Cape wild dog on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called the painted dog or Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a
Dogs
', W.H. Lizars, Edinburgh, p. 261–69 The African wild dog was first described scientifically in 1820 by Coenraad Jacob Temminck, after examining a specimen from the coast of
 The African wild dog possesses the most specialized adaptations among the canids for coat colour, diet, and for pursuing its prey through its cursorial (running) ability. It possesses a graceful skeleton, and the loss of the first digit on its forefeet increases its stride and speed. This adaptation allows it to pursue prey across open plains for long distances. The teeth are generally
The African wild dog possesses the most specialized adaptations among the canids for coat colour, diet, and for pursuing its prey through its cursorial (running) ability. It possesses a graceful skeleton, and the loss of the first digit on its forefeet increases its stride and speed. This adaptation allows it to pursue prey across open plains for long distances. The teeth are generally
 In 2018,
In 2018,
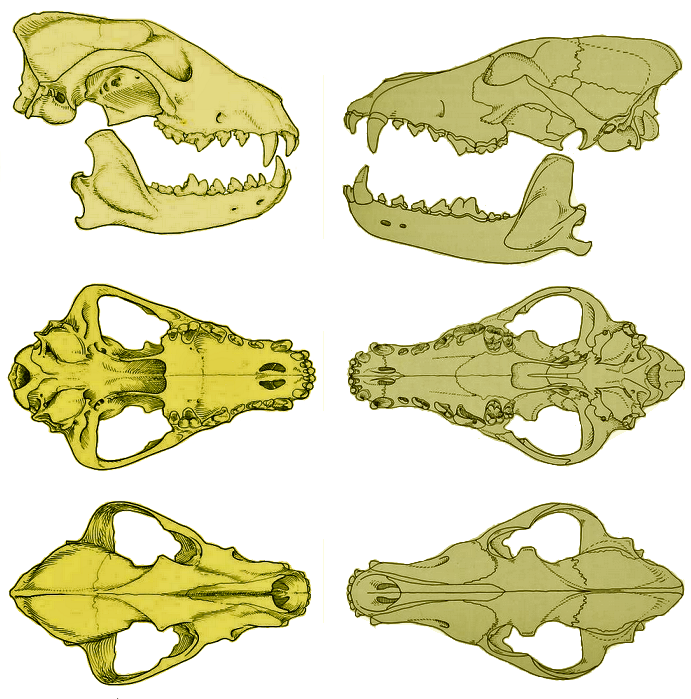 The African wild dog is the bulkiest and most solidly built of African canids.Rosevear, D. R. (1974).
The African wild dog is the bulkiest and most solidly built of African canids.Rosevear, D. R. (1974).
The carnivores of West Africa
'. London : Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). pp. 75–91. . The species stands in shoulder height, measures in head-and-body length and has a tail length of . Body weight of adults range from . On average, dogs from East Africa weigh around while in southern Africa, males reportedly weighed a mean of and females a mean of . By body mass, they are only outsized amongst other extant canids by the gray wolf The fur of the African wild dog differs significantly from that of other canids, consisting entirely of stiff bristle-hairs with no underfur. It gradually loses its fur as it ages, with older individuals being almost naked. Colour variation is extreme, and may serve in visual identification, as African wild dogs can recognise each other at distances of . Some geographic variation is seen in coat colour, with northeastern African specimens tending to be predominantly black with small white and yellow patches, while southern African ones are more brightly coloured, sporting a mix of brown, black and white coats. Much of the species' coat patterning occurs on the trunk and legs. Little variation in facial markings occurs, with the muzzle being black, gradually shading into brown on the cheeks and forehead. A black line extends up the forehead, turning blackish-brown on the back of the ears. A few specimens sport a brown teardrop-shaped mark below the eyes. The back of the head and neck are either brown or yellow. A white patch occasionally occurs behind the fore legs, with some specimens having completely white fore legs, chests and throats. The tail is usually white at the tip, black in the middle and brown at the base. Some specimens lack the white tip entirely, or may have black fur below the white tip. These coat patterns can be asymmetrical, with the left side of the body often having different markings from that of the right.
The fur of the African wild dog differs significantly from that of other canids, consisting entirely of stiff bristle-hairs with no underfur. It gradually loses its fur as it ages, with older individuals being almost naked. Colour variation is extreme, and may serve in visual identification, as African wild dogs can recognise each other at distances of . Some geographic variation is seen in coat colour, with northeastern African specimens tending to be predominantly black with small white and yellow patches, while southern African ones are more brightly coloured, sporting a mix of brown, black and white coats. Much of the species' coat patterning occurs on the trunk and legs. Little variation in facial markings occurs, with the muzzle being black, gradually shading into brown on the cheeks and forehead. A black line extends up the forehead, turning blackish-brown on the back of the ears. A few specimens sport a brown teardrop-shaped mark below the eyes. The back of the head and neck are either brown or yellow. A white patch occasionally occurs behind the fore legs, with some specimens having completely white fore legs, chests and throats. The tail is usually white at the tip, black in the middle and brown at the base. Some specimens lack the white tip entirely, or may have black fur below the white tip. These coat patterns can be asymmetrical, with the left side of the body often having different markings from that of the right.

