithynia (127– 94 BC), marrying Ariarathenes's widow, Laodice. Mithridates VI then ousted Nicomedes, replacing him with Aríarathes VI's son Ariarathes VII (116–101 BC), his mother Laodice acting as regent. Mithridates also had him killed and replaced with Mithridates own son, as Ariarathes IX (101–96 BC). In 97 BC there was a rebellion against this proxy monarchy and Ararathes VII's brother known as Ariarathes VIII
Ariarathes VIII Epiphanes ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Ἐπιφανής, Ariaráthēs Epiphanḗs; reigned c. 101–c. 96 BC and in 95), King of Cappadocia, was the second son of Ariarathes VI of Cappadocia and wife Laodice of Cappadocia. Ariarat ...
was called upon but swiftly dealt with by Mithridates. The death of both of the sons of Ariarthanes VI effectively extinguished the dynasty. This turmoil then prompted Nicomedes to attempt to insert a pretender claiming to be a third brother. At this point Rome intervened, Mithridates withdrew, Ariarathes IX was deposed yet again and the Cappadocians were allowed to choose a new king, Ariobarzanes I (95-c. 63 BC).
By this stage Cappadocia was effectively a Roman protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
and Ariobarzanes required regular intervention from Rome to protect him from the incursions of Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
(95–55 BC). However, siding with Rome in the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of th ...
against Pontus he was able to enlarge his domains before abdicating in favour of his son, Ariobarzanes II (c.63–c.51 BC). Although Cappadocia continued as an independent state longer than its neighbours, it continued to require help from Rome to maintain its borders. Rome also controlled the succession. Ariobarzanes II married Athenais Philostorgos II Athenais Philostorgos II (Greek: ''η Άθηναἷς Φιλόστοργος Β''), also known as Athenais Philostorgus II or Athenais of Pontus, was a princess of the Kingdom of Pontus, and queen of Cappadocia by marriage to King Ariobarzanes II P ...
, daughter of Mithridates VI and was succeeded by his son Ariobarzanes III Ariobarzanes III, surnamed ''Eusebes Philorhomaios'', "Pious and Friend of the Romans" ( grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης Εὐσεβής Φιλορώμαιος, Ariobarzánēs Eusebḗs Philorōmaíos), was the king of Cappadocia from ca. 51 BC unti ...
(51–c.42 BC) who added Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
to his territory but was executed by the Romans for opposing their control, being succeeded by his brother Ariarathes X (42–36 BC) who fared little better being executed by Mark Anthony and replaced with Archelaus (38 BC – 17 AD) a Cappadocian nobleman. Archelaus survived by switching allegiance from Mark Anthony to Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, later Emperor Augustus (27 BC – 14 AD), at the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ...
(31 BC) gaining Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
. He also united Cappadocia with Pontus by marrying with Augustus' blessing, the client queen Pythodorida of Pontus (8 BC – 38 AD). In 17 BC he was summoned to Rome by the new Emperor, Tiberius (14–37 AD) whom he had angered by supporting a rival, and Tiberius declared Cappadocia a Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
ending the kingdom. Pythodorida returned to Pontus, Lesser Armenia was given to his step-son Artaxias III
Artaxias III, also known as Zeno-Artaxias, ( el, Άρταξίας, 13 BC–34 AD) was a Pontic prince and later a Roman Client King of Armenia.
Artaxias birth name was Zenon ( el, Ζήνων). He was the first son and child born to Roman Clien ...
(18 – 35 AD), and the remaining territories to his son.
Cilicia 323–67 BC
Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
lay at the eastern end of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
coast, just north of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
. It was separated from the Anatolian Plateau
The Anatolian Plateau () is a plateau that occupies most of Turkey's surface area. The elevation of the plateau ranges from 600 to 1,200 meters (2,000 to 4,000 ft). Mount Erciyes near Kayseri is the peak at 3,917 m (12,851 ft) ...
to the north and west by the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
, connected only by a narrow pass, the Cilician Gates
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates ha ...
. To the west lay Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
, to the east the Amanus Mountains
The Nur Mountains ( tr, Nur Dağları, "Mountains of Holy Light"), formerly known as Alma-Dağ, the ancient Amanus ( grc, Ἁμανός), medieval Black Mountain, or Jabal al-Lukkam in Arabic, is a mountain range in the Hatay Province of south ...
separated it from Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. In ancient times Cilicia was naturally divided into two areas, ''Cilicia Trachaea'' (Κιλικία Τραχεία; Rugged or Rough Cilicia), a mountainous area in the west and ''Cilicia Pedias'' (Κιλικία Πεδιάς; Flat Cilicia, also Kilikia Leia or Smooth Cilicia), the flat plains to the east divided by the River Lamus, now called Limonlu Çayı. A major east-west trading route passed through it exiting through the Cilician Gates.[
Cilicia had historically been ruled by the ]Syennesis
Syennesis ( grc, Συέννεσις) was the name of a number of men in classical antiquity. In particular it seems to have been a common name of the native kings of Cilicia.
* Syennesis (5th century), a figure in the conflict of Artaxerxes II ...
dynasty, with their seat at Tarsus.[ Even as a Persian satrapy for some of the time, Cilicia was ruled by tributary kings. Following the division of ]Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's empire Cilicia was governed by Philotas
Philotas ( el, Φιλώτας; 365 BC – October 330 BC) was the eldest son of Parmenion, one of Alexander the Great's most experienced and talented generals. He rose to command the Companion Cavalry, but was accused of conspiring against Alex ...
(323–321 BC), then Philoxenus. Following the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his ...
in 301 BC Cilicia became a battleground between the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
and Ptolemaic empires in their Syrian Wars
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of t ...
. Following the partition of 301 BC after the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his ...
Pleistarchus
Pleistarchus ( grc-gre, Πλείσταρχος ; died c. 458 BC) was the Agiad King of Sparta from 480 to 458 BC.
Biography
Pleistarchus was born as a prince, likely the only son of King Leonidas I and Queen Gorgo. His grandparents were King ...
the son of Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
and brother of Cassander
Cassander ( el, Κάσσανδρος ; c. 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and ''de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
A son of Antipater and a conte ...
ruled it separately, but he was almost immediately expelled by Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
the son of Antigonus I
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( grc-gre, Ἀντίγονος Μονόφθαλμος , 'the One-Eyed'; 382 – 301 BC), son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian Greek nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he serve ...
the following year. Cilicia had a habit of changing hands frequently, Demetrius losing it in 286 BC and then regaining it.
Following the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
in 188 BC, between the Romans and the Seleucid Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
, Cilicia was left to Antiochus, despite losing most lands west of there.[Cambridge Ancient History vol. viii 335]
In the 2nd century BC, Cilicia was notorious for the pirates based along the southern Tracheian coast. After the death of Antiochus VII
Antiochus VII Euergetes ( el, Ἀντίοχος Ευεργέτης; c. 164/160 BC129 BC), nicknamed Sidetes ( el, Σιδήτης) (from Side, a city in Asia Minor), also known as Antiochus the Pious, was ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire ...
Sidetes (138–129) the Seleucid Empire had become reduced to Syria and adjacent Cilicia. At one stage the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
was divided with Philip I Philip(p) I may refer to:
* Philip I of Macedon (7th century BC)
* Philip I Philadelphus (between 124 and 109 BC–83 or 75 BC)
* Philip the Arab (c. 204–249), Roman Emperor
* Philip I of France (1052–1108)
* Philip I (archbishop of Cologne) (1 ...
(95–84 BC) ruling in Cilicia while his twin Antiochus IX ruled in Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
. With the rise of more independent states in Asia Minor, Cilicia came under the hegemony of various surrounding kingdoms, sometimes partitioned. during the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
(88–63 BC) between Rome and Pontus and their ally Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
, Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
of Armenia (95–55 BC) that state vastly expanded its borders at the expense of the Seleucids, and incorporated Cilicia c. 80 BC, until forced to retreat from the advancing Romans.
Roman influence was being felt in Cilicia as early as 116 BC.
In 67 BC Pompey who had suppressed the pirates created the Roman province of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
as the second province in Asia Minor, eventually stretching between the provinces of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
to the west and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in the east, adding Cicilia Pedias in 63 BC. By the time of the Emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
(27 BC – 14 AD) Cicilia had been dismembered, divided between the provinces of Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
and Syria and client rulers in Cilicia Trachea.[
In the 1st century BC Cilicia was tied to Pontus. Darius of Pontus being replaced by Rome with Polemon I in 37 BC. When Polemon died in 8 BC, his widow Pythodorida ruled Cilicia and Pontus. She was succeeded by her son Polemon II (38 BC – 74 AD) on her death, although he lost the Pontian throne in 62 AD.
Cilicia was a very diverse area, both geographically and demographically and parts of it remained difficult for any occupying power to subdue.
During this period, minor dynasts existed within Cilicia such as Zenophanes in Olba, and ]Antipater of Derbe Antipater of Derbe ( grc, Ἀντίπατρος) was a tyrant or prince of Derbe. He was a friend of Cicero's, one of whose letters, of uncertain date, is addressed on Antipater's behalf to Quintus Philippus, proconsul of the province of Asia, who ...
in Isauria
Isauria ( or ; grc, Ἰσαυρία), in ancient geography, is a rugged, isolated, district in the interior of Asia Minor, of very different extent at different periods, but generally covering what is now the district of Bozkır and its surro ...
and Tarcondimotus in northern Amanus.
Armenia 331–1 BC


Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
lay to the north-east of the Anatolian region, on the Armenian highlands to the south and west of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
. Its boundaries fluctuated during the 1st millennium BC but at times extended from the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
.
Armenia in the 1st century BC formed a mountainous region in eastern Anatolia, bounded to the south by Syria and Mesopotamia and to the east by that part of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
known as Media Atropatene, which represents modern day Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
and the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
River. To the west lay Cappadocia and Commagene. It included the area around Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake ...
, the Araxes
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exc ...
valley (emptying into the Caspian Sea), and reached north to Lake Sevan
Lake Sevan ( hy, Սևանա լիճ, Sevana lich) is the largest body of water in both Armenia and the Caucasus region. It is one of the largest freshwater high-altitude (alpine) lakes in Eurasia. The lake is situated in Gegharkunik Province, ...
as far as Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a pe ...
in the lower Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
. The Armenian highlands were geographically separated from the Mesopotamian plains, and was approached through Sophene to the south west and across the Euphrates at Tomisa in Cappadocia. The horses bred on the Armenian lands made it attractive to its neighbours.[
A satrapy under the Persians, it was largely ruled by the ]Orontid dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
. Mithrenes
Mithrenes ( el, Mιθρένης or Mιθρίνης) was a Persian commander of the force that garrisoned the citadel of Sardis. According to Cyril Toumanoff, he was also a member of the Orontid dynasty, of Iranian origin. Waldemar Heckel, on the o ...
(331–333 BC), the local Persian commander surrendered to Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
following the Battle of Granicus
The Battle of the Granicus in May 334 BC was the first of three major battles fought between Alexander the Great of Macedon and the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The battle took place on the road from Abydus to Dascylium, at the crossing of the ...
(334 BC) and was appointed to be the local satrap as had been his father Orontes II
Orontes II (Old Persian: ''*Arvanta-'') was a Persian noble living in the 4th century BC. He is probably to be identified as the satrap of Armenia under Darius III, and may in fact have succeeded Darius in this position when Darius ascended the t ...
