Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
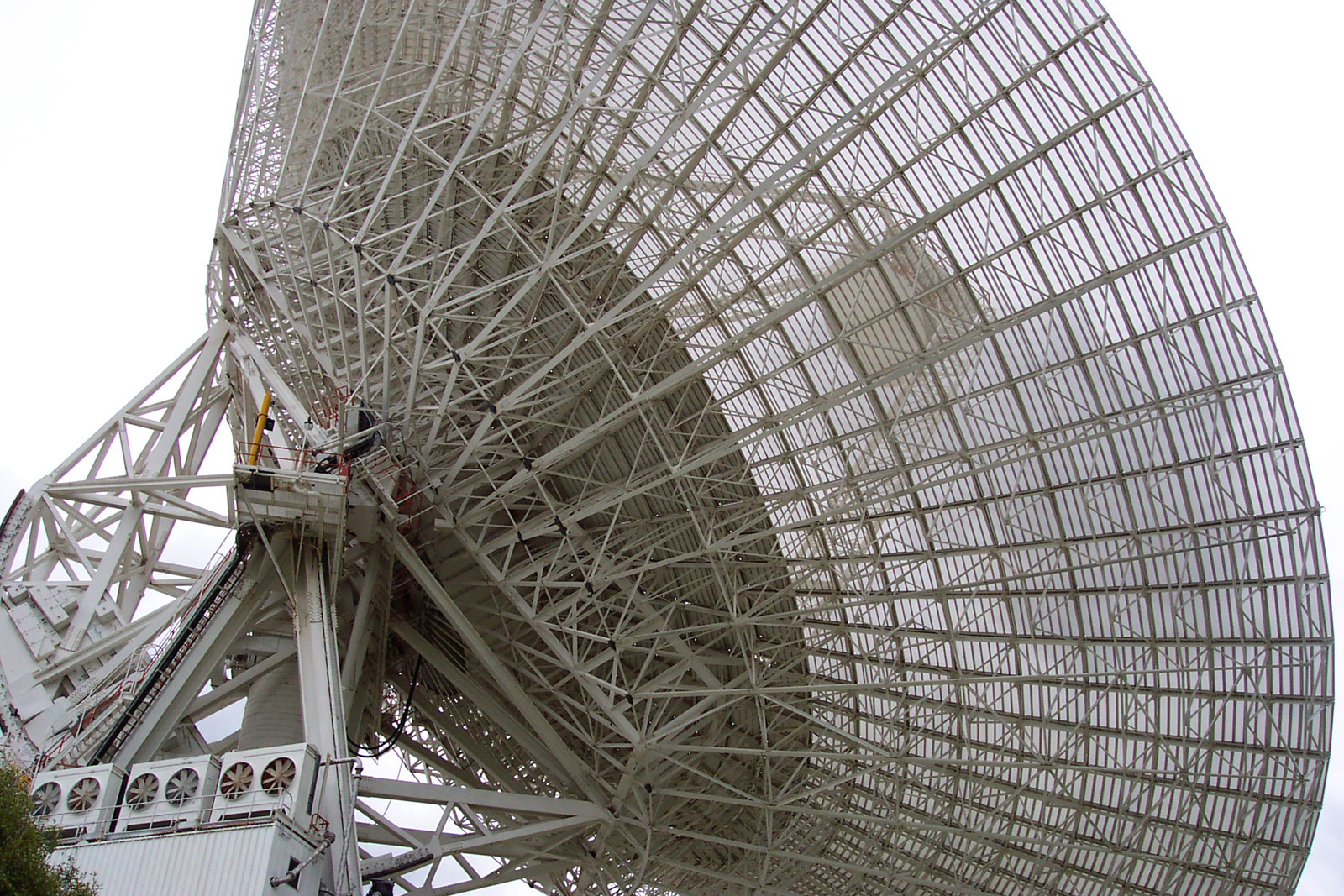 The Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) is a satellite communication station, part of the Deep Space Network of
The Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) is a satellite communication station, part of the Deep Space Network of
 During the mid 1960s NASA built three tracking stations in the Australian Capital Territory.
*The Tidbinbilla Tracking Station (now known as CDSCC) was opened in 1965 and is the only NASA tracking station in Australia still in operation. During the
During the mid 1960s NASA built three tracking stations in the Australian Capital Territory.
*The Tidbinbilla Tracking Station (now known as CDSCC) was opened in 1965 and is the only NASA tracking station in Australia still in operation. During the
Partners in space: CSIRO and NASA - video
Official CDSCC Webpage
Official CSIRO pages
Tidbinbilla Tracking Station tribute site
Honeysuckle Creek tribute siteNASA's GRO Remote Terminal System Installed at Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex
{{Authority control Earth stations in the Australian Capital Territory Space programme of Australia Deep Space Network 1965 establishments in Australia CSIRO NASA facilities in Australia
 The Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) is a satellite communication station, part of the Deep Space Network of
The Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) is a satellite communication station, part of the Deep Space Network of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, La Cañada Flintridge, California ...
