Chittagong, Bangladesh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in

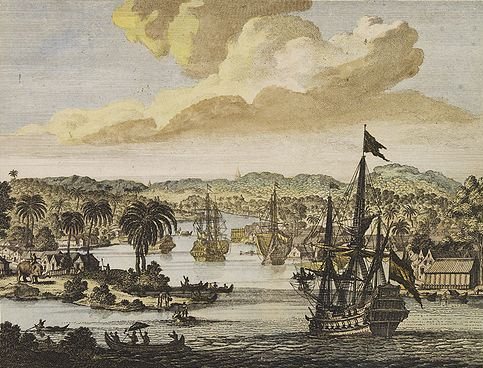

 During the 13th and 16th centuries,
During the 13th and 16th centuries, 
 In 1666, the Mughal government of Bengal led by viceroy
In 1666, the Mughal government of Bengal led by viceroy
/ref> In 1685, the British East India Company sent out an expedition under Admiral Nicholson with the instructions to seize and fortify Chittagong on behalf of the English; however, the expedition proved abortive. Two years later, the company's Court of Directors decided to make Chittagong the headquarters of their Bengal trade and sent out a fleet of ten or eleven ships to seize it under Captain Heath. However, after reaching Chittagong in early 1689, the fleet found the city too strongly held and abandoned their attempt at capturing it. The city was possessed by the Nawab of Bengal until 1793 when East India Company took complete control of the former Mughal province of Bengal. The
 Chittagong lies at . It straddles the coastal foothills of the Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh. The Karnaphuli River runs along the southern banks of the city, including its central business district. The river enters the Bay of Bengal in an
Chittagong lies at . It straddles the coastal foothills of the Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh. The Karnaphuli River runs along the southern banks of the city, including its central business district. The river enters the Bay of Bengal in an
 The
The 
File:Aerial View of Shah Amanat Bridge 3.jpg, Industrial plants near the Shah Amanat Bridge
File:Straddle carrier from Port of Chittagong (01).jpg,
A substantial share of Bangladesh's national GDP is attributed to Chittagong. The port city contributes 12% of the nation's economy. Chittagong generates for 40% of Bangladesh's industrial output, 80% of its 
 An inhabitant of Chittagong is called ''Chittagonian'' in English. For centuries, the port city has been a
An inhabitant of Chittagong is called ''Chittagonian'' in English. For centuries, the port city has been a 
 During the medieval period, many poets thrived in the region when it was part of the Bengal Sultanate and the Kingdom of Mrauk U. Under the patronage of Sultan
During the medieval period, many poets thrived in the region when it was part of the Bengal Sultanate and the Kingdom of Mrauk U. Under the patronage of Sultan

 At the 2011 Census, Chittagong had a population of more than 2.5 million, and it's Metropolitan Area had a population of 4,009,423. By gender, the population was 54.36% male and 45.64% female, and the literacy rate in the city was approximately 72 percent, in 2020.
At the 2011 Census, Chittagong had a population of more than 2.5 million, and it's Metropolitan Area had a population of 4,009,423. By gender, the population was 54.36% male and 45.64% female, and the literacy rate in the city was approximately 72 percent, in 2020.
CplusTv
gained vast popularity. The channel is YouTube- and social network-based, and it reached the 1 million followers milestone on Facebook. Chittagong has been featured in all aspects of Bangladeshi popular culture, including television, movies, journals, music and books. Nearly all televisions and radios in Bangladesh have coverage in Chittagong. Renowned
Chittagong has been featured in all aspects of Bangladeshi popular culture, including television, movies, journals, music and books. Nearly all televisions and radios in Bangladesh have coverage in Chittagong. Renowned

 The education system of Chittagong is similar to that of rest of Bangladesh, with four main forms of schooling. The general education system, conveyed in both Bangla and English versions, follows the curriculum prepared by the
The education system of Chittagong is similar to that of rest of Bangladesh, with four main forms of schooling. The general education system, conveyed in both Bangla and English versions, follows the curriculum prepared by the
 The Chittagong Medical College Hospital is the largest state-owned hospital in Chittagong. The Chittagong General Hospital, established in 1901, is the oldest hospital in the city. The Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases (BITID) is based the city. Other government-run medical centers in the city include the Family Welfare Centre, TB Hospital, Infectious Disease Hospital, Diabetic Hospital, Mother and Children Hospital, and the Police Hospital. Among the city's private hospitals are the Bangabandhu Memorial Hospital (BBMH), Chittagong Metropolitan Hospital, Chevron Clinic, Surgiscope Hospital, CSCR, Centre Point Hospital, Park View Hospital, Max Hospital & diagnosis, Imperial Hospital LTD., Evercare Hospital Ltd., National Hospital and Mount Hospital Ltd.
The Chittagong Medical College Hospital is the largest state-owned hospital in Chittagong. The Chittagong General Hospital, established in 1901, is the oldest hospital in the city. The Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases (BITID) is based the city. Other government-run medical centers in the city include the Family Welfare Centre, TB Hospital, Infectious Disease Hospital, Diabetic Hospital, Mother and Children Hospital, and the Police Hospital. Among the city's private hospitals are the Bangabandhu Memorial Hospital (BBMH), Chittagong Metropolitan Hospital, Chevron Clinic, Surgiscope Hospital, CSCR, Centre Point Hospital, Park View Hospital, Max Hospital & diagnosis, Imperial Hospital LTD., Evercare Hospital Ltd., National Hospital and Mount Hospital Ltd.
 Private Medical Colleges:
* University of Science & Technology Chittagong
* BGC TRUST medical College Chittagong
* Chittagong Ma o shishu Hospital
* Southern Medical College
* Marine City Medical College
Private Medical Colleges:
* University of Science & Technology Chittagong
* BGC TRUST medical College Chittagong
* Chittagong Ma o shishu Hospital
* Southern Medical College
* Marine City Medical College
 As the population of the city has begun to grow extensively, the Chittagong Development Authority (CDA) has undertaken some transportation initiatives aimed at easing the traffic congestion in Chittagong. Under this plan, the CDA, along with the Chittagong City Corporation, has constructed some flyovers and expanded the existing roads within the city. There are also some other major expressways and flyovers under-construction, most notably the Chittagong City Outer Ring Road, which runs along the coast of Chittagong city. This
As the population of the city has begun to grow extensively, the Chittagong Development Authority (CDA) has undertaken some transportation initiatives aimed at easing the traffic congestion in Chittagong. Under this plan, the CDA, along with the Chittagong City Corporation, has constructed some flyovers and expanded the existing roads within the city. There are also some other major expressways and flyovers under-construction, most notably the Chittagong City Outer Ring Road, which runs along the coast of Chittagong city. This
 The
The  * Oman Air
* Air Arabia
* Bangladesh Biman
* US Bangla Airlines
* Al Zajera airlines
* Salam Airlines
* Fly Dubai
* Novo airlines
* Oman Air
* Air Arabia
* Bangladesh Biman
* US Bangla Airlines
* Al Zajera airlines
* Salam Airlines
* Fly Dubai
* Novo airlines

 Chittagong has produced numerous cricketers, footballers, and athletes, who have performed at the national level.
Chittagong has produced numerous cricketers, footballers, and athletes, who have performed at the national level.
Official Web Portal of Chittagong
Chittagong City Corporation
Chittagong Development Authority
Chittagong Metropolitan Police
* {{Authority control Bay of Bengal Chittagong District Former colonies in Asia Former Portuguese colonies Populated coastal places in Bangladesh Populated places in Chittagong Division Port cities in Asia Portuguese colonisation in Asia
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
after Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest ...
and third largest city in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
region. It is the administrative seat of the eponymous division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
and district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
. It hosts the busiest seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as ...
on the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
. The city is located on the banks of the Karnaphuli River
Karnaphuli ( bn, কর্ণফুলি ''Kôrnophuli''; also spelt Karnafuli), or Khawthlangtuipui (in Mizo, meaning "western river"), is the largest and most important river in Chattogram and the Chattogram Hill Tracts. It is a wide rive ...
between the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
and the Bay of Bengal. The Greater Chittagong Area had a population of more than 5.2 million in 2022. In 2020, the city area had a population of more than 3.9 million.
One of the world's oldest ports with a functional natural harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
for centuries, Chittagong appeared on ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
maps, including on Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book '' Geography'', written . Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manu ...
. It was located on the southern branch of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
. In the 9th century, merchants from the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
established a trading post in Chittagong. The port fell to the Muslim conquest of Bengal during the 14th century. It was the site of a royal mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury and is un ...
under the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
, Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the domina ...
and Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Between the 15th and 17th centuries, Chittagong was also a center of administrative, literary, commercial and maritime activities in Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
, a narrow strip of land along the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal which was under strong Bengali influence for 350 years. During the 16th century, the port became a Portuguese trading post and João de Barros
João de Barros () (1496 – 20 October 1570), called the ''Portuguese Livy'', is one of the first great Portuguese historians, most famous for his '' Décadas da Ásia'' ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India, Asia, and southe ...
described it as "the most famous and wealthy city of the Kingdom of Bengal". The Mughal Empire expelled the Portuguese and Arakanese in 1666. Like the rest of Bengal British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
took control of the city in 1793. The Port of Chittagong
The Chittagong Port ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম বন্দর) is the main seaport of Bangladesh. Located in Bangladesh's port city of Chittagong and on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the port handles over 90 percent of Bangladesh's ...
was re-organized in 1887 and its busiest shipping links were with British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. In 1928, Chittagong was declared a "Major Port" of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Chittagong was a base for Allied Forces engaged in the Burma Campaign. The port city began to expand and industrialize during the 1940s, particularly after the Partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
. The city was the historic terminus of the Assam Bengal Railway and Pakistan Eastern Railway
The Pakistan Eastern Railway ( ur, , bn, পাকিস্তান পূর্বাঞ্চলীয় রেলপথ) was one of two divisions of Pakistan Railways which operated between 1961 and 1971. The company was headquartered in ...
. During the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali ...
in 1971, Chittagong was the site of the Bangladeshi declaration of independence
The independence of Bangladesh was declared on 26 March 1971 at the onset of the Bangladesh Liberation War by Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman; the following day the declaration was broadcast by Major Ziaur Rahman in a radio broadcast. On ...
. The port city has benefited from the growth of heavy industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); o ...
, logistics, and manufacturing in Bangladesh. Trade unionism was strong during the 1990s.
