Bulgarian Armed Forces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bulgarian Army ( bg, Българска армия, Bŭlgarska armiya) is the military of
 The modern Bulgarian military dates back to 1878. On 22 July 1878 (10 July O.S.) a total of 12 battalions of '' opalchentsi'' who participated in the Liberation war, formed the Bulgarian armed forces. According to the
The modern Bulgarian military dates back to 1878. On 22 July 1878 (10 July O.S.) a total of 12 battalions of '' opalchentsi'' who participated in the Liberation war, formed the Bulgarian armed forces. According to the
 In March 1910 an Albanian insurrection broke out in Kosovo. In August Montenegro followed Bulgaria's precedent by becoming a kingdom. In 1911 Italy launched an invasion of Tripolitania, which was quickly followed by the occupation of the Dodecanese Islands. The Italians' decisive military victories over the Ottoman Empire greatly influenced the Balkan states to prepare for war against Turkey. Thus, in the spring of 1912 consultations among the various Christian Balkan nations resulted in a network of military alliances that became known as the
In March 1910 an Albanian insurrection broke out in Kosovo. In August Montenegro followed Bulgaria's precedent by becoming a kingdom. In 1911 Italy launched an invasion of Tripolitania, which was quickly followed by the occupation of the Dodecanese Islands. The Italians' decisive military victories over the Ottoman Empire greatly influenced the Balkan states to prepare for war against Turkey. Thus, in the spring of 1912 consultations among the various Christian Balkan nations resulted in a network of military alliances that became known as the  Bulgaria's war aims were focused on
Bulgaria's war aims were focused on
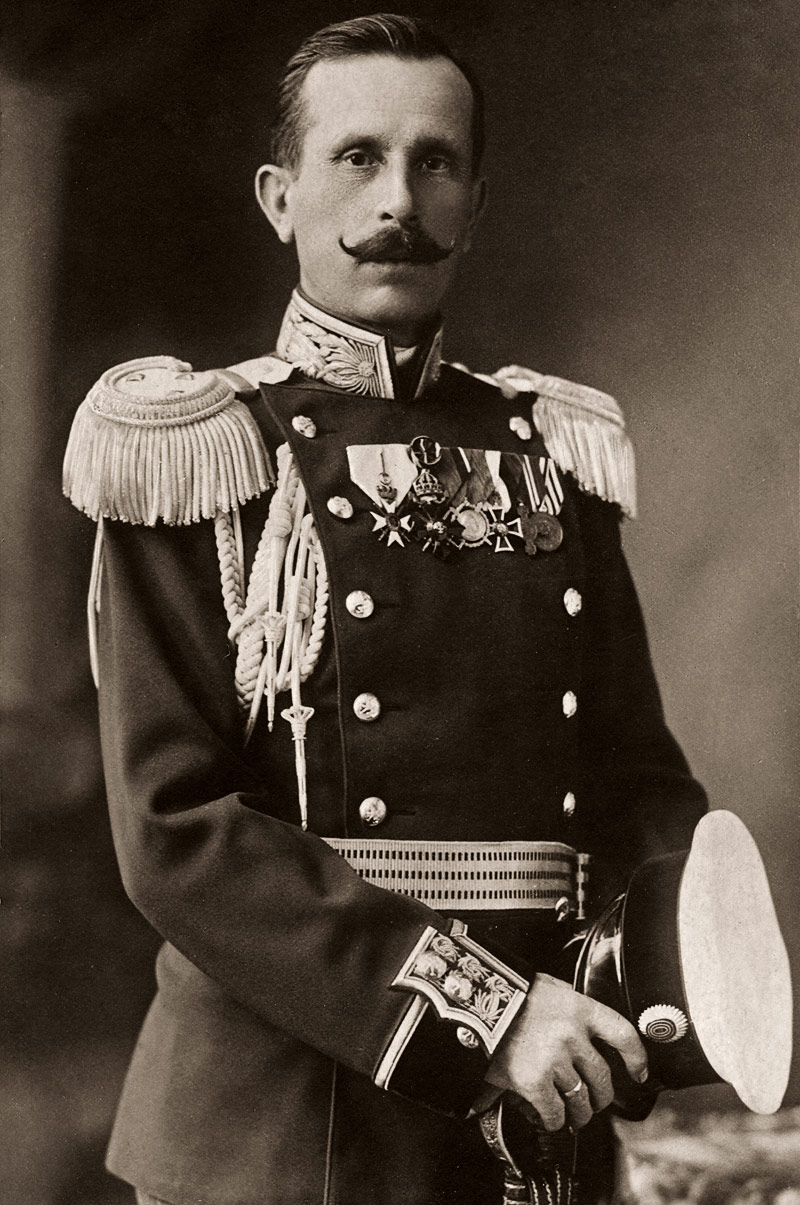 The
The
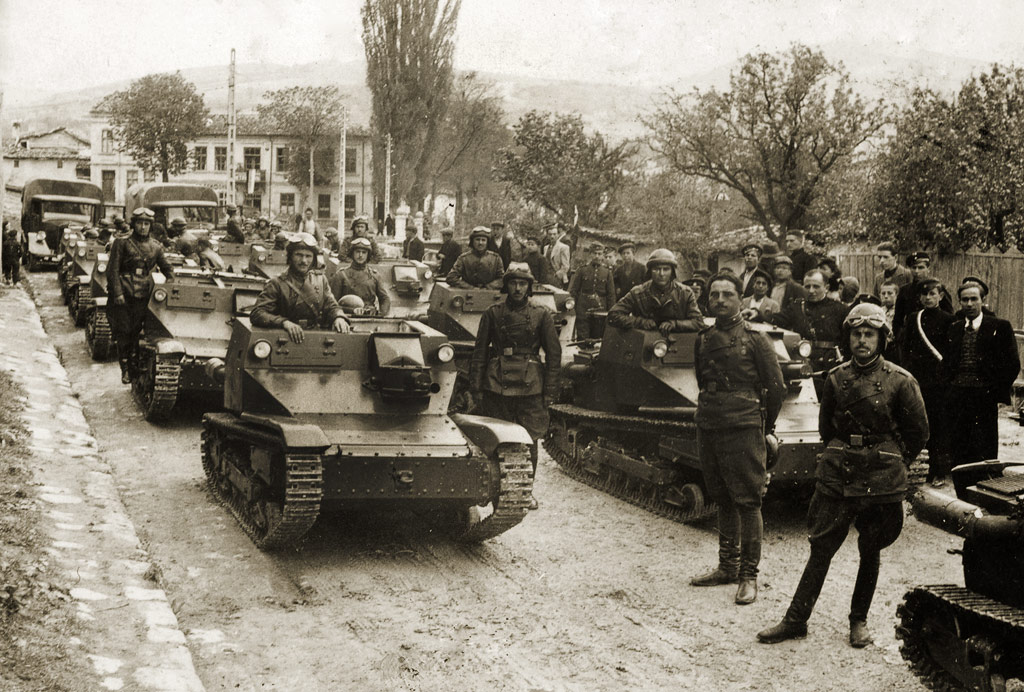 The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine proved to be a severe blow to Bulgaria's military. According to the treaty, the country had no right to organize a conscription-based military. The professional army was to be no more than 20,000 men, including internal forces and border guards. Equipping the army with tanks, submarines, bombers and heavy artillery was strictly prohibited, although Bulgaria managed to get around some of these prohibitions. Nevertheless, on the eve of World War II the Bulgarian army was still well-trained and well-equipped. In fact, the Bulgarian Army had been expanded in 1935.
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine proved to be a severe blow to Bulgaria's military. According to the treaty, the country had no right to organize a conscription-based military. The professional army was to be no more than 20,000 men, including internal forces and border guards. Equipping the army with tanks, submarines, bombers and heavy artillery was strictly prohibited, although Bulgaria managed to get around some of these prohibitions. Nevertheless, on the eve of World War II the Bulgarian army was still well-trained and well-equipped. In fact, the Bulgarian Army had been expanded in 1935.
