Church of St. Vincent Ferrer (Manhattan) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Church of St. Vincent Ferrer is a Roman Catholic parish in the
The Catholic Church in the United States of America: Undertaken to Celebrate the Golden Jubilee of His Holiness, Pope Pius X. Volume 3: The Province of Baltimore and the Province of New York, Section 1: Comprising the Archdiocese of New York and the Diocese of Brooklyn, Buffalo and Ogdensburg Together with some Supplementary Articles on Religious Communities of Women.
'. (New York City: The Catholic Editing Company, 1914), p.379.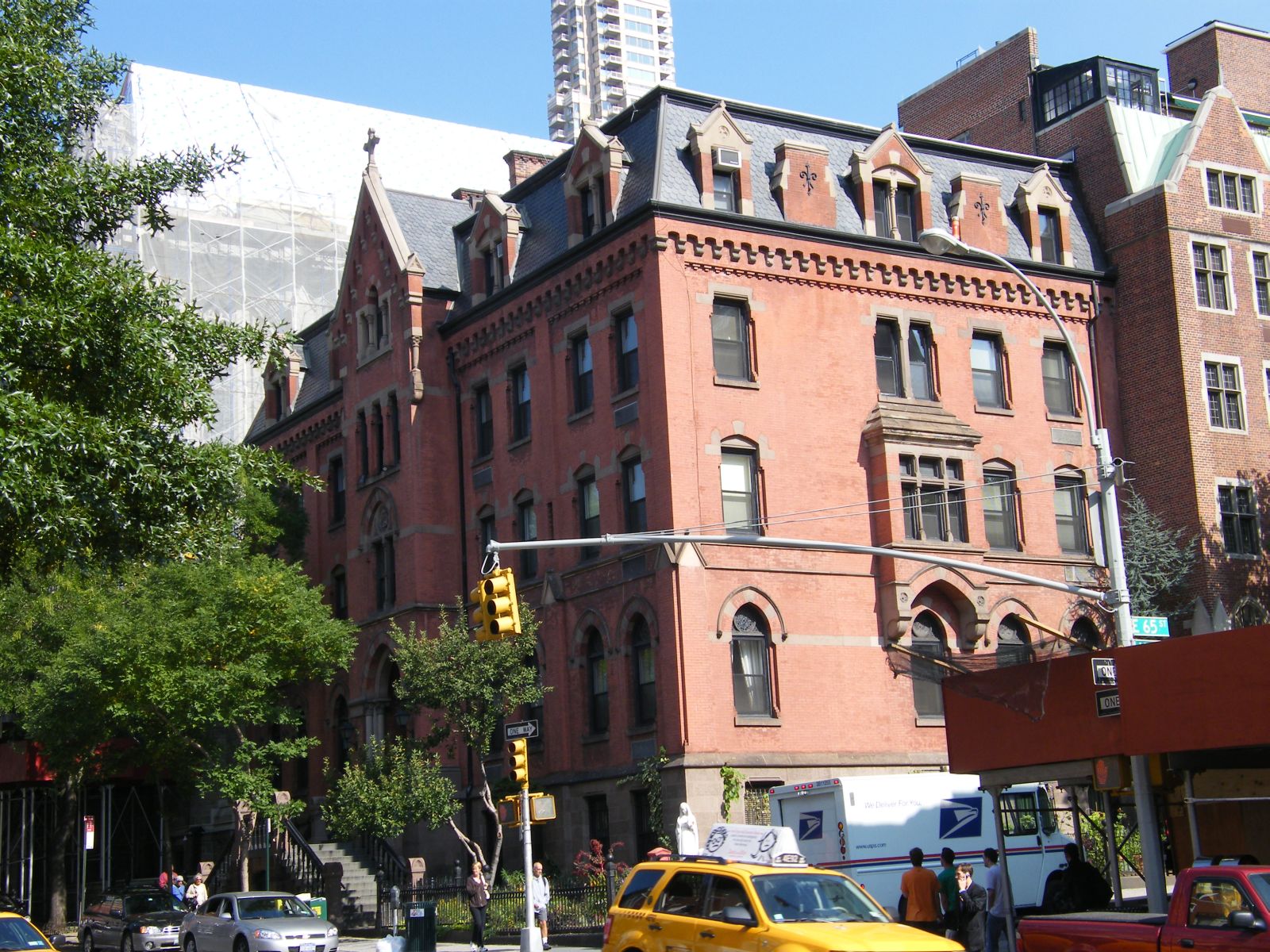 By 1879 the construction was expanded and on December 12, a second church was dedicated. Its first Mass was celebrated on the feast day of St. Vincent Ferrer, September 8, 1879. At the same time the order decided to build a
By 1879 the construction was expanded and on December 12, a second church was dedicated. Its first Mass was celebrated on the feast day of St. Vincent Ferrer, September 8, 1879. At the same time the order decided to build a
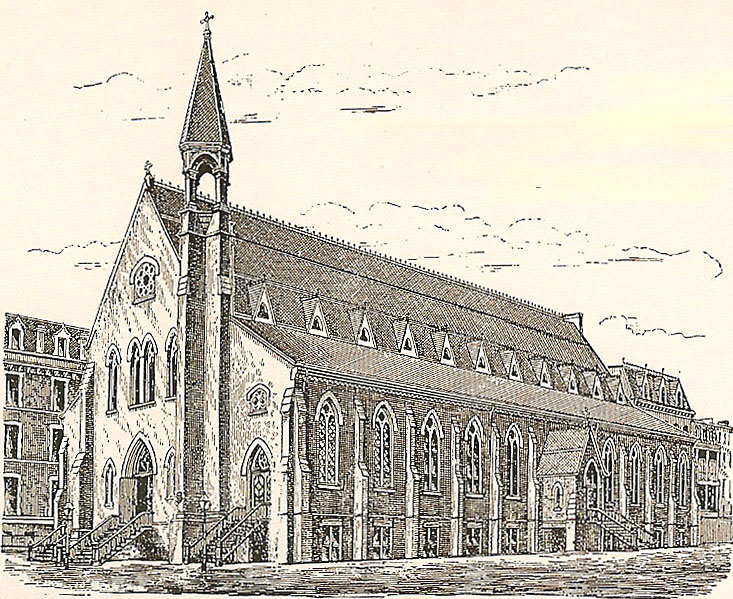 The architect wrote to a friend that he considered St. Vincent Ferrer his best Gothic work; he designed the Gothic Revival church in the style of 14th-century French Gothic, with echoes of Romanesque. Lee Lawrie's carving of the Cross above the entrance was the first time one had been located on the exterior of an American Catholic church, and is still one of the few instances.
The architect wrote to a friend that he considered St. Vincent Ferrer his best Gothic work; he designed the Gothic Revival church in the style of 14th-century French Gothic, with echoes of Romanesque. Lee Lawrie's carving of the Cross above the entrance was the first time one had been located on the exterior of an American Catholic church, and is still one of the few instances.  The school building quickly outgrew its intended design, and a new one was built over it in 1948. Architects Elliott Chisling-Ferenz & Taylor designed a building with sympathetic Gothic motifs that help it blend into the older buildings. Following
The school building quickly outgrew its intended design, and a new one was built over it in 1948. Architects Elliott Chisling-Ferenz & Taylor designed a building with sympathetic Gothic motifs that help it blend into the older buildings. Following
Church of St. Vincent Ferrer (New York, N.Y.) architectural drawings, 1908-1928
{{Authority control
Upper East Side
The Upper East Side, sometimes abbreviated UES, is a neighborhood in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 96th Street to the north, the East River to the east, 59th Street to the south, and Central Park/Fifth Avenue to the wes ...
of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
. It was built in 1918 by the Dominicans; the attached priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of ...
serves as the headquarters of the Eastern United States Province of the order. Its architecture has some unusual features: above the front entrance is one of the few statues of the Crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the victim is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross or beam and left to hang until eventual death from exhaustion and asphyxiation. It was used as a punishment by the Persians, Carthagi ...
on the exterior of an American Catholic church; and inside, the Stations of the Cross depict Christ with oil paintings instead of statuary or carvings. It has two Schantz pipe organs. The church building, at the corner of Lexington Avenue and East 66th Street in the Lenox Hill section of the Upper East Side, has been called "one of New York's greatest architectural adornments."