Chittagong accounts for 12% of Bangladesh's GDP, including 40% of industrial output, 80% of international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significa ...
, and 50% of tax
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
revenue. The port city is home to many of the oldest and largest companies in the country. The Port of Chittagong is one of the busiest ports in South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
. The largest base of the Bangladesh Navy
The Bangladesh Navy ( bn, বাংলাদেশ নৌবাহিনী, Bangladesh Nou Bahini) is the naval warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces, responsible for Bangladesh's of maritime territorial area, and the defence of impor ...
is located in Chittagong, along with an air base of the Bangladesh Air Force
The Bangladesh Air Force (BAF) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ বিমান বাহিনী, Bangladesh Biman Bahini) is the aerial warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The Air Force is primarily responsible for air defence of ...
, garrisons of the Bangladesh Army
The Bangladesh Army is the land warfare branch and the largest component of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The primary mission of the Army is to provide necessary forces and capabilities to deliver the Bangladeshi government's security and defe ...
and the main base of the Bangladesh Coast Guard
The Bangladesh Coast Guard ( bn, বাংলাদেশ কোস্ট গার্ড; BCG) is the maritime law enforcement force of Bangladesh. It is a paramilitary force which is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Home Affairs. Its ...
. The eastern zone of the Bangladesh Railway
Bangladesh Railway ( bn, বাংলাদেশ রেলওয়ে) is the state-owned rail transport agency of Bangladesh. It operates and maintains all railways in the country, and is overseen by the Directorate General of Bangladesh Ra ...
is based in Chittagong. The Chittagong Stock Exchange
The Chittagong Stock Exchange ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম স্টক এক্সচেঞ্জ) is a stock exchange based in the port city Chittagong, Bangladesh. It is one of the twin financial hubs of the country, alongside the Dha ...
is one of the twin stock markets of Bangladesh with over 700 listed companies. The Chittagong Tea Auction Chittagong Tea Auction center was established on 16 July 1949. Teas manufactured throughout Bangladesh are sold in bulk to buyers through an open auction which is conducted once a week. During each tea season, 45 auctions are held at this auction ce ...
is a commodity exchange dealing with Bangladeshi tea. The CEPZ and KEPZ are key industrial zones with foreign direct investments. The city is served by Shah Amanat International Airport
Shah Amanat International Airport ( bn, শাহ আমানত আন্তর্জাতিক বিমানবন্দর ''Shah Amanôt Antôrjatik Bimanbôndôr'') is an international airport serving Bangladesh's southeastern port ...
for domestic and external flights. Chittagong has a high degree of religious and ethnic diversity among Bangladeshi cities, despite having a great Bengali Muslim
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
majority. Minorities include Bengali Hindus
Bengali Hindus ( bn, বাঙ্গালী হিন্দু/বাঙালি হিন্দু, translit=Bāṅgālī Hindu/Bāṅāli Hindu) are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Benga ...
, Bengali Christians
Bengali Christians ( bn, বাঙালি খ্রিস্টান) are adherents of Christianity among the Bengali people. Christianity took root in Bengal after the arrival of Portuguese voyagers in the 16th century. It witnessed furthe ...
, Bengali Buddhists
Bengali Buddhists ( bn, বাঙালি বৌদ্ধ) are a religious subgroup of the Bengalis who adhere to or practice the religion of Buddhism. Bengali Buddhist people mainly live in Bangladesh and Indian states West Bengal and Tripura. ...
, Chakmas, Marmas, Tripuris
The Tripuri (also known as Tripura, Tipra, Tiprasa, Twipra) are an ethnic group originating in the Indian state of Tripura. They are the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through th ...
, Garos and others.
Etymology
Theetymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
of ''Chittagong'' is uncertain. One explanation credits the first Arab traders for ''shatt ghangh'' ( ar, شط غنغ) where ''shatt'' means "delta" and ''ghangh'' stood for the Ganges. The Arakanese chronicle that a king named Tsu-la-taing Tsandaya (Sula Taing Chandra), after conquering Bengal, set up a stone pillar as a trophy/memorial at the place since called ''Tst-ta-gaung'' as the limit of conquest. This Arakanese king ascended the throne in Arakan year 311 ME, corresponding to 952 A.D. He conquered this place two years later. This stone pillar with the inscription ''Tset-ta-gaung'', meaning 'to make war is improper, cannot be a myth. However, the local name of the city (in Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
or Chittagonian) ''Chatga'' ( bn, চাটগা), which is a corruption of ''Chatgao'' ( bn, চাটগাঁও) or ''Chatigao'' ( bn, চাটিগাঁও), and officially ''Chottogram'' ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম) bears the meaning of "village or town of ''Chatta'' (possibly a caste or tribe)." Therefore, Bengali name ''Chattagrama'', the Chinese ''Tsa-ti-kiang'', ''Cheh-ti.gan'' and the European ''Chittagong'' are but the deformed versions of the Arakanese name ''Tset-ta-gaung''.
The port city has been known by various names in history, including ''Chatigaon'', ''Chatigam'', ''Chattagrama'', ''Islamabad'', ''Chattala'', ''Chaityabhumi'' and ''Porto Grande De Bengala''.
Name
The Bengali word for Chittagong, ''Chottogram (চট্টগ্রাম)'', has the suffix "-gram" (গ্রাম) meaning village inStandard Bengali
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken of t ...
. A legend dates the name to the spread of Islam, when a Muslim lit a ''chati'' (lamp) at the top of a hill in the city and called out '' Azaan'' for people. The city was renamed ''Islamabad (City of Islam)'' and continues to be used in the old city during the Mughal era. In April 2018, the Cabinet Division of the Bangladesh Government decided to change the city's name to Chattogram, based on its Bengali spelling and pronunciation.
Chittagong is popularly known as Baro Auliyar Desh (Land of twelve Sufi saints).
History

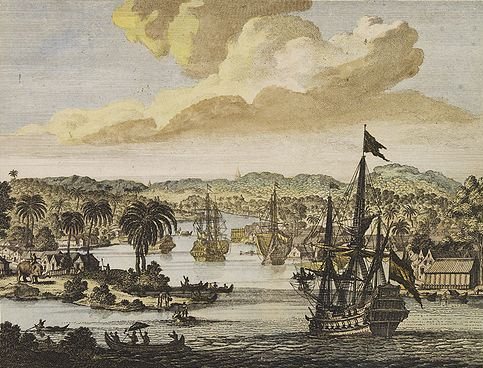
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with ...
fossils and tools unearthed in the region indicate that Chittagong has been inhabited since Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
times. It is an ancient port city, with a recorded history dating back to the 4th century BC. Its harbour was mentioned in Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book '' Geography'', written . Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manu ...
in the 2nd century as one of the most impressive ports in the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
. The region was part of the ancient Bengali Samatata
Samataṭa (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-ṭa'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of ''Sounagoura'' is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much ...
and Harikela
Harikela () was an ancient empire located in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, it was a neighboring independent and independent township of ancient East Bengal, which had a continuous existence of about 500 years. The s ...
kingdoms. The Chandra dynasty
The Chandra kingdom was a Buddhist kingdom, originating from the Indian subcontinent, which ruled the Samatata region of Bengal, as well as northern Arakan. Later it was a neighbor to the Pala Empire to the north. Rulers of Chandra kingdom were ...
once dominated the area, and was followed by the Varman dynasty
The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the G ...
and Deva dynasty.
Chinese traveler Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
described the area as "a sleeping beauty rising from mist and water" in the 7th century.
Arab Muslim traders frequented Chittagong from the 9th century. In 1154, Al-Idrisi wrote of a busy shipping route between Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
and Chittagong, connecting it with the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
capital of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
.
Many Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
missionaries settled in Chittagong and played an instrumental role in the spread of Islam
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territorie ...
.
Sultan Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah
Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah ( bn, ফখরুদ্দীন মুবারক শাহ, fa, ; reigned: 1338–1349), also known simply as Fakhra, was the founder of an independent sultanate comprising modern-day eastern and southeastern Banglad ...
of Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
conquered Chittagong in 1340, making it a part of Sultanate of Bengal. It was the principal maritime gateway to the kingdom, which was reputed as one of the wealthiest states in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
. Medieval Chittagong was a hub for maritime trade with China, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, the Middle East, and East Africa. It was notable for its medieval trades in pearls, silk, muslin, rice, bullion, horses, and gunpowder. The port was also a major shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to bef ...
hub.
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim ...
visited the port city in 1345. Niccolò de' Conti, from Venice, also visited around the same time as Battuta. Chinese admiral Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
's treasure fleet anchored in Chittagong during imperial missions to the Sultanate of Bengal.
Chittagong featured prominently in the military history of the Bengal Sultanate, including during the Reconquest of Arakan
The restoration of Min Saw Mon was a military campaign led by the Bengal Sultanate to help Min Saw Mon regain control of his Launggyet Dynasty. The campaign was successful. Min Saw Mon was restored to the Launggyet throne, and northern Arakan becam ...
and the Bengal Sultanate–Kingdom of Mrauk U War of 1512–1516.

 During the 13th and 16th centuries,
During the 13th and 16th centuries, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
heavily colonized the port city of Chittagong, initially arriving for trade and to spread Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
. Most Arab settlers arrived from the trade route between Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Chittagong, and were perhaps the prime reason for the spread of Islam to Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
. The first Persian settlers also arrived for trade and religious purposes, with the possible goal of Persianisation
Persianization () or Persification (; fa, پارسیسازی), is a sociological process of cultural change in which a non-Persian society becomes "Persianate", meaning it either directly adopts or becomes strongly influenced by the Persian ...
as well. Persians and other Iranic peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
have deeply affected the history of the Bengal Sultanate, with Persian being one of the main languages of the Muslim state, as well as also influencing the Chittagonian language and writing scripts. It has been affirmed that much of the Muslim population in Chittagong are descendants of the Arab and Persian settlers.
Two decades after Vasco Da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link ...
's landing in Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
, the Bengal Sultanate permitted the Portuguese settlement in Chittagong to be established in 1528. It became the first European colonial enclave in Bengal. The Bengal Sultanate lost control of Chittagong in 1531 after Arakan declared independence and the established Kingdom of Mrauk U. This altered geopolitical landscape allowed the Portuguese unhindered control of Chittagong for over a century.
