Causes of income inequality in the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Causes of income inequality in the United States describes the reasons for the unequal distribution of income in the US and the factors that cause it to change over time. This topic is subject to extensive ongoing research, media attention, and political interest.
Inequality Trends in Some Developed OECD countries
In J. K. S. & J. Baudot (Ed.), ''Flat World, Big Gaps'' (159–74). New York: ZED Books (published in association with the United Nations).Income distribution and poverty – OECD
October 2011. p. 13 Researchers have offered several potential rationales.Congressional Budget Office: Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007
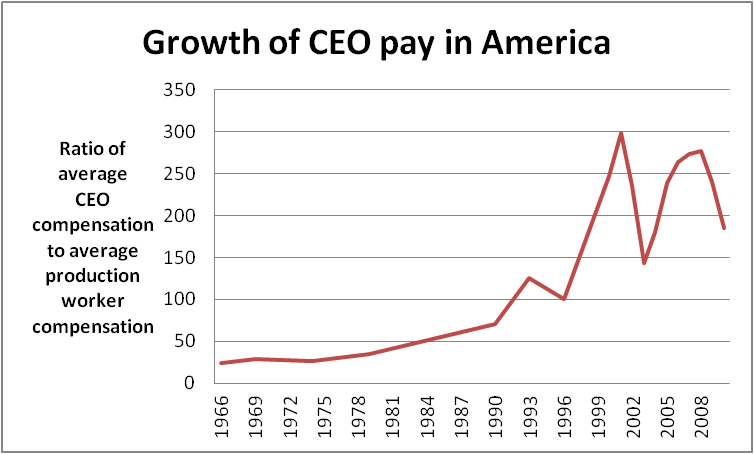
October 2011. p. xi Various rationales conflict or overlap. They include: *''globalization'' – Lesser-skilled American workers have been losing ground in the face of competition from workers in Asia and other emerging economies. * ''skills'' – The rapid pace of progress in information technology has increased the relative demand for higher-skilled workers. *''superstars'' – Compensation in many sectors turned into a tournament in which the winner is richly rewarded, while the runners-up get far less. This affects both workers and investors (in dominant firms). * ''tax policy'' – Pre-tax income inequality in the U.S. is similar to other developed countries, but markedly rises after taxes and transfers. * ''immigration'' – Relatively high levels of immigration of less-skilled workers since 1965 may have reduced wages for American-born high school dropouts. *''decline of unions'' – Unions helped increase wages, benefits and working conditions. Unionized workers declined from over 30% to around 12%. *''social norms –'' Social norms constrained executive pay. CEO pay rose from around 40 times the average workers pay in the 1970s to over 350 times in the early 2000s.



by Timothy Noah (September 14, 2010) It wasn't until 2006 that the US imported more manufactured goods from low-wage (developing) countries than from high-wage (advanced) economies. Inequality increased during the 2000–2010 decade not because of stagnating wages for less-skilled workers, but because of accelerating incomes of the top 0.1%. Author Timothy Noah estimates that "trade", increases in imports are responsible for just 10% of the "Great Divergence" in income distribution. Journalist
 As of the mid- to late- decade of the 2000s, the most common explanation for income inequality in America was "skill-biased technological change" (SBTC) – "a shift in the production technology that favors skilled over unskilled
As of the mid- to late- decade of the 2000s, the most common explanation for income inequality in America was "skill-biased technological change" (SBTC) – "a shift in the production technology that favors skilled over unskilled
by Timothy Noah, ''Slate'' (September 8, 2010) However the timing of the great technological change of the era – internet use by business starting in the late 1990s – does not match that of the growth of income inequality (starting in the early 1970s but slackening somewhat in the 1990s). Nor does the introduction of technologies that increase the demand for more skilled workers seem to be generally associated with a divergence in household income among the population. Inventions of the 20th century such as AC electric power, the automobile, airplane, radio, television, the washing machine, Xerox machine, each had an economic impact similar to computers, microprocessors and internet, but did not coincide with greater inequality. Another explanation is that the ''combination'' of the introduction of technologies that increase the demand for skilled workers, ''and'' the failure of the American education system to provide a sufficient increase in those skilled workers has bid up those workers' salaries. An example of the slowdown in education growth in America (that began about the same time as the Great Divergence began) is the fact that the average person born in 1945 received two more years of schooling than his parents, while the average person born in 1975 received only half a year more of schooling."The United States of Inequality. Entry 9: How the Decline in K–12 Education Enriches College Graduates,"
by Timothy Noah, ''Slate.com'' (September 15, 2010) Author Timothy Noah's "back-of-the-envelope" estimation based on "composite of my discussions with and reading of the various economists and political scientists" is that the "various failures" in America's education system are "responsible for 30%" of the post-1978 increase in inequality.
 Income levels vary by gender and race with median income levels considerably below the national median for females compared to men with certain racial demographics.
Despite considerable progress in pursuing gender and racial equality, some social scientists like Richard Schaeffer attribute these discrepancies in income partly to continued discrimination.
Among women, part of the wage gap is due to employment choices and preferences. Women are more likely to consider factors other than salary when looking for employment. On average, women are less willing to travel or relocate, take more hours off and work fewer hours, and choose college majors that lead to lower paying jobs. Women are also more likely to work for governments or non-profits which pay less than the private sector.
According to this perspective certain ethnic minorities and women receive fewer promotions and opportunities for occupation and economic advancement than others. In the case of women this concept is referred to as the
Income levels vary by gender and race with median income levels considerably below the national median for females compared to men with certain racial demographics.
Despite considerable progress in pursuing gender and racial equality, some social scientists like Richard Schaeffer attribute these discrepancies in income partly to continued discrimination.
Among women, part of the wage gap is due to employment choices and preferences. Women are more likely to consider factors other than salary when looking for employment. On average, women are less willing to travel or relocate, take more hours off and work fewer hours, and choose college majors that lead to lower paying jobs. Women are also more likely to work for governments or non-profits which pay less than the private sector.
According to this perspective certain ethnic minorities and women receive fewer promotions and opportunities for occupation and economic advancement than others. In the case of women this concept is referred to as the  Since 1953 the income gap between male and female workers has decreased considerably but remains relatively large. Women currently earn significantly more Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees than men and almost as many Doctorates. Women are projected to have passed men in Doctorates earned in 2006–2007, and to earn nearly two thirds of Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees by 2016.
Though it is important to note that income inequality between sexes remained stark at all levels of educational attainment. Between 1953 and 2005 median earnings as well as educational attainment increased, at a far greater pace for women than for men. Median income for female earners male earners increased 157.2% versus 36.2% for men, over four times as fast. Today the median male worker earns roughly 68.4% more than their female counterparts, compared to 176.3% in 1953. The median income of men in 2005 was 2% higher than in 1973 compared to a 74.6% increase for female earners.
Racial differences remained stark as well, with the highest earning sex-gender demographic of workers aged 25 or older, Asian males (who were roughly tied with white males) earning slightly more than twice as much as the lowest-earning demographic, Hispanic females. As mentioned above, inequality between races and gender persisted at similar education levels. Racial differences were overall more pronounced among male than among female income earners. In 2009, Hispanics were more than twice as likely to be poor than non-Hispanic whites, research indicates. Lower average English ability, low levels of educational attainment, part-time employment, the youthfulness of Hispanic household heads, and the 2007–09 recession are important factors that have pushed up the Hispanic poverty rate relative to non-Hispanic whites. During the early 1920s, median earnings decreased for both sexes, not increasing substantially until the late 1990s. Since 1974 the median income for workers of both sexes increased by 31.7% from $18,474 to $24,325, reaching its high-point in 2000.
Since 1953 the income gap between male and female workers has decreased considerably but remains relatively large. Women currently earn significantly more Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees than men and almost as many Doctorates. Women are projected to have passed men in Doctorates earned in 2006–2007, and to earn nearly two thirds of Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees by 2016.
Though it is important to note that income inequality between sexes remained stark at all levels of educational attainment. Between 1953 and 2005 median earnings as well as educational attainment increased, at a far greater pace for women than for men. Median income for female earners male earners increased 157.2% versus 36.2% for men, over four times as fast. Today the median male worker earns roughly 68.4% more than their female counterparts, compared to 176.3% in 1953. The median income of men in 2005 was 2% higher than in 1973 compared to a 74.6% increase for female earners.
Racial differences remained stark as well, with the highest earning sex-gender demographic of workers aged 25 or older, Asian males (who were roughly tied with white males) earning slightly more than twice as much as the lowest-earning demographic, Hispanic females. As mentioned above, inequality between races and gender persisted at similar education levels. Racial differences were overall more pronounced among male than among female income earners. In 2009, Hispanics were more than twice as likely to be poor than non-Hispanic whites, research indicates. Lower average English ability, low levels of educational attainment, part-time employment, the youthfulness of Hispanic household heads, and the 2007–09 recession are important factors that have pushed up the Hispanic poverty rate relative to non-Hispanic whites. During the early 1920s, median earnings decreased for both sexes, not increasing substantially until the late 1990s. Since 1974 the median income for workers of both sexes increased by 31.7% from $18,474 to $24,325, reaching its high-point in 2000.
 In the context of concern over income inequality, a number of economists, such as
In the context of concern over income inequality, a number of economists, such as
Isabel Sawhill & John E. Morton. February 21, 2007. Economic Mobility Project, Washington, D.C.. December 4, 2007. Since abundant supply decreases market value, the possession of scarce skills considerably increases income. Among the
 U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed nations pre-tax, but is among the worst after-tax and transfers. This indicates the U.S. tax policies redistribute income from higher income to lower income households relatively less than other developed countries. Journalist
U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed nations pre-tax, but is among the worst after-tax and transfers. This indicates the U.S. tax policies redistribute income from higher income to lower income households relatively less than other developed countries. Journalist
 A key factor in income inequality/equality is the effective rate at which income is taxed coupled with the progressivity of the tax system. A
A key factor in income inequality/equality is the effective rate at which income is taxed coupled with the progressivity of the tax system. A
October 2011. p. 20 and figure 12. the CBO found that,
in the multi-part series "The United States of Inequality." ''Slate'', September 9, 2010. The lowest marginal rate for the bottom fell from 14 to 11 percent. However the effective rate on top earners before Reagan's tax cut was much lower because of loopholes and charitable contributions. Robert Bellafiore and Madison Mauro, writing for the Tax Foundation, calculated that effective tax rates for the richest Americans has declined since 1986. But the share of income taxes paid by the richest Americans has increased, due to tax expenditures increasing the number of low-income Americans with negative tax rates.