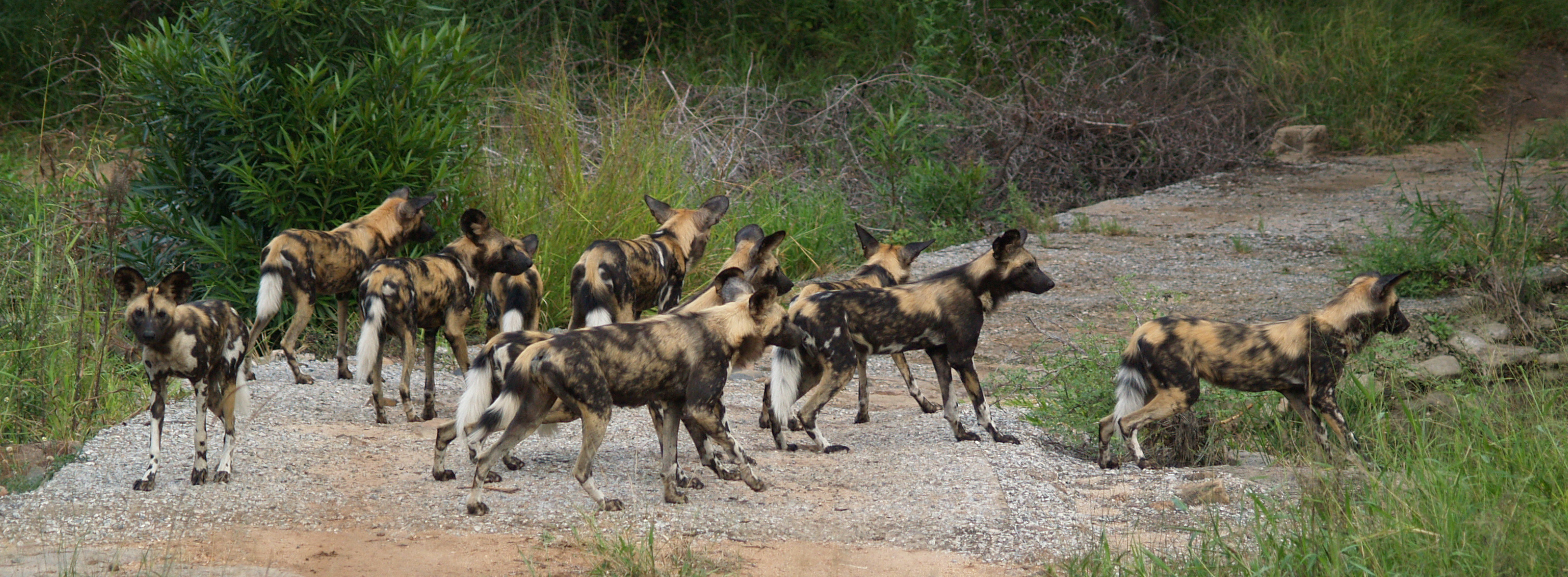
 The African wild dog has very strong social bonds, stronger than those of sympatric lions and spotted hyenas; thus, solitary living and hunting are extremely rare in the species.Kingdon, Jonathan (1988). ''East African mammals: an atlas of evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part 1''. University of Chicago Press. pp. 36–53. . It lives in permanent packs consisting of two to 27 adults and yearling pups. The typical pack size in Kruger National Park and the Maasai Mara is four or five adults, while packs in Moremi and Selous contain eight or nine. However, larger packs have been observed and temporary aggregations of hundreds of individuals may have gathered in response to the seasonal migration of vast
The African wild dog has very strong social bonds, stronger than those of sympatric lions and spotted hyenas; thus, solitary living and hunting are extremely rare in the species.Kingdon, Jonathan (1988). ''East African mammals: an atlas of evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part 1''. University of Chicago Press. pp. 36–53. . It lives in permanent packs consisting of two to 27 adults and yearling pups. The typical pack size in Kruger National Park and the Maasai Mara is four or five adults, while packs in Moremi and Selous contain eight or nine. However, larger packs have been observed and temporary aggregations of hundreds of individuals may have gathered in response to the seasonal migration of vast
 A species-wide study showed that by preference, where available, five species were the most regularly selected prey, namely the greater kudu,
A species-wide study showed that by preference, where available, five species were the most regularly selected prey, namely the greater kudu,
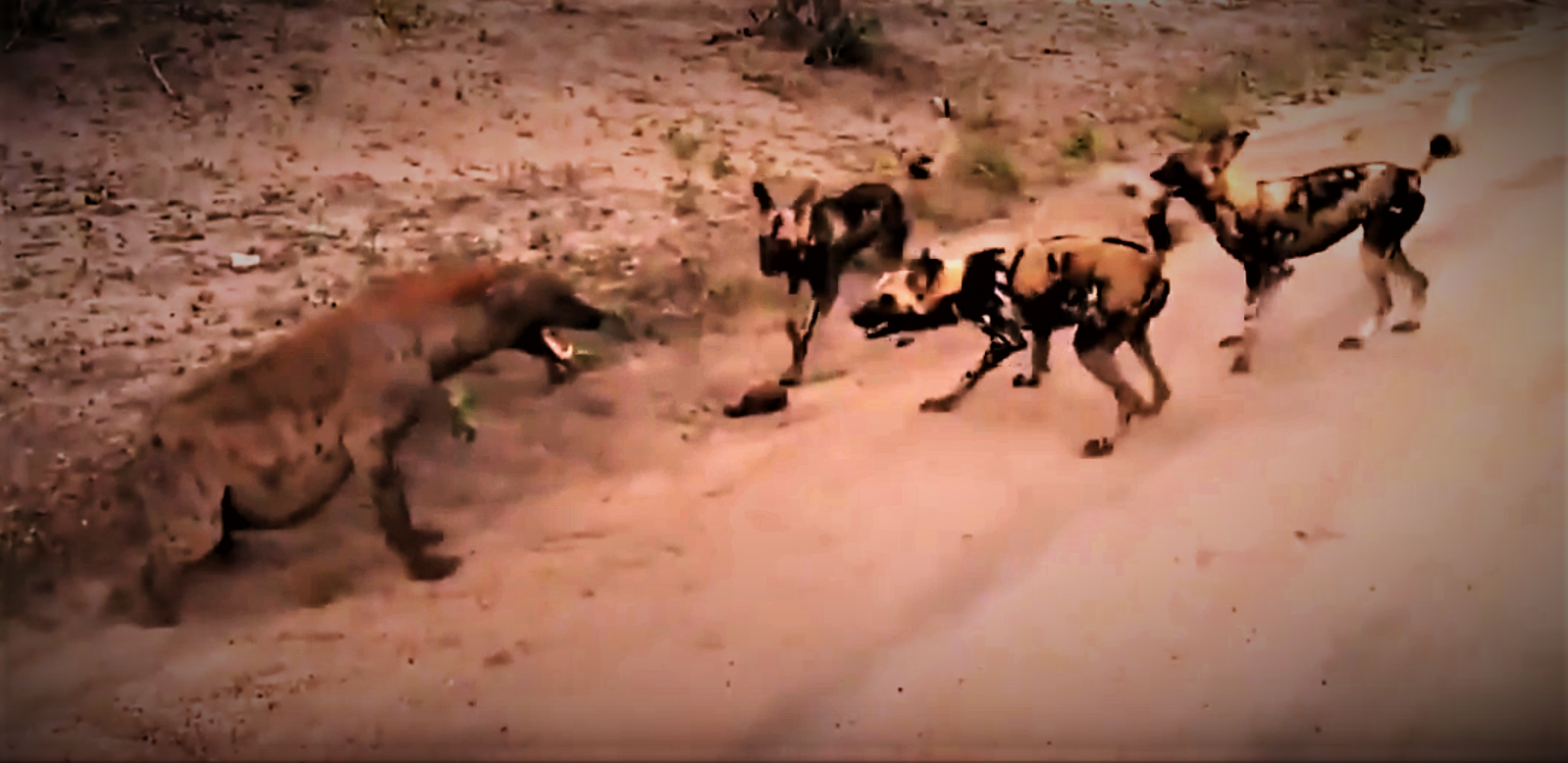 Lions dominate African wild dogs and are a major source of mortality for both adults and pups. Population densities of African wild dogs are low in areas where lions are more abundant. One pack reintroduced into Etosha National Park was destroyed by lions. A population crash in lions in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Ngorongoro Crater during the 1960s resulted in an increase in African wild dog sightings, only for their numbers to decline once the lions recovered. As with other large predators killed by lion prides, the dogs are usually killed and left uneaten by the lions, indicating the competitive rather than predatory nature of the larger species' dominance. However, a few cases have been reported of old and wounded lions falling prey to African wild dogs.Schaller, G. B. (1972). ''The Serengeti lion: A study of predator-prey relations''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 188. . On occasion, packs of wild dogs have been observed defending pack members attacked by single lions, sometimes successfully. One pack in the Okavango in March 2016 was photographed by safari guides waging "an incredible fight" against a lioness that attacked a subadult dog at an impala kill, which forced the lioness to retreat, although the subadult dog died. A pack of four wild dogs was observed furiously defending an old adult male dog from a male lion that attacked it at a kill; the dog survived and rejoined the pack.
Spotted hyenas are important kleptoparasites and follow packs of African wild dogs to appropriate their kills. They typically inspect areas where African wild dogs have rested and eat any food remains they find. When approaching African wild dogs at a kill, solitary hyenas approach cautiously and attempt to take off with a piece of meat unnoticed, though they may be mobbed in the attempt. When operating in groups, spotted hyenas are more successful in pirating African wild dog kills, though the latter's greater tendency to assist each other puts them at an advantage against spotted hyenas, which rarely work cooperatively. Cases of African wild dogs scavenging from spotted hyenas are rare. Although African wild dog packs can easily repel solitary hyenas, on the whole, the relationship between the two species is a one-sided benefit for the hyenas, with African wild dog densities being negatively correlated with high hyena populations. Beyond piracy, cases of interspecific killing of African wild dogs by spotted hyenas are documented. African wild dogs are apex predators, normally only fatally losing contests to larger social carnivores, although anecdotally Nile crocodiles may opportunistically and rarely prey upon a wild dog. When briefly unprotected, wild dog pups may occasionally be vulnerable to large eagles, such as the martial eagle, when they venture out of their dens.
