Canon EOS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Canon EOS (Electro-Optical System) is an
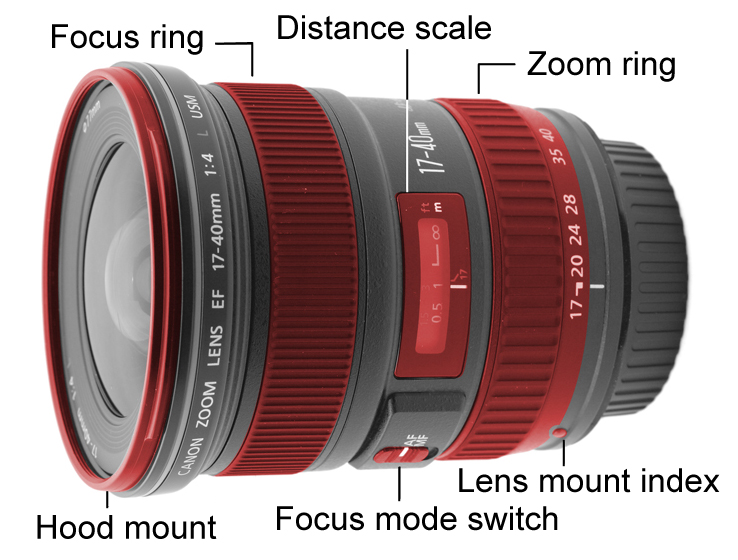 The bayonet-style EF lens mount is at the centre of the EOS camera system. Breaking compatibility with the earlier FD mount, it was designed with no mechanical linkages between moving parts in the lens and in the camera. The aperture and focus are controlled via electrical contacts, with motors in the lens itself. This was similar in some ways to Canon's earlier attempt at AF with the T80. Other manufacturers including
The bayonet-style EF lens mount is at the centre of the EOS camera system. Breaking compatibility with the earlier FD mount, it was designed with no mechanical linkages between moving parts in the lens and in the camera. The aperture and focus are controlled via electrical contacts, with motors in the lens itself. This was similar in some ways to Canon's earlier attempt at AF with the T80. Other manufacturers including
 The flash system in the EOS cameras has gone through a number of evolutions since its first implementation. The basic EOS flash system was actually developed not for the first EOS camera, but rather for the last high-end FD-mount manual-focus camera, the T90, launched in 1986. This was the first Canon camera with
The flash system in the EOS cameras has gone through a number of evolutions since its first implementation. The basic EOS flash system was actually developed not for the first EOS camera, but rather for the last high-end FD-mount manual-focus camera, the T90, launched in 1986. This was the first Canon camera with
File:EOS 650D.jpg, Canon EOS 650D, a Canon entry-level DSLR
File:EOS M weiss Frontal mit Speedlite 90EX.jpg, Canon EOS M, Canon's first mirrorless system camera
 Most prosumer and professional level EOS cameras feature a large quick control dial (QCD) on the camera back. The first consumer-level EOS camera with this feature was the EOS 760D/Rebel T6s, announced in February 2015. This feature allows easy adjustment of certain parameters using the thumb. The QCD is used for quick access to often-used functions that would otherwise require a more complicated procedure of button presses and dial clicks. Settings such as ISO button, Exposure Compensation button, or menus are all easily available through the QCD.
Cameras equipped with the QCD can easily be operated with one hand (forefinger on the main dial, thumb on the QCD) without taking the eye off the viewfinder.
A QCD is programmed to perform useful functions, which may include setting exposure compensation, setting of aperture in manual exposure mode, and scrolling of images and menus in digital EOS cameras.
Most prosumer and professional level EOS cameras feature a large quick control dial (QCD) on the camera back. The first consumer-level EOS camera with this feature was the EOS 760D/Rebel T6s, announced in February 2015. This feature allows easy adjustment of certain parameters using the thumb. The QCD is used for quick access to often-used functions that would otherwise require a more complicated procedure of button presses and dial clicks. Settings such as ISO button, Exposure Compensation button, or menus are all easily available through the QCD.
Cameras equipped with the QCD can easily be operated with one hand (forefinger on the main dial, thumb on the QCD) without taking the eye off the viewfinder.
A QCD is programmed to perform useful functions, which may include setting exposure compensation, setting of aperture in manual exposure mode, and scrolling of images and menus in digital EOS cameras.
