China in world languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The names of China include the many contemporary and historical appellations given in various languages for the East Asian country known as ''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' (/, "middle country") in its national language,
 ''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' (õĖŁÕ£ŗ) is the most common
''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' (õĖŁÕ£ŗ) is the most common
p. 93-94
As early as the From the Qin to Ming dynasty literati discussed ''Zhongguo'' as both a historical place or territory and as a culture. Writers of the Ming period in particular used the term as a political tool to express opposition to expansionist policies that incorporated foreigners into the empire. In contrast foreign conquerors typically avoided discussions of ''Zhongguo'' and instead defined membership in their empires to include both Han and non-Han peoples.
From the Qin to Ming dynasty literati discussed ''Zhongguo'' as both a historical place or territory and as a culture. Writers of the Ming period in particular used the term as a political tool to express opposition to expansionist policies that incorporated foreigners into the empire. In contrast foreign conquerors typically avoided discussions of ''Zhongguo'' and instead defined membership in their empires to include both Han and non-Han peoples.
ŃäćŃä¦ŃäŻ╦Ŗ ŃäŹŃä©Ńäø╦Ŗ , w6 = T╩╗ai┬▓-wan┬╣ Min┬▓-kuo┬▓ , p6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łngu├│ , tp6 = T├Īiwan M├Łngu├│ , myr6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łn'gw├│ , mps6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łngu├│, gr6 = Tair'uan Min'gwo , psp6 = Taiwan Minkuo , poj6 = T├ói-o├ón B├«n-kok, tl6 = T├ói-u├ón B├«n-kok, phfs6 = Th├▓i-v├Ān M├¼n-koet Th├▓i-v├ón M├¼n-koet In 1912, China adopted its official name, Chunghwa Minkuo (rendered in pinyin Zh┼Źnghu├Ī M├Łngu├│) or in English as the "Republic of China", which also has sometimes been referred to as " Republican China" or the "Republican Era" (), in contrast to the empire it replaced, or as " Nationalist China", after the ruling Chinese Nationalist Party ( Kuomintang). (''Chunghwa'') is a term that pertains to "China" while (''Minkuo''), literally "People's State" or "Peopledom", stands for "republic". The name had stemmed from the party manifesto of Tongmenghui in 1905, which says the four goals of the Chinese revolution was "to expel the
 The traditional etymology, proposed in the 17th century by
The traditional etymology, proposed in the 17th century by
The clash of empires
', p. 77. . "Scholars have dated the earliest mentions of ''C─½na'' to the ''R─üm─üyana'' and the ''Mah─übh─ürata'' and to other Sanskrit sources such as the Hindu Laws of Manu." Some Chinese and Indian scholars argued for the state of Jing (, another name for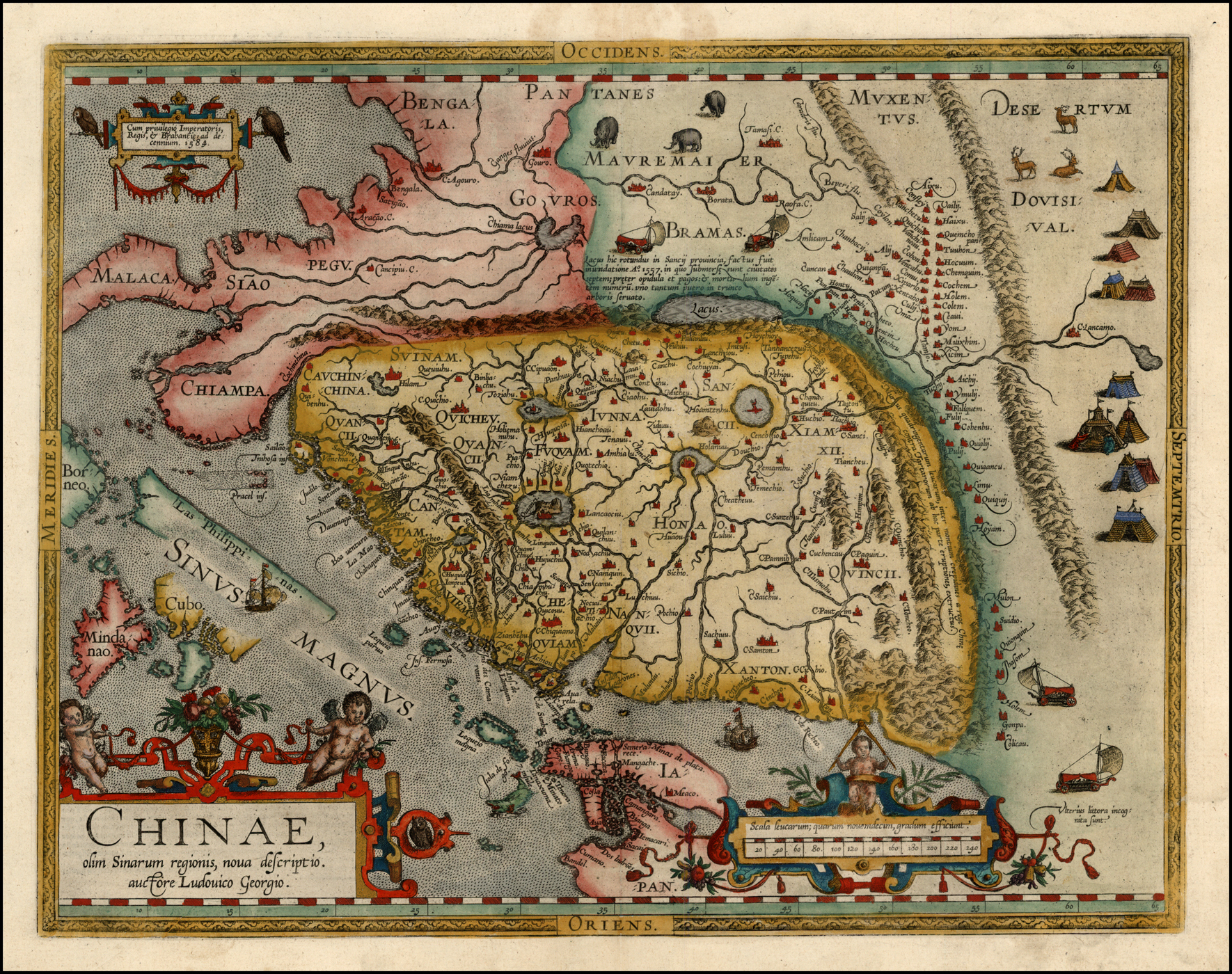
 ''S─½nae'' was an ancient Greek and Roman name for some people who dwelt south of the Seres (Serica) in the eastern extremity of the habitable world. References to the Sinae include mention of a city that the Romans called ''S─ōra M─ōtropolis'', which may be modern Chang'an. The Latin prefixes ''Sino-'' and ''Sin-'' as well as words such as ''Sinica'', which are traditionally used to refer to China or the Chinese, came from ''S─½nae''. It is generally thought that ''Ch─½na'', ''S─½na'' and ''Th─½na'' are variants that ultimately derived from Qin, which was the westernmost state in China that eventually formed the Qin Dynasty. There are however other opinions on its etymology (See section on China above). Henry Yule thought that this term may have come to Europe through the Arabs, who made the China of the farther east into ''Sin'', and perhaps sometimes into ''Thin''. Hence the ''Thin'' of the author of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, who appears to be the first extant writer to employ the name in this form; hence also the Sin├” and Thinae of Ptolemy.
Some denied that Ptolemy's Sinae really represented the Chinese as Ptolemy called the country ''S─ōrice'' and the capital ''S─ōra'', but regarded them as distinct from ''S─½nae''. Marcian of Heraclea (a condenser of Ptolemy) tells us that the "nations of the Sinae lie at the extremity of the habitable world, and adjoin the eastern Terra incognita". The 6th century Cosmas Indicopleustes refers to a "country of silk" called ''Tzinista'', which is understood as referring to China, beyond which "there is neither navigation nor any land to inhabit". It seems probable that the same region is meant by both. According to Henry Yule, Ptolemy's misrendering of the
''S─½nae'' was an ancient Greek and Roman name for some people who dwelt south of the Seres (Serica) in the eastern extremity of the habitable world. References to the Sinae include mention of a city that the Romans called ''S─ōra M─ōtropolis'', which may be modern Chang'an. The Latin prefixes ''Sino-'' and ''Sin-'' as well as words such as ''Sinica'', which are traditionally used to refer to China or the Chinese, came from ''S─½nae''. It is generally thought that ''Ch─½na'', ''S─½na'' and ''Th─½na'' are variants that ultimately derived from Qin, which was the westernmost state in China that eventually formed the Qin Dynasty. There are however other opinions on its etymology (See section on China above). Henry Yule thought that this term may have come to Europe through the Arabs, who made the China of the farther east into ''Sin'', and perhaps sometimes into ''Thin''. Hence the ''Thin'' of the author of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, who appears to be the first extant writer to employ the name in this form; hence also the Sin├” and Thinae of Ptolemy.
Some denied that Ptolemy's Sinae really represented the Chinese as Ptolemy called the country ''S─ōrice'' and the capital ''S─ōra'', but regarded them as distinct from ''S─½nae''. Marcian of Heraclea (a condenser of Ptolemy) tells us that the "nations of the Sinae lie at the extremity of the habitable world, and adjoin the eastern Terra incognita". The 6th century Cosmas Indicopleustes refers to a "country of silk" called ''Tzinista'', which is understood as referring to China, beyond which "there is neither navigation nor any land to inhabit". It seems probable that the same region is meant by both. According to Henry Yule, Ptolemy's misrendering of the
 From Chinese ''Manzi'' (southern barbarians). The division of North China and South China under the Jin dynasty and Song dynasty weakened the idea of a unified China, and it was common for non-Han peoples to refer to the politically disparate North and South by different names for some time. While Northern China was called
From Chinese ''Manzi'' (southern barbarians). The division of North China and South China under the Jin dynasty and Song dynasty weakened the idea of a unified China, and it was common for non-Han peoples to refer to the politically disparate North and South by different names for some time. While Northern China was called
Standard Mandarin
Standard Chinese ()ŌĆöin linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin ChineseŌĆöis a modern standar ...
. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, the name in English for the country, was derived from Portuguese in the 16th century, and became common usage in the West in the subsequent centuries. It is believed to be a borrowing from Middle Persian, and some have traced it further back to Sanskrit. It is also thought that the ultimate source of the name China is the Chinese word "Qin" (), the name of the dynasty that unified China but also existed as a state for many centuries prior. There are, however, other alternative suggestions for the origin of the word.
Chinese names for China, aside from ''Zhongguo'', include '' Zh┼Źnghu├Ī'' (/, "central beauty"), ''Hu├Īxi├Ā
''Huaxia'' (ĶÅ»ÕżÅ, ) is a historical concept representing the Chinese nation, and came from the self-awareness of a common cultural ancestry by the various confederations of pre-Qin ethnic ancestors of Han people.
Etymology
The earliest e ...
'' (/, "beautiful grandness"), ''Sh├®nzh┼Źu'' (, "divine state") and ''JiŪözh┼Źu'' (, "nine states"). '' H├Ān'' (/) and '' T├Īng'' () are common names given for the Chinese ethnicity, despite the Chinese nationality (''Zh┼Źnghu├Ī M├Łnz├║'') not referencing any singular ethnicity. The People's Republic of China () and Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
() are the official names for the two contemporary sovereign states currently claiming sovereignty over the traditional area of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. " Mainland China" is used to refer to areas under the jurisdiction of the PRC, usually excluding Hong Kong and Macau.
There are also names for China used around the world that are derived from the languages of ethnic groups other than the Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
; examples include "Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which ...
" from the Khitan language
Khitan or Kitan ( in large script or in small, ''Khitai''; , ''Q├¼d─ünyŪö''), also known as Liao, is a now-extinct language once spoken in Northeast Asia by the Khitan people (4th to 13th century). It was the official language of the Liao Empir ...
and "Tabgach" from Tuoba.
Sinitic names
Zhongguo
Pre-Qing
 ''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' (õĖŁÕ£ŗ) is the most common
''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' (õĖŁÕ£ŗ) is the most common Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
name for China in modern times. The earliest appearance of this two-character term is on the bronze vessel He ''zun'' (dating to 1038ŌĆō), during the early Western Zhou period. The phrase "zhong guo" came into common usage in the Warring States period (475ŌĆō221 BCE), when it referred to the "Central States"; the states of the Yellow River Valley of the Zhou era, as distinguished from the tribal periphery. In later periods, however, ''Zhongguo'' was not used in this sense. Dynastic names were used for the state in Imperial China and concepts of the state aside from the ruling dynasty were little understood. Rather, the country was called by the name of the dynasty, such as "Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
" (), "Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century ŌĆō 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (ÕöÉ) b ...
" (), "Great Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
" (''Da Ming'' ), " Great Qing" (''Da Qing'' ), as the case might be. Until the 19th century when the international system came to require a common legal language, there was no need for a fixed or unique name.p. 93-94
As early as the
Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
, ''Zhongguo'' could be understood as either the domain of the capital or used to refer the Chinese civilization (''zhuxia'' Ķ½ĖÕżÅ "the various Xia" or ''zhuhua'' Ķ½ĖĶÅ» "various Hua"), and the political and geographical domain that contained it, but Tianxia was the more common word for this idea. This developed into the usage of the Warring States period when, other than the cultural-civilizational community, it could be the geopolitical area of Chinese civilization, equivalent to Jiuzhou. In a more limited sense it could also refer to the Central Plain or the states of Zhao, Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (ĶĪø, 1040ŌĆō209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (ķŁÅ, 403ŌĆō225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
, and Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
, etc., geographically central amongst the Warring States. Although ''Zhongguo'' could be used before the Song dynasty period to mean the transdynastic Chinese culture or civilization to which Chinese people belonged, it was in the Song dynasty when writers used ''Zhongguo'' as a term to describe the transdynastic entity with different dynastic names over time but having a set territory and defined by common ancestry, culture, and language.
There were different usages of the term ''Zhongguo'' in every period. It could refer to the capital of the emperor to distinguish it from the capitals of his vassals, as in Western Zhou. It could refer to the states of the Central Plain Central Plain or Central Plains may refer to:
Regions
* Zhongyuan, a plain in Northern China in the lower reaches of the Yellow River which was the cradle of Chinese civilisation
** Central Plains Economic Zone
* Central Plain (Wisconsin), one ...
to distinguish them from states in outer regions. The '' Shi Jing'' defines ''Zhongguo'' as the capital region, setting it in apposition to the capital city. During the Han dynasty, three usages of ''Zhongguo'' were common. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' uses ''Zhongguo'' to denote the capital, and also uses the concept ''zhong'' ("center, central") and ''zhongguo'' to indicate the center of civilization: "There are eight famous mountains in the world: three in Man and Yi (the barbarian wilds), five in ''Zh┼Źnggu├│''." () In this sense, the term ''Zhongguo'' is synonymous with ''Hu├Īxi├Ā'' (/) and ''Zh┼Źnghu├Ī'' (/), names of China that were first authentically attested since Warring States period and Eastern Jin period, respectively.
 From the Qin to Ming dynasty literati discussed ''Zhongguo'' as both a historical place or territory and as a culture. Writers of the Ming period in particular used the term as a political tool to express opposition to expansionist policies that incorporated foreigners into the empire. In contrast foreign conquerors typically avoided discussions of ''Zhongguo'' and instead defined membership in their empires to include both Han and non-Han peoples.
From the Qin to Ming dynasty literati discussed ''Zhongguo'' as both a historical place or territory and as a culture. Writers of the Ming period in particular used the term as a political tool to express opposition to expansionist policies that incorporated foreigners into the empire. In contrast foreign conquerors typically avoided discussions of ''Zhongguo'' and instead defined membership in their empires to include both Han and non-Han peoples.
Qing
''Zhongguo'' appeared in a formal international legal document for the first time during the Qing dynasty in the Treaty of Nerchinsk, 1689. The term was then used in communications with other states and in treaties. The Manchu rulers incorporated Inner Asian polities into their empire, and Wei Yuan, a statecraft scholar, distinguished the new territories from ''Zhongguo'', which he defined as the 17 provinces of " China proper" plus the Manchu homelands in the Northeast. By the late 19th century the term had emerged as a common name for the whole country. The empire was sometimes referred to as Great Qing but increasingly as ''Zhongguo'' (see the discussion below). ''Dulimbai Gurun'' is theManchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
name for China, with "Dulimbai" meaning "central" or "middle," and "Gurun" meaning "nation" or "state." The historian Zhao Gang writes that "not long after the collapse of the Ming, China hongguobecame the equivalent of Great Qing (Da Qing)ŌĆöanother official title of the Qing state", and "Qing and China became interchangeable official titles, and the latter often appeared as a substitute for the former in official documents." The Qing dynasty referred to their realm as "''Dulimbai Gurun''" in Manchu. The Qing equated the lands of the Qing realm (including present day Manchuria, Xinjiang, Mongolia, Tibet and other areas) as "China" in both the Chinese and Manchu languages, defining China as a multi-ethnic state, rejecting the idea that China only meant Han areas; both Han and non-Han peoples were part of "China". Officials used "China" (though not exclusively) in official documents, international treaties, and foreign affairs, and the "Chinese language" (Manchu: ''Dulimbai gurun i bithe'') referred to Chinese, Manchu, and Mongol languages, and the term "Chinese people" (; Manchu: ''Dulimbai gurun i niyalma'') referred to all Han, Manchus, and Mongol subjects of the Qing. Ming loyalist Han literati held to defining the old Ming borders as China and using "foreigner" to describe minorities under Qing rule such as the Mongols, as part of their anti-Qing ideology.
When the Qing conquered Dzungaria in 1759, they proclaimed that the new land was absorbed into ''Dulimbai Gurun'' in a Manchu language memorial. The Qing expounded on their ideology that they were bringing together the "outer" non-Han Chinese like the Inner Mongols, Eastern Mongols, Oirat Mongols, and Tibetans together with the "inner" Han Chinese, into "one family" united in the Qing state, showing that the diverse subjects of the Qing were all part of one family, the Qing used the phrase "" () or "" (), to convey this idea of "unification" of the different peoples. A Manchu language version of a treaty with the Russian Empire concerning criminal jurisdiction over bandits called people from the Qing as "people of the Central Kingdom (Dulimbai Gurun)". In the Manchu official Tulisen's Manchu language account of his meeting with the Torghut Mongol leader Ayuki Khan, it was mentioned that while the Torghuts were unlike the Russians, the "people of the Central Kingdom" (''dulimba-i gurun/'') were like the Torghut Mongols, and the "people of the Central Kingdom" referred to the Manchus.
Mark Elliott noted that it was under the Qing that "China" transformed into a definition of referring to lands where the "state claimed sovereignty" rather than only the Central Plains area and its people by the end of the 18th century.
Elena Barabantseva also noted that the Manchu referred to all subjects of the Qing empire regardless of ethnicity as "Chinese" (), and used the term () as a synonym for the entire Qing empire while using "H├Ān r├®n" () to refer only to the core area of the empire, with the entire empire viewed as multiethnic.