 Taxes on income derived from capital (e.g., financial assets, property and businesses) primarily affect higher income groups, who own the vast majority of capital. For example, in 2010 approximately 81% of stocks were owned by the top 10% income group and 69% by the top 5%. Only about one-third of American households have stock holdings more than $7,000. Therefore, since higher-income taxpayers have a much higher share of their income represented by capital gains, lowering taxes on capital income and gains increases after-tax income inequality.
Capital gains taxes were reduced around the time income inequality began to rise again around 1980 and several times thereafter. During 1978 under President
Taxes on income derived from capital (e.g., financial assets, property and businesses) primarily affect higher income groups, who own the vast majority of capital. For example, in 2010 approximately 81% of stocks were owned by the top 10% income group and 69% by the top 5%. Only about one-third of American households have stock holdings more than $7,000. Therefore, since higher-income taxpayers have a much higher share of their income represented by capital gains, lowering taxes on capital income and gains increases after-tax income inequality.
Capital gains taxes were reduced around the time income inequality began to rise again around 1980 and several times thereafter. During 1978 under President
"How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective"
''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' Volume 21, Number 1 – Winter 2007
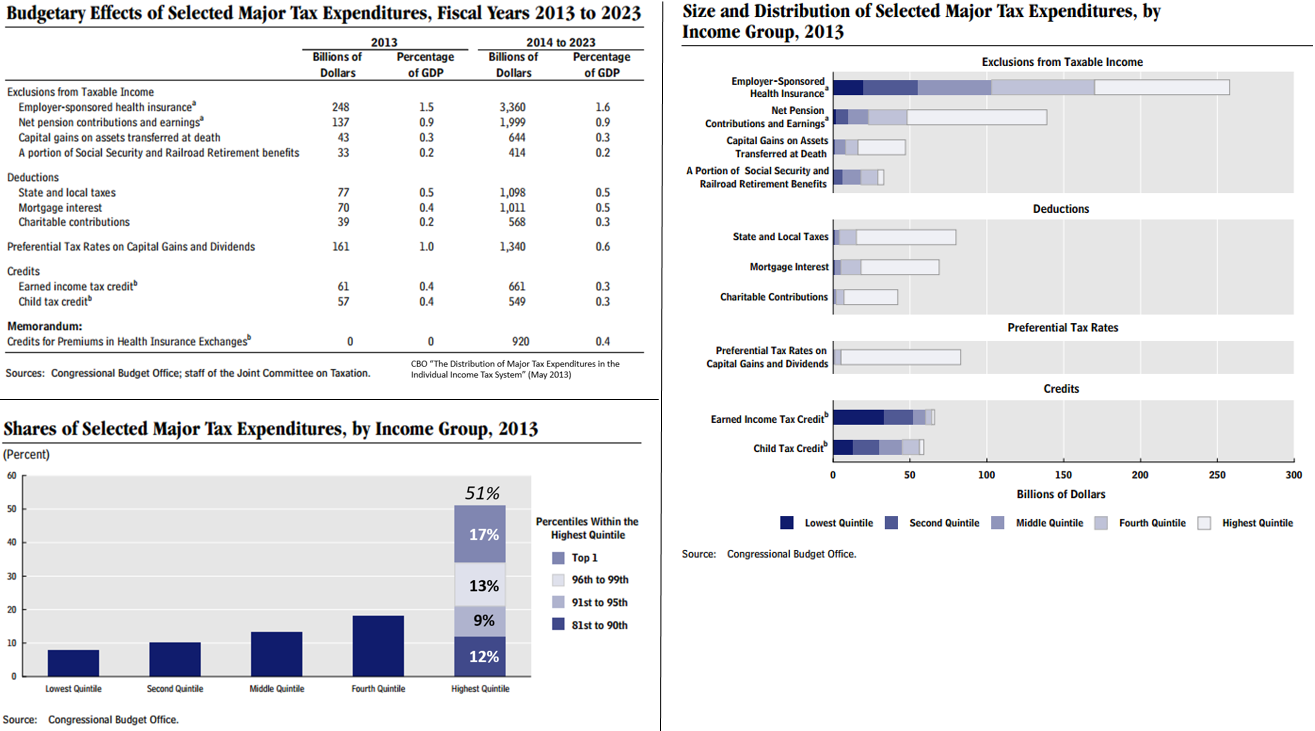 Tax expenditures (i.e., exclusions, deductions, preferential tax rates, and
Tax expenditures (i.e., exclusions, deductions, preferential tax rates, and
 The era of inequality growth has coincided with a dramatic decline in labor union membership from 20% of the labor force in 1983 to about 12% in 2007. Classical and
The era of inequality growth has coincided with a dramatic decline in labor union membership from 20% of the labor force in 1983 to about 12% in 2007. Classical and
By Timothy Noah, ''Slate.com'', September 12, 2010 However, more recently, research has shown that unions' ability to reduce income disparities among members outweighed other factors and its net effect has been to reduce national income inequality. The decline of unions has hurt this leveling effect among men, and one economist (Berkeley economist
What Unions No Longer Do
''
Global income inequality: Where the U.S. ranks
''
Timothy Noah, ''The New Republic'', November 18, 2011 Summarizing Bartels's findings, journalist
 According to political scientists Jacob Hacker and Paul Pierson writing in the book
According to political scientists Jacob Hacker and Paul Pierson writing in the book
 The
The
By Timothy Noah From 1970 to 2007, the foreign-born proportion of America's population grew from 5% to 11%, most of whom had lower education levels and incomes than native-born Americans. But the contribution of this increase in supply of low-skill labor seem to have been relatively modest. One estimate stated that immigration reduced the average annual income of native-born "high-school dropouts" ("who roughly correspond to the poorest tenth of the workforce") by 7.4% from 1980 to 2000. The decline in income of better educated workers was much less. Author Timothy Noah estimates that "immigration" is responsible for just 5% of the "Great Divergence" in income distribution, as does economist
''The Economist'' (September 21, 2010)Krugman, P. (2007). ''The conscience of a liberal''. New York: W. W. Norton.

''
March 2014 For example, measured relative to GDP, total compensation and its component wages and salaries have been declining since 1970. This indicates a shift in income from labor (persons who derive income from hourly wages and salaries) to capital (persons who derive income via ownership of businesses, land and assets). Wages and salaries have fallen from approximately 51% GDP in 1970 to 43% GDP in 2013. Total compensation has fallen from approximately 58% GDP in 1970 to 53% GDP in 2013. To put this in perspective, five percent of U.S. GDP was approximately $850 billion in 2013. This represents an additional $7,000 in wages and salaries for each of the 120 million U.S. households.
The Rise and Fall of Neoliberal Capitalism
'' (
p. 43
/ref> As such, the advent of the neoliberal era has seen a sharp increase in income inequality through the decline of unionization, stagnant wages for workers and the rise of CEO supersalaries. According to
Is the U.S. a Good Model for Reducing Social Exclusion in Europe?
The Fissured Workplace: Why Work Became So Bad for So Many and What Can Be Done to Improve It
''
CBO-Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979-2007-October 25, 2011CBO-Trends in the Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2011 - November 12, 2014Emmanuel Saez-Striking it Richer-September 3, 2013
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States income inequality (causes) Income in the United States Economic inequality in the United States
Income inequality in the United States
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in t ...
grew significantly beginning in the early 1970s, after several decades of stability. The US consistently exhibits higher rates of income inequality than most developed nations, arguably due to the nation's relatively less regulated markets.Weeks, J. (2007)Inequality Trends in Some Developed OECD countries
In J. K. S. & J. Baudot (Ed.), ''Flat World, Big Gaps'' (159–74). New York: ZED Books (published in association with the United Nations).Income distribution and poverty – OECD
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
According to the Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a federal agency within the legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
Inspired by California's Legislative Analyst's Office that manages ...
, "the precise reasons for the ecentrapid growth in income at the top are not well understood", but "in all likelihood," an "interaction of multiple factors" was involved.Congressional Budget Office: Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007October 2011. p. 13 Researchers have offered several potential rationales.Congressional Budget Office: Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007
October 2011. p. xi Various rationales conflict or overlap. They include: *''globalization'' – Lesser-skilled American workers have been losing ground in the face of competition from workers in Asia and other emerging economies. * ''skills'' – The rapid pace of progress in information technology has increased the relative demand for higher-skilled workers. *''superstars'' – Compensation in many sectors turned into a tournament in which the winner is richly rewarded, while the runners-up get far less. This affects both workers and investors (in dominant firms). * ''tax policy'' – Pre-tax income inequality in the U.S. is similar to other developed countries, but markedly rises after taxes and transfers. * ''immigration'' – Relatively high levels of immigration of less-skilled workers since 1965 may have reduced wages for American-born high school dropouts. *''decline of unions'' – Unions helped increase wages, benefits and working conditions. Unionized workers declined from over 30% to around 12%. *''social norms –'' Social norms constrained executive pay. CEO pay rose from around 40 times the average workers pay in the 1970s to over 350 times in the early 2000s.
Divergence of productivity and compensation

Overall
One view of economic equity is that employee compensation should rise with productivity (defined as real output per hour of labor worked). In other words, if the employee produces more, they should be paid accordingly. If pay lags behind productivity, income inequality grows, as labor's share of the output is falling, while capital's share (generally higher-income owners) is rising. According to a June 2017 report from the non-partisanBureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of t ...