File:Canon EOS Kiss X8i 2015 CP+.jpg, Canon EOS Kiss X8i, also known as 750D and Rebel T8i
File:Canon EOS 100D - 7.jpg, Canon EOS 100D compact DSLR camera
File:Canon EOS 9000D front-left 2017 CP+.jpg, Canon EOS 9000D, also known as 77D semi mid-range DSLR
File:Canon EOS 90D with EF-S 18-135mm.jpg, Canon EOS 90D mid-range camera
File:WikiGrenier - Canon EOS 7D Mark II 02.jpg, Canon EOS 7D Mark II high-end APS-C DSLR
File:Canon EOS 5D Mark IV (Front), 1803241116, ako.jpg, Canon EOS 5D Mark IV Full Frame DSLR
File:Canon EOS-1DX Mark III.jpg, Canon EOS-1D X Mark III, the highest-end Full Frame DSLR camera of Canon as of January 2021
File:Canon EOS M Blogger Event 02 cropped.jpg, Canon EOS M MILC camera
File:Canon EOS M3.jpg, Canon EOS M3, entry-level mirrorless camera
File:Canon EOS M50 black 03.jpg, Canon EOS M50, also known as EOS Kiss M in Japan
File:Canon EOS M5 front-left 2017 CP+.jpg, Canon EOS M5, the highest-end APS-C mirrorless camera of Canon as of January 2021
File:Canon EOS R.jpg, Canon EOS R, the first Full Frame MILC of Canon
File:Canon R6 und RF 85 2,0-8067.jpg, Canon EOS R6 with RF 85mm f2 lens attached
File:Canon R5 mit RF 35 1.8-8051.jpg, Canon EOS R5 with a 35mm lens
File:Canon EOS R3.jpg, Canon EOS R3
File:Canon EOS-1N.jpg, Canon EOS-1N high-end film autofocus camera
File:CanonEos650.jpg, Canon EOS 650, the first camera in the Canon EOS serias
File:Canon EOS 300, 1803102122, ako.jpg, Canon EOS 300 entry-level film SLR camera
File:Canon EOS IX E Austin Calhoon Photograph.jpg,
 Prior to the introduction of the EOS D30 digital SLR,
Prior to the introduction of the EOS D30 digital SLR,
EOS Camera Systems homepage at Canon.com
Canon EF Lens Catalogue 2018
The Canon EOS FAQs
Flash Photography with Canon EOS Cameras ŌĆō Part 1
ŌĆ
ŌĆ
EOS magazine
{{DEFAULTSORT:Canon Eos Canon EOS cameras
autofocus
An autofocus (or AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system ...
single-lens reflex camera
A single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system (hence "reflex" from the mirror's reflection) that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin l ...
(SLR) and mirrorless camera series produced by Canon Inc. Introduced in 1987 with the Canon EOS 650
The Canon EOS 650 is a 35 mm single-lens reflex camera. It was introduced on 2 March 1987, Canon's 50th anniversary,
and discontinued in February 1989.
It was the first camera in Canon's new EOS series, which was designed from scratch to suppor ...
, all EOS cameras used 35 mm film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
until October 1996 when the EOS IX was released using the new and short-lived APS film. In 2000, the D30 was announced, as the first digital SLR
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between ...
designed and produced entirely by Canon. Since 2005, all newly announced EOS cameras have used digital image sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of c ...
s rather than film. The EOS line is still in production as Canon's current digital SLR
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between ...
(DSLR) range, and, with the 2012 introduction of the Canon EOS M, Canon's mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera
A mirrorless camera is a photo camera featuring a single, removable lens and a digital display.
The camera does not have a reflex mirror or optical viewfinder like a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera, but may have an electronic ...
(MILC) system. In 2018 the system was further extended with the introduction of the EOS R camera, Canon's first full frame mirrorless interchangeable lens system.
The development project was called "EOS" (Electro Optical System). EOS is also the name of the goddess of dawn in Greek mythology, which further signifies the design's generational stature.
The EOS emblem was created using Handel Gothic typography.
It competes primarily with the Nikon F
The Nikon F camera, introduced in April 1959, was Nikon's first SLR camera. It was one of the most advanced cameras of its day. Although many of the concepts had already been introduced elsewhere, it was revolutionary in that it was the first ...
series and its successors, as well as autofocus SLR systems from Olympus Corporation
is a Japanese manufacturer of optics and reprography products. Olympus was established on 12 October 1919, initially specializing in microscopes and thermometers. Olympus holds roughly a 70-percent share of the global endoscope market, estimate ...