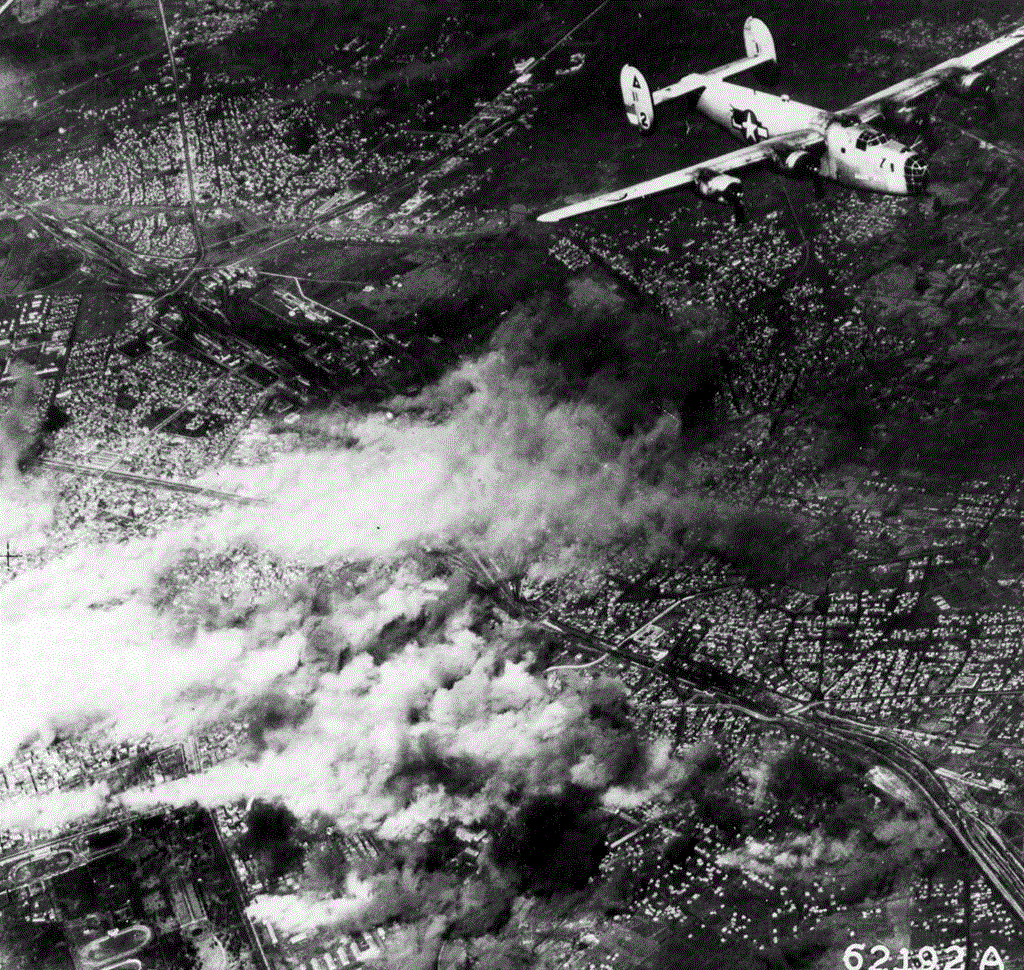 On 1 March 1941, Bulgaria signed the
On 1 March 1941, Bulgaria signed the
 With the collapse of the
With the collapse of the
In 2002, Bulgaria disbanded the Rocket Forces despite nationwide protests, and has disbanded its submarine component. Bulgaria is to have 27,000 standing troops by 2014, consisting of 14,310 troops in the land forces, 6,750 in the air force, 3,510 in the navy and 2,420 in the joint command. In 2018, the Bulgarian Armed Forces numbers around 33,150 soldiers, 73 aircraft, 2234 vehicles including 531 tanks, and 29 naval assets.

The organisation of the Ministry of Defence includes: * General Administration * Specialised Administration * Inspectorate of the Ministry of Defence * Protocol Unit of the Ministry of Defence * Financial Control and Material Accountability Unit * Internal Audit Directorate of the Ministry of Defence * Information Security Directorate of the Ministry of Defence * Defence Staff Structures directly subordinated to the Ministry of Defence include: * Military Information Service, Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Director ** Directorate ** Information Division ** Analysis Division ** Resources Supply Division * Military Police Service, Sofia (commanded by a Brigade General/ Commodore) ** Military Police Command ** Military Police Operational Company (MRAV Sand Cat) ** Regional Military Police Service Sofia ** Regional Military Police Service Plovdiv ** Regional Military Police Service Pleven ** Regional Military Police Service Varna ** Regional Military Police Service Sliven ** Military Police Service Logistics and Training Centre, Sofia * Military Geographical Service ** MGS Headquarters ** Geographical Information Support Centre ** Geodesic Observatory (GPS Observatory) ** Military Geographical Centre ** Information Security Unit ** Financial Comptroller * Stationary Communications and Information System ** Communications and Information Centre ** Government Communications Support Centre, ** Operational Centres ** Engineering and CIS recovery Centre ** Stationary Communications Network * National Guards Unit, Sofia (commanded by a Colonel) ** Headquarters ** 1st Guards Battalion ** 2nd Mixed Guards Battalion ** National Guards Unit Representative Military Band ** Armed Forces Representative Dance Company ** Guardsmen Training Centre ** Logistics Support Company * Military Medical Academy, Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Chief of the MMA, Chief of the MATH - Sofia and General Surgeon of the Bulgarian Armed Forces ** Deputy Chief for Diagnostics and Medical Treatment Activities ** Deputy Chief for Education and Scientific Activities ** Deputy Chief for Medical Support of Military Units and Overseas Military Missions ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Sofia ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital (informally known as the Naval Hospital)- Varna ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Plovdiv ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Sliven ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Pleven ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital "Saint George the Victorious" - Pomorie ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital "Caleroya" - Hisar ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital - Bankya ** Military Medical Quick Reaction Force (expeditionary disaster and crisis relief unit) ** Psychological Health and Prevention Centre ** Scientific and Application Centre for Military Medical Expertise and Aviation and Seaborne Medicine ** Scientific and Application Centre for Military Epidemiology and Hygiene * Military Academy " Georgi Stoykov Rakovski", Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Command *** Commandant of the Military Academy *** Deputy Chief for Study and Scientific Activities *** Deputy Chief for Administrative Activities and Logistics ** Administrative Units *** Personnel and Administrative Support Department *** Logistics Department *** Study and Scientific Activities Department *** Financial Department *** Library and Publishing Activities Sector *** Public Relations, International Activities and Protocol Sector ** Training Units *** National Security and Defence College *** Command Staff College *** Peacekeeping Operations and Computer Simulations Sector *** Foreign Languages Studies Department ** Perspective Defence Research Institute * National Military University "
 Bulgaria's total military personnel as of 2014 is 37,100, of which 30,400 (80.1%) are active military personnel and 8,100 (11.9%) are civilian personnel. The Land Forces are the largest branch, with at least 18,000 men serving there. In terms of percentage, 53% of all Army personnel are in the Land Forces, 25% are in the Air Force, 13% are in the Navy and 9% are in the Joint Forces Command. Annual spending per soldier amounts to 30,000 leva (~ 15,000 euro) and is scheduled to increase to 43,600 leva by 2014.
Unlike many former Soviet bloc militaries, discipline and morale problems are not common. During the Communist era, the army members enjoyed extensive social privileges. After the fall of Communism and Bulgaria's transition to a market economy, wages fell severely. For almost a decade social benefits were virtually non-existent, and some of them have been restored but recently. Nikolai Tsonev, defence minister under the 2005–2009 cabinet, undertook steps to provide the members of the military and their families with certain privileges in terms of healthcare and education, and to improve living conditions.
Military education in Bulgaria is provided in military universities and academies. Due to cuts in spending and manpower some universities have been disbanded and their campuses were included as faculties of other, larger educational entities. The largest institutions of military education in Bulgaria are:
*
Bulgaria's total military personnel as of 2014 is 37,100, of which 30,400 (80.1%) are active military personnel and 8,100 (11.9%) are civilian personnel. The Land Forces are the largest branch, with at least 18,000 men serving there. In terms of percentage, 53% of all Army personnel are in the Land Forces, 25% are in the Air Force, 13% are in the Navy and 9% are in the Joint Forces Command. Annual spending per soldier amounts to 30,000 leva (~ 15,000 euro) and is scheduled to increase to 43,600 leva by 2014.
Unlike many former Soviet bloc militaries, discipline and morale problems are not common. During the Communist era, the army members enjoyed extensive social privileges. After the fall of Communism and Bulgaria's transition to a market economy, wages fell severely. For almost a decade social benefits were virtually non-existent, and some of them have been restored but recently. Nikolai Tsonev, defence minister under the 2005–2009 cabinet, undertook steps to provide the members of the military and their families with certain privileges in terms of healthcare and education, and to improve living conditions.
Military education in Bulgaria is provided in military universities and academies. Due to cuts in spending and manpower some universities have been disbanded and their campuses were included as faculties of other, larger educational entities. The largest institutions of military education in Bulgaria are:
*
 The Land Forces practice extensive year-round military training in various conditions. Cooperative drills with the United States are very common, the last series of them conducted in 2008. Bulgaria's most recent full-scale exercise simulating a foreign invasion was carried out in 2009. It was conducted at the Koren range, and included some 1,700 personnel with tanks, ATGMs, attack aircraft, AA guns and armored vehicles. The combat skills of individual soldiers are on a very high level, on par with troops of the U.S. Army.
Until recent years the Air Force suffered somewhat from fuel shortages; a problem which was overcome in 2008. Fighter pilots have year-round flights, but gunship pilots do not fly often due to the yet unfulfilled modernization of the Mi-24 gunships. Due to financial difficulties fighter pilots have 60 hours of flying time per year, only a third of the national norm of 180 hours.
The Navy also has some fuel shortage problems, but military training is still effective. The most recent overseas operation of the Navy was along the coast of Libya as part of
The Land Forces practice extensive year-round military training in various conditions. Cooperative drills with the United States are very common, the last series of them conducted in 2008. Bulgaria's most recent full-scale exercise simulating a foreign invasion was carried out in 2009. It was conducted at the Koren range, and included some 1,700 personnel with tanks, ATGMs, attack aircraft, AA guns and armored vehicles. The combat skills of individual soldiers are on a very high level, on par with troops of the U.S. Army.
Until recent years the Air Force suffered somewhat from fuel shortages; a problem which was overcome in 2008. Fighter pilots have year-round flights, but gunship pilots do not fly often due to the yet unfulfilled modernization of the Mi-24 gunships. Due to financial difficulties fighter pilots have 60 hours of flying time per year, only a third of the national norm of 180 hours.