(336–331 BC). With the death of Alexander and subsequent division of the empire in 323 BC, Armenia was granted to Neoptolemus
In Greek mythology, Neoptolemus (; ), also called Pyrrhus (; ), was the son of the warrior Achilles and the princess Deidamia, and the brother of Oneiros. He became the mythical progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Molossians of ancient Ep ...
(323–321 BC). Neoptolemus, however, conspired and was killed in battle with Eumenes in 321 BC. With the subsequent fall of Eumenes, Mithrenes re-assumed power (321–317 BC) and declared himself king. He was succeeded by Orontes III (317–260 BC) and relative stability apart from his unsuccessful struggles with the minor kingdom of Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
on his south-western frontier. During this time the capital was moved from Armavir to Yervandashat
Yervandashat or Eruandashat ( hy, Երվանդաշատ), was an Armenian city and one of the 13 historic capitals of Armenia, serving as a capital city between 210 and 176 BC during the Orontid rule over Armenia and the beginning of their succes ...
in 302 BC. During this time Armenia fell under the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
in the tripartite division. However, the degree of control of the Seleucids, who were constantly at war, over Armenia varied. Under subsequent monarchs, including Orontes' son Sames (260 BC) and grandson Arsames I
Arsames I (Greek: ; peo, 𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠𐎶) seems to have taken control of Commagene, Sophene and Armenia in the year 260 BC after the death of his grandfather Orontes III, king of Armenia, and his father Sames, king of Commagene.
Name
"Arsa ...
(260–228 BC) that grip was loosened further allowing Armenia to acquire not only Sophene but Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which s ...
, the next minor kingdom to the west, bordering on Cilicia and Cappadocia. However, the enlarged kingdom became divided in the next generation, Xerxes (228–212 BC) ruling Sophene and Commagene, while his brother Orontes IV (212–200 BC) ruled Armenia.
However, Antiochus the Great, the Seleucid King (223–187 BC), led the last expansion of his kingdom, overthrowing and killing Orontes IV and bringing Armenia directly under Seleucid control in 212 BC, and appointing two satraps (strategos
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek to mean military general. In the Helleni ...
), Artaxias (Artaxerxes) and Zariadris. The retreat of the Seleucid forces from Europe and their defeat at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
(190 BC) allowed Armenia to throw off Seleucid rule, the satraps assuming kingship under a new Artaxiad dynasty (189 BC – 12 AD). Zariadris took the south (Sophene) following Xerxes' assassination. Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from gr, Άρταξίας; in hy, Արտաշէս, translit=Artašēs) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling ...
(190–160 BC) led a revolt against Antiochus.[ He reunited Armenian-speaking peoples in the region, often divided by surrounding states. In this context, the Armenian lands to the west of the Euphrates were known as Armenia Minor (]Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
), as opposed to Greater Armenia to the east. Artaxias also moved the capital again, this time to Artashat
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
(Artaxata). He was succeeded by his son Artavasdes I (160–115 BC) whose major problem was incursions by Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
to the east.
The period of greatest Armenian expansion occurred with Tigranes II (The Great; 95–55 BC) who made it the most powerful state east of Rome, as the various kingdoms of western Anatolia were absorbed into the Roman sphere of influence. He consolidated his influence within Armenia, once again taking over Sophene after deposing Artanes he king. This was the period of the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
(88–63 BC) between Pontus, his north western neighbour, and Rome. He formed an alliance with Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
of Pontus (120–63 BC), marrying his daughter Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
. By acquiring Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
he effectively reduced the Seleucid empire to a rump state. The aggressive behaviour of both Pontus and Armenia inevitably and fatally brought them into conflict with the eastward Roman expansion with the Armenians suffering a decisive defeat at the Battle of Tigranocerta
The Battle of Tigranocerta (, ''Tigranakerti tchakatamart'') was fought on 6 October 69 BC between the forces of the Roman Republic and the army of the Kingdom of Armenia led by King Tigranes the Great. The Roman force, led by Consul Lucius ...
(69 BC). By 67 BC Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
had arrived in eastern Anatolia with the express purpose of crushing these two states. Tigranes surrendered in 66 BC, and Armenia became a client state. The remaining members of the dynasty, which eventually petered out in 1 BC, had an uneasy relationship with both Rome to the west and Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
to the east. Rome saw Armenia as a buffer state in relation to Parthia, requiring frequent interventions by the Romans.
Minor kingdoms
Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
and Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which s ...
were among minor Anatolian states that at times were independent kingdoms and at others were annexed to surrounding territories. Both lay to the west of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
proper, adjoining Pontus, Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, from north to south.
= Sophene
=
Sophene had been a province of ancient Armenia but became independent following the division of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's empire. At times it incorporated Commagene. It was nominally part of the Seleucid empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
at least after 200 BC but with the weakening of that empire by the Romans after 190 BC it again became independent under Roman influence with Zariadres declaring himself king, before being annexed by Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
of Armenia (c. 80 BC). It later became a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
. The capital city was Carcathiocerta, near Eğil
Eğil ( Hittite: 𒅔𒃲𒀀𒉿 ''Ingalawa'', ota, اکيل, ku, Egil) is a town and district of Diyarbakır Province of Turkey. As of 2018, the district's population is 23,369. The elected mayor Mustafa Akkul of the Peoples' Democratic Party ...
, on the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
river.
= Commagene
=
Commagene, a country on the west bank of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
was at times part of Sophene and of Armenia. As with Sophene it came more firmly under Seleucid control in the Antiochian
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
expansion until 163 BC when Ptolemaeus
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
(163–130 BC) revolted and established an independent state. Antiochus I Theos (70–38 BC) submitted to Pompey in 64 BC during his campaign against Armenia and Pontus, and allied Commagene with the Romans for which part of Mesopotamia was added to the kingdom. He managed to keep Commagene relatively independent until he was deposed by Mark Antony in 38 BC. Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
annexed Commagene to the province of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in 17 AD. Its capital was at Samosata
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.[Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...]
.[
]
Rhodes
The island of Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
, off the southwestern tip of Anatolia is not technically part of Anatolia, but formed an important strategic role in Anatolian history, formed alliances, and also ruled areas of southwestern Anatolia for a time. Under Persian rule Rhodes fell under the same satrap as the adjacent mainland areas. The Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
in (188 BC) established Roman control over western Anatolia and the retreat of the Seleucids from this area. The Republic of Rhodes, as an ally of Rome in the war, was granted former Seleucid lands sharing western Anatolia with Pergamon including Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
and Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
, referred to as the Peræa Rhodiorum.[
]
Roman period
Roman Republic 190 – 27 BC
 By 282 BC Rome had subdued northern Italy, and as a result of the
By 282 BC Rome had subdued northern Italy, and as a result of the Pyrrhic War
The Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.
A sk ...
(280–275 BC) established supremacy over the Greek colonies of southern Italy. Shortly afterwards the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
became embroiled in the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three ye ...
(264–146 BC) BC with Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
in the western Mediterranean. As a result of these wars Rome found itself with overseas colonies and was now an imperial power. The next encounter with the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
arose from Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
expansion and consequent Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC). Direct invasion of Anatolia did not occur until the Seleucid Empire expanded its frontiers into Europe, and was crushed by Rome and its allies in 190 BC, forcing it to retreat to the eastern part of the region. Following this the major powers of western and central Anatolia (Pergamon, Bithynia, Pontus and Cappadocia) were frequently at war, with increasing Roman intervention politically and militarily. The Roman presence increased from sporadic intervention, to creating client states
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
to direct rule by provincilisation.
Part of Roman foreign policy was the declaration of foreign states as ''socius et amicus populi romani'' (ally and friend of the Roman people) by treaty agreements.
Roman intervention in Anatolia 3rd – 1st centuries BC
The rule of Rome in Anatolia was unlike any other part of their empire because of their light hand with regards to government and organization. Controlling unstable elements within the region was made simpler by the bequeathal of both Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
and Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
to the Romans by their kings.
Punic (264–146 BC) and Macedonian (214–148 BC) Wars
 In the
In the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
, Rome had suffered in Spain, Africa, and Italy because of the impressive strategies of Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Pu ...
, the Carthaginian general. When Hannibal entered into an alliance with Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon a ...
(221–179 BC) in 215 BC, Rome used a small naval force with the Aetolian League
The Aetolian (or Aitolian) League ( grc-gre, Κοινὸν τῶν Αἰτωλῶν) was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia in central Greece. It was probably established during the early Hellen ...
to help ward off Hannibal in the east and to prevent Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
ian expansion in western Anatolia. Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the fi ...
of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
(241–197 BC) the dominant western Anatolian power, traveled to Rome along with Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
and helped convince the Romans that war against Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
was necessary. The Roman general Titus Quinctius Flamininus
Titus Quinctius Flamininus (c. 228 – 174 BC) was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece.
Family background
Flamininus belonged to the minor patrician '' gens'' Quinctia. The family had a glorious plac ...
not only soundly defeated Philip's army in the Battle of Cynoscephalae
The Battle of Cynoscephalae ( el, Μάχη τῶν Κυνὸς Κεφαλῶν) was an encounter battle fought in Thessaly in 197 BC between the Roman army, led by Titus Quinctius Flamininus, and the Antigonid dynasty of Macedon, led by Phil ...
in 197 BC, but also brought further hope to the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
when he said that an autonomous Greece and Greek cities in Anatolia was what Rome desired.
Seleucid invasion of Europe and retreat from western Anatolia 196–188 BC
During the period just after Rome's victory, the Aetolian League
The Aetolian (or Aitolian) League ( grc-gre, Κοινὸν τῶν Αἰτωλῶν) was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia in central Greece. It was probably established during the early Hellen ...
desired some of the spoils left in the wake of Philip's defeat, and requested a shared expedition with the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
emperor Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
(223–187 BC) to obtain it. Despite warnings by Rome, Antiochus entered Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
in 196 BC, and crossed into Greece by 192 BC, deciding to ally himself with the League
League or The League may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Leagues'' (band), an American rock band
* ''The League'', an American sitcom broadcast on FX and FXX about fantasy football
Sports
* Sports league
* Rugby league, full contact footba ...
. This was intolerable for Rome, and they soundly defeated him in Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
at Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
in 191 BC, forcing his retreat to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, near Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
.Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
(197–159 BC) of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
met Antiochus in the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
in 189 BC. There Antiochus was overwhelmed by an intensive cavalry charge by the Romans and an outflanking maneuver by Eumenes. Because of the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopy ...
the following year, Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
was granted all of the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
lands north of the Taurus mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
(Phrygia, Lydia, Pisidia, Pamphylia, and parts of Lycia) and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
was given all that remained (part of Lycia and Caria).
A stronger Pergamon suited Roman interests as a buffer state between the Aegean and the Seleucid Empire. However, Rome needed to intervene on a number of occasions to ensure the integrity of the enlarged territory, including wars against Prusias I
Prusias I Cholus (Greek: Προυσίας ὁ Χωλός "the Lame"; c. 243 – 182 BC) was a king of Bithynia, who reigned from c. 228 to 182 BC.
Life and Reign
Prusias was a vigorous and energetic leader; he fought a war against Byzantium ...
of Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
(187–183 BC) and Pharnaces I
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblin ...
of Pontus (183–179 BC). Following Eumenes' support for Rome in the Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman ...
(170 – 168 BC) Macedon's power had been crushed and Rome no longer felt the need for such a strong Pergamon, and the Senate set about weakening it, negotiating with Eumenes' brother Attalus II Philadelphus
Attalus II Philadelphus (Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antalya) ...
