British colonies in North America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the
/ref> The Dominion of Canada was formed under the British North America (BNA) Act, 1867, also referred to as the Constitution Act, 1867. Following

 When the
When the
 Although
Although
/ref> Other denominations also at one time included Bermuda with Nova Scotia or Canada. Following the separation of the Church of England from the
 Nova Scotia was split into modern-day
Nova Scotia was split into modern-day 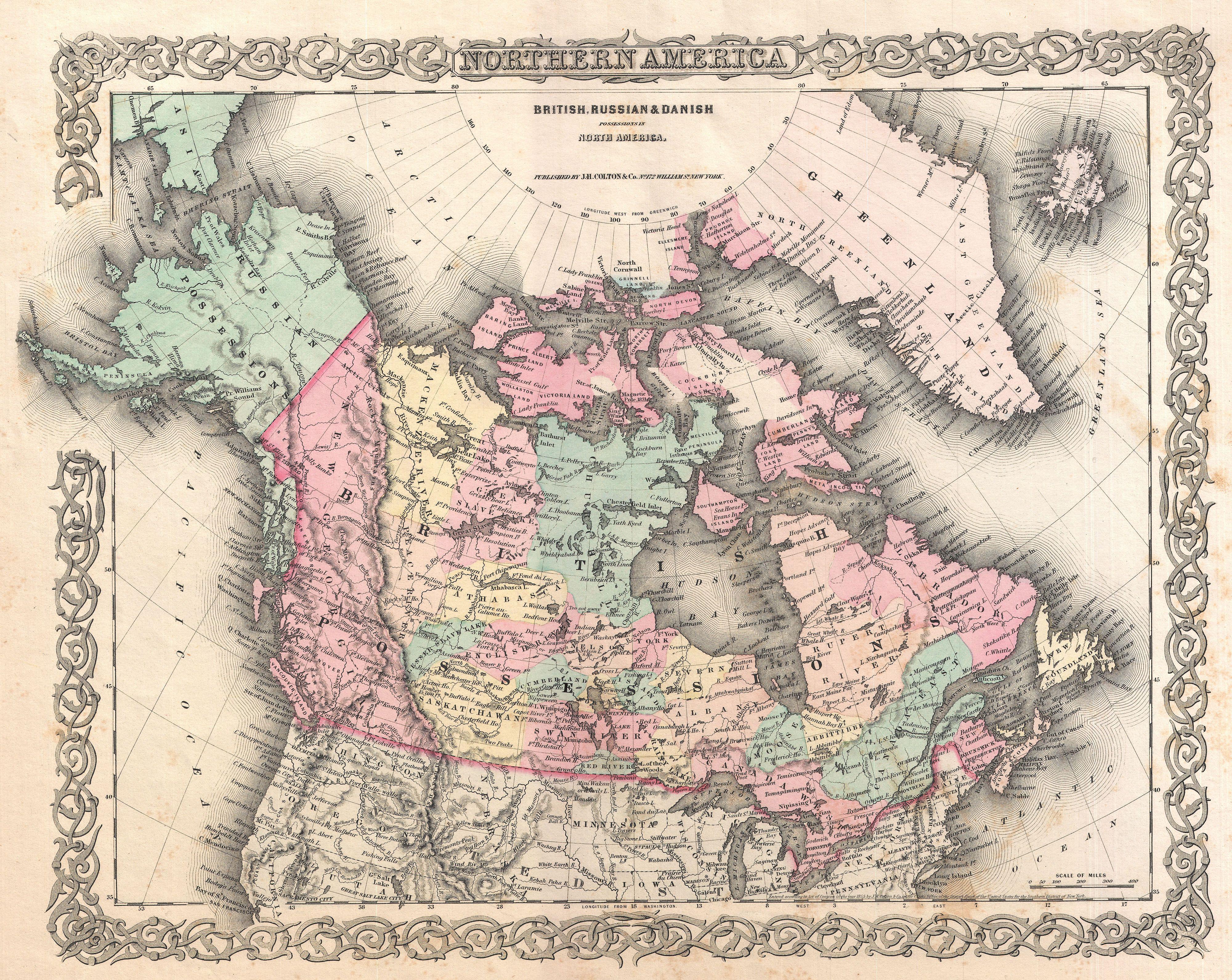 After threats and squabbles over rich timber lands, the boundary with
After threats and squabbles over rich timber lands, the boundary with
64
"Up to 1846 the postal services in British North America were administered from London through a deputy residing in the colonies."