The Navy also has some fuel shortage problems, but military training is still effective. The most recent overseas operation of the Navy was along the coast of Libya as part of
 The Land Forces are functionally divided into Deployable and Reserve Forces. Their main functions include deterrence, defence, peace support and
The Land Forces are functionally divided into Deployable and Reserve Forces. Their main functions include deterrence, defence, peace support and
 The Navy has traditionally been the smallest component of the Bulgarian military. Established almost simultaneously with the Ground forces in 1879, initially it consisted of a small fleet of boats on the
The Navy has traditionally been the smallest component of the Bulgarian military. Established almost simultaneously with the Ground forces in 1879, initially it consisted of a small fleet of boats on the
 In the past decade Bulgaria has been trying actively to restructure its army as a whole and a lot of attention has been placed on keeping the aging Russian aircraft operational. Currently the attack and defence branches of the Bulgarian air force are mainly MiG-29s and Su-25s. About 15 MiG-29 fighters have been modernised in order to meet
In the past decade Bulgaria has been trying actively to restructure its army as a whole and a lot of attention has been placed on keeping the aging Russian aircraft operational. Currently the attack and defence branches of the Bulgarian air force are mainly MiG-29s and Su-25s. About 15 MiG-29 fighters have been modernised in order to meet
 The Bulgarian-American Joint Military Facilities were established by a Defence Cooperation Agreement signed by the United States and Bulgaria in April 2006. Under the agreement, U.S. forces can conduct training at several bases in the country, which remain under Bulgarian command and under the Bulgarian flag. Under the agreement, no more than 2,500 U.S. military personnel can be located at the joint military facilities.
'' Foreign Policy'' magazine lists
The Bulgarian-American Joint Military Facilities were established by a Defence Cooperation Agreement signed by the United States and Bulgaria in April 2006. Under the agreement, U.S. forces can conduct training at several bases in the country, which remain under Bulgarian command and under the Bulgarian flag. Under the agreement, no more than 2,500 U.S. military personnel can be located at the joint military facilities.
'' Foreign Policy'' magazine lists
Бяла книга на Въоръжените сили (White Paper of the Armed Forces)
Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria, 2011. * Wikisource:Great Battles of Bulgaria
Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria
* https://web.archive.org/web/20110528070137/http://www.wikileaks.ch/cable/2007/10/07SOFIA1271.html – U.S. Embassy Sofia views via
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
. The commander-in-chief is the president of Bulgaria
The president of the Republic of Bulgaria is the head of state of Bulgaria and the commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian Army. The official residence of the president is at Boyana Residence, Sofia. After the completion of the second round of votin ...
. The Ministry of Defense is responsible for political leadership, while overall military command is in the hands of the Defense Staff, headed by the Chief of the Defense. There are three main branches of the Bulgarian military, named literally the Land Forces, the Air Forces and the Naval Forces (the term "Bulgarian Army" refers to them encompassed all together).
Throughout history, the Army has played a major role in defending the country's sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
. Only several years after its inception in 1878, Bulgaria became a regional military power and was involved in several major wars – Serbo-Bulgarian War (1885), First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
(1912–13), Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies r ...
(1913), First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1915–1918) and Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
(1941–1945), during which the Army gained considerable combat experience. During the Cold War, the People's Republic of Bulgaria
The People's Republic of Bulgaria (PRB; bg, Народна Република България (НРБ), ''Narodna Republika Balgariya, NRB'') was the official name of Bulgaria, when it was a socialist republic from 1946 to 1990, ruled by the ...
maintained one of the largest militaries in the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist repub ...
, numbering an estimated 152,000 troops in 1988. Since the Fall of Communism
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nat ...
, the political leadership has decided to pursue a pro-NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
policy, thus reducing military personnel and weaponry. Bulgaria joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization on 29 March 2004.
The patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
of the Bulgarian Army is St. George. The Armed Forces Day or St. George's Day (6 May) is an official holiday in Bulgaria.
History of the Bulgarian Army
Medieval Period
Tarnovo Constitution
The Tarnovo Constitution ( bg, Търновска конституция) was the first constitution of Bulgaria.
It was adopted on 16 April 1879 ( O.S.) by the Constituent National Assembly held in Veliko Tarnovo as part of the establishment of ...
, all men between 21 and 40 years of age were eligible for military service. In 1883 the military was reorganised in four infantry brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
B ...
s (in Sofia, Pleven, Ruse and Shumen) and one cavalry brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
B ...
.
Serbo-Bulgarian war
The Serbo-Bulgarian War was the first armed conflict after Bulgaria's liberation. It was a result of the unification withEastern Rumelia
Eastern Rumelia ( bg, Източна Румелия, Iztochna Rumeliya; ota, , Rumeli-i Şarkî; el, Ανατολική Ρωμυλία, Anatoliki Romylia) was an autonomous province (''oblast'' in Bulgarian, '' vilayet'' in Turkish) in the Ott ...
, which happened on 6 September 1885. The unification was not completely recognised, however, and one of the countries that refused to recognise the act was the Kingdom of Serbia. The Austro-Hungarian Empire had been expanding its influence in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and was particularly opposed. Serbia also feared this would diminish its dominance in the region. In addition, Serbian ruler Milan Obrenović IV
Milan Obrenović ( sr-cyr, Милан Обреновић, Milan Obrenović; 22 August 1854 – 11 February 1901) reigned as the prince of Serbia from 1868 to 1882 and subsequently as king from 1882 to 1889. Milan I unexpectedly abdicated in ...
was annoyed that Serbian opposition leaders like Nikola Pašić
Nikola Pašić ( sr-Cyrl, Никола Пашић, ; 18 December 1845 – 10 December 1926) was a Serbian and Yugoslav politician and diplomat who was a leading political figure for almost 40 years. He was the leader of the People's Radical ...
, who had escaped persecution after the Timok Rebellion
The Timok Rebellion ( sh, Timočka buna; ro, Răscoala Timoceană) was a popular uprising that began in eastern Serbia (now the region of the Timok Valley) on 28 September 1883, led by the People's Radical Party. It has been called the most imp ...
, had found asylum in Bulgaria. Lured by Austria-Hungary's promises of territorial gains from Bulgaria (in return for concessions in the western Balkans), Milan IV declared war on Bulgaria on 14 November 1885.
Military strategy relied largely on surprise, as Bulgaria had moved most of its troops near the border with the Ottoman Empire, in the southeast. As it happened, the Ottomans did not intervene and the Serbian army's advance was stopped after the Battle of Slivnitsa
The Battle of Slivnitsa ( bg, Битка при Сливница, sr, Битка на Сливници) was a victory of the Bulgarian army over the Serbians on 17–19 November 1885 in the Serbo-Bulgarian War. It solidified the unification ...
. The main body of the Bulgarian army travelled from the Ottoman border in the southeast to the Serbian border in the northwest to defend the capital, Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
. After the defensive battles at Slivnitsa and Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
, Bulgaria began an offensive that took the city of Pirot. At this point the Austro-Hungarian Empire stepped in, threatening to join the war on Serbia's side if Bulgarian troops did not retreat. Fighting lasted for only 14 days, from 14–28 November. A peace treaty was signed in Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of ...
on 19 February 1886. No territorial changes were made to either country, but Bulgarian unification was recognised by the Great Powers.
First Balkan War
Instability in the Balkan region in the early 1900s quickly became a precondition for a new war. Serbia's aspirations towards Bosnia and Herzegovina were thwarted by the Austrian annexation of the province in October 1908, so the Serbs focused their attention ontoKosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, and to the south for expansion. Greek officers, revolting in August 1909, had secured the appointment of a progressive government under Eleftherios Venizelos, which they hoped would resolve the Cretan issue in Greece's favor and reverse their defeat of 1897 by the Ottomans. Bulgaria, which had secured Ottoman recognition of its independence in April 1909 and enjoyed the friendship of Russia, also looked to districts of Ottoman Thrace and Macedonia for expansion.
 In March 1910 an Albanian insurrection broke out in Kosovo. In August Montenegro followed Bulgaria's precedent by becoming a kingdom. In 1911 Italy launched an invasion of Tripolitania, which was quickly followed by the occupation of the Dodecanese Islands. The Italians' decisive military victories over the Ottoman Empire greatly influenced the Balkan states to prepare for war against Turkey. Thus, in the spring of 1912 consultations among the various Christian Balkan nations resulted in a network of military alliances that became known as the
In March 1910 an Albanian insurrection broke out in Kosovo. In August Montenegro followed Bulgaria's precedent by becoming a kingdom. In 1911 Italy launched an invasion of Tripolitania, which was quickly followed by the occupation of the Dodecanese Islands. The Italians' decisive military victories over the Ottoman Empire greatly influenced the Balkan states to prepare for war against Turkey. Thus, in the spring of 1912 consultations among the various Christian Balkan nations resulted in a network of military alliances that became known as the Balkan League
The League of the Balkans was a quadruple alliance formed by a series of bilateral treaties concluded in 1912 between the Eastern Orthodox kingdoms of Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia and Montenegro, and directed against the Ottoman Empire, which at the ...
. The Great Powers, most notably France and Austria-Hungary, reacted to this diplomatic sensation by trying to dissuade the League from going to war, but failed.