Portuguese ships from Goa and Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has bee ...
began frequenting the port city in the 16th century. The '' cartaz'' system was introduced and required all ships in the area to purchase naval trading licenses from the Portuguese settlement. Slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and piracy flourished. The nearby island of Sandwip
Sandwip ( bn, সন্দ্বীপ, Shondip) is an island located along the southeastern coast of Bangladesh in the Chattogram District. Along with the island of Urir Char, it is a part of the Sandwip Upazila.
Description
Sandwip is locate ...
was conquered in 1602. In 1615, the Portuguese Navy
The Portuguese Navy ( pt, Marinha Portuguesa, also known as ''Marinha de Guerra Portuguesa'' or as ''Armada Portuguesa'') is the naval branch of the Portuguese Armed Forces which, in cooperation and integrated with the other branches of the Port ...
defeated a joint Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and Arakanese fleet near the coast of Chittagong.

 In 1666, the Mughal government of Bengal led by viceroy
In 1666, the Mughal government of Bengal led by viceroy Shaista Khan
Mirza Abu Talib (22 November 1600 – 1694), better known as Shaista Khan, was a general and the subahdar of Mughal Bengal. A maternal uncle to the emperor Aurangzeb, he acted as a key figure during his reign. Shaista Khan initially governed ...
moved to retake Chittagong from Portuguese and Arakanese control. They launched the Mughal conquest of Chittagong. The Mughals attacked the Arakanese from the jungle with a 6,500-strong army, which was further supported by 288 Mughal naval ships blockading the Chittagong harbor.Trudy, Ring; M. Salkin, Robert; La Boda, Sharon; Edited by Trudy Ring (1996). International dictionary of historic places. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. . Retrieved 21 June 2015. After three days of battle, the Arakanese surrendered. The Mughals expelled the Portuguese from Chittagong. Mughal rule ushered a new era in the history of Chittagong territory to the southern bank of Kashyapnadi (Kaladan river). The port city was renamed Islamabad. The Grand Trunk Road connected it with North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
and Central Asia. Economic growth increased due to an efficient system of land grants for clearing hinterlands for cultivation. The Mughals also contributed to the architecture of the area, including the building of Fort Ander and many mosques. Chittagong was integrated into the prosperous greater Bengali economy, which also included Orissa
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of S ...
and Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
. Shipbuilding increased dramatically under the Mughal rule, and the Ottoman Sultans had many Ottoman warships built in Chittagong during this period.Chittagong, Asia and Oceania: International Dictionary of Historic Place/ref> In 1685, the British East India Company sent out an expedition under Admiral Nicholson with the instructions to seize and fortify Chittagong on behalf of the English; however, the expedition proved abortive. Two years later, the company's Court of Directors decided to make Chittagong the headquarters of their Bengal trade and sent out a fleet of ten or eleven ships to seize it under Captain Heath. However, after reaching Chittagong in early 1689, the fleet found the city too strongly held and abandoned their attempt at capturing it. The city was possessed by the Nawab of Bengal until 1793 when East India Company took complete control of the former Mughal province of Bengal. The
First Anglo-Burmese War
The First Anglo-Burmese War ( my, ပထမ အင်္ဂလိပ်-မြန်မာ စစ်; ; 5 March 1824 – 24 February 1826), also known as the First Burma War, was the first of three wars fought between the British and Burmes ...
in 1823 threatened the British hold on Chittagong. There were several rebellions against British rule, notably during the Indian rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the for ...
, when the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th companies of the 34th Bengal Infantry Regiment revolted and released all prisoners from the city's jail. In a backlash, the rebels were suppressed by the Sylhet Light Infantry.
Railways were introduced in 1865, beginning with the Eastern Bengal Railway
The Eastern Bengal Railway (full name: "Eastern Bengal Railway Company"; shortened EBR) was one of the pioneering railway companies that operated from 1857 to 1942, in Bengal and Assam provinces of British India.
History
Formation
The Eastern ...
connecting Chittagong to Dacca
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
and Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
. The Assam Bengal Railway connected the port city to its interior economic hinterland, which included the world's largest tea and jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', which is in the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is '' Corchorus ol ...
producing regions, as well as one of the world's earliest petroleum industries. Chittagong was a major center of trade with British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. It hosted many prominent companies of the British Empire, including James Finlay, Duncan Brothers, Burmah Oil, the Indo-Burma Petroleum Company, Lloyd's, Mckenzie and Mckenzie, the Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China, Turner Morrison, James Warren, the Raleigh Brothers, Lever Brothers, and the Shell Oil Company.
The Chittagong armoury raid
The Chittagong armoury raid, also known as the Chittagong uprising, was an attempt on 18 April 1930 to raid the armoury of police and auxiliary forces from the Chittagong armoury in the Bengal Presidency of British India (now in Bangladesh) b ...
by Bengali revolutionaries in 1930 was a major event in British India's anti-colonial history.
During World War II, Chittagong became a frontline city in the Southeast Asian Theater. It was a critical air, naval and military base for Allied Forces during the Burma Campaign against Japan. The Imperial Japanese Army Air Force
The Imperial Japanese Army Air Service (IJAAS) or Imperial Japanese Army Air Force (IJAAF; ja, 大日本帝國陸軍航空部隊, Dainippon Teikoku Rikugun Kōkūbutai, lit=Greater Japan Empire Army Air Corps) was the aviation force of the Im ...
carried out air raids on Chittagong in April and May 1942, in the run-up to the aborted Japanese invasion of Bengal. British forces were forced to temporarily withdraw to Comilla and the city was evacuated. After the Battle of Imphal
)
, partof = the Operation U-Go during the Burma Campaign in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II
, image = Imphalgurkhas.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = Gurkhas advancing with Grant tanks ...
, the tide turned in favor of the Allied Forces. Units of the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
Tenth Air Force
The Tenth Air Force (10 AF) is a unit of the U.S. Air Force, specifically a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). 10 AF is headquartered at Naval Air Station Fort Worth Joint Reserve Base/Carswell Field (formerly Carswel ...
were stationed in Chittagong Airfield between 1944 and 1945.Maurer, Maurer. Air Force Combat Units of World War II. Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama: Office of Air Force History, 1983. American squadrons included the 80th Fighter Group
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number o ...
, which flew P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive ...
fighters over Burma; the 8th Reconnaissance Group
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the ...
; and the 4th Combat Cargo Group
The 4th Combat Cargo Group was a World War II United States Army Air Forces combat organization that served in Tenth Air Force as part of the China Burma India Theater of World War II.
Overview
Combat Cargo Groups were to be self-contained group ...
. Commonwealth forces included troops from Britain, India, Australia, and New Zealand. The war had major negative impacts on the city, including the growth of refugees and the Great Famine of 1943.
Many wealthy Chittagonians profited from wartime commerce. The Partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
in 1947 made Chittagong the chief port of East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
. In the 1950s, Chittagong witnessed increased industrial development. Among pioneering industrial establishments included those of Chittagong Jute Mills, the Burmah Eastern Refinery, the Karnaphuli Paper Mills
Karnaphuli Paper Mills is a government-owned corporation, Government-owned paper pulp and paper manufacturer in Chittagong, Bangladesh established in 1953 by Pakistan Industrial Development Corporation. In 1964 it was sold to Dawood Group. After t ...
, and Pakistan National Oil. However, East Pakistanis complained of a lack of investment in Chittagong in comparison to Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
in West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
, even though East Pakistan generated more exports and had a larger population. The Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
demanded that the country's naval headquarters be shifted from Karachi to Chittagong.
During the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali ...
in 1971, Chittagong witnessed heavy fighting between rebel Bengali military regiments and the Pakistan Army. It covered Sector 1
Sector 1 is an administrative unit of Bucharest located in the northern part of the city. It contains also the northwestern districts of Băneasa and Pipera. Sector 1 is thought to be the wealthiest sector in Bucharest. Like each of Bucharest se ...
in the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
chain of command. Major Ziaur Rahman
Lt. General Ziaur Rahman (19 January 1936 – 30 May 1981), was a Bangladeshi military officer and politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1977 to 1981. He was assassinated on 30 May 1981 in Chittagong in an army coup ...
was the sector commander. The Bangladeshi Declaration of Independence was broadcast from Kalurghat
Kalurghat ( bn, কালুরঘাট) is located several miles north of the port city of Chittagong, Bangladesh, and is mostly famous for several heavy industries located there. A bridge near Kalurghat on the Karnaphuli River connects Chittag ...
Radio Station and transmitted internationally through foreign ships in Chittagong Port. Ziaur Rahman
Lt. General Ziaur Rahman (19 January 1936 – 30 May 1981), was a Bangladeshi military officer and politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1977 to 1981. He was assassinated on 30 May 1981 in Chittagong in an army coup ...
and M A Hannan
M. A. Hannan (February 10, 1930 – June 12, 1974) was a politician of Bangladesh.
Early life
M. A. Hannan born in Tehat, West Bengal on 10 February 1930. His father was Maulana Muhammad Muhibur Rahman, who was a Congress politician who later ...
announced the independence declaration from Chittagong. It began the journey of Swadhin Bangla Betar Kendra
Swadhin Bangla Betar Kendra ( bn, স্বাধীন বাংলা বেতার কেন্দ্র, lit=Free Bengal Radio Centre) was the radio broadcasting centre of Bengali nationalist forces during the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1 ...
which contributed heavily towards the Liberation. The Pakistani military, and supporting Razakar Razakar (رضا کار) is etymologically an Arabic word which literally means volunteer. The word is also common in Urdu language as a loanword. On the other hand, in Bangladesh, razakar is a pejorative word meaning a traitor or Judas.
In Pakis ...
militias, carried out widespread atrocities against civilians in the city. Mukti Bahini naval commandos drowned several Pakistani warships during Operation Jackpot in August 1971. In December 1971, the Bangladesh Air Force
The Bangladesh Air Force (BAF) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ বিমান বাহিনী, Bangladesh Biman Bahini) is the aerial warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The Air Force is primarily responsible for air defence of ...
and the Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct ...
carried out the heavy bombing of facilities occupied by the Pakistani military. A naval blockade
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
was also enforced.
