The Bugis people (
pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of
South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi ( id, Sulawesi Selatan) is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sul ...
(the others being
Makassar
Makassar (, mak, ᨆᨀᨔᨑ, Mangkasara’, ) is the capital of the Indonesian province of South Sulawesi. It is the largest city in the region of Eastern Indonesia and the country's fifth-largest urban center after Jakarta, Surabaya, Meda ...
and
Toraja), in the south-western province of
Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
, third-largest island of
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
. The Bugis in 1605 converted to
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
from
Animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning ' breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things— animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather syst ...
. The main religion embraced by the Bugis is Islam, with a small minority adhering to Christianity or a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called ''Tolotang''.
Despite the population numbering only around six million, the Bugis are influential in the politics in modern Indonesia, and historically influential on the
Malay peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
,
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
,
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
,
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up ...
and other parts of the
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arch ...
where they have migrated, starting in the late seventeenth century. The third president of Indonesia,
B. J. Habibie, and a former vice president of Indonesia,
Jusuf Kalla
Muhammad Jusuf Kalla (; born 15 May 1942) is an Indonesian politician and businessman who served as the 10th and 12th vice president of Indonesia, the only vice president in Indonesian history to serve two non-consecutive terms in office (2004� ...
, are Bugis. In Malaysia, the former prime minister
Muhyiddin Yassin has Bugis ancestry.
The Bugis people speak a distinct regional language in addition to
Indonesian, called
Bugis
The Bugis people (pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar and Toraja), in the south-western province of Sulawesi ...
(), with several different dialects. The Bugis language belongs to the
South Sulawesi language group; other members include
Makassarese,
Toraja,
Mandar and
Massenrempulu. The name Bugis is an
exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group ...
which represents an older form of the name; ''(To) Ugi'' is the
endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
.
Origins and antecedents
Toalean — Pre-Austronesian South Sulawesi
The earliest inhabitant of South Sulawesi is potentially related to the
Wajak Man, of the
Proto-Australoid origin. There are a few
flake materials found in
Walanae River valley and
Maros
Maros is a town in the South Sulawesi province of Indonesia close to the provincial capital of Makassar. It is the capital of the Maros Regency.
Maros is the location of the Indonesian Cereals Research Institute, a branch of the Indonesian A ...
, likely dating between 40,000 and 19,000 BC. The
hunter-gatherer culture in South Sulawesi is also known as
Toalean culture, and largely based on blade, flake and
microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Th ...
complex. They are probably of Melanesoid or Australoid stock, hence related to the contemporary
population of New Guinea or
Australian aborigines
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isla ...
.
In 2015, the remains of
Bessé´, a young woman was unearthed Leang Panninge, South Sulawesi. Dated over 7,200 years old, half of her DNA was identified to be connected to the indigenous Australians, the people in New Guinea and the Western Pacific; together with a previously unknown and unique human lineage that diverged approximately 37,000 years ago. Her DNA provided important evidence pertaining to the understanding on ancient human migration.
The arrival of Austronesians

Their
Austronesian ancestors settled on
Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
around 2500 B.C. There is "historical linguistic evidence of some late
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
immigration of Austronesian speakers to South Sulawesi from
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
"—which means that the Bugis have "possible ultimate ancestry in South China", and that as a result of this immigration, "there was an infusion of an exogenous population from
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
or
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
." Migration from South China by some of the paternal ancestors of the Bugis is also supported by studies of
Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of ...
s.
Christian Pelras, an
anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms an ...
, hypothesized that the proto-Bugis were potentially arrived from abroad, possibly from
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
, to the western seaboard of South Sulawesi. Their arrival was largely drawn to control the mineral and natural resources in the hinterland. As the group began to spread towards the interior of the present-day Bugis heartland, they become increasingly diverged from their neighbouring
Makassarese,
Mandarese and
Torajan
The Torajans are an ethnic group indigenous to a mountainous region of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Their population is approximately 1,100,000, of whom 450,000 live in the regency of Tana Toraja ("Land of Toraja"). Most of the population is Chr ...
brethren; simultaneously, the proto-Bugis too would assimilated the sparce former
Austronesian populations in the area, a process whereby the native would gradually adopted the language of the new arrivals. Hence, a redesigned hybrid-identity through
ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
emerged, binding the original elements derived from the indigenous people together with the introduction of revolutionary techniques, items and ideas bought by the new settlers, including
weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
,
metal arts and
theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the s ...
doctrine. The society however, remains largely divided between two separate classes, the prevailing nobility and the common people.
Tana Ogi — Land of the Bugis
The homeland of the Bugis is the area around
Lake Tempe
Lake Tempe () is a lake in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is located at . The town of Sengkang is situated to the east of the lake.
See also
* List of lakes of Indonesia
This is a list of the notable lakes of Indonesia. Indonesia has 521 natu ...
and Lake Sidenreng in the Walannae Depression in the south-west peninsula of Sulawesi. It was here that the ancestors of the present-day Bugis settled, probably in the mid- to late second millennium B.C. The area is rich in fish and wildlife and the annual fluctuation of Lake Tempe (a reservoir lake for the
Bila and Walannae rivers) allows speculative planting of wet rice, while the hills can be farmed by
swidden
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed veg ...
or
shifting cultivation
Shifting cultivation is an agricultural system in which plots of land are cultivated temporarily, then abandoned while post-disturbance fallow vegetation is allowed to freely grow while the cultivator moves on to another plot. The period of cu ...
, wet rice, hunting and gathering.
Around A.D. 1200, the availability of prestigious imported goods including Chinese and South-East Asian ceramics and Gujerati print-block textiles, coupled with newly discovered sources of iron ore in
Luwu stimulated an agrarian revolution which expanded from the great lakes region into the lowland plains to the east, south and west of the Walennae depression. This led over the next four hundred years to the development of the major kingdoms of South Sulawesi, and the social transformation of chiefly societies into hierarchical proto-states.
History
Early society
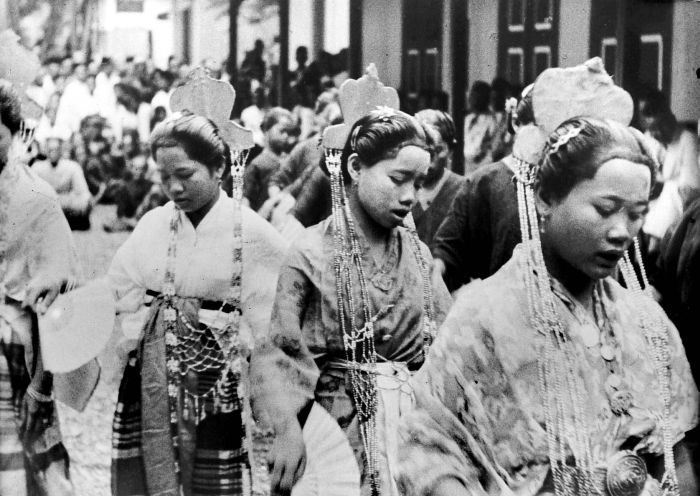

The lifestyle of ancient Bugis people were, to some extent, preserved by the pagan
Torajan people
The Torajans are an ethnic group indigenous to a mountainous region of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Their population is approximately 1,100,000, of whom 450,000 live in the regency of Tana Toraja ("Land of Toraja"). Most of the population is ...
until the dawn of the 20th century. Their homes were mainly constructed on
stilts and the communities were likely to be scattered along the river banks, sea or lake shores. The main undertakings during this period were farming
rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
,
millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
,
adlay and other edible crops, catching fish and shellfish, obtaining forest produce and hunting wild animals.
Buffaloes were imported and used for important occasions.
The earliest inhabitants potentially clad under a simple clothing. The women potentially wore a
skirt; while for the men, a
loincloth and possibly a headcloth. Remains of
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
and
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
ornaments have also been retrieved based on archeological evidence.
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
is evident, although
bamboo containers were more extensively used together with the usage of bamboo knives. The weapons were sourced from iron and stones together with helmets and shields made from
rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan, is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the closed- canopy old-growth tropical fores ...
.
Theologically, the early Bugis potentially practiced
ancestor worshipping. There were also ancient rituals related to agriculture and fertility. They generally
buried their corpses, although there were several cases where the deceased body were being
disposed by immersion in the sea or lakes, or by positioned in trees. Other mortuary practices includes
cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a Cadaver, dead body through Combustion, burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India ...
, especially for the rulers.
Despite being located in a sparsely populated communities, they were not living in an absolute isolation with the outside world. Instead, trade and commerce were held high and regarded to be of pivotal importance in the society. The archeological findings near
Bantaeng
Bantaeng Regency (''Kabupaten Bantaeng''; ) is a regency of South Sulawesi Province in Indonesia. It covers an area of 395.83 km2 and had a population of 176,984 at the 2010 Census, rising to 196,716 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as a ...
and
Ara
ARA may refer to:
Media and the arts
* American-Romanian Academy of Arts and Sciences
* '' Artistička Radna Akcija'', compilation album released in former Yugoslavia
* Associate of the Royal Academy, denoting membership in the British Royal Acad ...
unearthed ancient artifacts dating from 300 to 100 BC, denoting evidence that the southern part of Sulawesi has played an integral role in the axis of early
insulindian trade. There are also traces of imported Chinese and other
continental Southeast Asian ceramics and stonewear found in the pre-Islamic cemeteries.
However, in contrast to much of Southeast Asia, the indicators of Hindu and Buddhist materials are rather sparse in South Sulawesi cultures. Their
writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable fo ...
, and some of their names and words, along with few
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
bronze images found in Mandar and Bantaeng only suggest that the existence of trade relations made with the western
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arch ...
and the presence of
foreigners alike. It is likely that despite being benefited with the trade relationship, they would resist external
assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
* Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
** Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the prog ...
. Thus, outside elements are almost absent in the development of
native religion and the indigenous states.
The intensity on the early insulindian trade has led to a gradual shift in terms of the economic development, social construct, political interest and the balance of power amongst the South Sulawesi people, which has fundamentally led to the Bugis states, dynasties and polities began to flourish.
The growth of Bugis kingdoms

The progress of
inter-insular commercial activities and the increasing interactions with
Maritime Silk Road were potentially among the main factors contributing to the economic prosperity for a few leading South Sulawesi communities. The period between 1200 and 1600 witnessed a radical change throughout the political landscape of lowland
South Sulawesi Peninsula.
The trade in South Sulawesi was based on the export of rare commodities, a business which was easily dominated by an exclusive
ruling class
In sociology, the ruling class of a society is the social class who set and decide the political and economic agenda of society. In Marxist philosophy, the ruling class are the capitalist social class who own the means of production and by ex ...
. The administrative structure is fairly basic, a majority of the states are small and in a form of a local chiefdom. A small population is sufficient to assist the elite with food, physical work and military assistance to preserve their state's independence.
However, by the 15th century, a major economic revolution taken place, and
agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
become an important economic foundation. To continue their powers in the
agrarian-based society, the ruling elites are now required to handle the growth on the
rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
-producing territories to accommodate a major
population boom. Hence, in order adapt with the economic and societal change, a new system and intermediaries are needed.
Trade and commerce however, still retains its essential importance for the South Sulawesi economy. Rice become a major source of export; and at the same time, the economy is stimulated by the import of prestige goods from other parts of archipelago. The area potentially experienced exceptional growth following the
rise of Malacca as a regional
entrepôt. Conversely, the wealth for the elite families in South Sulawesi would also consequently rose due to this intensive commercial transactions, despite the fact that trade is now not solely regarded as their single source of riches.
Emergence of new political strengths over the Peninsula

In the 1500s,
Luwu was the major political force in the Bugis heartland, with its authority proclaimed throughout a large section of the peninsula. Nevertheless, new players that would resist its dominance were already beginning to take shape by the end of the century.
The impact following the rise of Malacca were more visible in the western coast of South Sulawesi, an area with a high concentration of
Malay merchants. It slowly gained the attention of the kingdoms of Soppeng and Sindereng, with the pursuit to include the area in their territorial expansions, these Bugis states have already
lost their direct sea access in the west coast by Luwu.
Sidenreng, a tributary under the domain of Soppeng had slowly grown into prominence and slowly seemed to be resistant to accept Luwu's dominance in the area. In cooperation with a few Bugis kingdoms in the western coast — Sawitto', Alitta, Suppa' and Bacukiki'; as well as Rappang in the interior, they formed a loose confederation known as
Aja'tappareng ('the lands west of the lake').
Conversely, the neighbouring Bugis territory of
Wajo also possessed an aspiration for an autonomy against Luwu, and it too started to extend their influence and powers in the surrounding areas. By 1490, they entered an agreement with Luwu, and in the agreement they would no longer be considered as "its servant" but as a "Luwu's child". By 1498, the Wajorse enthroned Arung Matoa Puang ri Ma'galatung as their ruler, he would later turn the domain as one of the major Bugis Kingdom.
The lower western seaboard, the Bugis Kingdom of
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
under the rule of King Kerrampelua' (c.1433–83) had also enacted an expansion plan to absorb parts of neighboring Luwu territories into its vassalage. Thus, by two centuries later, it has become an area for intense confrontation between the two kingdoms.
While the
Makassarese, traditionally occupied the deep down in the south and the western coast of the peninsula were mainly concentrated their political powers in
Siang and Bantaeng (the latter was potentially still under Luwu's nominal control). However, the small twin states of
Gowa and Tallo (better known by foreigners as a single state of Makassar) were started to gain its importance during this period.
Bugis-Makassar society in the 16th century
By the 16th century, the Bugis life is noted by a flourishing tolerance towards
foreign influences, overseas products were no longer limited to the ruling class, but also among the
commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
s as well. The method of home construction, remains the same. Sketches from few western sources in the first half of 17th century illustrates tall and strong wooded home raised on piles.
Nonetheless, inside of the more wealthy homes, some foreign furnitures, namely tables and chairs began to emerge, and basic wall opening sometimes become real windows with
shutters. The Bugis names for these objects signaled their
Portuguese connection, ''Jandela'' (window) deriving from ''Janela'', ''Kadera'' (chairs) from ''Cadeira''; and ''Mejang'' (table) from ''Mesa''. A gradual change is also noted in the
household tools and utensils, including glasses and Iberian-style jugs and trays. There were also the adoption of few Portuguese games notably
dice
Dice (singular die or dice) are small, throwable objects with marked sides that can rest in multiple positions. They are used for generating random values, commonly as part of tabletop games, including dice games, board games, role-playing ...
, card game and marbles. The Portuguese and Spaniards also introduced new food and produce in the local diet, mainly from the
New World crops:
sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato ('' Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable. The young ...
and
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, and also other important items —
manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
,
maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
and
chilies.

During the period, the women don under a baggy trousers and pants; the usage of short
tunics and sleeves were also noted by the free married women. For the affluent male, there were potentially also a favour towards western
shirt
A shirt is a cloth garment for the upper body (from the neck to the waist).
Originally an undergarment worn exclusively by men, it has become, in American English, a catch-all term for a broad variety of upper-body garments and undergarments. ...
s and hats; and sometimes being paired together with a
plume, and a
jacket
A jacket is a garment for the upper body, usually extending below the hips. A jacket typically has sleeves, and fastens in the front or slightly on the side. A jacket is generally lighter, tighter-fitting, and less insulating than a coat, which ...
. The slave class and the male commoners however, would usually go
topless.
The aftershocks following the
Fall of Malacca were potentially being strongly felt in South Sulawesi. As noted from
Tomé Pires in Suma Oriental, few traders from ‘The Macassar Islands’, including the Bugis and
Bajo were amongst the people who arrived in Melaka to trade, although they are small in numbers. Conversely, the Muslim-Malay traders from
Patani
Patani Darussalam ( Bahasa Malayu Arabic : , also sometimes Patani Raya or Patani Besar, "Greater Patani"; th, ปาตานี) is a historical region in the Malay peninsula. It includes the southern Thai provinces of Pattani, Yala (Jal ...
,
Pahang
Pahang (; Jawi: , Pahang Hulu Malay: ''Paha'', Pahang Hilir Malay: ''Pahaeng'', Ulu Tembeling Malay: ''Pahaq)'' officially Pahang Darul Makmur with the Arabic honorific ''Darul Makmur'' (Jawi: , "The Abode of Tranquility") is a sultanate and ...
, and
Ujung Tanah in the
Malay peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
; as well as from
Champa
Champa ( Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd ...
in
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
; and
Minangkabau in
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
settled throughout the port cities in the western coast, including Suppa’, Pancana-Tanete, Siang, Tallo, Sanrabone and Gowa. Due to this extensive bilateral connection, the people of South Sulawesi were generally well aware on the political-religious changes taken place in the western half of the archipelago.
It can be inferred that following the Conquest of Malacca by the
Portuguese Conquistadors, the trading links intensified between South Sulawesi to other commercial powerhouse: namely Johor and Patani in the Peninsula,
Acheh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a spe ...
in Sumatera,
Banjarmasin in
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
and
Demak in
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
— all having the
status as a bastion for Islamic faith. However, as far as the mid 16th century, South Sulawesi persist to be one of the few remaining significant domains in the regional native trading network where
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
has yet to take hold.
Early attempts to Christianize the Bugis states
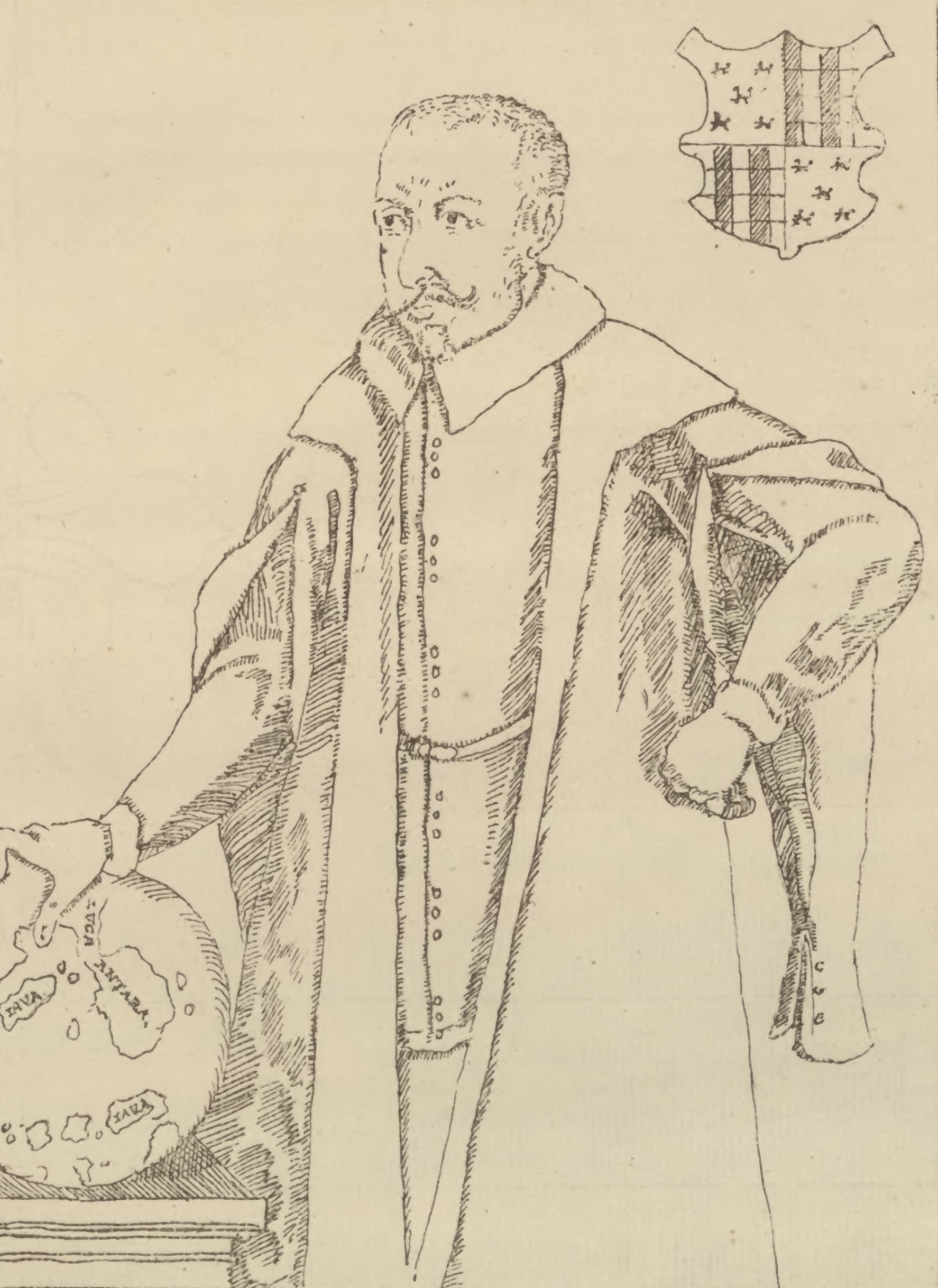