Lions dominate African wild dogs and are a major source of mortality for both adults and pups. Population densities of African wild dogs are low in areas where lions are more abundant. One pack reintroduced into Etosha National Park was destroyed by lions. A population crash in lions in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Ngorongoro Crater during the 1960s resulted in an increase in African wild dog sightings, only for their numbers to decline once the lions recovered. As with other large predators killed by lion prides, the dogs are usually killed and left uneaten by the lions, indicating the competitive rather than predatory nature of the larger species' dominance. However, a few cases have been reported of old and wounded lions falling prey to African wild dogs.Schaller, G. B. (1972). ''The Serengeti lion: A study of predator-prey relations''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 188. . On occasion, packs of wild dogs have been observed defending pack members attacked by single lions, sometimes successfully. One pack in the Okavango in March 2016 was photographed by safari guides waging "an incredible fight" against a lioness that attacked a subadult dog at an impala kill, which forced the lioness to retreat, although the subadult dog died. A pack of four wild dogs was observed furiously defending an old adult male dog from a male lion that attacked it at a kill; the dog survived and rejoined the pack.
Spotted hyenas are important kleptoparasites and follow packs of African wild dogs to appropriate their kills. They typically inspect areas where African wild dogs have rested and eat any food remains they find. When approaching African wild dogs at a kill, solitary hyenas approach cautiously and attempt to take off with a piece of meat unnoticed, though they may be mobbed in the attempt. When operating in groups, spotted hyenas are more successful in pirating African wild dog kills, though the latter's greater tendency to assist each other puts them at an advantage against spotted hyenas, which rarely work cooperatively. Cases of African wild dogs scavenging from spotted hyenas are rare. Although African wild dog packs can easily repel solitary hyenas, on the whole, the relationship between the two species is a one-sided benefit for the hyenas, with African wild dog densities being negatively correlated with high hyena populations. Beyond piracy, cases of interspecific killing of African wild dogs by spotted hyenas are documented. African wild dogs are apex predators, normally only fatally losing contests to larger social carnivores, although anecdotally Nile crocodiles may opportunistically and rarely prey upon a wild dog. When briefly unprotected, wild dog pups may occasionally be vulnerable to large eagles, such as the martial eagle, when they venture out of their dens.
 Artistic depictions of African wild dogs are prominent on cosmetic palettes and other objects from Egypt's Prehistoric Egypt, predynastic period, likely symbolising order over chaos and the transition between the wild and the domestic dog. Predynastic hunters may have also identified with the African wild dog, as the Hunters Palette shows them wearing the animals' tails on their belts. By the History of ancient Egypt#Dynastic Egypt, dynastic period, African wild dog illustrations became much less represented, and the animal's symbolic role was largely taken over by the wolf.Hendrickx, S. (2006). The dog, the ''Lycaon pictus'' and order over chaos in Predynastic Egypt. [in:] Kroeper, K.; Chłodnicki, M. & Kobusiewicz, M. (eds.), ''Archaeology of Early Northeastern Africa''. Studies in African Archaeology 9. Poznań: Poznań Archaeological Museum: 723–749.
Artistic depictions of African wild dogs are prominent on cosmetic palettes and other objects from Egypt's Prehistoric Egypt, predynastic period, likely symbolising order over chaos and the transition between the wild and the domestic dog. Predynastic hunters may have also identified with the African wild dog, as the Hunters Palette shows them wearing the animals' tails on their belts. By the History of ancient Egypt#Dynastic Egypt, dynastic period, African wild dog illustrations became much less represented, and the animal's symbolic role was largely taken over by the wolf.Hendrickx, S. (2006). The dog, the ''Lycaon pictus'' and order over chaos in Predynastic Egypt. [in:] Kroeper, K.; Chłodnicki, M. & Kobusiewicz, M. (eds.), ''Archaeology of Early Northeastern Africa''. Studies in African Archaeology 9. Poznań: Poznań Archaeological Museum: 723–749.
African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) from NE Kenya: Recent records and conservation issues
Zoology Department Research Report. National Museum of Kenya. * Wozencraft, W. C. (November 2005). D. E. Wilson and D. M. Reeder (eds.)
''Mammal Species of the World''
(3rd edition). Johns Hopkins University Press. . * Van Lawick, H. & Goodall, J. (1971). ''Innocent Killers''. Houghton Mifflin Company Boston
painteddog.org
Painted Dog Conservation Website
painteddog.co.uk/
Painted Dog Conservation United Kingdom Website
African Wild Dog Conservancy
African Wild Dog Watch
Wild Dog conservation in Zimbabwe
* [http://www.awf.org/wildlives/4548 African wild dogs: Wildlife summary] at African Wildlife Foundation
The Zambian Carnivore Programme
Save the African wild dog
Wildentrust.org
Painted Dog Conservation (conservation organization)
Photos, videos and information from ARKive
ibream wild dog project
at WCN Wildlife Conservation Network {{Authority control African wild dogs, Apex predators Canina (subtribe) Carnivorans of Africa Endangered fauna of Africa Fauna of the Sahara Mammals described in 1820, African wild dog Mammals of Sub-Saharan Africa Species endangered by habitat fragmentation
native species
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is equ ...
to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
'' Lycaon'', which is distinguished from ''Canis
''Canis'' is a genus of the Caninae which includes multiple extant species, such as wolves, dogs, coyotes, and golden jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-developed skulls and de ...
'' by dentition highly specialised for a hypercarnivorous
A hypercarnivore is an animal which has a diet that is more than 70% meat, either via active predation or by scavenging. The remaining non-meat diet may consist of non-animal foods such as fungi, fruits or other plant material. Some extant exampl ...
diet, and by a lack of dewclaw
A dewclaw is a digit – vestigial in some animals – on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles (including some extinct orders, like certain theropods). It commonly grows higher on the leg than the rest of the foot, such that in digit ...
s. It is estimated that about 6,600 adults (including 1,400 mature individuals) live in 39 subpopulations that are all threatened by habitat fragmentation, human persecution, and outbreaks of disease. As the largest subpopulation probably comprises fewer than 250 individuals, the African wild dog has been listed as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and in ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
since 1990.
The species is a specialised diurnal hunter of antelopes, which it catches by chasing them to exhaustion. Its natural enemies are lions and spotted hyenas: the former will kill the dogs where possible, whilst hyenas are frequent kleptoparasite
Kleptoparasitism (etymologically, parasitism by theft) is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, which can mean when foo ...
s.
Like other canids, the African wild dog regurgitates food for its young, but also extends this action to adults, as a central part of the pack's social life. The young are allowed to feed first on carcasses.
The African wild dog has been respected in several hunter-gatherer societies, particularly those of the San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia ...
and Prehistoric Egypt.
Naming
The English language has several names for the African wild dog, including African hunting dog, Cape hunting dog, painted hunting dog, painted dog, and painted lycaon. One conservation organisation is promoting the name 'painted wolf' as a way of rebranding the species, as wild dog has several negative connotations that could be detrimental to its image. Nevertheless, the name "African wild dog" is still widely used, However, the name "painted dog" was found to be the most likely to counteract negative perceptions of the species.Taxonomic and evolutionary history
Taxonomy
The earliest written reference to the species appears to be from Oppian, who wrote of the ''thoa'', a hybrid between the wolf and leopard, which resembles the former in shape and the latter in colour. Solinus's ''Collea rerum memorabilium'' from the third century AD describes a multicoloured wolf-like animal with a mane native toEthiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.Smith, C. H. (1839). Dogs
', W.H. Lizars, Edinburgh, p. 261–69 The African wild dog was first described scientifically in 1820 by Coenraad Jacob Temminck, after examining a specimen from the coast of
Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
. He named the animal ''Hyaena picta'', erroneously classifying it as a species of hyena. It was later recognised as a canid
Canidae (; from Latin, '' canis'', " dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found withi ...
by Joshua Brookes
Joshua Brookes (24 November 1761 – 10 January 1833) was a British anatomist and naturalist.
