Camp Peary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Camp Peary is an approximately 9,000 acre U.S. military reservation in York County near
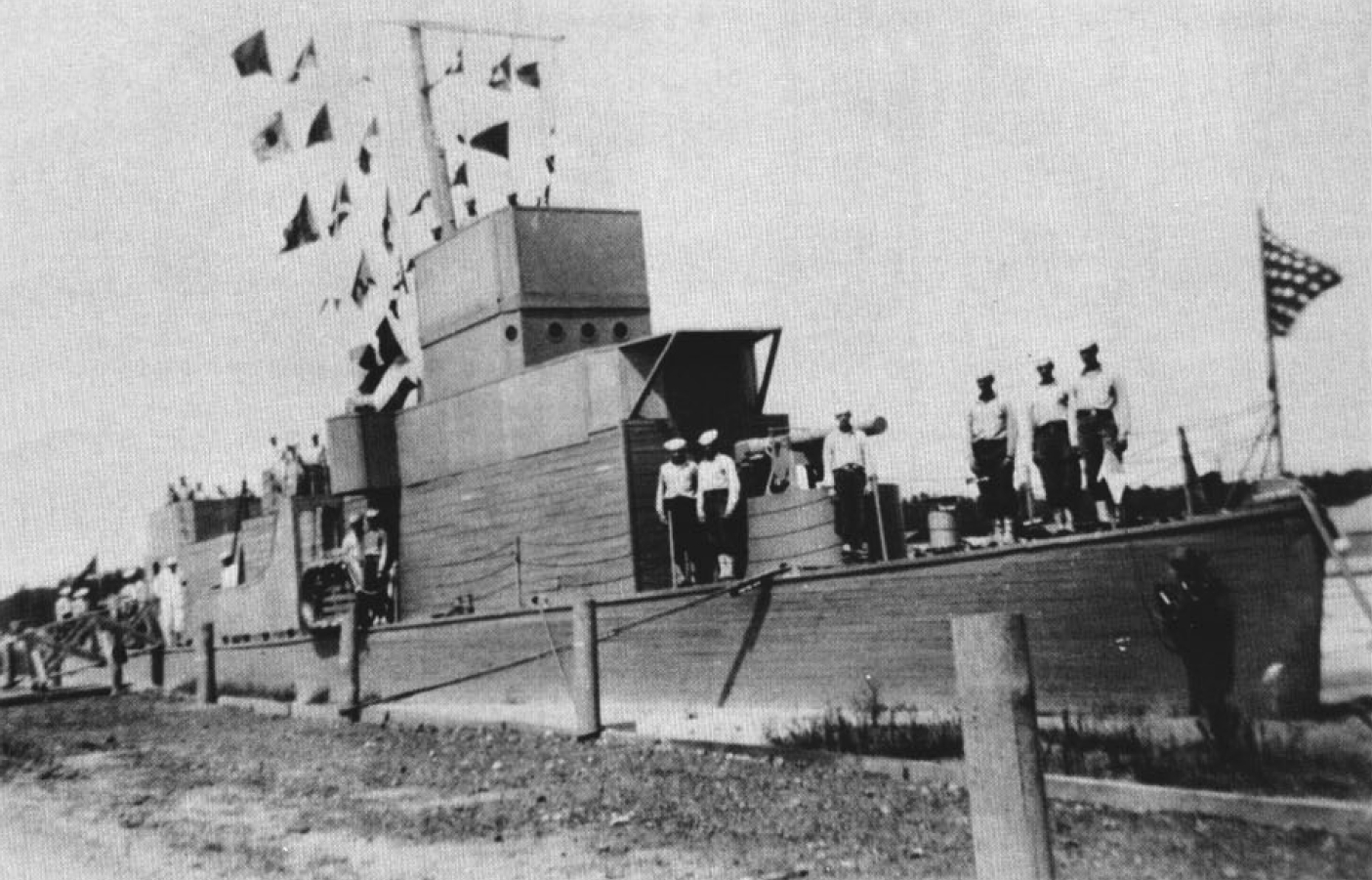 During
During
 At the outset of the War, the preliminary training of the Seabees had been carried out at Naval Training Stations across the country. That lasted a short period until boot training was consolidated at Camp Allen Virginia. Camp Allen was replaced by Camp Bradford which in turn was replaced by Camp Peary. The initial
At the outset of the War, the preliminary training of the Seabees had been carried out at Naval Training Stations across the country. That lasted a short period until boot training was consolidated at Camp Allen Virginia. Camp Allen was replaced by Camp Bradford which in turn was replaced by Camp Peary. The initial
/ref> Another 100,000 men would go through the camp before training there ceased in June of 1944. During that period the Seabees established over 60 trade schools on the base. In June of 1943 the dynamite and demolition school opened. Some of its first graduates included the first six classes of Seabee volunteers for the Naval Combat Demolition Units. After June 1944 Seabee boot camp was moved to Camp Endicott,
Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is ...