While early contacts with Islam had been made since 1490 with the trading relationship between Siang and Malacca, most Bugis were still believer of the native patturioloang religion. In year 1540, two aristocrats from Makassar were
baptized
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost i ...
in
Ternate. They later embarked on another visit the following year and bought many of the region's previous materials, including gold,
sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus '' Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for ...
and iron weapons. Antonio de Paiva, a Portuguese trader, made multiple voyages between Sulawesi and
Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has bee ...
from 1542, potentially intrigued by the potential riches of the region. During his expedition to the Bugis states of Suppa' and Siang, he was involved in a
theological discussion and was requested to baptize La Putebulu, Datu of Suppa' and his family, followed by king of Siang in 1544. The baptism was also concluded with a
military alliance
A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations concerning national security. Nations in a military alliance agree to active participation and contribution to the defense of others in the alliance in the event of a crisis. (Online) ...
with both states.
De Paiva's return to Malacca was not only together with official gifts to the
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kn ...
, but also accompanied with four young Bugis men who would later attend the Jesuit college in
Indian Goa. The two Bugis Kings also requested priests and a possible military support from the Portuguese Malaccan governor, potentially to curb the increasing peril imposed by the neighboring Makassarese states of Gowa-Tallo. Further baptism continued in 1545 by a priest, Father Vicente Viegas, which was involved the Christianization of Bugis rulers in Alitta and Bacukiki', according to
Manuel Godinho de Erédia
Manuel Godinho de Erédia, or Emanuel Godinho de Erédia (16 July 1563 – 1623), was a Bugis-Portuguese writer and cartographer. He wrote a number of books, including an early account of the Malay Peninsula that is a source of information on th ...
, kings of Sawitto and Sidenreng also participated, all were allies of Suppa' part of
Ajatappareng alliance.
Relations with Portuguese were still good, until an elopement between a Portuguese officer and daughter of La Putebulu from Suppa was exposed as they married secretly in Malacca, which would result in the birth of
Manuel Godinho de Erédia
Manuel Godinho de Erédia, or Emanuel Godinho de Erédia (16 July 1563 – 1623), was a Bugis-Portuguese writer and cartographer. He wrote a number of books, including an early account of the Malay Peninsula that is a source of information on th ...
. The Portuguese vessel had to rapidly left Sulawesi to avoid severe violence and they did not dared to travel back to the island until 1559. One member of the voyage, Manuel Pinto, decided to remain in South Sulawesi, he recorded the political development and involved in discussions with several Bugis-Makassar rulers in the region before returning to Malacca (via Java). However Datu of Suppa and its population alongside other
Ajatappareng Ajatappareng was a historical region in the western part of South Sulawesi (today part of Indonesia) consisting of five allied principalities: Sidenreng, Suppa, Rappang, Sawitto, Bacukiki and Alitta. They formed an alliance during the sixteent ...
states remain largely Christians according to
Manuel Godinho de Erédia
Manuel Godinho de Erédia, or Emanuel Godinho de Erédia (16 July 1563 – 1623), was a Bugis-Portuguese writer and cartographer. He wrote a number of books, including an early account of the Malay Peninsula that is a source of information on th ...
.
Following the restoration of economic relations with the Portuguese Malacca in 1559, there were repeated requests made from South Sulawesi primarily
Ajatappareng Ajatappareng was a historical region in the western part of South Sulawesi (today part of Indonesia) consisting of five allied principalities: Sidenreng, Suppa, Rappang, Sawitto, Bacukiki and Alitta. They formed an alliance during the sixteent ...
states for priests, however not many were available and the Portuguese did not consider Bugis as their prime concern. Not until 1584 did the Portuguese send four
Franciscans
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
fathers to the area, and their stay was a short one. Also not known were the fates of the four Bugis men sent for education in
Indian Goa. Subsequently, no new attempts to baptized Sulawesi were taken after the period, nor Portuguese military support against invasion by King of Gowa-Tallo, Karaeng Lakiyung Tunipalangga, which annexed and vassalized Siang alongside other
Ajatappareng Ajatappareng was a historical region in the western part of South Sulawesi (today part of Indonesia) consisting of five allied principalities: Sidenreng, Suppa, Rappang, Sawitto, Bacukiki and Alitta. They formed an alliance during the sixteent ...
states.
Quest for prestige, influence and powers over the Peninsula

During the resumption of Portuguese-South Sulawesi relations in 1559, the political dynamic of the region had effectively morphed. The Makassarese state of Gowa had exerted his influence towards the north, and absorbed many Bugis states that have had a friendly relations towards the Portuguese.
Simultaneously, the Kingdom of Bone also commenced its southward expansion, and soon come into a direct contact with the Makassarese. Both kingdoms are pursuing dominance in the entirety of the Peninsula together with the important trade routes.
Conflict between the two powers were bound to happen, and a major war broke out in 1562. Gowa was assisted by Luwu; and also by Wajo and Soppeng, the latter two would probably preferred in favour of a distant sovereign like Luwu or Gowa, as they would furnish Wajo and Soppeng with a greater autonomy in contrast to a nearby kingdom like Bone, which would likely dominate them.
The war concluded in 1565 and a
peace negotiation
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surren ...
followed afterwards. The two states agreed in the Tengka River as their respective spheres of influence under the Treaty of Caleppa. The citizens of Bone and Gowa were also awarded equal rights in each other's jurisdiction.
The ambitions for dominance continued in South Sulawesi. Between 1570 and 1591, several military operations were conducted by Gowa, in which oftentimes with the support of Luwu. Although a distant power, Gowa tend to be rather hard towards its Bugis vassals of Wajo and Soppeng, this made these two states become inclined to the invitation by Bone to restore their
autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one' ...
. In 1590, the three kingdoms (Wajo, Soppeng and Bone) entered an alliance known as ''Tellumpocco'e'', 'the Three Summits' or 'the Big Three'.
In 1590, Daeng Mammeta embarked on another campaign to annihilate Wajo, but he was killed during an
amok. A truce was followed soon after in 1591, the peace negotiation, under the Treaty of Caleppa was thus renewed.
The Islamisation of Bugis-Makassar-Mandar

In the later half of the 16th century, the contest between Islam and Christianity was still largely undecided in South Sulawesi Peninsula. Most of the surrounding kingdoms in Sulawesi have already become Muslims under the sway of
Ternate-Gorontalo in 1525 and
Buton in 1542. There were already individual converts in South Sulawesi.
In 1550, the Malay-Muslim community of Macassar were awarded special privileges by the ruler of Gowa according to ''Lontarak Patturiolonga''. However, in 1575, during the visit by Abdul Makmur (Dato' ri Bandang), one of the Minangkabau proselytizers of Islam, he noted that there are several difficulties to convert the locals — the superfluous liking towards
dried boar flesh, raw deer liver diced with blood (lawa) and palm liquor. He then embarked to promulgate the teaching of Islam in the
Kingdom of Kutei, eastern Borneo, in which he was more triumphant. In 1580, the Sultan of Ternate, Babullah, advised the ruler of Gowa to embrace the teaching of Islam, the king declined. However, as a gesture of kindness, he awarded the Makassar-Malay community the consent to construct a
mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
.
Abdul Makmur returned to Makassar with Sulaiman (Dato' ri Pa'timang) and Abdul Jawad (Dato' ri Tiro). All three of them are from Minangkabau and likely to have been educated in Aceh, before they visited Johor-Riau to study South Sulawesi culture from Bugis-Makassar sailors, followed by study under
Wali Songo
The Wali Songo (also transcribed as Wali Sanga) are revered saints of Islam in Indonesia, especially on the island of Java, because of their historic role in the spread of Islam in Indonesia. The word ''wali'' is Arabic for "trusted one" (" ...
of
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, in a proselytization mission facilitated by Sultan of Johor. After their new attempts to introduce the Islamic teaching once more met with opposition, they left for
Luwu. This was because Luwu was the spiritual center of South Sulawesi and its indigenous belief of Dewata SewwaE had some similarities with Islam.
They successfully converted the Pattiarase, Datu of Luwu and in February 1605 he took the name of Sultan Muhammad. The group then revisited Makassar and the three of them later managed promoted Islam to the Gowan ruler, to become Muslim under the name of Sultan Ala’uddin. In November 1607, the first public
prayers were promulgated in the newly constructed Tallo' Mosque. Conversion began slowly and adapted with native Ammatoa practitioners centered in Bulukumba.
The twin kingdom of Gowa and Tallo persuaded other South Sulawesi Kingdoms to emulate their move on adopting Islam as their religion. When this invitation was declined, they launched a series of military actions known as "the Islamic wars". In 1608, the west coast states of Bacukiki', Suppa', Sa wino' and Mandar; and in the east coast, Akkotengeng and Sakkoli' submitted; followed by subjugation of Sidenreng and Soppeng in 1609, Wajo in 1610.
Pursuant to the submission from the Bugis state of Bone in 1611, most of the South Sulawesi Peninsula (with the exception of Toraja highlands) have accepted Islam.
Bone, subsequently would continue to Islamize its two vassal states located in the edge of the Torajan realm — namely Enrekang and Duri.
The Islamisation in most of South Sulawesi have provided a platform for a faith and ideological revolution. Islamic laws and principles were observed and absorbed into the Makassar, Bugis and Mandar cultures.
Dato' ri Bandang directed first towards the foundation of
Sharia principles on the land, having emphasis on the importance of religious service at the
circumcision ceremony,
marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
and
funerals. However, with the exception of funeral rites which were absolutely Islamized; other rites of passage based on the Islamic understanding were simply incorporated with the existing traditional practices, norms and customs. As for prohibition, there are also strong enforcement against
adultery
Adultery (from Latin ''adulterium'') is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal ...
and the
consumption of pork; other behaviors including consuming alcohol and opium, offerings to sacred places, worshipping at regalia, lending money with interest (
Riba
The Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) is a professional body for architects primarily in the United Kingdom, but also internationally, founded for the advancement of architecture under its royal charter granted in 1837, three supp ...
) and
gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of value ("the stakes") on a random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy are discounted. Gambling thus requires three ele ...
were also condemned.
As Islamization was slowly taking root among the society in the peninsula, mosques were built in each of the states and domains, appointments were made for the position of
qadi
A qāḍī ( ar, قاضي, Qāḍī; otherwise transliterated as qazi, cadi, kadi, or kazi) is the magistrate or judge of a '' sharīʿa'' court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and mino ...
,
imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve ...
and
khatib.
Despite being devout Muslims, the process did not serve as a hindrance towards the Makassarese Muslim King of Gowa to maintain a friendly relationship with Portuguese and Christianity. Despite so, the Bugis and Makassarese realms became Muslim and were now prevented to convert to Christianity by the local ruler.
The twilight of dominance

Beginning from the end of the 17th century and the dawn of the 19th, the course of South Sulawesi societies were rocked with a series of monumental changes in the local statecraft, including the Fall of Makassar, internal disputes, political conflicts and the growing secondary influence from the western
consumerism
Consumerism is a social and economic order that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing amounts. With the Industrial Revolution, but particularly in the 20th century, mass production led to overproduction—the su ...
.
Close to twenty years after the century-long intense power struggle between Gowa and Bone for the conquest on the Peninsula, another war had broken between the two rivaling powers. The war traced its origin from a domestic affair in the Kingdom of Bone, who was ruled from 1631 to 1634 by La Ma'daremmeng. The king enforced rules based on the strong Islamic principles, including removing the pagan bissu and forbidding the consumption of palm beer and other superstition. The final straw was the prohibition of slavery, which resulted the rebellion by the
mother of the king. She later then sought the assistance of Gowa and a major military operation ensured. The Makassarese forces managed to achieve success and captured 30,000 Bugis prisoners, including La’daremmeng and installed a Makassarese governor. After a subsequent revolt, Bone was transformed into a full-fledged colony. This resulted the anger amongst the Bone people and its nobility.

The opportunity for the Bone came after the victorious Dutch attack in 1660. Required to sign an unfavorable truce, the Makassar requested 10,000 Bone people for a forced ditch digging as defense against potential attacks from the land. Few Bone noblemen, including Arung Pallaka, took refuge in the neighbouring Buton and presented for a Bugis-Dutch alliance against Makassar. The war against Makassar erupted in 1666, with the Bugis-Dutch alliance being assisted with troops from Ternate,
Ambon and Buton. The sole Makassarese alliance during the war were the Bugis state of Wajo and the local Malay community.
Sultan
Hasanuddin of Gowa was obliged to sign the treaty of Bongaya on 18 November 1667. This required the Makassarese powers to removed most of its fortification, relinquish its trade in spices, end its import of foreign goods with the exception of the Dutch East India Company, banish the Portuguese and other non-Dutch Europeans, and reject any other attempts of suzerainty, in both Bugis lands or other parts of the archipelago. In 1669, Sultan Hasanuddin abdicated from the throne.
The Dutch have succeeded to achieve its goal after the fall of Makassar, but they are not the sole victor; another was the Bugis State of Bone, despite having a few restriction following the treaty that it also signed, the kingdom would effectively maintain its sovereignty until the 19th century. Hence, in the Bone narration, Arung Palakka holds the status as an independence warrior; while in Makassar heritage, the rivaling Sultan Hasanuddin is hailed as the hero for the Makassarese.
Once liberated from Makassar, it has possibly set the stage for Bone to hold an unchallenged power across the whole peninsula. However, the prospect of
unifying all the Bugis lands under a sole ruler was stopped by the existence of the Dutch in the region. The peninsula then continued to persist under a mosaic of various small and large
confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical iss ...
s.
A new golden age

One of the major turning point following the conquest of Makassar was the change in the design of navigation and
emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanent ...
routes among the South Sulawesi people. The cosmopolitan port city of Makassar become a crucial maritime starting point for not only for the Makassarese, but also for the Bugis who seek for wealth and fame in the western Archipelago, as the Dutch set a heavy restriction for their access on the eastern
spice islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
.
Many of the Bugis settled in the
Riau Archipelago
The Riau Archipelago is a ''geographic'' term (as opposed to administrative region) for the core group of islands within the Riau Islands Province in Indonesia, and located south of Singapore and east of Riau on Sumatra. Before the province of ...
, in the proximity of the courts of
Johore. A crucial meeting point between the regional and global trade routes, they launched their naval influence in various directions on commerce and politics, including the Malay Peninsula,
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Sumatra and western coast of Borneo. Here they challenged against the Dutch for the dominance in the tin-mining exports. They also heavily involved in the dynastic disputes among the kings, and through armed actions, military-based traditions and political marriage, they navigated to become one of the formidable players within the inner Malay political circle. The age also marked with other closely interconnected waves of migration and trade towards
Batavia, northern coast of Jawa,
Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
, Madura, Alor Island, Alor, the
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up ...
, southern-eastern Borneo, Sulu Archipelago and other parts of Sulawesi in search of riches, prestige and political influence.
During the same period, they ushered a new golden era. With the consolidation of Islamic faith and values on one side, and the recognition as one of the major maritime society on the other; the two redefining elements that would be infused to become part and parcel with the Bugis identity until the early 20th century.
Culture
Language and dialects