, Pentax, Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
/Minolta
was a Japanese manufacturer of cameras, camera accessories, photocopiers, fax machines, and laser printers. Minolta Co., Ltd., which is also known simply as Minolta, was founded in Osaka, Japan, in 1928 as . It made the first integrated aut ...
, and Panasonic
formerly between 1935 and 2008 and the first incarnation of between 2008 and 2022, is a major Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka. It was founded by K┼Źnosuke Matsushita in 1918 as a lightbulb ...
/ Leica.
At the heart of the system is the EF lens mount
The EF lens mount is the standard lens mount on the Canon EOS family of SLR film and digital cameras. EF stands for "Electro-Focus": automatic focusing on EF lenses is handled by a dedicated electric motor built into the lens. Mechanically, it i ...
, which replaced the previous FD lens mount, which mainly supported only manual-focus lenses. The EOS R full frame camera introduced a new lens mount to the system ŌĆō the RF mount.
EF lens mount
 The bayonet-style EF lens mount is at the centre of the EOS camera system. Breaking compatibility with the earlier FD mount, it was designed with no mechanical linkages between moving parts in the lens and in the camera. The aperture and focus are controlled via electrical contacts, with motors in the lens itself. This was similar in some ways to Canon's earlier attempt at AF with the T80. Other manufacturers including
The bayonet-style EF lens mount is at the centre of the EOS camera system. Breaking compatibility with the earlier FD mount, it was designed with no mechanical linkages between moving parts in the lens and in the camera. The aperture and focus are controlled via electrical contacts, with motors in the lens itself. This was similar in some ways to Canon's earlier attempt at AF with the T80. Other manufacturers including Contax
Contax (stylised as CONTAX in the Kyocera era) began as a German camera model in the Zeiss Ikon line in 1932, and later became a brand name. The early cameras were among the finest in the world, typically featuring high quality Zeiss interchan ...
(with its G series of interchangeable-lens 35 mm rangefinder cameras), Nikon
(, ; ), also known just as Nikon, is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, specializing in optics and imaging products. The companies held by Nikon form the Nikon Group.
Nikon's products include cameras, camera ...
's 1983 F3AF, and Olympus
Olympus or Olympos ( grc, ßĮī╬╗Žģ╬╝ŽĆ╬┐Žé, link=no) may refer to:
Mountains
In antiquity
Greece
* Mount Olympus in Thessaly, northern Greece, the home of the twelve gods of Olympus in Greek mythology
* Mount Olympus (Lesvos), located in Le ...
(with its Four Thirds System) have since embraced this type of direct drive system. It is a large lens mount compared to most of its competition, enabling the use of larger aperture lenses.
EOS flash system
 The flash system in the EOS cameras has gone through a number of evolutions since its first implementation. The basic EOS flash system was actually developed not for the first EOS camera, but rather for the last high-end FD-mount manual-focus camera, the T90, launched in 1986. This was the first Canon camera with
The flash system in the EOS cameras has gone through a number of evolutions since its first implementation. The basic EOS flash system was actually developed not for the first EOS camera, but rather for the last high-end FD-mount manual-focus camera, the T90, launched in 1986. This was the first Canon camera with through-the-lens In photography, through-the-lens metering (TTL metering) refers to a feature of cameras whereby the intensity of light reflected from the scene is measured through the lens; as opposed to using a separate metering window or external hand-held lig ...
(TTL) flash metering, although other brands had been metering that way for some time. It also introduced the A-TTL (Advanced TTL) system for better flash exposure in program mode, using infrared preflashes to gauge subject distance.
This system was carried over into the early EOS cameras wholesale. A-TTL largely fell out of favor, and was replaced by E-TTL (Evaluative TTL). This used a pre-flash for advanced metering, and used the autofocus
An autofocus (or AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system ...
system to judge where the main subject was for more accurate exposure. E-TTL II, which was an enhancement in the camera's firmware
In computing, firmware is a specific class of computer software that provides the low-level control for a device's specific hardware. Firmware, such as the BIOS of a personal computer, may contain basic functions of a device, and may provide h ...
only, replaced E-TTL from 2004.