In late September both the League and the Ottoman Empire mobilised their armies. Montenegro was the first to declare war, on 25 September ( O.S.)/ 8 October. The other three states, after issuing an impossible ultimatum to the Porte on 13 October, declared war on Turkey on 17 October. The Balkan League relied on 700,000 troops, 370,000 of whom were Bulgarians. Bulgaria, often dubbed "the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
of the Balkans", was militarily the most powerful of the four states, with a large, well-trained and well-equipped army. The peacetime army of 60,000 troops was expanded during the war to 370,000, with almost 600,000 men mobilized in total out of a population of 4,300,000. The Bulgarian field army consisted of nine infantry divisions, one cavalry division and 1,116 artillery units. Commander-in-Chief was Tsar Ferdinand, while the actual command was in the hands of his deputy, Gen. Mikhail Savov. The Bulgarians also possessed a small navy of six torpedo boats, which were restricted to operations along the country's Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast.
 Bulgaria's war aims were focused on
Bulgaria's war aims were focused on Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and Macedonia. For the latter, Bulgaria had a secret agreement with Serbia to divide it between them, signed on 13 March 1912 during the negotiations that led to the establishment of the Balkan League. However, it was not a secret that Bulgaria's target was the fulfillment of the never-materialized Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-18 ...
, signed after the Russo-Turkish War, 1877–78. They deployed their main force in Thrace, forming three armies. The First Army, under Gen. Vasil Kutinchev
Vasil Ivanov Kutinchev ( bg, Васил Иванов Кутинчев) (born 25 February 1859 in Rusçuk; died 30 March 1941) was a Bulgarian officer. He began his military career in 1879 after graduating from the Military School in Sofia . On 13 ...
with three infantry divisions, was deployed to the south of Yambol
Yambol ( bg, Ямбол ) is a town in Southeastern Bulgaria and administrative centre of Yambol Province. It lies on both banks of the Tundzha river in the historical region of Thrace. It is occasionally spelled ''Jambol''.
Yambol is the ad ...
, with direction of operations along the Tundzha River. The Second Army, under Gen. Nikola Ivanov
Nikola Ivanov ( bg, Никола Иванов) (2 March 1861, Kalofer – 10 September 1940, Sofia) was a Bulgarian general and a minister of defence of the Kingdom of Bulgaria.
One of the first graduate of the General Staff Military Academy ...
with two infantry divisions and one infantry brigade, was deployed west of the First and was assigned to capture the strong fortress of Adrianople (now Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders ...
). According to the plans, the Third Army, under Gen. Radko Dimitriev
Radko Dimitriev ( bg, Радко Димитриев) (24 September 1859 in Gradets – 18 October 1918 near Pyatigorsk) was a Bulgarian general, Head of the General Staff of the Bulgarian Army from 1 January 1904 to 28 March 1907, as well ...
, was deployed east of and behind the First and was covered by the cavalry division hiding it from the Turkish view. The Third Army had three infantry divisions and was assigned to cross the Stranja mountain and to take the fortress of Lozengrad ( Kirk Kilisse). The 2nd and 7th divisions were assigned independent roles, operating in western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace ( el, �υτικήΘράκη, '' ytikíThráki'' ; tr, Batı Trakya; bg, Западна/Беломорска Тракия, ''Zapadna/Belomorska Trakiya''), also known as Greek Thrace, is a geographic and histori ...
and eastern Macedonia, respectively.
The first great battles were at the Adrianople– Kirk Kilisse defensive line, where the Bulgarian 1st and 3rd Armies (together 110,000 men) defeated the Ottoman East Army (130,000 men) near Gechkenli, Seliolu and Petra. The fortress of Adrianople was besieged
Besieged may refer to:
* the state of being under siege
* ''Besieged'' (film), a 1998 film by Bernardo Bertolucci
{{disambiguation ...
and Kirk Kilisse was taken without resistance under the pressure of the Bulgarian Third Army. The initial Bulgarian attack by First and Third Army defeated the Turkish forces, numbering some 130,000, and reached the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via t ...
. However, the Turks, with the aid of fresh reinforcements from the Asian provinces, established their third and strongest defensive position at the Chataldja Line, across the peninsula where Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
is located. New Turkish forces landed at Bulair and Şarköy, but after heavy fighting they were crushed by the newly formed 4th Bulgarian Army under the command of Gen Stiliyan Kovachev
Stiliyan Kovachev ( bg, Стилиян Ковачев) (born on 26 February 1860 in Yanbolu (Yambol), died on 11 July 1939 in Sofia) was a Bulgarians, Bulgarian general. During the First Balkan War he commanded the Rodopi Detachment and later 4t ...
. The offensive at Chataldja failed, too. On 11 March the final Bulgarian assault on Adrianople began. Under the command of Gen. Georgi Vazov the Bulgarians, reinforced with two Serb divisions, conquered the "untakeable" city. On 17/30 May a peace treaty was signed between Turkey and the Balkan Alliance. The First Balkan War, which lasted from October 1912-May 1913, strengthened Bulgaria's position as a regional military power, significantly reduced Ottoman influence over the Balkans and resulted in the formation of an independent Albanian state.
Second Balkan War
The peace settlement of the First Balkan War proved unsatisfactory for both Serbia and Bulgaria. Serbia refused to cede a part of the territories in Macedonia, which it occupied and promised to give to Bulgaria according to a secret agreement. Serbia, on its side, was not satisfied with the independence of Albania and sought a secret alliance with Greece. Armed skirmishes between Serbian and Bulgarian troops occurred. On 16 June 1913, just a few months after the end of the first war, the Bulgarian government ordered an attack on Serbian and Greek positions in Macedonia, without declaring war. Almost all of Bulgaria's 500,000-man standing army was positioned against these two countries, on two fronts—western and southern—while the borders with Romania and theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
were left almost unguarded. Montenegro sent a 12,000-strong force to assist the Serbs. Exhausted from the previous war, which took the highest toll on Bulgaria, the Bulgarian army soon turned to the defensive. Romania attacked from the north and northeast and the Ottoman Empire also intervened in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
. Allied numerical superiority was almost 2:1. After a month and two days of fighting, the war ended as a moral disaster for Bulgaria, and at the same time its economy was ruined and its military demoralised.
First World War
 The
The Kingdom of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria ( bg, Царство България, translit=Tsarstvo Balgariya), also referred to as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom ( bg, Трето Българско Царство, translit=Treto Balgarsko Tsarstvo, links=no), someti ...
participated in World War I on the side of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
between 15 October 1915, when the country declared war on Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
, and 29 September 1918, when the Armistice of Thessalonica was signed. In the aftermath of the Balkan Wars, Bulgarian opinion turned against Russia and the western powers, whom the Bulgarians felt had done nothing to help them. The government of Vasil Radoslavov
Vasil Hristov Radoslavov ( bg, Васил Христов Радославов) (27 July 1854 – 21 October 1929) was a leading Bulgarian liberal politician who twice served as Prime Minister. He was Premier of the country throughout most ...
aligned the country with Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, even though this meant also becoming an ally of the Ottomans, Bulgaria's traditional enemy. However, Bulgaria now had no claims against the Ottomans, whereas Serbia, Greece and Romania (allies of Britain and France) were all in possession of lands perceived in Bulgaria as its own.
In 1915 Germany promised to restore the boundaries according to the Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-18 ...
and Bulgaria, which had the largest army in the Balkans, declared war on Serbia in October of that year. In the First World War Bulgaria decisively asserted its military capabilities. The second Battle of Doiran, with Gen. Vladimir Vazov as commander, inflicted a heavy blow on the numerically superior British army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
, which suffered 12,000 casualties against 2,000 from the opposite side. One year later, during the third battle of Doiran, the United Kingdom, supported by Greece, once again suffered a humiliating defeat, losing 3,155 men against just about 500 on the Bulgarian side. The reputation of the French army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
also suffered badly. The Battle of the Red Wall was marked by the total defeat of the French forces, with 5,700 out of 6,000 men killed. The 261 Frenchmen who survived were captured by Bulgarian soldiers.
Despite the outstanding victories, Germany was near defeat, which meant that Bulgaria would be left without its most powerful ally. The Russian Revolution of February 1917 had a great effect in Bulgaria, spreading antiwar and anti-monarchist sentiment among the troops and in the cities. In June Radoslavov's government resigned. In 1919 Bulgaria officially left the war with the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine (french: Traité de Neuilly-sur-Seine) required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly ...
.
The army between the World Wars
 The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine proved to be a severe blow to Bulgaria's military. According to the treaty, the country had no right to organize a conscription-based military. The professional army was to be no more than 20,000 men, including internal forces and border guards. Equipping the army with tanks, submarines, bombers and heavy artillery was strictly prohibited, although Bulgaria managed to get around some of these prohibitions. Nevertheless, on the eve of World War II the Bulgarian army was still well-trained and well-equipped. In fact, the Bulgarian Army had been expanded in 1935.
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine proved to be a severe blow to Bulgaria's military. According to the treaty, the country had no right to organize a conscription-based military. The professional army was to be no more than 20,000 men, including internal forces and border guards. Equipping the army with tanks, submarines, bombers and heavy artillery was strictly prohibited, although Bulgaria managed to get around some of these prohibitions. Nevertheless, on the eve of World War II the Bulgarian army was still well-trained and well-equipped. In fact, the Bulgarian Army had been expanded in 1935.