The Bugis language constitutes a part of the larger Austronesian languages, Austronesian family. It is among the major languages located in the southwest hempisphere of Sulawesi, the others being Makassar language, Makassar, Toraja language, Toraja, Massenrempulu language, Massenrempulu and
Mandar. These languages collectively belong to the South Sulawesi languages.
Bugis speakers are dominant in the most of the Kabupaten, districts in South Sulawesi — namely Bone Regency, Bone, Soppeng Regency, Soppeng, Wajo Regency, Wajo, Sidenreng Rappang Regency, Sidrap, Pinrang Regency, Pinrang, Barru Regency, Barru, Sinjai Regency, Sinjai, and Parepare. In Bulukumba Regency, Bulukumba, Pangkajene and Islands Regency, Pangkep, and Maros Regency, Maros, the populations are checkerboarded between Bugis and Makassar-speaking villages, each villages having their own separate language identity intact. A similarly unsharp language border can also be observed in the northwestern coastal towns of Pinrang Regency, Pinrang (in South Sulawesi Province) and Polewali Mandar Regency, Polmas (in West Sulawesi), being a transitional area between the traditional Bugis and Mandarese cultural areas.
Located in the periphery of the Bugis-Torajan world, the Massenrempulu people (constituting Duri, Enrekang, Maiwa and Malimpung groups) from Enrekang Regency, Enrekang and northern Pinrang Regency, Pindrang as well as the Taeʼ language, Tae' speakers of Luwu are also occasionally identified and embraced as among the subgroups of the Bugis family due to the shared tradition and common religious affiliation. Culturally, they formed a Continuum (measurement)#Linguistics, continuum between the Bugis and Toraja people; linguistically, the Massenrempulu's and Tae's mother tongue generally inherited a closer linguistic intelligibility with the Torajan language.
Despite having some divergence in the local expression and dialects, the Bugis variants (with the exception of Massenrempulu and Tae', when considered) commonly retain a high level of mutual intelligibility between one another. Nonetheless, it is an accepted practice amongst the mainstream Bugis society to distinguish themselves regionally and culturally based on the location of their traditional and ancestral states.
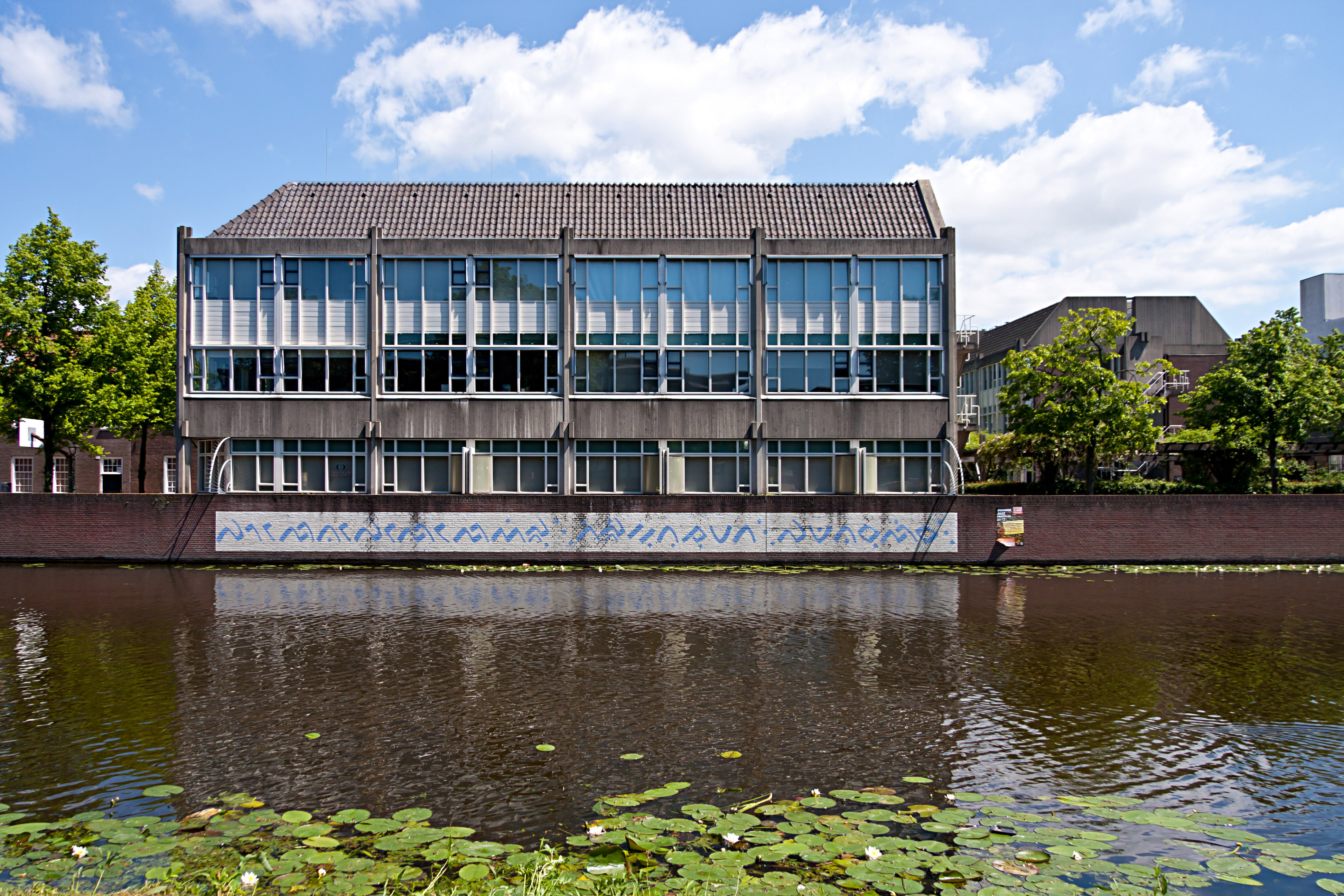

There are a subtle differences on the language spoken in these areas and linguist identified these versions as separate dialects (rather than distinct languages). Presently, there are ten main branches of Bugis Dialects — Bone, Camba, Pangkep, Sidrap, Pasangkayu Regency, Pasangkayu, Sinjai, Soppeng, Wajo, Barru and Luwu Regency, Luwu, as well as dozens of smaller subdialects deriving from the main branches. However, some researchers are divided whether Sawitto — a divergent Bugis variety spoken in central Pinrang — remains under the same language group or being diverged enough to be considered as a separate language.
The present-day Bugis people are mostly Multilingualism, bilingual. In South Sulawesi, they use two leading languages, either Bugis or
Indonesian, tailored based on the environment, social circle and activities. Bahasa Indonesia is largely incepted on official situations, it is the language of formal education, Administration (law), administration, mass media and modern literature; Bahasa Indonesia is also prevalent during conversation with non-Bugis speakers. In the informal and casual settings around the Bugis-speaking circle, a Code-switching, code-switch would be a commonplace, or intertwined with elements of both languages in varying degrees, such as speaking Bahasa Indonesia with a strong Bugis-influenced elements and vice versa.
In the South Sulawesi province, the Bugis affixes such as –ki’, -ko, na-, -ji, - mi, etc. are emulated and conceived in the Indonesian-Bugis mixed language, hybrid. The Bugis-Indonesian fixture is not exclusively confined in the borders of South Sulawesi, the pattern can also be heard in other parts of Indonesia with a visible Bugis population. Outside the province, the language hybrid is not solely influenced by Bahasa Indonesia, but alongside traces of other local languages and dialects amalgamated with the diaspora Bugis language. Similarly beyond Indonesia, the extension of the language blend can also be seen in parts of Malaysia and Singapore, home to a sizable Bugis community. Instead of having influenced with Bahasa Indonesia, the Bugis communities in these countries would also be influenced by the Malay language, Malay language and its local dialects.
Outside from their ancestral heartland in the lowland plains of South Sulawesi, the Bugis language, dialects and hybrids are found throughout their extensive network of diaspora and ethnic enclaves in Sulawesi and all across Insular Southeast Asia. However, presently there tends to be a pronounced language shift among the diaspora outside of South Sulawesi, hence the understanding and the command on the Bugis language may vary based on the personal background, exposure and contacts with their ancestral language.
Philosophy

The Bugis-Makassar possessed a rich heritage, philosophy, religious and social structure. Their customs are based on the concept ''Pangadereng'' - originally consist of ''Adat, Ade’'' (custom), ''Rapang'' (Jurisprudence), ''Bicara'' (Judiciary) and ''Warik'' (Social system); following the Islamisation of the Bugis-Makassar, ''Syara (Syariah) was incorporated into its core values.
Another fundamental local wisdom includes ''Siri' na pacce''. It serves as a guidance, social convention and moral conduct. ''Siri'' signifies the consolidation a demeanor of shame and self-esteem, it acted as a pillar that bear the importance of dignity, virtue, esteem, solidarity and responsibility. ''Siri'' is essential for someone to be regarded as a ''tau'' (human). ''Pacce'' manifest as a presence of compassion and solidarity. It involves a person's ability on emotional intelligence, which includes love, sadness, pain, and solidarity. Other interpretation of ''Pecce'' revolves on self-sacrifice, hard work, and abstinence. In addition to the Bugis and Makassarese, the traditional ethos is also shared by their northern cousins — the Torajan people, Torajans and
Mandarese.
Translated as the "four corners" — ''Sulappa Eppa'' represents the ancient philosophy, ideas and theories of the Bugis-Makassar on the notion that the universe was built in a form of a giant rhombus, created by four salient fundamentals — wind, fire, water and soil, earth. Thus, the classical Bugis-Makassar aesthetic vibes, images and nuances are largely created and envisioned in a dominant four-angle, cornered composure; including on their traditional writing scripts (the Lontara script, lontara), architectural floor plan, layouts, ceremonial cuisines (''songko'' and ''songkolo''), artistic designs, textile (sarong motives) and philosophical values. The four elements are also synonymously evoked by four distinct colors — wind (yellow), fire (red), water (white) and earth (black). Additionally, the ''Lipa' Sabbe'' or ''sarung sutra'' (a sarung-cloth made from silk) signifies as an embodiment to honor the refined Bugis-Makassar identity in its purest form.
Traditional script

The Lontara script, Lontara traced its origin from the Kawi script; however, it has received a localized development and modification to accommodate the writings in the Bugis, Makassar and Mandar language. It was traditionally used for formal and official documents such as contracts, trade laws, treaties, maps, and Logbook, journals, both in Western Book design, book format and in the traditional palm-leaf manuscript. Following the rise of South Sulawesi as a naval powerhouse in eastern archipelago, the script expanded its influence, being introduced and incorporated as the Lonta Ende in Flores, Mbojo in eastern Sumbawa and Satera Jontal in western Sumbawa, albeit with alternations for the latter languages.
Its designation, "Lontara" was acquired from the term ''Lontar'', the Javanese language, Javanese and Malay language, Malay name from Palmyra Palm, whose leaves were commonly utilized for writing the manuscripts. It is also sometimes characterized as the Bugis script, as many of the historical writings are widely found in this language. In the Bugis Language, the writing system is styled as ''"urupu sulapa eppa"'', being described as "square" or "four-cornered letters", which served as a vivid illustration of the early Bugis-Makassar interpretation on the four ingredients that molded the universe — fire, water, earth and air.
During the Dutch colonization of Dutch East Indies, East Indies, the writing system is largely being superseded with the introduction of Latin Alphabet. Nonetheless, the script still retains its intimate cultural importance amongst the Bugis-Makassar society in their homeland and being use for the traditional ceremony, calendar and literature; as well as in personal documents and handwritten items, for instance, in letters and notes. The script is also being taught in many schools in South Sulawesi and the usage are visible on some street signs across the province. Presently, there is also notable efforts by Indonesian typographers and graphic designers on introducing the script to a larger audience beyond its traditional borders.
In addition to Lontara, there is also another form of Bugis-Makassar traditional writing based on the Arabic-script, known as the Serang Alphabet. Relatively on an almost similar parallel module with its sister scripts, Jawi script, Jawi and Pegon script, Pegon for Malay and Javanese respectively, the Serang writing system incorporated the usage of Arabic script, Arabic elements with few additional characters to integrate with the local language.
Folklore and literary traditions

Bugis literature connotes to the forms of literature expressed in the Bugis language — which comprises both Literature, written and oral traditions. The earliest works of Bugis literature were verbally transmitted, written literature began to arose and gradually codified with the evolution of the Lontara script, Lontara script by the 1400s. Its foundation largely coincides and intersects with the Makassarese literature — of whom it shared a closely related development with. The Bugis literary tradition mainly focuses on the wisdom, moral, social life and cultural environment of the Bugis identity.
Bugis folk literature is an oral composition deeply rooted in Bugis understanding and perception of life — in the form of prose, poetry and Lyrics, lyric. The classification raging from various short poems, ''élong''; long narrative poems, ''tolo; playful sayings, such as riddles, ''atteppungeng'' and nursery rhymes; magical spells, ''jappi, baca-baca''; pre-Islamic ritual expressions, ''sabo, sessukeng, lawolo''; precepts, ''pappaseng''; and oaths of allegiance, ''aru''. Other important oral heritage includes — stories, ''curita''; sermons, ''katoba''; and Speech recognition, speeches. Although they are essentially verbal, many of the works are also subsequently being written in the language.

Writings in the Lontara Script was likely to be first appeared around 1400. The earliest texts were inscribed on palm leaves, followed by volumes of Handwriting, handwritten composition on paper manuscripts, potentially from 1500 onwards, or even earlier. The works of literature commonly commissioned by writing specialists known as ''palôntara'', the ''palôntara'' is being delegated the task as a researcher on creating and compiling the Bugis manuscripts. The manuscripts tend to be rich and varied, with a plethora of theme (arts), themes and subjects — including History, historical chronicles, poems, law, legal works, ritual texts, manuals, ethics, among few. Printing, Printed materials in the Bugis language were introduced in the latter half of the 19th century, albeit with a smaller circulation, such as in Dictionary, dictionaries, Grammar, grammars books, Chrestomathy, chrestomathies and translations.
Consist of over 6,000 pages, the La Galigo is regarded as the magnum opus in the Bugis literary heritage. Written in the old Bugis language, the chronicle, saga traced its origin from the early oral traditions. The poetic text serves as a revered almanac and provide narrations about the ancient understanding on humanity and kingdoms. In the Bugis culture, episodes from La Galigo are commonly reenacted through chant and Poetry, poetic recitation performance led by a La Galigo specialist, known as ''passure''. The performance is sometimes held during festivals, wedding or during a Housewarming party, house-moving ceremony. In 2012, two of the La Galigo manuscripts are included in UNESCO, UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme.
However, the largest collection of Bugis literature is in the form of family Genealogy, genealogies. It is regarded as an important family heirloom, especially amongst the members of nobility and aristocratic families. Some dated as early as 1400 — about two hundred years prior to their Islamisation, the early Bugis genealogies provide a rare glimpse on the culture and ideology of an early and literate
Austronesian society.
Dress, textiles and weaving traditions

In the traditional Bugis-Makassar culture, textiles and clothes are revered and occupied a special place in the society. Historically, the colours and motives donned by the wearer possessed an important indicator and serves as a defining symbol on the person's identity, age and status.
The term Baju Bodo derived from the Makassarese language, being described as "short clothing". Conversely, in the Bugis language, it is also known as ''Waju Tokko'' and ''Waju Ponco. A short-sleeved tunic, the costume is commonly worn together with silk or a woven sarong. The attire traced its origin as early as the 9th century, following the introduction of muslin cloth by the foreign traders to the harbors of South Sulawesi. The textile, being thin and light, is highly suitable to accommodate the local tropical weather in the region. In addition to muslin cloth, the Baju Bodo is also commonly sourced from pineapple-fiber fabric and cotton.

With the rise of Islamisation among the Bugis-Makassar, another closely related form of Baju Bodo emerged. Having a longer sleeve, the ''Baju La’bu'' (from Makassarese 'long'), also known as ''Bodo Panjang'' (both defined as "long cloth") is tailored in accordance of Islamic interpretation of ''Intimate parts in Islam, Aurat'' and modesty. The Baju La’bu is also traditionally made from silk, a departure from the semi-transparent and translucent fabric of its predecessor.
The Bugis-Makassarese Woven fabric, handloom industry potentially commenced in the 1400s. The locally-made sarung motives were initially basic, having rudimentary stripes of vertical, horizontal or in a checkered pattern, potentially inspired by ''Sulappa Eppa'' (the four elements) foundations. By the 1600s, the designs are becoming progressively ornamented, with the inclusion of a multitude of geometrical shapes, contour and sequence. Almost in a coordination with the function of Baju Bodo in the past, the motives and design of the sarung would also be used to denote the status of its wearer. The sarung material is usually sourced from silk and cotton.
The corresponding mode for the Bugis male is known as ''Jas Tutu or ''Jas Tutup'' (an "enclosed coat"), the garment is in a form of long-sleeved coat with a collar. The Jas Tutu is also synonymous to be worn with the ''Songkok recca/Pabiring/Songkok To Bone'' (Bugis songkok), ''Lipa’ Sabbe'' (sarong) and a gold or silver-coloured button. The Bugis-styled Songkok is made of woven rattan and golden thread. During a traditional wedding ceremony, the groom would also accompanied by a highly elaborated accessories, including ''Tataroppeng'' (Keris), ''Pabekkeng'' (Belt (clothing), belt), ''Rope'' (Songket), ''Sigara'' (headgear), ''Salempang'' (sling), ''Gelang'' (bangle) and ''Sapu tangan'' (handkerchief).
In the present day, the Baju Bodo and Jas Tutu are largely being reserved as a formal wear, the sightings are common during weddings, as well as in other ceremonial and cultural functions.
Culinary traditions

The Bugis cuisine constitutes an essential part of its heritage, comprises various culinary styles and recipes frequently associated with the Bugis people. It shares many common gastronomical traditions and characteristics with the surrounding Makassarese, Mandarese and Torajans. Many of the meals are indigenously developed in the island of Sulawesi, with a focus on native ingredients; while others exhibit a notably stronger Fusion cuisine, outside influences and customized according to the local taste bud, palates.
Foreign cooking techniques in the South Sulawesi cuisine can be seen on the adoption of ''Jalangkote'', a small Frying, fried pie adopted from Portuguese ''papeda (food), papeda''. The fillings for ''Jalangkote'' usually consist of rice vermicelli (denoting Chinese cuisine, Chinese influence) combined with sliced vegetables, boiled eggs and mincemeat. Meanwhile Indian cuisine, Indian elements are visible and demonstrated in the localised dishes, for instance the creamy ''Gagape'', ''Toppa Lada'' and the spicy ''Juku palumara''.
There is also a wide array of cuisines that signifies a bolder Cuisine#Regional cuisines, endemic origin: Rice cake#Indonesian, Rice cakes are particularly popular with the likes of ''Burasa and ''Tumbu/Lapa-lapa/Langka''. The rice dumplings are Steaming, steamed and wrapped in leave containers with coconut milk, thus contributing to its rich and creamy flavor. It is usually served as a substitute for white rice and eaten together with soups or other side dishes. Another distinguished forms of rice cake in the Bugis-Makassar community includes ''Gogos'' — Roasting, roasted glutinous rice with fish fillings, wrapped in banana leaf. It is commonly being eaten as snacks.

The peninsula's long coastline has contributed a great fishing industry in the region, creating Seafood, oceanic produce as an important part of the meal. Dishes such as ''Pa’Deme'' (anchovies sambal), ''Bajabu'' (''serundeng''), ''Lawa Bale'' (marinated raw fish) and the clear broth soups of ''Pallu Kacci'' and ''Pallumara'' captures its extensive maritime connection. In addition to seafood, there is also a diverse culinary traditions with the emphasis on meat, which can be seen in the hearty Low-temperature cooking, slow cooked dishes, namely ''Nasu Likku, ''Nasu Palekko'' and ''Goré-Goré''. The meals are usually acted as an accompanying side dish to compliment the ''Nasi Putih'' (plain white rice), or in other cases, the rice cakes.
Banana occupied a major importance after rice in the Bugis Staple food, staple, as it is widely cultivated in South Sulawesi. Aside from being eaten fresh after a meal, Banana-based meals are extensive in the forms of snacks and desserts — raging from the sweet tasting ''Berongko'' (steamed Banana pudding), caramelized ''Sanggara' Balanda'', to crispy and savory snacks such as ''Sanggara Pappek'' (smashed bananas).
Other popular meals associated with the Bugis includes congee dishes — ''Barobbo'' (rice and maize, corn porridge) and the sago-based ''Kapurung''; and traditional ''Kues'', notably the ''Kue bugis'', ''Kue Dange'', ''Kue Sikaporo'' and ''Bolu Peca''. Due to the extensive and continuous friendly interactions with the kindred Makassarese people, many of the unique Makassarese meals are also widely enjoyed by the Bugis, including ''Coto Makassar'', ''Sop Sodara'', ''Pallubasa'' and ''Konro'', or desserts like ''Cucuru' Te'ne'' and ''Es Palu Butong''.
Beyond their native soil, Burasa' and other Bugis-Makassar traditional cuisines are also commonly presented as a ceremonial dish by their diaspora community. It is prepared as a significant legacy to honor their ancestral roots from the plains of South Sulawesi.
Weaponry and military traditions
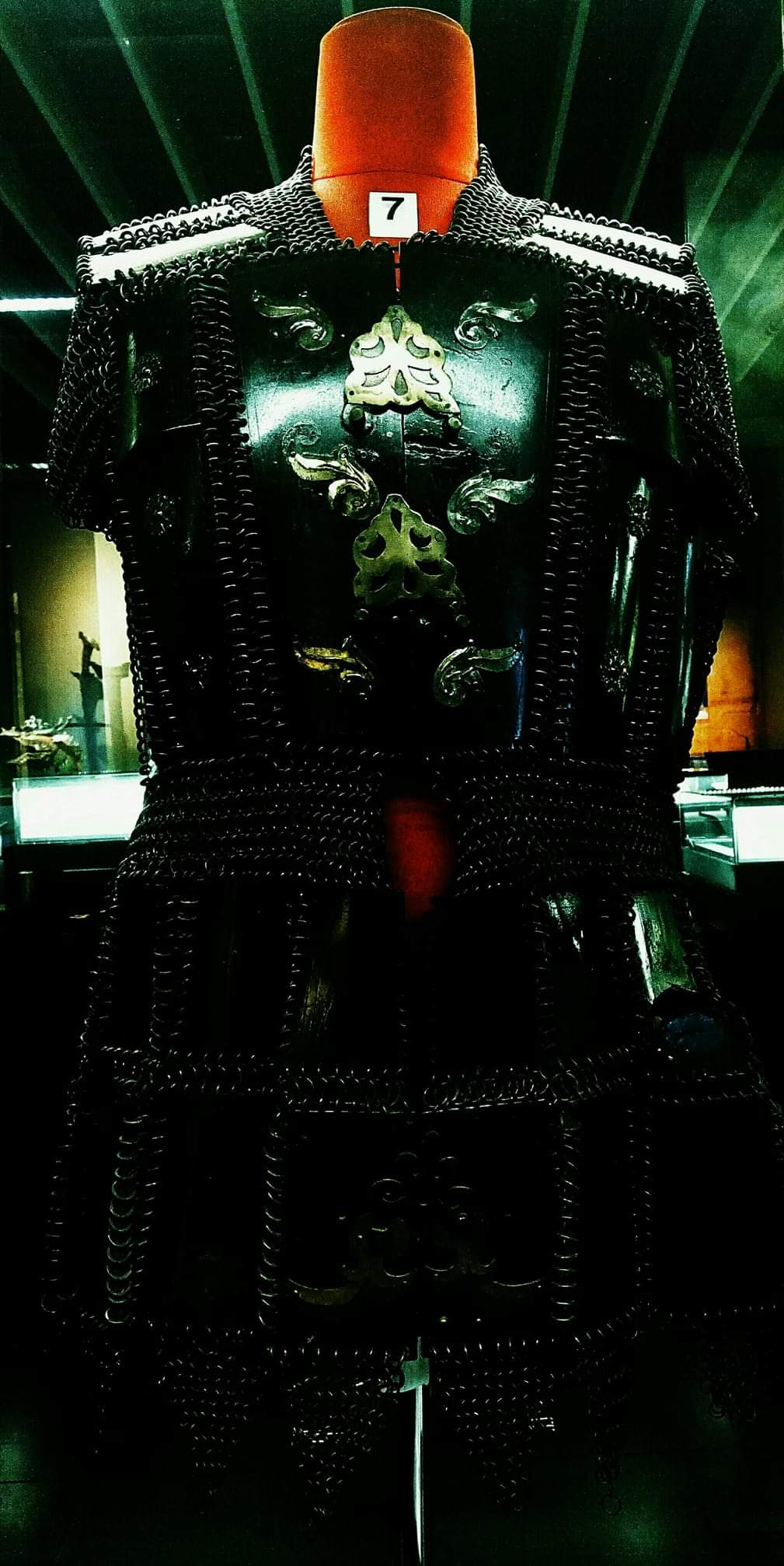