(JPL), located at Tidbinbilla in the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
. Opened in 1965, the complex was used for tracking the Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
, and along with its two sister stations at Goldstone, California
The Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex (GDSCC), commonly called the Goldstone Observatory, is a satellite ground station located in Fort Irwin in the U.S. state of California. Operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), its m ...
and Madrid, Spain is now used for tracking and communicating with NASA's spacecraft, particularly interplanetary missions. Its DSS-43 antenna is the only antenna on Earth that can send commands to Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', ...
. It is managed in Australia by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research.
CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO ...
(CSIRO) for NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation program (SCaN) at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.
Location
The complex is located in the Paddys River (a tributary of the Cotter River) valley, about 20 km fromCanberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
in the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
. The complex is part of the Deep Space Network run by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). It is commonly referred to as the Tidbinbilla Deep Space Tracking Station and was officially opened on 19 March 1965 by then Prime Minister of Australia
The prime minister of Australia is the head of government of the Commonwealth of Australia. The prime minister heads the executive branch of the federal government of Australia and is also accountable to federal parliament under the princip ...
Sir Robert Menzies.
The station is separated from Canberra by the Murrumbidgee River and, more importantly, the Coolamon Ridge, Urambi Hills, and Bullen Range, which help shield the dishes from the city's radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the up ...
(RF) noise. Located nearby is the Tidbinbilla Nature Reserve.
Management
The CSIRO manages most of NASA's activities in Australia. In February 2010 CSIRO took over direct management of the site with the establishment of CASS (CSIRO Astronomy and Space Science). Previous to this CDSCC had been managed by external sub-contractor organisations, such as Raytheon Australia from 2003–2010;BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenue ...
(formerly British Aerospace Australia) 1990–2003; AWA Electronic Services -1990.
History

 During the mid 1960s NASA built three tracking stations in the Australian Capital Territory.
*The Tidbinbilla Tracking Station (now known as CDSCC) was opened in 1965 and is the only NASA tracking station in Australia still in operation. During the
During the mid 1960s NASA built three tracking stations in the Australian Capital Territory.
*The Tidbinbilla Tracking Station (now known as CDSCC) was opened in 1965 and is the only NASA tracking station in Australia still in operation. During the Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
program, Tidbinbilla was used for tracking the Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
.
*The Orroral Valley Tracking Station () was opened in May 1965 in what is now part of Namadgi National Park. Its role was orbiting satellite support, although it also supported the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. It was closed in 1985.
* Honeysuckle Creek Tracking Station () opened in 1967 and was built primarily to support the Apollo Moon missions, mainly communications with the Apollo Command Module. After the cancellation of the Apollo Project the station supported Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations ...
until its re-entry in 1979 when the station joined the Deep Space Network in support of the Viking and Voyager projects. 1981 saw the closure of the station and its 26 m antenna was moved to CDSCC to become known as Deep Space Station 46. After the antenna was removed the rest of the facility was dismantled and knocked down. Its foundation, access road and parking area are all that remains of the facility.
Antennas
As of late 2016 the station has five large antennas, called Deep Space Stations (DSS), each identified by a number: DSS-34, DSS-35, DSS-36, DSS-43, and DSS-45. The CDSCC also uses theParkes radio telescope Parkes may refer to:
* Sir Henry Parkes (1815–1896), Australian politician, one of the earliest and most prominent advocates for Australian federation
Named for Henry Parkes
* Parkes, New South Wales, a regional town
* Parkes Observatory, a rad ...
in central New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
at busy times to receive data from spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
(then designated DSS-49). There has been ongoing construction since 2010 building additional 34 m beam waveguide antenna. Construction of DSS-35 began in July 2010. The station's collimation tower is located approximately 3 km to the north-west, on Black Hill.
Funding
CDSCC costs about per year to run, and is funded by NASA.See also
*Carnarvon Tracking Station
The Carnarvon Tracking Station was an Earth tracking station in Australia, located 10 kilometres (6.2 miles) south of Carnarvon, Western Australia. It operated from 1963 until 1975, during which it supported the Gemini, Apollo and Skylab ...
* OTC Satellite Earth Station Carnarvon
* Parkes Observatory
Parkes Observatory is a radio astronomy observatory, located north of the town of Parkes, New South Wales, Australia. It hosts Murriyang, the 64 m CSIRO Parkes Radio Telescope also known as "The Dish", along with two smaller radio telescopes ...
References
External links
Partners in space: CSIRO and NASA - video
Official CDSCC Webpage
Official CSIRO pages
Tidbinbilla Tracking Station tribute site
Honeysuckle Creek tribute site
{{Authority control Earth stations in the Australian Capital Territory Space programme of Australia Deep Space Network 1965 establishments in Australia CSIRO NASA facilities in Australia