World War II
The government of theKingdom of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria ( bg, Царство България, translit=Tsarstvo Balgariya), also referred to as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom ( bg, Трето Българско Царство, translit=Treto Balgarsko Tsarstvo, links=no), someti ...
under Prime Minister Bogdan Filov declared a position of neutrality upon the outbreak of World War II. Bulgaria was determined to observe it until the end of the war but it hoped for bloodless territorial gains, especially in the lands with a significant Bulgarian population occupied by neighbouring countries after the Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies r ...
and World War I. However, it was clear that the central geopolitical position of Bulgaria in the Balkans would inevitably lead to strong external pressure by both World War II factions. Turkey had a non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a tr ...
with Bulgaria. On 7 September 1940 Bulgaria succeeded in negotiating a recovery of Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja, South Dobruja or Quadrilateral ( Bulgarian: Южна Добруджа, ''Yuzhna Dobrudzha'' or simply Добруджа, ''Dobrudzha''; ro, Dobrogea de Sud, or ) is an area of northeastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silis ...
with the Treaty of Craiova
The Treaty of Craiova ( bg, Крайовска спогодба, Krayovska spogodba; ro, Tratatul de la Craiova) was signed on 7 September 1940 and ratified on 13 September 1940 by the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the Kingdom of Romania. Under its te ...
(see Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
). Southern Dobruja had been part of Romania since 1913. This recovery of territory reinforced hopes for resolving other territorial problems without direct involvement in the war. The country joined the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
in 1941, when German troops preparing to invade Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Greece reached the Bulgarian borders and demanded permission to pass through its territory.
 On 1 March 1941, Bulgaria signed the
On 1 March 1941, Bulgaria signed the Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive milit ...
and officially joined the Axis bloc. After a short period of inaction, the army launched an operation against Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Greece. The goal of reaching the shores of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
and completely occupying the region of Macedonia was successful. Even though Bulgaria did not send any troops to support the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
, its navy was involved in a number of skirmishes with the Soviet Black Sea Fleet, which attacked Bulgarian shipping. Besides this, Bulgarian armed forces garrisoned in the Balkans battled various resistance groups. The Bulgarian government declared a token war on the United Kingdom and the United States near the end of 1941, an act that resulted in the bombing of Sofia and other Bulgarian cities by Allied aircraft.
Some communist activists managed to begin a guerrilla movement, headed by the underground Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP; bg, Българска Комунистическа Партия (БКП), Balgarska komunisticheska partiya (BKP)) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria from 1946 until 198 ...
. A resistance movement called Otechestven front (Fatherland front, Bulgarian: Отечествен фронт) was set up in August 1942 by the Communist Party, the Zveno
Zveno ( bg, Звено, lit=link), ''Politicheski krŭg "Zveno"'', officially Political Circle "Zveno" was a Bulgarian political organization, founded in 1930 by Bulgarian politicians, intellectuals and Bulgarian Army officers. It was associated ...
movement and a number of other parties to oppose the elected government, after a number of Allied victories indicated that the Axis might lose the War. In 1943 Tsar Boris III
Boris III ( bg, Борѝс III ; Boris Treti; 28 August 1943), originally Boris Klemens Robert Maria Pius Ludwig Stanislaus Xaver (Boris Clement Robert Mary Pius Louis Stanislaus Xavier) , was the Tsar of the Kingdom of Bulgaria from 1918 until h ...
died suddenly. In the summer of 1944, after having crushed the Nazi defense around Iaşi and Chişinău, the Soviet Army
uk, Радянська армія
, image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg
, alt =
, caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army
, start_date ...
was approaching the Balkans and Bulgaria. On 23 August 1944 Romania quit the Axis Powers, declared war on Germany and allowed Soviet forces to cross its territory to reach Bulgaria. On 26 August 1944 the Fatherland Front made the decision to incite an armed rebellion against the government, which led to the appointment of a new government on 2 September. Support for the government was withheld by the Fatherland Front, since it was composed of pro-Nazi elements, in a desperate attempt to hold on to power. On 5 September 1944 the Soviet Union declared war and invaded Bulgaria. On 8 September 1944 the Bulgarian army joined the Soviet Union in its war against Germany.
Cold War era
As theRed Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
invaded Bulgaria in 1944 and installed a communist government, the armed forces were rapidly forced to reorganise following the Soviet model, and were renamed the Bulgarian People's Army
The Bulgarian People's Army ( bg, Българска народна армия, БНА, translit=Balgarska narodna armiya, BNA) was the army of the People's Republic of Bulgaria. It comprised the Bulgarian Land Forces, Air Force and Air Defence, ...
(''Bohlgarska Narodna Armija, BNA''). Moscow quickly supplied Bulgaria with T-34-85 tanks, SU-100
The SU-100 ('' Samokhodnaya Ustanovka'' 100) was a Soviet tank destroyer armed with the D-10S 100 mm anti-tank gun in a casemate superstructure. It was used extensively during the last year of World War II and saw service for many years af ...
guns, Il-2 attack planes and other new combat machinery. As the country was a Soviet satellite, it was a part of the Eastern Bloc and entered the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist repub ...
as one of its founders. By this time the army had expanded to over 200,000 men with hundreds of thousands of more reserve troops. Military service was obligatory. A special defensive line
In gridiron football, a lineman is a player who specializes in play at the line of scrimmage. The linemen of the team currently in possession of the ball are the offensive line, while linemen on the opposing team are the defensive line. A numb ...
, known as the Krali Marko defensive line, was constructed along the entire border with Turkey. It was heavily fortified with concrete walls and turrets of T-34, Panzer III
The ''Panzerkampfwagen III'', commonly known as the Panzer III, was a medium tank developed in the 1930s by Germany, and was used extensively in World War II. The official German ordnance designation was Sd.Kfz. 141. It was intended to fight ot ...
and Panzer IV
The ''Panzerkampfwagen'' IV (Pz.Kpfw. IV), commonly known as the ''Panzer'' IV, was a German medium tank developed in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 161.
The Pan ...
tanks.
The army was involved in a number of border skirmishes from 1948 to 1952, repulsing several Greek attacks, and took part in the suppression of the Prague Spring events. In the meantime, during the rule of Todor Zhivkov
Todor Hristov Zhivkov ( bg, Тодор Христов Живков ; 7 September 1911 – 5 August 1998) was a Bulgarian communist statesman who served as the ''de facto'' leader of the People's Republic of Bulgaria (PRB) from 1954 until 1989 ...
, a significant military-industrial complex was established, capable of producing armored vehicles, self-propelled artillery, small arms and ammunition, as well as aircraft engines and spare parts. Bulgaria provided weapons and military expertise to Algeria, Yemen, Libya, Iraq, Nicaragua, Egypt and Syria. Some military and medical aid was also supplied to North Korea and North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; vi, Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed f ...
in the 1950s and 1960s. During the 1970s the Air Force was at the apogee of its power, possessing at least 500 modern combat aircraft in its inventory. Training in the Bulgarian People's Army was exhaustive even by Soviet standards; however, it was never seen as a major force within the Warsaw Pact. In 1989, when the Cold War was coming to its end, the army (the combined number of ground, air and naval forces) numbered about 120,000 men, most of them conscripts. There were, however, a number of services which, while falling outside of Ministry of Defense jurisdiction in peacetime, were considered part of the armed forces. These were foremost the Labour Troops (construction forces), the People's Militia (the police forces of the country, which fell under Ministry of the Interior jurisdiction, but the ministry was itself a militarized structure) and, more importantly, its Interior Troops, the Border Troops—which in different periods fell under either Ministry of Defense or Ministry of the Interior control—Civil Defense Service, the Signals Troops (government communications) and the Transport Troops (mostly railway infrastructure maintenance), which were two separate services under the Postal and Communications Committee (a ministry), etc. The combined strength of the Bulgarian People's Army and all those services reached well over 325,000 troops.
Modern era
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist repub ...
and the end of the Cold War, Bulgaria could no longer support a vast military. A rapid reduction in personnel and active equipment was to be carried out in parallel with a general re-alignment of strategic interests. In 1990, Bulgaria had a total of more than 2,400 tanks, 2,000 armored vehicles, 2,500 large caliber artillery systems, 300 fighter and bomber aircraft, 100 trainer aircraft, more than 40 combat and 40 transport helicopters, 4 submarines, 6 fast missile craft, 2 frigates, 5 corvettes, 6 torpedo boats, 9 patrol craft, 30 minesweepers and 21 transport vessels. Due to the economic crisis that affected most former Eastern bloc countries, a steady reform in the military could not be carried out; much of the equipment fell into disrepair and some of it was smuggled and sold to the international black market. Inadequate payments, fuel and spare part shortages and the disbandment of many capable units led to an overall drop in combat readiness, morale and discipline.
After partially recovering from the 1990s crisis, the Bulgarian military became a part of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. Even before that, Bulgaria sent a total of 485 soldiers to Iraq (2003–2008) as a participant in the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
, and maintained a 608-men strong force in Afghanistan as part of ISAF
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
. Bulgaria had a significant missile arsenal, including 67 SCUD-B, 50 FROG-7 and 24 SS-23 ballistic missiles.StandartNews.com "Никой не разбра, че горихме ракети през 1973 г. (in Bulgarian)In 2002, Bulgaria disbanded the Rocket Forces despite nationwide protests, and has disbanded its submarine component. Bulgaria is to have 27,000 standing troops by 2014, consisting of 14,310 troops in the land forces, 6,750 in the air force, 3,510 in the navy and 2,420 in the joint command. In 2018, the Bulgarian Armed Forces numbers around 33,150 soldiers, 73 aircraft, 2234 vehicles including 531 tanks, and 29 naval assets.