excerpt and text search
* Cooke, Jacob E. ''Encyclopedia of the North American Colonies'' (3 vol 1993) * Foster, Stephen, ed. ''British North America in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries'' (Oxford History of the British Empire Companion) (2014
excerpt and text search
11 essays by scholars * Garner, John. ''The franchise and politics in British North America, 1755–1867'' (U of Toronto Press, 1969) * Gipson, Lawrence Henry. ''The British Empire Before the American Revolution'' (15 vol., 1936–70), extremely comprehensive study; Pulitzer Prize * Morton, W. L. ''The Kingdom of Canada: A General History from Earliest Times'' (1969) * Savelle, Max. ''Empires To Nations: Expansion In America 1713–1824'' (1974
online
{{Coord missing, North America Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former colonies in North America History of Canada by period 19th century in Canada 19th century in the British Empire 19th century in North America 1790s in Canada 1900s in Canada English-speaking countries and territories
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
began in the 16th century in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James (Powhatan) River about southwest of the center of modern Williamsburg. It was ...
, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
along the Atlantic coast of North America.
The British Empire's colonial territories in North America were greatly expanded in connection with the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the S ...
, which formally concluded the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
, referred to by the English colonies in North America as the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
, and by the French colonies as . With the ultimate acquisition of most of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
(), British territory in North America was more than doubled in size, and the exclusion of France also dramatically altered the political landscape of the continent.
The term ''British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas fro ...
'' was used to refer to the British Empire's colonial territories in North America prior to the United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ( ...
, most famously in the 1774 address of Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
to the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Nav ...
entitled: ''A Summary View of the Rights of British America''.
The term ''British North America'' was initially used following the subsequent Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Great Britain and representatives of the United States of America on September 3, 1783, officially ended the American Revolutionary War and overall state of conflict ...
, which concluded the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
and confirmed the independence of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
's Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
. The terms British America and British North America continued to be used for Britain's remaining territories in North America, but the term British North America came to be used more consistently in connection with the provinces that would eventually form the Dominion of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, following the Report on the Affairs of British North America
The ''Report on the Affairs of British North America'', (1839) commonly known as the ''Durham Report'' or ''Lord Durham's Report'', is an important document in the history of Quebec, Ontario, Canada and the British Empire.
The notable Briti ...
(1839), called the Durham Report.Lord Durham, 1839. "Report on the Affairs of British North America from the Earl of Durham, Her Majesty's High Commissioner"/ref> The Dominion of Canada was formed under the British North America (BNA) Act, 1867, also referred to as the Constitution Act, 1867. Following
royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
of the BNA Act, three of the provinces of British North America (New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
(which would become the Canadian provinces of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
)) joined to form "''One Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
under the Crown of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, with a Constitution similar in Principle to that of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
,''" on July 1, 1867, the date of Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominio ...
.
The Atlantic island of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
(originally administered by the Virginia Company and, with The Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the a ...
, considered with North America prior to 1783), was grouped with the Maritime provinces from 1783 until formation of the Dominion of Canada in 1867, and thereafter generally with the colonies in the British West Indies (although the Church of England continued to place Bermuda under the Bishop of Newfoundland
The Anglican Diocese of Newfoundland was, from its creation in 1839 until 1879, the Diocese of Newfoundland and Bermuda, with the Cathedral of St. John the Baptist at St. John's, Newfoundland, and a chapel-of-ease named ''Trinity Church'' in the ...
until 1919).
Over its duration, British North America comprised the British Empire's colonial territories in North America from 1783 to 1907, not including the Caribbean. These territories include those forming modern-day Canada, as well as all or large parts of six Midwestern U.S. states (Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and t ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, and the northeastern part of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
), which were formed out of the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
, and large parts of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, which had originally been within the French territory of Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and earl ...
.
Political divisions

 When the
When the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
began its efforts to settle in North America in the late 16th Century, it ignored Spain's long-asserted claim of sovereignty over the entire continent (Spain's similar claim to all of South America had been refuted when the Pope had divided that continent between it and Portugal in the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
). Spain's area of settlement was limited to only very southern parts of North America, however, and it had little ability to enforce its sovereignty. Disregarding, as did Spain, the sovereignty of the indigenous nations, England claimed the entire continent (though its western and northern boundaries were not yet clear), which it named ''Virginia'' in honour of the virgin queen, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
.