Canon Speedlite
Canon's EOS flash system refers to the photographic flash mechanism used on Canon's film ( 35mm and APS) or digital EOS single-lens reflex cameras. The line was first introduced in 1987. It has gone through a number of revisions over the years, ...
-brand flashes have evolved alongside the cameras. They are capable of wired and wireless multi-flash setups, the latter using visible or infrared pulses to synchronise. Later models, including RT in their model name, can also communicate via radio links, where up to 16 units can make up a network. Canon also produces Speedlite accessories, including the OC-E3 Off-Camera Shoe Cord, which can be used to hand-hold the flash while allowing the camera to control it through the cord. The Off-Camera Shoe Cord is popular among portrait photographers who need to have more control over lighting than a camera mounted flash can offer.
EOS cameras
As of 2017, Canon has released no fewer than 70 EOS SLR and DSLR camera models, starting with the introduction of the EOS 650 in 1987. In the 1990s, Canon worked with Kodak to produce digital camera bodies, starting with the EOS DCS 3 in 1995. The first digital EOS SLR camera wholly designed and manufactured by Canon was the EOS D30, released in 2000. Canon sold two EOS cameras designed to use the APS film format, the EOS IX and the EOS IX Lite. Canon also sold a manual-focus camera, the Canon EF-M, which used the same EF lens mount as the EOS cameras. It came with all the automatic and manual exposure functions but lacked autofocus. It came equipped with a split-screen/microprismfocusing screen
A focusing screen is a flat translucent material, either a ground glass or Fresnel lens, found in a system camera that allows the user of the camera to preview the framed image in a viewfinder
In photography, a viewfinder is what the pho ...
for precise manual focusing.
Eye-controlled focusing
Through the tracking of eyeball movements, EOS cameras equipped with eye-controlled focusing (ECF) (some identifiable by the suffix E) were able to select the desired autofocus point in the scene, based on where the user was looking in the viewfinder frame. ECF was especially useful in sports photography where the subject may shift its position in the frame rapidly. EOS cameras equipped with ECF were the EOS A2E (U.S. model names are shown; see the table below for equivalents in other countries), EOS Elan IIE, EOS IXe, EOS-3, EOS Elan 7E, and EOS Elan 7NE. Canon did not continue its use of eye-controlled focusing for its digital SLRs. The EOS Elan 7NE was the last EOS camera to have this function, until in 2021 Canon reintroduced eye-controlled focus with the EOS R3.Quick control dial
 Most prosumer and professional level EOS cameras feature a large quick control dial (QCD) on the camera back. The first consumer-level EOS camera with this feature was the EOS 760D/Rebel T6s, announced in February 2015. This feature allows easy adjustment of certain parameters using the thumb. The QCD is used for quick access to often-used functions that would otherwise require a more complicated procedure of button presses and dial clicks. Settings such as ISO button, Exposure Compensation button, or menus are all easily available through the QCD.
Cameras equipped with the QCD can easily be operated with one hand (forefinger on the main dial, thumb on the QCD) without taking the eye off the viewfinder.
A QCD is programmed to perform useful functions, which may include setting exposure compensation, setting of aperture in manual exposure mode, and scrolling of images and menus in digital EOS cameras.
Most prosumer and professional level EOS cameras feature a large quick control dial (QCD) on the camera back. The first consumer-level EOS camera with this feature was the EOS 760D/Rebel T6s, announced in February 2015. This feature allows easy adjustment of certain parameters using the thumb. The QCD is used for quick access to often-used functions that would otherwise require a more complicated procedure of button presses and dial clicks. Settings such as ISO button, Exposure Compensation button, or menus are all easily available through the QCD.
Cameras equipped with the QCD can easily be operated with one hand (forefinger on the main dial, thumb on the QCD) without taking the eye off the viewfinder.
A QCD is programmed to perform useful functions, which may include setting exposure compensation, setting of aperture in manual exposure mode, and scrolling of images and menus in digital EOS cameras.