Organization

Defence Staff
The Bulgarian Armed Forces are headquartered inSofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, where most of the Defence staff is based. Until recently the supreme military institution was the General Staff and the most senior military officer was known as the Chief of the General Staff. After the latest military reform has been implemented the General Staff became a department within the Ministry of Defence and for that matter its name had to be changed to match the new situation. For that reason the former GS became the Defence Staff and the supreme military commander became the Chief of Defence. Currently headed by Chief of Defence admiral Emil Eftimov, the Defence Staff is responsible for operational command of the Bulgarian Army and its three major branches. Deputies: Vice Admiral Petar Petrov, General Atanas Zaprianov, General Dimitar Zekhtinov.
General rank positions in the Bulgarian Army:
Ministry of Defence
* Defense Staff
** Chief of Defence - General/ Admiral
** Deputy Chief of Defence - Lieutenant-General/ Vice-Admiral
** Deputy Chief of Defence - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Director, "Operations and Readiness" Directorate - Brigade General/ Commodore
** Director, "Strategical Planning" Directorate - Brigade General/ Commodore
** Director, "Communication and Information Systems" Directorate - Brigade General/ Commodore
** Director, "Logistics" Directorate - Brigade General/ Commodore
* Joint Forces Command
** Commander, Joint Forces Command – Lieutenant-General/ Vice-Admiral
** Deputy Commander, Joint Forces Command – Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Chief of Staff, Joint Forces Command – Brigade General/ Commodore
* Land Forces
** Commander, Land Forces - Major-General
** Deputy Commander, Land Forces - Brigade General
** Chief of Staff, Land Forces – Brigade General
*** Commander, 2nd Mechanised Brigade – Brigade General
*** Commander, 61st Mechanised Brigade – Brigade General
* Air Forces
** Commander, Air Forces - Major-General
** Deputy Commander, Air Forces - Brigade General
*** Commander, 3rd Air Base – Brigade General
*** Commander, 24th Air Base – Brigade General
* Navy
** Commander, Naval Forces - Rear-Admiral
** Deputy Commander, Naval Forces - Commodore
*** Commander Naval Base - Commodore
* Military Police Service, directly subordinated to the Minister of Defense
** Director, Military Police Service - Brigade General/ Commodore
* Military Intelligence Service, directly subordinated to the Minister of Defense
** Director, Military Intelligence Service - civil servant, equal in rank to a Brigade General/ Commodore
* Military education institutions, directly subordinated to the Minister of Defense
** Chief of the "Georgy Stoykov Rakovski" Military Academy - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Chief of the Military Medical Academy and the Armed Forces Medical Service - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Chief of the "Vasil Levski" National Military University - Brigade General
* Other positions at the Ministry of Defense
** Military Advisor on Military Security Matters to the Supreme Commander-in-Chief, the President of the Republic of Bulgaria - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Military Representative of the Chief of Defense at the NATO Military Committee and at the EU Military Committee - Lieutenant-General/ Vice-Admiral
** Director of the Cooperation and Regional Security Directorate at the NATO Military Committee - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Deputy Commander of the NATO Rapid Deployment Corps - Greece (Thessaloniki) - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** National Military Representative at the NATO Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
In addition to the aforementioned positions, there are general rank positions in the National Intelligence Service and the National Close Protection Service (the bodyguard service to high-ranking officials and visiting dignitaries). These two services are considered part of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Bulgaria, but are directly subordinated to the President of Bulgaria and fall out of the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Defense.
* National Intelligence Service
** Director, National Intelligence Service - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Deputy Director, National Intelligence Service - Brigade General/ Commodore
* National Close Protection Service
** Director, National Close Protection Service - Major-General/ Rear-Admiral
** Deputy Director, National Close Protection Service - Brigade General/ Commodore
With the establishment of the State Agency for National Security - SANS (Bulgarian: Darzhavna Agentsiya za Natsionalna Sigurnost - DANS, Държавна агенция за национална сигурност - ДАНС) part of the military security personnel came under its authority. Before that the security aspects of the armed forces were handled by a unified organisation under the General Staff - the "Military Service of Security and Military Police". After the formation of SANS the service was split, with the military counter-intelligence personnel entering the newly formed structure and the military police personnel staying under Ministry of Defense subordination. While technically civilian servants not part of the armed forces, the military counter-intelligence personnel of the State Agency of National Security retain their military ranks.
Ministry of Defence
Ministry of DefenceThe organisation of the Ministry of Defence includes: * General Administration * Specialised Administration * Inspectorate of the Ministry of Defence * Protocol Unit of the Ministry of Defence * Financial Control and Material Accountability Unit * Internal Audit Directorate of the Ministry of Defence * Information Security Directorate of the Ministry of Defence * Defence Staff Structures directly subordinated to the Ministry of Defence include: * Military Information Service, Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Director ** Directorate ** Information Division ** Analysis Division ** Resources Supply Division * Military Police Service, Sofia (commanded by a Brigade General/ Commodore) ** Military Police Command ** Military Police Operational Company (MRAV Sand Cat) ** Regional Military Police Service Sofia ** Regional Military Police Service Plovdiv ** Regional Military Police Service Pleven ** Regional Military Police Service Varna ** Regional Military Police Service Sliven ** Military Police Service Logistics and Training Centre, Sofia * Military Geographical Service ** MGS Headquarters ** Geographical Information Support Centre ** Geodesic Observatory (GPS Observatory) ** Military Geographical Centre ** Information Security Unit ** Financial Comptroller * Stationary Communications and Information System ** Communications and Information Centre ** Government Communications Support Centre, ** Operational Centres ** Engineering and CIS recovery Centre ** Stationary Communications Network * National Guards Unit, Sofia (commanded by a Colonel) ** Headquarters ** 1st Guards Battalion ** 2nd Mixed Guards Battalion ** National Guards Unit Representative Military Band ** Armed Forces Representative Dance Company ** Guardsmen Training Centre ** Logistics Support Company * Military Medical Academy, Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Chief of the MMA, Chief of the MATH - Sofia and General Surgeon of the Bulgarian Armed Forces ** Deputy Chief for Diagnostics and Medical Treatment Activities ** Deputy Chief for Education and Scientific Activities ** Deputy Chief for Medical Support of Military Units and Overseas Military Missions ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Sofia ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital (informally known as the Naval Hospital)- Varna ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Plovdiv ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Sliven ** Multiprofile Active Treatment Hospital - Pleven ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital "Saint George the Victorious" - Pomorie ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital "Caleroya" - Hisar ** Follow-up Long-term Treatment and Rehabilitation Hospital - Bankya ** Military Medical Quick Reaction Force (expeditionary disaster and crisis relief unit) ** Psychological Health and Prevention Centre ** Scientific and Application Centre for Military Medical Expertise and Aviation and Seaborne Medicine ** Scientific and Application Centre for Military Epidemiology and Hygiene * Military Academy " Georgi Stoykov Rakovski", Sofia (commanded by a Major-General/ Rear-Admiral) ** Command *** Commandant of the Military Academy *** Deputy Chief for Study and Scientific Activities *** Deputy Chief for Administrative Activities and Logistics ** Administrative Units *** Personnel and Administrative Support Department *** Logistics Department *** Study and Scientific Activities Department *** Financial Department *** Library and Publishing Activities Sector *** Public Relations, International Activities and Protocol Sector ** Training Units *** National Security and Defence College *** Command Staff College *** Peacekeeping Operations and Computer Simulations Sector *** Foreign Languages Studies Department ** Perspective Defence Research Institute * National Military University "
Vasil Levski
Vasil Levski ( bg, Васил Левски, spelled in old Bulgarian orthography as , ), born Vasil Ivanov Kunchev (; 18 July 1837 – 18 February 1873), was a Bulgarian revolutionary who is, today, a national hero of Bulgaria. Dubbed t ...
", Veliko Tarnovo (commanded by a Brigade General)
** Combined Arms Education Department, Veliko Tarnovo
** Artillery and Communication Systems Education Department, Shumen
** NCO School, Veliko Tarnovo
** Foreign Languages and Computer Systems Education Department, Shumen
* Higher Air Force School "Georgi Benkovski
Georgi Benkovski ( bg, Георги Бенковски) (1843 – 12 May 1876) was the pseudonym of Gavril Gruev Hlatev (Гаврил Груев Хлътев), a Bulgarian revolutionary and leading figure in the organization and direction of the Bu ...
", Dolna Mitropoliya (commanded by a Brigade General, temporarily a faculty of the NMU, reinstated on January 20, 2020)
*Higher Naval School "Nikola Yonkov Vaptsarov
Nikola Yonkov Vaptsarov ( bg, Никола Йонков Вапцаров; 7 December 1909 – 23 July 1942) was a Bulgarian poet, communist and revolutionary. Working most of his life as a machinist, he only wrote in his spare time. Despite the ...
", Varna (commanded by a Commodore)
** Chief of the Higher Naval Officer School
** Deputy Chief for Administration and Logistics
** Deputy Chief for Studies and Schience Activities
** Navigation Department
** Engineering Department
** Post-Graduate Qualification Department
** Professional Petty Officers College
* Defence Institute, Sofia
** The Defence Institute is the research and development administration of the MoD. It includes the:
** Administration and Financial Management Department
** Military Standardisation, Quality and Certification Department
** Armament, Equipment and Materials Development Department
** Armament, Equipment and Materials Testing and Control Department
** C4I Systems Development Department
* Commandment Service of the Ministry of Defence, Sofia
** The Commandment Service is an institution in charge of real estate management, transportation, library services, documentation publishing and communications support for the central administration of the MoD, transportation support to the immediate MoD personnel, classified information, cryptographic and perimeter security for the MoD administration buildings.