A plethora of blades, Knife, knives and firearms constitute the arsenal of Bugis-Makassar weaponry. However, Badik is hailed as the traditional weapon strongly associated with their identity and possessed a revered status in the sociological construct of the Bugis-Makassar society. The item is not solely perceived as a mere weapon, but as an emblem designated to represent the personal character of its owner. It is historically used as a vital tool for hunting animals and as a self-defense mechanism.
In the traditional Bugis-Makassar understanding, the hierarchal level of Badik is regarded as a second after the Kris, Keris. A far-cry from the Badik which known to have an almost universal usage throughout all ranks of the society, the ''Keris Pusaka'' (the "Dynasty Keris") is reserved as an important family regalia amongst the elite royal houses in South Sulawesi. Thus, historically the Badik received a prevalent identity as a companion for the Bugis-Makassar man.
In the past, Badik is used as a tool of defense to protect an individual and the family honor. The doctrine is largely based on the philosophical interpretation of ''Siri'', a cornerstone of the Bugis-Makassar culture, siri represents a responsibility to maintain the dignity in the society. The concept is historically entranced in the cognitive psyche amongst the people and traditionally become a binding force on the moral values and social system. Badik is also commonly passed from one generation to another, acting as an important family heirloom.

Another important sword owned by the Bugis is the Keris, also known as ''Tappi''. It has some minor different features in contrast to the Javanese Keris; however, the Bugis Keris is noted to bear a closer anatomical resembles with the Malay-version of the dagger, the item potentially being introduced by the Malays to the people of South Sulawesi. Almost parallel with the Badik, the Keris equally carried a revered symbol amongst many Bugis-Makassar people.
In addition to Badik and Keris, they were known to host a multitude of classical armaments. Most of the items are collectively classified under the ''parewa bessi'' (Iron weapons) category made by the Bugis-Makassar blacksmiths. Some of the other notable collections include ''Alamang/Sundang'', a long-sword; ''Bessing'', a spear; ''Kanna'', shield; Pantu’, a traditional Stick-fighting, fighting stick; Baju Rantai, ''Waju Rante'', Armour, armor; and ''Tado'', a trapping rope.
The art of weapon among the Bugis-Makassar is constantly developed through the millennia. The ancient peoples of South Sulawesi are recorded to have a usage of blowgun, blowpipes with poisoned Dart (missile), darts, spears, short swords, kris and rattan helmets. By the early modern era, the Bugis-Makassar gained further exposure on the artillery knowledge with the introduction of various firearms: muskets, culverins and cannons that enhance their warfare and combatant skills. Mail and plate armour, Mail armor with metal plates (''baju lamina'') is estimated to be used starting from this era, and still being worn until the 19th century.
The strong mutual relationship between the arms development and its militaristic culture formed the advantageous momentum that fueled to their quest for political advancement and influence outside from the traditional Bugis-Makassar homeland. It become one of the wielding tools that seals their historical figures and status as soldiers, Mercenary, mercenaries, warriors and fighters throughout the maritime realm.
Traditional architecture

In the Bugis society, architecture is regarded as an emblem of philosophy, designed to endorse the occupier belief, faith and understanding about cosmos and universe. It is strongly rooted in its long and rich history, blending elements on the native interpretation of cosmology with culture, faith, mythology, aesthetic and functionality. The Bugis architectural style is broadly classed together with the Makassarese, of whom it shares strong architectural features and identity.
Based on the Bugis philosophical understanding, a home is regarded as the legitimate expression of the spiritual rite of passage as a human being: a place to be born, a place to raised and nurtured as a child, a place to become a husband and wife, and a place to perish. Consequently, the habitation is designed to be solemn, sacred and highly revered. It provides ones with a place for solitude, energy, nourishment, well-being and honour to its dwellers. The presence of a home in the Bugis society is part-and-parcel with life, hence home ownership is regarded in utmost importance — to commemorate life and to become a beacon symbol of life.

In the Bugis culture, architecture is not only solely perceived as a question of practice, but a subject of
theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the s ...
dialogue. The formula of ''Sulapa Eppa'' (the four elements) was interpreted and constructed with such intention. The layout plan for the Bugis buildings would commonly have a rectangular and symmetrical consistency, the aim is to intergrade with the early Bugis understanding that the universe is in a form of a giant rhombus and the four ingredients that created the universe (wind, water, fire and earth); together with the four wind directions (north, south, east and west). Thus, the Bugis houses would traditionally faces north, as an origin for positive energy; or towards east, the dawn of light.
The houses were commissioned into three separate levels, signifying the three position of the universe based on the pre-Islamic Bugis interpretation. ''Rakeang'' (the upper world) — a tribute to the heavens above, the attic is designed to be the apex of the house and it is regarded to be a sacred place to store rice, crops and important heirlooms. ''Ale Bola'' (the middle world), appeared for a respect to the human world, thus represented by the living and the common space of the house. ''Awa Bola'' (the underworld), a place of dark and ferocious, this concept was exemplified by the shed and where the livestock are stored beneath the human dwelling.
The concept of ''rupa-tau'' ('likeness of a person') is also extensively explored and adopted in the Bugis architectural principles. This led to the building structured as a grand manifestation on an anatomical relationship. The housing framework was monumentally characterized by distinct components based on a human physique: ''Aje-bola'' (the foot), by the stilts of the house; ''ale-bola'' (torso, body), the common living space; ''ulu-bola'' (the head), the roof; and ''posi-bola'' (the navel) by the middle area of the house.
The development of the Bugis architecture is originated on the belief that a home is constructed with an optimistic faith for a greater future. Based on the classical Bugis myth and understanding, the stars, skies and constellations held a great divine significance; in response, a human is entrusted to maintain the harmonious arrangement of the universe — in order to have a safer and tranquil life, as well as to avoid natural calamities (notably floods, landslides, tornado and earthquake). Thus, such ethos and essences are extensively emulated, absorbed and vividly radiated in the traditional Bugis architectural fundamentals.
Maritime, mercantile and migratory traditions
Across archipelagic Southeast Asia, the Bugis-Makassar earned the reputation as sailors, navigators and Seamanship, seafaring traders. Their salient foundation largely coordinated with the extensive shipbuilding traditions, nautical skills and the dominant presence in the inter-insular trade routes.
Conversely, they too acquired the title as "The Vikings of Southeast Asia". Their extensive maritime and trading expedition has historically bought them to be as one of the notable regional players in the transoceanic journeys to Indochina, Macau, Manila, Papua and northern Australia, together with the Southeast Asian islands that lies between these areas. Their large voyaging ships were commonly use to carry and transport exotic spices,
sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus '' Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for ...
, textiles, rice, luxury marine products, porcelains, pearls and other important goods and materials across the ancient spice trade routes.
Their seafaring odysseys were largely aided by padewakang, one of the early type of Bugis-Makassar vessel, which later morphed into the palari. Steep in history, the first of such watercraft was born based on the legendary tradition of Sulawesi.
Up until the nineteenth century, the classic Padekawang was traditionally led by a captain, known as ''nakoda'' or ''anakoda''; followed by his second-in-command, the ''juragang''. It is also usual for the ship to have two wikt:steersman, steersman, ''jurumudi'' — delegated the task on directing the ship's course; two ''jurubatu'' — wikt:depth sounder, sounders, responsible to measure the depth on approaching the coast, reefs or shoals; and a single secretary — known as ''jurutulisi'', acting as an agent on behalf of the owner of the vessel. The names are largely adopted from the Malay language, with an influence from Persian language, Persian, such as the term of ''wikt:nakhoda, nakhoda''.

In order to identify the course of their maritime routes, the sailors would typically inclined to use a multitude of convergent nautical practice, from determining the Sunrise, rising and Sunset, setting points of the sun; the location horizon, stars and constellations; the marine environment — the flow of the oceanic Swell (ocean), swell, the form of the waves, the water appearance; fauna — the actions of the fish and the flight arrangement of the birds; the wind directions; and specific Geography, geographical landmarks.
The original pinisi-rigged ship (palari), is about in length overall, with light laden waterline of .
[}] Smaller palari is only about 10 m in length.
A two-Mast (sailing), masted sailing vessel, the name "pinisi" derives from the type of gaff rig, use for its configuration. Its unique large tripod-shaped mainsails and masts give its unparalleled design composition, a departure from other western ships. In the contemporary era, palari is also equipped with Engine, motors for its seafaring journeys.
There are many revered shipbuilding centers in the region, including Ara, Tanah Lemo and Bira. However, the Konjo, a subgroup of the Makassarese, are particularly known as one of the respected master builders of pinisi-rigged ships, enjoying a long-prized tradition of watercraft and boat-production, a knowledge commonly inherited from fathers to sons for centuries.
For the Konjos in Bulukumba, the boatmaking identity is deeply rooted to their lives as a precious embodiment of art, culture and rituals. Being a highly dedicated wikt:boatsmith, boatsmith community, the Konjo people are traditionally restricted from sailing to the seas, as their elders feared that their clan would not return to their homeland, creating a perilous risk of losing their valuable shipbuilding wisdom amongst their kinsmen. Thus in South Sulawesi, the transoceanic sailing responsibility were vastly executed by their closely related brethren — the Bugis and Makassarese.
The rich nautical culture of Bugis-Makassar is equally captured and reinforced by a plethora of ships — ranging from ''penjajap'', warship; Pajala (boat), pajala, a smaller boat, also used for fishing; palari, another descendant of the padewakang; Lambo (boat), Lambo, a trading boat; and the early ships of ''Somba Lete'' and Tanja sail, ''sompe tanja''. These vessels collectively have left a significant impact on the local and regional development.
As the seafaring identity began to take root in the coastal South Sulawesi society, it gradually become a profound icon that navigated their influence and presence in the region. Following the Bugis-Makassar Human migration, migratory tradition known as ''sompe'' (to sail) and ''malleke' dapureng''; it was here, from among these historical ships, vessels and boats that many Bugis and Makassar man, woman and children braved away from their traditional heartland in search of Economic migrant, economic pursuits, prosperity and opportunities, while others embarked for an educational experience, adventure, personal dignity, military quest or prestigious political ambitions. Thus, most, if not all Bugis in the diaspora may ultimately traced their ancestral origin to one of the ''Pasompe (a term for people who sailed/ventured beyond their native soil). Tales and trails from the past waves of sails and settlements can still be witnessed until the present day, evidently illustrated by their extensive centuries-old ethnic enclaves and various diaspora communities established throughout the islands and coastal regions of maritime Southeast Asia.
Rice and agrarian traditions

A visible departure from the extensive Maritime history, maritime and Seamanship, nautical culture dominated by their coastal brethren, the inland Bugis-Makassar country bear witness to its strong
agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
legacy. Regarded as among the most important crop amongst the society, rice has been cultivated across the peninsula for centuries. The grain has been deeply ingrained to their agricultural way of life for generations. It is not only hailed as a primary food source on the Diet (nutrition), diet, but also woven into the social, legends, theories, economic, Politics, political and ideological fabric. In a sense, their traditional identity is also being coexisted by an agrarian culture.
The simple grain is regarded as among the essence of their traditions, it has indeed enjoyed a complex and long connections with the Bugis-Makassar. The earliest trace of rice in maritime Southeast Asia was found in Ulu Leang Cave, in Maros, South Sulawesi. Dated between 4000 BC to 2000 BC, the grains potentially tied up with the arrival of their Austronesian ancestors to the region, or among the earlier Toalean hunter-gatherer society.
Rice serves a nourishment, deeply embedded to their historical development. By the 14th century, their radical transformation from local warlords to major kingdoms was largely coincides by the unprecedented population boom across the peninsula, which in turn being a correlated result intersected from the earlier improvement of the agricultural practices. Blood, sweat and tears have had been shed over the soil in the quest of favorable harvests, for instance during the 16th century, the
Ajatappareng Ajatappareng was a historical region in the western part of South Sulawesi (today part of Indonesia) consisting of five allied principalities: Sidenreng, Suppa, Rappang, Sawitto, Bacukiki and Alitta. They formed an alliance during the sixteent ...
confederation (constituting the Bugis states of Sidenreng, Rappang, Suppa', Bacukiki, Alitta', and Sawitto) was incorporated by the expansionist pursuit by Gowa, driven by their ambitions to control the bountiful local corps of the region.
In their ancient beliefs and understanding, rice was perceived as a symbolism associated with providence and of creation, as well as blessing and joy by linking ancient customs, mythology and the people. The cultivation of the grains has had led to the development of an economic life circle centered primarily around the core of agriculture. Rooted in the pre-Islamic belief system, the ''mappalili'' (paddy growing season) was organized among the Bugis to pray for a plentiful crop season, while the grand harvest festival was held by the agrarian societies act as a joyous thanksgiving conclusion after a successful harvest. Rice is also highly venerated, based on the historical Bugis manual-almanac known as ''Kutika'', only during specific schedules, day and time were permitted for cultivating activities; at home, the rice is stored at the attic of the house, signifying its zenith position in the social order; while during war, the destruction of rice fields was perceived as a highly forbidden taboo.
The creed of Bugis-Makassar states was undoubtedly built on horticulture standing as its salient pillar. Rice, Rice farming also has influenced many other aspects of the their old economic activities. During the medieval era, it become one of the earliest main commodities of exports from the South Sulawesi heartlands to the rest of the insular Southeast Asia. The commodities may also serves as an early guidance to their fundamental mercantile and enterprising skills, before being rapidly evolved into amongst their major tools of trade during their maritime involvement in the regional trade routes.
The rice-reigned supremacy and its strong agrarian foundations of the South Sulawesi people persist until this day. In 2021, the province was estimated to produce 2.94 million tonnes of rice, becoming among the prominent rice bowls in modern-day Indonesia.
Festivals, celebrations and religious traditions

The Islamisation of Bugis-Makassar states initiated by Luwu and Gowa in the 17th century has greatly morphed the religious landscape throughout the peninsula. As a consequence, most of the liturgical festivals by the Bugis are primarily coordinated with the Islamic calendar, albeit embraced with a strong sense on the localized cultural orientations.
The biannual ''Hari Raya'' (eid) celebrations of Eid al-Fitr, Idul Fitri and Eid al-Adha, Idul Adha are regarded as the largest festivals for the Bugis. The Idul Fitri (known as ''Maleppe'', meaning "release" in the Bugis language) serves as a triumphal rite after completing a month of Fasting in Islam, fasting and religious activities during Ramadan, Ramadhan. The term ''Mallepe'' holds a philosophical symbol as a release from the sins and the bad habits of a person. While Idul Adha is a dedicated religious observance held to commemorate the sacrifice made by Prophet Ibrahim.
There are a diverse religio-cultural activates shared during both of the merriments. A day before eid, many Bugis families would prepare ''Burasa and ''Tumbu'' rice cakes in a tradition known as ''Ma’burasa'' and ''Ma’tumbu''. The tradition of visiting friends, relatives and holding a grand feast for visitors are also central — known as Lebaran#Halal bi-halal, Massiara, the visits usually commenced after the eid prayers. Additionally, many would also take the day to ask the forgiveness and reconcile between one another, while some would dispose their old clothes into the sea or rivers as a sign of a new beginning and chapter in life.

Other common traditions during eid includes ''Mabbaca-baca'', a solemn thanksgiving dua gathering and feast led by the community religious leaders known as Puang Anre Guru'' or ''Daeng Imam''. A visit the Cemetery, final resting place of the departed love ones is also a major commonplace during the season, in the custom known as ''Masiara Kuburu'', the Lebaran#Visiting graves, visit to the grave is regarded as a gesture of love, respect and dignity.
The positive and goodwill communal spirit is also continued in a various of religious and cultural programs. In addition to eid, the Bugis organized a prolific traditions to commemorate its faith and identity, including Ramadan, a holy month dedicated by fasting and various religious activities. ''Maulu/ma maulu’'' (Mawlid), honoring the birth of Muhammad, Prophet Muhammmad, special ceremonial meals and colorful eggs would be given to the mosque attendees to monumentalize the meaningful day; ''Esso Sura'' (Ashura), remembrance of Muharram, where a special porridge (known as ''Bubu Petu'' and ''Bella Pitunrupa'') are prepared, the day also marked as a major shopping period for the Bugis-Makassar, as many would traditionally buy new house utensils during the Ashura. Furthermore, the Bugis and Makassar families would also arrange ''Massuro Baca'', special ceremonial doa and feast held a week before Ramadhan to remember the departed relatives, as well as a preparation to cleanse the inner-self before the holy month.