After the war, the Soviet Navy was tasked with clearing mines in Chittagong Port and restoring its operational capability. 22 vessels of the Soviet Pacific Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Pacific Fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Russian Pacific Fleet Great emblem
, dates = 1731–present
, country ...
sailed from Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, ...
to Chittagong in May 1972. The process of clearing mines in the dense water harbor took nearly a year and claimed the life of one Soviet marine. Chittagong soon regained its status as a major port, with cargo tonnage surpassing pre-war levels in 1973. In free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
reforms launched by President Ziaur Rahman in the late 1970s, the city became home to the first export processing zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to cu ...
s in Bangladesh. Zia was assassinated
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
during an attempted military coup in Chittagong in 1981. The 1991 Bangladesh cyclone
The 1991 Bangladesh cyclone was among the deadliest tropical cyclones on record. Forming out of a large area of convection over the Bay of Bengal on April 24, the tropical cyclone initially developed gradually while meandering over the sout ...
inflicted heavy damage on the city. The Japanese government financed the construction of several heavy industries and an international airport in the 1980s and 90s. Bangladeshi private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The ...
investments increased since 1991, especially with the formation of the Chittagong Stock Exchange in 1995. The port city has been the pivot of Bangladesh's emerging economy
An emerging market (or an emerging country or an emerging economy) is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were ...
in recent years, with the country's rising GDP growth rate.
Geography
Topography
 Chittagong lies at . It straddles the coastal foothills of the Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh. The Karnaphuli River runs along the southern banks of the city, including its central business district. The river enters the Bay of Bengal in an
Chittagong lies at . It straddles the coastal foothills of the Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh. The Karnaphuli River runs along the southern banks of the city, including its central business district. The river enters the Bay of Bengal in an estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
located west of downtown Chittagong. Mount Sitakunda is the highest peak in Chittagong District, with an elevation of . Within the city itself, the highest peak is Batali Hill at . Chittagong has many lakes that were created under the Mughal rule. In 1924, an engineering team of the Assam Bengal Railway established the Foy's Lake
Foy's Lake is a man-made lake in Chittagong, Bangladesh. It was created in 1924 by constructing a dam across the stream that came down from the hills in the northern part of Chittagong. The purpose of creating an artificial lake was to provide ...
.
Major sediment outflows from the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers form tidal flats around the city.
Ecological hinterland
The Chittagong Division is known for its richbiodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
. Over 2000 of Bangladesh's 6000 flowering plants grow in the region. Its hills and jungles are laden with waterfalls
A waterfall is a point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in several w ...
, fast flowing river streams and elephant reserves. St. Martin's Island
Saint Martin Island ( bn, সেন্টমার্টিন দ্বীপ) is a small island (area only 3 km2) in the northeastern part of the Bay of Bengal, about 9 km south of the tip of the Cox's Bazar-Teknaf peninsula, and fo ...
, within the Chittagong Division, is the only coral island
A coral island is a type of island formed from coral detritus and associated organic material. It occurs in tropical and sub-tropical areas, typically as part of a coral reef which has grown to cover a far larger area under the sea.
Ecosystem
...
in the country. The fishing port of Cox's Bazar
Cox's Bazar (; bn, কক্সবাজার, Kôksbajar; ) is a city, fishing port, tourism centre, and district headquarters in Southeastern Bangladesh. It is located south of the city of Chittagong. Cox's Bazar is also known by the n ...
is home to one of the world's longest natural beaches. In the east, there are the three hill districts of Bandarban
Bandarban ( bn, বান্দরবান, Chakma: 𑄝𑄚𑄴𑄘𑄧𑄢𑄴𑄝𑄚𑄴) is a district in South-Eastern Bangladesh, and a part of the Chittagong Division. It is one of the three hill districts of Bangladesh and a part of ...
, Rangamati
Rangamati (Bengali: রাঙ্গামাটি;) is the administrative headquarter and town of Rangamati Hill District in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. The town is located at 22°37'60N 92°12'0E and has an altitude of . The dist ...
, and Khagrachari
Khagrachari ( bn, খাগড়াছড়ি) is a district in the Chittagong Division of Southeastern Bangladesh. It is a part of the Chittagong Hill Tracts region.
History
The Chittagong Hill Tracts was under the reign of the Tripura Sta ...
, home to the highest mountains in Bangladesh. The region has numerous protected areas, including the Teknaf Game Reserve and the Sitakunda Botanical Garden and Eco Park.
Patenga beach in the main seafront of Chittagong, located west of the city.
Climate
Under theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, Chittagong has a tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(Am).
Chittagong is vulnerable to North Indian Ocean tropical cyclones. The deadliest tropical cyclone to strike Chittagong was the 1991 Bangladesh cyclone
The 1991 Bangladesh cyclone was among the deadliest tropical cyclones on record. Forming out of a large area of convection over the Bay of Bengal on April 24, the tropical cyclone initially developed gradually while meandering over the sout ...
, which killed 138,000 people and left as many as 10 million homeless.
Government
 The
The Chittagong City Corporation
Chattogram City Corporation (CCC) is a self-governing agency that governs the municipal areas of Chattogram and some adjoining areas of south-eastern Bangladesh.
CCC government is elected by popular vote every 5 years.
Administration
Chattogr ...
(CCC) is responsible for governing municipal areas in the Chittagong Metropolitan Area. It is headed by the Mayor of Chittagong. The mayor and ward councilors are elected every five years. The mayor is Awami League leader A. J. M. Nasiuruddin, as of May 2015. The city corporation's mandate is limited to basic civic services, however, the CCC is credited for keeping Chittagong one of the cleaner and most eco-friendly cities in Bangladesh. Its principal sources of revenue are municipal taxes and conservancy charges. The Chittagong Development Authority
Chattogram Development Authority (CDA) is a self-governing organization in Chittagong, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in t ...
is responsible for implementing the city's urban planning.
The Deputy Commissioner and District Magistrate
A District Collector-cum-District Magistrate (also known as Deputy Commissioner in some states) is an All India Service officer of the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) cadre who is responsible for ''land revenue collection'', ''canal revenu ...
are the chiefs of local administration as part of the Government of Bangladesh. Law enforcement is provided by the Chittagong Metropolitan Police
Chattogram Metropolitan Police (CMP), former Chittagong Metropolitan Police, is the chief law enforcement agency in Chattogram, the second largest city in Bangladesh. It was established in 1978 under the Chittagong Metropolitan Police Ordinance app ...
and the Rapid Action Battalion-7. The District and Sessions Judge is the head of the local judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
on behalf of the Supreme Court of Bangladesh
The Supreme Court of Bangladesh ( bn, বাংলাদেশ সুপ্রীম কোর্ট) is the highest court of law in Bangladesh. It is composed of the High Court Division and the Appellate Division, and was created by Part VI C ...
. The Divisional Special Judge's Court is located in the colonial-era Chittagong Court Building.
Military
Chittagong is a strategically important military port on the Bay of Bengal. The Chittagong Naval Area is the principal base of the Bangladesh Navy and the home port of most Bangladeshi warships. TheBangladesh Naval Academy
The Bangladesh Naval Academy is situated at the mouth of the Karnaphuli River at Patenga, Chittagong District, Bangladesh. Bathed by the river Karnaphuli on the east and sheltered on the south by the Bay of Bengal, BNA stands in a panoramic nat ...
and the navy's elite special force- Special Warfare Diving and Salvage (SWADS) are also based in the city. The Bangladesh Army
The Bangladesh Army is the land warfare branch and the largest component of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The primary mission of the Army is to provide necessary forces and capabilities to deliver the Bangladeshi government's security and defe ...
's 24th Infantry Division is based in Chittagong Cantonment
Chattogram Cantonment is situated near Bayezid Bostami of Chattogram, Bangladesh. It is the headquarters of 24th infantry division.
History
An Indian army tank captured by the East Bengal Regiment (based in Chattogram cantonment) near Lahore ...
, and the Bangladesh Air Force maintains the BAF Zahurul Haq Air Base in Chittagong. The city is also home to the Bangladesh Military Academy
Bangladesh Military Academy (BMA) is the officers training institute for the officer cadets of Bangladesh Army. It is located in Bhatiary, near Chittagong Hill Tracts, in the Chittagong District of south-east Bangladesh, about 13 kilometres ...
, the premier training institute for the country's armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
.
Diplomatic representation
In the 1860s, the American Consulate-General in theBengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia an ...
included a consular agency in Chittagong. Today, Chittagong hosts an assistant high commission of India and a consulate general of Russia. The city also has honorary consul
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
ates of Turkey, Japan, Germany, South Korea, Malaysia, Italy, and the Philippines.
Economy
Straddle carrier
A straddle carrier or straddle truck is a freight-carrying vehicle that carries its load underneath by "straddling" it, rather than carrying it on top like a conventional truck. The advantage of the straddle carrier is its ability to load and unloa ...
s moving shipping containers in Chittagong Port
File:Aziz Court Building Chittagong.jpg, Aziz Court Imperial is the city's tallest building as of November 2022
File:Central Railway Building (17233793446).jpg, Central Railway Building
File:Apartments in South Khulshi (01).jpg, Apartments in Khulshi
File:Chittagong City.JPG, Chittagong city with Radisson Blu Bay View Hotel in the background
File:Patenga night view.jpg, ships seen from Patenga
international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significa ...
and 50% of its governmental revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive rev ...
. The Chittagong Stock Exchange
The Chittagong Stock Exchange ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম স্টক এক্সচেঞ্জ) is a stock exchange based in the port city Chittagong, Bangladesh. It is one of the twin financial hubs of the country, alongside the Dha ...
has more than 700 listed companies, with a market capitalisation
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by ...
of US$32 billion in June 2015. The city is home to many of the country's oldest and largest corporations. The Port of Chittagong handled US$60 billion in annual trade in 2011, ranking 3rd in South Asia after the Port of Mumbai and the Port of Colombo
The Port of Colombo (known as Port of Kolomtota during the early 14th Century Kotte Kingdom) is the largest and busiest port in Sri Lanka and the Indian Ocean. Located in Colombo, on the southwestern shores on the Kelani River, it serves as an ...
. The port is part of the Maritime Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
that runs from the Chinese coast via the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popula ...
to the Mediterranean and on to the Upper Adriatic region of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
with rail connections to Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
.
The Agrabad
Agrabad ( bn, আগ্রাবাদ) is a downtown central business district, commercial and financial area in Chattogram, the second largest city of Bangladesh. Located close to the city's harbor, it hosts numerous Bangladeshi and internati ...
area is the main central business district of the city. Major Bangladeshi conglomerates headquartered in Chittagong include M. M. Ispahani Limited
M.M. Ispahani Limited ( bn, এম এম ইস্পাহানি লিমিটেড), also known as The Ispahani Group, is a Bangladeshi conglomerate headquartered in Chittagong. Founded in 1820, it is the oldest company in Bangladesh and ...
