Clamp connection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
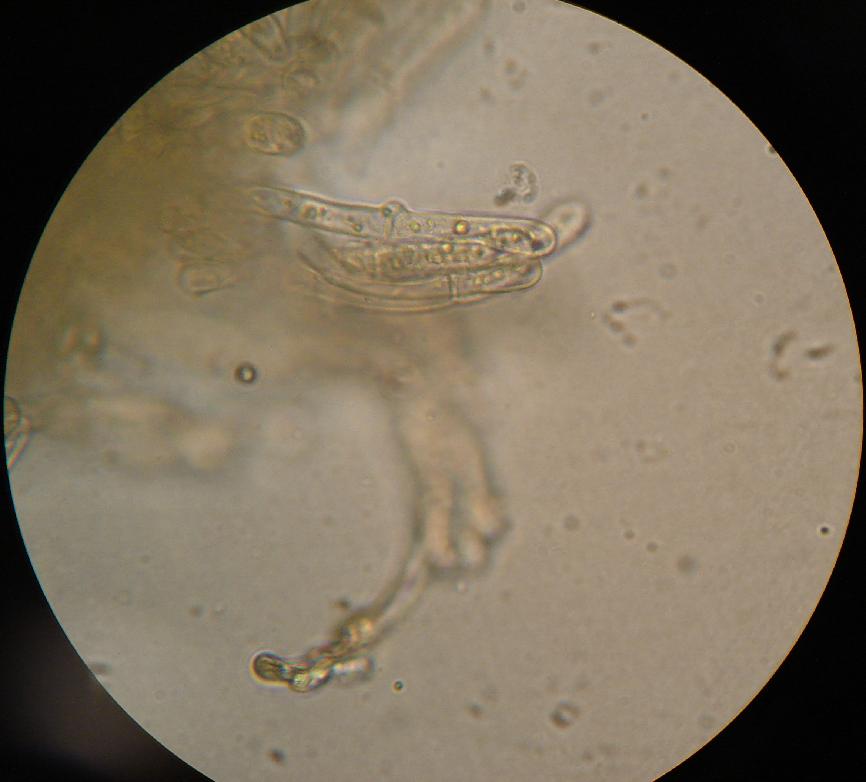 A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain

 Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes
Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes
 A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
, or segment of hypha separated by septa
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five c ...
(cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite- sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. ''Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reprod ...
of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
.
Formation
mitotic division
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei (orange circles) begin to migrate from one another to opposite ends of the cell. Once all these steps have occurred a septum forms, separating each set of nuclei.
Use in classification
Clamp connections are structures unique to the phylum Basidiomycota. Many fungi from this phylum produce spores inbasidiocarp
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome, or basidioma () is the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; rusts and smuts do ...
s (fruiting bodies, or mushrooms), above ground. Though clamp connections are exclusive to this phylum, not all species of Basidiomycota possess these structures. As such, the presence or absences of clamp connections has been a tool in categorizing genera and species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
.
Fossil record
A fungal mycelium containing abundant clamp connections was found that dated to the Pennsylvanian era (298.9–323.2 Mya). This fossil, classified in the form genus '' Palaeancistrus'', has hyphae that compare with extantsaprophytic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi ( ...
basidiomycetes. The oldest known clamp connections exist in hyphae present in the fossil fern '' Botryopteris antiqua'', which predate ''Palaeancistrus'' by about 25 Ma.
References
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite journal , author=Dennis, Robert L. , year=1970 , title=A middle Pennsylvanian basidiomycete mycelium with clamp connections , journal=Mycologia , volume=62 , issue=3 , pages=578–584 , jstor=3757529 , doi=10.2307/3757529 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0062/003/0578.htm {{cite journal , author=Furtado, João S. , year=1966 , title=Significance of the clamp-connection in the basidiomycetes , journal=Persoonia , volume=4 , issue=1 , pages=125–144 , url=http://www.repository.naturalis.nl/document/570025 {{cite journal , author1=Krings, Michael , author2=Dotzler, Nora , author3=Galtier, Jean , author4=Taylor, Thomas N. , year=2011 , title=Oldest fossil basidiomycete clamp connections , journal=Mycoscience , volume=52 , issue=1 , pages=18–23 , doi=10.1007/s10267-010-0065-4, hdl=1808/13681 , hdl-access=free Fungal morphology and anatomy