The church is under the patronage of Saint Vincent Ferrer
Vincent Ferrer, OP ( ca-valencia, Sant Vicent Ferrer , es, San Vicente Ferrer, it, San Vincenzo Ferreri, german: Sankt Vinzenz Ferrer, nl, Sint-Vincent Ferrer, french: Saint Vincent Ferrier; 23 January 1350 – 5 April 1419) was a Kingdom of V ...
, a Dominican preacher
A preacher is a person who delivers sermons or homilies on religious topics to an assembly of people. Less common are preachers who preach on the street, or those whose message is not necessarily religious, but who preach components such as ...
from Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. It was made a New York City designated landmark
The New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission (LPC) is the New York City agency charged with administering the city's Landmarks Preservation Law. The LPC is responsible for protecting New York City's architecturally, historically, and cu ...
in 1967. Seventeen years later, in 1984, the church and priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of ...
, designed in 1881 by William Schickel, were listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
.
St. Vincent Ferrer High School
St. Vincent Ferrer High School is an American all-girls', private, Roman Catholic high school, located on the Upper East Side of the Manhattan borough of New York City, New York.
It is located within the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York ...
for girls is on its grounds and is administered by resident Dominican Sisters. Members also work in charitable efforts like local shelters and food pantries
A food bank is a non-profit, charitable organization that distributes food to those who have difficulty purchasing enough to avoid hunger, usually through intermediaries like food pantries and soup kitchens. Some food banks distribute food direct ...
. They are also involved in interfaith
Interfaith dialogue refers to cooperative, constructive, and positive interaction between people of different religious traditions (i.e. "faiths") and/or spiritual or humanistic beliefs, at both the individual and institutional levels. It is ...
lobbying for affordable housing
Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on af ...
in Manhattan.
Grounds
The church complex comprises four buildings, all on theblock
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
between East 65th and 66th on the east side of Lexington. Across the street are low rowhouse
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house ( UK) or townhouse ( US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings share side walls. In the United Sta ...
s; just to the north are the Seventh Regiment Armory
The Seventh Regiment Armory, also known as Park Avenue Armory, is a historic National Guard armory building located at 643 Park Avenue in the Upper East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. The building is a brick and stone structure b ...
, a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
, and the apartment building at 131–35 East 66th Street, also a city landmark. The entire site is less than
The address of the church, as listed in 1892, was 871 Lexington Avenue. Within the site, four buildings – the church, priory, Holy Name Society building and St. Vincent Ferrer High School
St. Vincent Ferrer High School is an American all-girls', private, Roman Catholic high school, located on the Upper East Side of the Manhattan borough of New York City, New York.
It is located within the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York ...
— are connected by adjoining walls. All are architecturally compatible, but only the church and priory are considered contributing properties
In the law regulating historic districts in the United States, a contributing property or contributing resource is any building, object, or structure which adds to the historical integrity or architectural qualities that make the historic distri ...
due to their age and simpler architecture.
The cruciform church is built of limestone laid in a random ashlar pattern on three sides. The east (rear) elevation, barely visible from the street, is faced in brick. On the west, facing Lexington Avenue, is the five- bayNew York City Landmarks Preservation Commission
The New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission (LPC) is the New York City agency charged with administering the city's Landmarks Preservation Law. The LPC is responsible for protecting New York City's architecturally, historically, and cu ...
, ; February 28, 1967. tower. It has two engaged octagonal towers flanking the large rose window, with stone tracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support the ...
forming conjoined trefoil
A trefoil () is a graphic form composed of the outline of three overlapping rings, used in architecture and Christian symbolism, among other areas. The term is also applied to other symbols with a threefold shape. A similar shape with four ring ...
s, in the center of the upper stage. Below the window is a tall round-arched entryway and stone steps topped with a carving of the Crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the victim is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross or beam and left to hang until eventual death from exhaustion and asphyxiation. It was used as a punishment by the Persians, Carthagi ...