Joseph W. Esherick Joseph W. Esherick (Chinese name: , born 1942) is an emeritus professor of modern Chinese history at the University of California, San Diego. He is the holder of thHwei-chih and Julia Hsiu Chair in Chinese Studies Esherick is a graduate of Harvard C ...
noted that while the Qing Emperors governed frontier non-Han areas in a different, separate system under the Lifanyuan The Lifan Yuan (; ; Mongolian: ąōą░ą┤ą░ą░ą┤ ą£ąŠąĮą│ąŠą╗čŗąĮ čéė®čĆąĖą╣ą│ ąĘą░čüą░čģ čÅą▓ą┤ą╗čŗąĮ čÅą░ą╝, ''╬│ada╬│adu mong╬│ul un t├Čr├╝-yi jasaqu yabudal-un yamun'') was an agency in the government of the Qing dynasty of China which administered ...
and kept them separate from Han areas and administration, it was the Manchu Qing Emperors who expanded the definition of ''Zhongguo'' () and made it "flexible" by using that term to refer to the entire Empire and using that term to other countries in diplomatic correspondence, while some Han Chinese subjects criticized their usage of the term and the Han literati Wei Yuan used ''Zhongguo'' only to refer to the seventeen provinces of China and three provinces of the east (Manchuria), excluding other frontier areas. Due to Qing using treaties clarifying the international borders of the Qing state, it was able to inculcate in the Chinese people a sense that China included areas such as Mongolia and Tibet due to education reforms in geography which made it clear where the borders of the Qing state were even if they didn't understand how the Chinese identity included Tibetans and Mongolians or understand what the connotations of being Chinese were. The Treaty of Nanking (1842) English version refers to "His Majesty the Emperor of China" while the Chinese refers both to "The Great Qing Emperor" (''Da Qing Huangdi'') and to ''Zhongguo'' as well. The Treaty of Tientsin
The Treaty of Tientsin, also known as the Treaty of Tianjin, is a collective name for several documents signed at Tianjin (then Postal Map Romanization, romanized as Tientsin) in June 1858. The Qing Empire, Qing dynasty, Russian Empire, Secon ...
(1858) has similar language.
In the late 19th century the reformer Liang Qichao argued in a famous passage that "our greatest shame is that our country has no name. The names that people ordinarily think of, such as Xia, Han, or Tang, are all the titles of bygone dynasties." He argued that the other countries of the world "all boast of their own state names, such as England and France, the only exception being the Central States." The Japanese term "''Shina
Shina may refer to:
* Shina language, an Indo-Aryan language spoken in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan
* Shina people, a Dardic ethnic group in Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan
People named Shina
* Shina Matsudo (born 1973), Japanese freestyle swimmer
* ...
''" was proposed as a basically neutral Western-influenced equivalent for "China". Liang and Chinese revolutionaries, such as Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 ŌĆō 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
, who both lived extensive periods in Japan, used ''Shina'' extensively, and it was used in literature as well as by ordinary Chinese. But with the overthrow of the Qing in 1911, most Chinese dropped ''Shina'' as foreign and demanded that even Japanese replace it with ''Zhonghua minguo'' or simply ''Zhongguo''. Liang went on to argue that the concept of ''tianxia'' had to be abandoned in favor of ''guojia'', that is, "nation," for which he accepted the term ''Zhongguo''. After the founding of the Chinese Republic in 1912, ''Zhongguo'' was also adopted as the abbreviation of ''Zhonghua minguo''.
Qing official Zhang Deyi objected to the western European name "China" and said that China referred to itself as Zhonghua in response to a European who asked why Chinese used the term ''guizi
''Guizi'' () is a pejorative Chinese slang term for foreigners. It has had a history of containing xenophobic connotations.
History
Starting with the arrival of European sailors in the sixteenth century, foreigners were often perceived in Chin ...
'' to refer to all Europeans.
In the 20th century after the May Fourth Movement, educated students began to spread the concept of ''Zh┼Źnghu├Ī'' (/), which represented the people, including 56 minority ethnic groups and the Han Chinese, with a single culture identifying themselves as "Chinese". The Republic of China and the People's Republic of China both used the title "Zh┼Źnghu├Ī" in their official names. Thus, ''Zh┼Źnggu├│'' became the common name for both governments, and "Zh┼Źnggu├│ r├®n" for their citizen
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
s, though Taiwanese people may reject being called as such. Overseas Chinese
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, refe ...
are referred to as ''hu├Īqi├Īo'' (/), "Chinese overseas", or ''hu├Īy├¼'' (/), "Chinese descendants" (i.e., Chinese children born overseas).
Middle Kingdom
The English translation of ''Zhongguo'' as the "Middle Kingdom" entered European languages through the Portuguese in the 16th century and became popular in the mid 19th century. By the mid 20th century the term was thoroughly entrenched in the English language to reflect the Western view of China as the inwards looking Middle Kingdom, or more accurately the ''Central Kingdom''. Endymion Wilkinson points out that the Chinese were not unique in thinking of their country as central, although China was the only culture to use the concept for their name. The term ''Zhongguo'' was also not commonly used as a name for China until quite recently, nor did it mean the "Middle Kingdom" to the Chinese, or even have the same meaning throughout the course of history ( see above).= "Zh┼Źnggu├│" in different languages
= *Burmese
Burmese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia
* Burmese people
* Burmese language
* Burmese alphabet
* Burmese cuisine
* Burmese culture
Animals
* Burmese cat
* Burmese chicken
* Burmese (hor ...
:
* ca, Pa├Łs del Mig (The Middle's Country/State)
* cs, ┼ś├Ł┼Īe st┼Öedu ("The Empire of the Center")
* nl, Middenrijk ("Middle Empire" or "Middle Realm")
* English: ''Middle Kingdom'', ''Central Kingdom''
* fi, Keskustan valtakunta ("The State of the Center")
* french: Empire du milieu ("Middle Empire") or ("Middle Kingdom")
* german: Reich der Mitte ("Middle Empire")
* Greek: (, "Middle Empire") or (, "Central Empire")
* hmn, Suav Teb (), (), ()
* hu, K├Čz├®ps┼æ birodalom ("Middle Empire")
* id, Tiongkok (from , the Hokkien name for China)
* it, Impero di Mezzo ("Middle Empire")
* Japanese: (; )
* Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
: ()
* Korean: (; )
* Li:
* Lojban: jugygu'e or .djunguos.
* Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
: () or () were the official names for "China" in Manchu language
* Mongolian: (), the official name for "China" used in Inner Mongolia
* pl, Państwo Środka ("The State of the Center")
* pt, Estado Central ("Central State")
* russian: ąĪčĆąĄą┤ąĖąĮąĮąŠąĄ ą”ą░čĆčüčéą▓ąŠ (; "Middle Kingdom")
* sk, R├Ł┼Īa stredu ("The Empire of the Center")
* es, Pa├Łs del Centro (The Middle's Country/State)
* sv, Mittens rike (The Middle's Kingdom/Empire/Realm/State)
* Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
: (), a PRC-era loanword from Mandarin; the normal Tibetan term for China (proper) is rgya nak (ÓĮóÓŠÆÓŠ▒Ó╝ŗÓĮōÓĮé), lit. the "black country."
* tok, ma Sonko
* ug, ž¼█ć┌Ł┌»┘ł, Junggo
* vi, Trung Quốc ()
* ii, ĻŹÅĻć®(''Zho guop'')
* Zhuang: (older orthography: )
= "Zh┼Źnghu├Ī" in different languages
= * id, Tionghoa (from , the Hokkien counterpart) * Japanese: (; ) * Korean: (; ) *Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
: ()
* Li:
* Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
: ()
* Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
: (''krung hwa'')
* ug, ž¼█ć┌Łž«█枦, Jungxua
* vi, Trung hoa ()
* ii, ĻŹÅĻēĖ (''Zho huop'')
* Zhuang: (Old orthography: )
Huaxia
The name ''Huaxia'' (/; ) is generally used as a sobriquet in Chinese text. Under traditional interpretations, it is the combination of two words which originally referred to the elegance of the traditional attire of the Han Chinese and the Confucian concept of rites. * ''Hua'' which means "flowery beauty" (''i.e.'' having beauty of dress and personal adornment ). * ''Xia'' which means greatness or grandeur (''i.e.'' having greatness of social customs/courtesy/polite manners and rites/ceremony ). In the original sense, Huaxia refers to a confederation of tribesŌĆöliving along the Yellow RiverŌĆöwho were the ancestors of what later became the Han ethnic group in China. During the Warring States (475ŌĆō221 BCE), the self-awareness of the Huaxia identity developed and took hold in ancient China.Zhonghua minzu
''Zhonghua minzu'' is a term meaning Chinese nation in the sense of a multi-ethnic national identity. Though originally rejected by the PRC, it has been used officially since the 1980s for nationalist politics.Tianchao and Tianxia
''Tianchao'' (; ), translated as "heavenly dynasty" or "Celestial Empire;" and ''Tianxia'' (; ) translated as " under heaven," are both phrases that have been used to refer to China. These terms were usually used in the context of civil wars or periods of division, with the term ''Tianchao'' evoking the idea of the realm's ruling dynasty was appointed by heaven; or that whoever ends up reunifying China is said to have ruled ''Tianxia'', or everything under heaven. This fits with the traditional Chinese theory of rulership in which the emperor was nominally the political leader of the entire world and not merely the leader of a nation-state within the world. Historically the term was connected to the later Zhou Dynasty (c.ŌĆē1046ŌĆō256 BCE), especially theSpring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
(eighth to fourth century BCE) and the Warring States period (from there to 221 BCE, when China was reunified by the Qin state). The phrase ''Tianchao'' continues to see use on Chinese internet discussion boards, in reference to China.
The phrase ''Tianchao'' was first translated into English and French in the early 19th century, appearing in foreign publicans and diplomatic correspondences, with the translated phrase "Celestial Empire" occasionally used to refer to China. During this period, the term ''celestial'' was used by some to refer to the subjects of the Qing dynasty in a non-prejudicial manner, derived from the term "Celestial Empire". However, the term ''celestial'' was also used in a pejorative manner during the 19th century, in reference to Chinese immigrants in Australasia and North America. The translated phrase has largely fallen into disuse in the 20th century.