Early life
Brookes studied under William Hunter, William Hewson, Andrew Marshall, and John Sheldon, in London. He then attended the practice of ...
in 1827, and renamed ''Lycaon tricolor''. The root word of ''Lycaon'' is the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
λυκαίος (''lykaios''), meaning "wolf-like". The specific epithet ''pictus'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "painted"), which derived from the original ''picta'', was later returned to it, in conformity with the International Rules on Taxonomic Nomenclature.Bothma, J. du P. & Walker, C. (1999). ''Larger Carnivores of the African Savannas'', Springer, pp. 130–157,
Paleontologist George G. Simpson placed the African wild dog, the dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
, and the bush dog together in the subfamily Simocyon
''Simocyon'' ("short-snouted dog") is a genus of extinct carnivoran mammal in the family Ailuridae. ''Simocyon'', which was about the size of a mountain lion, lived in the late Miocene and early Pliocene epochs, and has been found in Europe, Asi ...
inae on the basis of all three species having similarly trenchant carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
s. This grouping was disputed by Juliet Clutton-Brock
Juliet Clutton-Brock, FSA, FZS (6 September 1933 – 21 September 2015) was an English zooarchaeologist and curator, specialising in domesticated mammals. From 1969 to 1993, she worked at the Natural History Museum. Between 1999 and 2006, she w ...
, who argued that, other than dentition, too many differences exist between the three species to warrant classifying them in a single subfamily.
Evolution
 The African wild dog possesses the most specialized adaptations among the canids for coat colour, diet, and for pursuing its prey through its cursorial (running) ability. It possesses a graceful skeleton, and the loss of the first digit on its forefeet increases its stride and speed. This adaptation allows it to pursue prey across open plains for long distances. The teeth are generally
The African wild dog possesses the most specialized adaptations among the canids for coat colour, diet, and for pursuing its prey through its cursorial (running) ability. It possesses a graceful skeleton, and the loss of the first digit on its forefeet increases its stride and speed. This adaptation allows it to pursue prey across open plains for long distances. The teeth are generally carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
-shaped, and its premolars
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
are the largest relative to body size of any living carnivoran
Carnivora is a monophyletic order of placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all cat-like and dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are formally referred to as carnivorans, ...
except for the spotted hyena. On the lower carnassials (first lower molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
), the talonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone ...
has evolved to become a cutting blade for flesh-slicing, with a reduction or loss of the post-carnassial molars. This adaptation also occurs in two other hypercarnivores – the dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
and the bush dog. The African wild dog exhibits one of the most varied coat colours among the mammals. Individuals differ in patterns and colours, indicating a diversity of the underlying genes. The purpose of these coat patterns may be an adaptation for communication, concealment, or temperature regulation. In 2019, a study indicated that the ''lycaon'' lineage diverged from ''Cuon'' and ''Canis'' 1.7 million years ago through this suite of adaptations, and these occurred at the same time as large ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ca ...
(its prey) diversified.
The oldest ''L. pictus'' fossil dates back to 200,000 years ago and was found in HaYonim Cave, Israel. The evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of the African wild dog is poorly understood due to the scarcity of fossil finds. Some authors consider the extinct ''Canis'' subgenus ''Xenocyon
''Xenocyon'' ("strange dog") is an extinct subgenus of ''Canis''. The group includes ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''africanus'', ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''antonii'' and ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''falconeri'' that gave rise to ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'' ...
'' as ancestral to both the genus ''Lycaon'' and the genus '' Cuon'', which lived throughout Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
and Africa from the Early Pleistocene to the early Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
. Others propose that ''Xenocyon'' should be reclassified as ''Lycaon''. The species ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''falconeri'' shared the African wild dog's absent first metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones ar ...
(dewclaw
A dewclaw is a digit – vestigial in some animals – on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles (including some extinct orders, like certain theropods). It commonly grows higher on the leg than the rest of the foot, such that in digit ...
), though its dentition was still relatively unspecialised. This connection was rejected by one author because ''C''. (''X''.) ''falconeri'' lacks metacarpal, which is a poor indication of phylogenetic closeness to the African wild dog, and the dentition was too different to imply ancestry.
Another ancestral candidate is the Plio-Pleistocene '' L. sekowei'' of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
on the basis of distinct accessory cusps on its premolars and anterior accessory cuspids on its lower premolars. These adaptions are found only in ''Lycaon'' among living canids, which shows the same adaptations to a hypercarnivorous diet. ''L. sekowei'' had not yet lost the first metacarpal absent in ''L. pictus'' and was more robust than the modern species, having 10% larger teeth.
The African wild dog genetically diverged from other canid lineages between and is thought to be isolated from gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HG ...
with other canid species.
Admixture with the dhole
 In 2018,
In 2018, whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a ...
was used to compare the dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
(''Cuon alpinus'') with the African wild dog. There was strong evidence of ancient genetic admixture between the two. Today, their ranges are remote from each other; however, during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
era the dhole could be found as far west as Europe. The study proposes that the dhole's distribution may have once included the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, from where it may have admixed with the African wild dog in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. However, there is no evidence of the dhole having existed in the Middle East or North Africa.
Subspecies
, five subspecies are recognised by MSW3: Nevertheless, although the species is genetically diverse, these subspecific designations are not universally accepted. East African and Southern African wild dog populations were once thought to be genetically distinct, based on a small number of samples. More recent studies with a larger number of samples showed that extensive intermixing has occurred between East African and Southern African populations in the past. Some unique nuclear and mitochondrialallele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s are found in Southern African and northeastern African populations, with a transition zone encompassing Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalaha ...
, Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
and southeastern Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
between the two. The West African wild dog population may possess a unique haplotype, thus possibly constituting a truly distinct subspecies. The original Serengeti
The Serengeti ( ) ecosystem is a Geography of Africa, geographical region in Africa, spanning northern Tanzania. The protected area within the region includes approximately of land, including the Serengeti National Park and several game res ...
and Maasai Mara population of painted dogs is known to have possessed a unique genotypes, but these genotypes may be extinct.
Physical description
 The African wild dog is the bulkiest and most solidly built of African canids.Rosevear, D. R. (1974).
The African wild dog is the bulkiest and most solidly built of African canids.Rosevear, D. R. (1974). The carnivores of West Africa
'. London : Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). pp. 75–91. . The species stands in shoulder height, measures in head-and-body length and has a tail length of . Body weight of adults range from . On average, dogs from East Africa weigh around while in southern Africa, males reportedly weighed a mean of and females a mean of . By body mass, they are only outsized amongst other extant canids by the gray wolf
species complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each oth ...
.Estes, R. (1992). ''The behavior guide to African mammals: including hoofed mammals, carnivores, primates''. University of California Press. pp. 410–419. . Females are generally 3–7% smaller than males. Compared to members of the genus ''Canis'', the African wild dog is comparatively lean and tall, with outsized ears and lacking dewclaw
A dewclaw is a digit – vestigial in some animals – on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles (including some extinct orders, like certain theropods). It commonly grows higher on the leg than the rest of the foot, such that in digit ...
s. The middle two toepads are usually fused. Its dentition also differs from that of ''Canis'' by the degeneration of the last lower molar, the narrowness of the canines and proportionately large premolars, which are the largest relative to body size of any carnivore other than hyenas. The heel of the lower carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
M1 is crested with a single, blade-like cusp, which enhances the shearing capacity of the teeth, thus the speed at which prey can be consumed. This feature, termed "trenchant heel", is shared with two other canids: the Asian dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
and the South American bush dog. The skull is relatively shorter and broader than those of other canids.