. On the north and south the bays are divided by buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral ( ...
es supporting the steeply pitched copper roof
Inside, the entire nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
is finished in the exterior limestone. In addition to the rose window, all the side windows are filled with stained glass. Pews and choir stalls are in ornate carved wood, and the altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
is set off by a carved stone reredos. At the rear the oak pulpit is decorated with carvings in medieval Gothic style. The Stations of the Cross are represented by oil paintings. A large four- manual console
Console may refer to:
Computing and video games
* System console, a physical device to operate a computer
** Virtual console, a user interface for multiple computer consoles on one device
** Command-line interface, a method of interacting with ...
in the choir controls the two Schantz pipe organs, Opus 2145 in the choir and Opus 2224 in the west gallery. The interior also features two relics of St. Vincent Ferrer in the church and the only example of a hanging pyx that is not in a museum.
The priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of ...
, at the northeast corner of 65th and Lexington, is a five-story brick building on a brownstone foundation
Foundation may refer to:
* Foundation (nonprofit), a type of charitable organization
** Foundation (United States law), a type of charitable organization in the U.S.
** Private foundation, a charitable organization that, while serving a good cause ...
. Its facades are decorated with alternating stone and brick voussoir
A voussoir () is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault.
Although each unit in an arch or vault is a voussoir, two units are of distinct functional importance: the keystone and the springer. The ...
s, arched openings, stone bands at the imposts, pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s and buttresses. The roofline is lined with stone and brick corbels below the cornice, with elongated stone corbels on the projecting gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
d entrance tower in the center of the east (front) facade. A high brownstone stoop with cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impur ...
newel
A newel, also called a central pole or support column, is the central supporting pillar of a staircase. It can also refer to an upright post that supports and/or terminates the handrail of a stair banister (the "newel post"). In stairs having st ...
s and rails leads from the street to a deeply recessed, arched first floor entrance with clustered colonnettes. The mix of the brick and stone with the slate tiling on the dormer-pierced mansard roof gives the building a polychromatic
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors.
Ancient Egypt
Colossal statu ...
effect.
The Holy Name Society building and school are both similar structures of brick and stone. Much of their detailing and ornament, such as their buttresses and tracery, echoes or mirrors that found on the church and priory. The Society building and school date to 1930 and 1948 respectively and are not considered sufficiently historic to be included in the National Register listing with the church and priory at this time.
History
19th century
In the 1860s, a Dominican priest from France, Father Thomas Martin, was sent to the Diocese of New York and took up residence in a brownstone on Lexington Avenue and 62nd Street. Others followed, and the Dominicans became popular among the city's Catholic population.John McCloskey
John McCloskey (March 10, 1810 – October 10, 1885) was a senior-ranking American prelate of the Catholic Church. He was the first American born Archbishop of New York from 1864 until his death in 1885, having previously served as Bishop o ...
, the archbishop of the Diocese of New York and the first American cardinal, asked them to establish a parish on what is now the Upper East Side
The Upper East Side, sometimes abbreviated UES, is a neighborhood in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 96th Street to the north, the East River to the east, 59th Street to the south, and Central Park/Fifth Avenue to the wes ...
. Father Martin and the other priests borrowed $10,000 ($ in contemporary dollars), bought 18 lots totaling at the present location and began to construct a chapel on the northeast corner of 65th Street. The first Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
was offered in this chapel on July 2, 1867.Remigius Lafort, S.T.D., Censor, The Catholic Church in the United States of America: Undertaken to Celebrate the Golden Jubilee of His Holiness, Pope Pius X. Volume 3: The Province of Baltimore and the Province of New York, Section 1: Comprising the Archdiocese of New York and the Diocese of Brooklyn, Buffalo and Ogdensburg Together with some Supplementary Articles on Religious Communities of Women.
'. (New York City: The Catholic Editing Company, 1914), p.379.