Islamic elements are also materialized during celebrations on an individual level. Being a predominantly Muslim community, the act of ''Mabbarazanji/Barzanji'' (Mawlid al-Barzanjī), communal prayers and praise to Prophet Muhammad is regarded as among the focal points during such ceremonies. The Bugis would commonly organized a ''selamatan'' feast for divine favor, protection, thanksgiving and gratitude - including Islamic marital practices, weddings, newborn celebration, aqiqah, house construction ceremony, sending a pilgrim for umrah and hajj, and funerals.
The importance of such personal and communal ceremonies collectively act as a testament of their mainstream ethnic character. It serves as a bind, propelled to their rite of passage as a Muslims, Muslim and a manifestation of their cultural identity. The events also performed as a juxtaposition, intertwined between the essence of religion and custom; together with a sense of responsibility to solidify their values into the contemporary era.
Historically, there are also some regional events deeply rooted to their ancient beliefs, reflected by their pre-Islamic past, geographical location, local demographic and occupation. In a few agrarian Bugis communities, the grand harvest festivals of ''Mappangolo Datu Ase'', ''Mappadendang'', ''Manre Sipulung'', ''Maccerak Ase'' and ''Maccerak Rakkapeng'' acted as a thanksgiving and celebratory gesture for the abundance of harvest obtained. Meanwhile, in the coastal and lakeside communities where fishery industry is regarded to be in the utmost importance, they would commemorate with ''Maccera Tappareng'' and ''Maccerak Tasik''. However, with the rise of various socioeconomic and educational revolution, together with mass Industrialisation, industrialization and the introduction of modern History of agriculture, farming and fishing techniques throughout the 19th and 20th century, the collective impact of these festivals began to waned in favor of a much aligned practice with Islamic understanding among the mainstream Bugis society. Despite so, such regional celebration offered a brief outlook on the past, on a traditional ancient religion of a once agrarian community.
Musical traditions and performing arts

Music and dance has long occupied an integral part of the people in the South Sulawesi. It is considered as an ancient art form, pictured as a dramatic and complex encapsulation of the heritage. The Bugis performing arts can be broadly divided into four distinct categories — entertainment medium, ritualistic performance, court dance and martial arts.
In the Bugis culture, choreography is regarded as a form of folkloric entertainment. It has enjoyed a long creative industry and maintained a close relationship with the people. It is usually presented during the communal occasions and used as a celebratory expression to commemorate significant events. The best known Bugis dance genre are ''Pajaga'', and the more lively Pajogek — combining the elements of Ronggeng, Jaipongan, Jaipong and accompanied by a pair of ''gendeng'' (drum). Other type of dances include Zapin, Jeppeng, having a fusion of stronger Islamic elements; and ''Tari Paduppa'', a traditional welcome dance.
In the past, the performing arts played an extensive role on the Bugis ritualistic function and observance. During such Mysticism, magico-religious ceremonies, esoteric energy were present and ancient dance techniques were accomplished by a Bugis Shamanism, shaman, known as ''Bissu''. The depiction was characterized by a combination of spiritual aura and artistic elements to achieve a high level of possession-trance. The practice of possession used to be conducted by a ''Bissu'' during a vital cultural rite, such as to commemorate the beginning of the ''mappalili'' (Paddy field, paddy growing season) or during the important royal functions. Among the well-known ritualistic Bugis performance includes ''Tari Maggiri'', ''Tari Alusu'' and ''Maddewata''.