(BLS), productivity rose in tandem with employee compensation (a measure which includes wages as well as benefits such as health insurance) from the 1940s through the 1970s. However, since then productivity has grown faster than compensation. BLS refers to this as the "productivity-compensation gap", an issue which has garnered much attention from academics and policymakers. BLS reported this gap occurs across most industries: "When examined at a detailed industry level, the average annual percent change in productivity outpaced compensation in 83 percent of 183 industries studied" measured from 1987–2015.
For example, in the information industry, productivity increased at an annual average rate of 5.0% over the 1987-2015 period, while compensation increased at about a 1.5% rate, resulting in a 3.5% productivity gap. In Manufacturing, the gap was 2.7%; in Retail Trade 2.6%; and in Transportation and Warehousing 1.3%. This analysis adjusted for inflation using the Consumer Price Index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
Overview
A CPI is a statistica ...
or CPI, a measure of inflation based on what is consumed, rather than what is produced.
Analyzing the gap
BLS explained the gap between productivity and compensation can be divided into two components, the effect of which varies by industry: 1) Recalculating the gap using an industry-specific inflation adjustment ("industry deflator") rather than consumption (CPI); and 2) The change in labor's share of income, defined as how much of a business' revenue goes to workers as opposed to intermediate purchases (i.e., cost of goods) and capital (owners) in that industry. The difference in deflators was the stronger effect among high productivity growth industries, while the change in labor's share of income was the stronger effect among most other industries. For example, the 3.5% productivity gap in the information industry was composed of a 2.1% difference in deflators and about a 1.4% due to change in labor share. The 2.7% gap in Manufacturing included 1.0% due to deflator and 1.7% due to change in labor share.Reasons for the gap
BLS explained the decline in labor share as likely driven by three factors that vary by industry: *Globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
: Income that might have gone to domestic workers is going to foreign workers due to offshoring (i.e., production and service activities in other countries).
*Increased automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
: More automation means more share of income attributed to capital.
*Faster capital depreciation: Information assets depreciate more rapidly than machinery; the latter were the greater share of the capital base in the past. This may require a higher capital share to generate income than in the past.
Market factors
Globalization


Globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
refers to the integration of economies in terms of trade, information, and jobs. Innovations in supply chain management
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) is the management of the flow of goods and services including all processes that transform raw materials into final products between businesses and locations. This can include the movement and stor ...
enabled goods to be sourced in Asia and shipped to the United States less expensively than in the past. This integration of economies, particularly with the U.S. and Asia, had dramatic impacts on income inequality globally.
Economist Branko Milanovic Branko (Cyrillic script: Бранко; ) is a South Slavic male given name found in all of the former Yugoslavia. It is related to the names Branimir and Branislav, and the female equivalent is Branka.
People named Branko include:
* Branko Babi� ...
analyzed global income inequality, comparing 1988 and 2008. His analysis indicated that the global top 1% and the middle classes of the emerging economies (e.g., China, India, Indonesia, Brazil and Egypt) were the main winners of globalization during that time. The real (inflation adjusted) income of the global top 1% increased approximately 60%, while the middle classes of the emerging economies (those around the 50th percentile of the global income distribution in 1988) rose 70–80%. For example, in 2000, 5 million Chinese households earned between $11,500 and $43,000 in 2016 dollars. By 2015, 225 million did. On the other hand, those in the middle class of the developed world (those in the 75th to 90th percentile in 1988, such as the American middle class) experienced little real income gains. The richest 1% contains 60 million persons globally, including 30 million Americans (i.e., the top 12% of Americans by income were in the global top 1% in 2008), the most out of any country.
While economists who have studied globalization agree imports have had an effect, the timing of import growth does not match the growth of income inequality. By 1995 imports of manufactured goods from low-wage countries totalled less than 3% of US gross domestic product."The United States of Inequality, Entry 7: Trade Didn't Create Inequality, and Then It Did,"by Timothy Noah (September 14, 2010) It wasn't until 2006 that the US imported more manufactured goods from low-wage (developing) countries than from high-wage (advanced) economies. Inequality increased during the 2000–2010 decade not because of stagnating wages for less-skilled workers, but because of accelerating incomes of the top 0.1%. Author Timothy Noah estimates that "trade", increases in imports are responsible for just 10% of the "Great Divergence" in income distribution. Journalist
James Surowiecki
James Michael Surowiecki ( ; born April 30, 1967) is an American journalist. He was a staff writer at ''The New Yorker'', where he wrote a regular column on business and finance called "The Financial Page".
Background
Surowiecki was born in Meri ...
notes that in the last 50 years, companies and the sectors of the economy providing the most employment in the US – major retailers, restaurant chains, and supermarkets – are ones with lower profit margins and less pricing power than in the 1960s; while sectors with high profit margins and average salaries – like high technology – have relatively few employees.
Some economists claim that it is WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
-led globalization and competition from developing countries, especially China, that has resulted in the recent decline in labor's share of income and increased unemployment in the U.S. And the Economic Policy Institute
The Economic Policy Institute (EPI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit American, left-leaning think tank based in Washington, D.C., that carries out economic research and analyzes the economic impact of policies and proposals. Affiliated with the labor mo ...
and the Center for Economic and Policy Research
The Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) is a progressive American think tank that specializes in economic policy. Based in Washington, D.C. CEPR was co-founded by economists Dean Baker and Mark Weisbrot in 1999.
Considered a left-lea ...
argue that some trade agreements such as the Trans-Pacific Partnership
The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), or Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement, was a highly contested proposed trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim economies, Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singa ...
could result in further job losses and declining wages.
One argument contrary to the globalization/technology hypothesis relates to variation across countries. Japan, Sweden and France did not experience significant increases in income inequality during the 1979–2010 period, although the U.S. did. The top 1% income group continued to receive less than 10% of the income share in these countries, while the U.S. share rose from 10% to over 20%. Economist Emmanuel Saez
Emmanuel Saez (born November 26, 1972) is a French, naturalized American economist who is Professor of Economics at the University of California, Berkeley. His work, done with Thomas Piketty and Gabriel Zucman, includes tracking the incomes of th ...
wrote in 2014: "Differences across countries rule out technical change/globalization as the sole explanation ... Policies play a key role in shaping inequality (tax and transfer policies, regulations, education)."
Superstar hypothesis
Eric Posner
Eric Andrew Posner (; born December 5, 1965) is an American lawyer and legal scholar who has served as a counsel for the Department of Justice Antitrust Division since 2022. As a law professor at the University of Chicago Law School, Posner has ...
and Glen Weyl
Eric Glen Weyl (born May 6, 1985) is an economist and a researcher at Microsoft Research New England and author of the book ''Radical Markets: Uprooting Capitalism and Democracy for a Just Society'' with co-author Eric Posner.
Weyl is co-creator ...
point out that inequality can be predominantly explained by the superstar hypothesis. In their opinion Piketty fails to observe the accelerated turnover that is occurring in the Forbes 400; only 35 people from the original 1982 list remain today. Many have fallen off as a result of heavy spending, large-scale philanthropy, and bad investments. The current Forbes 400 is now primarily made up of newly wealthy business owners, not heirs and heiresses. In parallel research, the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
's Steven Kaplan and Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
's Joshua Rauh note that 69% of those on the Forbes list are actually first generation wealth creators. That figure has risen dramatically since 1982 when it stood at 40%.
Ed Dolan supports the globalization and superstar hypothesis but points out that the high earnings are based, to some extent, on moral hazard
In economics, a moral hazard is a situation where an economic actor has an incentive to increase its exposure to risk because it does not bear the full costs of that risk. For example, when a corporation is insured, it may take on higher risk ...
like "Bonus-based compensation schemes with inadequate clawback
The term clawback or claw back refers to any money or benefits that have been given out, but are required to be returned (clawed back) due to special circumstances or events, such as the monies having been received as the result of a financial crim ...
for losses" and the shift of losses to shareholders, unsecured creditors, or taxpayers. Paul Krugman argues that for the US the surge in inequality to date is mainly due to supersalaries but capital has nonetheless been significant too. And when the current generation of the 1% turn over their wealth to their heirs these become rentiers, people who live off accumulated capital. Two decades from now America could turn into a rentier-dominated society even more unequal than Belle Époque
The Belle Époque or La Belle Époque (; French for "Beautiful Epoch") is a period of French and European history, usually considered to begin around 1871–1880 and to end with the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era ...
Europe.
One study extended the superstar hypothesis to corporations, with firms that are more dominant in their industry (in some cases due to oligopoly or monopoly) paying their workers far more than the average in the industry. Another study noted that "superstar firms" is another explanation for the decline in the overall share of income (GDP) going to workers/labor as opposed to owners/capital.
Education
Income differences between the varying levels of educational attainment (usually measured by the highest degree of education an individual has completed) have increased. Expertise and skill certified through an academic degree translates into increased scarcity of an individual's occupational qualification which in turn leads to greater economic rewards. As the United States has developed into apost-industrial society
In sociology, the post-industrial society is the stage of society's development when the service sector generates more wealth than the manufacturing sector of the economy.
The term was originated by Alain Touraine and is closely related to si ...
more and more employers require expertise that they did not a generation ago, while the manufacturing sector which employed many of those lacking a post-secondary education is decreasing in size.Zweig, M. (2004). ''The What's Class Got To Do With It?'' Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
In the resulting economic job market the income discrepancy between the working class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
and the professional
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and skil ...
with the higher academic degrees, who possess scarce amounts of certified expertise, may be growing.
Households in the upper quintiles are generally home to more, better educated and employed working income earners, than those in lower quintiles.
Among those in the upper quintile, 62% of householders were college graduates, 80% worked full-time and 76% of households had two or more income earners, compared to the national percentages of 27%, 58% and 42%, respectively.
Upper-most sphere US Census Bureau data indicated that occupational achievement and the possession of scarce skills correlates with higher income.