, BSRM
The Bangladesh Steel Re-Rolling Mills Ltd., commonly known as BSRM, is a Bangladeshi steel manufacturing company based in Chittagong. It is the largest construction steel manufacturer company in Bangladesh.
History
In 1952, five Indian busines ...
, A K Khan & Company
A K Khan & Co. Ltd. is one of the oldest Bangladeshi conglomerates headquartered in Chittagong. It was established in 1945 by Abul Kashem Khan during the Second World War.
Projects
The company is planning to setup a tyre plant under joint coll ...
, PHP Group, James Finlay Bangladesh, the Habib Group
The Habib Group is a prominent Bangladeshi industrial conglomerate. Founded in Chittagong in 1947, it employs over 20,000 people and has various interests in textiles, aviation, cement, steel, real estate, insurance and banking
A bank is ...
, the S. Alam Group of Industries
S.Alam Group is a Bangladeshi industrial conglomerate. S. Alam Group also has investment in banking, leasing, insurance, stock brokering, and merchant banking. The industries under this group include food and allied products, steel, banking, cons ...
, Seamark Group
Seamark Group is a multinational food processing conglomerate wholesale company with offices in Manchester, Chittagong, New Jersey and Brooklyn. The company was founded in 1976 and established in 1991 by Iqbal, Bilal and Kamal Ahmed.
Hi ...
, KDS Group
KDS Group is a business and industrial conglomerates of Bangladesh, which is based in Chittagong but with extensive operations in Dhaka as well. It has also established offices and agencies in India, Hong Kong and is currently expanding into Eu ...
and the T. K. Group of Industries. Major state-owned
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public owne ...
firms headquartered there include Pragati Industries, the Jamuna Oil Company, the Bangladesh Shipping Corporation and the Padma Oil Company. The Chittagong Export Processing Zone was ranked by the UK-based magazine, ''Foreign Direct Investment'', as one of the leading special economic zone
A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increas ...
s in the world, in 2010. Other SEZs include the Karnaphuli Export Processing Zone Karnaphuli Export Processing Zone is an export processing zone in Bangladesh located at the city of Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, ...
and Korean EPZ. The city's key industrial sectors include petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
, shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to bef ...
, chemicals, pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
s, textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', which is in the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is '' Corchorus ol ...
, leather goods
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
, vegetable oil refineries, glass manufacturing, electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
and motor vehicles
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of people or cargo.
The veh ...
. The Chittagong Tea Auction sets the price of Bangladesh Tea. The Eastern Refinery is Bangladesh's largest oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liq ...
. GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the tent ...
has had operations in Chittagong since 1967. Western Marine Shipyard is a leading Bangladeshi shipbuilder and exporter of medium-sized ocean-going vessels. In 2011–12, Chittagong exported approximately US$4.5 billion in ready-made garments. The Karnaphuli Paper Mills
Karnaphuli Paper Mills is a government-owned corporation, Government-owned paper pulp and paper manufacturer in Chittagong, Bangladesh established in 1953 by Pakistan Industrial Development Corporation. In 1964 it was sold to Dawood Group. After t ...
were established in 1953.
International banks operating in Chittagong include HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational universal bank and financial services holding company. It is the largest bank in Europe by total assets ahead of BNP Paribas, with US$2.953 trillion as of December 2021. In 2021, HSBC had $10.8 tr ...
, Standard Chartered
Standard Chartered plc is a multinational bank with operations in consumer, corporate and institutional banking, and treasury services. Despite being headquartered in the United Kingdom, it does not conduct retail banking in the UK, and around 9 ...
and Citibank NA
Citibank, N. A. (N. A. stands for " National Association") is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of financial services multinational Citigroup. Citibank was founded in 1812 as the City Bank of New York, and later became First National City Ba ...
.
Chittagong is often called Bangladesh's commercial capital due to its diversified industrial base and seaport. The port city has ambitions to develop as a global financial center and regional transshipment
Transshipment, trans-shipment or transhipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
One possible reason for transshipment is to change the means of transport during the journey (e.g ...
hub, given its proximity to North East India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
and Southwest China.

CBDs
*Agrabad
Agrabad ( bn, আগ্রাবাদ) is a downtown central business district, commercial and financial area in Chattogram, the second largest city of Bangladesh. Located close to the city's harbor, it hosts numerous Bangladeshi and internati ...
*O R Nizam Road O R Nizam Road is a major road which crosses the Asian Highway in Chattogram, Bangladesh. The road has been named after Obaidur Rahman Nizam (1902-1970), who was popularly known as O R Nizam. He was the Mayor of Chattogram City for almost 15 years. ...
*Strand Road, Chittagong
Strand Road ( bn, স্ট্র্যান্ড রোড) is an important commercial road in downtown Agrabad, Chattogram, Bangladesh. It is located alongside docks of the Port of Chattogram. The road was developed under British rule in the ...
Financial and commodity markets
*Chittagong Stock Exchange
The Chittagong Stock Exchange ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম স্টক এক্সচেঞ্জ) is a stock exchange based in the port city Chittagong, Bangladesh. It is one of the twin financial hubs of the country, alongside the Dha ...
*Chittagong Tea Auction Chittagong Tea Auction center was established on 16 July 1949. Teas manufactured throughout Bangladesh are sold in bulk to buyers through an open auction which is conducted once a week. During each tea season, 45 auctions are held at this auction ce ...
Trade associations
*Chittagong Chamber of Commerce & Industry
The Chittagong Chamber of Commerce & Industry (CCCI), established in 1906, is an industry-led and industry-managed organization which represents the business and corporate sector in Chittagong, Bangladesh. The organization acts as a major advocate ...
Industrial areas
* Chittagong Export Processing Zone *Karnaphuli Export Processing Zone Karnaphuli Export Processing Zone is an export processing zone in Bangladesh located at the city of Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, ...
Culture
 An inhabitant of Chittagong is called ''Chittagonian'' in English. For centuries, the port city has been a
An inhabitant of Chittagong is called ''Chittagonian'' in English. For centuries, the port city has been a melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throu ...
for people from all over the world. Its historic trade networks have left a lasting impact on its language, culture, and cuisine. The Chittagonian language
Chittagonian ( ''saṭgãia'' or ''siʈaiŋga'') is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of the Chittagong Division in Bangladesh. Its speakers identify with Bengali culture and the Bengali language, but Chittagonian and Bengali are not mut ...
has many Arabic, Persian, English and Portuguese loanwords. The popular traditional feast of ''Mezban'' features the serving of hot beef dish with white rice. Another dish named ''kala-bhuna'' of Chittagong, which is made with traditional spices, mustard oil, and beef through a special cooking style, is also renowned all over Bangladesh. The cultivation of pink pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
s is a historic activity in Chittagong. Its Mughal-era name, ''Islamabad'' (City of Islam), continues to be used in the old city. The name was given due to the port city's history as a gateway for early Islamic missionaries in Bengal. Notable Islamic architecture in Chittagong can be seen in the historic Bengal Sultanate-era Hammadyar Mosque and the Mughal fort of Anderkilla. Chittagong is known as the ''Land of the Twelve Saints'' due to the prevalence of major Sufi Muslim shrines in the district. Historically, Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality ...
played an important role in the spread of Islam in the region. Prominent dargah
A dargah ( fa, درگاه ''dargâh'' or ''dargah'', Turkish: ''dergâh'', Hindustani: ''dargah'' दरगाह درگاہ, bn, দরগাহ ''dorgah'') is a shrine or tomb built over the grave of a revered religious figure, often ...
s include the mausoleum of Shah Amanat and the shrine of Bayazid Bastami
Abū Yazīd Ṭayfūr bin ʿĪsā bin Surūshān al-Bisṭāmī (al-Basṭāmī) (d. 261/874–5 or 234/848–9), commonly known in the Iranian world as Bāyazīd Bisṭāmī ( fa, بایزید بسطامی), was a PersianWalbridge, John. " ...
. The Bastami shrine hosts a pond of black softshell turtles.
 During the medieval period, many poets thrived in the region when it was part of the Bengal Sultanate and the Kingdom of Mrauk U. Under the patronage of Sultan
During the medieval period, many poets thrived in the region when it was part of the Bengal Sultanate and the Kingdom of Mrauk U. Under the patronage of Sultan Alauddin Husain Shah
Ala-ud-din Husain Shah ( bn, আলাউদ্দিন হোসেন শাহ (1494–1519)Majumdar, R.C. (ed.) (2006). ''The Delhi Sultanate'', Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, pp.215-20 was an independent late medieval Sultan of Bengal, who ...
's governor in Chittagong, Kabindra Parameshvar wrote his Pandabbijay, a Bengali adaptation of the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
. Daulat Qazi
Daulat Qazi ( bn, দৌলত কাজী; ) was a medieval Bengali poet, was born into a Qazi family in the village of Sultanpur in Raozan Upazila, Chittagong. Not getting any recognition at home, he left for Arakan, where he seems to have been ...
lived in the region during the 17th-century reign of the Kingdom of Mrauk U. Chittagong is home to several important Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
temples, including the Chandranath Temple
Chandranath Temple ( bn, চন্দ্রনাথ মন্দির or ''Chandronath mondir''), located on top of the Chandranath Hill, is a famous Shakti Peeth located near Sitakunda in Bangladesh where, as per Hindu sacred texts, the ri ...
on the outskirts of the city, which is dedicated to the Hindu goddess Sita
Sita (; ) also called as Janaki and Vaidehi is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic, ''Ramayana''. She is the consort of Rama, the avatar of the god Vishnu, and is regarded as a form of Vishnu's consort, Lakshmi. She ...
. The city also hosts the country's largest Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
monastery and council of monks. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Chittagong is the oldest catholic mission in Bengal.
Major cultural organizations in the city include the Theatre Institute Chittagong and the Chittagong Performing Arts Academy. The city has a vibrant contemporary art
Contemporary art is the art of today, produced in the second half of the 20th century or in the 21st century. Contemporary artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their art is a dynamic ...
scene.
Being home to the pioneering rock bands in the country like Souls and LRB, Chittagong is regarded as the "birthplace of Bangladeshi rock music".
Demographics

 At the 2011 Census, Chittagong had a population of more than 2.5 million, and it's Metropolitan Area had a population of 4,009,423. By gender, the population was 54.36% male and 45.64% female, and the literacy rate in the city was approximately 72 percent, in 2020.