Martial art also serves as an outlook that mirrors the symbolic ideals of its strong Militarism, militaristic tradition — courage, power, heroism, prestige, strength and preparation for war. Elements of Martial arts, martial skills were largely drawn from the local fighting culture and being incorporated in a repertoire of Bugis performing arts, such as in ''Manunencak/Mencak Baruga'' (Bugis Pencak silat, Pencak Silat), ''Mallanca'' and ''Masempek''. A close parallel can equally be observed in the Bugis war dance. The combatant qualities were emulated to commemorate the fortitude and spirit of the military class. The Bugis war dance of ''Penjaga Welado'', ''Pajaga Gilireng'' and ''Pajaga Mutaro'' extensively captures such rendition.
Historically enjoyed a royal patronage, the Bugis Historical dance, court ballet consist of a juxtaposed movement of fast and slow; and a contrast between passive and active, such adaptation can be seen in the Bugis courtly portrayal in ''Pajaga Boneballa Anakdara'', ''Pajaga Lelengbata Tulolo'' and ''Pajaga Lili''. The artistic styles constitute the essence of Bugis Aesthetics, aesthetic impulses — involving various movements, gestures, poise, balance and music. Historically among the members of Bugis nobility, dance was perceived as a social importance to develop and mold an individual's personal qualities on ''kedo'' (manners, mannerism) and ''ampe'' (Speech act, speech) according to the royal standards and etiquettes.
The Bugis also hosted a multitude of classical instruments, including ''Soling'', flutes; ''Kacapi'' and ''Talindo'', string musical instruments; ''Jalappa/Kancing-Kancing'', a traditional cymbal; ''Aloso/Laluso'', a Bugis percussion instrument, similar to Shekere; ''Gesok–Gesok/Keso–Keso'', a Bugis-styled Rebab; ''Kendang, Gendrang'' (not to be mistaken with Makassarese "Ganrang"), a two-headed drum; and ''Puik Puik/Pui–Pui'', a classical trumpet. As with many Sulawesian musical traditions, the Gendrang occupied a prominent and sacred role in Bugis musical traditions forming the base of many accompaniments, although somewhat less revered compared with the Makassarese. In recent years, Makassarese Ganrang traditions have eroded the education of Bugis Gendrang, although sharing many similarities, such as using multiples drums with different patterns to create syncophation.
The Bugis art of dance was predominantly being inherited via an oral tradition from one generation to another. To some extent, each of the artforms serves as an episode to the past and navigated as a kaleidoscope narration on the development of their ethnic identity – from the once prevalent ancient ancestral beliefs led by a ''Gender in Bugis society, Bissu''; the royal court and military tradition during the classical era; the extensive bilateral cultural exchange with the Makassarese; and the subsequent Islamisation of the mainstream Bugis society.
See also
* Indonesian Malaysians#Bugis, Bugis in Malaysia, the Bugis diaspora in Malaysia
* Malays in Singapore#The Bugis, Bugis in Singapore, the Bugis diaspora in Singapore
* Gender in Bugis society, the gender interpretation amongst the classical and pre-Islamic Bugis society
* List of Bugis people, a list of notable people of Bugis descent
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{Navboxes
, title = Articles related to Bugis
, list =
{{Ethnic groups in Indonesia
{{Ethnic groups in Malaysia
{{Ethnic groups in Singapore
Bugis people,
Ethnic groups in Indonesia
Ethnic groups in Malaysia
Ethnic groups in Singapore
Muslim communities of Indonesia
 The lifestyle of ancient Bugis people were, to some extent, preserved by the pagan
The lifestyle of ancient Bugis people were, to some extent, preserved by the pagan  The progress of inter-insular commercial activities and the increasing interactions with Maritime Silk Road were potentially among the main factors contributing to the economic prosperity for a few leading South Sulawesi communities. The period between 1200 and 1600 witnessed a radical change throughout the political landscape of lowland South Sulawesi Peninsula.
The trade in South Sulawesi was based on the export of rare commodities, a business which was easily dominated by an exclusive
The progress of inter-insular commercial activities and the increasing interactions with Maritime Silk Road were potentially among the main factors contributing to the economic prosperity for a few leading South Sulawesi communities. The period between 1200 and 1600 witnessed a radical change throughout the political landscape of lowland South Sulawesi Peninsula.
The trade in South Sulawesi was based on the export of rare commodities, a business which was easily dominated by an exclusive  During the period, the women don under a baggy trousers and pants; the usage of short tunics and sleeves were also noted by the free married women. For the affluent male, there were potentially also a favour towards western
During the period, the women don under a baggy trousers and pants; the usage of short tunics and sleeves were also noted by the free married women. For the affluent male, there were potentially also a favour towards western  While early contacts with Islam had been made since 1490 with the trading relationship between Siang and Malacca, most Bugis were still believer of the native patturioloang religion. In year 1540, two aristocrats from Makassar were
While early contacts with Islam had been made since 1490 with the trading relationship between Siang and Malacca, most Bugis were still believer of the native patturioloang religion. In year 1540, two aristocrats from Makassar were  During the resumption of Portuguese-South Sulawesi relations in 1559, the political dynamic of the region had effectively morphed. The Makassarese state of Gowa had exerted his influence towards the north, and absorbed many Bugis states that have had a friendly relations towards the Portuguese.
Simultaneously, the Kingdom of Bone also commenced its southward expansion, and soon come into a direct contact with the Makassarese. Both kingdoms are pursuing dominance in the entirety of the Peninsula together with the important trade routes.
Conflict between the two powers were bound to happen, and a major war broke out in 1562. Gowa was assisted by Luwu; and also by Wajo and Soppeng, the latter two would probably preferred in favour of a distant sovereign like Luwu or Gowa, as they would furnish Wajo and Soppeng with a greater autonomy in contrast to a nearby kingdom like Bone, which would likely dominate them.
The war concluded in 1565 and a
During the resumption of Portuguese-South Sulawesi relations in 1559, the political dynamic of the region had effectively morphed. The Makassarese state of Gowa had exerted his influence towards the north, and absorbed many Bugis states that have had a friendly relations towards the Portuguese.
Simultaneously, the Kingdom of Bone also commenced its southward expansion, and soon come into a direct contact with the Makassarese. Both kingdoms are pursuing dominance in the entirety of the Peninsula together with the important trade routes.
Conflict between the two powers were bound to happen, and a major war broke out in 1562. Gowa was assisted by Luwu; and also by Wajo and Soppeng, the latter two would probably preferred in favour of a distant sovereign like Luwu or Gowa, as they would furnish Wajo and Soppeng with a greater autonomy in contrast to a nearby kingdom like Bone, which would likely dominate them.
The war concluded in 1565 and a  In the later half of the 16th century, the contest between Islam and Christianity was still largely undecided in South Sulawesi Peninsula. Most of the surrounding kingdoms in Sulawesi have already become Muslims under the sway of Ternate-Gorontalo in 1525 and Buton in 1542. There were already individual converts in South Sulawesi.
In 1550, the Malay-Muslim community of Macassar were awarded special privileges by the ruler of Gowa according to ''Lontarak Patturiolonga''. However, in 1575, during the visit by Abdul Makmur (Dato' ri Bandang), one of the Minangkabau proselytizers of Islam, he noted that there are several difficulties to convert the locals — the superfluous liking towards dried boar flesh, raw deer liver diced with blood (lawa) and palm liquor. He then embarked to promulgate the teaching of Islam in the Kingdom of Kutei, eastern Borneo, in which he was more triumphant. In 1580, the Sultan of Ternate, Babullah, advised the ruler of Gowa to embrace the teaching of Islam, the king declined. However, as a gesture of kindness, he awarded the Makassar-Malay community the consent to construct a
In the later half of the 16th century, the contest between Islam and Christianity was still largely undecided in South Sulawesi Peninsula. Most of the surrounding kingdoms in Sulawesi have already become Muslims under the sway of Ternate-Gorontalo in 1525 and Buton in 1542. There were already individual converts in South Sulawesi.
In 1550, the Malay-Muslim community of Macassar were awarded special privileges by the ruler of Gowa according to ''Lontarak Patturiolonga''. However, in 1575, during the visit by Abdul Makmur (Dato' ri Bandang), one of the Minangkabau proselytizers of Islam, he noted that there are several difficulties to convert the locals — the superfluous liking towards dried boar flesh, raw deer liver diced with blood (lawa) and palm liquor. He then embarked to promulgate the teaching of Islam in the Kingdom of Kutei, eastern Borneo, in which he was more triumphant. In 1580, the Sultan of Ternate, Babullah, advised the ruler of Gowa to embrace the teaching of Islam, the king declined. However, as a gesture of kindness, he awarded the Makassar-Malay community the consent to construct a  Beginning from the end of the 17th century and the dawn of the 19th, the course of South Sulawesi societies were rocked with a series of monumental changes in the local statecraft, including the Fall of Makassar, internal disputes, political conflicts and the growing secondary influence from the western
Beginning from the end of the 17th century and the dawn of the 19th, the course of South Sulawesi societies were rocked with a series of monumental changes in the local statecraft, including the Fall of Makassar, internal disputes, political conflicts and the growing secondary influence from the western  The opportunity for the Bone came after the victorious Dutch attack in 1660. Required to sign an unfavorable truce, the Makassar requested 10,000 Bone people for a forced ditch digging as defense against potential attacks from the land. Few Bone noblemen, including Arung Pallaka, took refuge in the neighbouring Buton and presented for a Bugis-Dutch alliance against Makassar. The war against Makassar erupted in 1666, with the Bugis-Dutch alliance being assisted with troops from Ternate, Ambon and Buton. The sole Makassarese alliance during the war were the Bugis state of Wajo and the local Malay community.
Sultan Hasanuddin of Gowa was obliged to sign the treaty of Bongaya on 18 November 1667. This required the Makassarese powers to removed most of its fortification, relinquish its trade in spices, end its import of foreign goods with the exception of the Dutch East India Company, banish the Portuguese and other non-Dutch Europeans, and reject any other attempts of suzerainty, in both Bugis lands or other parts of the archipelago. In 1669, Sultan Hasanuddin abdicated from the throne.
The Dutch have succeeded to achieve its goal after the fall of Makassar, but they are not the sole victor; another was the Bugis State of Bone, despite having a few restriction following the treaty that it also signed, the kingdom would effectively maintain its sovereignty until the 19th century. Hence, in the Bone narration, Arung Palakka holds the status as an independence warrior; while in Makassar heritage, the rivaling Sultan Hasanuddin is hailed as the hero for the Makassarese.
Once liberated from Makassar, it has possibly set the stage for Bone to hold an unchallenged power across the whole peninsula. However, the prospect of unifying all the Bugis lands under a sole ruler was stopped by the existence of the Dutch in the region. The peninsula then continued to persist under a mosaic of various small and large
The opportunity for the Bone came after the victorious Dutch attack in 1660. Required to sign an unfavorable truce, the Makassar requested 10,000 Bone people for a forced ditch digging as defense against potential attacks from the land. Few Bone noblemen, including Arung Pallaka, took refuge in the neighbouring Buton and presented for a Bugis-Dutch alliance against Makassar. The war against Makassar erupted in 1666, with the Bugis-Dutch alliance being assisted with troops from Ternate, Ambon and Buton. The sole Makassarese alliance during the war were the Bugis state of Wajo and the local Malay community.
Sultan Hasanuddin of Gowa was obliged to sign the treaty of Bongaya on 18 November 1667. This required the Makassarese powers to removed most of its fortification, relinquish its trade in spices, end its import of foreign goods with the exception of the Dutch East India Company, banish the Portuguese and other non-Dutch Europeans, and reject any other attempts of suzerainty, in both Bugis lands or other parts of the archipelago. In 1669, Sultan Hasanuddin abdicated from the throne.
The Dutch have succeeded to achieve its goal after the fall of Makassar, but they are not the sole victor; another was the Bugis State of Bone, despite having a few restriction following the treaty that it also signed, the kingdom would effectively maintain its sovereignty until the 19th century. Hence, in the Bone narration, Arung Palakka holds the status as an independence warrior; while in Makassar heritage, the rivaling Sultan Hasanuddin is hailed as the hero for the Makassarese.
Once liberated from Makassar, it has possibly set the stage for Bone to hold an unchallenged power across the whole peninsula. However, the prospect of unifying all the Bugis lands under a sole ruler was stopped by the existence of the Dutch in the region. The peninsula then continued to persist under a mosaic of various small and large  One of the major turning point following the conquest of Makassar was the change in the design of navigation and
One of the major turning point following the conquest of Makassar was the change in the design of navigation and 
 There are a subtle differences on the language spoken in these areas and linguist identified these versions as separate dialects (rather than distinct languages). Presently, there are ten main branches of Bugis Dialects — Bone, Camba, Pangkep, Sidrap, Pasangkayu Regency, Pasangkayu, Sinjai, Soppeng, Wajo, Barru and Luwu Regency, Luwu, as well as dozens of smaller subdialects deriving from the main branches. However, some researchers are divided whether Sawitto — a divergent Bugis variety spoken in central Pinrang — remains under the same language group or being diverged enough to be considered as a separate language.
The present-day Bugis people are mostly Multilingualism, bilingual. In South Sulawesi, they use two leading languages, either Bugis or Indonesian, tailored based on the environment, social circle and activities. Bahasa Indonesia is largely incepted on official situations, it is the language of formal education, Administration (law), administration, mass media and modern literature; Bahasa Indonesia is also prevalent during conversation with non-Bugis speakers. In the informal and casual settings around the Bugis-speaking circle, a Code-switching, code-switch would be a commonplace, or intertwined with elements of both languages in varying degrees, such as speaking Bahasa Indonesia with a strong Bugis-influenced elements and vice versa.
In the South Sulawesi province, the Bugis affixes such as –ki’, -ko, na-, -ji, - mi, etc. are emulated and conceived in the Indonesian-Bugis mixed language, hybrid. The Bugis-Indonesian fixture is not exclusively confined in the borders of South Sulawesi, the pattern can also be heard in other parts of Indonesia with a visible Bugis population. Outside the province, the language hybrid is not solely influenced by Bahasa Indonesia, but alongside traces of other local languages and dialects amalgamated with the diaspora Bugis language. Similarly beyond Indonesia, the extension of the language blend can also be seen in parts of Malaysia and Singapore, home to a sizable Bugis community. Instead of having influenced with Bahasa Indonesia, the Bugis communities in these countries would also be influenced by the Malay language, Malay language and its local dialects.
Outside from their ancestral heartland in the lowland plains of South Sulawesi, the Bugis language, dialects and hybrids are found throughout their extensive network of diaspora and ethnic enclaves in Sulawesi and all across Insular Southeast Asia. However, presently there tends to be a pronounced language shift among the diaspora outside of South Sulawesi, hence the understanding and the command on the Bugis language may vary based on the personal background, exposure and contacts with their ancestral language.
There are a subtle differences on the language spoken in these areas and linguist identified these versions as separate dialects (rather than distinct languages). Presently, there are ten main branches of Bugis Dialects — Bone, Camba, Pangkep, Sidrap, Pasangkayu Regency, Pasangkayu, Sinjai, Soppeng, Wajo, Barru and Luwu Regency, Luwu, as well as dozens of smaller subdialects deriving from the main branches. However, some researchers are divided whether Sawitto — a divergent Bugis variety spoken in central Pinrang — remains under the same language group or being diverged enough to be considered as a separate language.
The present-day Bugis people are mostly Multilingualism, bilingual. In South Sulawesi, they use two leading languages, either Bugis or Indonesian, tailored based on the environment, social circle and activities. Bahasa Indonesia is largely incepted on official situations, it is the language of formal education, Administration (law), administration, mass media and modern literature; Bahasa Indonesia is also prevalent during conversation with non-Bugis speakers. In the informal and casual settings around the Bugis-speaking circle, a Code-switching, code-switch would be a commonplace, or intertwined with elements of both languages in varying degrees, such as speaking Bahasa Indonesia with a strong Bugis-influenced elements and vice versa.
In the South Sulawesi province, the Bugis affixes such as –ki’, -ko, na-, -ji, - mi, etc. are emulated and conceived in the Indonesian-Bugis mixed language, hybrid. The Bugis-Indonesian fixture is not exclusively confined in the borders of South Sulawesi, the pattern can also be heard in other parts of Indonesia with a visible Bugis population. Outside the province, the language hybrid is not solely influenced by Bahasa Indonesia, but alongside traces of other local languages and dialects amalgamated with the diaspora Bugis language. Similarly beyond Indonesia, the extension of the language blend can also be seen in parts of Malaysia and Singapore, home to a sizable Bugis community. Instead of having influenced with Bahasa Indonesia, the Bugis communities in these countries would also be influenced by the Malay language, Malay language and its local dialects.
Outside from their ancestral heartland in the lowland plains of South Sulawesi, the Bugis language, dialects and hybrids are found throughout their extensive network of diaspora and ethnic enclaves in Sulawesi and all across Insular Southeast Asia. However, presently there tends to be a pronounced language shift among the diaspora outside of South Sulawesi, hence the understanding and the command on the Bugis language may vary based on the personal background, exposure and contacts with their ancestral language.
 The Bugis-Makassar possessed a rich heritage, philosophy, religious and social structure. Their customs are based on the concept ''Pangadereng'' - originally consist of ''Adat, Ade’'' (custom), ''Rapang'' (Jurisprudence), ''Bicara'' (Judiciary) and ''Warik'' (Social system); following the Islamisation of the Bugis-Makassar, ''Syara (Syariah) was incorporated into its core values.
Another fundamental local wisdom includes ''Siri' na pacce''. It serves as a guidance, social convention and moral conduct. ''Siri'' signifies the consolidation a demeanor of shame and self-esteem, it acted as a pillar that bear the importance of dignity, virtue, esteem, solidarity and responsibility. ''Siri'' is essential for someone to be regarded as a ''tau'' (human). ''Pacce'' manifest as a presence of compassion and solidarity. It involves a person's ability on emotional intelligence, which includes love, sadness, pain, and solidarity. Other interpretation of ''Pecce'' revolves on self-sacrifice, hard work, and abstinence. In addition to the Bugis and Makassarese, the traditional ethos is also shared by their northern cousins — the Torajan people, Torajans and Mandarese.
Translated as the "four corners" — ''Sulappa Eppa'' represents the ancient philosophy, ideas and theories of the Bugis-Makassar on the notion that the universe was built in a form of a giant rhombus, created by four salient fundamentals — wind, fire, water and soil, earth. Thus, the classical Bugis-Makassar aesthetic vibes, images and nuances are largely created and envisioned in a dominant four-angle, cornered composure; including on their traditional writing scripts (the Lontara script, lontara), architectural floor plan, layouts, ceremonial cuisines (''songko'' and ''songkolo''), artistic designs, textile (sarong motives) and philosophical values. The four elements are also synonymously evoked by four distinct colors — wind (yellow), fire (red), water (white) and earth (black). Additionally, the ''Lipa' Sabbe'' or ''sarung sutra'' (a sarung-cloth made from silk) signifies as an embodiment to honor the refined Bugis-Makassar identity in its purest form.
The Bugis-Makassar possessed a rich heritage, philosophy, religious and social structure. Their customs are based on the concept ''Pangadereng'' - originally consist of ''Adat, Ade’'' (custom), ''Rapang'' (Jurisprudence), ''Bicara'' (Judiciary) and ''Warik'' (Social system); following the Islamisation of the Bugis-Makassar, ''Syara (Syariah) was incorporated into its core values.
Another fundamental local wisdom includes ''Siri' na pacce''. It serves as a guidance, social convention and moral conduct. ''Siri'' signifies the consolidation a demeanor of shame and self-esteem, it acted as a pillar that bear the importance of dignity, virtue, esteem, solidarity and responsibility. ''Siri'' is essential for someone to be regarded as a ''tau'' (human). ''Pacce'' manifest as a presence of compassion and solidarity. It involves a person's ability on emotional intelligence, which includes love, sadness, pain, and solidarity. Other interpretation of ''Pecce'' revolves on self-sacrifice, hard work, and abstinence. In addition to the Bugis and Makassarese, the traditional ethos is also shared by their northern cousins — the Torajan people, Torajans and Mandarese.
Translated as the "four corners" — ''Sulappa Eppa'' represents the ancient philosophy, ideas and theories of the Bugis-Makassar on the notion that the universe was built in a form of a giant rhombus, created by four salient fundamentals — wind, fire, water and soil, earth. Thus, the classical Bugis-Makassar aesthetic vibes, images and nuances are largely created and envisioned in a dominant four-angle, cornered composure; including on their traditional writing scripts (the Lontara script, lontara), architectural floor plan, layouts, ceremonial cuisines (''songko'' and ''songkolo''), artistic designs, textile (sarong motives) and philosophical values. The four elements are also synonymously evoked by four distinct colors — wind (yellow), fire (red), water (white) and earth (black). Additionally, the ''Lipa' Sabbe'' or ''sarung sutra'' (a sarung-cloth made from silk) signifies as an embodiment to honor the refined Bugis-Makassar identity in its purest form.
 The Lontara script, Lontara traced its origin from the Kawi script; however, it has received a localized development and modification to accommodate the writings in the Bugis, Makassar and Mandar language. It was traditionally used for formal and official documents such as contracts, trade laws, treaties, maps, and Logbook, journals, both in Western Book design, book format and in the traditional palm-leaf manuscript. Following the rise of South Sulawesi as a naval powerhouse in eastern archipelago, the script expanded its influence, being introduced and incorporated as the Lonta Ende in Flores, Mbojo in eastern Sumbawa and Satera Jontal in western Sumbawa, albeit with alternations for the latter languages.
Its designation, "Lontara" was acquired from the term ''Lontar'', the Javanese language, Javanese and Malay language, Malay name from Palmyra Palm, whose leaves were commonly utilized for writing the manuscripts. It is also sometimes characterized as the Bugis script, as many of the historical writings are widely found in this language. In the Bugis Language, the writing system is styled as ''"urupu sulapa eppa"'', being described as "square" or "four-cornered letters", which served as a vivid illustration of the early Bugis-Makassar interpretation on the four ingredients that molded the universe — fire, water, earth and air.
During the Dutch colonization of Dutch East Indies, East Indies, the writing system is largely being superseded with the introduction of Latin Alphabet. Nonetheless, the script still retains its intimate cultural importance amongst the Bugis-Makassar society in their homeland and being use for the traditional ceremony, calendar and literature; as well as in personal documents and handwritten items, for instance, in letters and notes. The script is also being taught in many schools in South Sulawesi and the usage are visible on some street signs across the province. Presently, there is also notable efforts by Indonesian typographers and graphic designers on introducing the script to a larger audience beyond its traditional borders.
In addition to Lontara, there is also another form of Bugis-Makassar traditional writing based on the Arabic-script, known as the Serang Alphabet. Relatively on an almost similar parallel module with its sister scripts, Jawi script, Jawi and Pegon script, Pegon for Malay and Javanese respectively, the Serang writing system incorporated the usage of Arabic script, Arabic elements with few additional characters to integrate with the local language.
The Lontara script, Lontara traced its origin from the Kawi script; however, it has received a localized development and modification to accommodate the writings in the Bugis, Makassar and Mandar language. It was traditionally used for formal and official documents such as contracts, trade laws, treaties, maps, and Logbook, journals, both in Western Book design, book format and in the traditional palm-leaf manuscript. Following the rise of South Sulawesi as a naval powerhouse in eastern archipelago, the script expanded its influence, being introduced and incorporated as the Lonta Ende in Flores, Mbojo in eastern Sumbawa and Satera Jontal in western Sumbawa, albeit with alternations for the latter languages.
Its designation, "Lontara" was acquired from the term ''Lontar'', the Javanese language, Javanese and Malay language, Malay name from Palmyra Palm, whose leaves were commonly utilized for writing the manuscripts. It is also sometimes characterized as the Bugis script, as many of the historical writings are widely found in this language. In the Bugis Language, the writing system is styled as ''"urupu sulapa eppa"'', being described as "square" or "four-cornered letters", which served as a vivid illustration of the early Bugis-Makassar interpretation on the four ingredients that molded the universe — fire, water, earth and air.
During the Dutch colonization of Dutch East Indies, East Indies, the writing system is largely being superseded with the introduction of Latin Alphabet. Nonetheless, the script still retains its intimate cultural importance amongst the Bugis-Makassar society in their homeland and being use for the traditional ceremony, calendar and literature; as well as in personal documents and handwritten items, for instance, in letters and notes. The script is also being taught in many schools in South Sulawesi and the usage are visible on some street signs across the province. Presently, there is also notable efforts by Indonesian typographers and graphic designers on introducing the script to a larger audience beyond its traditional borders.