The "college premium" refers to the increase in income to workers with four-year college degrees relative to those without. The college premium doubled from 1980 to 2005, as the demand for college-educated workers has exceeded the supply. Economists Goldin and Katz estimate that the increase in economic returns to education was responsible for about 60% of the increase in wage inequality between 1973 and 2005. The supply of available graduates did not keep up with business demand due primarily to increasingly expensive college educations. Annual tuition at public and private universities averaged 4% and 20% respectively of the annual median family income from the 1950s to 1970s; by 2005 these figures were 10% and 45% as colleges raised prices in response to demand. Economist David Autor wrote in 2014 that approximately two-thirds of the rise in income inequality between 1980 and 2005 was accounted for by the increased premium associated with education in general and post-secondary education in particular.
Two researchers have suggested that children in low income families are exposed to 636 words an hour, as opposed to 2,153 words in high income families during the first four formative years of a child's development. This, in turn, led to low achievement in later schooling due to the inability of the low income group to verbalize concepts.
A psychologist has stated that society stigmatizes poverty. Conversely, poor people tend to believe that the wealthy have been lucky or have earned their money through illegal means. She believes that both attitudes need to be discarded if the nation is to make headway in addressing the issue of inequality. She suggests that college not be a litmus test of success; that valorizing of one profession as more important than another is a problem.
Skill-biased technological change
 As of the mid- to late- decade of the 2000s, the most common explanation for income inequality in America was "skill-biased technological change" (SBTC) – "a shift in the production technology that favors skilled over unskilled
As of the mid- to late- decade of the 2000s, the most common explanation for income inequality in America was "skill-biased technological change" (SBTC) – "a shift in the production technology that favors skilled over unskilled labor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
by increasing its relative productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
and, therefore, its relative demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ...
". For example, one scholarly colloquium on the subject that included many prominent labor economists estimated that technological change was responsible for over 40% of the increase in inequality. Other factors like international trade, decline in real minimum wage, decline in unionization and rising immigration, were each responsible for 10–15% of the increase.
Education has a notable influence on income distribution. In 2005, roughly 55% of income earners with doctorate degrees – the most educated 1.4% – were among the top 15 percent earners. Among those with master's degrees – the most educated 10% – roughly half had incomes among the top 20 percent of earners. Only among households in the top quintile were householders with college degrees in the majority.
But while the higher education commonly translates into higher income, and the highly educated are disproportionately represented in upper quintile households, differences in educational attainment fail to explain income discrepancies between the top 1 percent and the rest of the population. Large percentages of individuals lacking a college degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to students upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions commonly offer degrees at various levels, usually including unde ...
are present in all income demographics, including 33% of those with heading households with six figure incomes.
From 2000 to 2010, the 1.5% of Americans with an M.D., J.D., or M.B.A. and the 1.5% with a PhD saw median income gains of approximately 5%. Among those with a college or master's degree (about 25% of the American workforce) average wages dropped by about 7%, (though this was less than the decline in wages for those who had not completed college). Post-2000 data has provided "little evidence" for SBTC's role in increasing inequality. The wage premium for college educated has risen little and there has been little shift in shares of employment to more highly skilled occupations.
Approaching the issue from occupations that have been replaced or downgraded since the late 1970s, one scholar found that jobs that "require some thinking but not a lot" – or moderately skilled middle-class occupations such as cashiers, typists, welders, farmers, appliance repairmen – declined the furthest in wage rates and/or numbers. Employment requiring either more skill or less has been less affected."The United States of Inequality, Entry 4: Did Computers Create Inequality?"by Timothy Noah, ''Slate'' (September 8, 2010) However the timing of the great technological change of the era – internet use by business starting in the late 1990s – does not match that of the growth of income inequality (starting in the early 1970s but slackening somewhat in the 1990s). Nor does the introduction of technologies that increase the demand for more skilled workers seem to be generally associated with a divergence in household income among the population. Inventions of the 20th century such as AC electric power, the automobile, airplane, radio, television, the washing machine, Xerox machine, each had an economic impact similar to computers, microprocessors and internet, but did not coincide with greater inequality. Another explanation is that the ''combination'' of the introduction of technologies that increase the demand for skilled workers, ''and'' the failure of the American education system to provide a sufficient increase in those skilled workers has bid up those workers' salaries. An example of the slowdown in education growth in America (that began about the same time as the Great Divergence began) is the fact that the average person born in 1945 received two more years of schooling than his parents, while the average person born in 1975 received only half a year more of schooling."The United States of Inequality. Entry 9: How the Decline in K–12 Education Enriches College Graduates,"
by Timothy Noah, ''Slate.com'' (September 15, 2010) Author Timothy Noah's "back-of-the-envelope" estimation based on "composite of my discussions with and reading of the various economists and political scientists" is that the "various failures" in America's education system are "responsible for 30%" of the post-1978 increase in inequality.
Race and gender disparities
 Income levels vary by gender and race with median income levels considerably below the national median for females compared to men with certain racial demographics.
Despite considerable progress in pursuing gender and racial equality, some social scientists like Richard Schaeffer attribute these discrepancies in income partly to continued discrimination.
Among women, part of the wage gap is due to employment choices and preferences. Women are more likely to consider factors other than salary when looking for employment. On average, women are less willing to travel or relocate, take more hours off and work fewer hours, and choose college majors that lead to lower paying jobs. Women are also more likely to work for governments or non-profits which pay less than the private sector.
According to this perspective certain ethnic minorities and women receive fewer promotions and opportunities for occupation and economic advancement than others. In the case of women this concept is referred to as the
Income levels vary by gender and race with median income levels considerably below the national median for females compared to men with certain racial demographics.
Despite considerable progress in pursuing gender and racial equality, some social scientists like Richard Schaeffer attribute these discrepancies in income partly to continued discrimination.
Among women, part of the wage gap is due to employment choices and preferences. Women are more likely to consider factors other than salary when looking for employment. On average, women are less willing to travel or relocate, take more hours off and work fewer hours, and choose college majors that lead to lower paying jobs. Women are also more likely to work for governments or non-profits which pay less than the private sector.
According to this perspective certain ethnic minorities and women receive fewer promotions and opportunities for occupation and economic advancement than others. In the case of women this concept is referred to as the glass ceiling
A glass ceiling is a metaphor usually applied to women, used to represent an invisible barrier that prevents a given demographic from rising beyond a certain level in a hierarchy.Federal Glass Ceiling Commission''Solid Investments: Making Full ...
keeping women from climbing the occupational ladder.
In terms of race, Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous people ...
are far more likely to be in the highest earning 5 percent than the rest of Americans. Studies have shown that African Americans are less likely to be hired than White Americans with the same qualifications. The continued prevalence of traditional gender roles and ethnic stereotypes may partially account for current levels of discrimination. In 2005, median income levels were highest among Asian and White males and lowest among females of all races, especially those identifying as African American or Hispanic. Despite closing gender and racial gaps, considerable discrepancies remain among racial and gender demographics, even at the same level of educational attainment. The economic success of Asian Americans may come from how they devote much more time to education than their peers. Asian Americans have significantly higher college graduation rates than their peers and are much more likely to enter high status and high income occupations.
 Since 1953 the income gap between male and female workers has decreased considerably but remains relatively large. Women currently earn significantly more Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees than men and almost as many Doctorates. Women are projected to have passed men in Doctorates earned in 2006–2007, and to earn nearly two thirds of Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees by 2016.
Though it is important to note that income inequality between sexes remained stark at all levels of educational attainment. Between 1953 and 2005 median earnings as well as educational attainment increased, at a far greater pace for women than for men. Median income for female earners male earners increased 157.2% versus 36.2% for men, over four times as fast. Today the median male worker earns roughly 68.4% more than their female counterparts, compared to 176.3% in 1953. The median income of men in 2005 was 2% higher than in 1973 compared to a 74.6% increase for female earners.
Racial differences remained stark as well, with the highest earning sex-gender demographic of workers aged 25 or older, Asian males (who were roughly tied with white males) earning slightly more than twice as much as the lowest-earning demographic, Hispanic females. As mentioned above, inequality between races and gender persisted at similar education levels. Racial differences were overall more pronounced among male than among female income earners. In 2009, Hispanics were more than twice as likely to be poor than non-Hispanic whites, research indicates. Lower average English ability, low levels of educational attainment, part-time employment, the youthfulness of Hispanic household heads, and the 2007–09 recession are important factors that have pushed up the Hispanic poverty rate relative to non-Hispanic whites. During the early 1920s, median earnings decreased for both sexes, not increasing substantially until the late 1990s. Since 1974 the median income for workers of both sexes increased by 31.7% from $18,474 to $24,325, reaching its high-point in 2000.
Since 1953 the income gap between male and female workers has decreased considerably but remains relatively large. Women currently earn significantly more Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees than men and almost as many Doctorates. Women are projected to have passed men in Doctorates earned in 2006–2007, and to earn nearly two thirds of Associate's, Bachelor's, and master's degrees by 2016.
Though it is important to note that income inequality between sexes remained stark at all levels of educational attainment. Between 1953 and 2005 median earnings as well as educational attainment increased, at a far greater pace for women than for men. Median income for female earners male earners increased 157.2% versus 36.2% for men, over four times as fast. Today the median male worker earns roughly 68.4% more than their female counterparts, compared to 176.3% in 1953. The median income of men in 2005 was 2% higher than in 1973 compared to a 74.6% increase for female earners.
Racial differences remained stark as well, with the highest earning sex-gender demographic of workers aged 25 or older, Asian males (who were roughly tied with white males) earning slightly more than twice as much as the lowest-earning demographic, Hispanic females. As mentioned above, inequality between races and gender persisted at similar education levels. Racial differences were overall more pronounced among male than among female income earners. In 2009, Hispanics were more than twice as likely to be poor than non-Hispanic whites, research indicates. Lower average English ability, low levels of educational attainment, part-time employment, the youthfulness of Hispanic household heads, and the 2007–09 recession are important factors that have pushed up the Hispanic poverty rate relative to non-Hispanic whites. During the early 1920s, median earnings decreased for both sexes, not increasing substantially until the late 1990s. Since 1974 the median income for workers of both sexes increased by 31.7% from $18,474 to $24,325, reaching its high-point in 2000.