** Director
** Deputy Director
** Chief Legal Advisor
** Financial Comptroler
** Administrative Department
** Financial Department
** Business Department
** Transportation Support Department
** Support Department
** CIS Support Department
** Technical Centre for Armed Forces Information Security
* Executive Agency for the Military Clubs and Recreational Activities, Sofia
* National Museum of Military History, Sofia
Defence Staff
The Defence Staff, formerly called the General Staff of the Bulgarian Army, is the supreme professional institution for military expertise and command and supervision of the armed forces under the Ministry of Defence umbrella. It includes: * Operations and Preparedness Directorate * Logistics Directorate * Strategical Planning Directorate * Communication and Information Systems Directorate * Office of the Cabinet of the Chief of Defence * Office for Joint Military Installations * Joint Forces Command ** Land Forces Command ** Air Forces Command ** Naval Forces CommandJoint Forces Command
In 2010 the Ministry of Defence completed a thorough study of the defence policy and issued a ''White Book'', or a ''White Paper on Defence'', calling for a major overhaul of the structure of Defence Forces. According to the document the military of the Republic of Bulgaria should include two mechanizedbrigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
B ...
s, four regiments (Logistics, Artillery, Engineering, SpecOps), four battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions a ...
s (Reconnaissance, Mechanized, NBC, psychological operations) in the Land Forces; two air bases, SAM air defense base and Air force training base in the Air Force; and one naval base consisting of two homeports in the Navy. There are seven brigade level formations, including the two mechanised brigades and the special forces brigade of the army, the two air bases of the air force, the naval base and the logistical brigade of the JOC. Currently deployed units are as follows:
Joint Forces Command
* Military Command Centre
* Centre for Radiological, Chemical, Biological and Ecological Environment Monitoring and Control
* Support Centre of the JFC
* Mobile Communication and Information System
* Logistics Brigade
** Brigade Headquarters
** 1st Transport Battalion, Sofia
** 2nd Transport Battalion, Burgas
** Central Supply Base, Negushevo
** repair and maintenance bases
** depots, storage facilities and technical inspection units
* Movement Control Headquarters
* Centre for Documentation Support of the JFC
* Operational Archive of the Bulgarian Army
* Joint Forces Training Range "Novo Selo"
* National Military Study Complex "Charalitsa"
The three armed services of the Bulgarian Army - the Land, Air and Naval Forces are subordinated to the recently formed Joint Forces Command:
* Land Forces Command
* Naval Forces Command
* Air Forces Command
The previous 62nd Signals Brigade at Gorna Malina
Gorna Malina ( bg, Горна Малина, ) is a village in western Bulgaria, part of Sofia Province. It is the administrative centre of Gorna Malina municipality, which lies in the central eastern part of Sofia Province, 20-30 kilometres east o ...
was responsible for maintaining the higher military communication lines. Next to the functions of the Signals Regiment in the Sofia suburb of Suhodol, the brigade had at least three dispersed ''signals regiments for government communications'', such as the 75th Signals Regiment (Lovech
Lovech ( bg, Ловеч, Lovech, ) is a city in north-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the Lovech Province and of the subordinate Lovech Municipality. The city is located about northeast from the capital city of Sofia. Near ...
), the 65th Signals Regiment (Nova Zagora
Nova Zagora ( bg, Нова Загора ) is a town located in the southeastern plains of Bulgaria in Sliven Province. It is the administrative centre of Nova Zagora Municipality. As of December 2009, the town had a population of 19,562 inhabita ...
) and at least one additional unknown Signals Regiment in the Rila-Pirin
, photo=Pirin-mountains-Bansko.jpg
, photo_caption=Pirin scenery in winter
, country= Bulgaria,
, parent=
, geology= granite, gneiss, marble, limestone
, area_km2=2585
, range_coordinates =
, length_km=80 , length_orientation= north-s ...
mountain massif. The modern successor of the 62nd Signals Brigade are the Stationary Communication and Information System (''Стационарна Комуникационна Информационна Система'' (''СКИС'')) of the Defence Staff (which fulfills also the tasks of SIGINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
and Cyber Defence next to its strategic communications mission) and the Mobile Communication and Information System (''Мобилна Комуникационна Информационна Система'' (''МКИС'')) of the Joint Forces Command.
Joint Special Operations Command
The 68th Special Forces Brigade was removed from the Land Forces' ORBAT on 1 February 2017, de facto becoming the country's fourth combat service. Unlike Bulgaria's Land, Air and Naval Forces however it fell outside of the Joint Forces Command structure, having been assigned directly under the authority of the Chief of Defence. The brigade was transformed into the JSOC, taking effect on November 1, 2019 and its commander, Brigade General Yavor Mateev was promoted to amajor general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
as the chief of the new command.
Personnel and education
Vasil Levski National Military University
, mottoeng =
, established = 26 November 1878
, endowment =
, rector = Brigadier-General Ivan Georgiev Malamov
, vice_chancellor =
, city = Veliko Tarnovo
, state =
, country = Bulgaria
, students =
, undergrad =
, postgrad =
, other =
, ...
* Rakovski Defence and Staff College
The Georgi Rakovski Military Academy ( bg, Военна академия „Георги Стойков Раковски“), based in Sofia, is Bulgaria's oldest military institution of higher education. It is named after Bulgarian revolutionary ...
* Nikola Vaptsarov Naval Academy
* Military Medical Academy – a mixed military academy/hospital institution
Training
 The Land Forces practice extensive year-round military training in various conditions. Cooperative drills with the United States are very common, the last series of them conducted in 2008. Bulgaria's most recent full-scale exercise simulating a foreign invasion was carried out in 2009. It was conducted at the Koren range, and included some 1,700 personnel with tanks, ATGMs, attack aircraft, AA guns and armored vehicles. The combat skills of individual soldiers are on a very high level, on par with troops of the U.S. Army.
Until recent years the Air Force suffered somewhat from fuel shortages; a problem which was overcome in 2008. Fighter pilots have year-round flights, but gunship pilots do not fly often due to the yet unfulfilled modernization of the Mi-24 gunships. Due to financial difficulties fighter pilots have 60 hours of flying time per year, only a third of the national norm of 180 hours.
The Navy also has some fuel shortage problems, but military training is still effective. The most recent overseas operation of the Navy was along the coast of Libya as part of
The Land Forces practice extensive year-round military training in various conditions. Cooperative drills with the United States are very common, the last series of them conducted in 2008. Bulgaria's most recent full-scale exercise simulating a foreign invasion was carried out in 2009. It was conducted at the Koren range, and included some 1,700 personnel with tanks, ATGMs, attack aircraft, AA guns and armored vehicles. The combat skills of individual soldiers are on a very high level, on par with troops of the U.S. Army.
Until recent years the Air Force suffered somewhat from fuel shortages; a problem which was overcome in 2008. Fighter pilots have year-round flights, but gunship pilots do not fly often due to the yet unfulfilled modernization of the Mi-24 gunships. Due to financial difficulties fighter pilots have 60 hours of flying time per year, only a third of the national norm of 180 hours.
The Navy also has some fuel shortage problems, but military training is still effective. The most recent overseas operation of the Navy was along the coast of Libya as part of Operation Unified Protector
Operation Unified Protector was a NATO operation in 2011 enforcing United Nations Security Council resolutions 1970 and 1973 concerning the Libyan Civil War and adopted on 26 February and 17 March 2011, respectively. These resolutions imposed ...
.
Budget
After the collapse of the Warsaw pact, Bulgaria lost the ability to acquire cheap fuel and spares for its military. A large portion of its nearly 2,000T-55
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Soviet main battle tanks introduced in the years following the Second World War. The first T-54 prototype was completed at Nizhny Tagil by the end of 1945.Steven Zaloga, T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tank ...
tanks fell into disrepair, and eventually almost all of them were scrapped or sold to other countries. In the early 1990s the budget was so small, that regulars only received token-value payments. Many educated and well-trained officers lost the opportunity to educate younger soldiers, as the necessary equipment and basis lacked adequate funding. Military spending increased gradually, especially in the last 10 years. As of 2005, the budget was no more than $400 mln., while military spending for 2009 amounted to more than $1.3 bln. – almost a triple increase for 4 years. Despite this growth, the military still does not receive sufficient funds for modernisation. An example of bad spending plans is the large-scale purchasing of transport aircraft, while the Air Force has a severe need of new fighters (the MiG-29s, even though modernised, are nearing their operational limits). The planned procurement of 2–4 Gowind class corvettes has been cancelled. As of 2009, military spending was about 1.98% of GDP. In 2010 the budget is to be only 1.3% due to the international financial crisis.
Land Forces
crisis management
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and envir ...
, humanitarian and rescue missions, as well as social functions within Bulgarian society. Active troops in the land forces number about 18,000 men, and reserve troops number about 13,000.
The equipment of the land forces is impressive in terms of numbers, but most of it is nonoperational and scheduled to be scrapped or refurbished and exported to other nations. Bulgaria has a military stockpile of about 5,000,000 small arms, models ranging from World War II-era MP 40
The MP 40 (''Maschinenpistole 40'') is a submachine gun chambered for the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge. It was developed in Nazi Germany and used extensively by the Axis powers during World War II.