(c. 160–138 BC) and Prusias while declaring the recently defeated Galatians (184 BC) free. By the time his brother Attalus II succeeded him, Pergamonian power was on the decline, and the last dynast Attalus III (138–133 BC) bequeathed his kingdom to Rome. After a brief revolt by Eumenes III 133–129 BC, it became the Province of Asia under Roman consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
Aquillius Manius the Elder.[Hornblower(1996).]

Involvement with central Anatolian politics 190–17 BC
The interior of Anatolia had been relatively stable despite occasional incursions by the Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
ns until the rise of the kingdoms of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and Pontus in the 2nd century BC.
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
under Ariarathes IV (220 – 163 BC) was initially allied with the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
in their war against Rome. However, Ariarathes changed alliances following the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
(190 BC), becoming Rome's friend, and joined Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
against Pontus. His son, Ariarathes V Philopator (163 – 130 BC), continued his father's policy of alliance with Rome, joining Rome and Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus ( Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antal ...
of Pergamon (160–138 BC) in 154 BC in a war against Prusias II of Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
(182–149 BC). He died assisting Rome overcoming the pretender Eumenes III of Pergamon (133–129 BC) in 131 BC. His reign was marked by internal conflict that required Rome to intervene to restore him. From this stage onward Rome increasingly intervened in Cappadocian affairs, assisting it against Pontus and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
, creating a client state in 95 BC, and a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
in 17 BC.
Pontus had been an independent kingdom since the rule of Mithridates (302 – 266 BC) when the threat of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
had been removed. Pontus maintained an uneasy alliance with the Seleucids and was involved in a number of regional wars, particularly under Pharnaces I
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblin ...
(c. 190 – c. 155 BC) some of which attracted Roman intervention. There was a brief period of collaboration with Rome under Mithridates V (c. 150 – 120 BC) assisting the Romans in suppressing a revolt by the pretender of Pergamon, Eumenes III. This all changed under Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
(120 – 63 BC) whose aggressive expansionist powers swept through Anatolia but soon brought him into direct conflict with Rome and the ultimately fatal Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provi ...
(88–63 BC).
Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
, the other major kingdom in western Anatolia, had varying relations with Rome, and in particular its ally Pergamon. The last monarch, Nicomedes IV (94 – 74 BC) bequeathed his kingdom to Rome, precipitating the Mithridatic Wars between Rome when Pontus claimed Bithynia.
Pontus and the Mithridatic Wars 89–63 BC
Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
(120–63 BC) quickly set about creating his own empire. In his first thrust to extend his frontiers along the Black Sea litoral he avoided drawing the attention of Rome. Rome was preoccupied with other issues that precluded it paying attention to events east of the Province of Asia. This included the Jugurthan 111–104 BC and Cimbric Wars (113–101 BC) as well as dealing with the Scordisci
The Scordisci ( el, Σκορδίσκοι) were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically ...
.
Rome, however, noticed once Mithridates turned his eye west in 108 BC, partitioning Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
with Nicomedes III of Bithynia (127–94 BC). They not only ignored Roman orders to withdraw but marched into Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
. Next was Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
, where Mithridates installed a nephew, Ariarathes VII (116–101 BC), whom he had assassinated shortly afterwards. About this time he sent envoys to Rome to elicit support for his claims, but was not successful and instead rome dispatched Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
in c. 99 BC to take him to task. Amongst further turmoil in that kingdom, he again sent to Rome for support of his latest candidate as did his rival. The Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
promptly ordered Mithridates out of Cappadocia (and Nicomedes out of Paphlagonia). Mithridates appears to have withdrawn by 89 BC, while Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had t ...
the Governor of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
was dispatched to install a new Cappadocian king ( Ariobarzanes I (95–c.63 BC).
By 91 BC Rome was again distracted by war, this time against Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
rebels known as the Social War (91–88 BC), when two critical events occurred. Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
(95–55 BC) ascended the throne of Armenia in 95 BC and allied himself to Mithridates through marriage, while Nicomedes died in 94 BC leaving his kingdom to his young son Nicomedes IV (94–74 BC), creating a potential opportunity for territorial expansion. Tigranes marched into Cappadocia, Ariobarzanes fled to Rome and Nicomedes was expelled. Rome became alarmed, ordered the restoration of both monarchs and sent Manius Aquillius and Manlius Maltimus to deal with the problem, and Pontus and Armenia drew back.
= First war 89–84 BC
=
 By now both Bithynia and Cappadocia were ruled by Roman protégés and were indebted to Rome who urged them to invade Pontus, a fatal miscalculation. Nicomedes invaded Pontus, Mithridates complained to Rome, boasted of his power and allies and unwisely hinted that Rome was vulnerable. The Roman Commissioners declared a state of war and the
By now both Bithynia and Cappadocia were ruled by Roman protégés and were indebted to Rome who urged them to invade Pontus, a fatal miscalculation. Nicomedes invaded Pontus, Mithridates complained to Rome, boasted of his power and allies and unwisely hinted that Rome was vulnerable. The Roman Commissioners declared a state of war and the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridat ...
(89–84 BC) was launched.
The war went well initially for the allies during 89–88 BC, since Rome was still involved in the Social War, taking Phrygia, Mysia, Bithynia, parts of the Aegean Ccoast, Paphlagonia, Caria, Lycea, Lycaonia and Pamphylia. Aquillius was defeated in the first direct engagement with the Romans, in Bithynia although the troops were actually raised locally. The other Roman commander was C. Cassius, governor of Asia, whose seat was at Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, and as Mithridates overran the province, both fled from the mainland. Aquillius was handed back to Mithridates who executed him. Roman rule in Anatolia had been crushed, although a few areas of Asia Minor managed to hold out.
Although Sulla was then appointed to deal with Mithridates, events moved very slowly. However, worse was to come later in 88 BC. the ' Asiatic (or 'Ephesian') Vespers', was the slaughter of tens of thousands of Romans and Italians ordered by Mithridates. Having cleansed Asia Minor of Romans, Mithridates looked further afield, his next victim that year being Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
, but it held out, and he moved on to the Aegean islands, taking Delos
The island of Delos (; el, Δήλος ; Attic: , Doric: ), near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island ar ...
. A number of mainland Greek states welcomed the advance of the Pontian monarch, Sulla not having set out for Greece from Italy until 87 BC. Meanwhile, Mithridates had overcome the Roman army in Macedonia. When the two armies finally met, Sulla inflicted two defeats on the Pontic forces at the battles of Chaeronea
Chaeronea (English: or ; el, Χαιρώνεια , ) is a village and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece, located about 35 kilometers east of Delphi. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Livadeia, of which ...
(86 BC) and Orchomenus (85 BC) restoring Roman rule to Greece. Pontus sued for peace, faced with widespread revolts in Anatolia. Mithridates was to give up Asia and Paphlagonia, to hand back Bithynia to Nicomedes and Cappadocia to Ariobarzanes. In return he was allowed to continue ruling in Pontus as an ally of Rome, having abandoned all territories south and west of the Halys.Flaccus Flaccus was a composer from the 2nd century BC, of whom little is known. He was either a freedman or a slave of one of Terence's patrons and wrote musical scores for Terence's comedies (playing or composing music was no occupation for a free citizen ...
and then by Gaius Flavius Fimbria
Gaius Flavius Fimbria (c. 115 – 85 BC) was a Roman general. Born to a recently distinguished senatorial family, he became one of the most violent and bloodthirsty partisans of the consul Cornelius Cinna and his ally, Gaius Marius, in the civ ...
which crossed from Macedonia through Thrace to Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
and ravaged western Asian Minor before inflicting a defeat on the Pontic forces on the Rhyndacus river. This finally led Mithridates to accept Sulla's terms (Treaty of Dardanos
The Treaty of Dardanos (85 BC) was a treaty between Rome and Pontus signed between Lucius Cornelius Sulla of Rome and King Mithridates VI of Pontus. It ended the First Mithridatic War.
Defeat of Mithridates
Due the victories over Mithridates by ...
).
Sulla set about re-organising the Roman administration in Western anatolia until 84 BC. Those cities that had resisted Mithridates were rewarded, for instance Rhodes regained the Peraea lost in the Macedonian wars. Those that had collaborated were forced to pay reparations. The combined effects of the war and aftermath were ruinous for the region and piracy abounded. Mithradates himself faced internal problems
= Second war 83–81 BC
=
Given that many Romans thought that Mithridates had got off rather lightly following the first war, provocation was almost inevitable. Sulla left Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
in 84 BC to return to Rome and make war on his enemies, where he would eventually become dictator. He left Lucius Licinius Murena to govern the province of Asia. Murena proceeded to intervene in Cappadocia in 83 BC, where Mithrodates was also interfering with the recently restored Ariobarzanes I (95–63 BC). After two further raids with less justifiable pretexts, Mithridates retaliated, pursuing Murena and inflicting a number of defeats on Murena until Sulla (who had less territorial ambition than Murena) intervened and both antagonists withdrew to their former positions.
Murena had refused to recognise the treaty on a technicality and the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
refused to ratify it despite Mithridates' efforts. Mithridates realised Rome would remain a potential threat but nevertheless continued to respect the treaty, but made military preparations for the possibility of a third war. The next step by Rome was to restore control over the areas to the south east which they had lost in the first war (Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
, Pisidia
Pisidia (; grc-gre, Πισιδία, ; tr, Pisidya) was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Pamphylia, northeast of Lycia, west of Isauria and Cilicia, and south of Phrygia, corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Ant ...
and Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west b ...
). So the area was brought under provincial administration by creating Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
(which technically included none of the historical Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
n territory further east) under Publius Servilius, as pro-Consul (78–74 BC). Servilius set about cleansing the Pamphylian coast of pirates before subduing Pisidia and Isauria
Isauria ( or ; grc, Ἰσαυρία), in ancient geography, is a rugged, isolated, district in the interior of Asia Minor, of very different extent at different periods, but generally covering what is now the district of Bozkır and its surro ...
. The building of military roads through Cilicia now created a new potential threat to Mithridates and Pontus.

= Third war 75–63 BC
=
When Nicomedes IV of Bithynia
Nicomedes IV Philopator ( grc-gre, Νικομήδης Φιλοπάτωρ) was the king of Bithynia from c. 94 BC to 74 BC. (''numbered as III. not IV.'') He was the first son and successor of Nicomedes III of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wro ...
(94–74 BC) died, leaving his kingdom to Rome, he created not only a potential power vacuum, but further encircled Pontus. The Senate had instructed the propraetor
In ancient Rome a promagistrate ( la, pro magistratu) was an ex-consul or ex-praetor whose ''imperium'' (the power to command an army) was extended at the end of his annual term of office or later. They were called proconsuls and propraetors. Thi ...
of the province of Asia to take over Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
. This coincided with the death of Servilius' successor as proconsul of Cilicia, which then came under the command of Lucius Licinius Lucullus, while Bithynia was assigned to Marcus Aurelius Cotta
Marcus Aurelius Cotta was a Roman politician and general who was consul in 74 BC. He was posted to Bithynia with a Roman fleet as part of the Third Mithridatic War. He was defeated by King Mithridates VI of Pontus. Rescued by his fellow consul he ...
. Both consuls were instructed to prepare to pursue Mithridates, by Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
.
By the time Lucullus arrived in 73 BC, Mithridates was anticipating him. Lucullus was assembling his legions in northern Phrygia, when Mithridates advanced rapidly through Paphlagonia into Bithynia, where he joined his naval forces and defeated the Roman fleet commanded by Cotta at the Battle of Chalcedon. Having besieged Cotta in Chalcedon
Chalcedon ( or ; , sometimes transliterated as ''Chalkedon'') was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari (modern Üsküdar) and it is now a district of the cit ...