Incentives
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
Chairman Ben Bernanke, have talked about the importance of incentives: "...without the possibility of unequal outcomes tied to differences in effort and skill, the economic incentive for productive behavior would be eliminated, and our market-based economy ... would function far less effectively."Economic Mobility: Is the American Dream Alive and Well?Isabel Sawhill & John E. Morton. February 21, 2007. Economic Mobility Project, Washington, D.C.. December 4, 2007. Since abundant supply decreases market value, the possession of scarce skills considerably increases income. Among the
American lower class
In the United States, the lower class are those at or near the lower end of the socio-economic hierarchy. As with all social classes in the United States, the lower class is loosely defined and its boundaries and definitions subject to debate ...
, the most common source of income was not occupation, but government welfare.
Stock buybacks
Writing in the ''Harvard Business Review'' in September 2014, William Lazonick blamed record corporate stock buybacks for reduced investment in the economy and a corresponding impact on prosperity and income inequality. Between 2003 and 2012, the 449 companies in the S&P 500 used 54% of their earnings ($2.4 trillion) to buy back their own stock. An additional 37% was paid to stockholders as dividends. Together, these were 91% of profits. This left little for investment in productive capabilities or higher income for employees, shifting more income to capital rather than labor. He blamed executive compensation arrangements, which are heavily based onstock options
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date ...
, stock awards and bonuses for meeting earnings per share
Earnings per share (EPS) is the monetary value of earnings per outstanding share of common stock for a company. It is a key measure of corporate profitability and is commonly used to price stocks.
In the United States, the Financial Accounting ...
(EPS) targets (EPS increases as the number of outstanding shares decreases). Restrictions on buybacks were greatly eased in the early 1980s. He advocates changing these incentives to limit buybacks.
U.S. companies are projected to increase buybacks to $701 billion in 2015 according to Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs () is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, H ...
, an 18% increase over 2014. For scale, annual non-residential fixed investment (a proxy for business investment and a major GDP component) was estimated to be about $2.1 trillion for 2014.
Journalist Timothy Noah
Timothy Robert Noah (born 1958), an American journalist and author, is a staff writer at ''The New Republic.'' Previously he was labor policy editor for ''Politico'', a contributing writer at MSNBC.com, a senior editor of ''The New Republic'' ass ...
wrote in 2012 that: "My own preferred hypothesis is that stockholders appropriated what once belonged to middle-class wage earners." Since the vast majority of stocks are owned by higher income households, this contributes to income inequality. Journalist Harold Meyerson
Harold Meyerson (born 1950) is an American journalist, opinion columnist and socialist. In 2009 ''The Atlantic Monthly'' named him one of "the most influential commentators in the nation" as part of their list "The Atlantic 50."
Early life and ...
wrote in 2014 that: "The purpose of the modern U.S. corporation is to reward large investors and top executives with income that once was spent on expansion, research, training and employees."
Tax and transfer policies
Background
 U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed nations pre-tax, but is among the worst after-tax and transfers. This indicates the U.S. tax policies redistribute income from higher income to lower income households relatively less than other developed countries. Journalist
U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed nations pre-tax, but is among the worst after-tax and transfers. This indicates the U.S. tax policies redistribute income from higher income to lower income households relatively less than other developed countries. Journalist Timothy Noah
Timothy Robert Noah (born 1958), an American journalist and author, is a staff writer at ''The New Republic.'' Previously he was labor policy editor for ''Politico'', a contributing writer at MSNBC.com, a senior editor of ''The New Republic'' ass ...
summarized the results of several studies his 2012 book ''The Great Divergence'':
*Economists Piketty and Saez reported in 2007, that U.S. taxes on the rich had declined over the 1979–2004 period, contributing to increasing after-tax income inequality. While dramatic reductions in the top marginal income tax rate contributed somewhat to worsening inequality, other changes to the tax code (e.g., corporate, capital gains, estate, and gift taxes) had more significant impact. Considering all federal taxes, including the payroll tax, the effective tax rate on the top 0.01% fell dramatically, from 59.3% in 1979 to 34.7% in 2004. CBO reported an effective tax rate decline from 42.9% in 1979 to 32.3% in 2004 for the top 0.01%, using a different income measurement. In other words, the effective tax rate on the very highest income taxpayers fell by about one-quarter.
*CBO estimated that the combined effect of federal taxes and government transfers reduced income inequality (as measured by the Gini Index) by 23% in 1979. By 2007, the combined effect was to reduce income inequality by 17%. So the tax code remained progressive, only less so.
*While pre-tax income is the primary driver of income inequality, the less progressive tax code further increased the share of after-tax income going to the highest income groups. For example, had these tax changes not occurred, the after-tax income share of the top 0.1% would have been approximately 4.5% in 2000 instead of the 7.3% actual figure.
Income taxes
 A key factor in income inequality/equality is the effective rate at which income is taxed coupled with the progressivity of the tax system. A
A key factor in income inequality/equality is the effective rate at which income is taxed coupled with the progressivity of the tax system. A progressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases.Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), ''Concepts of Taxation'', Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX The term ''progre ...
is a tax in which the effective tax rate
In a tax system, the tax rate is the ratio (usually expressed as a percentage) at which a business or person is taxed. There are several methods used to present a tax rate: statutory, average, marginal, and effective. These rates can also be p ...
increases as the taxable base amount increases.Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), ''Concepts of Taxation'', Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX Overall income tax rates in the U.S. are below the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
average, and until 2005 have been declining.
How much tax policy change over the last thirty years has contributed to income inequality is disputed. In their comprehensive 2011 study of income inequality (''Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007''),Congressional Budget Office: Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007October 2011. p. 20 and figure 12. the CBO found that,
The top fifth of the population saw a 10-percentage-point increase in their share of after-tax income. Most of that growth went to the top 1 percent of the population. All other groups saw their shares decline by 2 to 3 percentage points. In 2007, federal taxes and transfers reduced the dispersion of income by 20 percent, but that equalizing effect was larger in 1979. The share of transfer payments to the lowest-income households declined. The overall average federal tax rate fell.However, a more recent CBO analysis indicates that with changes to 2013 tax law (e.g., the expiration of the 2001-2003
Bush tax cuts
The phrase Bush tax cuts refers to changes to the United States tax code passed originally during the presidency of George W. Bush and extended during the presidency of Barack Obama, through:
* Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act o ...
for top earners and the increased payroll taxes passed as part of the Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
), the effective federal tax rates for the highest earning household will increase to levels not seen since 1979.
According to journalist Timothy Noah, "you can't really demonstrate that U.S. tax policy had a large impact on the three-decade income inequality trend one way or the other. The inequality trend for pre-tax income during this period was much more dramatic." Noah estimates tax changes account for 5% of the Great Divergence.
But many – such as economist Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist, who is Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for ''The New York Times''. In 2008, Krugman was th ...
– emphasize the effect of changes in taxation – such as the 2001 and 2003 Bush administration tax cuts which cut taxes far more for high-income households than those below – on increased income inequality.
Part of the growth of income inequality under Republican administrations (described by Larry Bartels) has been attributed to tax policy. A study by Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez found that "large reductions in tax progressivity since the 1960s took place primarily during two periods: the Reagan presidency in the 1980s and the Bush administration in the early 2000s."
During Republican President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
's tenure in office the top marginal income tax rate was reduced from over 70 to 28 percent, high top marginal rates like 70% being the sort in place during much of the period of great income equality following the "Great Compression".Noah, Timothy. "Can We Blame Income Inequality on Republicans"in the multi-part series "The United States of Inequality." ''Slate'', September 9, 2010. The lowest marginal rate for the bottom fell from 14 to 11 percent. However the effective rate on top earners before Reagan's tax cut was much lower because of loopholes and charitable contributions. Robert Bellafiore and Madison Mauro, writing for the Tax Foundation, calculated that effective tax rates for the richest Americans has declined since 1986. But the share of income taxes paid by the richest Americans has increased, due to tax expenditures increasing the number of low-income Americans with negative tax rates.
Taxes on capital
 Taxes on income derived from capital (e.g., financial assets, property and businesses) primarily affect higher income groups, who own the vast majority of capital. For example, in 2010 approximately 81% of stocks were owned by the top 10% income group and 69% by the top 5%. Only about one-third of American households have stock holdings more than $7,000. Therefore, since higher-income taxpayers have a much higher share of their income represented by capital gains, lowering taxes on capital income and gains increases after-tax income inequality.
Capital gains taxes were reduced around the time income inequality began to rise again around 1980 and several times thereafter. During 1978 under President
Taxes on income derived from capital (e.g., financial assets, property and businesses) primarily affect higher income groups, who own the vast majority of capital. For example, in 2010 approximately 81% of stocks were owned by the top 10% income group and 69% by the top 5%. Only about one-third of American households have stock holdings more than $7,000. Therefore, since higher-income taxpayers have a much higher share of their income represented by capital gains, lowering taxes on capital income and gains increases after-tax income inequality.
Capital gains taxes were reduced around the time income inequality began to rise again around 1980 and several times thereafter. During 1978 under President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
, the top capital gains tax rate was reduced from 49% to 28%. President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
's 1981 cut in the top rate on unearned income reduced the maximum capital gains rate to only 20% – its lowest level since the Hoover administration
Herbert Hoover's tenure as the 31st president of the United States began on his inauguration on March 4, 1929, and ended on March 4, 1933. Hoover, a Republican, took office after a landslide victory in the 1928 presidential election over Democr ...
, as part of an overall economic growth strategy. The capital gains tax rate was also reduced by President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
in 1997, from 28% to 20%. President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
reduced the tax rate on capital gains and qualifying dividends from 20% to 15%, less than half the 35% top rate on ordinary income.
