Byers Peninsula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Byers Peninsula is a mainly ice-free peninsula forming the west end of
Byers Peninsula is a mainly ice-free peninsula forming the west end of
General Geography and History of Livingston Island.
In: ''Bulgarian Antarctic Research: A Synthesis''. Eds. C. Pimpirev and N. Chipev. Sofia: St. Kliment Ohridski University Press, 2015. pp. 17-28.

 The peninsula has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 126) for its outstanding environmental values (specifically its biological diversity and terrestrial and lake ecosystems), and a combination of other values including scientific (terrestrial biology, limnology, ornithology, palaeolimnology, geomorphology and geology), historic (artefacts and refuge remains of early sealers) and wilderness values. It has diverse and well-developed vegetation, numerous lakes and freshwater pools which support the restricted-range insects '' Parochlus steinenii'' and ''
The peninsula has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 126) for its outstanding environmental values (specifically its biological diversity and terrestrial and lake ecosystems), and a combination of other values including scientific (terrestrial biology, limnology, ornithology, palaeolimnology, geomorphology and geology), historic (artefacts and refuge remains of early sealers) and wilderness values. It has diverse and well-developed vegetation, numerous lakes and freshwater pools which support the restricted-range insects '' Parochlus steinenii'' and ''
Measure 4 (2016), ATCM XXXIX Final Report. Santiago, 2016.
''BirdLife data zone: Important Bird Areas''. BirdLife International, 2019
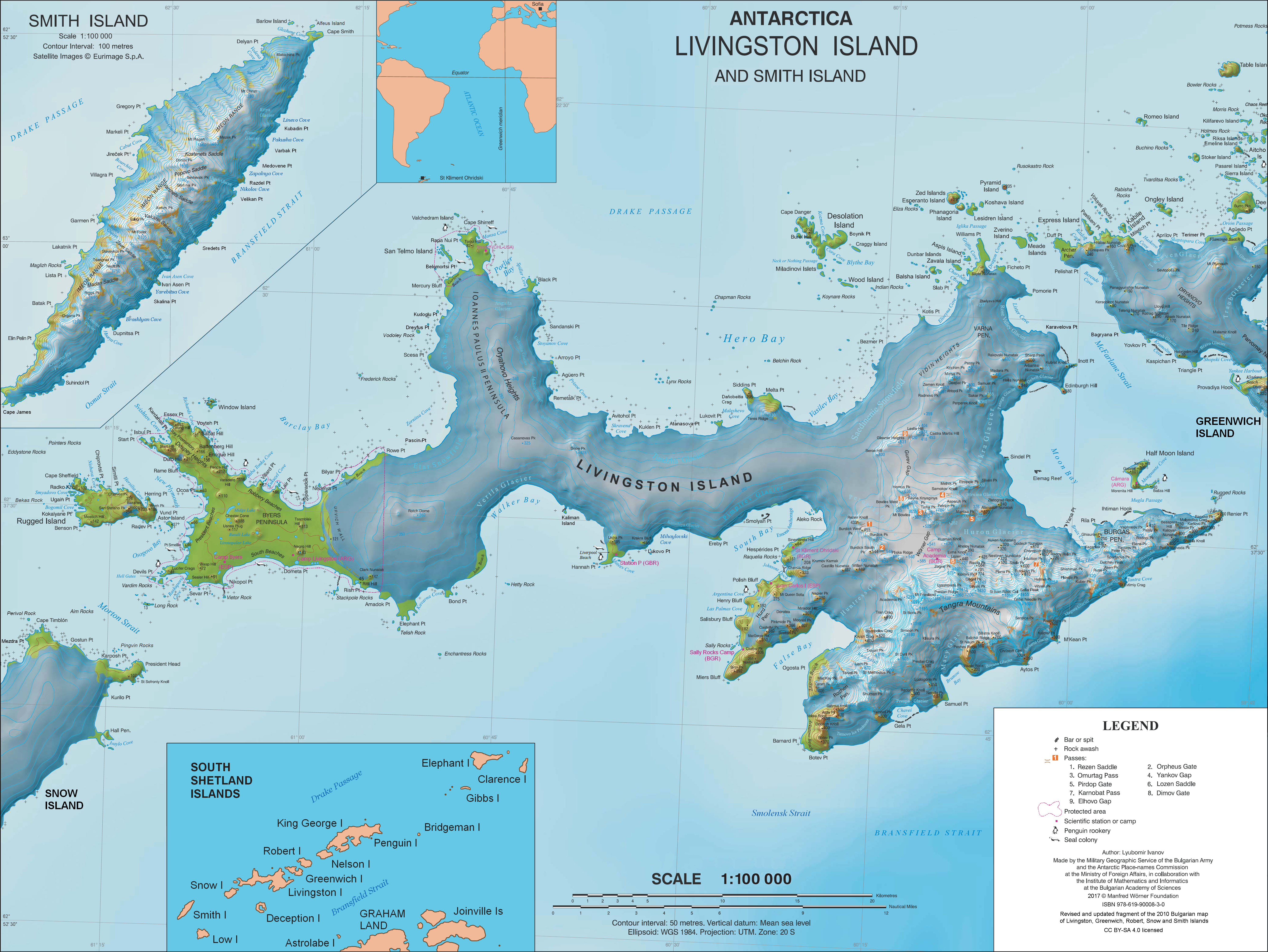
Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.
from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822.