Translations for ''Tianxia'' include:
* Russian: ą¤ąŠą┤ąĮąĄą▒ąĄčüąĮą░čÅ (''Podneb├®snaya''; lit. "under the heaven")
Jiangshan and Heshan
''Jiangshan'' (; ) and ''Heshan'' (; ) literally mean "rivers and mountains". This term is quite similar in usage to ''Tianxia'', and simply refers to the entire world, and here the most prominent features of which being rivers and mountains. The use of this term is also common as part of the phrase ''Jiangshan sheji'' (; ; lit. "rivers and mountains,soil and grain __NOTOC__
Soil and grain was a common political term in the Sinosphere for the state. Shejitan, the altars of soil and grain, were constructed alongside ancestral altars. Chinese monarchs of the Ming and Qing dynasties performed ceremonies of soil ...
"), suggesting the need to implement good governance.
Jiuzhou
The name ''Jiuzhou'' (; ) means "nine provinces". Widely used in pre-modern Chinese text, the word originated during the middle of Warring States period of China (c. 400ŌĆō221 BCE). During that time, the Yellow River river region was divided into nine geographical regions; thus this name was coined. Some people also attribute this word to the mythical hero and king, Yu the Great, who, in the legend, divided China into nine provinces during his reign. (Consult Zhou for more information.)Shenzhou
This name means ''Divine Realm'' or ''Divine Land'' (; ) and comes from the same period as Jiuzhou meaning "nine provinces". It was thought that the world was divided into nine major states, one of which is Shenzhou, which is in turn divided into nine smaller states, one of which is Jiuzhou mentioned above.Sihai
This name, '' Four Seas'' (; ), is sometimes used to refer to the world, or simply China, which is perceived as the civilized world. It came from the ancient notion that the world is flat and surrounded by sea.Han
The name ''Han'' (/; ) derives from the Han dynasty (206 BCŌĆōAD 220), who presided over China's first "golden age". The Han dynasty collapsed in 220 and was followed by a long period of disorder, including Three Kingdoms,Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
, and Southern and Northern dynasties periods. During these periods, various non-Han ethnic groups established various dynasties in northern China. It was during this period that people began to use the term "Han" to refer to the natives of North China, who (unlike the minorities) were the descendants of the subjects of the Han dynasty.
During the Yuan dynasty, subjects of the empire was divided into four classes: Mongols, Semu or "Colour-eyeds", Hans, and "Southerns". Northern Chinese were called Han, which was considered to be the highest class of Chinese. This class "Han" includes all ethnic groups in northern China including Khitan and Jurchen who have in most part sinicized during the last two hundreds years. The name "Han" became popularly accepted.
During the Qing dynasty, the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
rulers also used the name Han to distinguish the natives of the Central Plains from the Manchus. After the fall of the Qing government, the Han became the name of a nationality within China. Today the term "Han Persons", often rendered in English as Han Chinese, is used by the People's Republic of China to refer to the most populous of the 56 officially recognized ethnic groups of China. The "Han Chinese" are simply referred to as "Chinese" by some.
Tang
The name ''Tang'' (; ) comes from the Tang dynasty (618ŌĆō690, 705ŌĆō907) that presided over China's second golden age. It was during the Tang dynasty that South China was finally and fully Sinicized; Tang would become synonymous with China in Southern China and it is usually Southern Chinese who refer to themselves as "''People of Tang''" (, ). For example, the sinicization and rapid development of Guangdong during the Tang period would lead the Cantonese to refer to themselves as ''Tong-yan'' () in Cantonese, while China is called ''Tong-saan'' (; ).Chinatown
A Chinatown () is an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Africa and Austra ...
s worldwide, often dominated by Southern Chinese, also became referred to ''Tang people's Street'' (, Cantonese: Tong-yan-gaai; ). The Cantonese term ''Tongsan'' (Tang mountain) is recorded in Old Malay as one of the local terms for China, along with the Sanskrit-derived ''Cina''. It is still used in Malaysia today, usually in a derogatory sense.
Among Taiwanese, ''Tang mountain'' (Min-Nan: Tn╠ég-soaŌü┐) has been used, for example, in the saying, "has Tangshan father, no Tangshan mother" (; ). This refers how the Han people crossing the Taiwan Strait in the 17th and 18th centuries were mostly men, and that many of their offspring would be through intermarriage with Taiwanese aborigine
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 5 ...
women.
In Ryukyuan, Karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ) is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tii'' in Okinawan) under the ...
was originally called ''tii'' (, hand) or ''karatii'' (, Tang hand) because ''too-nu-kuku'' or ''kara-nu-kuku'' () was a common Ryukyuan name for China; it was changed to ''karate'' (, open hand) to appeal to Japanese people after the First Sino-Japanese War.
Dalu and Neidi
''D├Āl├╣'' (/; ), literally "big continent" or "mainland" in this context, is used as a short form of ''Zh┼Źngg├║o D├Āl├╣'' (/, Mainland China), excluding (depending on the context) Hong Kong and Macau, and/or Taiwan. This term is used in official context in both the mainland and Taiwan, when referring to the mainland as opposed to Taiwan. In certain contexts, it is equivalent to the term ''Neidi'' (; , literally "the inner land"). While ''Neidi'' generally refers to the interior as opposed to a particular coastal or border location, or the coastal or border regions generally, it is used in Hong Kong specifically to mean mainland China excluding Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan. Increasingly, it is also being used in an official context within mainland China, for example in reference to the separate judicial and customs jurisdictions of mainland China on the one hand and Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan on the other. The term ''Neidi'' is also often used in Xinjiang and Tibet to distinguish the eastern provinces of China from the minority-populated, autonomous regions of the west.Official names
People's Republic of China
The name New China has been frequently applied to China by the Chinese Communist Party as a positive political and social term contrasting pre-1949 China (the establishment of the PRC) and the new name of the socialist state, Zh┼Źnghu├Ī R├®nm├Łn G├▓ngh├®gu├│ (in the older postal romanization, Chunghwa Jenmin Konghokuo) or the "People's Republic of China" in English, was adapted from the CCP's short-lived Chinese Soviet Republic in 1931. This term is also sometimes used by writers outside mainland China. The PRC was known to many in the West during theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
as "Communist China" or "Red China" to distinguish it from the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
which is commonly called "Taiwan", "Nationalist China" or "Free China". In some contexts, particularly in economics, trade, and sports, "China" is often used to refer to mainland China to the exclusion of Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan.
The official name of the People's Republic of China in various official languages and scripts:
* Simplified Chinese: () ŌĆō Official language and script, used in mainland China, Singapore and Malaysia
* Traditional Chinese: () ŌĆō Official script in Hong Kong and Macau, and commonly used in Taiwan (ROC)
* English: People's Republic of China ŌĆō Official in Hong Kong
* Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
: As used within the Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekis ...
, ęÜčŗčéą░ą╣ ąźą░ą╗čŗęø ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗ (in Cyrillic script), ''Q─▒tay Xal─▒q Respwbl├»kas─▒'' (in Latin script), (in Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
); as used within the People's Republic of China, (in Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
), ą¢ę▒ęŻxčāą░ ąźą░ą╗čŗęø ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗ (in Cyrillic script), ''Ju├▒xwa Xal─▒q Respwbl├»kas─▒'' (in Latin script). The Cyrillic script is the predominant script in the Republic of Kazakhstan, while the Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
is normally used for the Kazakh language in the People's Republic of China.
* Korean: (; ''Junghwa Inmin Gonghwaguk'') ŌĆō Used in Yanbian Prefecture
Yanbian (; Chos┼Ån'g┼Łl: , ''Yeonbyeon''), officially known as the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture, is an autonomous prefecture in the east of Jilin Province, China. Yanbian is bordered to the north by Heilongjiang Province, on the west by ...
( Jilin) and Changbai County
Changbai Korean Autonomous County, or simply Changbai County (; Chos┼Ån'g┼Łl: ņןļ░▒Ēśä; Hangul: ņ░Įļ░öĒśä) is a county in southern Jilin province, China, facing Hyesan, North Korea. It is under the administration of the city of Baishan, to the ...
(Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost ...
)
* Manchurian: (''Dulimbai niyalmairgen gunghe' gurun'') or (''Junghūwa niyalmairgen gungheg'o'')
* Mongolian: (''B├╝g├╝de nayiramdaqu dumdadu arad ulus'') ŌĆō Official in Inner Mongolia; ąæ껹│ą┤ ąØą░ą╣čĆą░ą╝ą┤ą░čģ ąźčÅčéą░ą┤ ąÉčĆą┤ ąŻą╗čü (''B├╝gd Nairamdakh Khyatad Ard Uls'') ŌĆō used in Mongolia
* Portuguese: Rep├║blica Popular da China ŌĆō Official in Macau
* ŌĆō Official in PRC's Tibet
** ŌĆō Official in Tibet Government-in-Exile
* (''Jungxua Xelq Jumhuriyiti'') ŌĆō Official in Xinjiang
* Yi: (''Zho huop rep mip gop hop guop'') ŌĆō Official in Liangshan ( Sichuan) and several Yi-designated autonomous counties
* Zaiwa
Zaiwa (autonym: '; Tsaiwa, Tsaiva, ĶĮĮńō”; Burmese: ßĆćßĆŁßĆ»ßĆäßĆ║ßĆØßĆ½ßĆĖ/ßĆĪßĆćßĆ«ßĆĖ) is a Burmish language spoken in parts of southwest China and eastern Burma. There are around 100,000 speakers. It is also known as ''Atsi'', its name in ...