England's first successful settlement in North America was Jamestown, established by the Virginia Company of London in 1607, with the second actually being the Atlantic Ocean archipelago of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, added to the territory of the same company in 1612 (the company having been in occupation of the archipelago since the 1609 wreck there of its flagship, the Sea Venture
''Sea Venture'' was a seventeenth-century English sailing ship, part of the Third Supply mission to the Jamestown Colony, that was wrecked in Bermuda in 1609. She was the 300 ton purpose-built flagship of the London Company and a highly unusual ...
). Two areas of settlement in North America had been laid out in 1606, with the name ''Virginia'' coming to connote the southern area, between Latitude 34° and Latitude 41° North, administered by the Virginia Company of London. The short form of that company's name was actually the ''London Company'', but it came to be known popularly as the ''Virginia Company''. The northern area of settlement, which extended to 45° North (an area that would come to be known as New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
), was to be administered and settled by the Virginia Company of Plymouth
The Plymouth Company, officially known as the Virginia Company of Plymouth, was a division of the Virginia Company with responsibility for colonizing the east coast of America between latitudes 38° and 45° N.
History
The merchants (with ...
(or Plymouth Company), which established the Popham Colony in what is now Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
in 1606, but this was quickly abandoned and Plymouth Company's territory was absorbed into the London Company's.
Over the course of the 17th Century, ''Virginia'' would come to refer only to the polity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of ...
that is today the Commonwealth of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
in the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
, with later areas of settlement on the continent considered separate colonies under their own local administrations and all collectively designated as ''America'' (less often as ''North America''). The Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
(including the Principality of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
) and Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
remained separate nations until their 1707 unification to form the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
. Scotland's attempts to establish its own colonies in North America and Central America before 1707 had been short-lived, but England brought substantial trans-Atlantic possessions into the new union, when English America became British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas fro ...
. In 1775, on the eve of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, British America included territories in the Western Hemisphere northeast of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
, apart from the islands and claims of the British West Indies. These were:
* Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
* British Arctic Territories
The British Arctic Territories were a constituent region of British North America, composed of islands to the north of continental North America. They are now known as the Arctic Archipelago.
The British claim to the area was based on the dis ...
* the Floridas (East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
and West Florida, administered separately)
* Indian Reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty,
that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band."
In ...
* Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
* North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Due to the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact bounda ...
* Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
* Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
* Rupert's Land (the territory of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
)
* St. John's Island (later Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
)
* the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
(each one administered separately, soon to become the United States):
** Connecticut Colony
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
** Delaware Colony
Delaware Colony in the North American Middle Colonies consisted of land on the west bank of the Delaware River Bay. In the early 17th century the area was inhabited by Lenape and possibly the Assateague tribes of Native Americans. The first Eu ...
** Province of Georgia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
** Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an Kingdom of England, English and later British Empire, British colony in North America that existed from 1632 until 1776, when it joined the other twelve of the Thirteen Colonies in American Revolution, rebellion ag ...
** Province of Massachusetts Bay
The Province of Massachusetts Bay was a colony in British America which became one of the thirteen original states of the United States. It was chartered on October 7, 1691, by William III and Mary II, the joint monarchs of the kingdoms of ...
** Province of New Hampshire
The Province of New Hampshire was a colony of England and later a British province in North America. The name was first given in 1629 to the territory between the Merrimack and Piscataqua rivers on the eastern coast of North America, and was nam ...
** Province of New Jersey
The Province of New Jersey was one of the Middle Colonies of Colonial America and became the U.S. state of New Jersey in 1783. The province had originally been settled by Europeans as part of New Netherland but came under English rule after t ...
** Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the U ...
** Province of North Carolina
** Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to Wi ...
** Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations
The Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations was one of the original Thirteen Colonies established on the east coast of America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. It was founded by Roger Williams. It was an English colony from 1636 until 1 ...
** Province of South Carolina
** Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
Bermuda
The Somers Isles, orBermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, had been occupied by the Virginia Company since its flagship, the Sea Venture
''Sea Venture'' was a seventeenth-century English sailing ship, part of the Third Supply mission to the Jamestown Colony, that was wrecked in Bermuda in 1609. She was the 300 ton purpose-built flagship of the London Company and a highly unusual ...