, Mithridates continued west towards Cyzicus
Cyzicus (; grc, Κύζικος ''Kúzikos''; ota, آیدینجق, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peni ...
, in Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
. Lucullus went to relieve Cotta and then moved on to Cyzicus, which Mithridates was besieging. The city held out and Mithridates withdrew suffering heavy losses at the Battles of the Rhyndacus and Granicus in 72 BC. After a series of naval defeats Mithridates fell back to Pontus. He had also sent troops into Lycaonia and the southern regions of Asia to create support amongst Pisidians and Isaurians, but these were now repelled by the Galatians, under Deiotarus.
Lucullus then resumed his original plan and advanced through Galatia and Paphlagonia to Pontus in 72 BC. By 71 BC he was through the Iris and Lycus valleys and into Pontus where he engaged Mithridates at Cabira
Cabira or Kabeira (; el, τὰ Κάβειρα) was a town of ancient Pontus in Asia minor, at the base of the range of Paryadres, about 150 stadia south of Eupatoria or Magnopolis, which was at the junction of the Iris and the Lycus. Eupator ...
. The result was disastrous for the Pontic forces, and Mithridates fled to Armenia. The Romans then set about subduing Pontus and Lesser Armenia while trying to persuade Mithridates, now the guest of Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
to surrender. Tigranes spurned the Roman overtures and indicated he was prepared to fight, so Lucullus prepared to invade Armenia in 70 BC. In 69 he marched through Cappadocia to the Euphrates, crossing it at Tomisa and entering Sophene and the lands which Tigranes had recently acquired from the Seleucids and heading for the new imperial capital of Tigranocerta __NOTOC__
Tigranocerta ( el, Τιγρανόκερτα, ''Tigranόkerta''; Tigranakert; hy, Տիգրանակերտ), also called Cholimma or Chlomaron in antiquity, was a city and the capital of the Armenian Kingdom between 77 and 69 BCE. It bore ...
. There Tigranes found him besieging the city, and in the ensuing battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
, was routed, fleeing northwards.Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
. Lucullus was formally replaced in 67 BC by Marcius Rex, ordered to deal with the Cilician pirate problem, that was threatening the Roman food supply in the Aegean, and Acilius Glabrio to take over the eastern command. Lucullus withdrew back to Galatia and Mithridates promptly recovered all his lost territory. Meanwhile, the republic was changing the administrative governance of Anatolia to the praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge vari ...
ian model in 68 BC.
The piracy strategy initiated by Servilius in 78–75 BC was suspended during the years of fighting Mithridates. Roman naval forces were defeated in 70 BC attempting to deal with the Cretan pirates, and the problem spread to Italy itself. A new model was proposed in 67 BC by Aulus Gabinius
Aulus Gabinius (by 101 BC – 48 or 47 BC) was a Roman statesman and general. He was an avid supporter of Pompey who likewise supported Gabinius. He was a prominent figure in the latter days of the Roman Republic.
Career
In 67 BC, when trib ...
that overarched the provincial commands, under Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
as proconsul. These extraordinary powers were further extended in the next year by the Lex Manilia. In took him only three months during 67 BC to clear the seas. Meanwhile, apprised of the disaster at Zela, there were plans to transfer the command in Anatolia to Pompey, initiated by Gaius Manilius
Gaius Manilius was a Roman tribune of the plebs in 66 BC. He is primarily known for his Lex Manilia, the bill which gave Pompey the Great command of the war against Mithridates.
Career Freedmen Bill
At the beginning of his year of office as ...
(ably assisted by the oratory of Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
). The Lex Manilia essentially set aside the new commands of Marcius Rex and Acilius Glabrio. Pompey was granted considerable resources and explicit powers that Lucullus had never had, and command over the entire Anatolian region.
Pompey's first move was to persuade the Parthians to harass Tigranes' eastern flank. Following Roman tradition he offered Mithridates terms, but he rejected these. consequently Pompey engaged him at the Battle of Lycus in 66 BC inflicting great losses. Subsequently, Mithridates discovering that Tirganes would no longer support him, fled to Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
. Pompey, rather than pursue him, turned his attention to Tigranes, who pursued by Parthians surrendered promptly and was granted his inherited but not acquired lands, becoming a client kingdom
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
. Mithridates either committed suicide or was assassinated in 63 BC and Rome added Pontus as a protectorate along with Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
as a Roman province.Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a pe ...
and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
. By 65 BC he had concluded a truce with the Albanians before sweeping through Iberia and Colchis. He was later to be criticised for not eliminating Mithridates, who had taken refuge in the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
. He then completed the subdual of Albania before returning to Pontus and Lesser Armenia where he set about organising the Province of Pontus and Bithynia and the subordinate Anatolian kingdoms during 65–64 BC. During 64 BC he marched south through Cappadocia and Cilicia to Sytria meeting little opposition except briefly at Commagene. He then annexed Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
as a province, effectively ending the Seleucid Empire now based in Antioch.

Provincialisation of Anatolia 133 BC – 114 AD
 The
The Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
's policy regarding expansion and overseas territory was frequently conflicted. There were those who were satisfied with diplomacy, creating allies on its borders that acted as buffer states against more distant threats. On the other hand, there were those who saw opportunities for glory and riches. central government in rome was often far from civil and military commanders in the field, and local ambitions often dragged Rome into expanding its frontiers. The military exploits of Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
and Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
towards the end of the Mithridatic wars created an eastern expansion far beyond the vision of the Senate.
Policy in Anatolia had consisted of trade, influence and diplomacy with occasional military interventions to maintain the status quo when local kingdoms and empires became expansionist. That influence grew as Rome became the new superpower of the Mediterranean, and repeated interventions reduced many of the kingdoms in Anatolia to client state status. Sometimes Roman rule was forced on the republic by local events such as the bequeathing of kingdoms to Rome. Annexation of territory to form provinces was based on whether there was a trustworthy effective ruler who could rule in the interests of Rome or not.
Formal Roman rule began when Attalus III of Pergamon (138–133 BC) left his kingdom to Rome and it became the Province of Asia, briefly lost during the rebellion of Eumenes III (133–129 BC) and the early Mithridatic wars (89–85 BC), its frontiers were strengthened by creating the neighbouring province of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
to its east along the southwestern Mediterranean coast in 78 BC. A further bequest by Nicomedes IV of Bithynia (94–74 BC) added a neighbour to the northeast along the Black Sea coast, although it took another war before this could be settled properly and combined with its eastern neighbour Pontus to form Bithynia et Pontus in 64 BC. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
annexed Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in the east later that year to provide Roman rule over nearly all the southern coast. Once military conquest had been achieved Pompey set about re-organising internal government within Anatolia, including the all-important collection of taxes. He left Anatolia at the end of 62 BC, returning to Rome in triumph the next year.
Thus by Pompey's time the Roman provinces covered the west, north and south of Anatolia. In the centre Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
were ruled by Brogitarus (63–50 BC) initially as coruler with his father in law, Deiotarus (105–40 BC), and then his son Amyntas (36–25 BC) as a client state. Amyntas initially possessed Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west b ...
and successively added Isauria
Isauria ( or ; grc, Ἰσαυρία), in ancient geography, is a rugged, isolated, district in the interior of Asia Minor, of very different extent at different periods, but generally covering what is now the district of Bozkır and its surro ...
, Pisidia
Pisidia (; grc-gre, Πισιδία, ; tr, Pisidya) was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Pamphylia, northeast of Lycia, west of Isauria and Cilicia, and south of Phrygia, corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Ant ...
and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
. In 25 BC, Amyntas died while pursuing enemies in the Taurus mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
, and Rome claimed his lands as a new province, leaving western and central Anatolia completely in Roman hands. In the East the former Armenian kingdoms remained under local rule.
While much of Pontus ended up in the new province of Bithynia et Pontus, the east was divided into client kingdoms including Pontus, which continued until the last king, Polemon II (38–64 AD) was deposed by the Emperor Nero and Pontus became absorbed into the provincial system.
Cappadocia continued as an independent client, at one point being united with Pontus, until the Emperor Tiberius deposed the last monarch Archelaus (36 BC – 17 AD), creating a province of the same name.
Armenia continued as a client state after the Mithridatic wars, torn between Rome and Parthia, eventually becoming a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
under the Emperor Trajan in 114 AD.
Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
was for a short time a separate province (64–47 BC) before becoming absorbed into Syria. Pompey had enlarged it to include the western Taurus range and the coastal plains beyond it as far as the Amanus Mountains
The Nur Mountains ( tr, Nur Dağları, "Mountains of Holy Light"), formerly known as Alma-Dağ, the ancient Amanus ( grc, Ἁμανός), medieval Black Mountain, or Jabal al-Lukkam in Arabic, is a mountain range in the Hatay Province of south ...
that separate it from Syria. There remained, however, troublesome tribes in the northern mountains that no power had succeeded in subduing.
Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
in the extreme southwest remained independent until 43 AD when it became a province, and was then merged with the Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
n region of Galatia to form Lycia et Pamphylia.
The Trumvirates and last years of the Republic 61–27 BC
In the year's following Pompey's departure the Roman administration in Anatolia kept a wary and at times fearful eye on Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
on its eastern borders, while the central government in Rome was focussed on Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
and the events in Western Europe. There followed two centuries of conflict. In 53 BC Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome." Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, I ...
led an expedition from Syria into Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
which proved disastrous, the Parthians inflicting huge losses at the Battle of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Liciniu ...
in which he was killed. Sporadic raids by the Parthians against Syria continued, but were repelled and suffered a major reversal in 51 BC. However, Crassus' death unbalanced the First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gaius Julius Caesar, Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus and Marcus Licinius Crassus. The constitution of the Roman republic had many ve ...
of which he was a member, leading to the progressive difficulties between Pompey and Caesar.
The Republic
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
's preoccupation with civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
between Pompey and Caesar (49–45 BC) provided opportunity for further instability in Anatolia. Pharnaces II of Pontus
Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithrida ...
(63–47 BC) saw an opportunity to expand his realms in violation of his agreement with Pompey, moving into Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
and Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
, then part of Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
. The Galatians appealed to Caesar, but Pharnaces had already overrun a Roman army at the Battle of Nicopolis
The Battle of Nicopolis took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied crusader army of Hungarian, Croatian, Bulgarian, Wallachian, French, Burgundian, German, and assorted troops (assisted by the Venetian navy) at t ...
in 48 BC, occupying all of Pontus. Caesar, returning from his Egyptian campaign, landed at Antioch and met Pharnaces's forces at Zela in 47 BC and inflicted heavy losses on him, before returning to Rome, uttering the legendary '' Veni, vidi, vici''. Pontus continued under client kings until 17 BC, and Galatia until 25 BC.
Meanwhile, Caesar was planning to return to the east and deal with the Parthians who were once again harassing Syria, and avenge Crassius. Plans that were cut short by his assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
in 44 BC.
 With his death, Rome lapsed into yet another war, the
With his death, Rome lapsed into yet another war, the Liberators' civil war
The Liberators' civil war (43–42 BC) was started by the Second Triumvirate to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination. The war was fought by the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (the Second Triumvirate members) against the forces of Caesar's a ...
(43–42 BC). The conspirators (''Liberatores
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated by a group of senators on the Ides of March (15 March) of 44 BC during a meeting of the Senate at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey in Rome where the senators stabbed Caesar 23 ti ...
