Castle Dore on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Castle Dore is an
Castle Dore is an
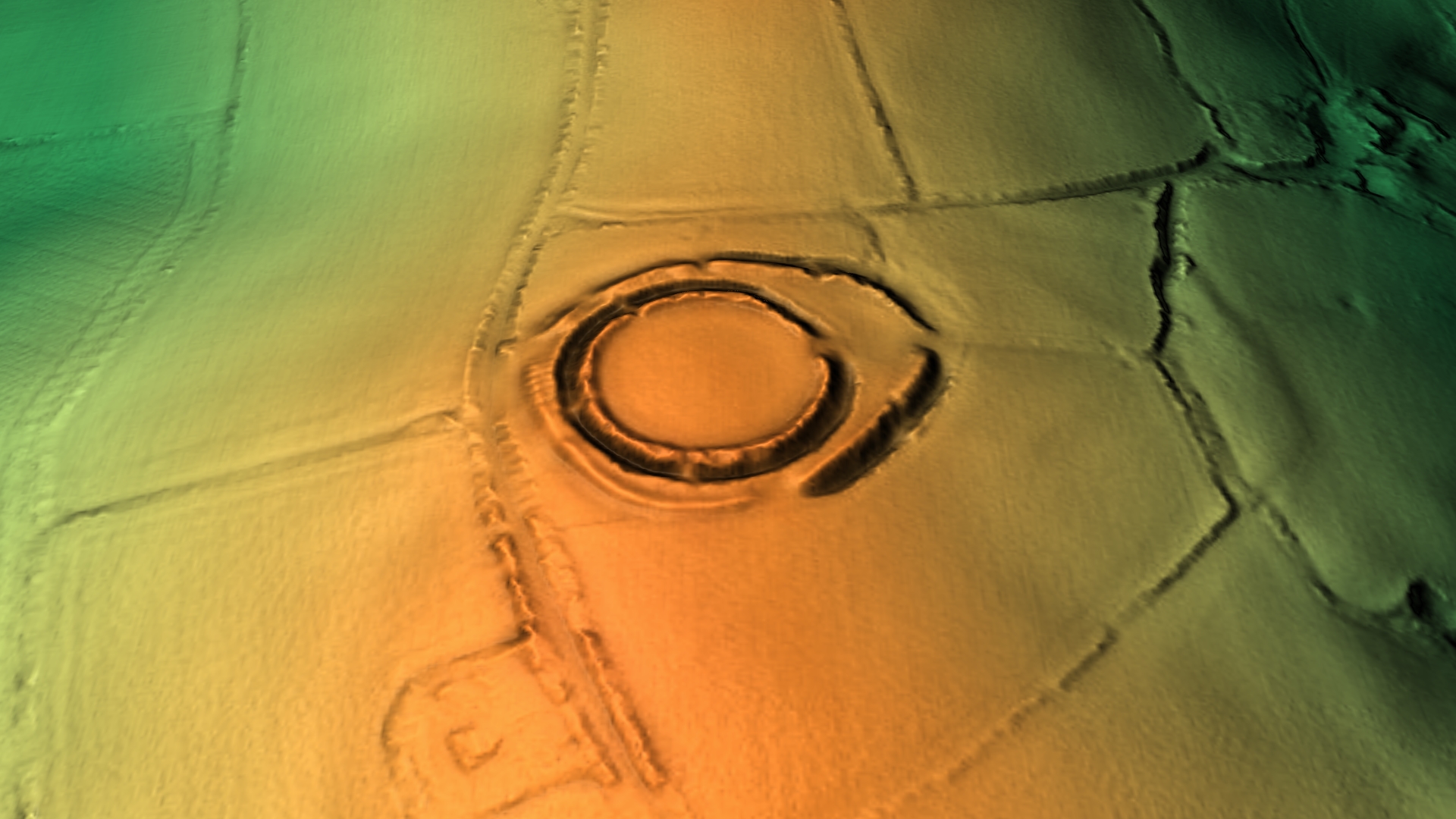 The perimeter of Castle Dore consists of two ditches (bivallate). The inner ditch is circular, measuring in diameter internally, and the outer ditch arced round it from the north to the south-east before widening in the north east to form an entrance. The ramparts (earth banks just inside the ditch) were raised later in the fort's history – from – the layout remained mostly the same aside from the entrance which was made more complex.
The perimeter of Castle Dore consists of two ditches (bivallate). The inner ditch is circular, measuring in diameter internally, and the outer ditch arced round it from the north to the south-east before widening in the north east to form an entrance. The ramparts (earth banks just inside the ditch) were raised later in the fort's history – from – the layout remained mostly the same aside from the entrance which was made more complex.
