CaOH2SEM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (
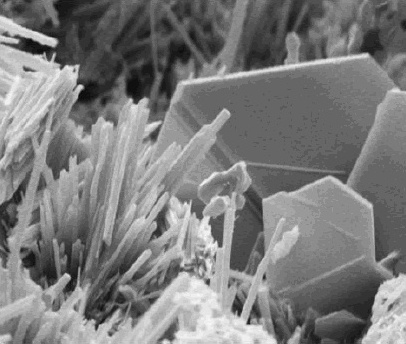 Calcium hydroxide adopts a
Calcium hydroxide adopts a
 In Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs, the word for calcium hydroxide is ''nextli''. In a process called ''
In Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs, the word for calcium hydroxide is ''nextli''. In a process called ''
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Calcium Hydroxide
*
MSDS Data Sheet
{{DEFAULTSORT:Calcium Hydroxide Building materials Calcium compounds Dental materials Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Intoxication E-number additives
calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
) is mixed or slaked with water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide.
Properties
Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide (portlandite
Portlandite is a hydroxide-bearing mineral typically included in the oxide mineral class. It is the naturally occurring form of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and the calcium analogue of brucite (Mg(OH)2).
Occurrence
Portlandite occurs in a variety ...
) dissolves in pure water to produce an alkaline solution with a pH of about 12.5. Calcium hydroxide solutions can cause chemical burns. At high pH values due to a common-ion effect The common-ion effect refers to the decrease in solubility of an ionic precipitate by the addition to the solution of a soluble compound with an ion in common with the precipitate. This behaviour is a consequence of Le Chatelier's principle for the ...
with the hydroxide anion , its solubility drastically decreases. This behavior is relevant to cement pastes. Aqueous solutions of calcium hydroxide are called limewater and are medium-strength bases, which react with acids and can attack some metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
s such as aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
(amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
One type of amphoteric species are amphipro ...
hydroxide dissolving at high pH), while protecting other metals, such as iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
and steel, from corrosion by passivation of their surface. Limewater turns milky in the presence of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate, a process called carbonatation
Carbonatation is a chemical reaction in which calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide and forms insoluble calcium carbonate:
:Ca(OH)2CO2->CaCO3H_2O
The process of forming a carbonate is sometimes referred to as "carbonation", although t ...
:
: Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
When heated to 512 °C, the partial pressure of water in equilibrium with calcium hydroxide reaches 101kPa (normal atmospheric pressure), which decomposes calcium hydroxide into calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
and water:
: Ca(OH)2 → CaO + H2O
Structure, preparation, occurrence
 Calcium hydroxide adopts a
Calcium hydroxide adopts a polymeric
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic an ...
structure, as do all metal hydroxides. The structure is identical to that of Mg(OH) (''brucite structure''); i.e., the cadmium iodide
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compoun ...
motif. Strong hydrogen bonds exist between the layers.
Calcium hydroxide is produced commercially by treating (slaking) lime with water:
:CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
In the laboratory it can be prepared by mixing aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
solutions of calcium chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.
Ca ...
and sodium hydroxide. The mineral form, portlandite
Portlandite is a hydroxide-bearing mineral typically included in the oxide mineral class. It is the naturally occurring form of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and the calcium analogue of brucite (Mg(OH)2).
Occurrence
Portlandite occurs in a variety ...
, is relatively rare but can be found in some volcanic, plutonic
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form '' intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March ...
, and metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
. It has also been known to arise in burning coal dumps.
The positively charged ionized species CaOH+ has been detected in the atmosphere of S-type star
An S-type star (or just S star) is a cool giant with approximately equal quantities of carbon and oxygen in its atmosphere. The class was originally defined in 1922 by Paul Merrill for stars with unusual absorption lines and molecular bands no ...
s.
Retrograde solubility
According to Hopkins and Wulff (1965), the decrease of calcium hydroxide solubility with temperature was known since the works ofMarcellin Berthelot
Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot (; 25 October 1827 – 18 March 1907) was a French chemist and Republican politician noted for the ThomsenBerthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic substa ...
(1875)Berthelot, M. (1875). Dissolution des acides et des alcalis. issolution of acids and alkalis In: Annales de Chimie et de Physique. Vol. 4, pp. 445–536. and Julius Thomsen (1883)Thomsen J. (1883). Thermochemische untersuchungen hermochemical studies Vol. III, Johann Ambrosius Barth Verlag, Leipzig. (see Thomsen–Berthelot principle
In thermochemistry, the Thomsen–Berthelot principle is a hypothesis in the history of chemistry which argued that all chemical changes are accompanied by the production of heat and that processes which occur will be ones in which the most heat ...
), when the presence of ions in aqueous solutions was still questioned. Since, it has been studied in detail by many authors, a.o., Miller and Witt (1929) or Johnston and Grove (1931) and refined many times (''e.g.'', Greenberg and Copeland (1960); Hopkins and Wulff (1965); Seewald and Seyfried (1991); Duchesne and Reardon (1995)).
The reason for this rather uncommon behavior is that the dissolution of calcium hydroxide in water is an exothermic process. Thus, according to Le Chatelier's principle
Le Chatelier's principle (pronounced or ), also called Chatelier's principle (or the Equilibrium Law), is a principle of chemistry used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on chemical equilibria. The principle is named after French c ...
, a lowering of temperature favours the elimination of the heat liberated through the process of dissolution and increases the equilibrium constant of dissolution of Ca(OH)2, and so increases its solubility at low temperature. This counter-intuitive temperature dependence of the solubility is referred to as "retrograde" or "inverse" solubility. The variably hydrated phases of calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris ...
(gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
, bassanite
Bassanite is a calcium sulfate mineral with formula CaSO4· H2O or 2CaSO4·H2O. In other words it has half a water molecule per CaSO4 unit, hence its synonym ''calcium sulfate hemihydrate''.
Bassanite was first described in 1910 for an occurrenc ...
and anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the ...
) also exhibit a retrograde solubility for the same reason because their dissolution reactions are exothermic.
Uses
Calcium hydroxide is commonly used to preparelime mortar
Lime mortar or torching is composed of lime and an aggregate such as sand, mixed with water. The ancient Egyptians were the first to use lime mortars, which they used to plaster their temples. In addition, the Egyptians also incorporated various ...
.
One significant application of calcium hydroxide is as a flocculant, in water and sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding e ...
. It forms a fluffy charged solid that aids in the removal of smaller particles from water, resulting in a clearer product. This application is enabled by the low cost and low toxicity of calcium hydroxide. It is also used in fresh-water treatment for raising the pH of the water so that pipes will not corrode where the base water is acidic, because it is self-regulating and does not raise the pH too much.
It is also used in the preparation of ammonia gas (NH3), using the following reaction:
: Ca(OH)2 + 2 NH4Cl → 2 NH3 + CaCl2 + 2 H2O
Another large application is in the paper industry, where it is an intermediate in the reaction in the production of sodium hydroxide. This conversion is part of the ''causticizing'' step in the Kraft process for making pulp.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . In the causticizing operation, burned lime is added to ''green liquor
Green liquor is the dissolved smelt of sodium carbonate, sodium sulfide and other compounds from the recovery boiler in the kraft process. The liquor's eponymous green colour arises from the presence of colloidal iron sulfide.
The green liquor ...
'', which is a solution primarily of sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate produced by dissolving ''smelt'', which is the molten form of these chemicals from the recovery furnace.
In orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of ...
crops, calcium hydroxide is used as a fungicide. Applications of 'lime water' prevent the development of cankers caused by the fungal pathogen ''Neonectria galligena
''Neonectria ditissima'' (syn. ''Neonectria galligena'') is a fungal plant pathogen. It causes cankers that can kill branches of trees by choking them off. Apple and beech trees are two susceptible species.
Host range
''Neonectria ditissima ...
''. The trees are sprayed when they are dormant in winter to prevent toxic burns from the highly reactive calcium hydroxide. This use is authorised in the European Union and the United Kingdom under Basic Substance regulations.
Calcium hydroxide is used in dentistry, primarily in the specialty of endodontics.
Food industry
Because of its lowtoxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
and the mildness of its basic properties, slaked lime is widely used in the food industry:
* In USDA certified food production in plants and livestock
* To clarify raw juice from sugarcane or sugar beets in the sugar industry, (see carbonatation
Carbonatation is a chemical reaction in which calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide and forms insoluble calcium carbonate:
:Ca(OH)2CO2->CaCO3H_2O
The process of forming a carbonate is sometimes referred to as "carbonation", although t ...
)
* To process water for alcoholic beverages and soft drinks
* Pickle cucumbers and other foods
* To make Chinese century eggs
* In maize preparation: removes the cellulose hull of maize kernels (see nixtamalization
Nixtamalization () is a process for the preparation of corn, or other grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater (but sometimes aqueous alkali metal carbonates), washed, and then hulled. The ter ...
)
* To clear a brine of carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
s of calcium and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
in the manufacture of salt for food and pharmaceutical uses
* In fortifying (Ca supplement) fruit drinks, such as orange juice, and infant formula
Infant formula, baby formula, or simply formula (American English); or baby milk, infant milk or first milk (British English), is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepar ...
* As a digestive aid (called Choona, used in India in ''paan
Betel nut chewing, also called betel quid chewing or areca nut chewing, is a practice in which areca nuts (also called "betel nuts") are chewed together with slaked lime and betel leaves for their stimulant and narcotic effects. The practice ...
'', a mixture of areca nuts
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ''Areca'' is derived from a name u ...
, calcium hydroxide and a variety of seeds wrapped in betel leaves)
* As a substitute for baking soda
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation ( Na+) and a bicarbonate anion ( HCO3� ...
in making ''papadam
A papad is an Indian deep fried dough of black gram bean flour, either fried or cooked with dry heat (flipped over an open flame) until crunchy. Other flours made from lentils, chickpeas, rice, tapioca, millet or potato are also used. ''Papad ...
''
* In the removal of carbon dioxide from controlled atmosphere produce storage rooms
* In the preparation of mushroom growing substrates
Native American uses
 In Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs, the word for calcium hydroxide is ''nextli''. In a process called ''
In Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs, the word for calcium hydroxide is ''nextli''. In a process called ''nixtamalization
Nixtamalization () is a process for the preparation of corn, or other grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater (but sometimes aqueous alkali metal carbonates), washed, and then hulled. The ter ...
'', maize is cooked with nextli to become , also known as hominy. Nixtamalization significantly increases the bioavailability of niacin
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is an organic compound and a form of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variet ...
(vitamin B3), and is also considered tastier and easier to digest. Nixtamal is often ground into a flour, known as ''masa
''Masa'' (or ''masa de maíz'') (; ) is a maize dough that comes from ground nixtamalized corn. It is used for making corn tortillas, '' gorditas'', ''tamales'', '' pupusas'', and many other Latin American dishes. It is dried and powdered into ...
'', which is used to make tortillas and tamales.
In chewing coca leaves, calcium hydroxide is usually chewed alongside to keep the alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
stimulants chemically available for absorption by the body. Similarly, Native Americans traditionally chewed tobacco leaves with calcium hydroxide derived from burnt mollusc shells to enhance the effects. It has also been used by some indigenous American tribes as an ingredient in ''yopo
''Anadenanthera peregrina'', also known as yopo, jopo, cohoba, parica or calcium tree, is a perennial tree of the genus ''Anadenanthera'' native to the Caribbean and South America. It grows up to tall, and has a horny bark. Its flowers grow ...
'', a psychedelic snuff prepared from the beans of some ''Anadenanthera
''Anadenanthera'' is a genus of South American trees in the Legume family, Fabaceae. The genus contains two to four species, including '' A. colubrina'' and '' A. peregrina''. These trees respectively are known to the western world primarily a ...
'' species.
Asian uses
Calcium hydroxide is typically added to a bundle ofareca nut
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ''Areca'' is derived from a name ...
and betel leaf called "paan
Betel nut chewing, also called betel quid chewing or areca nut chewing, is a practice in which areca nuts (also called "betel nuts") are chewed together with slaked lime and betel leaves for their stimulant and narcotic effects. The practice ...
" to keep the alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
stimulants chemically available to enter the bloodstream via sublingual absorption.
It is used in making ''naswar
Naswār ( ps, نسوار, Cyrillic script: насва́р), also called nās (ناس; на́с) or nasvay (نسوای; насвай), is a moist, powdered tobacco dip consumed mostly in Afghanistan and surrounding countries. Naswar is stuffed in ...
'' (also known as ''nass'' or ''niswar''), a type of dipping tobacco made from fresh tobacco leaves, calcium hydroxide (''chuna'' or ''soon''), and wood ash. It is consumed most in the Pathan
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
diaspora, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. Villagers also use calcium hydroxide to paint their mud houses in Afghanistan, Pakistan and India.
Health risks
Unprotected exposure to Ca(OH)2 can cause severe skin irritation, chemical burns, blindness, lung damage or rashes.See also
* Baralyme (carbon dioxide absorbent) *Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
* Lime mortar
Lime mortar or torching is composed of lime and an aggregate such as sand, mixed with water. The ancient Egyptians were the first to use lime mortars, which they used to plaster their temples. In addition, the Egyptians also incorporated various ...
* Lime plaster
Lime plaster is a type of plaster composed of sand, water, and lime, usually non-hydraulic hydrated lime (also known as slaked lime, high calcium lime or air lime). Ancient lime plaster often contained horse hair for reinforcement and pozzolan ...
* Plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
* Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(OH)2. It occurs in nature as the mineral brucite. It is a white solid with low solubility in water (). Magnesium hydroxide is a common component of antacids, such as milk ...
(less alkaline due to a lower solubility product)
* Soda lime
Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO chemicals, used in granular form in closed breathing environments, such as general anaesthesia, submarines, rebreathers and recompression chambers, to remove carbon dioxide from breathing gases to prevent ...
(carbon dioxide absorbent)
* Whitewash
Whitewash, or calcimine, kalsomine, calsomine, or lime paint is a type of paint made from slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) or chalk calcium carbonate, (CaCO3), sometimes known as "whiting". Various other additives are sometimes used.
...
References
External links
* *CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Calcium Hydroxide
*
MSDS Data Sheet
{{DEFAULTSORT:Calcium Hydroxide Building materials Calcium compounds Dental materials Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Intoxication E-number additives