: ' ŌĆō Official in Dehong ( Yunnan)
* Zhuang: ''Cunghvaz Yinzminz Gunghozgoz'' (Old orthography: ''Cu┼ŗŲģvaŲ© YinŲ©minŲ© Gu┼ŗŲģoŲ©'') ŌĆō Official in Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
The official name of the People's Republic of China in major neighboring countries official languages and scripts:
* Japanese: (, ''Ch┼½ka Jinmin Ky┼Źwakoku'') ŌĆō Used in Japan
* Russian: (''Kitayskaya Narodnaya Respublika'') ŌĆō Used in Russia and Central Asia
* Hindi: (''Cheenee janavaadee ganaraajy'') ŌĆō Used in India
* Urdu: (''Awami Jamhoriya Cheen'') ŌĆō Used in Pakistan
* Burmese
Burmese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia
* Burmese people
* Burmese language
* Burmese alphabet
* Burmese cuisine
* Burmese culture
Animals
* Burmese cat
* Burmese chicken
* Burmese (hor ...
: (''Tarotepyishusammataninengan'') ŌĆō Used in Myanmar
* Vietnamese: ŌĆō Used in Vietnam
* Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
: (''S╠ä─üß╣Łh─ürß╣ćrß║Īß╣Ł╠äh Prach─üchn C─½n'') ŌĆō Used in Thailand
* Khmer: ŌĆō Used in Cambodia
* Lao: (''Sathalanalad Pasasonchin'') ŌĆō Used in Laos
* Nepali
Nepali or Nepalese may refer to :
Concerning Nepal
* Anything of, from, or related to Nepal
* Nepali people, citizens of Nepal
* Nepali language, an Indo-Aryan language found in Nepal, the current official national language and a language spoken ...
: (''Jana Gaß╣ćat─üntrika C─½na'') ŌĆō Used in Nepal
Republic of China
, t5 = , s5 = , l5 = beautiful island , bpmf5 = ŃäłŃä©╦Ŗ Ńä”╦ć ŃäćŃäø╦Ŗ ŃäĢŃäÜ , w5 = Fu┬▓-├¬rh┬│-mo┬▓-sha┬╣ , p5 = F├║'─ørm├│sh─ü , tp5 = F├║'─ørm├│sha , mps5 = F├║─ørm├│sh─ü , gr5 = Fwueelmosha , mi5= , myr5=F├║─ørmw├│sh─ü , j5 = Fuk1ji5mo1saa1 , poj5 = Hok-n├Ł-m├┤═ś-sa , phfs5 = , altname6 = Republic of Taiwan , t6 = , s6 = , bpmf6 = ŃäŖŃä×╦Ŗ Ńä©ŃäóŃäćŃä¦ŃäŻ╦Ŗ ŃäŹŃä©Ńäø╦Ŗ , w6 = T╩╗ai┬▓-wan┬╣ Min┬▓-kuo┬▓ , p6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łngu├│ , tp6 = T├Īiwan M├Łngu├│ , myr6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łn'gw├│ , mps6 = T├Īiw─ün M├Łngu├│, gr6 = Tair'uan Min'gwo , psp6 = Taiwan Minkuo , poj6 = T├ói-o├ón B├«n-kok, tl6 = T├ói-u├ón B├«n-kok, phfs6 = Th├▓i-v├Ān M├¼n-koet Th├▓i-v├ón M├¼n-koet In 1912, China adopted its official name, Chunghwa Minkuo (rendered in pinyin Zh┼Źnghu├Ī M├Łngu├│) or in English as the "Republic of China", which also has sometimes been referred to as " Republican China" or the "Republican Era" (), in contrast to the empire it replaced, or as " Nationalist China", after the ruling Chinese Nationalist Party ( Kuomintang). (''Chunghwa'') is a term that pertains to "China" while (''Minkuo''), literally "People's State" or "Peopledom", stands for "republic". The name had stemmed from the party manifesto of Tongmenghui in 1905, which says the four goals of the Chinese revolution was "to expel the
Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
rulers, to revive ''Chunghwa'', to establish a Republic, and to distribute land equally among the people.()." The convener of Tongmenghui and Chinese revolutionary leader Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 ŌĆō 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
proposed the name ''Chunghwa Minkuo'' as the assumed name of the new country when the revolution succeeded.
With the separation from mainland China in 1949 as a result of the Chinese Civil War, the territory of the Republic of China has largely been confined to the island of Taiwan and some other small islands. Thus, the country is often simply referred to as simply " Taiwan", although this may not be perceived as politically neutral. (See Taiwan Independence
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
.) Amid the hostile rhetoric of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, the government and its supporters sometimes referred to itself as "Free China" or "Liberal China", in contrast to People's Republic of China (which was historically called the "Bandit-occupied Area" () by the ROC). In addition, the ROC, due to pressure from the PRC, was forced to use the name "Chinese Taipei
"Chinese Taipei" is the term used in various international organizations and tournaments for groups or delegations representing the Republic of China (ROC), a country commonly known as Taiwan.
Due to the One-China principle stipulated by th ...
" () whenever it participates in international forums or most sporting events such as the Olympic Games.
Taiwanese politician Mei Feng had criticised the official English name of the state "Republic of China" fails to translate the Chinese character "Min" ( English: people) according to Sun Yat-sen's original interpretations, while the name should instead be translated as "the People's Republic of China," which confuses with the current official name of China under communist control. To avoid confusion, the Chen Shui-ban led DPP administration began to put an aside of "Taiwan" next to the nation's official name since 2005.
The official name of the Republic of China in various official languages and scripts:
* English: Republic of China ŌĆō Official in Hong Kong, commonly used by the United States until 1979, Chinese Taipei ŌĆō official designation in several international organizations ( International Olympic Committee, FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''F├®d├®ration Internationale de Football Association'' ( French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
, Miss Universe, World Health Organization), Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu ŌĆō World Trade Organization, Governing authorities on Taiwan ŌĆō Official name used by the United States from 1979
* Traditional Chinese: (), (), (), () ŌĆō Official script in Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan and the islands controlled by the ROC
* Simplified Chinese: (), (), (), () ŌĆō Official language and script, used in Mainland China, Singapore and Malaysia
* Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
: As used within Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekis ...
, ęÜčŗčéą░ą╣ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗ (in Cyrillic script), ''Q─▒tay Respwbl├»kas─▒'' (in Latin script), (in Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
); as used within the People's Republic of China, ą¢ę▒ęŻxčāą░ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░čüčŗ (in Cyrillic script), ''Ju├▒xwa Respwbl├»kas─▒'' (in Latin script), (in Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
). The Cyrillic script is the predominant script in the Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekis ...
, while the Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
is normally used for the Kazakh language
The Kazakh or simply Qazaq (Latin: or , Cyrillic: or , Arabic Script: or , , ) is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia by Kazakhs. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. It is the official lan ...
in the People's Republic of China.
* Korean: (; ''Junghwa Minguk'') ŌĆō Official in Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture
* Manchurian: (''Dulimbai irgen' gurun'')
* Mongolian: ąöčāąĮą┤ą░ą┤ ąĖčĆą│菹Į čāą╗čü (''Dumdadu irgen ulus'') ŌĆō Official for its history name before 1949 in Inner Mongolia and Mongolia; ąæ껹│ą┤ ąØą░ą╣čĆą░ą╝ą┤ą░čģ ąźčÅčéą░ą┤ ąŻą╗čü (B├╝gd Nairamdakh Khyatad Uls) ŌĆō used in Mongolia for Roc in Taiwan
* Portuguese: ''Rep├║blica da China'' ŌĆō Official in Macau, ''Formosa'' ŌĆō former name
* , ŌĆō Official in PRC's Tibet
** ŌĆō Official in Tibet Government-in-Exile
* ŌĆō Official in Xinjiang
* Yi: (''Zho huop mip guop'') ŌĆō Official in Liangshan ( Sichuan) and several Yi-designated autonomous counties
* Zaiwa
Zaiwa (autonym: '; Tsaiwa, Tsaiva, ĶĮĮńō”; Burmese: ßĆćßĆŁßĆ»ßĆäßĆ║ßĆØßĆ½ßĆĖ/ßĆĪßĆćßĆ«ßĆĖ) is a Burmish language spoken in parts of southwest China and eastern Burma. There are around 100,000 speakers. It is also known as ''Atsi'', its name in ...
: ' ŌĆō Official in Dehong ( Yunnan)
* Zhuang: ''Cunghvaz Mingoz'' (Old orthography: ''Cu┼ŗŲģvaŲ© MinŲ©ŲģoŲ©'') ŌĆō Official in Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
The official name of the Republic of China in major neighboring countries official languages and scripts:
* Japanese: (; ''Ch┼½ka Minkoku'') ŌĆō Used in Japan
Japan ( ja, µŚźµ£¼, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
* Korean: (; ''Junghwa Minguk'') ŌĆō Used in Korea
* Russian: (''Kitayskaya Respublika'') ŌĆō Used in Russia and Central Asia
* Hindi: (''Cheenee ganaraajy'') ŌĆō Used in India
* Urdu: (''Jamhoriya Cheen'') ŌĆō Used in Pakistan
* Burmese
Burmese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia
* Burmese people
* Burmese language
* Burmese alphabet
* Burmese cuisine
* Burmese culture
Animals
* Burmese cat
* Burmese chicken
* Burmese (hor ...
: (''Tarotesammataninengan'') ŌĆō Used in Myanmar
* Vietnamese: ŌĆō Used in Vietnam
* Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
: (''S╠ä─üß╣Łh─ürß╣ćrß║Īß╣Ł╠äh C─½n'') ŌĆō Used in Thailand (during 1912ŌĆō1949)
* Khmer: ŌĆō Used in Cambodia
* Lao: (''Sathalanalad Chin'') ŌĆō Used in Laos
* Nepali
Nepali or Nepalese may refer to :
Concerning Nepal
* Anything of, from, or related to Nepal
* Nepali people, citizens of Nepal
* Nepali language, an Indo-Aryan language found in Nepal, the current official national language and a language spoken ...
