Cancer cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. 
File: Apocrine carcinoma - high mag.jpg, Carcinoma
File:Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia smear.jpg, Leukaemia
File:Burkitt lymphoma, touch prep, Wright stain.jpg, Lymphoma
File:Multiple myeloma (1) MG stain.jpg, Myeloma
File:Ewing sarcoma cells.png, Sarcoma
File:Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma - alt 2 -- intermed. mag.jpg, Mesothelioma
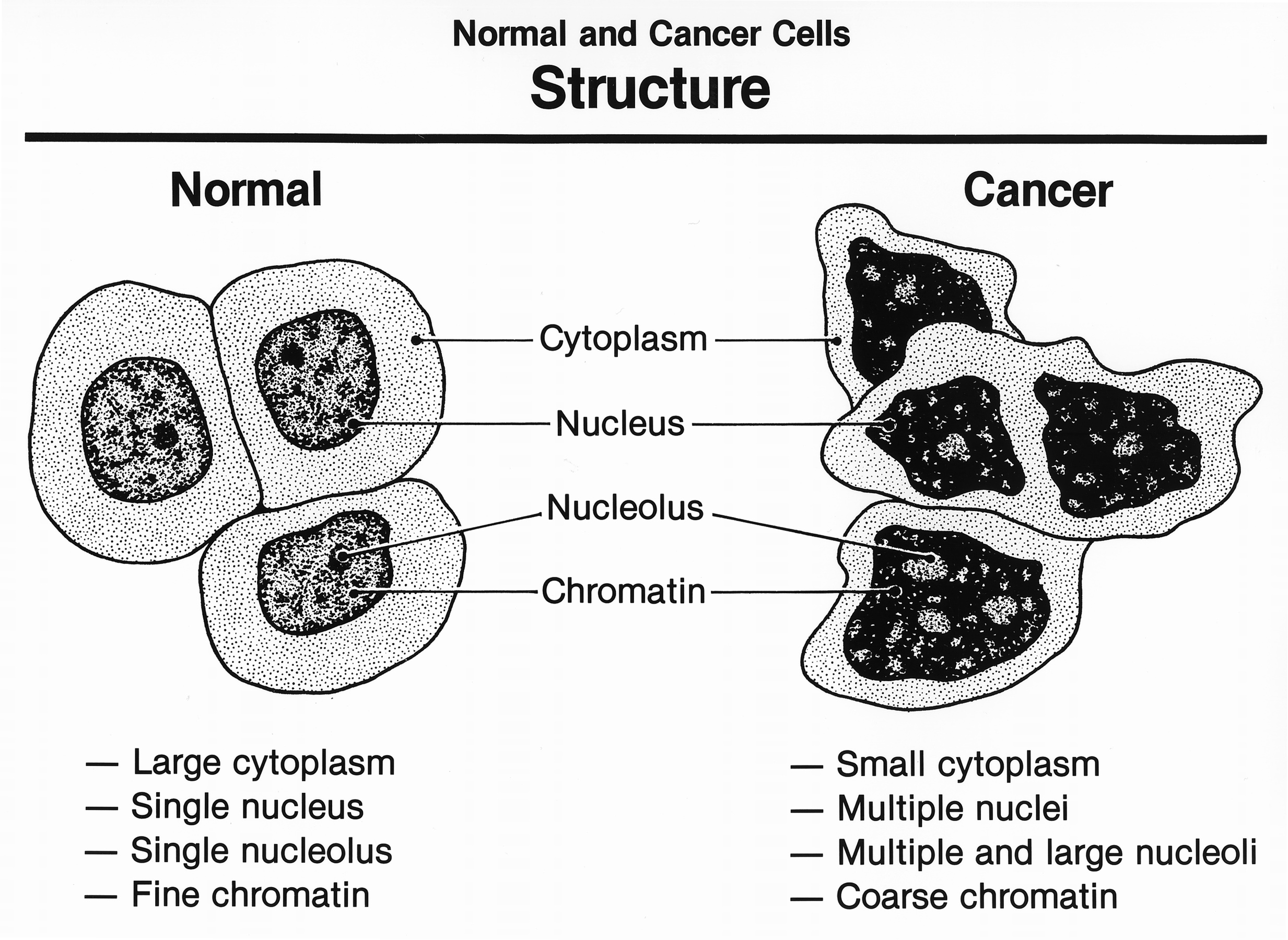 Cancer cells have distinguishing
Cancer cells have distinguishing
 Scientists have discovered a molecule on the surface of tumors that appears to promote drug resistance—by converting the tumor cells back into a
Scientists have discovered a molecule on the surface of tumors that appears to promote drug resistance—by converting the tumor cells back into a
The History of Cancer
Cancer.org. Retrieved on 2010-12-01 {{DEFAULTSORT:Cancer Cell Carcinogenesis
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these daughter cells are used to build new tissue or to replace cells that have died because of aging or damage. Healthy cells stop dividing when there is no longer a need for more daughter cells, but cancer cells continue to produce copies. They are also able to spread from one part of the body to another in a process known as metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
.

Classification
There are different categories of cancer cell, defined according to the cell type from which they originate. *Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoderm ...
, the majority of cancer cells are epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
in origin, beginning in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body.
* Leukaemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
, originate in the tissues responsible for producing new blood cells, most commonly in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
.
* Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include en ...
and myeloma, derived from cells of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
.
* Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal ( connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sar ...
, originating in connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
, including fat, muscle and bone.
* Central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, derived from cells of the brain and spinal cord.
* Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The most common area affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining ...
, originating in the mesothelium
The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura ( pleural cavity around the lungs), peritoneum ( abdominopelvic cavity including the mes ...
; the lining of body cavities.
Histology
 Cancer cells have distinguishing
Cancer cells have distinguishing histological
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
features visible under the microscope. The nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
is often large and irregular, and the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
may also display abnormalities.
Nucleus
The shape, size, protein composition, and texture of the nucleus are often altered inmalignant cells
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
. The nucleus may acquire grooves, folds or indentations, chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
may aggregate or disperse, and the nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of sign ...
can become enlarged. In normal cells, the nucleus is often round or solid in shape, but in cancer cells the outline is often irregular. Different combinations of abnormalities are characteristic of different cancer types, to the extent that nuclear appearance can be used as a marker in cancer diagnostics and staging.
Causes
Cancer cells are created when the genes responsible for regulatingcell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
are damaged. Carcinogenesis is caused by mutation and epimutation of the genetic material of normal cells, which upsets the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division in the body. The uncontrolled and often rapid proliferation of cells can lead to benign or malignant tumours (cancer). Benign tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of cells ( tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have r ...
s do not spread to other parts of the body or invade other tissues. Malignant tumors can invade other organs, spread to distant locations (metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
) and become life-threatening.
More than one mutation is necessary for carcinogenesis. In fact, a series of several mutations to certain classes of genes is usually required before a normal cell will transform into a cancer cell.
Damage to DNA can be caused by exposure to radiation, chemicals, and other environmental sources, but mutations also accumulate naturally over time through uncorrected errors in DNA transcription, making age another risk factor. Oncovirus
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the lette ...
es can cause certain types of cancer, and genetics are also known to play a role.
Stem cell research suggests that excess SP2 protein may turn stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
into cancer cells. However, a lack of particular co-stimulated molecules that aid in the way antigens react with lymphocytes can impair the natural killer cells' function, ultimately leading to cancer.
Pathology
Cells playing roles in the immune system, such asT-cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
, are thought to use a dual receptor system when they determine whether or not to kill sick or damaged human cells. If a cell is under stress, turning into tumors, or infected, molecules including MIC-A and MIC-B are produced so that they can attach to the surface of the cell. These work to help macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
detect and kill cancer cells.
Discovery
Early evidence of human cancer can be interpreted from Egyptian papers (1538 BCE) and mummified remains. In 2016, a 1.7 million year oldosteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) (or simply bone cancer) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma ...
was reported by Edward John Odes (a doctoral student in Anatomical Sciences from Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand () (locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which ...
Medical School, South Africa) and colleagues, representing the oldest documented malignant hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
cancer.
The understanding of cancer was significantly advanced during the Renaissance period and in to the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
. Sir Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
, a German biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize ...
and politician
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking, ...
, studied microscopic pathology, and linked his observations to illness. He is described as "the founder of cellular pathology". In 1845, Virchow and John Hughes Bennett
John Hughes Bennett PRCPE FRSE (31 August 1812 – 25 September 1875) was an English physician, physiologist and pathologist. His main contribution to medicine has been the first description of leukemia as a blood disorder (1845). The first pers ...
independently observed abnormal increase in white blood cells in patients. Virchow correctly identified the condition as blood disease, and named it ''leukämie'' in 1847 (later anglicised to leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
). In 1857, he was the first to describe a type of tumour
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
called chordoma that originated from the clivus (at the base of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
).
Telomerase
Cancer cells have unique features that make them "immortal" according to some researchers. The enzymetelomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euk ...
is used to extend the cancer cell's life span. While the telomeres of most cells shorten after each division, eventually causing the cell to die, telomerase extends the cell's telomeres. This is a major reason that cancer cells can accumulate over time, creating tumors.
Cancer stem cells and drug resistance
stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
-like state.
When the tumor cells began to exhibit drug resistance, the cells were ''simultaneously'' transforming into a stem cell-like state, which made them impervious to the drugs. It appeared that the treatment itself was driving this transformation by activating a specific molecular pathway. Luckily, several existing drugs, such as Bortezomib
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It is ...
for example, can attack this pathway and reverse the cellular transformation, thus 're-sensitizing' the tumor to treatment.
Treatment
In February 2019, medical scientists announced thatiridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
attached to albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
, creating a photosensitized molecule, can penetrate cancer cells
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these d ...
and, after being irradiated with light (a process called photodynamic therapy), destroy the cancer cells.
See also
*Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
*BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
*Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive sub ...
*Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
*Epidemiology of cancer
The epidemiology of cancer is the study of the factors affecting cancer, as a way to infer possible trends and causes. The study of cancer epidemiology uses epidemiological methods to find the cause of cancer and to identify and develop impro ...
*Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
*Tumour heterogeneity
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
References
Further reading
*External links
The History of Cancer
Cancer.org. Retrieved on 2010-12-01 {{DEFAULTSORT:Cancer Cell Carcinogenesis