 The fur of the African wild dog differs significantly from that of other canids, consisting entirely of stiff bristle-hairs with no underfur. It gradually loses its fur as it ages, with older individuals being almost naked. Colour variation is extreme, and may serve in visual identification, as African wild dogs can recognise each other at distances of . Some geographic variation is seen in coat colour, with northeastern African specimens tending to be predominantly black with small white and yellow patches, while southern African ones are more brightly coloured, sporting a mix of brown, black and white coats. Much of the species' coat patterning occurs on the trunk and legs. Little variation in facial markings occurs, with the muzzle being black, gradually shading into brown on the cheeks and forehead. A black line extends up the forehead, turning blackish-brown on the back of the ears. A few specimens sport a brown teardrop-shaped mark below the eyes. The back of the head and neck are either brown or yellow. A white patch occasionally occurs behind the fore legs, with some specimens having completely white fore legs, chests and throats. The tail is usually white at the tip, black in the middle and brown at the base. Some specimens lack the white tip entirely, or may have black fur below the white tip. These coat patterns can be asymmetrical, with the left side of the body often having different markings from that of the right.
The fur of the African wild dog differs significantly from that of other canids, consisting entirely of stiff bristle-hairs with no underfur. It gradually loses its fur as it ages, with older individuals being almost naked. Colour variation is extreme, and may serve in visual identification, as African wild dogs can recognise each other at distances of . Some geographic variation is seen in coat colour, with northeastern African specimens tending to be predominantly black with small white and yellow patches, while southern African ones are more brightly coloured, sporting a mix of brown, black and white coats. Much of the species' coat patterning occurs on the trunk and legs. Little variation in facial markings occurs, with the muzzle being black, gradually shading into brown on the cheeks and forehead. A black line extends up the forehead, turning blackish-brown on the back of the ears. A few specimens sport a brown teardrop-shaped mark below the eyes. The back of the head and neck are either brown or yellow. A white patch occasionally occurs behind the fore legs, with some specimens having completely white fore legs, chests and throats. The tail is usually white at the tip, black in the middle and brown at the base. Some specimens lack the white tip entirely, or may have black fur below the white tip. These coat patterns can be asymmetrical, with the left side of the body often having different markings from that of the right.
Behaviour
Social and reproductive behaviour

 The African wild dog has very strong social bonds, stronger than those of sympatric lions and spotted hyenas; thus, solitary living and hunting are extremely rare in the species.Kingdon, Jonathan (1988). ''East African mammals: an atlas of evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part 1''. University of Chicago Press. pp. 36–53. . It lives in permanent packs consisting of two to 27 adults and yearling pups. The typical pack size in Kruger National Park and the Maasai Mara is four or five adults, while packs in Moremi and Selous contain eight or nine. However, larger packs have been observed and temporary aggregations of hundreds of individuals may have gathered in response to the seasonal migration of vast
The African wild dog has very strong social bonds, stronger than those of sympatric lions and spotted hyenas; thus, solitary living and hunting are extremely rare in the species.Kingdon, Jonathan (1988). ''East African mammals: an atlas of evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part 1''. University of Chicago Press. pp. 36–53. . It lives in permanent packs consisting of two to 27 adults and yearling pups. The typical pack size in Kruger National Park and the Maasai Mara is four or five adults, while packs in Moremi and Selous contain eight or nine. However, larger packs have been observed and temporary aggregations of hundreds of individuals may have gathered in response to the seasonal migration of vast springbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
herds in Southern Africa.Nowak, Ronald M. (2005). ''Walker's Carnivores of the World''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press. p. 112. . Males and females have separate dominance hierarchies, with the latter usually being led by the oldest female. Males may be led by the oldest male, but these can be supplanted by younger specimens; thus, some packs may contain elderly male former pack leaders. The dominant pair typically monopolises breeding. The species differs from most other social species in that males remain in the natal pack, while females disperse (a pattern also found in primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s such as gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s, chimpanzees, and red colobus
Red colobuses are Old World monkeys of the genus ''Piliocolobus''. It was formerly considered a subgenus within the genus ''Procolobus'', which is now restricted to the olive colobus. They are closely related to the black-and-white colobus monke ...
es). Furthermore, males in any given pack tend to outnumber females 3:1. Dispersing females join other packs and evict some of the resident females related to the other pack members, thus preventing inbreeding and allowing the evicted individuals to find new packs of their own and breed. Males rarely disperse, and when they do, they are invariably rejected by other packs already containing males. Although arguably the most social canid, the species lacks the elaborate facial expressions and body language found in the gray wolf, likely because of the African wild dog's less hierarchical social structure. Furthermore, while elaborate facial expressions are important for wolves in re-establishing bonds after long periods of separation from their family groups, they are not as necessary to African wild dogs, which remain together for much longer periods.
African wild dog populations in East Africa appear to have no fixed breeding season, whereas those in Southern Africa usually breed during the April–July period. During estrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous ...
, the female is closely accompanied by a single male, which keeps other members of the same sex at bay. The copulatory tie characteristic of mating in most canids has been reported to be absent or very brief (less than one minute) in African wild dog, possibly an adaptation to the prevalence of larger predators in its environment. The gestation period lasts 69–73 days, with the interval between each pregnancy being 12–14 months typically. The African wild dog produces more pups than any other canid, with litters containing around six to 16 pups, with an average of 10, thus indicating that a single female can produce enough young to form a new pack every year. Because the amount of food necessary to feed more than two litters would be impossible to acquire by the average pack, breeding is strictly limited to the dominant female, which may kill the pups of subordinates. After giving birth, the mother stays close to the pups in the den, while the rest of the pack hunts. She typically drives away pack members approaching the pups until the latter are old enough to eat solid food at three to four weeks of age. The pups leave the den around the age of three weeks and are suckled outside. The pups are weaned at the age of five weeks, when they are fed regurgitated meat by the other pack members. By seven weeks, the pups begin to take on an adult appearance, with noticeable lengthening in the legs, muzzle, and ears. Once the pups reach the age of eight to 10 weeks, the pack abandons the den and the young follow the adults during hunts. The youngest pack members are permitted to eat first on kills, a privilege which ends once they become yearlings.
Ratio male/female
Packs of African wild dogs have a high ratio of males to females. This is a consequence of the males mostly staying with the pack whilst female offspring disperse and is supported by a changing sex-ratio in consecutive litters. Those born to maiden females contain a higher proportion of males, second litters are half and half and subsequent litters biased towards females with this trend increasing as females get older. As a result, the earlier litters provide stable hunters whilst the higher ratio of dispersals amongst the females stops a pack from getting too big.Sneeze communication and "voting"
African wild dog populations in theOkavango Delta
The Okavango Delta (or Okavango Grassland; formerly spelled "Okovango" or "Okovanggo") in Botswana is a swampy inland delta formed where the Okavango River reaches a tectonic trough at an altitude of 930–1,000 m in the central part of the en ...
have been observed "rallying" before they set out to hunt. Not every rally results in a departure, but departure becomes more likely when more individual dogs "sneeze". These sneeze
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth and ...
s are characterized by a short, sharp exhale through the nostrils. When members of dominant mating pairs sneeze first, the group is much more likely to depart. If a dominant dog initiates, around three sneezes guarantee departure. When less dominant dogs sneeze first, if enough others also sneeze (about 10), then the group will go hunting. Researchers assert that wild dogs in Botswana, "use a specific vocalization (the sneeze) along with a variable quorum response mechanism in the decision-making process o go hunting at a particular moment.