, was wrecked there in 1609, and the archipelago was officially added to the company's territory in 1612, then managed by a spin-off, the Somers Isles Company, until 1684, but maintained close links with Virginia and Carolina Colony (which had subsequently been settled from Bermuda under William Sayle
Captain William Sayle (c. 1590–1671) was a prominent British landholder who was Governor of Bermuda in 1643 and again in 1658. As an Independent in religion and politics, and an adherent of Oliver Cromwell, he was dissatisfied with life in Ber ...
in 1670). The British Government originally grouped Bermuda with North America (the archipelago is approximately east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
(with ''Cape Point'' on Hatteras Island being the nearest landfall); south of Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
; northeast of Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, and due north of the British Virgin Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = Territorial song
, song = "Oh, Beautiful Virgin Islands"
, image_map = File:British Virgin Islands on the globe (Americas centered).svg
, map_caption =
, mapsize = 290px
, image_map2 = Brit ...
.
 Although
Although Bermudians
This is a demography of the population of Bermuda including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population, including changes in the demographi ...
, with close ties of blood and trade to the southern continental colonies (especially Virginia and South Carolina), tended towards the rebels early in the American War of Independence, the control of the surrounding Atlantic by the Royal Navy meant there was no likelihood of the colony joining the rebellion. Although the rebels were supplied with ships and gunpowder by the Bermudians, Bermudian privateers soon turned aggressively on rebel shipping. After the acknowledgement by the British Government of the independence of the thirteen rebellious continental colonies in 1783, Bermuda was grouped regionally by the British Government with The Maritimes
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of C ...
and Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, and, more widely, with British North America.
Following the war, the Royal Navy spent a dozen years charting the barrier reef around Bermuda to discover the channel that enabled access to the northern lagoon, the Great Sound
The Great Sound is large ocean inlet (a sound) located in Bermuda. It may be the submerged remains of a Pre- Holocene volcanic caldera. Other geologists dispute the origin of the Bermuda Pedestal as a volcanic hotspot.
Geography
The Great Sound ...
, and Hamilton Harbour
Hamilton Harbour, formerly known as Burlington Bay, lies on the western tip of Lake Ontario, bounded on the northwest by the City of Burlington, on the south by the City of Hamilton, and on the east by Hamilton Beach (south of the Burlington ...
. Once this had been located, a base was established (initially at St. George's before the construction of the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda
HMD Bermuda ( Her/His Majesty's Dockyard, Bermuda) was the principal base of the Royal Navy in the Western Atlantic between American independence and the Cold War. The Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda had occupied a useful position astr ...
) in 1794, when Vice-Admiral Sir George Murray
Sir George Murray (6 February 1772 – 28 July 1846) was a British soldier and politician from Scotland.
Background and education
Murray was born in Perth, Scotland, the second son of Sir William Murray, of Ochtertyre, 5th Baronet (see Murr ...
, Commander-in-Chief of the new River St. Lawrence and Coast of America and North America and West Indies Station, set up the first Admiralty House, Bermuda at Rose Hill, St. George's. In 1813, the area of command became the ''North America Station'' again, with the West Indies falling under the Jamaica Station, and in 1816 it was renamed the ''North America and Lakes of Canada Station''. The headquarters was initially in Bermuda during the winter and Halifax during the summer (both of which were designated as Imperial fortresses, along with Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
and Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
), but Bermuda, became the year-round headquarters of the Station in 1821, when the area of command became the ''North America and West Indies Station''.Marilyn Gurney, The Kings Yard, Maritime Command Museum, Halifax. The Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax was finally transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack subma ...
in 1907.''The Andrew and The Onions: The Story of The Royal Navy in Bermuda, 1795–1975'', by Lieutenant-Commander B. Ian D. Stranack. Bermuda Maritime Museum Press
Prior to 1784, the Bermuda Garrison had been placed under the military Commander-in-Chief America in New York during the American War of Independence. A small regular infantry garrison had existed from 1701 to 1768, alongside the militia, and part of the Royal Garrison Battalion
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
had been stationed there in 1778 but that battalion was disbanded in Bermuda in 1784. The regular military garrison was re-established at Bermuda in 1794 by part of the British Army's 47th Regiment of Foot
The 47th (Lancashire) Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in Scotland in 1741. It served in North America during the Seven Years' War and American Revolutionary War and also fought during the Napoleonic Wars and ...