CBO reported in August 1990 that: "Of the 8 studies reviewed, five, including the two CBO studies, found that cutting taxes on capital gains is not likely to increase savings, investment, or GNP much if at all." Some of the studies indicated the loss in revenue from lowering the tax rate may be offset by higher economic growth, others did not.
Journalist Timothy Noah
Timothy Robert Noah (born 1958), an American journalist and author, is a staff writer at ''The New Republic.'' Previously he was labor policy editor for ''Politico'', a contributing writer at MSNBC.com, a senior editor of ''The New Republic'' ass ...
wrote in 2012 that: "Every one of these changes elevated the financial interests of business owners and stockholders above the well-being, financial or otherwise, or ordinary citizens." So overall, while cutting capital gains taxes adversely affects income inequality, its economic benefits are debatable.
Other tax policies
Rising inequality has also been attributed to President Bush's veto of tax harmonization, as this would have prohibited offshore tax havens.Debate over effects of tax policies
One study found reductions of total effective tax rates were most significant for individuals with highest incomes. (see "Federal Tax Rate by Income Group" chart) For those with incomes in the top 0.01 percent, overall rates of Federal tax fell from 74.6% in 1970, to 34.7% in 2004 (the reversal of the trend in 2000 with a rise to 40.8% came after the 1993 Clinton deficit reduction tax bill), the next 0.09 percent falling from 59.1% to 34.1%, before leveling off with a relatively modest drop of 41.4 to 33.0% for the 99.5–99.9 percent group. Although the tax rate for low-income earners fell as well (though not as much), these tax reductions compare with virtually no change – 23.3% tax rate in 1970, 23.4% in 2004 – for the US population overall. The study found the decline in progressivity since 1960 was due to the shift from allocation of corporate income taxes among labor and capital to the effects of the individual income tax.Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez"How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective"
''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' Volume 21, Number 1 – Winter 2007
Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist, who is Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for ''The New York Times''. In 2008, Krugman was th ...
also supports this claim saying, "The overall tax rate on these high income families fell from 36.5% in 1980 to 26.7% in 1989."
From the White House's own analysis, the federal tax burden for those making greater than $250,000 fell considerably during the late 1980s, 1990s and 2000s, from an effective tax of 35% in 1980, down to under 30% from the late 1980s to 2011.
Many studies argue that tax changes of S corporations
An S corporation, for United States federal income tax, is a closely held corporation (or, in some cases, a limited liability company (LLC) or a partnership) that makes a valid election to be taxed under Subchapter S of Chapter 1 of the Internal ...
confound the statistics prior to 1990. However, even after these changes inflation-adjusted average after-tax income grew by 25% between 1996 and 2006 (the last year for which individual income tax data is publicly available). This average increase, however, obscures a great deal of variation. The poorest 20% of tax filers experienced a 6% reduction in income while the top 0.1 percent of tax filers saw their income almost double. Tax filers in the middle
of the income distribution experienced about a 10% increase in income. Also during this period, the proportion of income from capital increased for the top 0.1 percent from 64% to 70%.
Transfer payments
Transfer payments refer to payments to persons such as social security, unemployment compensation, or welfare. CBO reported in November 2014 that: "Government transfers reduce income inequality because the transfers received by lower-income households are larger relative to their market income than are the transfers received by higher-income households. Federal taxes also reduce income inequality, because the taxes paid by higher-income households are larger relative to their before-tax income than are the taxes paid by lower-income households. The equalizing effects of government transfers were significantly larger than the equalizing effects of federal taxes from 1979 to 2011. CBO also reported that less progressive tax and transfer policies have contributed to greater after-tax income inequality: "As a result of the diminishing effect of transfers and federal taxes, the Gini index for income after transfers and federal taxes grew by more than the index for market income. Between 1979 and 2007, the Gini index for market income increased by 23 percent, the index for market income after transfers increased by 29 percent, and the index for income measured after transfers and federal taxes increased by 33 percent."Tax expenditures
 Tax expenditures (i.e., exclusions, deductions, preferential tax rates, and
Tax expenditures (i.e., exclusions, deductions, preferential tax rates, and tax credits
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "disc ...
) cause revenues to be much lower than they would otherwise be for any given tax rate structure. The benefits from tax expenditures, such as income exclusions for healthcare insurance premiums paid for by employers and tax deductions for mortgage interest, are distributed unevenly across the income spectrum. They are often what the Congress offers to special interests in exchange for their support. According to a report from the CBO that analyzed the 2013 data:
*The top 10 tax expenditures totalled $900 billion. This is a proxy for how much they reduced revenues or increased the annual budget deficit.
*Tax expenditures tend to benefit those at the top and bottom of the income distribution, but less so in the middle.
*The top 20% of income earners received approximately 50% of the benefit from them; the top 1% received 17% of the benefits.
*The largest single tax expenditure was the exclusion from income of employer sponsored health insurance ($250 billion).
*Preferential tax rates on capital gains and dividends were $160 billion; the top 1% received 68% of the benefit or $109 billion from lower income tax rates on these types of income.
Understanding how each tax expenditure is distributed across the income spectrum can inform policy choices.
Other causes
Shifts in political power
Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist, who is Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for ''The New York Times''. In 2008, Krugman was th ...
wrote in 2015 that: "Economists struggling to make sense of economic polarization are, increasingly, talking not about technology but about power." This market power hypothesis basically asserts that market power has concentrated in monopolies
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
and oligopolies
An oligopoly (from Greek ὀλίγος, ''oligos'' "few" and πωλεῖν, ''polein'' "to sell") is a market structure in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of large sellers or producers. Oligopolies often result from ...
that enable unusual amounts of income (" rents") to be transferred from the many consumers to relatively few owners. This hypothesis is consistent with higher corporate profits without a commensurate rise in investment, as firms facing less competition choose to pass a greater share of their profits to shareholders (such as through share buybacks and dividends) rather than re-invest in the business to ward off competitors.
One cause of this concentration of market power was the rightward shift in American politics toward more conservative policies since 1980, as politics plays a big role in how market power can be exercised. Policies that removed barriers to monopoly and oligopoly included anti-union laws, reduced anti-trust activity, deregulation (or failure to regulate) non-depository banking, contract laws that favored creditors over debtors, etc. Further, rising wealth concentration can be used to purchase political influence, creating a feedback loop.
Decline of unions
 The era of inequality growth has coincided with a dramatic decline in labor union membership from 20% of the labor force in 1983 to about 12% in 2007. Classical and
The era of inequality growth has coincided with a dramatic decline in labor union membership from 20% of the labor force in 1983 to about 12% in 2007. Classical and neoclassical economists
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good ...
have traditionally thought that since the chief purpose of a union is to maximize the income of its members, a strong but not all-encompassing union movement would lead to increased income inequality. However, given the increase in income inequality of the past few decades, either the sign of the effect must be reversed, or the magnitude of the effect must be small and a much larger opposing force has overridden it.The United States of Inequality, Entry 6: The Great Divergence and the death of organized labor.By Timothy Noah, ''Slate.com'', September 12, 2010 However, more recently, research has shown that unions' ability to reduce income disparities among members outweighed other factors and its net effect has been to reduce national income inequality. The decline of unions has hurt this leveling effect among men, and one economist (Berkeley economist
David Card
David Edward Card (born 1956) is a Canadian-American labour economist and professor of economics at the University of California, Berkeley. He was awarded half of the 2021 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirical contribution ...
) estimating about 15–20% of the "Great Divergence" among that gender is the result of declining unionization.
According to scholars, "As organized labor's political power dissipates, economic interests in the labor market are dispersed and policy makers have fewer incentives to strengthen unions or otherwise equalize economic rewards."Rosenfeld, Jake (2014). What Unions No Longer Do
''
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
. Unions were a balancing force, helping ensure wages kept up with productivity and that neither executives nor shareholders were unduly rewarded. Further, societal norms placed constraints on executive pay. This changed as union power declined (the share of unionized workers fell significantly during the Great Divergence, from over 30% to around 12%) and CEO pay skyrocketed (rising from around 40 times the average workers pay in the 1970s to over 350 times in the early 2000s). A 2015 report by the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
also attributes the decline of labor's share of GDP to deunionization, noting the trend "necessarily increases the income share of corporate managers' pay and shareholder returns ... Moreover, weaker unions can reduce workers' influence on corporate decisions that benefit top earners, such as the size and structure of top executive compensation."
Still other researchers think it is the labor movement's loss of national political power to promote equalizing "government intervention and changes in private sector behavior" has had the greatest impact on inequality in the US. Sociologist Jake Rosenfeld of the University of Washington argues that labor unions were the primary institution fighting inequality in the United States and helped grow a multiethnic middle class, and their decline has resulted in diminishing prospects for U.S. workers and their families. Timothy Noah estimates the "decline" of labor union power "responsible for 20%" of the Great Divergence. While the decline of union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
power in the US has been a factor in declining middle class incomes, they have retained their clout in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
.Tami Luhby (November 8, 2011)Global income inequality: Where the U.S. ranks
''
CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by ...
Money'' Retrieved September 2, 2013. In Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
, influential trade unions such as Fagligt Fælles Forbund
The United Federation of Workers in Denmark ( da, Fagligt Fælles Forbund, 3F) is a Danish labor union.
The union was formed in 2004, from the merger of the Danish Women Workers' Union and the Danish General Workers' Union. In 2006, the Restaur ...
(3F) ensure that fast-food workers earn a living wage
A living wage is defined as the minimum income necessary for a worker to meet their basic needs. This is not the same as a subsistence wage, which refers to a biological minimum, or a solidarity wage, which refers to a minimum wage tracking labor ...
, the equivalent of $20 an hour, which is more than double the hourly rate for their counterparts in the United States.
Critics of technological change as an explanation for the "Great Divergence" of income levels in America point to public policy and party politics, or "stuff the government did, or didn't do". They argue these have led to a trend of declining labor union membership rates and resulting diminishing political clout, decreased expenditure on social services, and less government redistribution. Moreover, the United States is the only advanced economy without a labor-based political party.