Inbreeding avoidance
Because the African wild dog largely exists in fragmented, small populations, its existence is endangered. Inbreeding avoidance by mate selection is characteristic of the species and has important potential consequences for population persistence. Inbreeding is rare within natal packs. Inbreeding behavior may have been selected against evolutionarily because it leads to the expression of recessive deleterious alleles. Computer simulations indicate that all populations continuing to avoid incestuous mating will become extinct within 100 years due to the unavailability of unrelated mates. Thus, the impact of reduced numbers of suitable unrelated mates will likely have a severe demographic impact on the future viability of small wild dog populations.Hunting and feeding behaviour
The African wild dog is a specialised pack hunter of common medium-sized antelopes.. It and the cheetah are the only primarily diurnal African large predators. The African wild dog hunts by approaching prey silently, then chasing it in a pursuit clocking at up to for 10–60 minutes. The average chase covers some , during which the prey animal, if large, is repeatedly bitten on the legs, belly, and rump until it stops running, while smaller prey is simply pulled down and torn apart. African wild dogs adjust their hunting strategy to the particular prey species. They will rush at wildebeest to panic the herd and isolate a vulnerable individual, but pursue territorial antelope species (which defend themselves by running in wide circles) by cutting across the arc to foil their escape. Medium-sized prey is often killed in 2–5 minutes, whereas larger prey such as wildebeest may take half an hour to pull down. Male wild dogs usually perform the task of grabbing dangerous prey, such as warthogs, by the nose. Hunting success varies with prey type, vegetation cover and pack size, but African wild dogs tend to be very successful: often more than 60% of their chases end in a kill, sometimes up to 90%. Despite their smaller size, they are much more consistently successful than lion (27–30%) and hyena (25–30%), but African wild dogs commonly lose their kills to these two large predators. An analysis of 1,119 chases by a pack of six Okavango wild dogs showed that most were short distance uncoordinated chases, and the ''individual'' kill rate was only 15.5 percent. Because kills are shared, each dog enjoyed an efficient benefit–cost ratio. Small prey such asrodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s, hares and birds are hunted singly, with dangerous prey such as cane rat
The genus ''Thryonomys'', also known as the cane rats or grasscutters, is a genus of rodent found throughout Africa south of the Sahara, the only members of the family Thryonomyidae. They are eaten in some African countries and are a pest species ...
s and porcupines being killed with a quick and well-placed bite to avoid injury. Small prey is eaten entirely, while large animals are stripped of their meat and organs, leaving the skin, head, and skeleton intact. The African wild dog is a fast eater, with a pack being able to consume a Thomson's gazelle
Thomson's gazelle (''Eudorcas thomsonii'') is one of the best known species of gazelles. It is named after explorer Joseph Thomson and is sometimes referred to as a "tommie". It is considered by some to be a subspecies of the red-fronted gazell ...
in 15 minutes. In the wild, the species' consumption is per African wild dog a day, with one pack of 17–43 individuals in East Africa having been recorded to kill three animals per day on average.
Unlike most social predators, African wild dogs will regurgitate food for other adults as well as young family members. Pups old enough to eat solid food are given first priority at kills, eating even before the dominant pair; subordinate adult dogs help feed and protect the pups.
Ecology
Habitat
The African wild dog is mostly found in savanna and Desert climate, arid zones, generally avoiding forested areas. This preference is likely linked to the animal's hunting habits, which require open areas that do not obstruct vision or impede pursuit. Nevertheless, it will travel through scrubland, scrub, woodland and montane areas in pursuit of prey. Forest-dwelling populations of African wild dogs have been identified, including one in the Harenna Forest, a wet montane forest up to in altitude in the Bale Mountains ofEthiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. At least one record exists of a pack being sighted on the summit of Mount Kilimanjaro. In Zimbabwe, the species has been recorded at altitudes of . In Ethiopia, this species has been found at great altitudes; several live wild dog packs have been sighted at altitudes of from 1,900 to 2,800 m, and a dead individual was found in June 1995 at on the Sanetti Plateau.
Diet
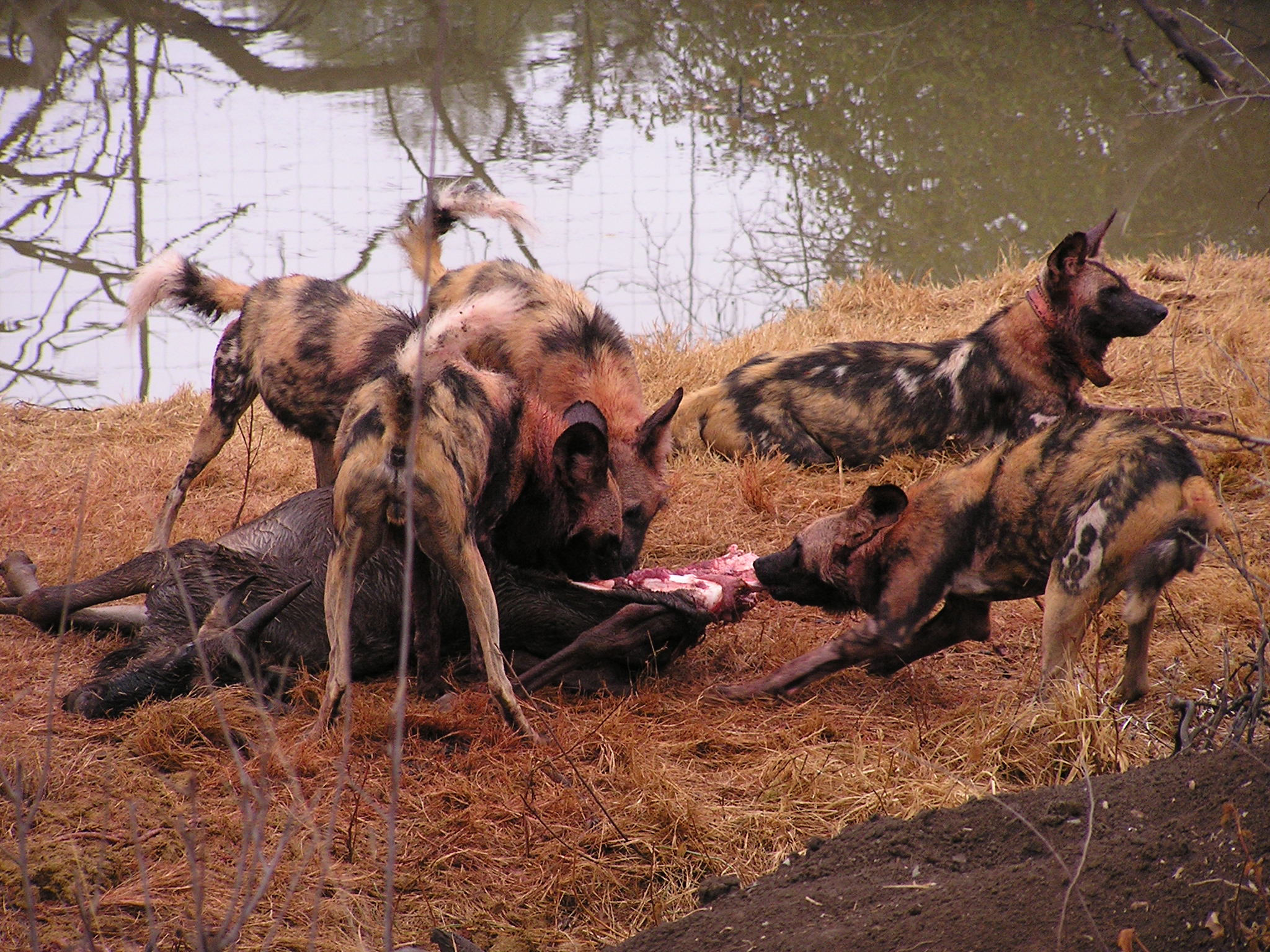
 A species-wide study showed that by preference, where available, five species were the most regularly selected prey, namely the greater kudu,
A species-wide study showed that by preference, where available, five species were the most regularly selected prey, namely the greater kudu, Thomson's gazelle
Thomson's gazelle (''Eudorcas thomsonii'') is one of the best known species of gazelles. It is named after explorer Joseph Thomson and is sometimes referred to as a "tommie". It is considered by some to be a subspecies of the red-fronted gazell ...