''), Marcus Junius Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Ser ...
and Gaius Cassius Longinus
Gaius Cassius Longinus (c. 86 BC – 3 October 42 BC) was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the co ...
seized all the eastern provinces. However, their combined forces were destroyed at the Battle of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Wars of the Second Triumvirate between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, at ...
on the Greek mainland in 42 BC, by those of the Second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created for Mark Antony, Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November 43 BC with ...
(Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, and Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
) 43–33 BC. Following this war Antony remained to govern in the east. There he found himself faced with further Parthian incursions, who had occupied Syria. Between 40 and 38 BC, the parthians penetrated as far as Caria.[Cambridge Ancient History vol. x 645] The Parthians were beaten back following both their 40 and 38 BC invasions. However, when Antony himself decided to invade Parthian territory in 33 BC the result was a disaster, although he made two further expeditions into Armenia. In 34 BC Antony and Cleopatra decided to distribute the eastern lands between their children ( Donations of Alexandria), precipitating yet another civil war (32–30 BC) and the end of the triumvirate.
Armenia was granted to Alexander Helios
Alexander Helios ( el, Ἀλέξανδρος Ἥλιος; late 40 BC – unknown, but possibly between 29 and 25 BC) was a Ptolemaic prince and was a son of Pharaoh Cleopatra VII of the Ptolemaic dynasty and Roman triumvir Mark Antony. Alexander' ...
and Syria and Cilicia to Ptolemy Philadelphus, while Antony retained Western Anatolia. Antony was defeated at the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ...
in 31 BC, and died the following year.
Of the surviving client kingdoms, Cappadocia was the most prominent but was plagued by internal unrest requiring frequent Roman intervention, sometimes for lack of cooperation. At various times it acquired lesser Armenia and parts of Cilicia, and was unified with Pontus.
Roman Empire 27 BC – 4th century
The Empire: The Principate 27 BC – 193 AD
 With Antony dead, and Lepidus marginalised, the second triumvirate was effectively dissolved, leaving Octavian as the sole power. Thus the republic came to and end. Octavian's powers progressively increased, he was granted the title ''Augustus'' by the Senate and adopted the title ''princeps senatus'' in 27 BC although technically a
With Antony dead, and Lepidus marginalised, the second triumvirate was effectively dissolved, leaving Octavian as the sole power. Thus the republic came to and end. Octavian's powers progressively increased, he was granted the title ''Augustus'' by the Senate and adopted the title ''princeps senatus'' in 27 BC although technically a consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
, and shortly after ''Imperator
The Latin word ''imperator'' derives from the stem of the verb la, imperare, label=none, meaning 'to order, to command'. It was originally employed as a title roughly equivalent to ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later it became a part o ...
'' in effect Emperor and the first phase of the Roman Empire, the Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate. ...
(27 BC – 284 AD) was born. In exchange for this redistribution of powers, a long history of civil wars came to an end, replaced by the Augustan age (27 BC – 14 AD). The endless wars had been devastating for Asia Minor.
Julio-Claudian dynasty 27 BC – 68 AD
Under Augustus, Galatia became a formal province in 25 BC strengthening direct Roman rule in western Anatolia, while in 27 BC Cilicia had been absorbed into Syria. Meanwhile, Cappadocia and Armenia continued as client states. A truce of sorts was worked out in 1 AD between the Romans and the Parthians. Augustus and his descendants formed the Julio-Claudian dynasty
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type= Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* ...
(27 BC – 68 AD). Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
(14–37) formed the province of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
in 17, on the death of the last king, Archelaus (38 BC – 17 AD). Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
(41–54) dissolved the Lycaean league and organised Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
into a province in 43. Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
(54–68) organised the remaining eastern portion of the kingdom of Pontus into a province, after deposing the last king, Polemon II (38–62). Polemon continued as King of Cilicia until his death. Pontus consisted of three districts: ''Pontus Galaticus'' in the west, bordering on Galatia which was incorporated into that territory; ''Pontus Polemoniacus'' in the centre, so called from its capital Polemonium
''Polemonium'', commonly called Jacob's ladders or Jacob's-ladders (the name derived from the Biblical story), is a genus of between 25 and 40 species of flowering plants in the family Polemoniaceae, native to cool temperate to arctic region ...
, from the Iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
to Pharnacia, annexed into Bithynia et Pontus; and ''Pontus Cappadocicus'' in the east, bordering on Cappadocia (Armenia Minor), was incorporated into that territory.
Armenia continued to be a flashpoint between the Romans and Parthians. War erupted again in 36, and again in 58 under Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
(54–68). After a disastrous battle of Rhandeia in 62. A compromise was worked out with a Parthian on the Armenian throne subject to Roman approval.
The Year of Four Emperors and Flavian dynasty 69–96 AD
 The Julio-Claudian dynasty ended with Nero's suicide, resulting in a period of instability in 69 until Vespasian (69–79) ascended, founding the
The Julio-Claudian dynasty ended with Nero's suicide, resulting in a period of instability in 69 until Vespasian (69–79) ascended, founding the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
. In 72 Vespasian united all the disparate elements of Cilicia into the Roman province, many of which had remained petty dynasties. Vespasian also created a new composite province of Lycia et Pamphylia in 72, out of Claudius' province of Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
and the Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
region of the province of Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ...
.
Nerva-Antonine dynasty 96–192 AD
 Following the assassination of
Following the assassination of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(81–96), the Empire passed into the hands of Nerva (96–98). The Nerva-Antonines presided over a period of relative peace and prosperity and its greatest territorial extent.
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(98–117) finally achieved provincialisation of the troubled region of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
in 114, albeit for only four years. War with Parthia broke out once again in the 2nd century, generally in Rome's favour. Parthia had broken with previous agreements of choosing Armenian kings subject to approval of Rome. Trajan's policy was to depart from previous policy, invading Armenia, during which the Parthian monarch of Armenia, Parthamasiris, was killed, and going on to create provinces in Mesopotamia and Assyria, and capturing the Parthian capital of Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
. Armenia was now no longer a buffer state. However, the victory was short-lived, Trajan being forced to withdraw to Antioch, and dying shortly afterwards in 117 AD.
Trajan's successor, Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania ...
(117–138), decided not to persist with the eastern provinces, and Armenia continued to be a source of conflict in this period. Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good E ...
(161–180) was faced with yet another invasion by Parthia on assuming the Imperial office. The war lasted five years and again the Parthian capital was sacked. A new threat was the Antonine Plague (165–180), which severely affected Asia.
The Year of Five Emperors and Severan Dynasty 193–235 AD
The Nerva-Antonine dynasty ended with the assassination of Commodus
Commodus (; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. ...
(177–192). Commodus' reign ended a period of good government, known as the Five Good Emperors, and is credited with being the beginning of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. It traces Western civilization (as well as the Islamic and Mongolian conquests) from the height of the Roman Empire to th ...
, following the era of the ''High Empire'' (70–192 AD). There followed another period of instability, the Year of Five Emperors, until Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
(193–211) became Emperor, initiating the Severan dynasty
The Severan dynasty was a Roman imperial dynasty that ruled the Roman Empire between 193 and 235, during the Roman imperial period. The dynasty was founded by the emperor Septimius Severus (), who rose to power after the Year of the Five Empero ...
(193–235).
In 193, the province of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
was divided by Severus into two sections, Syria Coele in the north, and Syria Phoenicia in the south.[ Armenia and the Parthians continued to be a problem in the east, with neither side gaining ground in the long term. This time Septimius Severus invaded Mesopotamia in 195 AD, sacking Ctesiphon again (197). ]Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor ...
(198–217) had some successes, but these were lost under his successor Macrinus (217–218). However, the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
itself was about to come to an end, being overthrown in 224 by the resurgent Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, a new threat to the eastern empire.
The Empire: the years of crisis 235–284, Schism 258–274 and Gothic invasion (255)
 The assassination of
The assassination of Alexander Severus
Marcus Aurelius Severus Alexander (1 October 208 – 21/22 March 235) was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 222 until 235. He was the last emperor from the Severan dynasty. He succeeded his slain cousin Elagabalus in 222. Alexander himself wa ...
(222–235), the last of the Severans, brought to an end the Augustan Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate. ...
, and the empire descended into its third crisis, this time lasting nearly fifty years. Twenty five emperors obtained power in the space of forty-nine years, with at least fifty one claiming it. Most were either murdered or died in military campaigns against Rome's enemies that were now pressing hard on her frontiers. In addition to instability in governance and civil war the crisis years were marked by hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as t ...
, plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
and the first schism within the empire. The profound changes between the preceding Principate and succeeding Dominate
The Dominate, also known as the late Roman Empire, is the name sometimes given to the " despotic" later phase of imperial government in the ancient Roman Empire. It followed the earlier period known as the "Principate". Until the empire was reuni ...
, coincide with a shift from classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
to late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
. It was also an era in which might of the far flung Roman Empire was now beginning to experience increasing pressure on its eastern and northern borders, whereas previously the balance of military power had concentrated on defending the eastern border.
Persia and the eastern front
During the crisis the eastern provinces felt they were on their own, and were not inclined to help prop up Rome against foreign attacks. The Roman–Parthian wars
The Roman–Parthian Wars (54 BC – 217 AD) were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.
Battles ...
were now the Roman–Sassanid wars. A Persian invasion starting in 236 in the reign of Gordian III
Gordian III ( la, Marcus Antonius Gordianus; 20 January 225 – February 244) was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor up to that point (until Valentinian II in 375). Gordian was the son of Anto ...
(238–244) prompted Roman retaliation, but in the ensuing battle to secure the eastern borders, the young Gordian was killed, and amongst the terms made was the ceding of Armenia to Persia. Persia again attacked in 251, annexing Armenia and invading Syria in the reign of Trebonianus Gallus
Gaius Vibius Trebonianus Gallus (206 – August 253) was Roman emperor from June 251 to August 253, in a joint rule with his son Volusianus.
Early life
Gallus was born in Italy, in a family with respected Etruscan senatorial background. He h ...
(251–253) but was eventually beaten off by the local Roman forces towards the end of his reign.
The capture of Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
and Chalcedon
Chalcedon ( or ; , sometimes transliterated as ''Chalkedon'') was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari (modern Üsküdar) and it is now a district of the cit ...
by the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
forced Valerian (253–260) to move his main troop deployments to Cappadocia, weakening his efforts to contain the Sassanid threat. In the course of these latter campaigns, Valerian became the first Roman emperor to be captured by enemy forces, in 260. The Sassanid forces penetrated as far west as Isauria and Cappadocia. The major part of the Roman response fell to the forces in Syrian outpost, Valerian's successor, Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; c. 218 – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empi ...
(260–268), being preoccupied in the west. Asia Minor then experienced the combined attacks of the Danubian Goths in the Balkans pouring into Thrace, while their Black Sea relatives ravaged coastal cities. A later emperor, Carus
Marcus Aurelius Carus (c. 222 – July or August 283) was Roman emperor from 282 to 283. During his short reign, Carus fought the Germanic tribes and Sarmatians along the Danube frontier with success.
He died while campaigning against th ...
(282–284), led an expedition east to restore Roman rule in Armenia and reverse earlier losses by taking on the Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, but died on the campaign.
Gothic invasion
 A new problem for Anatolia emerged during this period, with the expansion of the
A new problem for Anatolia emerged during this period, with the expansion of the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
during the 3rd century. Since the roads to central Europe through Macedonia, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-c ...
were all defended successfully by the Romans, the Goths found Anatolia to be irresistible due to its wealth and deteriorating defenses. Using a captured fleet of ships from the Bosphorus and flat-bottomed boats to cross the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, they sailed from Black Sea bases (Black Sea Goths) in 255 during the reign of Valerian (253–260) around the eastern shores, landing in the coastal city of Trebizond in Pontus. What ensued was a huge embarrassment for Pontus- the wealth of the city was absconded, a larger number of ships were confiscated, and they entered the interior without much resistance. A second invasion of Anatolia through Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
brought even more terror inland and wanton destruction. They entered the city of Chalcedon
Chalcedon ( or ; , sometimes transliterated as ''Chalkedon'') was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari (modern Üsküdar) and it is now a district of the cit ...