: (''Gaß╣ćat─üntrika C─½na'') ŌĆō Used in Nepal
Names in non-Chinese records
Names used in the parts of Asia, especially East and Southeast Asia, are usually derived directly from words in one of thelanguages of China
There are several hundred languages in China. The predominant language is Standard Chinese, which is based on central Mandarin, but there are hundreds of related Chinese languages, collectively known as ''Hanyu'' (, 'Han language'), that are spo ...
. Those languages belonging to a former dependency (tributary) or Chinese-influenced country have an especially similar pronunciation to that of Chinese. Those used in Indo-European languages, however, have indirect names that came via other routes and may bear little resemblance to what is used in China.
Chin, China
English, most Indo-European languages, and many others use various forms of the name ''China'' and theprefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the Word stem, stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy'' ...
"Sino-" or "Sin-" from the Latin ''Sina''. Europeans had knowledge of a country known in Greek as ''Thina'' or ''Sina'' from the early period; the '' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' from perhaps the first century AD recorded a country known as ''Thin'' (''╬Ė╬»╬Į''). The English name for "China" itself is derived from Middle Persian (''Ch─½n─½'' ). This modern word "China" was first used by Europeans starting with Portuguese explorers of the 16th century – it was first recorded in 1516 in the journal of the Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa. The journal was translated and published in England in 1555.
 The traditional etymology, proposed in the 17th century by
The traditional etymology, proposed in the 17th century by Martin Martini
Martino Martini () (20 September 1614 ŌĆō 6 June 1661), born and raised in Trento (Prince-Bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire), was a Jesuit missionary. As cartographer and historian, he mainly worked on ancient Imperial China.
Early years
Mar ...
and supported by later scholars such as Paul Pelliot and Berthold Laufer, is that the word "China" and its related terms are ultimately derived from the polity known as Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (ń¦”), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (ń¦”), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (Õż¦ń¦”), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
that unified China to form the Qin Dynasty (, Old Chinese: ''*dzin'') in the 3rd century BC, but existed as a state on the furthest west of China since the 9th century BC. "There are reasons however for believing the word was bestowed at a much earlier date, for it occurs in the Laws of Manu, which assert the ''Chinas'' to be degenerate Kshatriyas, and the Mahabharat, compositions many centuries older that imperial dynasty of ... And this name may have yet possibly been connected with the Ts'in, or some monarchy of the like title; for that Dynasty had reigned locally in Shen si from the ninth century before our era..." This is still the most commonly held theory, although the etymology is still a matter of debate according to the '' Oxford English Dictionary'', and many other suggestions have been mooted.
The existence of the word ''C─½na'' in ancient Indian texts was noted by the Sanskrit scholar Hermann Jacobi who pointed out its use in the Book 2 of ''Arthashastra
The ''Arthashastra'' ( sa, ÓżģÓż░ÓźŹÓżźÓżČÓżŠÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźŹÓż░Óż«ÓźŹ, ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, political science, economic policy and military strategy. Kautilya, also identified as Vishnugupta and Chanakya, is ...
'' with reference to silk and woven cloth produced by the country of ''C─½na'', although textual analysis suggests that Book 2 may not have been written long before 150 AD. The word is also found in other Sanskrit texts such as the ''Mah─übh─ürata
The ''Mah─übh─ürata'' ( ; sa, Óż«Óż╣ÓżŠÓżŁÓżŠÓż░ÓżżÓż«ÓźŹ, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''R─üm─üyaß╣ća''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
'' and the ''Laws of Manu
The ''Manusmß╣øiti'' ( sa, Óż«Óż©ÓźüÓżĖÓźŹÓż«ÓźāÓżżÓż┐), also known as the ''M─ünava-Dharma┼ø─üstra'' or Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitution among the many ' of Hinduism. In ancient India, the Rishi, sages often wrot ...
''. The Indologist Patrick Olivelle
Patrick Olivelle is an Indologist. A philologist and scholar of Sanskrit Literature whose work has focused on asceticism, renunciation and the dharma, Olivelle has been Professor of Sanskrit and Indian Religions in the Department of Asian Studi ...
argued that the word ''C─½n─ü'' may not have been known in India before the first century BC, nevertheless he agreed that it probably referred to Qin but thought that the word itself was derived from a Central Asian language.Liu, Lydia He, The clash of empires
', p. 77. . "Scholars have dated the earliest mentions of ''C─½na'' to the ''R─üm─üyana'' and the ''Mah─übh─ürata'' and to other Sanskrit sources such as the Hindu Laws of Manu." Some Chinese and Indian scholars argued for the state of Jing (, another name for
Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BCŌĆō223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BCŌĆō202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BCŌĆō70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
) as the likely origin of the name. Another suggestion, made by Geoff Wade, is that the '' C─½n─üh'' in Sanskrit texts refers to an ancient kingdom centered in present-day Guizhou, called Yelang, in the south Tibeto-Burman highlands. The inhabitants referred to themselves as ''Zina'' according to Wade.
The term ''China'' can also be used to refer to:
* a modern state, indicating the People's Republic of China (PRC) or the Republic of China (ROC), where recognized;
* " Mainland China" (/, ''Zh┼Źnggu├│ D├Āl├╣'' in Mandarin), which is the territory of the PRC minus the two special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau;
* " China proper", a term used to refer to the historical heartlands of China without peripheral areas like Manchuria, Inner Mongolia, Tibet, and Xinjiang
In economic contexts, " Greater China" (/, ''d├Ā Zh┼Źnghu├Ī d├¼q┼½'') is intended to be a neutral and non-political way to refer to Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan.
Sinologist
Sinology, or Chinese studies, is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of China primarily through Chinese philosophy, language, literature, culture and history and often refers to Western scholarship. Its origin "may be traced to the ex ...
s usually use "Chinese" in a more restricted sense, akin to the classical usage of ''Zhongguo'', to the Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
ethnic group, which makes up the bulk of the population in China and of the overseas Chinese
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, refe ...
.

List of derived terms
* Afrikaans: ''Sjina,'' spelling now obsolete and spelled as ''China'' (pronunciation is the same) () *Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
: ''Kinë'' ()
*Amharic
Amharic ( or ; (Amharic: ), ', ) is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas, and also serves as a lingua franca for all oth ...
: ''Chayna'' (from English)
* Armenian: šēš½šČšĪšĮš┐šĪšČ ()
*Assamese
Assamese may refer to:
* Assamese people, a socio-ethnolinguistic identity of north-eastern India
* People of Assam, multi-ethnic, multi-linguistic and multi-religious people of Assam
* Assamese language, one of the easternmost Indo-Aryan language ...
: ()
*Azeri
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic people living mainly in Azerbaijan (Iran), northwestern Iran and the Azerbaijan, Republi ...
: ''├ćin'' ()
* Basque: ''Txina'' ()
*Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
: ()
* Burma: ''ßĆÉßĆøßĆ»ßĆÉßĆ║'' ()
*Catalan: ''Xina'' ()
*Chinese: ''Zh─½n├Ā'' (obsolete and considered offensive due to historical Japanese usage; originated from early Chinese translations of Buddhist texts in Sanskrit)
* Chinese: Zh├©nd├Ān transcription of the Sanskrit/Pali "C─½nasth─üna" in the Buddhist texts.
* Czech: ''─ī├Łna'' ()
*Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
: ''Kina'' ()
* Dutch: ''China'' ()
*English: ''China''
*Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communi ...
: ''─łinujo'' or ''─łinio'', or ''─żinujo'' (archaic)
*Estonian
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also ...
: ''Hiina'' ()
* Filipino: ''Tsina'' ()
* Finnish: ''Kiina'' ()
*French: ''Chine'' ()
* Galician: ''China'' ()
*Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
: ßā®ßāśßā£ßāößāŚßāś ()
*German: ''China'' ( and , in the southern part of the German-speaking area also )
* Greek: ╬Ü╬»╬Į╬▒ (''K├Łna'') ()
*Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub- ...
: ''C─½n'' (IPA )
*Hindustani
Hindustani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India)
* Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, whose two official norms are Hindi and Urdu
* Fiji Hindi, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in Fiji, and ...
: ''C─½n'' or (IPA )
* Hungarian: ''K├Łna'' ()
* Icelandic: ''K├Łna'' ()
*Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
: ''Cina'' ()
* Interlingua: ''China''
* Irish: ''An tS├Łn'' ()
* Italian: ''Cina'' ()
*Japanese: ''Shina'' () ŌĆō considered offensive in China, now largely obsolete in Japan and avoided out of deference to China (the name ''Ch┼½goku'' is used instead); See Shina (word)
is a largely archaic Japanese name for China. The word was originally used neutrally in both the Chinese and Japanese languages, but came to be perceived as derogatory by the Chinese during the course of the Sino-Japanese Wars. As a result, ...
and kotobagari
is a sardonic term which refers to the reluctance to use words that are considered potentially offensive or politically incorrect in the Japanese language. For instance words such as , , , , ''kichigai'' ( or "crazy"), , and are currently not u ...
.
* Javanese: ''Cina'' (low speech level); ''Cinten'' (high speech level)
*Kapampangan Kapampangan, Capampa├▒gan or Pampangan may refer to:
*Kapampangan people of the Philippines
*Kapampangan language
Kapampangan or Pampangan is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary ...
: ''Sina''
* Khmer: ()
* Korean: ''Jina'' (; )
* Latvian: ''─Č─½na'' ()
*Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
: ''Kinija'' ()
*Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
: ''ąÜąĖąĮą░'' (Kina) ()
*Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
: ''Cina'' ()
* Malayalam: ''Cheenan''/''Cheenathi''
*Maltese
Maltese may refer to:
* Someone or something of, from, or related to Malta
* Maltese alphabet
* Maltese cuisine
* Maltese culture
* Maltese language, the Semitic language spoken by Maltese people
* Maltese people, people from Malta or of Malte ...