Península Byers, Isla Livingston.
Mapa topográfico a escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1992. (Map image on p. 55 of the linked study) * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. )
South Shetland Islands: Livingston Island, Byers Peninsula.
Scale 1:50000 satellite map. UK Antarctic Place-names Committee, 2010.
Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).
Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017.
 Byers Peninsula is part of the mise-en-scène in the Antarctica
Byers Peninsula is part of the mise-en-scène in the Antarctica ''The Killing Ship.''
Susanna Gregory Website, 2019
Byers Peninsula.
SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * {{Coord, 62, 38, S, 61, 05, W, source:GNIS, display=title Peninsulas of Livingston Island Antarctic Specially Protected Areas Important Bird Areas of Antarctica Seabird colonies Penguin colonies

 Byers Peninsula is a mainly ice-free peninsula forming the west end of
Byers Peninsula is a mainly ice-free peninsula forming the west end of Livingston Island
Livingston Island (Russian name ''Smolensk'', ) is an Antarctic island in the Southern Ocean, part of the South Shetlands Archipelago, a group of Antarctic islands north of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was the first land discovered south of 60 ...
in the South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1 ...
of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
. It occupies , borders Ivanov Beach
Ivanov Beach ( bg, Иванов бряг, Ivanov bryag, ) is a mostly ice-free beach on the Drake Passage stretching in southwest–northeast direction on the southeast coast of Barclay Bay in western Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands in ...
to the northeast and is separated from Rotch Dome on the east by the ridge of Urvich Wall. The peninsula features more than 60 meltwater streams and as many lakes, notably Midge Lake
Midge Lake is the largest among numerous freshwater lakes on the ice-free Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The feature is arcuate in shape, extending 575 m in southwest-northeast direction and 125 ...
, Limnopolar Lake and Basalt Lake. Byers Peninsula has a regime of special environmental protection under the Antarctic Treaty System and requires a permit to enter.
History
The feature was named by theUK Antarctic Place-names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and ...
in 1958 for James Byers, a New York shipowner who tried unsuccessfully in August 1820 to induce the United States Government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
to found a settlement in and take possession of the South Shetland Islands. Byers organized and sent out a fleet of American sealers from New York to the South Shetland Islands in 1820–21. It was visited by early 19th century American and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
sealers who came almost exclusively from New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
, New York and England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. They operated on President Beaches
President Beaches is a series of beaches which extend for 6 nautical miles (11 km) along the broad western end of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica between Start Point to the north and Devils Poin ...
, Robbery Beaches
Robbery Beaches are beaches extending along the north side of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica between Essex Point to the west and Nedelya Point to the east. They are crossed by Eridanus Stream and Bed ...
and South Beaches, and built dwellings and shelter such as those still preserved at Sealer Hill
Sealer Hill is a hill rising to 70 m in the southwest part of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It surmounts Nikopol Point and Sevar Point to the east-southeast and west-southwest, respectively. The a ...
and Lair Point
Lair Point is a point projecting 570 m into Barclay Bay from Robbery Beaches on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and forming the east side of the entrance to Kukuzel Cove. Dominated by Lair Hill (96 m) ...
.L. IvanovGeneral Geography and History of Livingston Island.
In: ''Bulgarian Antarctic Research: A Synthesis''. Eds. C. Pimpirev and N. Chipev. Sofia: St. Kliment Ohridski University Press, 2015. pp. 17-28.
Antarctic Specially Protected Area

 The peninsula has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 126) for its outstanding environmental values (specifically its biological diversity and terrestrial and lake ecosystems), and a combination of other values including scientific (terrestrial biology, limnology, ornithology, palaeolimnology, geomorphology and geology), historic (artefacts and refuge remains of early sealers) and wilderness values. It has diverse and well-developed vegetation, numerous lakes and freshwater pools which support the restricted-range insects '' Parochlus steinenii'' and ''
The peninsula has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 126) for its outstanding environmental values (specifically its biological diversity and terrestrial and lake ecosystems), and a combination of other values including scientific (terrestrial biology, limnology, ornithology, palaeolimnology, geomorphology and geology), historic (artefacts and refuge remains of early sealers) and wilderness values. It has diverse and well-developed vegetation, numerous lakes and freshwater pools which support the restricted-range insects '' Parochlus steinenii'' and ''Belgica antarctica
''Belgica antarctica'', the Antarctic midge, is a species of flightless midge, endemic to the continent of Antarctica. At long, it is the largest purely terrestrial animal native to the continent.
It also has the smallest known insect genome as ...
'', and well-preserved sub-fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
bones in raised beach
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011/ref> or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,P ...
es. It also has the greatest concentration of historical sites in Antarctica, containing the remains of refuges, with their contemporary artefacts, and shipwrecks of early 19th century sealing expeditions.
The eastern boundary of the protected area was shifted eastwards to 60º53'45"W in 2016 to include besides Byers Peninsula also all ice-free ground and ice sheet west of Clark Nunatak and Rowe Point, increasing the overall surface area of the protected territory to . Excepting Vardim Rocks, no offshore islets or rocks are protected. In particular, Rugged Island, Window Island and Astor Island
Astor Island is an island lying between Rugged Island and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surface area .
The feature was named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1958 for B. Astor of the New Y ...
are not protected.
Two restricted zones in the protected territory that are of scientific importance to Antarctic microbiology have been further designated with greater restriction placed on access with the aim of preventing microbial or other contamination by human activity: Ray Promontory in the west, and northwestern Rotch Dome, northern Urvich Wall Ridge and adjacent deglaciated ground on Ivanov Beach
Ivanov Beach ( bg, Иванов бряг, Ivanov bryag, ) is a mostly ice-free beach on the Drake Passage stretching in southwest–northeast direction on the southeast coast of Barclay Bay in western Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands in ...
in the east.Management Plan for Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 126 Byers Peninsula.Measure 4 (2016), ATCM XXXIX Final Report. Santiago, 2016.
Important Bird Area
The protected territory ''ASPA 126 Byers Peninsula'' has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies ofAntarctic tern
The Antarctic tern (''Sterna vittata'') is a seabird in the family Laridae. It ranges throughout the southern oceans and is found on small islands around Antarctica as well as on the shores of the mainland. Its diet consists primarily of small fis ...
s (1760 pairs) and kelp gull
The kelp gull (''Larus dominicanus''), also known as the Dominican gull, is a gull that breeds on coasts and islands through much of the Southern Hemisphere. The nominate ''L. d. dominicanus'' is the subspecies found around South America, part ...
s (450 pairs). Other birds nesting on the peninsula include chinstrap and gentoo penguin
The gentoo penguin ( ) (''Pygoscelis papua'') is a penguin species (or possibly a species complex) in the genus ''Pygoscelis'', most closely related to the Adélie penguin (''P. adeliae'') and the chinstrap penguin (''P. antarcticus''). The ea ...
s, Wilson's and black-bellied storm petrels, Cape petrels, southern giant petrels, imperial shag
The imperial shag or imperial cormorant (''Leucocarbo atriceps'') is a black and white cormorant native to southern South America, primarily in rocky coastal regions, but locally also at large inland lakes. Some taxonomic authorities, including ...
s, brown skua
The brown skua (''Stercorarius antarcticus''), also known as the Antarctic skua, subantarctic skua, southern great skua, southern skua, or hākoakoa (Māori), is a large seabird that breeds in the subantarctic and Antarctic zones and moves furthe ...
s and snowy sheathbill
The snowy sheathbill (''Chionis albus''), also known as the greater sheathbill, pale-faced sheathbill, and paddy, is one of two species of sheathbill. It is usually found on the ground. It is the only land bird native to the Antarctic continent. ...
s. Large numbers of southern elephant seal
The southern elephant seal (''Mirounga leonina'') is one of two species of elephant seals. It is the largest member of the clade Pinnipedia and the order Carnivora, as well as the largest extant marine mammal that is not a cetacean. It gets its ...
s haul out during their breeding season.Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island.''BirdLife data zone: Important Bird Areas''. BirdLife International, 2019
See also
*Camp Byers
Camp Byers ( es, Campamento Byers) is a Spanish seasonal base camp on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The locality is also designated for use as an International Field Camp. When necessary for scient ...
* Camp Livingston
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
* Livingston Island
Livingston Island (Russian name ''Smolensk'', ) is an Antarctic island in the Southern Ocean, part of the South Shetlands Archipelago, a group of Antarctic islands north of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was the first land discovered south of 60 ...
Maps

Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.
from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822.
Península Byers, Isla Livingston.
Mapa topográfico a escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1992. (Map image on p. 55 of the linked study) * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. )
South Shetland Islands: Livingston Island, Byers Peninsula.
Scale 1:50000 satellite map. UK Antarctic Place-names Committee, 2010.
Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).
Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017.
In fiction
 Byers Peninsula is part of the mise-en-scène in the Antarctica
Byers Peninsula is part of the mise-en-scène in the Antarctica thriller novel
Thriller is a genre of fiction, having numerous, often overlapping subgenres. Thrillers are characterized and defined by the moods they elicit, giving viewers heightened feelings of suspense, excitement, surprise, anticipation and anxiety. S ...
''The Killing Ship'' authored by Elizabeth Cruwys
Susanna Gregory is the pseudonym of Elizabeth Cruwys, a Cambridge academic who was previously a coroner's officer. She writes detective fiction, and is noted for her series of mediaeval mysteries featuring Matthew Bartholomew, a teacher of medici ...
and Beau Riffenburgh under their joint alias Simon Beaufort in 2016.Susanna Gregory Website, 2019
Notes
References
Byers Peninsula.
SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * {{Coord, 62, 38, S, 61, 05, W, source:GNIS, display=title Peninsulas of Livingston Island Antarctic Specially Protected Areas Important Bird Areas of Antarctica Seabird colonies Penguin colonies