, using it as a base by which to expand their operations, sacking Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
, Prusa, Apamea, and Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
in turn. Only the turn of the weather as winter approached kept them from penetrating further into Anatolia. However, the Goths continued their seaborn attacks not only around the coastline of Anatolia, but in Greece and Italy as well. Amongst their raids was the destruction of the Temple of Diana in Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
and the city itself in 263. Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
(275–276) successfully took on the Gothic invaders of Anatolia, and this was continued by a subsequent emperor, Probus Probus may refer to:
People
* Marcus Valerius Probus (c. 20/30–105 AD), Roman grammarian
* Marcus Pomponius Maecius Probus, consul in 228
* Probus (emperor), Roman Emperor (276–282)
* Probus of Byzantium (–306), Bishop of Byzantium from 29 ...
(276–82).
Schism, reunification and division
By 258 the empire was breaking up with the defection of the western provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, to form the Gallic Empire
The Gallic Empire or the Gallic Roman Empire are names used in modern historiography for a breakaway part of the Roman Empire that functioned ''de facto'' as a separate state from 260 to 274. It originated during the Crisis of the Third Century, ...
. In 260 the provinces in the east including Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
broke away to form the Palmyrene Empire
The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt, ...
(260–273). This stretched all the way to Ancyra, and even attempted to annex Bithynia. Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited ...
(270–275), one of the Illyrian emperors, was an exception to the general pattern in this era, succeeding in re-uniting the empire by 274.
By the time of Carus, the idea of two empires, west and east was emerging. Carus appointed one of his sons, Carinus
Marcus Aurelius Carinus (died 285) was Roman emperor from 283 to 285. The elder son of emperor Carus, he was first appointed ''Caesar'' and in the beginning of 283 co-emperor of the western portion of the empire by his father. Official accoun ...
(282–285) as co-emperor for the western empire, while he and his other son, Numerian
Numerian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Numerius Numerianus; died November 284) was Roman emperor from 283 to 284 with his older brother Carinus. They were sons of Carus, a general raised to the office of praetorian prefect under Emperor Probus in 282. ...
(283–284) concerned themselves with the east. Numerian died before returning west leaving Carinus to face a newly proclaimed emperor, Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
, who subsequently triumphed.
The Empire: The Dominate 284 – 4th century
The Tetrarchy and first Eastern Empire 284–324
 Order and stability was restored when
Order and stability was restored when Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
(284–305) obtained power following the death of the last Crisis Emperors, Numerian
Numerian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Numerius Numerianus; died November 284) was Roman emperor from 283 to 284 with his older brother Carinus. They were sons of Carus, a general raised to the office of praetorian prefect under Emperor Probus in 282. ...
(282–284), and overcoming his brother Carinus
Marcus Aurelius Carinus (died 285) was Roman emperor from 283 to 285. The elder son of emperor Carus, he was first appointed ''Caesar'' and in the beginning of 283 co-emperor of the western portion of the empire by his father. Official accoun ...
, ushering in the next and final phase of the Roman Empire, The Dominate
The Dominate, also known as the late Roman Empire, is the name sometimes given to the " despotic" later phase of imperial government in the ancient Roman Empire. It followed the earlier period known as the "Principate". Until the empire was reuni ...
.
Diocletian managed to secure the frontiers and instituted sweeping administrative reforms that affected all the provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, preparing them for the new millennia and the transition to the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. He continued Carus' tradition by instituting a system of Tetrarchs, and dividing the responsibility for the empire between them. The term ''Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
'' became the name of senior emperors, while junior emperors were known as ''Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
''. In the initial arrangement, or Diarchy, Diocletian entrusted the west to his junior Caesar (later Augustus) Maximian while he took charge of the east.
= First Tetrarchy 293–305
=
This evolved into a tetrachy in 293, the empire being divided into four, but each Caesar reporting to an Augustus. The new co-emperors were Galerius and Constantius Chlorus, Constantius, forming the First Tetrarchy (293–305). Thus Diocletian and Maximian were the ''Augusti'' (senior emperors) with Galerius and Constantius as ''Caesares'' (junior emperors).
There were now four Tetrarchic Capitals, with the east being governed from Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
in Bithynia et Pontus, Bithynia (now Izmit), where he had originally been proclaimed emperor. This became the base for defence against invasion from the Balkans and Persia's Sassanids and Diocletian's capital.
In the Diocletian reforms provinces were divided into smaller units, almost doubling the total number soon after 293, replicating the original regions of Asia Minor. Asia was divided into seven smaller provinces, and Bithynia three (Bithynia, Honorias and Paphlagonia). Galatia lost its northern and southern parts to the new provinces of Paphlagonia and Lycaonia, respectively. Lycia et Pamphylia was once again split into its two constituent units. Cappadocia lost its Pontic and Lesser Armenian territories. Another innovation was the establishment of Roman diocese, Dioceses, an intermediate administrative structure that combined together several provinces, although Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
used the term when he was governor of Cilicia (51 BC). Anatolia was restructured into three dioceses, which were eventually grouped under the Praetorian prefecture of the East, Praetorian Prefecture of the East (''praefectura praetorio Orientis''); Diocese of Asia, Asia (Asiana), Diocese of Pontus, Pontus (Pontica) and Diocese of the East, East (Oriens). (''see navbox below'')
Armenia returned to the Roman sphere in 287 as a vassal state under Tiridates III of Armenia, Tiridates III (287–330) and more formally as protectorate in 299. On the eastern front, Persia renewed hostilities in 296, inflicting losses on Galerius' forces, until Diocletian brought in new troops from further west the following year and clashed with the Persians in lesser Armenia, and pursued them all the way to Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
in 298, effectively ending the campaign.
= Second Tetrarchy 305–308
=
In 305, both ''Augusti'' stepped down, an unprecedented constitutional step, the agreement being that both ''Caesares'' would be promoted to ''Augusti'', and new ''Caesares'' appointed. This happened but the expected new ''Caesares'' were not, as expected, the sons of former emperors, Maxentius (son of the now retired ''Augustus'' Maximian) and Constantine I, Constantine (son of the new Augustus Constantius), but rather Flavius Valerius Severus and Maximinus II, Maximinus. Galerius was now Augustus of the East and the Second Tetrarchy was formed with Constantius and Galerius as ''Augusti'' and Severus and Maximinus as Caesares, and heirs apparent. This oversight was to prove fatal to Diocletian's vision of a tetrarchy.
Constantius died in 306 and Galerius raised Severus to ''Augustus'' as expected. However, Constantine, who would have been eligible for the vacant role of ''Caesar'', was elected as Augustus by his troops, in competition with Severus, while Maxentius the other overlooked candidate for ''Caesar'' simultaneously challenged Severus and indeed deposed and murdered him, declaring himself Augustus, while his father Maximian also attempted to return to power and take the role of ''Augustus''. This left multiple candidates for the Tetrarchical roles.
= Third Tetrarchy and Civil War 308–313
=
In 308 Galerius and Diocletian attempted a diplomatic solution, summoning an Imperial Conference that elected Licinius as Augustus of the West, with Constantine as his ''Caesar'', while the incumbents, Galerius and Maximinus continued in the east, as a Third Tetrarchy. this proved unworkable and both Maxentius and Constantine, originally overlooked as ''Caesares'' continued to stake their claims, and by 309 they became full ''Augusti'' and the empire dissolved into civil war between 309 and 313.
Relative to the western parts of the empire, the eastern empire was stable. The transition from Diocletian to Galerius proceeded smoothly in 305. Upon assuming the role of ''Augustus'', Galerius assigned Maximinus to Egypt and Syria. On Galerius'death in 311, Maximinus divided the east seizing Asia Minor, with Licinius as western ''Augustus''. When Maximinus fell out with Licinius, he crossed the Bosphorus, took Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
and engaged the latter in 313 at Battle of Tzirallum, Tzirallum in Thrace, at which he was routed, but was pursued across Asia Minor to Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus by Licinius.
= Diarchy 313–324
=
At the end of the wars there remained two empires and two emperors. Constantine had disposed of Maxentius in 312 and agreed to repartition the empire, with Constantine in the west and Licinius in the East. Licinius was immediately engaged in dealing with the Persian situation. By the following year (314) the two emperors were at war, which simmered over a decade. Constantine eventually besieged Licinius in Byzantium in 324, defeated his fleet at the Battle of Hellespont. Licinius fell back on Bithynia, where he surrendered at the Battle of Chrysopolis. Constantine then declared himself sole emperor of a reunited empire (324–337).
Constantinian dynasty 324–363
At the end of the 3rd century, the vast empire was beset by administrative and fiscal problems, and much of the power lay in the hands of the military, while there was no clear principle of succession and dynasties were short lived, their fate often determined by force of arms rather than legitimacy. The empire was divided culturally with Latin predominating in the west, and Greek in the east, while eastern ideas, such as Mithraism were spreading (including Constantine and his family). Another increasing cultural force was the Palestinian religion of Christianity, although demonstrating considerable heterogeneity of orthodoxy. Diocletian had carried out major reforms after the years of crisis, but the empire slipped into chaos once again on his abdication and it fell to Constantine to restore stability and continue the process of reform. From the time of Constantine I's accession in 324 to the death of Julian the Apostate, Julian in 363, the empire was ruled by the Constantinian dynasty (Neo-flavians).[
]
= Constantine I 324–337
=
Constantine I, later referred to as ''Constantine the Great'', ruled from 324 to 337 and his career was dominated by two considerations, the role of religion in the empire and the need for an Eastern capital. Because his reign coincided with the spread of Christianity his life has been obscured by legend as the first Christian emperor. In Diocletian's reign, Constantine was a regular visitor to the court at Nicomedia, and again under Galerius. At the end of the civil wars in 324 he once again found himself in Bithynia. Successive Roman emperors were becoming dissatisfied with Rome as an administrative centre, with its traditions which were at odds with their new more Eastern ways, and far from the theatres of war that consumed them. Many of them had spent little time in Rome and had created centres for themselves elsewhere.[Runciman, Steven (1933). Byzantine Civilization. Methuen, London]
 Constantine considered a number of candidate cities as a new eastern capital, before deciding on
Constantine considered a number of candidate cities as a new eastern capital, before deciding on Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
in 330, initially designated ''Nova Roma'' (New Rome), but then Constantinopolis in Constantine's honour (although its official title remained ''Nova Roma Constantinopolitana''). Byzantium had long been considered of strategic importance, guarding the access from the Black Sea to the Aegean. Various emperors had either fortified or dismantled its fortifications depending on which power was using it and for what. Byzantium featured in Constantine's last war against Licinius in which Constantine had besieged the city, and after the war was over he further investigated its potential. He set about renewing the city almost immediately, inaugurating it in 330. This is a year sometimes picked as the beginning of the Byzantine Empire. The new capital was to be distinguished from the old by being simultaneously Christian and Greek (although was initially mainly Latin speaking like its Balkan hinterland) and a centre of culture.[
Constantine's major contribution to religion in the empire was to summon the elders of the Christian world to the great First Council of Nicaea, Council of Nicaea in 325 to resolve differences and establish orthodoxy, such as the date of Easter. The other great influence was his mother, Helena (Empress), Helena who set about re-establishing the sacred sites of Palestine.