 Archaeologist
Archaeologist  During the English civil war, the final defeat of Essex's army was witnessed at the site. On 31 August 1644, whilst attempting a retreat from Lostwithiel to Fowey, Essex was forced to draw up his baggage train and remaining guns within the fort. Just before nightfall one regiment disbanded in disorder signalling impending surrender or death. By morning it was clear that his demoralised soldiers could not be trusted and Essex chose to flee.
During the English civil war, the final defeat of Essex's army was witnessed at the site. On 31 August 1644, whilst attempting a retreat from Lostwithiel to Fowey, Essex was forced to draw up his baggage train and remaining guns within the fort. Just before nightfall one regiment disbanded in disorder signalling impending surrender or death. By morning it was clear that his demoralised soldiers could not be trusted and Essex chose to flee.
 Castle Dore is an
Castle Dore is an Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
(ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales ...
) near Fowey
Fowey ( ; kw, Fowydh, meaning 'Beech Trees') is a port town and civil parish at the mouth of the River Fowey in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town has been in existence since well before the Norman invasion, with the local ch ...
in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
located at . It was probably occupied from the 5th or 4th centuries BC until the 1st century BC. It consists of two ditches surrounding a circular area in diameter. Excavated in the 1930s, it is one of the most intensively investigated Iron Age hillforts in Cornwall.
Description and history
 The perimeter of Castle Dore consists of two ditches (bivallate). The inner ditch is circular, measuring in diameter internally, and the outer ditch arced round it from the north to the south-east before widening in the north east to form an entrance. The ramparts (earth banks just inside the ditch) were raised later in the fort's history – from – the layout remained mostly the same aside from the entrance which was made more complex.
The perimeter of Castle Dore consists of two ditches (bivallate). The inner ditch is circular, measuring in diameter internally, and the outer ditch arced round it from the north to the south-east before widening in the north east to form an entrance. The ramparts (earth banks just inside the ditch) were raised later in the fort's history – from – the layout remained mostly the same aside from the entrance which was made more complex.
Ralegh Radford
Courtenay Arthur Ralegh Radford (7 November 1900 – 27 December 1998) was an English archaeologist and historian who pioneered the exploration of the Dark Ages of Britain and popularised his findings in many official guides and surveys for the O ...
led excavations at Castle Dore between 1936 and 1937. Five decades later, the work still represented the most intensive investigation of a hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
in Cornwall. At the time of Radford's work, archaeologists tended to concentrate on the defences in the course of examining hillforts; Radford, however, investigated the interior and found posthole
In archaeology a posthole or post-hole is a cut feature used to hold a surface timber or stone. They are usually much deeper than they are wide; however, truncation may not make this apparent. Although the remains of the timber may survive, most p ...
s belonging to huts of at least two distinct phases of occupation.
Radford's initial interpretation was that the fort had been reoccupied in the 5th and 6th centuries AD; however, later reinterpretation based on a greater understanding of post-Roman archaeology concluded that the occupation at Castle Dore was restricted to the Iron Age. The use of radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
at other sites lead to greater understanding of the contexts within which Iron Age pottery was found. The dating of the first phase of activity at Castle Dore was revised from the 2nd century BC to the 5th or 4th centuries BC.
 During the English civil war, the final defeat of Essex's army was witnessed at the site. On 31 August 1644, whilst attempting a retreat from Lostwithiel to Fowey, Essex was forced to draw up his baggage train and remaining guns within the fort. Just before nightfall one regiment disbanded in disorder signalling impending surrender or death. By morning it was clear that his demoralised soldiers could not be trusted and Essex chose to flee.
During the English civil war, the final defeat of Essex's army was witnessed at the site. On 31 August 1644, whilst attempting a retreat from Lostwithiel to Fowey, Essex was forced to draw up his baggage train and remaining guns within the fort. Just before nightfall one regiment disbanded in disorder signalling impending surrender or death. By morning it was clear that his demoralised soldiers could not be trusted and Essex chose to flee.
See also
*'' Castle Dor'', a 1942 historical novel byDaphne du Maurier
Dame Daphne du Maurier, Lady Browning, (; 13 May 1907 – 19 April 1989) was an English novelist, biographer and playwright. Her parents were actor-manager Sir Gerald du Maurier and his wife, actress Muriel Beaumont. Her grandfather was Geor ...
(1961)
* Castle an Dinas, St. Columb Major
*Prideaux Castle
Prideaux Castle is a multivallate Iron Age hillfort situated atop a 133 m (435 ft) high conical hill near the southern boundary of the parish of Luxulyan, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is also sometimes referred to as ''Pridea ...
References
Notes Bibliography * *Further reading
* {{Cornwall, state=collapsed Hill forts in Cornwall Iron Age Britain Locations associated with Arthurian legend Iron Age sites in Cornwall Military history of Cornwall