: ''─Ŗina'' ()
*Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
: ''C─½n'' (IPA )
*Nepali
Nepali or Nepalese may refer to :
Concerning Nepal
* Anything of, from, or related to Nepal
* Nepali people, citizens of Nepal
* Nepali language, an Indo-Aryan language found in Nepal, the current official national language and a language spoken ...
: ''C─½n'' (IPA )
* Norwegian: ''Kina'' ()
*Pahlavi
Pahlavi may refer to:
Iranian royalty
*Seven Parthian clans, ruling Parthian families during the Sasanian Empire
*Pahlavi dynasty, the ruling house of Imperial State of Persia/Iran from 1925 until 1979
**Reza Shah, Reza Shah Pahlavi (1878ŌĆō1944 ...
: ''─ī─½n─½''
* Persian: ''Ch─½n'' ()
*Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
: ''Chiny'' ()
* Portuguese: ''China'' ()
*Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
: ''China'' ()
* Serbo-Croatian: ''Kina'' or ()
* Sinhala: ''Chinaya'' ÓČĀÓĘōÓČ▒ÓČ║
* Slovak: ''─ī├Łna'' ()
* Spanish: ''China'' ()
* Somali: ''Shiinaha''
*Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
: ''Kina'' ()
*Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nati ...
: ''C─½nam'' ()
*Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
: (' )
*Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
: ''Rgya Nag'' ()
*Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: ''├ćin'' ()
* Vietnamese: ''Chß║źn ─É├Īn ķ£ćµŚ”'' ( or Chi Na µö»ķéŻ ()(in Buddhist texts).
*Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
: ''Tsieina'' ()
Seres, Ser, Serica
''S─ōres'' (╬Żß┐åŽü╬ĄŽé) was the Ancient Greek and Roman name for the northwestern part of China and its inhabitants. It meant "of silk," or "land where silk comes from." The name is thought to derive from the Chinese word for silk, ''s─½'' (/; Middle Chinese ''s╔©'', Old Chinese *''sl╔»'', perZhengzhang
Zhengzhang Shangfang (; ; 9 August 1933 ŌĆō 19 May 2018) was a Chinese linguist, known for his reconstruction of Old Chinese.
Zhengzhang was born as Zheng Xiangfang ( ; ) in Yongjia County, on the outskirts of Wenzhou. As and have the same ...
). It is itself at the origin of the Latin for silk, "''s─ōrica''". See the main article Serica
Serica (, grc, ╬Ż╬ĘŽü╬╣╬║╬¼) was one of the easternmost countries of Asia known to the Ancient Greek and Roman geographers. It is generally taken as referring to North China
North China, or Huabei () is a List of regions of China, geogr ...
for more details.
* Ancient Greek: ╬Żß┐åŽü╬ĄŽé '' Seres'', ╬Ż╬ĘŽü╬╣╬║ŽīŽé ''Serikos''
* Latin: ''Serica''
* Old Irish: ''Seiria'', as seen in D├║an in ch├│icat cest
"D├║an in ch├│icat cest" ("a poem in fifty questions") is a medieval school poem in Middle Irish, also known by its incipit "Iarfaigid lib c├│ecait cest."
Overview
The poem was sourced from British Library, MS Egerton 1782 and first published by ...
This may be a back formation
In etymology, back-formation is the process or result of creating a new word via inflection, typically by removing or substituting actual or supposed affixes from a lexical item, in a way that expands the number of lexemes associated with the ...
from ''s─ōrikos'' (Žā╬ĘŽü╬╣╬║ŽīŽé), "made of silk", from ''s─ōr'' (Žā╬«Žü), "silkworm", in which case ''S─ōres'' is "the land where silk comes from."
Sinae, Sin
 ''S─½nae'' was an ancient Greek and Roman name for some people who dwelt south of the Seres (Serica) in the eastern extremity of the habitable world. References to the Sinae include mention of a city that the Romans called ''S─ōra M─ōtropolis'', which may be modern Chang'an. The Latin prefixes ''Sino-'' and ''Sin-'' as well as words such as ''Sinica'', which are traditionally used to refer to China or the Chinese, came from ''S─½nae''. It is generally thought that ''Ch─½na'', ''S─½na'' and ''Th─½na'' are variants that ultimately derived from Qin, which was the westernmost state in China that eventually formed the Qin Dynasty. There are however other opinions on its etymology (See section on China above). Henry Yule thought that this term may have come to Europe through the Arabs, who made the China of the farther east into ''Sin'', and perhaps sometimes into ''Thin''. Hence the ''Thin'' of the author of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, who appears to be the first extant writer to employ the name in this form; hence also the Sin├” and Thinae of Ptolemy.
Some denied that Ptolemy's Sinae really represented the Chinese as Ptolemy called the country ''S─ōrice'' and the capital ''S─ōra'', but regarded them as distinct from ''S─½nae''. Marcian of Heraclea (a condenser of Ptolemy) tells us that the "nations of the Sinae lie at the extremity of the habitable world, and adjoin the eastern Terra incognita". The 6th century Cosmas Indicopleustes refers to a "country of silk" called ''Tzinista'', which is understood as referring to China, beyond which "there is neither navigation nor any land to inhabit". It seems probable that the same region is meant by both. According to Henry Yule, Ptolemy's misrendering of the
''S─½nae'' was an ancient Greek and Roman name for some people who dwelt south of the Seres (Serica) in the eastern extremity of the habitable world. References to the Sinae include mention of a city that the Romans called ''S─ōra M─ōtropolis'', which may be modern Chang'an. The Latin prefixes ''Sino-'' and ''Sin-'' as well as words such as ''Sinica'', which are traditionally used to refer to China or the Chinese, came from ''S─½nae''. It is generally thought that ''Ch─½na'', ''S─½na'' and ''Th─½na'' are variants that ultimately derived from Qin, which was the westernmost state in China that eventually formed the Qin Dynasty. There are however other opinions on its etymology (See section on China above). Henry Yule thought that this term may have come to Europe through the Arabs, who made the China of the farther east into ''Sin'', and perhaps sometimes into ''Thin''. Hence the ''Thin'' of the author of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, who appears to be the first extant writer to employ the name in this form; hence also the Sin├” and Thinae of Ptolemy.
Some denied that Ptolemy's Sinae really represented the Chinese as Ptolemy called the country ''S─ōrice'' and the capital ''S─ōra'', but regarded them as distinct from ''S─½nae''. Marcian of Heraclea (a condenser of Ptolemy) tells us that the "nations of the Sinae lie at the extremity of the habitable world, and adjoin the eastern Terra incognita". The 6th century Cosmas Indicopleustes refers to a "country of silk" called ''Tzinista'', which is understood as referring to China, beyond which "there is neither navigation nor any land to inhabit". It seems probable that the same region is meant by both. According to Henry Yule, Ptolemy's misrendering of the Indian Sea
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
as a closed basin meant that Ptolemy must also have misplaced the Chinese coast, leading to the misconception of Serica and Sina as separate countries.
In the Hebrew Bible, there is a mention of a faraway country Sinim The land of Sin ( he, ūĪų┤ūÖū¤) or Sinim (from: he, ūĪų┤ūÖūĀų┤ūÖūØ, i.e. the inhabitants of the land of Sin, or the people of Sin) is a biblical hapax legomenon that appears in Isaiah 49:12: "Behold, these shall come from far: and, lo, these from t ...
in the Book of Isaiah
The Book of Isaiah ( he, ūĪūżū© ūÖū®ūóūÖūöūĢ, ) is the first of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible and the first of the Major Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. It is identified by a superscription as the words of the 8th-century BC ...
49:12 which some had assumed to be a reference to China. In Genesis 10:17, a tribes called the Sinites were said to be the descendants of Canaan, the son of Ham, but they are usually considered to be a different people, probably from the northern part of Lebanon.
* Arabic: ''Ṣīn''
* French/English (prefix of adjectives): ''Sino-'' (i.e. Sino-American), ''Sinitic'' (the Chinese language family).
* Hebrew: ''Sin''
* ga, An tS├Łn
* la, S─½nae
* gd, Sìona
Cathay
This group of names derives from Khitan, an ethnic group that originated in Manchuria and conquered parts of Northern China early tenth century forming the Liao dynasty, and later in the twelfth century dominated Central Asia as theKara Khitan
The Qara Khitai, or Kara Khitai (), also known as the Western Liao (), officially the Great Liao (), was a Sinicized dynastic regime based in Central Asia ruled by the Khitan Yel├╝ clan. The Qara Khitai is considered by historians to be an ...
Khanate. Due to long period of domination of Northern China and then Central Asia by these nomadic conquerors, the name Khitan become associated with China to the people in and around the northwestern region. Muslim historians referred to the Kara Khitan state as ''Khitay'' or ''Khitai''; they may have adopted this form of "Khitan" via the Uyghurs of Kocho in whose language the final -n or -ń became -y. The name was then introduced to medieval and early modern Europe through Islamic and Russian sources. In English and in several other European languages, the name "Cathay" was used in the translations of the adventures of Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
, which used this word for northern China. Words related to Khitay are still used in many Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
and Slavic languages to refer to China. However, its use by Turkic speakers within China, such as the Uyghurs, is considered pejorative by the Chinese authority who tried to ban it.
* Belarusian
Belarusian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Belarus
* Belarusians, people from Belarus, or of Belarusian descent
* A citizen of Belarus, see Demographics of Belarus
* Belarusian language
* Belarusian culture
* Belarusian cuisine
* Byelor ...