As of 2011, several state legislatures have launched initiatives aimed at lowering wages, labor standards, and workplace protections for both union and non-union workers.
The economist Joseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the Joh ...
argues that "Strong unions have helped to reduce inequality, whereas weaker unions have made it easier for CEOs, sometimes working with market forces that they have helped shape, to increase it." The long fall in unionization in the U.S. since WWII has seen a corresponding rise in the inequality of wealth and income.
A study by Kristal and Cohen reported that rising wage inequality was driven more by declining unions and the fall in the real value of the minimum wage, with twice as much impact as technology.
Political parties and presidents
Liberal political scientistLarry Bartels
Larry Martin Bartels (born May 16, 1956) is an American political scientist and the Co-Director of the Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions and Shayne Chair in Public Policy and Social Science at Vanderbilt University. Prior to his appo ...
has found a strong correlation between the party of the president and income inequality in America since 1948. (see below)Kelly, N.J. (2009). ''The Politics of Income Inequality in the United States''. New York: Cambridge University Press. Examining average annual pre-tax income growth from 1948 to 2005 (which encompassed most of the egalitarian Great Compression The Great Compression refers to "a decade of extraordinary wage compression" in the United States in the early 1940s. During that time, economic inequality as shown by wealth distribution and income distribution between the rich and poor became much ...
and the entire inegalitarian Great Divergence
The Great Divergence or European miracle is the socioeconomic shift in which the Western world (i.e. Western Europe and the parts of the New World where its people became the dominant populations) overcame pre-modern growth constraints and em ...
) Bartels shows that under Democratic presidents (from Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
forward), the greatest income gains have been at the bottom of the income scale and tapered off as income rose. Under Republican presidents, in contrast, gains were much less but what growth there was concentrated towards the top, tapering off as you went down the income scale.Paul Ryan: Inequality, Take TwoTimothy Noah, ''The New Republic'', November 18, 2011 Summarizing Bartels's findings, journalist
Timothy Noah
Timothy Robert Noah (born 1958), an American journalist and author, is a staff writer at ''The New Republic.'' Previously he was labor policy editor for ''Politico'', a contributing writer at MSNBC.com, a senior editor of ''The New Republic'' ass ...
referred to the administrations of Democratic presidents as "Democrat-world", and GOP administrations as "Republican-world":
The pattern of distribution of growth appears to be the result of a whole host of policies,
including not only the distribution of taxes and benefits but also the government's stance toward unions, whether the minimum wage rises, the extent to which the government frets about inflation versus too-high interest rates, etc., etc.Noah admits the evidence of this correlation is "circumstantial rather than direct", but so is "the evidence that smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer." In his 2017 book ''The Great Leveler'', historian
Walter Scheidel
Walter Scheidel (born 9 July 1966) is an Austrian historian who teaches ancient history at Stanford University, California. Scheidel's main research interests are ancient social and economic history, pre-modern historical demography, and comp ...
point out that, starting in the 1970s, both parties shifted towards promoting free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
, with Republicans moving further to the political right than Democrats to the political left. He notes that Democrats have been instrumental in the financial deregulation of the 1990s and have largely neglected social welfare issues while increasingly focusing on issues pertaining to identity politics
Identity politics is a political approach wherein people of a particular race, nationality, religion, gender, sexual orientation, social background, social class, or other identifying factors develop political agendas that are based upon these i ...
. The Clinton Administration
Bill Clinton's tenure as the 42nd president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1993, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive election victory over Re ...
in particular continued promoting free market, or neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
, reforms which began under the Reagan Administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over D ...
.
Non-party political action
 According to political scientists Jacob Hacker and Paul Pierson writing in the book
According to political scientists Jacob Hacker and Paul Pierson writing in the book Winner-Take-All Politics
''Winner-Take-All Politics: How Washington Made the Rich Richer—and Turned Its Back on the Middle Class'' is a book by political scientists Jacob S. Hacker and Paul Pierson. In it the authors argue that contrary to conventional wisdom, the dr ...
, the important policy shifts were brought on not by the Republican Party but by the development of a modern, efficient political system, especially lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agency, regulatory agencie ...
, by top earners – and particularly corporate executives and the financial services industry. The end of the 1970s saw a transformation of American politics away from a focus on the middle class, with new, much more effective, aggressive and well-financed lobbyists and pressure groups acting on behalf of upper income groups. Executives successfully eliminated any countervailing power or oversight of corporate managers (from private litigation, boards of directors and shareholders, the Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against market ...
or labor unions).
The financial industry's success came from successfully pushing for deregulation of financial markets, allowing much more lucrative but much more risky investments from which it privatized the gains while socializing the losses with government bailouts. (the two groups formed about 60% of the top 0.1 percent of earners.) All top earners were helped by deep cuts in estate and capital gains taxes, and tax rates on high levels of income.
Arguing against the proposition that the explosion in pay for corporate executives – which grew from 35X average worker pay in 1978 to over 250X average pay before the 2007 recession – is driven by an increased demand for scarce talent and set according to performance, Krugman points out that multiple factors outside of executives' control govern corporate profitability, particularly in short term when the head of a company like Enron
Enron Corporation was an American energy, commodities, and services company based in Houston, Texas. It was founded by Kenneth Lay in 1985 as a merger between Lay's Houston Natural Gas and InterNorth, both relatively small regional companies. ...
may look like a great success. Further, corporate boards follow other companies in setting pay even if the directors themselves disagree with lavish pay "partly to attract executives whom they consider adequate, partly because the financial market will be suspicious of a company whose CEO isn't lavishly paid." Finally "corporate boards, largely selected by the CEO, hire compensation experts, almost always chosen by the CEO" who naturally want to please their employers.
Lucian Arye Bebchuk, Jesse M. Fried, the authors of ''Pay Without Performance'', critique of executive pay
Executive compensation is composed of both the financial compensation (executive pay) and other non-financial benefits received by an executive from their employing firm in return for their service. It is typically a mixture of fixed salary, variab ...
, argue that executive capture of corporate governance is so complete that only public relations, i.e. public `outrage`, constrains their pay. This in turn has been reduced as traditional critics of excessive pay – such as politicians (where need for campaign contributions from the richest outweighs populist indignation), media (lauding business genius), unions (crushed) – are now silent.
In addition to politics, Krugman postulated change in norms of corporate culture have played a factor. In the 1950s and 60s, corporate executives had (or could develop) the ability to pay themselves very high compensation through control of corporate boards of directors, they restrained themselves. But by the end of the 1990s, the average real annual compensation of the top 100 C.E.O.'s skyrocketed from $1.3 million – 39 times the pay of an average worker – to $37.5 million, more than 1,000 times the pay of ordinary workers from 1982 to 2002. Journalist George Packer
George Packer (born August 13, 1960) is a US journalist, novelist, and playwright. He is best known for his writings for ''The New Yorker'' and ''The Atlantic'' about U.S. foreign policy and for his book '' The Assassins' Gate: America in Iraq''. ...
also sees the dramatic increase in inequality in America as a product of the change in attitude of the American elite, which (in his view) has been transitioning itself from pillars of society to a special interest group."The Broken Contract", By George Packer, ''Foreign Affairs
''Foreign Affairs'' is an American magazine of international relations and U.S. foreign policy published by the Council on Foreign Relations, a nonprofit, nonpartisan, membership organization and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy and ...
'', November/December 2011 Author Timothy Noah estimates that what he calls "Wall Street and corporate boards' pampering" of the highest earning 0.1% is "responsible for 30%" of the post-1978 increase in inequality.
Immigration
 The
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, also known as the Hart–Celler Act and more recently as the 1965 Immigration Act, is a federal law passed by the 89th United States Congress and signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. The l ...
increased immigration to America, especially of non-Europeans.The Great DivergenceBy Timothy Noah From 1970 to 2007, the foreign-born proportion of America's population grew from 5% to 11%, most of whom had lower education levels and incomes than native-born Americans. But the contribution of this increase in supply of low-skill labor seem to have been relatively modest. One estimate stated that immigration reduced the average annual income of native-born "high-school dropouts" ("who roughly correspond to the poorest tenth of the workforce") by 7.4% from 1980 to 2000. The decline in income of better educated workers was much less. Author Timothy Noah estimates that "immigration" is responsible for just 5% of the "Great Divergence" in income distribution, as does economist
David Card
David Edward Card (born 1956) is a Canadian-American labour economist and professor of economics at the University of California, Berkeley. He was awarded half of the 2021 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirical contribution ...
.
While immigration was found to have slightly depressed the wages of the least skilled and least educated American workers, it doesn't explain rising inequality among high school and college graduates. Scholars such as political scientists Jacob S. Hacker
Jacob Stewart Hacker (born 1971) is an American professor and political scientist. He is the director of the Institution for Social and Policy Studies and a professor of political science at Yale University. Hacker has written works on social poli ...
, Paul Pierson
Paul Pierson (born 1959) is an American professor of political science specializing in comparative politics and holder of the John Gross Endowed Chair of Political Science at the University of California, Berkeley. From 2007-2010 he served at UC ...
, Larry Bartels
Larry Martin Bartels (born May 16, 1956) is an American political scientist and the Co-Director of the Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions and Shayne Chair in Public Policy and Social Science at Vanderbilt University. Prior to his appo ...
and Nathan Kelly, and economist Timothy Smeeding question the explanation of educational attainment and workplace skills point out that other countries with similar education levels and economies have not gone the way of the US, and that the concentration of income in the US hasn't followed a pattern of "the 29% of Americans with college degrees pulling away" from those who have less education.Bartels, L. M. (2008). ''Unequal democracy: The political economy of the new gilded age''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.Smeeding, T. (2005). Public policy, economic inequality, and poverty: The United States in comparative perspective. ''Social Science Quarterly, 86'', 956–83."American politics, Democracy in America: ''Winner-Take-All Politics''. It's a pretty good book."''The Economist'' (September 21, 2010)Krugman, P. (2007). ''The conscience of a liberal''. New York: W. W. Norton.