 By 1879 the construction was expanded and on December 12, a second church was dedicated. Its first Mass was celebrated on the feast day of St. Vincent Ferrer, September 8, 1879. At the same time the order decided to build a
By 1879 the construction was expanded and on December 12, a second church was dedicated. Its first Mass was celebrated on the feast day of St. Vincent Ferrer, September 8, 1879. At the same time the order decided to build a priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of ...
at the church to serve as its provincial headquarters. It commissioned William Schickel, a German-born architect who had recently completed his first major work in New York, the John Crimmins House at 40 East 68th Street. The priory's intricate use of materials and its overall polychromy
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors.
Ancient Egypt
Colossal statu ...
, characteristics of the High Victorian Gothic style popular in the late 19th century, reflect Schickel's training in Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
and the strong influence there of Friedrich von Gärtner
Friedrich von Gärtner (10 December 1791 in Koblenz – 21 April 1847 in Munich) was a German architect.
Biography
His father was also an architect, and moved in 1804 to Munich, where young Gärtner received his first education in archite ...
. It was the first of many buildings Schickel would design for the New York diocese. Five years later, in 1884, the first school was built.
20th and 21st centuries
The church would serve the congregation until 1914, when it was demolished in order to begin construction of a new one designed byBertram Grosvenor Goodhue
Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue (April 28, 1869 – April 23, 1924) was an American architect celebrated for his work in Gothic Revival and Spanish Colonial Revival design. He also designed notable typefaces, including Cheltenham and Merrymount for ...
, who had recently struck out on his own from Cram, Goodhue & Ferguson. While it was being built, the congregation worshipped in a temporary building at East 67th Street.
 The architect wrote to a friend that he considered St. Vincent Ferrer his best Gothic work; he designed the Gothic Revival church in the style of 14th-century French Gothic, with echoes of Romanesque. Lee Lawrie's carving of the Cross above the entrance was the first time one had been located on the exterior of an American Catholic church, and is still one of the few instances.
The architect wrote to a friend that he considered St. Vincent Ferrer his best Gothic work; he designed the Gothic Revival church in the style of 14th-century French Gothic, with echoes of Romanesque. Lee Lawrie's carving of the Cross above the entrance was the first time one had been located on the exterior of an American Catholic church, and is still one of the few instances. Guastavino tile
The Guastavino tile arch system is a version of Catalan vault introduced to the United States in 1885 by Spanish architect and builder Rafael Guastavino (1842–1908). It was patented in the United States by Guastavino in 1892.
Description
...
was used on the interior to provide for excellent acoustics;. Goodhue had Charles Connick
Charles Jay Connick (1875–1945) was a prominent American painter, muralist, and designer best known for his work in stained glass in the Gothic Revival style. Born in Springboro, Pennsylvania, Connick eventually settled in the Boston area where ...
's stained glass windows positioned so that the colors complemented each other. He also decided that, reflecting the Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of ...
's Spanish origins, the representations of Christ at each of the Stations of the Cross would be oil paintings rather than the statuary or carvings more commonly used in American Catholic churches. The images were painted by Telford and Ethel Paullin in imitation of styles from different countries and eras, which accounts for the changing color of Christ's robe between them.
As originally planned the church was to have a fifteen-story flèche
Flèche or Fleche may refer to:
*Flèche (architecture), a type of church spire
*Flèche (cycling), a team cycling competition
*Flèche (fencing)
The flèche is an aggressive offensive fencing technique used with foil and épée.
Background
...
. As construction progressed that became unfeasible. A former stream that passed under the site, as well as the construction of the IRT Lexington Avenue Line
The IRT Lexington Avenue Line (also known as the IRT East Side Line and the IRT Lexington–Fourth Avenue Line) is one of the lines of the A Division of the New York City Subway, stretching from Lower Manhattan north to 125th Street in Eas ...
subway tunnels, made it impossible to lay a sufficient foundation. On October 22, 1916, the construction of the present incarnation of St. Vincent was completed, at a cost of $1.5 million ($ in contemporary dollars). It was dedicated on May 5, 1918, when over 50,000 people attended.