Multi-point autofocus system
Currently, top-line EOS cameras have either 61 or 65 user-selectable autofocus (AF) points. Autofocus is a camera's ability to focus a lens automatically on an object by pressing down on the shutter button. Autofocus most often chooses the closest image in the field of view to focus on. The following EOS cameras feature such a system, with 61 points unless otherwise indicated: * The EOS 5D Mark III, introduced in March 2012. * The EOS-1D X, announced in October 2011 and originally scheduled for sale in April 2012, but delayed until June 2012. Since replaced by a Mark II version. * The EOS 7D Mark II, on sale since November 2014. This APS-C body has Canon's first (and so far only) 65-point AF system. * The EOS 5Ds and 5Ds R, two closely related higher-resolution full-frame bodies otherwise similar to the 5D MkIII, announced in February 2015 with sales beginning in June of that year. * The EOS-1D X Mark II, the replacement for the original 1D X, announced in February 2016 with sales expected to begin in April of that year. * The EOS 5D Mark IV, announced in August 2016 as the replacement for the 5D Mk III. The release of the 5D Mark III gave Canon the lead once again in this category; previously, its top-line cameras had 45 AF points, which led the industry until Nikon released its D3 and D300 DSLRs with 51-point AF systems. A higher number of AF points increases the chances of a sharply focused photograph in situations where the subject travels across the frame at high speeds (e.g. sports, wildlife). Having so many AF points also helps relieve the photographer from having to use the 'lock focus and recompose' method of framing a photograph that can introduce focusing inaccuracy. The camera generally focuses on the closest object or on human faces, which may not be what the photographer wants, so EOS cameras equipped with a multi-point AF system still allow the photographer to manually select an AF point. The EOS-3, EOS-1v, all EOS-1D models prior to the EOS-1D X, EOS 80D, EOS 77D, and EOS 800D/Rebel T7i feature a 45-point AF system. Most Canon DSLRs introduced since late 2005, starting from the EOS 20D and the Rebel XTi (400D), feature a nine-point AF system in a diamond-shape formation. The EOS 5D, released in 2005, takes this 9-point AF system a step further by introducing six more 'invisible' AF points (i.e., not user selectable) in helping the camera acquire focus faster during subject tracking. There have been several exceptions to Canon's recent rule of a 9-point AF system. The EOS 1000D (Rebel XS) has the 7-point AF system of most older Canon DSLRs. The EOS 7D, released in 2009, has a 19-point AF layout, fitting essentially within the same diamond-shaped area of the frame as the nine-point layout. The EOS 70D, released in August 2013, inherited the 7D's 19-point layout, but with fewer AF control options. The 70D system was in turn handed down to the EOS 750D (Rebel T6i) and760D
76 or Seventy-Six may refer to:
Common uses
* 76 (number)
* One of the years 76 BC, AD 76, 1776, 1876, 1976, 2076
Places
* Seventy Six, Kentucky
* Seventy-Six, Missouri
* Seventy-Six Township, Iowa (disambiguation), several places
Arts, en ...
(Rebel T6s), announced in February 2015. As mentioned above, the EOS 5D Mark III, EOS-1D X, EOS 5DS/5DS R, and EOS-1D X Mark II have 61-point AF layouts. The EOS 6D, released in October 2012, has an 11-point layout. The EOS 80D, announced in 2016, marked the return of 45-point AF systems to the Canon EOS line, as well as the first appearance of a 45-point system in a non-professional body. This system was brought downmarket in 2017 with its inclusion in the upper-entry-level EOS 77D and mid-entry-level EOS 800D/Rebel T7i.
For the earlier generation of 45-point AF system, the central column of 1 or 2 sensors (7 in all up to EOS-1Ds Mk II, EOS-1D Mk II N) are cross-type sensors, which are sensitive to both vertical and horizontal lines to offer a high degree of accuracy. The EOS-1Ds Mk III, replaced by the EOS-1D X, has 19 cross-type sensors for higher accuracy, as well as placing the cross-type sensors to complement the Rule of Thirds. The other Canon professional SLR replaced by the EOS-1D X, the APS-H EOS-1D Mk IV, has 39 cross-type sensors, a major increase from the 19 of the Mk III. Of the 61 AF points of the EOS-1D X and 5D MkIII, 21 central points and 20 outer points are cross-type, and five central points are dual-cross-type (sensitive to diagonal lines in addition to horizontal and vertical). All 65 points of the 7D MkII are cross-type, but only the center point is dual-cross-type.
Similarly, , all AF points on later generations of the X0D series (beginning with the 40D and continuing through the current 80D) are cross-type sensors for higher accuracy, and the center sensor is dual-cross-type for even greater accuracy and sensitivity. In June 2012, the EOS 650D (Rebel T4i) became the first consumer-level Canon to receive this AF system.