At the 2011 Census, Chittagong had a population of more than 2.5 million, and it's Metropolitan Area had a population of 4,009,423. By gender, the population was 54.36% male and 45.64% female, and the literacy rate in the city was approximately 72 percent, in 2020.
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, numbering approximately 3.44 million, form the overwhelming majority of the city's population, with the rest being predominantly Hindus, numbering approximately 480,000, and the remaining 2% belonging to other religions, such as Buddhism and Christianity.Chittagong was a melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throu ...
of ethnicities during the Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the domina ...
and Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
periods. Muslim immigration started as early as the seventh century, and significant Muslim settlements occurred during the medieval period. Muslim traders, rulers, and preachers from Persia and Arabia were the early Muslim settlers, and their descendants are the majority of the current Muslim population of the city. The city has a relatively wealthy and economically influential Shia Muslim
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
community, including Ismaili
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imām) to Ja'far al ...
s and Twelver
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
Shias. The city also has many ethnic minorities, especially members of indigenous groups from the frontier hills of Chittagong Division, including Chakmas, Rakhines and Tripuris
The Tripuri (also known as Tripura, Tipra, Tiprasa, Twipra) are an ethnic group originating in the Indian state of Tripura. They are the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through th ...
; as well as Rohingya
The Rohingya people () are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar (previously known as Burma). Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an ...
refugees. The Bengali-speaking Theravada Buddhists
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
of the area, known as ''Barua
Barua (also spelt as ''Baruah'', ''Barooah'', ''Baruwa'', ''Baroova'', ''Barooa'', ''Baroowa'', ''Borooah'', ''Boruah'', or ''Baroa'') is a common Assamese surname.
In Assam Valley History
Originally, the ''Barua'' surname was used as a milit ...
s'', are one of the oldest communities in Chittagong and one of the last remnants of Buddhism in Bangladesh. Descendants of Portuguese settlers, often known as ''Firingis'', also live in Chittagong, as well as Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, who largely live in the old Portuguese enclave of Paterghatta. There is also a small Urdu-speaking Bihari community living in the ethnic enclave known as ''Bihari Colony''.
Like other major urban centers in South Asia, Chittagong has experienced steady growth in its informal settlements
Informal housing or informal settlement can include any form of housing, shelter, or settlement (or lack thereof) which is illegal, falls outside of government control or regulation, or is not afforded protection by the state. As such, the info ...
as a result of the increasing economic activities in the city and emigration from rural areas. According to a poverty reduction publication of the International Monetary Fund, there were 1,814 slums
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily in ...
within the city corporation area, inhabited by about 1.8 million slum dwellers, the second highest in the country after the capital, Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest ...
. The slum dwellers often face eviction by the local authorities, charging them with illegal abode on government lands. In the early 1990s, Chittagong had a population of just over 1.5 million, of which there were an estimated 66,676 squatters living in 69 areas.
Media and communications
There are various newspapers, including daily newspapers, opposition newspapers, and business newspapers, based in Chittagong. Daily newspapers include Dainik Azadi, Peoples View, The Daily Suprobhat Bangladesh,Daily Purbokone
, type = Daily newspaper
, format = Broadsheet
, owner = The Purbokone Limited
, founder = Mohammad Yusuf Chowdhury
, publisher = Jasim Uddin
, president =
, e ...
, Life, Karnafuli, Jyoti, Rashtrobarta and Azan. Furthermore, there are several weekly and monthly newspapers. These include weeklies such as Chattala, Jyoti, Sultan, Chattagram Darpan, and the monthlies such as Sanshodhani, Purobi, Mukulika, and Simanto. The only press council in Chittagong is the Chittagong Press Club. Government-owned Bangladesh Television
Bangladesh Television ( bn, বাংলাদেশ টেলিভিশন), commonly known by its acronym BTV ( bn, বিটিভি), is the state-owned television network of Bangladesh. The network was originally established as the East ...
, with its Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in ...
station, and Bangladesh Betar
Bangladesh Betar ( bn, বাংলাদেশ বেতার; ), or BB is the state-owned radio broadcaster of Bangladesh, initially established as the Dhaka station of All India Radio in 1939. It was later made part of Radio Pakistan. After t ...
have transmission centers in the city. A local online news & media Channel based on the Chittagonian language was launched in 2016 calleCplusTv
gained vast popularity. The channel is YouTube- and social network-based, and it reached the 1 million followers milestone on Facebook.
Bollywood
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, refers to the film industry based in Mumbai, engaged in production of motion pictures in Hindi language. The popular term Bollywood, is a portmanteau of "Bombay" ...
film director Ashutosh Gowariker
Ashutosh Gowariker (born 15 February 1964) is an Indian film director, actor, screenwriter and producer who works in Hindi cinema. He is known for directing films "set on a huge canvas while boasting of an opulent treatment".
His is particular ...
directed a movie based on the 1930s Chittagong Uprising, Movie's name is Khelein Hum Jee Jaan Sey
''Khelein Hum Jee Jaan Sey'' () is an Indian Hindi-language historical action-adventure film directed by Ashutosh Gowariker and released on 3 December 2010. Starring Abhishek Bachchan, Deepika Padukone and Sikandar Kher, it was based on Manin ...
in which Abhishek Bachchan
Abhishek Bachchan (born 5 February 1976) is an Indian actor and film producer known for his work in Hindi films. Part of the Bachchan family, he is the son of actors Amitabh Bachchan and Jaya Bachchan and the grandson of poet Harivansh Rai Bach ...
played the lead role.
Utilities
The southern zone of theBangladesh Power Development Board
The Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) is a government agency operating under the Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources, Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. It was created as a public-sector organization to boost ...
is responsible for supplying electricity to city dwellers. The fire services are provided by the Bangladesh Fire Service & Civil Defence
The Bangladesh Fire Service & Civil Defence (FSCD) of the People's Republic of Bangladesh is an emergency service operating under the Security Services Division of the Ministry of Home Affairs. The Department's main goal is to provide fire protect ...
department, under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Total Electricity Consumption is approximately 1000 megawatts in the city proper.
But in the whole Chittagong urban and city proper, it will be 1300 megawatts plus-minus.
Ss power plant will be in production next year and its production power is 1320 megawatts
And it creates Chittagong city into the energy production hub of Bangladesh
The water supply and sewage systems are managed by the Chittagong Water Supply and Sewerage Authority (Chittagong WASA). Water is primarily drawn from Karnaphuli River and then purified in the Mohra Purification Plant.
Chittagong has extensive GSM
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation ( 2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such ...
and CDMA
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communicatio ...
coverage, served by all the major mobile operators of the country, including Grameenphone, Banglalink
Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd., d.b.a. Banglalink ( bn, বাংলালিংক; previously Orascom Telecom Bangladesh Ltd.) is a Bangladeshi telecommunications company headquartered in Dhaka. It's the third-largest mobile netwo ...
, Citycell
Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited, doing business as Citycell ( bn, সিটিসেল), was the oldest mobile operator of Bangladesh. It was 1st mobile operator company in Bangladesh and pioneer telecommunications network companies in Sout ...
, Robi, TeleTalk
Teletalk Bangladesh Limited DBA Teletalk ( bn, টেলিটক) is the only state-owned GSM, 3G, LTE, 5G based mobile phone operator in Bangladesh that started operating in 2004. As in August 2021, Teletalk has a subscriber base of 6.27 ...
and Airtel Bangladesh
Airtel ( bn, এয়ারটেল) is a Bangladeshi telecommunications company. It was managed by Bharti Airtel Bangladesh until 2016, when Bharti Airtel Bangladesh merged its operations into Robi Axiata Ltd. Following the merger, Airtel Ba ...
. However, landline telephone services are provided through the state-owned Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Board
BTCL or Bangladesh Telecommunications Company Limited is the largest telecommunications company in Bangladesh. The company was founded as the Bangladesh Telegraph & Telephone Board (BTTB) following Bangladesh's independence in 1971. On July 1, 2008 ...
(BTTB), as well as some private operators. BTTB also provides broadband Internet services, along with some private ISP
An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides services for accessing, using, or participating in the Internet. ISPs can be organized in various forms, such as commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or otherwise private ...
s, including the 4G service providers Banglalion
Banglalion Communications Ltd was a privately held Bangladeshi 4G wireless broadband operator. It used WiMAX technology. It had a nationwide licence from the Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) to provide broadband wireless ...
and Qubee.
Education and research

 The education system of Chittagong is similar to that of rest of Bangladesh, with four main forms of schooling. The general education system, conveyed in both Bangla and English versions, follows the curriculum prepared by the
The education system of Chittagong is similar to that of rest of Bangladesh, with four main forms of schooling. The general education system, conveyed in both Bangla and English versions, follows the curriculum prepared by the National Curriculum and Textbook Board
The National Curriculum and Textbook Board (NCTB) ( bn, জাতীয় শিক্ষাক্রম ও পাঠ্যপুস্তক বোর্ড) is an autonomous organisation under the Ministry of Education in Bangladesh, respo ...
, part of the Ministry of Education
An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ...
. Students are required to take four major board examinations: the Primary School Certificate (PSC), the Junior School Certificate The Junior School Certificate (JSC) is a public examination taken by students in Bangladesh after successful completion of eight years of schooling. It is followed by the Secondary School Certificate (SSC).
Before the JSC was introduced, an exam w ...
(JSC), the Secondary School Certificate
The Secondary School Certificate (SSC) or Secondary School Leaving Certificate (SSLC), Matriculation examination, is a public examination in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan conducted by educational boards for the successful completion of the seco ...
(SSC) and the Higher Secondary School Certificate
The Higher Secondary School Certificate is a secondary qualification in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan.
Higher Secondary Education
The Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education in Bangladesh recognises "Higher Secondary Education" und ...
(HSC) before moving onto higher education. The Board of Intermediate and Secondary Education, Chittagong
The Board of Intermediate and Secondary Education, Chattogram is an autonomous organization, mainly responsible for holding two public examinations (SSC & HSC). The board started its operation in the year 1995. Later The Board started Holding JSC ...
is responsible for administering SSC and HSC examinations within the city. The Madrasah
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
education system is primarily based on Islamic studies, though other subjects are also taught. Students are prepared according to the Dakhil and Alim examinations, which are controlled by the Bangladesh Madrasah Education Board
Bangladesh Madrasah Education Board ( bn, বাংলাদেশ মাদ্রাসা শিক্ষা বোর্ড) or Alia Madrasah Education Board started its activity independently in 1979. With the passage of time in Banglades ...
and are equivalent to SSC and HSC examinations of the general education system respectively. There are also several private schools in the city, usually referred to as ''English medium schools'', which follow the General Certificate of Education
The General Certificate of Education (GCE) is a subject-specific family of academic qualifications used in awarding bodies in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, Crown dependencies and a few Commonwealth countries. For some time, the Scottish e ...