In 1930 the Holy Name Society building was constructed. It was one of architect Wilfred E. Anthony's many designs for the Catholic Church, and considered one of his best overall. The oaken High Pulpit was installed in the sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
. Its 14th-century French Gothic detailings were consistent with the church's architecture.
Vatican II
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
in the 1960s, the Dominicans replaced their rite with the standard Roman Rite Mass of Paul VI
The Mass of Paul VI, also known as the Ordinary Form or Novus Ordo, is the most commonly used liturgy in the Catholic Church. It is a form of the Latin Church's Roman Rite and was promulgated by Pope Paul VI in 1969, published by him in the 19 ...
. A new altar was installed at the front of the choir, while the original High Altar at the rear continues to be used for reserving the Blessed Sacrament
The Blessed Sacrament, also Most Blessed Sacrament, is a devotional name to refer to the body and blood of Christ in the form of consecrated sacramental bread and wine at a celebration of the Eucharist. The term is used in the Latin Church of the ...
.
During the late 1960s and 1970s Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol (; born Andrew Warhola Jr.; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American visual artist, film director, and producer who was a leading figure in the Art movement, visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore th ...
, a devout Byzantine Catholic The term Greek Catholic Church can refer to a number of Eastern Catholic Churches following the Byzantine (Greek) liturgy, considered collectively or individually.
The terms Greek Catholic, Greek Catholic church or Byzantine Catholic, Byzantine Ca ...
who lived nearby, attended Mass regularly at St. Vincent Ferrer. Father Sam Matarazzo, the priest at the time, remembers him sitting quietly in the back of the church, taking neither communion nor confession
A confession is a statement – made by a person or by a group of persons – acknowledging some personal fact that the person (or the group) would ostensibly prefer to keep hidden. The term presumes that the speaker is providing information th ...
. He speculated that Warhol, one of many gay men who attended services at St. Vincent Ferrer despite Matarazzo's regular preaching of Catholic doctrine opposing homosexuality, was perhaps afraid of being recognized. Warhol himself said he was self-conscious about being seen crossing himself
Making the sign of the cross ( la, signum crucis), or blessing oneself or crossing oneself, is a ritual blessing made by members of some branches of Christianity. This blessing is made by the tracing of an upright cross or + across the body with ...
"the Orthodox way."
Later in the 20th century, contributions from William E. Simon
William Edward Simon (November 27, 1927 – June 3, 2000) was an American businessman and philanthropist who served as the 63rd United States Secretary of the Treasury. He became the Secretary of the Treasury on May 9, 1974, during the Nixon admi ...
and an anonymous donor allowed the church to purchase the newer of its two Schantz pipe organs. In the early 2000s a capital campaign allowed the church to install new heating and cooling systems, and restore its exterior. That latter project was complete in 2009.
On May 8, 2015, the Archdiocese of New York announced the merger of parishes between St Vincent Ferrer and St. Catherine of Siena Church. Both churches will remain open.
Programs and services
The church celebrates Mass three times a day and four times on Sunday.Vigil
A vigil, from the Latin ''vigilia'' meaning ''wakefulness'' ( Greek: ''pannychis'', or ''agrypnia'' ), is a period of purposeful sleeplessness, an occasion for devotional watching, or an observance. The Italian word ''vigilia'' has become gener ...
s are observed on Saturday nights and the evenings before Holy Days of Obligation
In the Catholic Church, holy days of obligation are days on which the faithful are expected to attend Mass, and engage in rest from work and recreation (id est, they are to refrain from engaging in work or activities that hinder the worship owed t ...
. The Sacrament of Reconciliation (confession) is offered all evenings except Sunday. The Liturgy of the Hours
The Liturgy of the Hours (Latin: ''Liturgia Horarum'') or Divine Office (Latin: ''Officium Divinum'') or ''Opus Dei'' ("Work of God") are a set of Catholic prayers comprising the canonical hours, often also referred to as the breviary, of the ...
is observed by the Dominican friars daily in the Friars' Chapel which is open to the public.