. Officially referred to as an Armed Forces Experimental Training Activity (AFETA) under the authority of the Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
, Camp Peary hosts a covert CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
training
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. I ...
facility known as "The Farm", which is used to train officers of the CIA's Directorate of Operations, as well as those of the DIA's Defense Clandestine Service
The Defense Clandestine Service (DCS) is an arm of the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), which conducts clandestine espionage, intelligence gathering activities and classified operations around the world to provide insights and answer national ...
, among other intelligence entities. Camp Peary has a sister facility, " The Point", located in Hertford, North Carolina
Hertford is a town and the county seat of Perquimans County, North Carolina, United States. The current population of Hertford, North Carolina is 1,912 based on the 2020 census. The US Census estimates the 2021 population at 1,925. The last offici ...
.
Camp Peary is named for Arctic explorer Rear Admiral Robert E. Peary. Porto Bello, the historic hunting lodge of Lord Dunmore
Earl of Dunmore is a title in the Peerage of Scotland.
History
The title was created in 1686 for Lord Charles Murray, second son of John Murray, 1st Marquess of Atholl. He was made Lord Murray of Blair, Moulin and Tillimet (or Tullimet) and V ...
, last royal governor of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, is listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
and is located on the grounds of Camp Peary.
Location
Comprising of land, of which about are unimproved or only partially improved. The Biglers Millpond occupies the site adjacent to the York River. The majority of Camp Peary falls within York County, though a small portion of the reservation near Skimino Creek at the western edge is located in James City County.World War II, relocations of residents
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, beginning in 1942, the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
took over a large area on the north side of the Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay. It is sometimes known as the ''Lower Peninsula'' to distinguish it from two other peninsulas to the n ...
in York County, Virginia
York County (formerly Charles River County) is a county in the eastern part of the Commonwealth of Virginia, located in the Tidewater. As of the 2020 census, the population was 70,045. The county seat is the unincorporated town of Yorktown.
L ...
which became known as Camp Peary, initially for use as a Seabee
, colors =
, mascot = Bumblebee
, battles = Guadalcanal, Bougainville, Cape Gloucester, Los Negros, Guam, Peleliu, Tarawa, Kwajalein, Saipan, Tinian, Iwo Jima, Philippin ...
training base. The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond t ...
(C&O) extended a spur track from its Richmond-Newport News main line tracks to the site from nearby Williamsburg, and established Magruder Station near the former unincorporated town of Magruder. As part of the process of converting the property to a military reservation, all residents of the entire towns of Magruder and Bigler's Mill had to vacate. The town of Magruder was a traditionally African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ensl ...
community, established for freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), emancipation (granted freedom ...
after the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
. It had been named for Confederate General John B. Magruder. A Civil War field hospital had occupied the site of Bigler's Mill near the York River. Although the graves in the church cemetery were not moved, many of the residents and the local Mount Gilead Baptist Church were relocated to the Grove community, located on U.S. Route 60 in adjacent James City County a few miles away, where a number of displaced residents from an area near Lackey
Lackey may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Places
* Lackey, Kentucky, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey, Mississippi, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey, Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey Ridge, ...
known simply as "the Reservation" had earlier relocated under similar circumstances during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
when what is now the Naval Weapons Station Yorktown was created.
Seabee training
 At the outset of the War, the preliminary training of the Seabees had been carried out at Naval Training Stations across the country. That lasted a short period until boot training was consolidated at Camp Allen Virginia. Camp Allen was replaced by Camp Bradford which in turn was replaced by Camp Peary. The initial
At the outset of the War, the preliminary training of the Seabees had been carried out at Naval Training Stations across the country. That lasted a short period until boot training was consolidated at Camp Allen Virginia. Camp Allen was replaced by Camp Bradford which in turn was replaced by Camp Peary. The initial Seabee
, colors =
, mascot = Bumblebee
, battles = Guadalcanal, Bougainville, Cape Gloucester, Los Negros, Guam, Peleliu, Tarawa, Kwajalein, Saipan, Tinian, Iwo Jima, Philippin ...
recruits of WWII were men who built Boulder Dam #REDIRECT Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression a ...