In addition to Lontara, there is also another form of Bugis-Makassar traditional writing based on the Arabic-script, known as the Serang Alphabet. Relatively on an almost similar parallel module with its sister scripts, Jawi script, Jawi and Pegon script, Pegon for Malay and Javanese respectively, the Serang writing system incorporated the usage of Arabic script, Arabic elements with few additional characters to integrate with the local language.
 Bugis literature connotes to the forms of literature expressed in the Bugis language — which comprises both Literature, written and oral traditions. The earliest works of Bugis literature were verbally transmitted, written literature began to arose and gradually codified with the evolution of the Lontara script, Lontara script by the 1400s. Its foundation largely coincides and intersects with the Makassarese literature — of whom it shared a closely related development with. The Bugis literary tradition mainly focuses on the wisdom, moral, social life and cultural environment of the Bugis identity.
Bugis folk literature is an oral composition deeply rooted in Bugis understanding and perception of life — in the form of prose, poetry and Lyrics, lyric. The classification raging from various short poems, ''élong''; long narrative poems, ''tolo; playful sayings, such as riddles, ''atteppungeng'' and nursery rhymes; magical spells, ''jappi, baca-baca''; pre-Islamic ritual expressions, ''sabo, sessukeng, lawolo''; precepts, ''pappaseng''; and oaths of allegiance, ''aru''. Other important oral heritage includes — stories, ''curita''; sermons, ''katoba''; and Speech recognition, speeches. Although they are essentially verbal, many of the works are also subsequently being written in the language.
Bugis literature connotes to the forms of literature expressed in the Bugis language — which comprises both Literature, written and oral traditions. The earliest works of Bugis literature were verbally transmitted, written literature began to arose and gradually codified with the evolution of the Lontara script, Lontara script by the 1400s. Its foundation largely coincides and intersects with the Makassarese literature — of whom it shared a closely related development with. The Bugis literary tradition mainly focuses on the wisdom, moral, social life and cultural environment of the Bugis identity.
Bugis folk literature is an oral composition deeply rooted in Bugis understanding and perception of life — in the form of prose, poetry and Lyrics, lyric. The classification raging from various short poems, ''élong''; long narrative poems, ''tolo; playful sayings, such as riddles, ''atteppungeng'' and nursery rhymes; magical spells, ''jappi, baca-baca''; pre-Islamic ritual expressions, ''sabo, sessukeng, lawolo''; precepts, ''pappaseng''; and oaths of allegiance, ''aru''. Other important oral heritage includes — stories, ''curita''; sermons, ''katoba''; and Speech recognition, speeches. Although they are essentially verbal, many of the works are also subsequently being written in the language.
 Writings in the Lontara Script was likely to be first appeared around 1400. The earliest texts were inscribed on palm leaves, followed by volumes of Handwriting, handwritten composition on paper manuscripts, potentially from 1500 onwards, or even earlier. The works of literature commonly commissioned by writing specialists known as ''palôntara'', the ''palôntara'' is being delegated the task as a researcher on creating and compiling the Bugis manuscripts. The manuscripts tend to be rich and varied, with a plethora of theme (arts), themes and subjects — including History, historical chronicles, poems, law, legal works, ritual texts, manuals, ethics, among few. Printing, Printed materials in the Bugis language were introduced in the latter half of the 19th century, albeit with a smaller circulation, such as in Dictionary, dictionaries, Grammar, grammars books, Chrestomathy, chrestomathies and translations.
Consist of over 6,000 pages, the La Galigo is regarded as the magnum opus in the Bugis literary heritage. Written in the old Bugis language, the chronicle, saga traced its origin from the early oral traditions. The poetic text serves as a revered almanac and provide narrations about the ancient understanding on humanity and kingdoms. In the Bugis culture, episodes from La Galigo are commonly reenacted through chant and Poetry, poetic recitation performance led by a La Galigo specialist, known as ''passure''. The performance is sometimes held during festivals, wedding or during a Housewarming party, house-moving ceremony. In 2012, two of the La Galigo manuscripts are included in UNESCO, UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme.
However, the largest collection of Bugis literature is in the form of family Genealogy, genealogies. It is regarded as an important family heirloom, especially amongst the members of nobility and aristocratic families. Some dated as early as 1400 — about two hundred years prior to their Islamisation, the early Bugis genealogies provide a rare glimpse on the culture and ideology of an early and literate Austronesian society.
Writings in the Lontara Script was likely to be first appeared around 1400. The earliest texts were inscribed on palm leaves, followed by volumes of Handwriting, handwritten composition on paper manuscripts, potentially from 1500 onwards, or even earlier. The works of literature commonly commissioned by writing specialists known as ''palôntara'', the ''palôntara'' is being delegated the task as a researcher on creating and compiling the Bugis manuscripts. The manuscripts tend to be rich and varied, with a plethora of theme (arts), themes and subjects — including History, historical chronicles, poems, law, legal works, ritual texts, manuals, ethics, among few. Printing, Printed materials in the Bugis language were introduced in the latter half of the 19th century, albeit with a smaller circulation, such as in Dictionary, dictionaries, Grammar, grammars books, Chrestomathy, chrestomathies and translations.
Consist of over 6,000 pages, the La Galigo is regarded as the magnum opus in the Bugis literary heritage. Written in the old Bugis language, the chronicle, saga traced its origin from the early oral traditions. The poetic text serves as a revered almanac and provide narrations about the ancient understanding on humanity and kingdoms. In the Bugis culture, episodes from La Galigo are commonly reenacted through chant and Poetry, poetic recitation performance led by a La Galigo specialist, known as ''passure''. The performance is sometimes held during festivals, wedding or during a Housewarming party, house-moving ceremony. In 2012, two of the La Galigo manuscripts are included in UNESCO, UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme.
However, the largest collection of Bugis literature is in the form of family Genealogy, genealogies. It is regarded as an important family heirloom, especially amongst the members of nobility and aristocratic families. Some dated as early as 1400 — about two hundred years prior to their Islamisation, the early Bugis genealogies provide a rare glimpse on the culture and ideology of an early and literate Austronesian society.
 In the traditional Bugis-Makassar culture, textiles and clothes are revered and occupied a special place in the society. Historically, the colours and motives donned by the wearer possessed an important indicator and serves as a defining symbol on the person's identity, age and status.
The term Baju Bodo derived from the Makassarese language, being described as "short clothing". Conversely, in the Bugis language, it is also known as ''Waju Tokko'' and ''Waju Ponco. A short-sleeved tunic, the costume is commonly worn together with silk or a woven sarong. The attire traced its origin as early as the 9th century, following the introduction of muslin cloth by the foreign traders to the harbors of South Sulawesi. The textile, being thin and light, is highly suitable to accommodate the local tropical weather in the region. In addition to muslin cloth, the Baju Bodo is also commonly sourced from pineapple-fiber fabric and cotton.
In the traditional Bugis-Makassar culture, textiles and clothes are revered and occupied a special place in the society. Historically, the colours and motives donned by the wearer possessed an important indicator and serves as a defining symbol on the person's identity, age and status.
The term Baju Bodo derived from the Makassarese language, being described as "short clothing". Conversely, in the Bugis language, it is also known as ''Waju Tokko'' and ''Waju Ponco. A short-sleeved tunic, the costume is commonly worn together with silk or a woven sarong. The attire traced its origin as early as the 9th century, following the introduction of muslin cloth by the foreign traders to the harbors of South Sulawesi. The textile, being thin and light, is highly suitable to accommodate the local tropical weather in the region. In addition to muslin cloth, the Baju Bodo is also commonly sourced from pineapple-fiber fabric and cotton.
 With the rise of Islamisation among the Bugis-Makassar, another closely related form of Baju Bodo emerged. Having a longer sleeve, the ''Baju La’bu'' (from Makassarese 'long'), also known as ''Bodo Panjang'' (both defined as "long cloth") is tailored in accordance of Islamic interpretation of ''Intimate parts in Islam, Aurat'' and modesty. The Baju La’bu is also traditionally made from silk, a departure from the semi-transparent and translucent fabric of its predecessor.
The Bugis-Makassarese Woven fabric, handloom industry potentially commenced in the 1400s. The locally-made sarung motives were initially basic, having rudimentary stripes of vertical, horizontal or in a checkered pattern, potentially inspired by ''Sulappa Eppa'' (the four elements) foundations. By the 1600s, the designs are becoming progressively ornamented, with the inclusion of a multitude of geometrical shapes, contour and sequence. Almost in a coordination with the function of Baju Bodo in the past, the motives and design of the sarung would also be used to denote the status of its wearer. The sarung material is usually sourced from silk and cotton.
The corresponding mode for the Bugis male is known as ''Jas Tutu or ''Jas Tutup'' (an "enclosed coat"), the garment is in a form of long-sleeved coat with a collar. The Jas Tutu is also synonymous to be worn with the ''Songkok recca/Pabiring/Songkok To Bone'' (Bugis songkok), ''Lipa’ Sabbe'' (sarong) and a gold or silver-coloured button. The Bugis-styled Songkok is made of woven rattan and golden thread. During a traditional wedding ceremony, the groom would also accompanied by a highly elaborated accessories, including ''Tataroppeng'' (Keris), ''Pabekkeng'' (Belt (clothing), belt), ''Rope'' (Songket), ''Sigara'' (headgear), ''Salempang'' (sling), ''Gelang'' (bangle) and ''Sapu tangan'' (handkerchief).
In the present day, the Baju Bodo and Jas Tutu are largely being reserved as a formal wear, the sightings are common during weddings, as well as in other ceremonial and cultural functions.
With the rise of Islamisation among the Bugis-Makassar, another closely related form of Baju Bodo emerged. Having a longer sleeve, the ''Baju La’bu'' (from Makassarese 'long'), also known as ''Bodo Panjang'' (both defined as "long cloth") is tailored in accordance of Islamic interpretation of ''Intimate parts in Islam, Aurat'' and modesty. The Baju La’bu is also traditionally made from silk, a departure from the semi-transparent and translucent fabric of its predecessor.
The Bugis-Makassarese Woven fabric, handloom industry potentially commenced in the 1400s. The locally-made sarung motives were initially basic, having rudimentary stripes of vertical, horizontal or in a checkered pattern, potentially inspired by ''Sulappa Eppa'' (the four elements) foundations. By the 1600s, the designs are becoming progressively ornamented, with the inclusion of a multitude of geometrical shapes, contour and sequence. Almost in a coordination with the function of Baju Bodo in the past, the motives and design of the sarung would also be used to denote the status of its wearer. The sarung material is usually sourced from silk and cotton.
The corresponding mode for the Bugis male is known as ''Jas Tutu or ''Jas Tutup'' (an "enclosed coat"), the garment is in a form of long-sleeved coat with a collar. The Jas Tutu is also synonymous to be worn with the ''Songkok recca/Pabiring/Songkok To Bone'' (Bugis songkok), ''Lipa’ Sabbe'' (sarong) and a gold or silver-coloured button. The Bugis-styled Songkok is made of woven rattan and golden thread. During a traditional wedding ceremony, the groom would also accompanied by a highly elaborated accessories, including ''Tataroppeng'' (Keris), ''Pabekkeng'' (Belt (clothing), belt), ''Rope'' (Songket), ''Sigara'' (headgear), ''Salempang'' (sling), ''Gelang'' (bangle) and ''Sapu tangan'' (handkerchief).
In the present day, the Baju Bodo and Jas Tutu are largely being reserved as a formal wear, the sightings are common during weddings, as well as in other ceremonial and cultural functions.
 The Bugis cuisine constitutes an essential part of its heritage, comprises various culinary styles and recipes frequently associated with the Bugis people. It shares many common gastronomical traditions and characteristics with the surrounding Makassarese, Mandarese and Torajans. Many of the meals are indigenously developed in the island of Sulawesi, with a focus on native ingredients; while others exhibit a notably stronger Fusion cuisine, outside influences and customized according to the local taste bud, palates.
Foreign cooking techniques in the South Sulawesi cuisine can be seen on the adoption of ''Jalangkote'', a small Frying, fried pie adopted from Portuguese ''papeda (food), papeda''. The fillings for ''Jalangkote'' usually consist of rice vermicelli (denoting Chinese cuisine, Chinese influence) combined with sliced vegetables, boiled eggs and mincemeat. Meanwhile Indian cuisine, Indian elements are visible and demonstrated in the localised dishes, for instance the creamy ''Gagape'', ''Toppa Lada'' and the spicy ''Juku palumara''.
There is also a wide array of cuisines that signifies a bolder Cuisine#Regional cuisines, endemic origin: Rice cake#Indonesian, Rice cakes are particularly popular with the likes of ''Burasa and ''Tumbu/Lapa-lapa/Langka''. The rice dumplings are Steaming, steamed and wrapped in leave containers with coconut milk, thus contributing to its rich and creamy flavor. It is usually served as a substitute for white rice and eaten together with soups or other side dishes. Another distinguished forms of rice cake in the Bugis-Makassar community includes ''Gogos'' — Roasting, roasted glutinous rice with fish fillings, wrapped in banana leaf. It is commonly being eaten as snacks.
The Bugis cuisine constitutes an essential part of its heritage, comprises various culinary styles and recipes frequently associated with the Bugis people. It shares many common gastronomical traditions and characteristics with the surrounding Makassarese, Mandarese and Torajans. Many of the meals are indigenously developed in the island of Sulawesi, with a focus on native ingredients; while others exhibit a notably stronger Fusion cuisine, outside influences and customized according to the local taste bud, palates.
Foreign cooking techniques in the South Sulawesi cuisine can be seen on the adoption of ''Jalangkote'', a small Frying, fried pie adopted from Portuguese ''papeda (food), papeda''. The fillings for ''Jalangkote'' usually consist of rice vermicelli (denoting Chinese cuisine, Chinese influence) combined with sliced vegetables, boiled eggs and mincemeat. Meanwhile Indian cuisine, Indian elements are visible and demonstrated in the localised dishes, for instance the creamy ''Gagape'', ''Toppa Lada'' and the spicy ''Juku palumara''.
There is also a wide array of cuisines that signifies a bolder Cuisine#Regional cuisines, endemic origin: Rice cake#Indonesian, Rice cakes are particularly popular with the likes of ''Burasa and ''Tumbu/Lapa-lapa/Langka''. The rice dumplings are Steaming, steamed and wrapped in leave containers with coconut milk, thus contributing to its rich and creamy flavor. It is usually served as a substitute for white rice and eaten together with soups or other side dishes. Another distinguished forms of rice cake in the Bugis-Makassar community includes ''Gogos'' — Roasting, roasted glutinous rice with fish fillings, wrapped in banana leaf. It is commonly being eaten as snacks.
 The peninsula's long coastline has contributed a great fishing industry in the region, creating Seafood, oceanic produce as an important part of the meal. Dishes such as ''Pa’Deme'' (anchovies sambal), ''Bajabu'' (''serundeng''), ''Lawa Bale'' (marinated raw fish) and the clear broth soups of ''Pallu Kacci'' and ''Pallumara'' captures its extensive maritime connection. In addition to seafood, there is also a diverse culinary traditions with the emphasis on meat, which can be seen in the hearty Low-temperature cooking, slow cooked dishes, namely ''Nasu Likku, ''Nasu Palekko'' and ''Goré-Goré''. The meals are usually acted as an accompanying side dish to compliment the ''Nasi Putih'' (plain white rice), or in other cases, the rice cakes.
Banana occupied a major importance after rice in the Bugis Staple food, staple, as it is widely cultivated in South Sulawesi. Aside from being eaten fresh after a meal, Banana-based meals are extensive in the forms of snacks and desserts — raging from the sweet tasting ''Berongko'' (steamed Banana pudding), caramelized ''Sanggara' Balanda'', to crispy and savory snacks such as ''Sanggara Pappek'' (smashed bananas).
Other popular meals associated with the Bugis includes congee dishes — ''Barobbo'' (rice and maize, corn porridge) and the sago-based ''Kapurung''; and traditional ''Kues'', notably the ''Kue bugis'', ''Kue Dange'', ''Kue Sikaporo'' and ''Bolu Peca''. Due to the extensive and continuous friendly interactions with the kindred Makassarese people, many of the unique Makassarese meals are also widely enjoyed by the Bugis, including ''Coto Makassar'', ''Sop Sodara'', ''Pallubasa'' and ''Konro'', or desserts like ''Cucuru' Te'ne'' and ''Es Palu Butong''.
Beyond their native soil, Burasa' and other Bugis-Makassar traditional cuisines are also commonly presented as a ceremonial dish by their diaspora community. It is prepared as a significant legacy to honor their ancestral roots from the plains of South Sulawesi.
The peninsula's long coastline has contributed a great fishing industry in the region, creating Seafood, oceanic produce as an important part of the meal. Dishes such as ''Pa’Deme'' (anchovies sambal), ''Bajabu'' (''serundeng''), ''Lawa Bale'' (marinated raw fish) and the clear broth soups of ''Pallu Kacci'' and ''Pallumara'' captures its extensive maritime connection. In addition to seafood, there is also a diverse culinary traditions with the emphasis on meat, which can be seen in the hearty Low-temperature cooking, slow cooked dishes, namely ''Nasu Likku, ''Nasu Palekko'' and ''Goré-Goré''. The meals are usually acted as an accompanying side dish to compliment the ''Nasi Putih'' (plain white rice), or in other cases, the rice cakes.
Banana occupied a major importance after rice in the Bugis Staple food, staple, as it is widely cultivated in South Sulawesi. Aside from being eaten fresh after a meal, Banana-based meals are extensive in the forms of snacks and desserts — raging from the sweet tasting ''Berongko'' (steamed Banana pudding), caramelized ''Sanggara' Balanda'', to crispy and savory snacks such as ''Sanggara Pappek'' (smashed bananas).
Other popular meals associated with the Bugis includes congee dishes — ''Barobbo'' (rice and maize, corn porridge) and the sago-based ''Kapurung''; and traditional ''Kues'', notably the ''Kue bugis'', ''Kue Dange'', ''Kue Sikaporo'' and ''Bolu Peca''. Due to the extensive and continuous friendly interactions with the kindred Makassarese people, many of the unique Makassarese meals are also widely enjoyed by the Bugis, including ''Coto Makassar'', ''Sop Sodara'', ''Pallubasa'' and ''Konro'', or desserts like ''Cucuru' Te'ne'' and ''Es Palu Butong''.
Beyond their native soil, Burasa' and other Bugis-Makassar traditional cuisines are also commonly presented as a ceremonial dish by their diaspora community. It is prepared as a significant legacy to honor their ancestral roots from the plains of South Sulawesi.
 A plethora of blades, Knife, knives and firearms constitute the arsenal of Bugis-Makassar weaponry. However, Badik is hailed as the traditional weapon strongly associated with their identity and possessed a revered status in the sociological construct of the Bugis-Makassar society. The item is not solely perceived as a mere weapon, but as an emblem designated to represent the personal character of its owner. It is historically used as a vital tool for hunting animals and as a self-defense mechanism.
In the traditional Bugis-Makassar understanding, the hierarchal level of Badik is regarded as a second after the Kris, Keris. A far-cry from the Badik which known to have an almost universal usage throughout all ranks of the society, the ''Keris Pusaka'' (the "Dynasty Keris") is reserved as an important family regalia amongst the elite royal houses in South Sulawesi. Thus, historically the Badik received a prevalent identity as a companion for the Bugis-Makassar man.
In the past, Badik is used as a tool of defense to protect an individual and the family honor. The doctrine is largely based on the philosophical interpretation of ''Siri'', a cornerstone of the Bugis-Makassar culture, siri represents a responsibility to maintain the dignity in the society. The concept is historically entranced in the cognitive psyche amongst the people and traditionally become a binding force on the moral values and social system. Badik is also commonly passed from one generation to another, acting as an important family heirloom.
A plethora of blades, Knife, knives and firearms constitute the arsenal of Bugis-Makassar weaponry. However, Badik is hailed as the traditional weapon strongly associated with their identity and possessed a revered status in the sociological construct of the Bugis-Makassar society. The item is not solely perceived as a mere weapon, but as an emblem designated to represent the personal character of its owner. It is historically used as a vital tool for hunting animals and as a self-defense mechanism.
In the traditional Bugis-Makassar understanding, the hierarchal level of Badik is regarded as a second after the Kris, Keris. A far-cry from the Badik which known to have an almost universal usage throughout all ranks of the society, the ''Keris Pusaka'' (the "Dynasty Keris") is reserved as an important family regalia amongst the elite royal houses in South Sulawesi. Thus, historically the Badik received a prevalent identity as a companion for the Bugis-Makassar man.
In the past, Badik is used as a tool of defense to protect an individual and the family honor. The doctrine is largely based on the philosophical interpretation of ''Siri'', a cornerstone of the Bugis-Makassar culture, siri represents a responsibility to maintain the dignity in the society. The concept is historically entranced in the cognitive psyche amongst the people and traditionally become a binding force on the moral values and social system. Badik is also commonly passed from one generation to another, acting as an important family heirloom.
 Another important sword owned by the Bugis is the Keris, also known as ''Tappi''. It has some minor different features in contrast to the Javanese Keris; however, the Bugis Keris is noted to bear a closer anatomical resembles with the Malay-version of the dagger, the item potentially being introduced by the Malays to the people of South Sulawesi. Almost parallel with the Badik, the Keris equally carried a revered symbol amongst many Bugis-Makassar people.
In addition to Badik and Keris, they were known to host a multitude of classical armaments. Most of the items are collectively classified under the ''parewa bessi'' (Iron weapons) category made by the Bugis-Makassar blacksmiths. Some of the other notable collections include ''Alamang/Sundang'', a long-sword; ''Bessing'', a spear; ''Kanna'', shield; Pantu’, a traditional Stick-fighting, fighting stick; Baju Rantai, ''Waju Rante'', Armour, armor; and ''Tado'', a trapping rope.
The art of weapon among the Bugis-Makassar is constantly developed through the millennia. The ancient peoples of South Sulawesi are recorded to have a usage of blowgun, blowpipes with poisoned Dart (missile), darts, spears, short swords, kris and rattan helmets. By the early modern era, the Bugis-Makassar gained further exposure on the artillery knowledge with the introduction of various firearms: muskets, culverins and cannons that enhance their warfare and combatant skills. Mail and plate armour, Mail armor with metal plates (''baju lamina'') is estimated to be used starting from this era, and still being worn until the 19th century.
The strong mutual relationship between the arms development and its militaristic culture formed the advantageous momentum that fueled to their quest for political advancement and influence outside from the traditional Bugis-Makassar homeland. It become one of the wielding tools that seals their historical figures and status as soldiers, Mercenary, mercenaries, warriors and fighters throughout the maritime realm.
Another important sword owned by the Bugis is the Keris, also known as ''Tappi''. It has some minor different features in contrast to the Javanese Keris; however, the Bugis Keris is noted to bear a closer anatomical resembles with the Malay-version of the dagger, the item potentially being introduced by the Malays to the people of South Sulawesi. Almost parallel with the Badik, the Keris equally carried a revered symbol amongst many Bugis-Makassar people.
In addition to Badik and Keris, they were known to host a multitude of classical armaments. Most of the items are collectively classified under the ''parewa bessi'' (Iron weapons) category made by the Bugis-Makassar blacksmiths. Some of the other notable collections include ''Alamang/Sundang'', a long-sword; ''Bessing'', a spear; ''Kanna'', shield; Pantu’, a traditional Stick-fighting, fighting stick; Baju Rantai, ''Waju Rante'', Armour, armor; and ''Tado'', a trapping rope.
The art of weapon among the Bugis-Makassar is constantly developed through the millennia. The ancient peoples of South Sulawesi are recorded to have a usage of blowgun, blowpipes with poisoned Dart (missile), darts, spears, short swords, kris and rattan helmets. By the early modern era, the Bugis-Makassar gained further exposure on the artillery knowledge with the introduction of various firearms: muskets, culverins and cannons that enhance their warfare and combatant skills. Mail and plate armour, Mail armor with metal plates (''baju lamina'') is estimated to be used starting from this era, and still being worn until the 19th century.
The strong mutual relationship between the arms development and its militaristic culture formed the advantageous momentum that fueled to their quest for political advancement and influence outside from the traditional Bugis-Makassar homeland. It become one of the wielding tools that seals their historical figures and status as soldiers, Mercenary, mercenaries, warriors and fighters throughout the maritime realm.
 In the Bugis society, architecture is regarded as an emblem of philosophy, designed to endorse the occupier belief, faith and understanding about cosmos and universe. It is strongly rooted in its long and rich history, blending elements on the native interpretation of cosmology with culture, faith, mythology, aesthetic and functionality. The Bugis architectural style is broadly classed together with the Makassarese, of whom it shares strong architectural features and identity.
Based on the Bugis philosophical understanding, a home is regarded as the legitimate expression of the spiritual rite of passage as a human being: a place to be born, a place to raised and nurtured as a child, a place to become a husband and wife, and a place to perish. Consequently, the habitation is designed to be solemn, sacred and highly revered. It provides ones with a place for solitude, energy, nourishment, well-being and honour to its dwellers. The presence of a home in the Bugis society is part-and-parcel with life, hence home ownership is regarded in utmost importance — to commemorate life and to become a beacon symbol of life.