Wage theft
A September 2014 report by the Economic Policy Institute claimswage theft
Wage theft is the failing to pay wages or provide employee benefits owed to an employee by contract or law. It can be conducted by employers in various ways, among them failing to pay overtime; violating minimum wage, minimum-wage laws; the miscl ...
is also responsible for exacerbating income inequality: "Survey evidence suggests that wage theft is widespread and costs workers billions of dollars a year, a transfer from low-income employees to business owners that worsens income inequality, hurts workers and their families, and damages the sense of fairness and justice that a democracy needs to survive."
Corporatism

Edmund Phelps
Edmund Strother Phelps (born July 26, 1933) is an American economist and the recipient of the 2006 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences.
Early in his career, he became known for his research at Yale's Cowles Foundation in the first half of ...
, published an analysis in 2010 theorizing that the cause of income inequality is not free market capitalism, but instead is the result of the rise of corporatism
Corporatism is a collectivist political ideology which advocates the organization of society by corporate groups, such as agricultural, labour, military, business, scientific, or guild associations, on the basis of their common interests. The ...
. Capitalism vs Corporatism - Edmund Phelps''
Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
.'' January 11, 2010). Corporatism, in his view, is the antithesis of free market capitalism. It is characterized by semi-monopolistic organizations and banks, big employer confederations, often acting with complicit state institutions in ways that discourage (or block) the natural workings of a free economy. The primary effects of corporatism are the consolidation of economic power and wealth with end results being the attrition of entrepreneurial and free market dynamism.
His follow-up book, ''Mass Flourishing'', further defines corporatism by the following attributes: power-sharing between government and large corporations (exemplified in the U.S. by widening government power in areas such as financial services, healthcare, and energy through regulation), an expansion of corporate lobbying and campaign support in exchange for government reciprocity, escalation in the growth and influence of financial and banking sectors, increased consolidation of the corporate landscape through merger and acquisition (with ensuing increases in corporate executive compensation), increased potential for corporate/government corruption and malfeasance, and a lack of entrepreneurial and small business development leading to lethargic and stagnant economic conditions.
Today, in the United States, virtually all of these economic conditions are being borne out. With regard to income inequality, the 2014 income analysis of University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
economist Emmanuel Saez
Emmanuel Saez (born November 26, 1972) is a French, naturalized American economist who is Professor of Economics at the University of California, Berkeley. His work, done with Thomas Piketty and Gabriel Zucman, includes tracking the incomes of th ...
confirms that relative growth of income and wealth is not occurring among small and mid-sized entrepreneurs and business owners (who generally populate the lower half of top one per-centers in income), but instead only among the top .1 percent of income distribution ... whom Paul Krugman describes as "super-elites - corporate bigwigs and financial wheeler-dealers." ... who earn $2,000,000 or more every year. The Distribution of US Wealth, Capital Income and Returns since 1913, Emmanuel Saez, Gabriel ZucmanMarch 2014 For example, measured relative to GDP, total compensation and its component wages and salaries have been declining since 1970. This indicates a shift in income from labor (persons who derive income from hourly wages and salaries) to capital (persons who derive income via ownership of businesses, land and assets). Wages and salaries have fallen from approximately 51% GDP in 1970 to 43% GDP in 2013. Total compensation has fallen from approximately 58% GDP in 1970 to 53% GDP in 2013. To put this in perspective, five percent of U.S. GDP was approximately $850 billion in 2013. This represents an additional $7,000 in wages and salaries for each of the 120 million U.S. households.
Larry Summers
Lawrence Henry Summers (born November 30, 1954) is an American economist who served as the 71st United States secretary of the treasury from 1999 to 2001 and as director of the National Economic Council from 2009 to 2010. He also served as pres ...
estimated in 2007 that the lower 80% of families were receiving $664 billion less income than they would be with a 1979 income distribution (a period of much greater equality), or approximately $7,000 per family.
Not receiving this income may have led many families to increase their debt burden, a significant factor in the 2007-2009 subprime mortgage crisis
The United States subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010 that contributed to the Financial crisis of 2007–2008, 2007–2008 global financial crisis. It was triggered by a large decline ...
, as highly leveraged homeowners suffered a much larger reduction in their net worth during the crisis. Further, since lower income families tend to spend relatively more of their income than higher income families, shifting more of the income to wealthier families may slow economic growth.
In another example, The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econo ...
propounds that a swelling corporate financial and banking sector has caused Gini Coefficients to rise in the U.S. since 1980: "Financial services' share of GDP in America doubled to 8% between 1980 and 2000; over the same period their profits rose from about 10% to 35% of total corporate profits, before collapsing in 2007–09. Bankers are being paid more, too. In America the compensation of workers in financial services was similar to average compensation until 1980. Now it is twice that average." The summary argument, considering these findings, is that if corporatism is the consolidation and sharing of economic and political power between large corporations and the state ... then a corresponding concentration of income and wealth (with resulting income inequality) is an expected by-product of such a consolidation.
Neoliberalism
Some economists, sociologists and anthropologists argue thatneoliberalism
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
, or the resurgence of 19th century theories relating to ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups. ...
'' economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
in the late 1970s, has been the significant driver of inequality. More broadly, according to ''The Handbook of Neoliberalism'', the term has "become a means of identifying a seemingly ubiquitous set of market-oriented policies as being largely responsible for a wide range of social, political, ecological and economic problems." Vicenç Navarro points to policies pertaining to the deregulation of labor markets, privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
of public institutions, union busting
Union busting is a range of activities undertaken to disrupt or prevent the formation of trade unions or their attempts to grow their membership in a workplace.
Union busting tactics can refer to both legal and illegal activities, and can range ...
and reduction of public social expenditures as contributors to this widening disparity. The privatization of public functions, for example, grows income inequality by depressing wages and eliminating benefits for middle class workers while increasing income for those at the top. The deregulation of the labor market undermined unions by allowing the real value of the minimum wage to plummet, resulting in employment insecurity and widening wage and income inequality. David M. Kotz, professor of economics at the University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst, UMass) is a public research university in Amherst, Massachusetts and the sole public land-grant university in Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded in 1863 as an agricultural college, it ...
, contends that neoliberalism "is based on the thorough domination of labor by capital."David M Kotz, The Rise and Fall of Neoliberal Capitalism
'' (
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2015), p. 43
/ref> As such, the advent of the neoliberal era has seen a sharp increase in income inequality through the decline of unionization, stagnant wages for workers and the rise of CEO supersalaries. According to
Emmanuel Saez
Emmanuel Saez (born November 26, 1972) is a French, naturalized American economist who is Professor of Economics at the University of California, Berkeley. His work, done with Thomas Piketty and Gabriel Zucman, includes tracking the incomes of th ...
:
Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvan ...
political science professor Pamela Blackmon attributes the trends of growing poverty and income inequality to the convergence of several neoliberal policies during Ronald Reagan's presidency, including the decreased funding of education, decreases in the top marginal tax rates, and shifts in transfer programs for those in poverty. Journalist Mark Bittman
Mark Bittman (born February 17, 1950) is an American food journalist, author, and former columnist for ''The New York Times''. Currently, he is a fellow at the Union of Concerned Scientists. Bittman has promoted VB6 (Vegan Before 6:00), a flexit ...
echoes this sentiment in a 2014 piece for ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'':
Fred L. Block
Fred L. Block (born June 28, 1947) is an American Sociology, sociologist, and Research Professor of Sociology at University of California, Davis, UC-Davis. Block is widely regarded as one of the world’s leading economic and political sociologist ...
and Margaret Somers
Margaret R. Somers is an American sociologist and Professor of Sociology and History at the University of Michigan She is the recipient of the inaugural Lewis A. Coser Award for Innovation and Theoretical Agenda-Setting in Sociology, Somers's wor ...
, in expanding on Karl Polanyi's critique of ''laissez-faire'' theories in '' The Great Transformation'', argue that Polanyi's analysis helps to explain why the revival of such ideas has contributed to the "persistent unemployment, widening inequality, and the severe financial crises that have stressed Western economies over the past forty years." John Schmitt and Ben Zipperer of the Center for Economic and Policy Research
The Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) is a progressive American think tank that specializes in economic policy. Based in Washington, D.C. CEPR was co-founded by economists Dean Baker and Mark Weisbrot in 1999.
Considered a left-lea ...
also point to economic liberalism as one of the causes of income inequality. They note that European nations, in particular the social democracies of Northern Europe with extensive and well funded welfare states
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equitabl ...
, have lower levels of income inequality and social exclusion than the United States.Schmitt, John and Ben Zipperer (2006).Is the U.S. a Good Model for Reducing Social Exclusion in Europe?
Center for Economic and Policy Research
The Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) is a progressive American think tank that specializes in economic policy. Based in Washington, D.C. CEPR was co-founded by economists Dean Baker and Mark Weisbrot in 1999.
Considered a left-lea ...
. Retrieved October 8, 2014.
See also
* Causes of poverty in the United States *Marginal revenue productivity theory of wages
The marginal revenue productivity theory of wages is a model of wage levels in which they set to match to the marginal revenue product of labor, MRP (the value of the marginal product of labor), which is the increment to revenues caused by the incr ...
*Wealth inequality in the United States
Wealth inequality in the United States is the unequal distribution of assets among residents of the United States. Wealth commonly includes the values of any homes, automobiles, personal valuables, businesses, savings, and investments, as wel ...
* Corporatocracy#United States
*Criticism of credit scoring systems in the United States
Credit scoring systems in the United States have garnered considerable criticism from various media outlets, consumer law organizations, government officials, debtors unions, and academics. Racial bias, discrimination against prospective employee ...
References
Further reading
* Weil, David.The Fissured Workplace: Why Work Became So Bad for So Many and What Can Be Done to Improve It
''
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2014.
External links
CBO-Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979-2007-October 25, 2011
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States income inequality (causes) Income in the United States Economic inequality in the United States
Income inequality in the United States
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in t ...