Constantine's administrative reforms included restructuring of the Praetorian prefectures. Under Diocletian, there were two prefectures, one per ''Augustus'', as their Grand Vizier, or Chief of Staff. In the civil wars that followed with multiple competing emperors, they proliferated. Constantine divided the civil duties of the Praetorian prefect, prefect from the military, by creating separate offices of ''magister peditum'' and ''magister equitum'' as well as ''magister officiorum''. The prefect was now purely a civil administrator. By 332 there were five prefectures, anticipating he division of the empire after his death. Some provincial boundaries were changed. In c. 330 ]Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
lost its eastern portions which became two components of Roman Armenia, Lesser Armenia, namely Armenia prima and Armenia secunda.
During his reign, conflict with the Persians over Armenia persisted and he was planning a major campaign at the time of his death.
 .
.
= Constantine's successors
=
Constantine I's succession was complicated being succeeded by three of his sons simultaneously; Constantine II (emperor), Constantine II (337–340), Constantius II (337–361) and Constans (337–350). They immediately set about carving up Constantine's empire, together with their cousin Dalmatius, Anatolia falling to Constantius II. Constantius rarely visited Constantinople being preoccupied with the eastern front, amongst other wars. During Constantius' reign the Praetorian prefecture of the East was established, incorporating the eastern dioceses, with its headquarters in Constantinople,
By 350 both of Constantius II's brothers had died and the empire was reunited under him. Constantius continued the tradition of appointing ''Caesares'', from his cousins. Of those Constantius Gallus, Gallus was appointed to rule the eastern provinces (351–354) until Constantius had him killed. The other was Julian the Apostate, Julian who was acclaimed emperor in 360 in competition with Constantius. However, the latter died before overt conflict broke out, and Julian ascended the throne (361–363). Although Julian's reign was relatively brief, his desire to return the empire to traditional gods earned him the nickname of Apostate. He was also noted for his purging of the civil service. He died campaigning in the east. With Julian's death, the short Constantinian dynasty came to an end. Very few Roman dynasties lasted more than three generations.
These were turbulent times, but from the rule of Augustus (27 BC – 14 AD) until that of Constantine I (306–337 AD), Anatolia enjoyed relative peace that allowed itself to grow as a region. Augustus removed all debts owed to the Roman Empire by the provinces and protectorates, making advanced progress possible. Roads were built to connect the larger cities in order to improve trade and transportation, and the abundance of high outputs in agricultural pursuits made more money for everyone involved. Settlement was encouraged, and local governors did not place a heavy burden upon the people with regards to taxation. The wealth gained from peace and prosperity prevented great tragedy as powerful earthquakes tore through the region, and help was given from the Roman government and other parties. It was also an age that produced some of the most respected scientific men of the classical period including the philosopher Dio Chrysostom, Dio of Bithynia, the physician Galen of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, and the historians Memnon of Heraclea and Cassius Dio of Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
.
Jovian and the Valentinians 363–378
Upon Julian's death, a military commander in his army, Jovian (emperor), Jovian (363–364) was chosen as the new emperor. He was not connected to Constantine's family and his brief reign was notable for re-establishing Christianity and for making a settlement with the Persians that was very much in their favour. He in turn was succeeded by Valentinian I (364–375), another soldier and founder of the Valentinianic dynasty, who almost immediately divided the empire again, moving to the west leaving the east in the hands of his brother Valens (364–378). Valens preoccupied himself with the east only to discover a Constatinian usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius had declared himself emperor resulting in a civil war. In the ensuing Battle of Thyatira in Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
in 366, Procopius was captured and killed.
Valens was faced with war on two fronts, with the Goths in the Balkans with whom he made a hasty peace in 369, so he could deal with the Persian attacks on Armenia. His problems were compounded by a revolt in Isauria
Isauria ( or ; grc, Ἰσαυρία), in ancient geography, is a rugged, isolated, district in the interior of Asia Minor, of very different extent at different periods, but generally covering what is now the district of Bozkır and its surro ...
, attacks by the Saracens on Syria, and having to send troops to help with the wars against the Barbarians in the west. He had made his capital, Antioch, but found conditions in the East deteriorating again with the Goths pouring into Thrace. In 378 Valens decided to confront them without waiting for reinforcements from the west meeting the invading army at the Battle of Adrianople. At the end of the battle Valens and much of his army lay dead.
Valens split Cappadocia, already much diminished into two provinces, Cappadocia prima in the north and Cappadocia secunda in the southwest around Tyana.
For a brief time the empire was reunited (378–9) under the western emperor Gratian (375–383), son of Valentinian I and nephew of Valens, before he realised he needed someone to rule in the east separately, dispatching his brother in law, Theodosius I (379–395), to Constantinople. In the west the Valentinians continued in power until the death of Valentinian III (425–455).
Theodosian dynasty 378–455



 Since Theodosius I (379–395) was only related to the Valentinians through marriage, he is regarded as the founder of a separate Theodosian dynasty. Like Constantine he is remembered in history as both ''Great'' and ''Saint''. He was also the last emperor to rule over both east and west. He continued the tradition of co-rulers, appointing his son Arcadius as co-ruler (383–395).
The situation in the west was extremely complex. On the death of Valentinian I in 375, Gratian (375–383) his son acceded to the throne but Valentinian I's generals proclaimed his four-year-old brother Valentinian II (375–392) necessitating a further division of the western empire. Gratian was killed in 383, by the usurper Magnus Maximus (383–388). Once Theodosius had disposed of him in 388, he was again sole ruler (388–393), Valentinian II only being 17, but technically a co-ruler with a guardian. However, he died in 392, whereupon another usurper, Eugenius appeared (392–394). Theodosius then appointed another son Honorius (emperor), Honorius (394–423) in the place of Valentinian, although he was only eight years old. Theodosius then disposed of Eugenius at the Battle of the Frigidus in 394.
Theodosius's major problems were with the Goths and his western frontier, which kept him away from Constantinople. He became notorious for his perpetration of the Massacre of Thessalonica in 390, and had to deal with all the problems going on in the west (see above). On the eastern front he came to an arrangement with the Sassanids, Sassenids in 384 over Roman Armenia, Armenia establishing a firm frontier, but essentially agreeing to give up most of Greater Armenia. This arrangement proved relatively stale over a long time.
Since Theodosius I (379–395) was only related to the Valentinians through marriage, he is regarded as the founder of a separate Theodosian dynasty. Like Constantine he is remembered in history as both ''Great'' and ''Saint''. He was also the last emperor to rule over both east and west. He continued the tradition of co-rulers, appointing his son Arcadius as co-ruler (383–395).
The situation in the west was extremely complex. On the death of Valentinian I in 375, Gratian (375–383) his son acceded to the throne but Valentinian I's generals proclaimed his four-year-old brother Valentinian II (375–392) necessitating a further division of the western empire. Gratian was killed in 383, by the usurper Magnus Maximus (383–388). Once Theodosius had disposed of him in 388, he was again sole ruler (388–393), Valentinian II only being 17, but technically a co-ruler with a guardian. However, he died in 392, whereupon another usurper, Eugenius appeared (392–394). Theodosius then appointed another son Honorius (emperor), Honorius (394–423) in the place of Valentinian, although he was only eight years old. Theodosius then disposed of Eugenius at the Battle of the Frigidus in 394.
Theodosius's major problems were with the Goths and his western frontier, which kept him away from Constantinople. He became notorious for his perpetration of the Massacre of Thessalonica in 390, and had to deal with all the problems going on in the west (see above). On the eastern front he came to an arrangement with the Sassanids, Sassenids in 384 over Roman Armenia, Armenia establishing a firm frontier, but essentially agreeing to give up most of Greater Armenia. This arrangement proved relatively stale over a long time.
 Despite all these events he was able to contribute considerably to Anatolian life. The great Obelisk of Theodosius, obelisk that he had transported from Alexandria to Constantinople in 390 still stands today. He rebuilt Constantine's great Forum of Theodosius, Forum in 393 and today it also bears his name. He also played a part in religious life, issuing an Edict of Thessalonica, edict in 380 that established the faith of the bishops of Rome and Alexandria as the official version of Christianity, that was still very heterogeneous. He was baptised and appointed the Patriarch of Constantinople. Then in 381 he continued Constantine's work in Nicaea by calling a new First Council of Constantinople, ecumenical council in Constantinople to entrench orthodoxy and repair relations with Rome.
During the 4th century, most of the provinces making up the Diocese of the East were split in two, e.g. Cilicia I, Cilicia II. The Armenian situation was complex. In the west (west of the
Despite all these events he was able to contribute considerably to Anatolian life. The great Obelisk of Theodosius, obelisk that he had transported from Alexandria to Constantinople in 390 still stands today. He rebuilt Constantine's great Forum of Theodosius, Forum in 393 and today it also bears his name. He also played a part in religious life, issuing an Edict of Thessalonica, edict in 380 that established the faith of the bishops of Rome and Alexandria as the official version of Christianity, that was still very heterogeneous. He was baptised and appointed the Patriarch of Constantinople. Then in 381 he continued Constantine's work in Nicaea by calling a new First Council of Constantinople, ecumenical council in Constantinople to entrench orthodoxy and repair relations with Rome.
During the 4th century, most of the provinces making up the Diocese of the East were split in two, e.g. Cilicia I, Cilicia II. The Armenian situation was complex. In the west (west of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
) lay the older territory of Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
, within the Diocese of Pontus, being lands most recently acquired from Cappadocia, and forming two provinces, Armenia prima and Armenia secunda. In the east there were also two territories. In the North lay Armenia maior had provincial status, while the southern part consisted of a federation of six satrapies or principalities (Angeghtun, Ingilene, Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
, Anzitene, Asthianene, Sophanene and Balabitene) allied to the empire.
Theodosius died in Milan in 395, and was buried in Constantinople. His sons Honorius (emperor), Honorius and Arcadius divided the empire between them and it was never again to be united. Thus the Eastern Empire was finally established by the beginning of the 5th century, as it entered the Middle Ages, while the west was to decay and Rome to be sacked under Honorius. The west limped on under a series of short lived emperors and progressively shrinking empire, in which the east frequently intervened, effectively ending with Julius Nepos (474–475).
Judaism and Christianity in Anatolia during Roman times
As the Roman Empire grew geographically it became increasingly diverse and the influence of many religions beyond the traditional Roman values was increasingly felt. Slowly a movement for religious tolerance developed.
Judaism
Jewish legend describes Jewish diaspora, Jewish dispersion from as early as the Book of Genesis and the time of Abraham. Although there may have been some settlement in the 4th century BC this was substantial before the time of the Seleucids. In about 210 BC, Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
relocated 2,000 families of Jews from Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
to Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
and Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empir ...
, and this migration continued throughout the remainder of the Empire's existence.
The principal centres were Apamea, Laodicea on the Lycus, and Hierapolis Euphratensis. Additional clues to the size of the Jewish influence in the area were provided by Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, who noted that a fellow Roman governor had halted the tribute sent to Jerusalem by Jews in 66 BC, and the record of Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
, where the people urged Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Agrippa to expel Jews because they were not active in their religious activities. The Romans provided some protection to Jewish communities after they occupied Anatolia in 188 BC. The existing Hellenistic communities were not favourably disposed to the distinct culture in their midst and initiated discriminatory measures. In contrast the emperors promised freedom of religious practice. Jewish communities in the area collected monies to send to Jerusalem. There was more assimilation and even hybrid religious practices.