In the Bugis society, architecture is regarded as an emblem of philosophy, designed to endorse the occupier belief, faith and understanding about cosmos and universe. It is strongly rooted in its long and rich history, blending elements on the native interpretation of cosmology with culture, faith, mythology, aesthetic and functionality. The Bugis architectural style is broadly classed together with the Makassarese, of whom it shares strong architectural features and identity.
Based on the Bugis philosophical understanding, a home is regarded as the legitimate expression of the spiritual rite of passage as a human being: a place to be born, a place to raised and nurtured as a child, a place to become a husband and wife, and a place to perish. Consequently, the habitation is designed to be solemn, sacred and highly revered. It provides ones with a place for solitude, energy, nourishment, well-being and honour to its dwellers. The presence of a home in the Bugis society is part-and-parcel with life, hence home ownership is regarded in utmost importance — to commemorate life and to become a beacon symbol of life.
 In order to identify the course of their maritime routes, the sailors would typically inclined to use a multitude of convergent nautical practice, from determining the Sunrise, rising and Sunset, setting points of the sun; the location horizon, stars and constellations; the marine environment — the flow of the oceanic Swell (ocean), swell, the form of the waves, the water appearance; fauna — the actions of the fish and the flight arrangement of the birds; the wind directions; and specific Geography, geographical landmarks.
The original pinisi-rigged ship (palari), is about in length overall, with light laden waterline of .} Smaller palari is only about 10 m in length. A two-Mast (sailing), masted sailing vessel, the name "pinisi" derives from the type of gaff rig, use for its configuration. Its unique large tripod-shaped mainsails and masts give its unparalleled design composition, a departure from other western ships. In the contemporary era, palari is also equipped with Engine, motors for its seafaring journeys.
There are many revered shipbuilding centers in the region, including Ara, Tanah Lemo and Bira. However, the Konjo, a subgroup of the Makassarese, are particularly known as one of the respected master builders of pinisi-rigged ships, enjoying a long-prized tradition of watercraft and boat-production, a knowledge commonly inherited from fathers to sons for centuries.
For the Konjos in Bulukumba, the boatmaking identity is deeply rooted to their lives as a precious embodiment of art, culture and rituals. Being a highly dedicated wikt:boatsmith, boatsmith community, the Konjo people are traditionally restricted from sailing to the seas, as their elders feared that their clan would not return to their homeland, creating a perilous risk of losing their valuable shipbuilding wisdom amongst their kinsmen. Thus in South Sulawesi, the transoceanic sailing responsibility were vastly executed by their closely related brethren — the Bugis and Makassarese.
The rich nautical culture of Bugis-Makassar is equally captured and reinforced by a plethora of ships — ranging from ''penjajap'', warship; Pajala (boat), pajala, a smaller boat, also used for fishing; palari, another descendant of the padewakang; Lambo (boat), Lambo, a trading boat; and the early ships of ''Somba Lete'' and Tanja sail, ''sompe tanja''. These vessels collectively have left a significant impact on the local and regional development.
As the seafaring identity began to take root in the coastal South Sulawesi society, it gradually become a profound icon that navigated their influence and presence in the region. Following the Bugis-Makassar Human migration, migratory tradition known as ''sompe'' (to sail) and ''malleke' dapureng''; it was here, from among these historical ships, vessels and boats that many Bugis and Makassar man, woman and children braved away from their traditional heartland in search of Economic migrant, economic pursuits, prosperity and opportunities, while others embarked for an educational experience, adventure, personal dignity, military quest or prestigious political ambitions. Thus, most, if not all Bugis in the diaspora may ultimately traced their ancestral origin to one of the ''Pasompe (a term for people who sailed/ventured beyond their native soil). Tales and trails from the past waves of sails and settlements can still be witnessed until the present day, evidently illustrated by their extensive centuries-old ethnic enclaves and various diaspora communities established throughout the islands and coastal regions of maritime Southeast Asia.
In order to identify the course of their maritime routes, the sailors would typically inclined to use a multitude of convergent nautical practice, from determining the Sunrise, rising and Sunset, setting points of the sun; the location horizon, stars and constellations; the marine environment — the flow of the oceanic Swell (ocean), swell, the form of the waves, the water appearance; fauna — the actions of the fish and the flight arrangement of the birds; the wind directions; and specific Geography, geographical landmarks.
The original pinisi-rigged ship (palari), is about in length overall, with light laden waterline of .} Smaller palari is only about 10 m in length. A two-Mast (sailing), masted sailing vessel, the name "pinisi" derives from the type of gaff rig, use for its configuration. Its unique large tripod-shaped mainsails and masts give its unparalleled design composition, a departure from other western ships. In the contemporary era, palari is also equipped with Engine, motors for its seafaring journeys.
There are many revered shipbuilding centers in the region, including Ara, Tanah Lemo and Bira. However, the Konjo, a subgroup of the Makassarese, are particularly known as one of the respected master builders of pinisi-rigged ships, enjoying a long-prized tradition of watercraft and boat-production, a knowledge commonly inherited from fathers to sons for centuries.
For the Konjos in Bulukumba, the boatmaking identity is deeply rooted to their lives as a precious embodiment of art, culture and rituals. Being a highly dedicated wikt:boatsmith, boatsmith community, the Konjo people are traditionally restricted from sailing to the seas, as their elders feared that their clan would not return to their homeland, creating a perilous risk of losing their valuable shipbuilding wisdom amongst their kinsmen. Thus in South Sulawesi, the transoceanic sailing responsibility were vastly executed by their closely related brethren — the Bugis and Makassarese.
The rich nautical culture of Bugis-Makassar is equally captured and reinforced by a plethora of ships — ranging from ''penjajap'', warship; Pajala (boat), pajala, a smaller boat, also used for fishing; palari, another descendant of the padewakang; Lambo (boat), Lambo, a trading boat; and the early ships of ''Somba Lete'' and Tanja sail, ''sompe tanja''. These vessels collectively have left a significant impact on the local and regional development.
As the seafaring identity began to take root in the coastal South Sulawesi society, it gradually become a profound icon that navigated their influence and presence in the region. Following the Bugis-Makassar Human migration, migratory tradition known as ''sompe'' (to sail) and ''malleke' dapureng''; it was here, from among these historical ships, vessels and boats that many Bugis and Makassar man, woman and children braved away from their traditional heartland in search of Economic migrant, economic pursuits, prosperity and opportunities, while others embarked for an educational experience, adventure, personal dignity, military quest or prestigious political ambitions. Thus, most, if not all Bugis in the diaspora may ultimately traced their ancestral origin to one of the ''Pasompe (a term for people who sailed/ventured beyond their native soil). Tales and trails from the past waves of sails and settlements can still be witnessed until the present day, evidently illustrated by their extensive centuries-old ethnic enclaves and various diaspora communities established throughout the islands and coastal regions of maritime Southeast Asia.
 A visible departure from the extensive Maritime history, maritime and Seamanship, nautical culture dominated by their coastal brethren, the inland Bugis-Makassar country bear witness to its strong
A visible departure from the extensive Maritime history, maritime and Seamanship, nautical culture dominated by their coastal brethren, the inland Bugis-Makassar country bear witness to its strong  The Islamisation of Bugis-Makassar states initiated by Luwu and Gowa in the 17th century has greatly morphed the religious landscape throughout the peninsula. As a consequence, most of the liturgical festivals by the Bugis are primarily coordinated with the Islamic calendar, albeit embraced with a strong sense on the localized cultural orientations.
The biannual ''Hari Raya'' (eid) celebrations of Eid al-Fitr, Idul Fitri and Eid al-Adha, Idul Adha are regarded as the largest festivals for the Bugis. The Idul Fitri (known as ''Maleppe'', meaning "release" in the Bugis language) serves as a triumphal rite after completing a month of Fasting in Islam, fasting and religious activities during Ramadan, Ramadhan. The term ''Mallepe'' holds a philosophical symbol as a release from the sins and the bad habits of a person. While Idul Adha is a dedicated religious observance held to commemorate the sacrifice made by Prophet Ibrahim.
There are a diverse religio-cultural activates shared during both of the merriments. A day before eid, many Bugis families would prepare ''Burasa and ''Tumbu'' rice cakes in a tradition known as ''Ma’burasa'' and ''Ma’tumbu''. The tradition of visiting friends, relatives and holding a grand feast for visitors are also central — known as Lebaran#Halal bi-halal, Massiara, the visits usually commenced after the eid prayers. Additionally, many would also take the day to ask the forgiveness and reconcile between one another, while some would dispose their old clothes into the sea or rivers as a sign of a new beginning and chapter in life.
The Islamisation of Bugis-Makassar states initiated by Luwu and Gowa in the 17th century has greatly morphed the religious landscape throughout the peninsula. As a consequence, most of the liturgical festivals by the Bugis are primarily coordinated with the Islamic calendar, albeit embraced with a strong sense on the localized cultural orientations.
The biannual ''Hari Raya'' (eid) celebrations of Eid al-Fitr, Idul Fitri and Eid al-Adha, Idul Adha are regarded as the largest festivals for the Bugis. The Idul Fitri (known as ''Maleppe'', meaning "release" in the Bugis language) serves as a triumphal rite after completing a month of Fasting in Islam, fasting and religious activities during Ramadan, Ramadhan. The term ''Mallepe'' holds a philosophical symbol as a release from the sins and the bad habits of a person. While Idul Adha is a dedicated religious observance held to commemorate the sacrifice made by Prophet Ibrahim.
There are a diverse religio-cultural activates shared during both of the merriments. A day before eid, many Bugis families would prepare ''Burasa and ''Tumbu'' rice cakes in a tradition known as ''Ma’burasa'' and ''Ma’tumbu''. The tradition of visiting friends, relatives and holding a grand feast for visitors are also central — known as Lebaran#Halal bi-halal, Massiara, the visits usually commenced after the eid prayers. Additionally, many would also take the day to ask the forgiveness and reconcile between one another, while some would dispose their old clothes into the sea or rivers as a sign of a new beginning and chapter in life.
 Other common traditions during eid includes ''Mabbaca-baca'', a solemn thanksgiving dua gathering and feast led by the community religious leaders known as Puang Anre Guru'' or ''Daeng Imam''. A visit the Cemetery, final resting place of the departed love ones is also a major commonplace during the season, in the custom known as ''Masiara Kuburu'', the Lebaran#Visiting graves, visit to the grave is regarded as a gesture of love, respect and dignity.
The positive and goodwill communal spirit is also continued in a various of religious and cultural programs. In addition to eid, the Bugis organized a prolific traditions to commemorate its faith and identity, including Ramadan, a holy month dedicated by fasting and various religious activities. ''Maulu/ma maulu’'' (Mawlid), honoring the birth of Muhammad, Prophet Muhammmad, special ceremonial meals and colorful eggs would be given to the mosque attendees to monumentalize the meaningful day; ''Esso Sura'' (Ashura), remembrance of Muharram, where a special porridge (known as ''Bubu Petu'' and ''Bella Pitunrupa'') are prepared, the day also marked as a major shopping period for the Bugis-Makassar, as many would traditionally buy new house utensils during the Ashura. Furthermore, the Bugis and Makassar families would also arrange ''Massuro Baca'', special ceremonial doa and feast held a week before Ramadhan to remember the departed relatives, as well as a preparation to cleanse the inner-self before the holy month.
Other common traditions during eid includes ''Mabbaca-baca'', a solemn thanksgiving dua gathering and feast led by the community religious leaders known as Puang Anre Guru'' or ''Daeng Imam''. A visit the Cemetery, final resting place of the departed love ones is also a major commonplace during the season, in the custom known as ''Masiara Kuburu'', the Lebaran#Visiting graves, visit to the grave is regarded as a gesture of love, respect and dignity.
The positive and goodwill communal spirit is also continued in a various of religious and cultural programs. In addition to eid, the Bugis organized a prolific traditions to commemorate its faith and identity, including Ramadan, a holy month dedicated by fasting and various religious activities. ''Maulu/ma maulu’'' (Mawlid), honoring the birth of Muhammad, Prophet Muhammmad, special ceremonial meals and colorful eggs would be given to the mosque attendees to monumentalize the meaningful day; ''Esso Sura'' (Ashura), remembrance of Muharram, where a special porridge (known as ''Bubu Petu'' and ''Bella Pitunrupa'') are prepared, the day also marked as a major shopping period for the Bugis-Makassar, as many would traditionally buy new house utensils during the Ashura. Furthermore, the Bugis and Makassar families would also arrange ''Massuro Baca'', special ceremonial doa and feast held a week before Ramadhan to remember the departed relatives, as well as a preparation to cleanse the inner-self before the holy month.
 Islamic elements are also materialized during celebrations on an individual level. Being a predominantly Muslim community, the act of ''Mabbarazanji/Barzanji'' (Mawlid al-Barzanjī), communal prayers and praise to Prophet Muhammad is regarded as among the focal points during such ceremonies. The Bugis would commonly organized a ''selamatan'' feast for divine favor, protection, thanksgiving and gratitude - including Islamic marital practices, weddings, newborn celebration, aqiqah, house construction ceremony, sending a pilgrim for umrah and hajj, and funerals.
The importance of such personal and communal ceremonies collectively act as a testament of their mainstream ethnic character. It serves as a bind, propelled to their rite of passage as a Muslims, Muslim and a manifestation of their cultural identity. The events also performed as a juxtaposition, intertwined between the essence of religion and custom; together with a sense of responsibility to solidify their values into the contemporary era.
Historically, there are also some regional events deeply rooted to their ancient beliefs, reflected by their pre-Islamic past, geographical location, local demographic and occupation. In a few agrarian Bugis communities, the grand harvest festivals of ''Mappangolo Datu Ase'', ''Mappadendang'', ''Manre Sipulung'', ''Maccerak Ase'' and ''Maccerak Rakkapeng'' acted as a thanksgiving and celebratory gesture for the abundance of harvest obtained. Meanwhile, in the coastal and lakeside communities where fishery industry is regarded to be in the utmost importance, they would commemorate with ''Maccera Tappareng'' and ''Maccerak Tasik''. However, with the rise of various socioeconomic and educational revolution, together with mass Industrialisation, industrialization and the introduction of modern History of agriculture, farming and fishing techniques throughout the 19th and 20th century, the collective impact of these festivals began to waned in favor of a much aligned practice with Islamic understanding among the mainstream Bugis society. Despite so, such regional celebration offered a brief outlook on the past, on a traditional ancient religion of a once agrarian community.
Islamic elements are also materialized during celebrations on an individual level. Being a predominantly Muslim community, the act of ''Mabbarazanji/Barzanji'' (Mawlid al-Barzanjī), communal prayers and praise to Prophet Muhammad is regarded as among the focal points during such ceremonies. The Bugis would commonly organized a ''selamatan'' feast for divine favor, protection, thanksgiving and gratitude - including Islamic marital practices, weddings, newborn celebration, aqiqah, house construction ceremony, sending a pilgrim for umrah and hajj, and funerals.
The importance of such personal and communal ceremonies collectively act as a testament of their mainstream ethnic character. It serves as a bind, propelled to their rite of passage as a Muslims, Muslim and a manifestation of their cultural identity. The events also performed as a juxtaposition, intertwined between the essence of religion and custom; together with a sense of responsibility to solidify their values into the contemporary era.
Historically, there are also some regional events deeply rooted to their ancient beliefs, reflected by their pre-Islamic past, geographical location, local demographic and occupation. In a few agrarian Bugis communities, the grand harvest festivals of ''Mappangolo Datu Ase'', ''Mappadendang'', ''Manre Sipulung'', ''Maccerak Ase'' and ''Maccerak Rakkapeng'' acted as a thanksgiving and celebratory gesture for the abundance of harvest obtained. Meanwhile, in the coastal and lakeside communities where fishery industry is regarded to be in the utmost importance, they would commemorate with ''Maccera Tappareng'' and ''Maccerak Tasik''. However, with the rise of various socioeconomic and educational revolution, together with mass Industrialisation, industrialization and the introduction of modern History of agriculture, farming and fishing techniques throughout the 19th and 20th century, the collective impact of these festivals began to waned in favor of a much aligned practice with Islamic understanding among the mainstream Bugis society. Despite so, such regional celebration offered a brief outlook on the past, on a traditional ancient religion of a once agrarian community.
 Music and dance has long occupied an integral part of the people in the South Sulawesi. It is considered as an ancient art form, pictured as a dramatic and complex encapsulation of the heritage. The Bugis performing arts can be broadly divided into four distinct categories — entertainment medium, ritualistic performance, court dance and martial arts.
In the Bugis culture, choreography is regarded as a form of folkloric entertainment. It has enjoyed a long creative industry and maintained a close relationship with the people. It is usually presented during the communal occasions and used as a celebratory expression to commemorate significant events. The best known Bugis dance genre are ''Pajaga'', and the more lively Pajogek — combining the elements of Ronggeng, Jaipongan, Jaipong and accompanied by a pair of ''gendeng'' (drum). Other type of dances include Zapin, Jeppeng, having a fusion of stronger Islamic elements; and ''Tari Paduppa'', a traditional welcome dance.
In the past, the performing arts played an extensive role on the Bugis ritualistic function and observance. During such Mysticism, magico-religious ceremonies, esoteric energy were present and ancient dance techniques were accomplished by a Bugis Shamanism, shaman, known as ''Bissu''. The depiction was characterized by a combination of spiritual aura and artistic elements to achieve a high level of possession-trance. The practice of possession used to be conducted by a ''Bissu'' during a vital cultural rite, such as to commemorate the beginning of the ''mappalili'' (Paddy field, paddy growing season) or during the important royal functions. Among the well-known ritualistic Bugis performance includes ''Tari Maggiri'', ''Tari Alusu'' and ''Maddewata''.
Music and dance has long occupied an integral part of the people in the South Sulawesi. It is considered as an ancient art form, pictured as a dramatic and complex encapsulation of the heritage. The Bugis performing arts can be broadly divided into four distinct categories — entertainment medium, ritualistic performance, court dance and martial arts.
In the Bugis culture, choreography is regarded as a form of folkloric entertainment. It has enjoyed a long creative industry and maintained a close relationship with the people. It is usually presented during the communal occasions and used as a celebratory expression to commemorate significant events. The best known Bugis dance genre are ''Pajaga'', and the more lively Pajogek — combining the elements of Ronggeng, Jaipongan, Jaipong and accompanied by a pair of ''gendeng'' (drum). Other type of dances include Zapin, Jeppeng, having a fusion of stronger Islamic elements; and ''Tari Paduppa'', a traditional welcome dance.
In the past, the performing arts played an extensive role on the Bugis ritualistic function and observance. During such Mysticism, magico-religious ceremonies, esoteric energy were present and ancient dance techniques were accomplished by a Bugis Shamanism, shaman, known as ''Bissu''. The depiction was characterized by a combination of spiritual aura and artistic elements to achieve a high level of possession-trance. The practice of possession used to be conducted by a ''Bissu'' during a vital cultural rite, such as to commemorate the beginning of the ''mappalili'' (Paddy field, paddy growing season) or during the important royal functions. Among the well-known ritualistic Bugis performance includes ''Tari Maggiri'', ''Tari Alusu'' and ''Maddewata''.
 Martial art also serves as an outlook that mirrors the symbolic ideals of its strong Militarism, militaristic tradition — courage, power, heroism, prestige, strength and preparation for war. Elements of Martial arts, martial skills were largely drawn from the local fighting culture and being incorporated in a repertoire of Bugis performing arts, such as in ''Manunencak/Mencak Baruga'' (Bugis Pencak silat, Pencak Silat), ''Mallanca'' and ''Masempek''. A close parallel can equally be observed in the Bugis war dance. The combatant qualities were emulated to commemorate the fortitude and spirit of the military class. The Bugis war dance of ''Penjaga Welado'', ''Pajaga Gilireng'' and ''Pajaga Mutaro'' extensively captures such rendition.
Historically enjoyed a royal patronage, the Bugis Historical dance, court ballet consist of a juxtaposed movement of fast and slow; and a contrast between passive and active, such adaptation can be seen in the Bugis courtly portrayal in ''Pajaga Boneballa Anakdara'', ''Pajaga Lelengbata Tulolo'' and ''Pajaga Lili''. The artistic styles constitute the essence of Bugis Aesthetics, aesthetic impulses — involving various movements, gestures, poise, balance and music. Historically among the members of Bugis nobility, dance was perceived as a social importance to develop and mold an individual's personal qualities on ''kedo'' (manners, mannerism) and ''ampe'' (Speech act, speech) according to the royal standards and etiquettes.
The Bugis also hosted a multitude of classical instruments, including ''Soling'', flutes; ''Kacapi'' and ''Talindo'', string musical instruments; ''Jalappa/Kancing-Kancing'', a traditional cymbal; ''Aloso/Laluso'', a Bugis percussion instrument, similar to Shekere; ''Gesok–Gesok/Keso–Keso'', a Bugis-styled Rebab; ''Kendang, Gendrang'' (not to be mistaken with Makassarese "Ganrang"), a two-headed drum; and ''Puik Puik/Pui–Pui'', a classical trumpet. As with many Sulawesian musical traditions, the Gendrang occupied a prominent and sacred role in Bugis musical traditions forming the base of many accompaniments, although somewhat less revered compared with the Makassarese. In recent years, Makassarese Ganrang traditions have eroded the education of Bugis Gendrang, although sharing many similarities, such as using multiples drums with different patterns to create syncophation.
The Bugis art of dance was predominantly being inherited via an oral tradition from one generation to another. To some extent, each of the artforms serves as an episode to the past and navigated as a kaleidoscope narration on the development of their ethnic identity – from the once prevalent ancient ancestral beliefs led by a ''Gender in Bugis society, Bissu''; the royal court and military tradition during the classical era; the extensive bilateral cultural exchange with the Makassarese; and the subsequent Islamisation of the mainstream Bugis society.
Martial art also serves as an outlook that mirrors the symbolic ideals of its strong Militarism, militaristic tradition — courage, power, heroism, prestige, strength and preparation for war. Elements of Martial arts, martial skills were largely drawn from the local fighting culture and being incorporated in a repertoire of Bugis performing arts, such as in ''Manunencak/Mencak Baruga'' (Bugis Pencak silat, Pencak Silat), ''Mallanca'' and ''Masempek''. A close parallel can equally be observed in the Bugis war dance. The combatant qualities were emulated to commemorate the fortitude and spirit of the military class. The Bugis war dance of ''Penjaga Welado'', ''Pajaga Gilireng'' and ''Pajaga Mutaro'' extensively captures such rendition.
Historically enjoyed a royal patronage, the Bugis Historical dance, court ballet consist of a juxtaposed movement of fast and slow; and a contrast between passive and active, such adaptation can be seen in the Bugis courtly portrayal in ''Pajaga Boneballa Anakdara'', ''Pajaga Lelengbata Tulolo'' and ''Pajaga Lili''. The artistic styles constitute the essence of Bugis Aesthetics, aesthetic impulses — involving various movements, gestures, poise, balance and music. Historically among the members of Bugis nobility, dance was perceived as a social importance to develop and mold an individual's personal qualities on ''kedo'' (manners, mannerism) and ''ampe'' (Speech act, speech) according to the royal standards and etiquettes.
The Bugis also hosted a multitude of classical instruments, including ''Soling'', flutes; ''Kacapi'' and ''Talindo'', string musical instruments; ''Jalappa/Kancing-Kancing'', a traditional cymbal; ''Aloso/Laluso'', a Bugis percussion instrument, similar to Shekere; ''Gesok–Gesok/Keso–Keso'', a Bugis-styled Rebab; ''Kendang, Gendrang'' (not to be mistaken with Makassarese "Ganrang"), a two-headed drum; and ''Puik Puik/Pui–Pui'', a classical trumpet. As with many Sulawesian musical traditions, the Gendrang occupied a prominent and sacred role in Bugis musical traditions forming the base of many accompaniments, although somewhat less revered compared with the Makassarese. In recent years, Makassarese Ganrang traditions have eroded the education of Bugis Gendrang, although sharing many similarities, such as using multiples drums with different patterns to create syncophation.
The Bugis art of dance was predominantly being inherited via an oral tradition from one generation to another. To some extent, each of the artforms serves as an episode to the past and navigated as a kaleidoscope narration on the development of their ethnic identity – from the once prevalent ancient ancestral beliefs led by a ''Gender in Bugis society, Bissu''; the royal court and military tradition during the classical era; the extensive bilateral cultural exchange with the Makassarese; and the subsequent Islamisation of the mainstream Bugis society.