Carbon lock-in on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carbon lock-in refers to the self-perpetuating inertia created by large
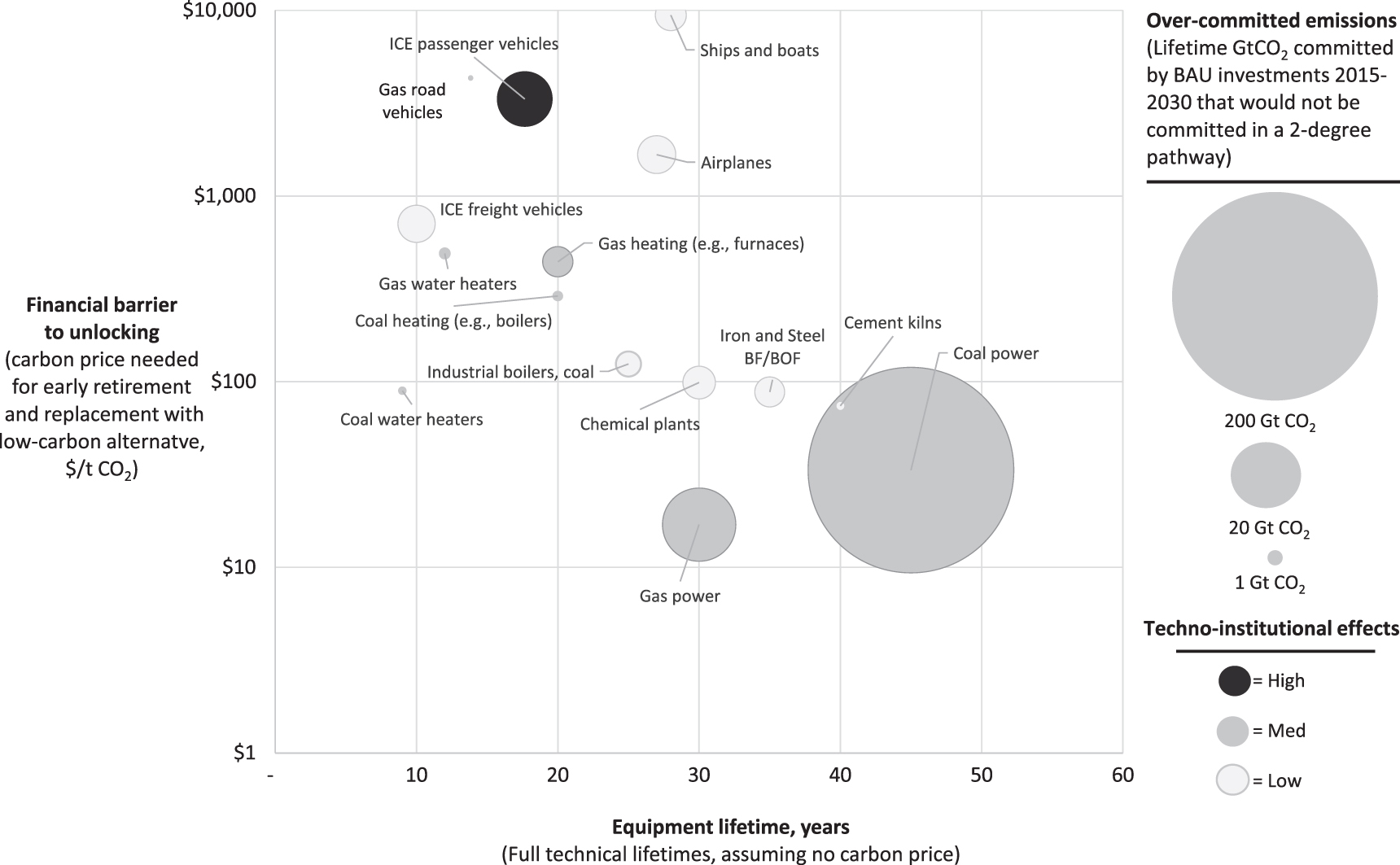 The carbon lock-in concept has gained more attention as China’s rapid industrial economic development has progressed. The concern is that if China pursues the same fossil-fuel driven economic development models of established industrial counties, building out extensive automobile-based infrastructures and fossil-fuel powered energy systems, they will lock-in persistent and growing
The carbon lock-in concept has gained more attention as China’s rapid industrial economic development has progressed. The concern is that if China pursues the same fossil-fuel driven economic development models of established industrial counties, building out extensive automobile-based infrastructures and fossil-fuel powered energy systems, they will lock-in persistent and growing
How ready is ‘capture ready’? - Preparing the UK power sector for carbon capture and storage.
Nils Markusson, Stuart Haszeldine. Commissioned independent report for WWF UK. May 2008. ; Carbon Lock-in and Policy:
Prospects for a global deal on climate change: Three European views.
mckinsey.com Sustainability & Resource Productivity. March 2009.
Phil England. The Ecologist. 2 July 2009.
William S. Becker. Huffington Post. 25 May 2011.
Carbon Market Prepares for Ukraine Deal.
Bridges Trade, BioRes News Digest. 12 June 2009.
David Morgan.
fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
-based energy systems that inhibits public and private efforts to introduce alternative energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a Orders of magnitude (time), human timescale. It includes sources such as Solar power, sunlight, wind power, wind, the movement of Hydropo ...
technologies. Related to the concept of technological lock-in, the concept is most used in relation to the challenge of altering the current energy infrastructure to respond to global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
.
The concept and term was first coined by Gregory C. Unruh in a 1999 Fletcher School
The Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy is the graduate school of international affairs of Tufts University, in Medford, Massachusetts. The School is one of America's oldest graduate schools of international relations and is well-ranked in its ...
, Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
doctoral thesis entitled "Escaping Carbon Lock-In." It has since gained popularity in climate change policy discussions, especially those focused on preventing the globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
of carbon lock-in to rapidly industrializing countries like China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.
The source of carbon lock-in inertia in energy systems arises from the co-evolution of large interdependent technological networks and the social institution
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions a ...
s and cultural practice
Cultural practice is the manifestation of a culture or sub-culture, especially in regard to the traditional and customary practices of a particular ethnic or other cultural groups.
The term is gaining in importance due to the increased controver ...
s that support and benefit from system growth. The growth of the system is fostered by increasing returns to scale
In economics, returns to scale describe what happens to long-run returns as the scale of production increases, when all input levels including physical capital usage are variable (able to be set by the firm). The concept of returns to scale arises ...
.
Introduction
According to Unruh: The concept emerged in response to what is termed the "climate policy
The politics of climate change results from different perspectives on how to respond to climate change. Global warming is driven largely by the emissions of greenhouse gases due to human economic activity, especially the burning of fossil fuels, ...
paradox," which recognizes that there is substantial scientific consensus
Scientific consensus is the generally held judgment, position, and opinion of the majority or the supermajority of scientists in a particular field of study at any particular time.
Consensus is achieved through scholarly communication at confe ...
that climate change is a real and present threat to humans and other species uniquely adapted to current climatic conditions. Similarly there is evidence that technologies exist which can lower the carbon intensity of economic activity
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and intera ...
in a cost-effective manner, including energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
innovations as well as some renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
applications. The existence of these apparent "win-win" no-regrets opportunities for society to act on climate concerns creates a paradox. If such technologies exist, and they are cost effective and help minimize climate-forcing emissions, why aren't they diffusing more rapidly? The conjecture is that industrial economies have become locked into fossil fuel technologies by past investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
s and policy decisions, the effects of positive feedback on increasing returns, and the economic growth of energy infrastructure.
A Co-Evolutionary Process
Carbon lock-in emerges over time asenergy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
and economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and o ...
in industrialized countries has proceeded. The carbon lock-in framework builds hierarchically from individual technological artifacts, usually manufactured by for-profit organizations, to technological systems of interdependent artifacts. As these systems grow, they begin to have important societal implications drawing in government regulation of the system’s growth and development. The government’s involvement with system management, be it for safety, universal service or other national interests, institutionalizes the system and signals the emergence of a techno-institutional complex.
Over time consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or uses purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. T ...
s and the public adapt their lifestyles to the capabilities of the technology and the system becomes embedded in society. Examples of this process can be seen in the growth of automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
-based transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
systems and fossil-fuel powered energy systems.
It is this co-evolutionary positive feedback development process that creates the lock-in condition and associated barriers to the diffusion of alternative technologies, even those with known superior environmental performance characteristics. A 2007 Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research and ...
report entitled “Carbon Lock-In: Barriers to Deploying Climate Change Mitigation Technologies” (sponsored by the U.S. Climate Change Technology Program, CCTP) classifies three major types of carbon lock-in barriers: cost effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) is a form of economic analysis that compares the relative costs and outcomes (effects) of different courses of action. Cost-effectiveness analysis is distinct from cost–benefit analysis, which assigns a monetar ...
, financial/legal and intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, cop ...
barriers. Escaping the lock-in condition requires overcoming these barriers.
Globalizing Carbon Lock-In
 The carbon lock-in concept has gained more attention as China’s rapid industrial economic development has progressed. The concern is that if China pursues the same fossil-fuel driven economic development models of established industrial counties, building out extensive automobile-based infrastructures and fossil-fuel powered energy systems, they will lock-in persistent and growing
The carbon lock-in concept has gained more attention as China’s rapid industrial economic development has progressed. The concern is that if China pursues the same fossil-fuel driven economic development models of established industrial counties, building out extensive automobile-based infrastructures and fossil-fuel powered energy systems, they will lock-in persistent and growing greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and lar ...
well into the future. The same arguments can be extended to all rapidly industrializing
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
countries including India. This concern is arising as scientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
is indicating that current emission growth must be stopped and global emissions reduced by upwards of 60% if humanity is to prevent substantial unwanted climate disruption.
Recent studies by Steven J. Davis and co-authors have quantified the future emissions that can be expected to be produced by current energy infrastructure and the magnitude of lock-in related to power plants being built each year in China and elsewhere.
See also
*Path dependence
Path dependence is a concept in economics and the social sciences, referring to processes where past events or decisions constrain later events or decisions. It can be used to refer to outcomes at a single point in time or to long-run equilibria ...
Notes and references
;General references * * * * * ;ReferencesFurther reading
*External links
; Addressing Carbon Lock-in through Carbon Capture and Storage:How ready is ‘capture ready’? - Preparing the UK power sector for carbon capture and storage.
Nils Markusson, Stuart Haszeldine. Commissioned independent report for WWF UK. May 2008. ; Carbon Lock-in and Policy:
Prospects for a global deal on climate change: Three European views.
mckinsey.com Sustainability & Resource Productivity. March 2009.
Phil England. The Ecologist. 2 July 2009.
William S. Becker. Huffington Post. 25 May 2011.
Carbon Market Prepares for Ukraine Deal.
Bridges Trade, BioRes News Digest. 12 June 2009.
David Morgan.
Global Arab Network
Global Arab Network (GAN) (in Arabic غلوبال اراب نتورك) is a comprehensive news and information service about the Arab world in English and Arabic, registered and based in London
London is the capital and largest city of En ...
- English News. 19 September 2009.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carbon Lock-In
Fossil fuels
Climate change and society
Economics and climate change