, impala, Cape bushbuck and blue wildebeest. More specifically, in East Africa, its most common prey is Thomson's gazelle, while in Central and Southern Africa, it targets impala, reedbuck, kob, lechwe and springbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
. and smaller prey such as dik-dik, hares, spring hares, insects and cane rats. Staple prey sizes are usually between , though some local studies put upper prey sizes as variously . In the case of larger species such as kudu and wildebeest, calves are largely but not exclusively targeted. However, certain packs in the Serengeti
The Serengeti ( ) ecosystem is a Geography of Africa, geographical region in Africa, spanning northern Tanzania. The protected area within the region includes approximately of land, including the Serengeti National Park and several game res ...
specialized in hunting adult plains zebras weighing up to quite frequently. Another study claimed that some prey taken by wild dogs could weigh up to . One pack was recorded to occasionally prey on bat-eared foxes, rolling on the carcasses before eating them. African wild dogs rarely scavenge, but have on occasion been observed to appropriate carcasses from spotted hyenas, leopards, cheetahs, lions, and animals caught in Animal trapping#Snares, snares.
Enemies and competitors
 Lions dominate African wild dogs and are a major source of mortality for both adults and pups. Population densities of African wild dogs are low in areas where lions are more abundant. One pack reintroduced into Etosha National Park was destroyed by lions. A population crash in lions in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Ngorongoro Crater during the 1960s resulted in an increase in African wild dog sightings, only for their numbers to decline once the lions recovered. As with other large predators killed by lion prides, the dogs are usually killed and left uneaten by the lions, indicating the competitive rather than predatory nature of the larger species' dominance. However, a few cases have been reported of old and wounded lions falling prey to African wild dogs.Schaller, G. B. (1972). ''The Serengeti lion: A study of predator-prey relations''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 188. . On occasion, packs of wild dogs have been observed defending pack members attacked by single lions, sometimes successfully. One pack in the Okavango in March 2016 was photographed by safari guides waging "an incredible fight" against a lioness that attacked a subadult dog at an impala kill, which forced the lioness to retreat, although the subadult dog died. A pack of four wild dogs was observed furiously defending an old adult male dog from a male lion that attacked it at a kill; the dog survived and rejoined the pack.
Spotted hyenas are important kleptoparasites and follow packs of African wild dogs to appropriate their kills. They typically inspect areas where African wild dogs have rested and eat any food remains they find. When approaching African wild dogs at a kill, solitary hyenas approach cautiously and attempt to take off with a piece of meat unnoticed, though they may be mobbed in the attempt. When operating in groups, spotted hyenas are more successful in pirating African wild dog kills, though the latter's greater tendency to assist each other puts them at an advantage against spotted hyenas, which rarely work cooperatively. Cases of African wild dogs scavenging from spotted hyenas are rare. Although African wild dog packs can easily repel solitary hyenas, on the whole, the relationship between the two species is a one-sided benefit for the hyenas, with African wild dog densities being negatively correlated with high hyena populations. Beyond piracy, cases of interspecific killing of African wild dogs by spotted hyenas are documented. African wild dogs are apex predators, normally only fatally losing contests to larger social carnivores, although anecdotally Nile crocodiles may opportunistically and rarely prey upon a wild dog. When briefly unprotected, wild dog pups may occasionally be vulnerable to large eagles, such as the martial eagle, when they venture out of their dens.
Lions dominate African wild dogs and are a major source of mortality for both adults and pups. Population densities of African wild dogs are low in areas where lions are more abundant. One pack reintroduced into Etosha National Park was destroyed by lions. A population crash in lions in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Ngorongoro Crater during the 1960s resulted in an increase in African wild dog sightings, only for their numbers to decline once the lions recovered. As with other large predators killed by lion prides, the dogs are usually killed and left uneaten by the lions, indicating the competitive rather than predatory nature of the larger species' dominance. However, a few cases have been reported of old and wounded lions falling prey to African wild dogs.Schaller, G. B. (1972). ''The Serengeti lion: A study of predator-prey relations''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 188. . On occasion, packs of wild dogs have been observed defending pack members attacked by single lions, sometimes successfully. One pack in the Okavango in March 2016 was photographed by safari guides waging "an incredible fight" against a lioness that attacked a subadult dog at an impala kill, which forced the lioness to retreat, although the subadult dog died. A pack of four wild dogs was observed furiously defending an old adult male dog from a male lion that attacked it at a kill; the dog survived and rejoined the pack.
Spotted hyenas are important kleptoparasites and follow packs of African wild dogs to appropriate their kills. They typically inspect areas where African wild dogs have rested and eat any food remains they find. When approaching African wild dogs at a kill, solitary hyenas approach cautiously and attempt to take off with a piece of meat unnoticed, though they may be mobbed in the attempt. When operating in groups, spotted hyenas are more successful in pirating African wild dog kills, though the latter's greater tendency to assist each other puts them at an advantage against spotted hyenas, which rarely work cooperatively. Cases of African wild dogs scavenging from spotted hyenas are rare. Although African wild dog packs can easily repel solitary hyenas, on the whole, the relationship between the two species is a one-sided benefit for the hyenas, with African wild dog densities being negatively correlated with high hyena populations. Beyond piracy, cases of interspecific killing of African wild dogs by spotted hyenas are documented. African wild dogs are apex predators, normally only fatally losing contests to larger social carnivores, although anecdotally Nile crocodiles may opportunistically and rarely prey upon a wild dog. When briefly unprotected, wild dog pups may occasionally be vulnerable to large eagles, such as the martial eagle, when they venture out of their dens.
Distribution
African wild dogs once ranged across much of sub-Saharan Africa, being absent only in the driest desert regions and lowland forests. The species has been largely exterminated in North and West Africa, and has been greatly reduced in number in Central Africa and northeast Africa. The majority of the species' population now occurs in Southern Africa and southern East Africa; more specifically in countries such asBotswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalaha ...
, Namibia, and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
. However, it is hard to track where they are and how many there are because of the loss of habitat.