Naming scheme of EOS
DSLR
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between a ...
and SLR cameras
Identical Canon models are sometimes marketed under different names in different parts of the world. For example, the ''EOS Rebel 2000'' known in the Americas is also known as ''EOS Kiss III'' in Japan, and '' EOS 300'' in other parts of the world.
Naming scheme of EOS M Series
MILC
A mirrorless camera is a photo camera featuring a single, removable lens and a digital display.
The camera does not have a reflex mirror or optical viewfinder like a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera, but may have an electronic ...
cameras
Naming scheme of EOS R Series
MILC
A mirrorless camera is a photo camera featuring a single, removable lens and a digital display.
The camera does not have a reflex mirror or optical viewfinder like a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera, but may have an electronic ...
cameras
Film cameras
This is a list of the 35 mm Film and APS Canon EOS models in order of introduction:Canon EOS iX
The EOS IX (world markets) or EOS IX E (Japanese market) is an APS-format single-lens reflex camera that was introduced by Canon Inc. of Japan in October 1996 as part of their EOS series SLR cameras. The other APS camera in this series is the C ...
, one of the few APS format analog SLRs of Canon with unconventional design
Digital cameras
 Prior to the introduction of the EOS D30 digital SLR,
Prior to the introduction of the EOS D30 digital SLR, Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
produced four digital SLRs also sold under the Canon brand. These cameras used a digital camera back with the image sensor and associated electronics designed and built by Kodak together with modified internals of the EOS-1N film SLR. Due to using the Canon EOS body, these four digital SLRs can accept EF lenses. The four cameras were:
After termination of the agreement by Canon, Kodak cooperated with Sigma
Sigma (; uppercase ╬Ż, lowercase Žā, lowercase in word-final position Žé; grc-gre, Žā╬»╬│╬╝╬▒) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase ╬Ż is used a ...
who at that time had a Canon licenseto produce the Kodak DCS Pro SLR/c based on a SA9 SLR body in 2004, which was compatible with EF lenses.
The following digital SLRs, starting from the D30, had bodies and sensors completely designed and manufactured by Canon (except for the Canon EOS-1D, which uses a Panasonic sourced CCD sensor).
Canon digital SLRs are equipped with a CMOS
Complementary metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
sensor (with the exception of EOS-1D that uses a CCD sensor). Canon designs and manufactures their own CMOS sensors.
See also
Canon
* Canon Corporation *Canon Cinema EOS
The Canon Cinema EOS (Cinema Electro-Optical System) autofocus digital photographic and cinematographic SLR and mirrorless interchangeable lens camera system was introduced in late 2011 with the Canon EOS C300 and followed by the Canon EOS C5 ...
* Canon FD lens mount
The Canon FD lens mount is a physical standard for connecting a photographic lens to a 35mm single-lens reflex camera body. The standard was developed by Canon of Japan and was introduced in March 1971 with the Canon F-1 camera. It served as t ...
* Canon FL
Canon FL refers to a lens mount standard for 35mm single-lens reflex cameras from Canon. It was introduced in April 1964 with the Canon FX camera, replacing the previous Canon R lens mount. The FL mount was in turn replaced in 1971 by the Ca ...
* Canon EF lens mount
The EF lens mount is the standard lens mount on the Canon EOS family of SLR film and digital cameras. EF stands for "Electro-Focus": automatic focusing on EF lenses is handled by a dedicated electric motor built into the lens. Mechanically, it ...
* Canon RF lens mount
The Canon RF lens mount is an interchangeable-lens mount developed by Canon for its full-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras, and featured first by the EOS R, followed by the EOS RP. The RF mount was announced in September 2018. In ...
* List of Canon products
* Canon EF-S lens mount, a derivative of the EF mount designed for DSLRs with APS-C sensors
* Canon EF-M lens mount, a derivative of the EF mount designed for MILCs with APS-C sensors
Single lens reflex
*Single lens reflex
A single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system (hence "reflex" from the mirror's reflection) that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin l ...
* Digital single lens reflex
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between a ...
* 35 mm film
References
External links
EOS Camera Systems homepage at Canon.com
Canon EF Lens Catalogue 2018
The Canon EOS FAQs
Flash Photography with Canon EOS Cameras ŌĆō Part 1
ŌĆ
ŌĆ
EOS magazine
{{DEFAULTSORT:Canon Eos Canon EOS cameras