.
The British Council
The British Council is a British organisation specialising in international cultural and educational opportunities. It works in over 100 countries: promoting a wider knowledge of the United Kingdom and the English language (and the Welsh lan ...
supervises the O Levels
The O-Level (Ordinary Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education. It was introduced in place of the School Certificate in 1951 as part of an educational reform alongside the more in-depth ...
and A levels
The A-Level (Advanced Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational au ...
examinations, conducted twice a year, through the Cambridge International
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
and Edexcel
Edexcel (also known since 2013 as Pearson Edexcel) is a British multinational education and examination body formed in 1996 and wholly owned by Pearson plc since 2005. It is the only privately owned examination board in the United Kingdom. It ...
examination board
An examination board (or exam board) is small board organization that sets examinations, is responsible for marking them, and distributes results. Some are run by governmental entities; some are run as not-for-profit organizations.
List of na ...
s. The Technical and Vocational education system is governed by the Directorate of Technical Education (DTE) and follow the curriculum prepared by Bangladesh Technical Education Board
The Bangladesh Technical Education Board is a state regulatory board responsible for monitoring and developing technical and vocational education in the secondary level (SSC), 2-year higher secondary level (HSC/Vocational), 4-year Diploma in Engi ...
(BTEB). Chittagong College
Chittagong College is a government college in Chittagong, Bangladesh. It is the second college established in Bangladesh after Dhaka College. It offers higher secondary education (HSC), bachelor's degree and master's degree.
History
Having begun ...
, established in 1869, is the earliest modern institution for higher education in the city. Chittagong Veterinary and Animal Sciences University
Chittagong Veterinary and Animal Sciences University (CVASU) ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম ভেটেরিনারি ও এনিম্যাল সাইন্সেস বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়) is a public univers ...
is the only public university located in Chittagong city. Chittagong Medical College
Chittagong Medical College (CMC) is situated in the port city of Chattogram, Bangladesh and is the oldest medical college in the south-eastern part of the country. It is affiliated with a tertiary level hospital where clinical students are tra ...
is the only government medical college in Chittagong.
University of Chittagong
The University of Chittagong ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়, caṭṭagram bishwabidyalay) is a public research university with multidisciplinary faculties situated across a 1754-acres hilly landmas ...
is located north and Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology
Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম প্রকৌশল ও প্রযুক্তি বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়), commonly referred to as CUET ( bn, চুয়েট), is a ...
is located north of the Chittagong city. The University of Chittagong, which was established in 1966 is one of the largest universities in Bangladesh. Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology, established in 1968, is one of the five public engineering universities in Bangladesh and the only such university in the Chittagong Division.
The city also hosts several other private universities and medical colleges. The BGC Trust University Bangladesh, Chittagong Independent University (CIU), Asian University for Women
Asian University for Women (AUW) is an independent, international university in Chittagong, Bangladesh seeking to educate a new generation of leaders in Asia. AUW admits students solely on the basis of merit, regardless of their family's incom ...
, Port City International University, East Delta University
East Delta University ( bn, ইস্ট ডেল্টা বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় or EDU) is a private university in Chittagong, Bangladesh. It received the government's license in 2006 and started its academic operation in F ...
, International Islamic University, Premier University, Southern University
Southern University and A&M College (Southern University, Southern, SUBR or SU) is a public historically black land-grant university in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. It is the largest historically black college or university (HBCU) in Louisiana, a ...
, University of Information Technology and Sciences and the University of Science & Technology Chittagong are among them. Chittagong has public, denominational, and independent schools. Public schools, including pre-schools, primary and secondary schools, and special schools are administered by the Ministry of Education and Chittagong Education Board
The Board of Intermediate and Secondary Education, Chattogram is an autonomous organization, mainly responsible for holding two public examinations (SSC & HSC). The board started its operation in the year 1995. Later The Board started Holding JSC ...
. Chittagong has governmental and non-governmental primary schools, international schools, and English medium schools. Jamia Ahmadiyya Sunnia Kamil Madrasa
Jamia Ahmadiyya Sunnia Kamil Madrasah ( ar, الجامعة الأحمدية السنية الكاملية; bn, জামেয়া আহমদিয়া সুন্নিয়া কামিল মাদরাসা)), popularly known as ...
is also a famous Islamic University
The term "Islamic university" ( ar, الجامعة الإسلامية, ''Jami'ah Islamiyah''), sometimes called madrasah jāmiʿah ( ar, مدرسة جامعة), can be used to describe secular educational institutions that were founded by people ...
which situated in Chittagong.
Research institutes
*Bangladesh Forest Research Institute
Bangladesh Forest Research Institute (BFRI) is an institute for forestry research in Bangladesh, located at Sholashahar, Chattogram.
History
Bangladesh Forest Research Institute was established in 1955 as East Pakistan Forest Research Laborator ...
*Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases
Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases is a government medical postgraduate institute and Hospital situated at Faujdarhat in Chittagong. It was established in 2013. There is an adjacent 20 bed Infectious Disease Hospital.
Hist ...
*Bangladesh Tea Board
The Bangladesh Tea Board or BTB, an autonomous body responsible for creating laws regarding tea production, controlling and encouraging the production of tea and is located in Nasirabad, Chittagong, Bangladesh. It is under the Ministry of Commer ...
Health
 The Chittagong Medical College Hospital is the largest state-owned hospital in Chittagong. The Chittagong General Hospital, established in 1901, is the oldest hospital in the city. The Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases (BITID) is based the city. Other government-run medical centers in the city include the Family Welfare Centre, TB Hospital, Infectious Disease Hospital, Diabetic Hospital, Mother and Children Hospital, and the Police Hospital. Among the city's private hospitals are the Bangabandhu Memorial Hospital (BBMH), Chittagong Metropolitan Hospital, Chevron Clinic, Surgiscope Hospital, CSCR, Centre Point Hospital, Park View Hospital, Max Hospital & diagnosis, Imperial Hospital LTD., Evercare Hospital Ltd., National Hospital and Mount Hospital Ltd.
The Chittagong Medical College Hospital is the largest state-owned hospital in Chittagong. The Chittagong General Hospital, established in 1901, is the oldest hospital in the city. The Bangladesh Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases (BITID) is based the city. Other government-run medical centers in the city include the Family Welfare Centre, TB Hospital, Infectious Disease Hospital, Diabetic Hospital, Mother and Children Hospital, and the Police Hospital. Among the city's private hospitals are the Bangabandhu Memorial Hospital (BBMH), Chittagong Metropolitan Hospital, Chevron Clinic, Surgiscope Hospital, CSCR, Centre Point Hospital, Park View Hospital, Max Hospital & diagnosis, Imperial Hospital LTD., Evercare Hospital Ltd., National Hospital and Mount Hospital Ltd.
 Private Medical Colleges:
* University of Science & Technology Chittagong
* BGC TRUST medical College Chittagong
* Chittagong Ma o shishu Hospital
* Southern Medical College
* Marine City Medical College
Private Medical Colleges:
* University of Science & Technology Chittagong
* BGC TRUST medical College Chittagong
* Chittagong Ma o shishu Hospital
* Southern Medical College
* Marine City Medical College
Transport
Transport in Chittagong is similar to that of the capital, Dhaka. Large avenues and roads are present throughout the metropolis. There are various bus systems and taxi services, as well as smaller 'baby' or 'CNG' taxis, which are tricycle-structured motor vehicles. Foreign and localridesharing companies
A ridesharing company (also known as a transportation network company, ride-hailing service; the vehicles are called app-taxis or e-taxis) is a company that, via websites and mobile apps, matches passengers with drivers of vehicles for hire th ...
like Uber
Uber Technologies, Inc. (Uber), based in San Francisco, provides mobility as a service, ride-hailing (allowing users to book a car and driver to transport them in a way similar to a taxi), food delivery ( Uber Eats and Postmates), pa ...
and Pathao are operating in the city. There are also traditional manual rickshaws, which are very common.
Road
 As the population of the city has begun to grow extensively, the Chittagong Development Authority (CDA) has undertaken some transportation initiatives aimed at easing the traffic congestion in Chittagong. Under this plan, the CDA, along with the Chittagong City Corporation, has constructed some flyovers and expanded the existing roads within the city. There are also some other major expressways and flyovers under-construction, most notably the Chittagong City Outer Ring Road, which runs along the coast of Chittagong city. This
As the population of the city has begun to grow extensively, the Chittagong Development Authority (CDA) has undertaken some transportation initiatives aimed at easing the traffic congestion in Chittagong. Under this plan, the CDA, along with the Chittagong City Corporation, has constructed some flyovers and expanded the existing roads within the city. There are also some other major expressways and flyovers under-construction, most notably the Chittagong City Outer Ring Road, which runs along the coast of Chittagong city. This ring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop, bypass or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city, or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist i ...
includes a marine drive along with five feeder roads, and is also meant to strengthen the embankment of the coast. The government has also began the construction of a underwater expressway tunnel through the Karnaphuli river to ensure better connectivity between the northern and southern parts of Chittagong. This tunnel will be the first of its kind in South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
.
The N1 (Dhaka-Chittagong Highway), a major arterial national highway, is the only way to access the city by motor vehicle from most other parts of the country. It is considered a very busy and dangerous highway. This highway is also part of AH41 Asian Highway 41 (AH41) is a route of the Asian Highway Network, running from Teknaf in Chittagong Division, Bangladesh to Mongla in Khulna Division, Bangladesh.
It passes only through Bangladesh to provide connectivity between Port of Chittago ...
route of the Asian Highway Network
The Asian Highway Network (AH), also known as the Great Asian Highway, is a cooperative project among countries in Asia and the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) to improve their connectivity via hi ...
. It has been upgraded to 4 lanes. The N106 (Chittagong-Rangamati Highway) is another important national highway that connects the Chittagong Hill Tracts with the city.