North Africa
The species is very rare in North Africa, and whatever populations remain may be of high conservation value, as they are likely to be genetically distinct from other ''L. pictus'' populations.Fanshawe, J. H., Ginsberg, J. R., Sillero-Zubiri, C. & Woodroffe, R., eds. (1997). The Status & Distribution of Remaining Wild Dog Populations. In Rosie Woodroffe, Joshua Ginsberg & David MacDonald, eds., ''Status Survey and Conservation Plan: The African Wild Dog'': 11–56. IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group.West Africa
The species is faring poorly in most of West Africa, with the only potentially viable population occurring in Senegal's Niokolo-Koba National Park. African wild dogs are occasionally sighted in other parts of Senegal, Guinea and Mali.Central Africa
The species is doing poorly in Central Africa, being extinct in Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Republic of Congo. The only viable populations occur in the Central African Republic, Chad and especially Cameroon.East Africa
The African wild dog's range in East Africa is patchy, having been eradicated in Uganda and much of Kenya. A small population occupies an area encompassing southern Ethiopia, South Sudan, northern Kenya and probably northern Uganda. The species may still occur in small numbers in southern Somalia and it is almost certainly extinct in Rwanda, Burundi and Eritrea. Nevertheless, it remains somewhat numerous in southern Tanzania, particularly in the Selous Game Reserve and Mikumi National Park, both of which are occupied by what could be Africa's largest African wild dog population.Southern Africa
Southern Africa contains numerous viable African wild dog populations, one of which encompasses northern Botswana, northeastern Namibia and western Zimbabwe. In South Africa, around 400 specimens occur in the country's Kruger National Park. Zambia holds two large populations, one in Kafue National Park and another in the Luangwa Valley. However, the species is rare in Malawi and probably extinct in Mozambique.Threats
The African wild dog is primarily threatened by habitat fragmentation, which results in human–wildlife conflict, transmission of infectious diseases and high mortality rates. Surveys in the Central African Republic's Chinko area revealed that the African wild dog population decreased from 160 individuals in 2012 to 26 individuals in 2017. At the same time, transhumant Pastoralism, pastoralists from the border area with Sudan moved in the area with their livestock. Rangers confiscated large amounts of poison and found multiple lion cadavers in the camps of livestock herders. They were accompanied by armed merchants who also engage in poaching large herbivores, sale of bushmeat and trading lion skins.In culture
Ancient Egypt
 Artistic depictions of African wild dogs are prominent on cosmetic palettes and other objects from Egypt's Prehistoric Egypt, predynastic period, likely symbolising order over chaos and the transition between the wild and the domestic dog. Predynastic hunters may have also identified with the African wild dog, as the Hunters Palette shows them wearing the animals' tails on their belts. By the History of ancient Egypt#Dynastic Egypt, dynastic period, African wild dog illustrations became much less represented, and the animal's symbolic role was largely taken over by the wolf.Hendrickx, S. (2006). The dog, the ''Lycaon pictus'' and order over chaos in Predynastic Egypt. [in:] Kroeper, K.; Chłodnicki, M. & Kobusiewicz, M. (eds.), ''Archaeology of Early Northeastern Africa''. Studies in African Archaeology 9. Poznań: Poznań Archaeological Museum: 723–749.
Artistic depictions of African wild dogs are prominent on cosmetic palettes and other objects from Egypt's Prehistoric Egypt, predynastic period, likely symbolising order over chaos and the transition between the wild and the domestic dog. Predynastic hunters may have also identified with the African wild dog, as the Hunters Palette shows them wearing the animals' tails on their belts. By the History of ancient Egypt#Dynastic Egypt, dynastic period, African wild dog illustrations became much less represented, and the animal's symbolic role was largely taken over by the wolf.Hendrickx, S. (2006). The dog, the ''Lycaon pictus'' and order over chaos in Predynastic Egypt. [in:] Kroeper, K.; Chłodnicki, M. & Kobusiewicz, M. (eds.), ''Archaeology of Early Northeastern Africa''. Studies in African Archaeology 9. Poznań: Poznań Archaeological Museum: 723–749.
Ethiopia
According to Enno Littmann, the people ofEthiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
's Tigray Region believed that injuring a wild dog with a spear would result in the animal dipping its tail in its wounds and flicking the blood at its assailant, causing instant death. For this reason, Tigrean shepherds would repel wild dog attacks with pebbles rather than with edged weapons.
San people
The African wild dog also plays a prominent role in the mythology of Southern Africa'sSan people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia ...
. In one story, the wild dog is indirectly linked to the Origin-of-death myth, origin of death, as the hare is cursed by the moon to be forever hunted by African wild dogs after the hare rebuffs the moon's promise to allow all living things to be reborn after death. Another story has the god Cagn taking revenge on the other gods by sending a group of men transformed into African wild dogs to attack them, though who won the battle is never revealed. The San of Botswana see the African wild dog as the ultimate hunter and traditionally believe that shamans and medicine men can transform themselves into wild dogs. Some San hunters will smear African wild dog bodily fluids on their feet before a hunt, believing that doing so will give them the animal's boldness and agility. Nevertheless, the species does not figure prominently in San rock art, with the only notable example being a frieze in Mount Erongo showing a pack hunting two antelopes.De la Harpe R. & De la Harpe, P. (2010). "In search of the African wild dog: the right to survive". ''Sunbird'' p. 41. .
Ndebele
The Southern Ndebele people, Ndebele have a story explaining why the African wild dog hunts in packs: in the beginning, when the first wild dog's wife was sick, the other animals were concerned. An impala went to Hare, who was a medicine man. Hare gave Impala a calabash of medicine, warning him not to turn back on the way to Wild Dog's den. Impala was startled by the scent of a leopard and turned back, spilling the medicine. A zebra then went to Hare, who gave him the same medicine along with the same advice. On the way, Zebra turned back when he saw a black mamba, thus breaking the gourd. A moment later, a terrible howling is heard: Wild Dog's wife had died. Wild Dog went outside and saw Zebra standing over the broken gourd of medicine, so Wild Dog and his family chased Zebra and tore him to shreds. To this day, African wild dogs hunt zebras and impalas as revenge for their failure to deliver the medicine which could have saved Wild Dog's wife.In media
Documentary
* ''A Wild Dog's Tale'' (2013), a single painted dog (named Solo by researchers) befriends hyenas and jackals in Okavango, hunting together. Solo feeds and cares for jackal pups. * ''The Pale Pack'', Savage Kingdom, Season 1 (2016), was the story of Botswana African wild dog pack leaders Teemana and Molao written and directed by Brad Bestelink, and narrated by Charles Dance premiered on National Geographic. * Dynasties (2018 TV series), ''Dynasties'' (2018 TV series), episode 4, Produced by Nick Lyon: Tait is the elderly matriarch of a pack of painted wolves in Zimbabwe's Mana Pools National Park. Her pack is driven out of their territory by Tait's daughter, Blacktip, the matriarch of a rival pack in need of more space for their large family of 32. Their combined territory also shrunk over Tait's lifetime due to the expansion of human, hyena and lion territories. Tait leads her family into the territory of a lion pride in the midst of a drought, with Blacktip's pack in an eight month long pursuit. When Tait died, the pack was observed performing a rare "singing", the purpose of which is unclear.See also
* African Wild Dog Conservancy * Botswana Wild Dog Research Project * Harnas Wildlife Foundation * Institute of Zoology * Painted Dog Conservation * Wildlife Conservation NetworkExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * Githiru et al. (2007)African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) from NE Kenya: Recent records and conservation issues
Zoology Department Research Report. National Museum of Kenya. * Wozencraft, W. C. (November 2005). D. E. Wilson and D. M. Reeder (eds.)
''Mammal Species of the World''
(3rd edition). Johns Hopkins University Press. . * Van Lawick, H. & Goodall, J. (1971). ''Innocent Killers''. Houghton Mifflin Company Boston
External links
painteddog.org
Painted Dog Conservation Website
painteddog.co.uk/
Painted Dog Conservation United Kingdom Website
African Wild Dog Conservancy
African Wild Dog Watch
Wild Dog conservation in Zimbabwe
* [http://www.awf.org/wildlives/4548 African wild dogs: Wildlife summary] at African Wildlife Foundation
The Zambian Carnivore Programme
Save the African wild dog
Wildentrust.org
Painted Dog Conservation (conservation organization)
Photos, videos and information from ARKive
ibream wild dog project
at WCN Wildlife Conservation Network {{Authority control African wild dogs, Apex predators Canina (subtribe) Carnivorans of Africa Endangered fauna of Africa Fauna of the Sahara Mammals described in 1820, African wild dog Mammals of Sub-Saharan Africa Species endangered by habitat fragmentation