In the Common Era (AD) the Jewish communities were more accepted in the Hellenistic world, but (other than in Cappadocia) the ties with Judaea were weakening. Christianity made little impact on Judaism in Anatolia before the making of it a state religion.
Christianity
We have very little information regarding the spread of Christianity from the events recorded in Palestine (region), Palestine in the gospels to the Flavian dynasty, Flavians (69–96 AD), other than the life and works of St Paul recorded in the New Testament.
= The 1st century
=
Paul came originally from Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus in Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, but spent much of his early life in Jerusalem. Early accounts suggest a community practising in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, and likely elsewhere in Syria and neighbouring Palestine, where Paul spent some time. The following was predominantly an urban phenomenon. The Acts of the Apostles, our primary source suggests that converts were predominantly amongst the Jewish population, the Gentile following in Syria being the exception. Following the account of the Acts of the Apostles, we must rely on the various letters of Paul included in the New Testament, of which a number were to Anatolian churches (e.g. Letter to the Galatians, Galatians, Ephesians). From sources such as the Letter to the Galatians we learn that Paul spent a considerable time in the vicinity of his home town of Tarsus in Cilicia and that the church there was linked to the Syrian churches. Put together these various Pauline sources suggest considerable missionary activity by Paul and Barnabas throughout Anatolia, and adherence to the new faith in both Jewish and hellenised Gentile society. He appears to have made Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
, the metropolis of the province of Asia, his headquarters (54-56AD). Another New Testament source, the Book of Revelation, Revelation refers to the Seven Churches of Asia (Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prom ...
, Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, Thyatira, Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
, Alaşehir, Philadelphia, and Laodicea on the Lycus, Laodicea), a list which includes not only large urban centres but also smaller towns. Certainly Asia Minor appears to have been the centre of Christianity at least until the late 40s, before spreading across the Aegean and eventually Rome itself.Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwe ...
writes to the Roman emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
that so many different people are flocking to Christianity, leaving the temples vacated.
See also
*History of Anatolia
*Prehistory of Anatolia
*Ancient Regions of Anatolia
*Ancient kingdoms of Anatolia
*Medieval states in Anatolia
References
Sources
Reference works
Cambridge Ancient History Online 14 vols. 1970–2000
br /> ''Note: The original 11 vol. Cambridge Ancient History 1928–36 is no
available as free ebooks
'
Cambridge Companions to the Ancient World. 10 vols.Hastings, James. ''A Dictionary of the Bible: Dealing with Its Language, Literature, and Contents, Including the Biblical Theology''. Volume III: (Part I: Kir—Nympha). Minerva 2004 (reprinted from 1898).
Hornblower, Simon; Antony Spawforth (1996). ''The Oxford Classical Dictionary
''. Oxford University Press] .
John Lemprière. A classical dictionary, containing a copious account of all the proper names mentioned in antient authors... 1839
*McEvedy, Colin (1967). ''The Penguin Atlas of Ancient History''. Penguin.
*Marek, Christian (2010), ''Geschichte Kleinasiens in der Antike'' C. H. Beck, Munich, (review
.
*Smith W (ed.), Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography Walton and Maberly, London 1854. 2 vols
Direct Link to Online Version
General
Duncker, Max (1879). ''The History of Antiquity, Volume III''. Richard Bentley & Son.
*
Classical Period
*Charles Freeman (historian), Freeman, Charles (1999). ''Egypt, Greece and Rome: Civilizations of the Ancient Mediterranean''. Oxford University Press. .
*Ramsay, W.M. (1904). ''The Letters to the Seven Churches of Asia''. Hodder & Stoughton.
Shipley, Graham (2000) ''The Greek World After Alexander''. Routledge History of the Ancient World. (Routledge, New York)
Hellenistic
*Bevan, Edwyn Robert (1902). ''The House of Seleucus''. E. Arnold.
*Botsford, George Willis (1922). ''Hellenic History''. The Macmillan Company.
*Bury, John Bagnell (1913). ''A History of Greece to the Death of Alexander the Great''. Macmillan.
Persian
* Pierre Briant]
''From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire''
Eisenbrauns: 2002, Originally published in French as ''Histoire de l'Empire perse'', Fayard, Paris, 1996
Encyclopaedia IranicaAmélie Kuhrt. ''The Persian Empire''
Routledge, 2007. , 9780415436281
Philip De Souza. ''The Greek and Persian Wars 499–386 BC''
Volume 36 of Essential histories. Osprey Publishing, 2003,
Roman
*Mommsen, Theodor (1906). ''The History of Rome: The Provinces, from Caesar to Diocletian.'' Charles Scribner's Sons.
*Runciman, Steven (1933). ''Byzantine Civilization''. Methuen, London
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Anatolia
Classical Anatolia,

 The Medean Empire turned out to be short lived (c. 625 – 549 BC). By 550 BC, the
The Medean Empire turned out to be short lived (c. 625 – 549 BC). By 550 BC, the  By 550 BC Lydia controlled the Greek coastal cities, who paid tribute, and most of Anatolia, except
By 550 BC Lydia controlled the Greek coastal cities, who paid tribute, and most of Anatolia, except 

 The preceding events of the
The preceding events of the  Advancing on
Advancing on 

 In June 323 BC,
In June 323 BC,  On the death of
On the death of  After the brief reign of Seleucus II's son
After the brief reign of Seleucus II's son 
 While the Seleucids continued to maintain lands in south eastern Anatolia the empire was progressively weakened on all fronts, and became progressively unstable, torn by civil war in the 2nd century BC. After the death of
While the Seleucids continued to maintain lands in south eastern Anatolia the empire was progressively weakened on all fronts, and became progressively unstable, torn by civil war in the 2nd century BC. After the death of  The
The 



 By 282 BC Rome had subdued northern Italy, and as a result of the
By 282 BC Rome had subdued northern Italy, and as a result of the  In the
In the 

 The
The  With his death, Rome lapsed into yet another war, the
With his death, Rome lapsed into yet another war, the  With Antony dead, and Lepidus marginalised, the second triumvirate was effectively dissolved, leaving Octavian as the sole power. Thus the republic came to and end. Octavian's powers progressively increased, he was granted the title ''Augustus'' by the Senate and adopted the title ''princeps senatus'' in 27 BC although technically a
With Antony dead, and Lepidus marginalised, the second triumvirate was effectively dissolved, leaving Octavian as the sole power. Thus the republic came to and end. Octavian's powers progressively increased, he was granted the title ''Augustus'' by the Senate and adopted the title ''princeps senatus'' in 27 BC although technically a  A new problem for Anatolia emerged during this period, with the expansion of the
A new problem for Anatolia emerged during this period, with the expansion of the  Order and stability was restored when
Order and stability was restored when  Constantine considered a number of candidate cities as a new eastern capital, before deciding on
Constantine considered a number of candidate cities as a new eastern capital, before deciding on  .
.



 Since Theodosius I (379–395) was only related to the Valentinians through marriage, he is regarded as the founder of a separate Theodosian dynasty. Like Constantine he is remembered in history as both ''Great'' and ''Saint''. He was also the last emperor to rule over both east and west. He continued the tradition of co-rulers, appointing his son Arcadius as co-ruler (383–395).
The situation in the west was extremely complex. On the death of Valentinian I in 375, Gratian (375–383) his son acceded to the throne but Valentinian I's generals proclaimed his four-year-old brother Valentinian II (375–392) necessitating a further division of the western empire. Gratian was killed in 383, by the usurper Magnus Maximus (383–388). Once Theodosius had disposed of him in 388, he was again sole ruler (388–393), Valentinian II only being 17, but technically a co-ruler with a guardian. However, he died in 392, whereupon another usurper, Eugenius appeared (392–394). Theodosius then appointed another son Honorius (emperor), Honorius (394–423) in the place of Valentinian, although he was only eight years old. Theodosius then disposed of Eugenius at the Battle of the Frigidus in 394.
Theodosius's major problems were with the Goths and his western frontier, which kept him away from Constantinople. He became notorious for his perpetration of the Massacre of Thessalonica in 390, and had to deal with all the problems going on in the west (see above). On the eastern front he came to an arrangement with the Sassanids, Sassenids in 384 over Roman Armenia, Armenia establishing a firm frontier, but essentially agreeing to give up most of Greater Armenia. This arrangement proved relatively stale over a long time.
Since Theodosius I (379–395) was only related to the Valentinians through marriage, he is regarded as the founder of a separate Theodosian dynasty. Like Constantine he is remembered in history as both ''Great'' and ''Saint''. He was also the last emperor to rule over both east and west. He continued the tradition of co-rulers, appointing his son Arcadius as co-ruler (383–395).
The situation in the west was extremely complex. On the death of Valentinian I in 375, Gratian (375–383) his son acceded to the throne but Valentinian I's generals proclaimed his four-year-old brother Valentinian II (375–392) necessitating a further division of the western empire. Gratian was killed in 383, by the usurper Magnus Maximus (383–388). Once Theodosius had disposed of him in 388, he was again sole ruler (388–393), Valentinian II only being 17, but technically a co-ruler with a guardian. However, he died in 392, whereupon another usurper, Eugenius appeared (392–394). Theodosius then appointed another son Honorius (emperor), Honorius (394–423) in the place of Valentinian, although he was only eight years old. Theodosius then disposed of Eugenius at the Battle of the Frigidus in 394.
Theodosius's major problems were with the Goths and his western frontier, which kept him away from Constantinople. He became notorious for his perpetration of the Massacre of Thessalonica in 390, and had to deal with all the problems going on in the west (see above). On the eastern front he came to an arrangement with the Sassanids, Sassenids in 384 over Roman Armenia, Armenia establishing a firm frontier, but essentially agreeing to give up most of Greater Armenia. This arrangement proved relatively stale over a long time.
 Despite all these events he was able to contribute considerably to Anatolian life. The great Obelisk of Theodosius, obelisk that he had transported from Alexandria to Constantinople in 390 still stands today. He rebuilt Constantine's great Forum of Theodosius, Forum in 393 and today it also bears his name. He also played a part in religious life, issuing an Edict of Thessalonica, edict in 380 that established the faith of the bishops of Rome and Alexandria as the official version of Christianity, that was still very heterogeneous. He was baptised and appointed the Patriarch of Constantinople. Then in 381 he continued Constantine's work in Nicaea by calling a new First Council of Constantinople, ecumenical council in Constantinople to entrench orthodoxy and repair relations with Rome.
During the 4th century, most of the provinces making up the Diocese of the East were split in two, e.g. Cilicia I, Cilicia II. The Armenian situation was complex. In the west (west of the
Despite all these events he was able to contribute considerably to Anatolian life. The great Obelisk of Theodosius, obelisk that he had transported from Alexandria to Constantinople in 390 still stands today. He rebuilt Constantine's great Forum of Theodosius, Forum in 393 and today it also bears his name. He also played a part in religious life, issuing an Edict of Thessalonica, edict in 380 that established the faith of the bishops of Rome and Alexandria as the official version of Christianity, that was still very heterogeneous. He was baptised and appointed the Patriarch of Constantinople. Then in 381 he continued Constantine's work in Nicaea by calling a new First Council of Constantinople, ecumenical council in Constantinople to entrench orthodoxy and repair relations with Rome.
During the 4th century, most of the provinces making up the Diocese of the East were split in two, e.g. Cilicia I, Cilicia II. The Armenian situation was complex. In the west (west of the