Rail
Chittagong can also be accessed by rail. It has a station on themetre gauge
Metre-gauge railways are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
The metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires. In Europe, ...
, eastern section of the Bangladesh Railway, whose headquarters are also located within the city. There are two main railway stations, on Station Road and in the Pahartali Thana
Pahartali ( bn, পাহাড়তলী) is a thana of Chattogram District in Chattogram Division, Bangladesh.
Geography
Pahartali is located at . It has a total area 8.44 km².
It is bounded by Sitakunda Upazila on the north, Halishaha ...
. Trains to Dhaka, Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of the Sylhet Division. Located on the north bank of the Surma River at the eastern tip of Bengal, Sylhet has a subtropical climate ...
, Comilla
Comilla (; bn, কুমিল্লা, Kumillā, ), officially spelled Cumilla, is the fifth largest city of Bangladesh and second largest in Chittagong division. It is the administrative centre of the Comilla District. The name Comilla was ...
, and Bhairab are available from Chittagong. The Chittagong Circular Railway
Chittagong Circular Railway is a suburban railway system in the city of Chittagong in Bangladesh to ameliorate the commuters' suffering and improve traffic situation in the city. The construction was complete by February 2013 and it became operati ...
was introduced in 2013 to ease traffic congestion and to ensure better public transport service for commuters within the city. The railway includes high-speed DEMU
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also ...
trains each with a carrying capacity of 300 passengers. These DEMU trains also travel on the Chittagong-Laksham route which connects the city with Comilla.
Air
 The
The Shah Amanat International Airport
Shah Amanat International Airport ( bn, শাহ আমানত আন্তর্জাতিক বিমানবন্দর ''Shah Amanôt Antôrjatik Bimanbôndôr'') is an international airport serving Bangladesh's southeastern port ...
, located at South Patenga, serves as Chittagong's only airport. It is the second busiest airport in Bangladesh. The airport is capable of annually handling 1.5 million passengers and 6,000 tonnes of cargo. Known as ''Chittagong Airfield'' during World War II, the airport was used as a combat airfield, as well as a supply point and photographic reconnaissance base by the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
Tenth Air Force
The Tenth Air Force (10 AF) is a unit of the U.S. Air Force, specifically a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). 10 AF is headquartered at Naval Air Station Fort Worth Joint Reserve Base/Carswell Field (formerly Carswel ...
during the Burma Campaign 1944–45
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. It officially became a Bangladeshi airport in 1972 after Bangladesh's liberation war. International services fly to major cities of the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
as well as to Indian cities of Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
and Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
. At present, Middle Eastern airlines like Air Arabia
Air Arabia ( ar, العربية للطيران ''al-ʿArabiyya Lit-Ṭayarān'') is an Emirati low-cost airline with its head office in the A1 Building Sharjah Freight Center, Sharjah International Airport, UAE. The airline operates scheduled se ...
, Flydubai
Flydubai ( ar, فلاي دبي), legally Dubai Aviation Corporation ( ar, مؤسسة دبي للطيران), is an Emirati government-owned low-cost airline in Dubai, United Arab Emirates with its head office and flight operations in Terminal 2 ...
, Oman Air
Oman Air ( ar, الطيران العماني) is the national airline of the Sultanate of Oman. Based at Muscat International Airport in Seeb, Muscat, it operates domestic and international passenger services, as well as regional air taxi a ...
and SalamAir
SalamAir ( ar, طيران السلام, Ṭayarān as-salām) is a low-cost airline from Oman headquartered and based at Muscat International Airport.
History
Salam Air is owned by the Muscat National Development and Investment Company (ASAAS) w ...
operate flights from the city to these destinations along with airlines of Bangladesh
An airline is a company that provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for codeshare agreements, in which ...
. All Bangladeshi airlines operate regular domestic flights to Dhaka. The airport was formerly known as MA Hannan International Airport, but was renamed after a famous Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
saint Shah Amanat on 2 April 2005 by the Government.
Regional Communication with The Chittagong City:
 * Oman Air
* Air Arabia
* Bangladesh Biman
* US Bangla Airlines
* Al Zajera airlines
* Salam Airlines
* Fly Dubai
* Novo airlines
* Oman Air
* Air Arabia
* Bangladesh Biman
* US Bangla Airlines
* Al Zajera airlines
* Salam Airlines
* Fly Dubai
* Novo airlines
Sports

Tamim Iqbal
Tamim Iqbal Khan (Bengali: তামিম ইকবাল খান; born 20 March 1989), more popularly known as Tamim Iqbal, is a
Bangladeshi cricketer. He is the nephew of former Bangladesh skipper Akram Khan, the current chief selector of ...
, Akram Khan, Minhajul Abedin
Minhajul Abedin Nannu ( bn, মিনহাজুল আবেদিন নান্নু; born 25 September 1965) is a former Bangladeshi cricketer who played in 27 One Day Internationals from 1986 to 1999. He captained Bangladesh twice duri ...
, Aftab Ahmed, Nafees Iqbal
Mohammad Nafees Iqbal Khan ( bn, মোহাম্মদ নাফিস ইকবাল খান; born 31 January 1985), better known as Nafees Iqbal, is a former Bangladeshi international cricketer. He played as a right-handed opening batsman ...
, Nazimuddin, Faisal Hossain
Faisal Hossain (born 26 October 1978) is a Bangladeshi cricketer. He played international cricket for Bangladesh in 2004, one Test match and four One Day Internationals without establishing himself in the side. After poor performances at inter ...
, Tareq Aziz
Tareq Aziz ( bn, তারেক আজিজ; born 4 September 1983) is a former Bangladeshi international cricketer. He made his international debut for the Bangladesh cricket team in January 2002 against Pakistan
Career
He made his Twenty20 d ...
, Mominul Haque
Mominul Haque ( bn, মমিনুল হক; born 29 September 1991), also known as Muminul Showrav, is a Bangladeshi cricketer who is a former captain of the Bangladesh national team in Test matches. He is a left-handed batter.
Domestic c ...
, Irfan Sukkur
Irfan Sukkur (born 22 May 1993) is a Bangladeshi first-class and List A cricket player. He was born in Chittagong, Bangladesh. In November 2019, he was selected to play for the Rajshahi Royals in the 2019–20 Bangladesh Premier League. He score ...
, Yasir Ali Chowdhury, Nayeem Hasan
Mohammad Nayeem Hasan ( Bengali: মোহাম্মদ নাঈম হাসান; born 12 February 2000) is a Bangladeshi cricketer. He made his first-class debut for Chittagong Division in the 2016–17 National Cricket League on 10 Octo ...
, Minhajul Abedin Afridi are some of the most prominent figures among them. Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
is the most popular sport in Chittagong, while football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
, tennis and kabaddi
Kabaddi is a contact team sport. Played between two teams of seven players, the objective of the game is for a single player on offence, referred to as a "raider", to run into the opposing team's half of the court, touch out as many of their ...
are also popular. A number of stadiums are located in Chittagong with the main one being the multipurpose MA Aziz Stadium, which has a seating capacity
Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available, and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile tha ...
of 20,000 and hosts football matches in addition to cricket. MA Aziz Stadium was the stadium where Bangladesh achieved its first-ever Test cricket
Test cricket is a form of first-class cricket played at international level between teams representing full member countries of the International Cricket Council (ICC). A match consists of four innings (two per team) and is scheduled to last f ...
victory, against Zimbabwe in 2005. The stadium now focuses only on football, and is currently the main football venue of the city. Zohur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium
Zohur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium (Zahur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium) ( bn, জহুর আহমেদ চৌধুরী স্টেডিয়াম), abbreviated as ZAC Stadium or ZACS and previously known as Bir Shrestha Shahid Ruhul Amin Stadi ...
, is currently the main cricket venue of the city, which was awarded Test status in 2006, hosting both domestic and international cricket matches. The city hosted two group matches of the 2011 ICC Cricket World Cup, both taking place in Zohur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium. It also co-hosted 2014 ICC World Twenty20
The 2014 ICC World Twenty20 was the fifth ICC World Twenty20 competition, an international Twenty20 cricket tournament, that took place in Bangladesh from 16 March to 6 April 2014. It was played in three cities — Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet. ...
along with Dhaka and Sylhet, Zohur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium hosted 15 group stage matches. Other stadiums in Chittagong include the Women's Complex Ground. Major sporting clubs such as, Mohammedan Sporting Club and Abahani Chittagong are also located in the city. Chittagong is also home to the Bangladesh Premier League
The Bangladesh Premier League (BPL) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ প্রিমিয়ার লীগ) is a professional Twenty20 cricket league consisting of seven franchises. The BPL is one of the three professional cricket leagues in ...
franchise, the Chittagong Vikings
The Chattogram Challengers ( Chittagonian/ bn, চট্টগ্রাম চ্যালেঞ্জার্স) is a franchise cricket team which participates in the Bangladesh Premier League (BPL). The franchise was founded in 2012 & based ...
.Teams
*Chattogram Challengers
The Chattogram Challengers ( Chittagonian/ bn, চট্টগ্রাম চ্যালেঞ্জার্স) is a franchise cricket team which participates in the Bangladesh Premier League (BPL). The franchise was founded in 2012 & based ...
- BPL (Cricket)
*Chittagong Abahani Limited
Chittagong Abahani Limited ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম আবাহনী লিমিটেড), also spelled as Chattogram Abahani or Chittagong Abahoni, is a sports club based in Chittagong, Bangladesh. A wing of Abahani Limited wa ...
- BPL (Football)
* Acme Chattogram - HCT (Field hockey)
*
Twin towns – sister cities
*Goiânia
Goiânia (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian federative units of Brazil, state of Goiás. With a population of 1,536,097, it is the second-largest city in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West Region and the 10th-largest ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
* Kunming
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquar ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
See also
* Jamboree Park *Conquest of Chittagong
Mirza Abu Talib (22 November 1600 – 1694), better known as Shaista Khan, was a general and the subahdar of Mughal Bengal. A maternal uncle to the emperor Aurangzeb, he acted as a key figure during his reign. Shaista Khan initially governed ...
Notes
Explanatory notes
Citations
External links
Official Web Portal of Chittagong
Chittagong City Corporation
Chittagong Development Authority
Chittagong Metropolitan Police
* {{Authority control Bay of Bengal Chittagong District Former colonies in Asia Former Portuguese colonies Populated coastal places in Bangladesh Populated places in Chittagong Division Port cities in Asia Portuguese colonisation in Asia