, America's highways and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
skyscrapers. At Naval Construction Training Center Peary, Seabees were taught basic military order, discipline, weaponry, stevedoring, and construction trades. The Camp opened in November 3rd of 1942 with the 36th CB the first to train there while the first organized there was the 61st CB.U.S. Navy Seabee Museum facebook, Camp Peary, April 26, 201/ref> Another 100,000 men would go through the camp before training there ceased in June of 1944. During that period the Seabees established over 60 trade schools on the base. In June of 1943 the dynamite and demolition school opened. Some of its first graduates included the first six classes of Seabee volunteers for the Naval Combat Demolition Units. After June 1944 Seabee boot camp was moved to Camp Endicott,
Quonset Point
Quonset Point (), also known simply as Quonset, is a small peninsula in Narragansett Bay in the town of North Kingstown, Rhode Island. Its name is widely known from the Quonset hut, which was first manufactured there. ''Quonset'' is an Algo ...
, Rhode Island.
Base commander Capt. J.G. Ware had the idea to raise hogs on base so the recruits called the place Capt. Wares hog farm. Originally the hog yard was in the center of the camp, but the enlisted complained that the pigs were on high ground while they were in the mud. This got the hogs moved to a more obscure location, but still within the limits of the military reservation. A bulldozer was used for clearing the feed troughs and transporting slop from the galley to the hog yard. Eventually the farming enterprise made the news and it is from this history that base derives "The Farm" moniker used today.
German prisoners-of-war
Camp Peary's mission changed when a new need presented itself to the Navy. A portion of the land became a detention center forGerman prisoners of war in the United States
Members of the German military were interned as prisoners of war in the United States during World War I and World War II. In all, 425,000 German prisoners lived in 700 camps throughout the United States during World War II.
World War I
Hostil ...
(POWs). Many of them were Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
crewmen from captured German U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s and from ships the Germans thought lost at sea with crews presumed dead. It was important to keep the German authorities unaware of their capture, since knowledge that they had survived would mean that secret code books and Enigma machines thought lost at sea could also have been compromised. Learning that these men were being held as POWs, would almost certainly have caused the Germans to change the secret codes that had been broken by Allied codebreakers, thus, extra secrecy was necessary. There is information about life at the Camp and the German PoWs in the Herman Recht papers held by the College of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William ...
, a set of letters written by a clerk at the Camp.
Many of the former POWs stayed in Virginia and the United States after the war, and became naturalized as U.S. citizens.
Post-World War II use
Vacated by the Navy in 1946, Camp Peary became aVirginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
state forestry and game reserve for five years. A reservoir that had been built on the upper reaches of Queen's Creek
Queen's Creek is located in York County in the Virginia Peninsula area of the Hampton Roads region of southeastern Virginia in the United States. From a point of origin near the Waller Mill Reservoir in western York County, it flows northeasterly ...
to supply the substantial fresh water needs of Camp Peary when it was a Seabee base was divested to the City of Williamsburg. The Waller Mill Reservoir
Waller may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Waller, Pennsylvania
* Waller, Texas
* Waller, Washington
* Waller County, Texas
People
* Waller (surname)
* nickname of John Walsh (rugby league), English rugby league footballer in the 1960s a ...
formed the basis for the city's Waller Mill Park
Waller may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Waller, Pennsylvania
* Waller, Texas
* Waller, Washington
* Waller County, Texas
People
* Waller (surname)
* nickname of John Walsh (rugby league), English rugby league footballer in the 1960s a ...
, although the park is located north of the city limits in York County. A portion of the abandoned Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond t ...
spur from the Peninsula Extension
The Peninsula Extension which created the Peninsula Subdivision of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) was the new railroad line on the Virginia Peninsula from Richmond to southeastern Warwick County. Its principal purpose was to provide an ...
main line just east of near Ewell Station to the base (also built during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
) is now a recreational rail trail
A rail trail is a shared-use path on railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed, but may also share the right of way with active railways, light rail, or streetc ...
.
