Chesterfield Market Place railway station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
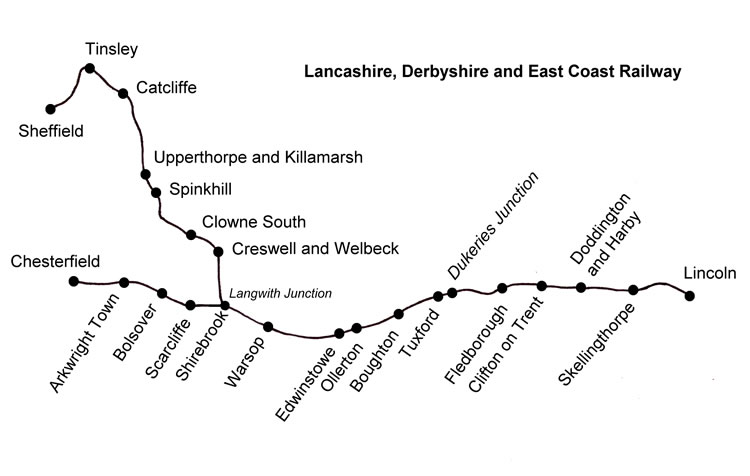

 Chesterfield Market Place railway station was a former
Chesterfield Market Place railway station was a former
1953 Working Timetable via ''flickr''
/ref> This ended in March 1957. From some point between 1951 and 1956, the station building became used by Charles Credland Ltd, a paint and wallpaper firm, which continued until demolition. Tracks were lifted in 1957/8 when the bridge over Park Road was demolished using explosives.
The station on a navigable Edwardian 6" OS map, with overlays
in ''National Library of Scotland''
The station and line
in ''Rail Maps Online''
in ''npe Map''
The station
in ''flickr''
The station on line CLN1
in ''Railway Codes''
The station in 1938
''Britain from Above'' (free login needed to zoom) {{Closed stations Derbyshire 1897 establishments in England 1951 disestablishments in England Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1897 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1951 Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Lancashire, Derbyshire and East Coast Railway stations Buildings and structures in Chesterfield, Derbyshire Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery


railway station
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
in the centre of the town of Chesterfield, Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the nor ...
, England.
Three stations
Chesterfield Market Place station was the third and final station to be built in the town. Services from the first two: * Chesterfield Midland, which remains open as "Chesterfield", and * Chesterfield Central, which closed in 1963 - ran north–south, but those from Chesterfield Market Place ran to the east.History
Opening
The station was opened as "Chesterfield" by the LD&ECR on 8 March 1897 and was the headquarters of the line. It was renamed "Chesterfield Market Place" on 1 January 1907. The station was closed to passengers by BR on 3 December 1951 because of the prohibitive cost of maintaining and repairingBolsover Tunnel
Bolsover Tunnel is a disused and infilled twin-track railway tunnel between Carr Vale and Scarcliffe in Derbyshire, England.
At it was the 18th longest railway tunnel in Britain prior to its closure in 1951.
History
The tunnel was opened by ...
, together with concerns over Doe Lea Viaduct and the limited amount of traffic. Goods services continued until 4 March 1957.
Market Place station was situated on West Bars, adjacent to two old inns; the White Horse and the Bird in Hand. To take advantage of the additional custom generated by the railway, the owners of the White Horse, William Stones brewery of Sheffield, applied to build a new hotel. This was approved by the licensing magistrates in April 1898.
As the licensing laws of the time prevented a pub from closing down during rebuilding, the new hotel was built in two parts. Building of the first phase commenced on the site of the Bird in Hand which had closed and had recently been demolished, its licence being transferred to the refreshment rooms in Market Place station. When the first part was complete the licence was transferred from the White Horse, along with the landlord, Job Siddall. The second phase was then erected on the site of the White Horse. The hotel, named after the Duke of Portland
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranke ...
, on whose estate much of the railway ran, was officially opened Christmas 1899 by the Earl of Rosebery
Earl of Rosebery is a title in the Peerage of Scotland created in 1703 for Archibald Primrose, 1st Viscount of Rosebery, with remainder to his issue male and female successively. Its name comes from Roseberry Topping, a hill near Archibald's wif ...
Archibald Primrose.