Designed in 1938 by Heinrich Vollmer with in ...
machine pistols to modern Steyr AUG, AK-74
The AK-74 ( Russian: , tr. ''Avtomat Kalashnikova obraztsa 1974 goda'', lit. 'Kalashnikov assault rifle model 1974) is an assault rifle designed by small arms designer Mikhail Kalashnikov in 1974. While primarily associated with the Soviet ...
, HK MP5, HK416
The Heckler & Koch HK416 is a gas-operated assault rifle chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO cartridge. It is designed and manufactured by the German company Heckler & Koch.
Although the design is based on the AR-15 class of firearm (specific ...
and AR-M12F assault rifles.
National guard unit
The National Guard of Bulgaria, founded in 1879, is the successor to the personal guards of KnyazAlexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of ...
. On 12 July of that year, the guards escorted the Bulgarian knyaz for the first time; today the official holiday of the National Guard is celebrated on 12 July. Throughout the years the structure of the guards has evolved, going from convoy to squadron, to regiment and, subsequent to 1942, to division. Today it includes military units for army salute and wind orchestra duties.
In 2001, the National Guard unit was designated an official military unit of the Bulgarian army and one of the symbols of state authority, along with the flag, the coat of arms and the national anthem. It is a formation, directly subordinate to the Minister of Defence and while legally part of the armed forces, it is totally independent from the Defence Staff.
Statistics and equipment
''Note'': This table shows combined active and reserve force.Most are listed here. In 2019 what remained from the scrapping of the previous new equipment some but not all of the T-72 Main battle tanks were sent for mechanical service for the first time in years. Most of the equipment that should be battle ready is in dire condition, old, rusty or non-functional, the rest about 50,000 tons of what was sold as scrap" can be found in some of the scrap depots near the railroad in Sofia including battle tanks, artillery, and other battle soviet era equipment.Navy
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
river. Bulgaria has a coastline of about 354 kilometres – thus, naval warfare is not considered a priority.
After the downturn in 1990, the Navy was largely overlooked and received almost no funding. No projects for modernisation were carried out until 2005, when a Wielingen class frigate (F912 Wandelaar) was acquired from Belgium. By 2009, Bulgaria acquired two more frigates of the same class. The first of them was renamed ''41 Drazki'' and took part in several operations and exercises, most notably the UNIFIL Maritime Patrol along the coast of Lebanon in 2006, and Operation Active Endeavour
Operation Active Endeavour was a maritime operation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. It operated in the Mediterranean Sea and was designed to prevent the movement of terrorists or weapons of mass destruction. It had collateral benefit ...
. It also participated in the enforcement of the naval blockade against Muammar Gaddafi's regime off the coast of Libya from 2011 until 2012.
The equipment is typical for a small navy, consisting mostly of light multi-purpose vessels – four frigates, three corvettes, five minesweepers, three fast missile craft and two landing ships. Other equipment includes a coastal defence missile battalion armed with locally modified P-15 Termit
The P-15 ''Termit'' (russian: П-15 "Термит"; en, termite) is an anti-ship missile developed by the Soviet Union's Raduga design bureau in the 1950s. Its GRAU designation was 4K40, its NATO reporting name was ''Styx'' or SS-N-2. China ...
missiles, a coastal artillery battery, a naval helicopter airbase and a marine special forces unit.
The Bulgarian Navy is centered in two main bases – in Varna and in Burgas
Burgas ( bg, Бургас, ), sometimes transliterated as ''Bourgas'', is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a pop ...
.
Air Force
 In the past decade Bulgaria has been trying actively to restructure its army as a whole and a lot of attention has been placed on keeping the aging Russian aircraft operational. Currently the attack and defence branches of the Bulgarian air force are mainly MiG-29s and Su-25s. About 15 MiG-29 fighters have been modernised in order to meet
In the past decade Bulgaria has been trying actively to restructure its army as a whole and a lot of attention has been placed on keeping the aging Russian aircraft operational. Currently the attack and defence branches of the Bulgarian air force are mainly MiG-29s and Su-25s. About 15 MiG-29 fighters have been modernised in order to meet NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
standards. The first aircraft arrived on 29 November 2007 and final delivery was due in 03/09. In 2006 the Bulgarian government signed a contract with Alenia Aeronautica
Alenia Aeronautica was an Italian aerospace company. Its subsidiaries included Alenia Aermacchi and Alenia Aeronavali.
Alenia Aeronautica was also the part-owner of ATR, a joint venture with European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS ...
for the delivery of five C-27J Spartan
The Alenia C-27J Spartan is a military transport aircraft developed and manufactured by Leonardo's Aircraft Division (formerly Alenia Aermacchi until 2016). It is an advanced derivative of Alenia Aeronautica's earlier G.222 (C-27A Spartan in ...
transport aircraft in order to replace the Soviet made An-24
The Antonov An-24 (Russian/Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-24) ( NATO reporting name: Coke) is a 44-seat twin turboprop transport/passenger aircraft designed in 1957 in the Soviet Union by the Antonov Design Bureau and manufactured by Kyiv, Ir ...
and An-26
The Antonov An-26 (NATO reporting name: Curl) is a twin-engined turboprop civilian and military transport aircraft, designed and produced in the Soviet Union from 1969 to 1986.Gordon, Yefim. Komissarov, Dmitry & Sergey. "Antonov's Turboprop Twin ...
, although the contract was later changed to only three aircraft. Modern EU-made transport helicopters were purchased in 2005 and a total of 12 Eurocopter Cougar
The Eurocopter AS532 Cougar (now Airbus Helicopters H215M) is a twin-engine, medium-weight, multipurpose helicopter developed by France. The AS532 is a development and upgrade of the Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma in its militarized form. Its civil ...
have been delivered (eight transport and four CSAR).Three Eurocopter AS565 Panther for the Bulgarian Navy in 2016.
Branches of the Air Force include: fighter aviation, assault aviation, intelligence aviation and transportation aviation, aid defence troops, radio-technical troops, communications troops, radio-technical support troops, logistics and medical troops.
The Bulgarian Ministry of Defense has announced plans to withdraw and replace the MiG-29 fighters with new F-16V Fighting Falcon by 2025–2026.
Aircraft inventory
With the exception of the Navy's small helicopter fleet, the Air Forces are responsible for all military aircraft in Bulgaria. The Air Forces' inventory numbers <50 aircraft, including combat jets and helicopters. Aircraft of western origin have only begun to enter the fleet, numbering of the total in service.Most is unusable, old and inactiveBulgarian-American cooperation
 The Bulgarian-American Joint Military Facilities were established by a Defence Cooperation Agreement signed by the United States and Bulgaria in April 2006. Under the agreement, U.S. forces can conduct training at several bases in the country, which remain under Bulgarian command and under the Bulgarian flag. Under the agreement, no more than 2,500 U.S. military personnel can be located at the joint military facilities.
'' Foreign Policy'' magazine lists
The Bulgarian-American Joint Military Facilities were established by a Defence Cooperation Agreement signed by the United States and Bulgaria in April 2006. Under the agreement, U.S. forces can conduct training at several bases in the country, which remain under Bulgarian command and under the Bulgarian flag. Under the agreement, no more than 2,500 U.S. military personnel can be located at the joint military facilities.
'' Foreign Policy'' magazine lists Bezmer Air Base
Bezmer Air Base is an air base for the Bulgarian Air Force. The base is situated in the eastern part of the Upper Thracian Lowland, in Yambol Oblast (Region), 10 km west of the city of Yambol and 30 km southeast of the city of Sliven, ...
as one of the six most important overseas facilities used by the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
.
Deployments
Both during Communist rule and after, Bulgaria has deployed troops with different tasks in various countries. The table below lists Bulgarian military deployments in foreign countries. Active missions are shown in bold.See also
*Defense industry of Bulgaria
Bulgaria is a NATO member country with a large indigenous defence industry. Most of its weaponry is of Soviet design, but with significantly improved performance. Bulgaria is ranked as a "medium" small arms exporter according to the Small Arms Surv ...
* Bulgaria and weapons of mass destruction
* Medieval Bulgarian Army
The medieval Bulgarian army was the primary military body of the First and the Second Bulgarian Empires, and some Puppet states of the former, like the Despotate of Dobruja. During the first decades after the foundation of the country, the army c ...
References
Sources
*Бяла книга на Въоръжените сили (White Paper of the Armed Forces)
Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria, 2011. * Wikisource:Great Battles of Bulgaria
Bibliography
* *External links
Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria
* https://web.archive.org/web/20110528070137/http://www.wikileaks.ch/cable/2007/10/07SOFIA1271.html – U.S. Embassy Sofia views via
United States diplomatic cables leak
The United States diplomatic cables leak, widely known as Cablegate, began on Sunday, 28 November 2010 when WikiLeaks began releasing classified cables that had been sent to the U.S. State Department by 274 of its consulates, embassies, and d ...
on appropriate future equipment purchases, 2007
* http://www.mediafire.com/download/heyrxhrnpqx06mz/Bulgarian_Military.docx and http://www.mediafire.com/download/ba571l7jiid2tf8/Bulgarian+Military.pdf - Download the word file and a pdf file for the Bulgarian Military's equipment list and specific details.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bulgarian Armed Forces
Military of Bulgaria
Permanent Structured Cooperation