and the Board of Ordnance also stationed an invalid company of the Royal Artillery
The Royal Regiment of Artillery, commonly referred to as the Royal Artillery (RA) and colloquially known as "The Gunners", is one of two regiments that make up the artillery arm of the British Army. The Royal Regiment of Artillery comprises t ...
there soon after. The Bermuda garrison was to be part of the Nova Scotia Command until 1869 (in 1815, Lieutenant-General Sir George Prevost was ''Captain-General and Governor-in-Chief in and over the Provinces of Upper-Canada, Lower-Canada, Nova-Scotia, and New~Brunswick, and their several Dependencies, Vice-Admiral of the same, Lieutenant-General and Commander of all His Majesty’s Forces in the said Provinces of Lower Canada and Upper-Canada, Nova-Scotia and New-Brunswick, and their several Dependencies, and in the islands of Newfoundland, Prince Edward, Cape Breton and the Bermudas, &c. &c. &c.'' Beneath Prevost, the staff of the British Army in ''the Provinces of Nova-Scotia, New-Brunswick, and their Dependencies, including the Islands of Newfoundland, Cape Breton, Prince Edward and Bermuda'' were under the Command of Lieutenant-General Sir John Coape Sherbrooke
General Sir John Coape Sherbrooke, (29 April 1764 – 14 February 1830) was a British soldier and colonial administrator. After serving in the British army in Nova Scotia, the Netherlands, India, the Mediterranean (including Sicily), and Spa ...
. Below Sherbrooke, the Bermuda Garrison was under the immediate control of the Lieutenant-Governor of Bermuda, Major-General George Horsford).), and was expanded greatly during the 19th Century, both to defend the colony as a naval base and to launch amphibious operations against the Atlantic coast of the United States in any war that should transpire.
The Royal Navy, British Army, Royal Marines, and Colonial Marines forces based in Bermuda carried out actions of this sort during the American War of 1812, when the Royal Navy's blockade of the Atlantic seaboard of the United States was orchestrated from Bermuda (New England, where support for the United States Government's war against Britain was low and from which Britain continued to receive grain to feed its army engaged in the Peninsular War, was at first excluded from this blockade). In 1813, Lieutenant-Colonel, Sir Thomas Sydney Beckwith arrived in Bermuda to command an expeditionary force tasked with raiding the Atlantic Seaboard of the United States, specifically in the region of Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
. The force was to be composed of the infantry battalion then on garrison duty in Bermuda, the 102nd Regiment of Foot
The 102nd Regiment of Foot (Royal Madras Fusiliers) was a regiment of the British Army raised by the Honourable East India Company in 1742. It transferred to the command of the British Army in 1862. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with t ...
(with its Commanding Officer, Lieutenant-Colonel Charles James Napier
General Sir Charles James Napier, (; 10 August 178229 August 1853) was an officer and veteran of the British Army's Peninsular and 1812 campaigns, and later a Major General of the Bombay Army, during which period he led the military conquest o ...
as Second-in-Command) forming one brigade with Royal Marines and a unit recruited from French prisoners-of-war, which was under Napier's command, and another brigade formed under Lieutenant-Colonel Williams of the Royal Marines. The force took part in the Battle of Craney Island on 22 June 1813. The most famous action carried out during the war by forces from Bermuda was the Chesapeake Campaign, including the Burning of Washington in retribution for the "wanton destruction of private property along the north shores of Lake Erie" by American forces under Col. John Campbell in May 1814, the most notable being the Raid on Port Dover
The Raid on Port Dover was an episode during the War of 1812. American troops crossed Lake Erie to capture or destroy stocks of grain and destroy mills at Port Dover, Ontario, which were used to provide flour for British troops stationed on t ...
to draw United States forces away from the Canadian border. In 1828, His Excellency George, Earl of Dalhousie, (Baron Dalhousie, of Dalhousie Castle,) Knight Grand Cross of the Most Honourable Military Order of the Bath was ''Captain General and Governor in Chief in and over the Provinces of Lower-Canada, Upper-Canada, Nova-Scotia, and New-Brunswick, and their several dependencies, Vice-Admiral of the same, Lieutenant-General and Commander of all His Majesty’s Forces in the said Provinces, and their several dependencies, and in the Islands of Newfoundland, Prince Edward, and Bermuda, &c. &c c. &c.'' Beneath Dalhousie, the ''Provinces of Nova-Scotia, New-Brunswick, and their Dependencies, including the Island of Newfoundland, Cape Breton, Prince Edward and Bermuda'' were under the Command of His Excellency Lieutenant-General Sir James Kempt GCB, GCH''.
