Canet gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Canet guns were a series of weapon systems developed by the French engineer Gustave Canet (1846–1908), who worked as an engineer from 1872 to 1881 for the London Ordnance Works, then for Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, and from 1897 to 1907 for Schneider et Cie of Le Creusot.
The Canet guns were a series of weapon systems developed by the French engineer Gustave Canet (1846–1908), who worked as an engineer from 1872 to 1881 for the London Ordnance Works, then for Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, and from 1897 to 1907 for Schneider et Cie of Le Creusot.
 Canet developed a 38 cal naval gun, an extremely powerful weapon for its time, specifically for the export market. The gun was first selected by the Spanish Navy in 1884 as part of a large naval expansion program which called for six new
Canet developed a 38 cal naval gun, an extremely powerful weapon for its time, specifically for the export market. The gun was first selected by the Spanish Navy in 1884 as part of a large naval expansion program which called for six new

 M.Canet is also known for the development of the Schneider-Canet gun system for 75 mm iron BL mountain guns, and rapid-fire 120 mm and 152 mm guns.
M.Canet is also known for the development of the Schneider-Canet gun system for 75 mm iron BL mountain guns, and rapid-fire 120 mm and 152 mm guns.
The Canet gun
{{Commons category, Canet artillery Naval guns of France Artillery of France 320 mm artillery


 The Canet guns were a series of weapon systems developed by the French engineer Gustave Canet (1846–1908), who worked as an engineer from 1872 to 1881 for the London Ordnance Works, then for Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, and from 1897 to 1907 for Schneider et Cie of Le Creusot.
The Canet guns were a series of weapon systems developed by the French engineer Gustave Canet (1846–1908), who worked as an engineer from 1872 to 1881 for the London Ordnance Works, then for Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, and from 1897 to 1907 for Schneider et Cie of Le Creusot.
320 mm naval guns
 Canet developed a 38 cal naval gun, an extremely powerful weapon for its time, specifically for the export market. The gun was first selected by the Spanish Navy in 1884 as part of a large naval expansion program which called for six new
Canet developed a 38 cal naval gun, an extremely powerful weapon for its time, specifically for the export market. The gun was first selected by the Spanish Navy in 1884 as part of a large naval expansion program which called for six new battleship
A battleship is a large armour, armored warship with a main artillery battery, battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1 ...
s. The Spanish armaments firm Hontoria obtained a manufacturing license to produce the weapon, but due to budgetary reasons, only one vessel, the , was completed.
Canet was more successful in sales to the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
, when the gun was selected by the French military advisor and naval architect This is the top category for all articles related to architecture and its practitioners.
{{Commons category, Architecture occupations
Design occupations
Occupations ...
Louis-Émile Bertin as the main battery of the , new type of cruiser he had designed in 1887. The usage was consistent with the Jeune École philosophy, which advocated placing overwhelming firepower (strong guns, torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, ...
es) on relatively small ships. This philosophy was of great interest to the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
, which lacked the resources at the time to purchase modern pre-dreadnought battleship
A battleship is a large armour, armored warship with a main artillery battery, battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1 ...
s.
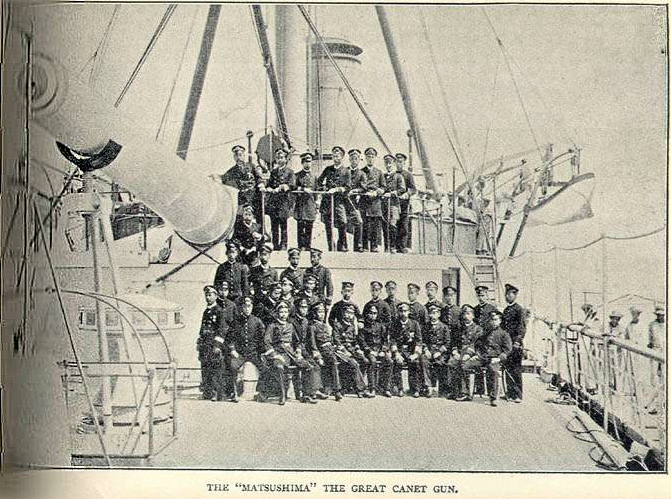
The guns supplied to Japan equipped the cruisers , , and . Each gun weighed 67 tons, and had a barrel long, firing a long projectile with weight of (or high explosive) for an effective range of .
The guns proved only marginally successful during the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
, due to a slow rate of fire, and numerous mechanical problems. The guns could not be aimed abeam, as their weight would cause the ship to roll over when fired. In combat, gunners were able to fire only around one shot per hour due to the time it took to reload.
Other guns
References
Bibliography
* *External links
The Canet gun
{{Commons category, Canet artillery Naval guns of France Artillery of France 320 mm artillery