Layout
The station was a substantial three storey structure with a long glass awning, it was quite unlike any other station on the line. Inside the station a glass-roofed concourse led to four curved platforms on two islands - 1 & 2, 4 & 5. In the centre, in place of the missing platform 3, was a release line for the locomotives. The adjacent goods depot was, at the time, the largest covered area in the town. Leaving the station, the line passed the Saxby and Farmer 80 lever station signal box, crossed Park Road by an arched brick bridge then travelled along a short length of embankment followed by Boythorpe Viaduct which crossed the MR's Brampton Branch and the industrial "Boythorpe Railway", then a longer stretch of embankment leading to a major viaduct at Horns Bridge, which passed over theMidland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had its headquarters. It ama ...
, main roads to Mansfield and Derby, the Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the ...
, Hyde's Sidings and the River Rother. It consisted of seven brick arches and four girder spans, 63 feet high. From there, the line climbed at 1 in 100 as far as the first summit at Duckmanton Tunnel, followed shortly by the station at Arkwright Town
Arkwright Town, commonly referred to as Arkwright, is a village in Sutton cum Duckmanton, North East Derbyshire, England, that is notable for having moved its location in the early 1990s.Metropolitan Housing Trust stakeholders' newsletter, Octob ...
.
Operations
Until 1927, the station was also served by Chesterfield Tramway which ran fromBrampton
Brampton ( or ) is a city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Brampton is a city in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and is a lower-tier municipality within Peel Region. The city has a population of 656,480 as of the 2021 Census, making it t ...
to Whittington. A dead end spur was built near the station and was situated on Market Place. At least one published photograph of the station shows the tramlines and overhead wires.
Passenger services
Chesterfield Market Place never had a Sunday service. In 1922, there were seven departures Monday to Friday, with four extra on Saturdays. The weekday seven consisted of: *Two all stations to Lincoln High St, later renamed Lincoln Central taking an hour and a half *Three all stations to taking three quarters of an hour, and *One all stations to Bolsover, later renamed Bolsover South taking twelve minutes. The Saturday extras consisted of one to Bolsover, one to Langwith Junction, later renamed Shirebrook North and two to Mansfield Central. A notable feature was the care taken to timetable services along the Beighton Branch to connect with Chesterfield services at Langwith Junction. At 10:44, for example, four trains would be standing at Langwith Junction: *10:46 to Chesterfield Market Place (from Lincoln) *10:46 to Lincoln (from Chesterfield) *10:50 to Sheffield Midland via the Beighton Branch, and *10:45 to Mansfield (ex-MR, later renamed Mansfield Town). Anyone catching the last weekday departure from Chesterfield, the 19:00 to Mansfield Central, could stay in his or her seat at Langwith Junction and arrive at Mansfield Central at 19:50 or change trains and arrive at Mansfield Town at 19:40. More journey opportunities were added in 1925 when the service from Nottingham Victoria through Skegby and which since inception in 1901 had inexplicably terminated at was extended the last mile to . This was a forlorn gesture, as the service was withdrawn throughout in 1931. The intersecting services along the Beighton Branch were withdrawn on the outbreak of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
with Mansfield Central services ending by 1945, leaving Chesterfield Market Place with two all stations trains to Lincoln plus some shorter workings to Shirebrook North and to Bolsover.
Closure
In August 1948, its unused track and space was put to work to house the Stephenson Centenary Exhibition of locomotives and rolling stock. As a last hurrah, special trains were run to the coast shortly before the station closed to passengers on 3 December 1951. After closure to passengers, the tracks into the platforms were lifted and the line to was singled and operated on the "one engine in steam" basis. This was perfectly adequate for the single daily freight train from Staveley./ref> This ended in March 1957. From some point between 1951 and 1956, the station building became used by Charles Credland Ltd, a paint and wallpaper firm, which continued until demolition. Tracks were lifted in 1957/8 when the bridge over Park Road was demolished using explosives.
Present day
The station was demolished in April 1973 and, following considerable redevelopment of the area, it has now been built upon. The current building occupying the space is Future Walk, the finance headquarters for the Post Office. A few signs of the old embankment can still be seen at the bottom of the car park.References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
The station on a navigable Edwardian 6" OS map, with overlays
in ''National Library of Scotland''
The station and line
in ''Rail Maps Online''
in ''npe Map''
The station
in ''flickr''
The station on line CLN1
in ''Railway Codes''
The station in 1938
''Britain from Above'' (free login needed to zoom) {{Closed stations Derbyshire 1897 establishments in England 1951 disestablishments in England Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1897 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1951 Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Lancashire, Derbyshire and East Coast Railway stations Buildings and structures in Chesterfield, Derbyshire Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery