CLE peptide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
CLE peptides (CLAVATA3/Embryo Surrounding Region-Related) are a group of

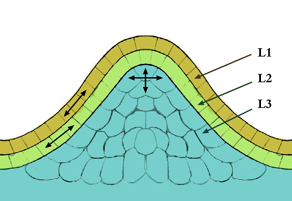 Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. There are two types of meristematic tissues 1) Apical Meristem 2) Lateral Meristem. The Apical Meristem is of two types; the shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function. Within plants SAM cells play a major role in the overall growth and development, this is due to the fact that all cells making up the major parts of the plant come from the shoot apical meristem (SAM). There are three different important area found within the SAM and they include the central zone, the peripheral zone), and the rib meristem. Each of these areas play an important in the production of new stem cells within the SAM. All SAMs are usually dome shaped and have structures that are layered and are described as the tunica and corpus. CLV3 plays an important role in regulating the production of stem cells within the Central Zone region of the (SAM), this is also true for the cell promoting WUSCHEL (WUS) gene. The combination of these two genes regulates stem cell production by WUS negatively or positively regulating the production of stem cells by controlling the CLV3 gene.;
Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. There are two types of meristematic tissues 1) Apical Meristem 2) Lateral Meristem. The Apical Meristem is of two types; the shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function. Within plants SAM cells play a major role in the overall growth and development, this is due to the fact that all cells making up the major parts of the plant come from the shoot apical meristem (SAM). There are three different important area found within the SAM and they include the central zone, the peripheral zone), and the rib meristem. Each of these areas play an important in the production of new stem cells within the SAM. All SAMs are usually dome shaped and have structures that are layered and are described as the tunica and corpus. CLV3 plays an important role in regulating the production of stem cells within the Central Zone region of the (SAM), this is also true for the cell promoting WUSCHEL (WUS) gene. The combination of these two genes regulates stem cell production by WUS negatively or positively regulating the production of stem cells by controlling the CLV3 gene.;
peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s found in plants that are involved with cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
. Production is controlled by the CLE genes. Upon binding to a CLE peptide receptor
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
in another cell, a chain reaction of events occurs, which can lead to various physiological and developmental processes. This signaling pathway is conserved in diverse land plants.
Background
Plants and animals alike both use small polypeptides for signaling in cell-to-cell communication. CLAVATA3/Embryo Surrounding Region-Related, also known as a plant peptide hormone, signaling is important for cell to cell signaling but also long distance communication. These two actions are especially important for plant cells because they are stationary and must perform cell expansion. In multicellular organisms cell-to-cell communication has been found to be very crucial for many growth processes that occur inside the organism. The 12 or 13 amino acid polypeptides are the mature forms of the CLE proteins that are derived from the conserved CLE domains. More and more CLE genes are being identified with more research being conducted in this area. CLE genes have not only been found in seed plants but also in lycophytes,bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in s ...
s, and green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
.
Genes
Most research that has been conducted on CLE peptide signaling has been conducted with ''Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organ ...
'', since this genome contains 32 members of the CLE gene family. CLV3 which belongs to the CLE family of genes is found within one or more tissues of ''Arabidopsis''. All 32 members of the CLE family share two characteristics that include: encoding of a small protein with a putative secretion signal at their N- termini and contain a conserved CLE motif at or near their C-termini. The 32 members of the CLE gene family originated from mutations of the original gene.
Structures
CLE peptides are coded by the CLE genes. These peptides vary in structure with each peptide structure performing a different job with in the plant. The minimal length of functioning CLE peptides has been found to be 12amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s with several critical residues. There are two different peptide structures that are found within the plant and they are A-type and B-type. When A-type hormones are secreted the plant slows down the rate of root growth whereas the secretion of B-type peptides effects the vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
growth of the plant. The secretion of A-type peptides speeds up the vascular development of the plant that is mediated by the B-type peptides. This suggests that these two types of peptides work together to regulate the growth of the plant. The specific peptides are:
A-type peptides
* CLE 1/3/4
* CLE 2
* CLE 5/6
* CLE 7
* CLE 8
* CLE 9
* CLE 10
* CLE 11
* CLE 12
* CLE 13
* CLE 14
* CLE 16
* CLE 17
* CLE 18
* CLE 19
* CLE 20
* CLE 21
* CLE 22
* CLE 25
* CLE 26
* CLE 27
* CLE 40
* CLE 45
B-type peptides
* CLE 41/44/TDIF
* CLE 42
* CLE 43
* CLE 46
Signaling in the shoot apical meristem

 Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. There are two types of meristematic tissues 1) Apical Meristem 2) Lateral Meristem. The Apical Meristem is of two types; the shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function. Within plants SAM cells play a major role in the overall growth and development, this is due to the fact that all cells making up the major parts of the plant come from the shoot apical meristem (SAM). There are three different important area found within the SAM and they include the central zone, the peripheral zone), and the rib meristem. Each of these areas play an important in the production of new stem cells within the SAM. All SAMs are usually dome shaped and have structures that are layered and are described as the tunica and corpus. CLV3 plays an important role in regulating the production of stem cells within the Central Zone region of the (SAM), this is also true for the cell promoting WUSCHEL (WUS) gene. The combination of these two genes regulates stem cell production by WUS negatively or positively regulating the production of stem cells by controlling the CLV3 gene.;
Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. There are two types of meristematic tissues 1) Apical Meristem 2) Lateral Meristem. The Apical Meristem is of two types; the shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function. Within plants SAM cells play a major role in the overall growth and development, this is due to the fact that all cells making up the major parts of the plant come from the shoot apical meristem (SAM). There are three different important area found within the SAM and they include the central zone, the peripheral zone), and the rib meristem. Each of these areas play an important in the production of new stem cells within the SAM. All SAMs are usually dome shaped and have structures that are layered and are described as the tunica and corpus. CLV3 plays an important role in regulating the production of stem cells within the Central Zone region of the (SAM), this is also true for the cell promoting WUSCHEL (WUS) gene. The combination of these two genes regulates stem cell production by WUS negatively or positively regulating the production of stem cells by controlling the CLV3 gene.;
Genes in other plants
CLE genes have been found in numerousmonocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae '' sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one ...
s, dicot
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, ...
s, and even moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta ('' sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and ...
. Research has even shown that some plants like rice contain the presence of a multi-CLE domain. Various CLE-like genes have also been found in the genomes of plant-parasitic nematodes such as beet, soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu ...
and potato cyst nematodes.
References
Further reading
* * * * * {{refend Cell signaling Peptides Plant hormones