The established Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
in Bermuda (since 1978, titled the Anglican Church of Bermuda) and Newfoundland was attached to the See of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
from 1825 to 1839 and from 1787 to 1839, respectively. From 1839, the island of Newfoundland and the coast of Labrador, as well as Bermuda, became parts of the Diocese of Newfoundland and Bermuda, with the shared Bishop ( Aubrey George Spencer being the first) alternating his residence between the two colonies. A separate Bermuda Synod was incorporated in 1879, but continued to share its Bishop with Newfoundland until 1919, when the separate position of Bishop of Bermuda
The Bishop of Bermuda is an episcopal title given to the ordinary of the Anglican Church of Bermuda, one of six extra-provincial Anglican churches within the Church of England overseen by the Archbishop of Canterbury. The present Bishop is Nick ...
was created (in 1949, on Newfoundland becoming a province of Canada, the Diocese of Newfoundland became part of the Anglican Church of Canada
The Anglican Church of Canada (ACC or ACoC) is the province of the Anglican Communion in Canada. The official French-language name is ''l'Église anglicane du Canada''. In 2017, the Anglican Church counted 359,030 members on parish rolls in 2,2 ...
; the Church of England in Bermuda, which was re-titled the Anglican Church of Bermuda in 1978, is today one of six extra-provincial Anglican churches
The extra-provincial Anglican churches are a group of small, semi-independent church entities within the Anglican Communion. Unlike the larger member churches of the Communion, extra-provincial churches are not part of an ecclesiastical province an ...
within the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
overseen by the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Just ...
).Anglican Diocese of Eastern Newfoundland and Labrador/ref> Other denominations also at one time included Bermuda with Nova Scotia or Canada. Following the separation of the Church of England from the
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Roman Catholic worship was outlawed in England (subsequently ''Britain'') and its colonies, including Bermuda, until the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791, and operated thereafter under restrictions until the Twentieth Century. Once Roman Catholic worship was established, Bermuda formed part of the Archdiocese of Halifax, Nova Scotia until 1953, when it was separated to become the Apostolic Prefecture of Bermuda Islands. The congregation of the first African Methodist Episcopal Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Church, usually called the AME Church or AME, is a predominantly African American Methodist denomination. It adheres to Wesleyan-Arminian theology and has a connexional polity. The African Methodist Episcopal ...
in Bermuda (St. John African Methodist Episcopal Church, erected in 1885 in Hamilton Parish
Hamilton Parish (originally Bedford Parish) is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It was renamed for Scottish aristocrat James Hamilton, 2nd Marquess of Hamilton (1589-1625) when he purchased the shares originally held in the Virginia Company ...
) had previously been part of the British Methodist Episcopal Church
The British Methodist Episcopal Church (BMEC) is a Protestant church in Canada that has its roots in the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AMEC) of the United States.
History
The AMEC had been formed in 1816 when a number of black congregations ...
of Canada.
New France (Nouvelle-France)
Britain acquired most of Acadia or Acadie, Nouvelle-France, in connection with Queen Anne's War of 1702–1713, and subsequent lands later. These territories would become the provinces ofNova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
, and Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, as well as parts of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
and territories that would eventually form part of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
.
Britain acquired much of the remainder of Canada (New France)
The colony of Canada was a French colony within the larger territory of New France. It was claimed by France in 1535 during the second voyage of Jacques Cartier, in the name of the French king, Francis I. The colony remained a French territory u ...
and the eastern half of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
, including West Florida, from France, and East Florida from Spain, by the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the S ...
, which ended the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
. (Spain had not taken possession of any of Louisiana, which had been ceded to it under the Treaty of Fontainebleau, from France until 1769.) By the Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Great Britain and representatives of the United States of America on September 3, 1783, officially ended the American Revolutionary War and overall state of conflict ...
, the United States acquired the part of Quebec south of the Great Lakes; at the same time Spain gained West Florida and regained East Florida.
 Nova Scotia was split into modern-day
Nova Scotia was split into modern-day Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
in 1784. The part of Quebec retained after 1783 was split into the primarily French-speaking Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec ...
and the primarily English-speaking Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North Americ ...
in 1791.