: ąÜč¢čéą░ą╣ (''Kitay'', )
* Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
: ąÜąĖčéą░ą╣ (''Kitay'', )
* Buryat: ąźąĖčéą░ą┤ (''Khitad'')
* Classical Mongolian
Classical Mongolian was the literary language of Mongolian which was first introduced shortly after 1600, when Ligdan Khan set his clergy the task of translating the whole of the Tibetan Buddhist canon, consisting of the Kanjur and Tanjur, into M ...
: ''Kitad''
* English: ''Cathay''
*French: ''Cathay''
* Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
: ęÜčŗčéą░ą╣ (''Q─▒tay''; )
* Kazan Tatar
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, čéą░čéą░čĆą╗ą░čĆ, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after t ...
: ąÜčŗčéą░ą╣ (''Q─▒tay'')
* Kyrgyz Kyrgyz, Kirghiz or Kyrgyzstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kyrgyzstan
*Kyrgyz people
*Kyrgyz national games
*Kyrgyz language
*Kyrgyz culture
*Kyrgyz cuisine
*Yenisei Kirghiz
*The Fuyü Gïrgïs language in Northeastern China
...
: ąÜčŗčéą░ą╣ (''K─▒taj''; )
*
* Mongolian: ąźčÅčéą░ą┤ (''Khyatad'') (the name for China used in the State of Mongolia)
* Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
: ''Kitaj'' (; now archaic)
* Portuguese: ''Catai'' ()
* Russian: ąÜąĖčéą░ą╣ (''Kitay'', )
* Serbo-Croatian: Kitaj or ąÜąĖčéą░čś (now archaic; from Russian)
* Slovene: ' ()
* Spanish: ''Catay''
* Tajik
Tajik, Tadjik, Tadzhik or Tajikistani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Tajikistan
* Tajiks, an ethnic group in Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Uzbekistan
* Tajik language, the official language of Tajikistan
* Tajik (surname)
* Tajik cu ...
: ąźąĖč鹊ą╣ ("Khitoy")
* Turkmen
Turkmen, T├╝rkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
: Hyta├Į ("ąźčŗčéą░ą╣")
* Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
: ąÜąĖčéą░ą╣ (''Kytai'')
*
* Uzbek: ''Xitoy'' (ąźąĖč鹊ą╣)
There is no evidence that either in the 13th or 14th century, Cathayans, ''i.e.'' Chinese, travelled officially to Europe, but it is possible that some did, in unofficial capacities, at least in the 13th century. During the campaigns of Hulagu (the grandson of Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ═Ī╩ā╩░i┼ŗ╔Ī╔¬s xa╦É┼ŗbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem├╝jin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ûgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
) in Persia (1256ŌĆō65), and the reigns of his successors, Chinese engineers were employed on the banks of the Tigris, and Chinese astrologer
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
s and physicians could be consulted. Many diplomatic
Diplomatics (in American English, and in most anglophone countries), or diplomatic (in British English), is a scholarly discipline centred on the critical analysis of documents: especially, historical documents. It focuses on the conventions, p ...
communications passed between the Hulaguid Ilkhan
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ž¦█ī┘ä ž«ž¦┘垦┘å, ''Ilx─ün─ün''), known to the Mongols as ''H├╝leg├╝ Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
s and Christian princes. The former, as the great khan's liegemen, still received from him their seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
of state; and two of their letters which survive in the archives of France exhibit the vermilion impressions of those seals in Chinese charactersŌĆöperhaps affording the earliest specimen of those characters to reach western Europe.
Tabgach
The word ''Tabgach
The Tuoba (reconstructed Middle Chinese pronunciation: *''t╩░ak-b╔øt''), also known as the Taugast or Tabgach ( otk, É▒āÉ░ēÉ░ŹÉ░▓ ''Tab╬│a─Ź''), was a Xianbei clan in Imperial China.Wei Shou. '' Book of Wei''. Vol. 1
During the Sixteen King ...
'' came from the metatheses of '' Tuoba'' (''*t'akbat''), a dominant tribe of the Xianbei and the surname of the Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties ...
emperors in the 5th century before sinicisation. It referred to Northern China, which was dominated by part-Xianbei, part-Han people.
* Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5thŌĆō6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman co ...
: ''Taugats''
* Orhon Kok-Turk: ''Tabgach'' (variations ''Tamgach'')
Nikan
''Nikan'' (Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) and ...
: , means "Han/China") was a Manchu ethnonym of unknown origin that referred specifically to the ethnic group known in English as the Han Chinese; the stem of this word was also conjugated as a verb, ''nikara(-mbi)'', and used to mean "to speak the Chinese language." Since ''Nikan'' was essentially an ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
and referred to a group of people (i.e., a nation) rather than to a political body (i.e., a state), the correct translation of "China (proper)" into the Manchu language is ''Nikan gurun'', literally the "Nikan state" or "country of the Nikans" (i.e., country of the Hans).
This exonym for the Han Chinese is also used in the Daur language, in which it appears as ''Niaken'' ( or ). As in the case of the Manchu language, the Daur word ''Niaken'' is essentially an ethnonym, and the proper way to refer to the country of the Han Chinese (i.e., "China" in a cultural sense) is ''Niaken gurun'', while ''niakendaaci-'' is a verb meaning "to talk in Chinese."
Kara
Japanese: ''Kara'' (; variously written in kanji as or ). An identical name was used by the ancient and medieval Japanese to refer to the country that is now known as Korea, and many Japanese historians and linguists believe that the word "Kara" referring to China and/or Korea may have derived from a metonymic extension of the appellation of the ancient city-states ofGaya
Gaya may refer to:
Geography Czech Republic
*Gaya (German and Latin), Kyjov (Hodon├Łn District), a town
Guinea
* Gaya or Gayah, a town
India
*Gaya, India, a city in Bihar
**Gaya Airport
*Bodh Gaya, a town in Bihar near Gaya
*Gaya district, Bi ...
.
The Japanese word ''karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ) is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tii'' in Okinawan) under the ...
'' (, lit. "empty hand") is derived from the Okinawan word ''karatii'' (, lit. "Chinese/Asian/foreign hand/trick/means/method/style") and refers to Okinawan martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; a ...
; the character for ''kara'' was changed to remove the connotation of the style originating in China.
Morokoshi
Japanese: ''Morokoshi'' (; variously written in kanji as or ). This obsolete Japanese name for China is believed to have derived from a ''kun'' reading of the Chinese compound ''Zh┼½yu├©'' or BŪÄiyu├© as "all the Yue" or "the hundred (i.e., myriad, various, or numerous) Yue," which was an ancient Chinese name for the societies of the regions that are now southern China. The Japanese common noun ''t┼Źmorokoshi'' (), which refers to maize, appears to contain an element cognate with the proper noun formerly used in reference to China. Although ''t┼Źmorokoshi'' is traditionally written with Chinese characters that literally mean "jade Shumillet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
," the etymology of the Japanese word appears to go back to "Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century ŌĆō 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (ÕöÉ) b ...
morokoshi," in which "morokoshi" was the obsolete Japanese name for China as well as the Japanese word for sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
, which seems to have been introduced into Japan from China.
Mangi
 From Chinese ''Manzi'' (southern barbarians). The division of North China and South China under the Jin dynasty and Song dynasty weakened the idea of a unified China, and it was common for non-Han peoples to refer to the politically disparate North and South by different names for some time. While Northern China was called
From Chinese ''Manzi'' (southern barbarians). The division of North China and South China under the Jin dynasty and Song dynasty weakened the idea of a unified China, and it was common for non-Han peoples to refer to the politically disparate North and South by different names for some time. While Northern China was called Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which ...
, Southern China was referred to as Mangi. Manzi often appears in documents of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty as a disparaging term for Southern China. The Mongols also called Southern Chinese ''Nangkiyas'' or ''Nangkiyad'', and considered them ethnically distinct from North Chinese. The word ''Manzi'' reached the Western world as ''Mangi'' (as used by Marco Polo), which is a name commonly found on medieval maps. Note however that the Chinese themselves considered ''Manzi'' to be derogatory and never used it as a self-appellation. Some early scholars believed ''Mangi'' to be a corruption of the Persian ''Machin'' () and Arabic ''M─üß╣Ż─½n'' (), which may be a mistake as these two forms are derived from the Sanskrit ''Maha Chin'' meaning Great China.
*Chinese: ''Manzi'' ()
* Latin: ''Mangi''
See also
*Little China (ideology)
Little China is a term referring to a politico-cultural ideology and phenomenon in which various Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese regimes identified themselves as "China" and regarded themselves to be legitimate successors to the Chinese civil ...
* Chinese romanization
Romanization of Chinese () is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Chinese. Chinese uses a logographic script and its characters do not represent phonemes directly. There have been many systems using Roman characters to represent Chin ...
* List of country name etymologies
This list covers English-language country names with their etymologies. Some of these include notes on indigenous names and their etymologies. Countries in ''italics'' are endonyms or no longer exist as sovereign political entities.
A
Afgha ...
* Names of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty () was an imperial Chinese dynasty ruled by the Aisin Gioro clan of Manchu ethnicity. Officially known as the Great Qing, the dynastic empire was also widely known in English as China and the Chinese Empire both during its existe ...
* Names of India
The Republic of India has two principal short names, each of which is historically significant, "India" and "Bharata". A third name, "Hindust─ün", is sometimes an alternative name for the region comprising most of the modern Indian states of ...
* Names of Japan
The word ''Japan'' is an exonym, and is used (in one form or another) by many languages. The Japanese names for Japan are Nippon () and Nihon (). They are both written in Japanese using the kanji .
During the third-century CE Three Kingdoms perio ...
* Names of Korea
There are various names of Korea in use today, all derived from ancient kingdoms and dynasties. The modern English name "Korea" is an exonym derived from the name Goryeo, also spelled ''Koryŏ'', and is used by both North Korea and South Korea in ...
* Names of Vietnam
* Île-de-France, similar French concept
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Countries and languages lists History of ChinaChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
Articles containing Mongolian script text
Geographical naming disputes