Then, in 1951, the U.S. Navy returned to the property, securing the portion north of the highway, which was State Route 168 at the time, and announced it closed to the public; it has been that way ever since. In June 1961, two months after the Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion (, sometimes called ''Invasión de Playa Girón'' or ''Batalla de Playa Girón'' after the Playa Girón) was a failed military landing operation on the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly fin ...
, the Navy announced it was officially opening a new facility at Harvey Point base, in Hertford, North Carolina
Hertford is a town and the county seat of Perquimans County, North Carolina, United States. The current population of Hertford, North Carolina is 1,912 based on the 2020 census. The US Census estimates the 2021 population at 1,925. The last offici ...
. A spokesman said that all four branches of the military would conduct "testing and evaluation of various classified materials and equipment" at the new site. He added that some of the training "now being done at Camp Peary, Va., will be transferred to Harvey Point."
The Farm
Camp Peary is known as "The Farm", a training facility run by theCentral Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
for the purpose of training CIA's clandestine officers, as well as officers of other organizations specializing in clandestine activities, such as the Defense Intelligence Agency
The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an intelligence agency and combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense, specializing in defense and military intelligence.
A component of the Department of Defense (DoD) and the ...
. The existence of this facility is widely known but has never been formally acknowledged by the U.S. government. Access to Camp Peary is strictly controlled, and visitors to the installation are escorted at all times. The portion of the original World War II Seabee base north of Interstate 64
Interstate 64 (I-64) is an east–west Interstate Highway in the Eastern United States. Its western terminus is at I-70, U.S. Route 40 (US 40), and US 61 in Wentzville, Missouri. Its eastern terminus is at an interchang ...
has been closed to the public since 1951. However, the roads and many structures of Magruder and Bigler's Mill are still there and many are occupied. An airport with a runway was added to the facility near the site of Bigler's Mill. Flight records show that at least 11 aircraft that appear to be owned by CIA front companies, and are believed to have been used as rendition aircraft
This page describes several aircraft that are alleged in media reports to have been used in the practice of extraordinary rendition, the extralegal transfer of prisoners from one country to another.
N313P
N313P was a tailnumber assigned to a Boe ...
by the CIA under the guise of charter flights, have landed on this runway.
Former CIA officer Bill Wagner attended a three-week interrogation course at The Farm in 1970. He claims it was the agency's "premier course", and that volunteers played the role of interrogation subjects in order to be guaranteed seats in future classes. Interrogators-in-training practiced techniques such as sleep deprivation
Sleep deprivation, also known as sleep insufficiency or sleeplessness, is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep to support decent alertness, performance, and health. It can be either chronic or acute and may vary ...
, deliberately tainted food, and mock executions. According to Wagner, the course was dropped from the CIA training curriculum after the Watergate scandal
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon from 1972 to 1974 that led to Nixon's resignation. The scandal stemmed from the Nixon administration's contin ...
, due to increased attention being paid to CIA practices.
See also
*Agent handling
In intelligence organizations, agent handling is the management of so-called agents (called secret agents or spies in common parlance), principal agents, and agent networks (called "assets") by intelligence officers typically known as case o ...
* CIA University
* Harvey Point
* ''Quantico'' (season 2)
* ''The Recruit __NOTOC__
Recruit can refer to:
Military
* Military recruitment
* Recruit training, in the military
* ''Rekrut'' (English: Recruit), a military recruit or low rank in German-speaking countries
* Seaman recruit Books
*''Le Réquisitionnaire'' (En ...
''
* Sherman Kent School for Intelligence Analysis
* Special Activities Center
The Special Activities Center (SAC) is a division of the United States Central Intelligence Agency responsible for covert and paramilitary operations. The unit was named Special Activities Division (SAD) prior to 2015. Within SAC there are two ...
* United States Army Intelligence Center
* Warrenton Training Center
Bibliography
* Lindsay Moran, ''Blowing My Cover: My Life as a CIA Spy'', 2005 * TJ Waters, ''Class 11: My Story Inside the CIA's First Post-9/11 Spy Class''References
External links
* * * {{coord, 37.33, -76.67, type:landmark_region:US-VA, display=title Central Intelligence Agency training facilities Military installations in Virginia Buildings and structures in York County, Virginia Williamsburg, Virginia Secret places in the United States Installations of the U.S. Department of Defense Defense Intelligence Agency 1942 establishments in Virginia Military installations established in 1942