After the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
, the Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
established the 49th parallel as the United States–British North America border from Rupert's Land west to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
. Then, in 1846, Britain and the United States split the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
. The United States was assigned lands south of the 49th parallel, but Britain retained all of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
(including south of the 49th parallel).
 After threats and squabbles over rich timber lands, the boundary with
After threats and squabbles over rich timber lands, the boundary with Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
was clarified by the Webster–Ashburton Treaty of 1842.
The Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for the provinces of Lower Canada and Upper Canada, two historical British colonies in present-day Canada. The two colonies were formed in 1791, when the British Parliament passed the '' Constitutional Act'', ...
were united into the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
in 1841.
On 1 July 1867, the Dominion of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec Ci ...
was created by the British North America Act, 1867. The confederation process brought together the provinces of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia. The former Province of Canada was split back into its two parts, with Canada East
Canada East (french: links=no, Canada-Est) was the northeastern portion of the United Province of Canada. Lord Durham's Report investigating the causes of the Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions recommended merging those two colonies. The ne ...
(Lower Canada) being renamed Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
, and Canada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
(Upper Canada) renamed Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
.
Following confederation in 1867, the British Army withdrew from Canada in 1871, handing military defence over to the Canadian Militia. With the consequent abolition of the British Army's Nova Scotia Command, and the office of its Commander-in-Chief for British North America, the still-growing Bermuda Garrison was elevated to a separate ''Bermuda Command''.]
Newfoundland, Rupert's Land and Other Territories of British North America
AlthoughNewfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
remained separate from Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
until 1949, Bermuda, following Canadian confederation, was increasingly perceived by the British Government as in, or at least grouped for convenience with, the British West Indies. The last administrative link to the Maritimes was the established church. In 1879 the Synod of the Church of England in Bermuda was formed and a Diocese of Bermuda became separate from the Diocese of Newfoundland, but continued to be grouped under the ''Bishop of Newfoundland and Bermuda'' until 1919, when Newfoundland and Bermuda each received its own bishop.
In 1870, Rupert's Land, which consisted of territories of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
, was annexed to Canada as the Northwest Territories, North-West Territories (NWT) and the new province of Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
. British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
, the British colony on the west coast north of the 49th parallel, including all of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
, joined as Canada's sixth province in 1871, and Prince Edward Island joined as the seventh in 1873. The boundary of British Columbia with Washington Territory was settled by arbitration in 1872, and with Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U ...
by arbitration in 1903.
The Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark).
Situated in the northern extremity of No ...
was ceded by Britain to Canada in 1880 and added to the North-West Territories. Later on, large sections of the NWT were split off as new territories (the Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
in 1898 and Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the '' Nunavut Act'' and the '' Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'' ...
in 1999), or provinces (Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
, both in 1905), or were added to existing provinces (Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec, in stages ending in 1912).
In 1907, the sole remaining British North American colony, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, was granted the status of a Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
, although starting in 1934 it returned to British administration under the Commission of Government. In 1949, the island of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, and its associated mainland territory of Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, joined Canada as the tenth province.
Canada became semi-independent beginning in 1867, and fully sovereign on foreign affairs beginning with the Statute of Westminster 1931
The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown.
Passed on 11 December 1931, the statute increased the sovereignty of the ...
. Canada gained the right to establish and accept foreign embassies, with the first one being in Washington, D.C.
Then the last vestiges of Canada's constitutional dependency upon Britain remained until Canadians from various provinces agreed on an internal procedure for amending the Canadian Constitution. This agreement was implemented when the British Parliament passed the Canada Act 1982 at the request of the Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada (french: Parlement du Canada) is the federal legislature of Canada, seated at Parliament Hill in Ottawa, and is composed of three parts: the King, the Senate, and the House of Commons. By constitutional convention, ...
. Maton, 1998, article
British North America colonies
Following the 1776 declaration of independence of the colonies that were to form the United States (which was to be recognised by the British Government in 1783), the areas that remained under British sovereignty were administered by the Home Office, which had been formed on 27 March 1782, and which also controlled the military until this was transferred to theWar Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
in 1794. The Home Office referred to the remaining North American continental colonies and the archipelago of Bermuda (located off North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
) as ''British North America'' and their administration was increasingly linked. In 1801, administration of the colonies was moved from the Home Office to the War Office (which became the ''War and Colonial Office''), with the Secretary of State for War
The Secretary of State for War, commonly called War Secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The Secretary of State for War headed the War Office and ...
thus becoming the Secretary of State for War and the Colonies until 1854, when the ''War and Colonial Office'' was split into the War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
(under the ''Secretary of State for War'') and the Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of c ...