Outside the church, the congregation's Social Concerns Committee coordinates involvement in charitable work in the area. Members host holiday parties and bingo
Bingo or B-I-N-G-O may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Gaming
* Bingo, a game using a printed card of numbers
** Bingo (British version), a game using a printed card of 15 numbers on three lines; most commonly played in the UK and Ireland
** Bi ...
games at the Women's Shelter in the neighboring Park Avenue Armory
__NOTOC__
The Park Avenue Armory Conservancy, generally known as Park Avenue Armory, is a nonprofit cultural institution within the historic Seventh Regiment Armory building located at 643 Park Avenue on New York City's Upper East Side. The ins ...
, staff the Yorkville Common Pantry and assist members of nearby Jan Hus Presbyterian Church in feeding the homeless on Tuesday nights. The congregation is also a member organization of East Congregations for Housing Justice, which advocates for affordable housing
Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on af ...
in Manhattan.
Notable people
Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol (; born Andrew Warhola Jr.; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American visual artist, film director, and producer who was a leading figure in the Art movement, visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore th ...
regularly attended Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
at the church.
In 2000, Prince Maximilian of Liechtenstein
Prince Maximilian Nikolaus Maria of Liechtenstein (born 16 May 1969), known professionally as Max von Liechtenstein, is a member of the Liechtenstein princely family and businessman. He is the second son of Prince Hans-Adam II and Princess Ma ...
and Angela Brown married at the church.
Several notable funeral masses have taken place at St. Vincent Ferrer. Dorothy Kilgallen's funeral mass took place on November 11, 1965, with 2,600 people in attendance. The funeral mass of politician Geraldine Ferraro
Geraldine Anne Ferraro (August 26, 1935 March 26, 2011) was an American politician, diplomat, and attorney. She served in the United States House of Representatives from 1979 to 1985, and was the Democratic Party's vice presidential nominee ...
took place on March 31, 2011; she and her husband John Zaccaro had been married at the church in 1960. The funeral mass of businesswoman Ivana Trump
Ivana Marie Trump (, ; February 20, 1949 – July 14, 2022) was a Czech-American businesswoman, media personality, socialite, fashion designer, author, and model. Ivana lived in Canada in the 1970s before relocating to the United States and m ...
took place on July 20, 2022, at St. Vincent Ferrer.
See also
*List of New York City Designated Landmarks in Manhattan from 59th to 110th Streets
The New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission (LPC), formed in 1965, is the New York City governmental commission that administers the city's Landmarks Preservation Law. Since its founding, it has designated over a thousand landmarks, class ...
*National Register of Historic Places listings in Manhattan from 59th to 110th Streets
This is intended to be a complete list of properties and districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places between 59th and 110th Streets in Manhattan. For properties and districts in other parts of Manhattan and the other islands of N ...
References
Further reading
*Kirkham, Richard, ''St Vincent Ferrer A Church For All Seasons''External links
*Church of St. Vincent Ferrer (New York, N.Y.) architectural drawings, 1908-1928
{{Authority control
Saint Vincent Ferrer
Vincent Ferrer, OP ( ca-valencia, Sant Vicent Ferrer , es, San Vicente Ferrer, it, San Vincenzo Ferreri, german: Sankt Vinzenz Ferrer, nl, Sint-Vincent Ferrer, french: Saint Vincent Ferrier; 23 January 1350 – 5 April 1419) was a Valencian ...
Vincent Ferrer
Vincent Ferrer, OP ( ca-valencia, Sant Vicent Ferrer , es, San Vicente Ferrer, it, San Vincenzo Ferreri, german: Sankt Vinzenz Ferrer, nl, Sint-Vincent Ferrer, french: Saint Vincent Ferrier; 23 January 1350 – 5 April 1419) was a Kingdom of V ...
Roman Catholic churches in Manhattan
Gothic Revival church buildings in New York City
Bertram Goodhue church buildings
Properties of religious function on the National Register of Historic Places in Manhattan
Religious organizations established in the 1860s
19th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in the United States
Roman Catholic churches completed in 1916
Roman Catholic churches completed in 1879
Churches completed in 1916
Upper East Side
Churches on the National Register of Historic Places in New York (state)
New York City Designated Landmarks in Manhattan