(under the Secretary of State for the Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the British Cabinet minister in charge of managing the United Kingdom's various colonial dependencies.
History
The position was first created in 1768 to deal with the increas ...
).
Prior to the signing of the 1846 Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to ...
, the North American continental colonies were as follows:
*Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the ...
(previously Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North Americ ...
and Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec ...
)
*Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
*Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
*New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
*Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
* Rupert's Land
*British Arctic Territories
The British Arctic Territories were a constituent region of British North America, composed of islands to the north of continental North America. They are now known as the Arctic Archipelago.
The British claim to the area was based on the dis ...
*Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the disputed Oregon Country. It was explored by the North West Company bet ...
/Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
(shared with the United States)
Administration
Besides the local colonial governments in each colony, British North America was administered directly via London. From 1783 through 1801, the British Empire, including British North America, was administered by the Home Office and by theHome Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, otherwise known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The home secretary leads the Home Office, and is responsible for all nationa ...
, then from 1801 to 1854 by the War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
(which became the ''War and Colonial Office'') and Secretary of State for War and Colonies (as the Secretary of State for War
The Secretary of State for War, commonly called War Secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The Secretary of State for War headed the War Office and ...
was renamed). From 1824, the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
was divided by the War and Colonial Office into four administrative departments, including ''NORTH AMERICA'', the ''WEST INDIES'', ''MEDITERRANEAN AND AFRICA'', and ''EASTERN COLONIES'', of which North America included:
NORTH AMERICA
* Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North Americ ...
, Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec ...
* New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
* Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
The Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of c ...
and War Office, and the Secretary of State for the Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the British Cabinet minister in charge of managing the United Kingdom's various colonial dependencies.
History
The position was first created in 1768 to deal with the increas ...
and the Secretary of State for War, were separated in 1854. The War Office, from then until the 1867 confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical iss ...
of the ''Dominion of Canada'', split the military administration of the British colonial and foreign stations into nine districts: ''North America And North Atlantic''; ''West Indies''; ''Mediterranean''; ''West Coast Of Africa And South Atlantic''; ''South Africa''; ''Egypt And The Sudan''; ''INDIAN OCEAN''; ''Australia''; and ''China''. North America And North Atlantic included the following ''stations'' (or garrisons):
NORTH AMERICA AND NORTH ATLANTIC
* New Westminster (British Columbia)
* Newfoundland
* Quebec
* Halifax
* Kingston, Canada West
* Bermuda
The postal system had a deputy based in British North America, with administration from London.''Rapport de L'assemblée Annuelle''. Canadian Historical Association, 1948. p64
"Up to 1846 the postal services in British North America were administered from London through a deputy residing in the colonies."
See also
* Atlantic history *British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas fro ...
* British West Indies
*British North America Acts
The British North America Acts 1867–1975 are a series of Acts of Parliament that were at the core of the constitution of Canada. Most were enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom and some by the Parliament of Canada. In Canada, som ...
*British colonization of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas was the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland and, after 1707, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the lat ...
*Canada under British rule
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
*Colonial government in the Thirteen Colonies The governments of the Thirteen Colonies of British America developed in the 17th and 18th centuries under the influence of the British constitution. After the Thirteen Colonies had become the United States, the experience under colonial rule would ...
*Colonial history of the United States
The colonial history of the United States covers the history of European colonization of North America from the early 17th century until the incorporation of the Thirteen Colonies into the United States after the Revolutionary War. In the ...
* Economic history of the United States#Colonial economy
* Former colonies and territories in Canada
* Historiography of the British Empire, with long bibliography
* History of Canada
*New England Colonies
The New England Colonies of British America included Connecticut Colony, the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Massachusetts Bay Colony, Plymouth Colony, and the Province of New Hampshire, as well as a few smaller short-lived colo ...
References
Sources
* * * *Further reading
* Bailyn, Bernard. ''The Peopling of British North America: An Introduction'' (1988excerpt and text search
* Cooke, Jacob E. ''Encyclopedia of the North American Colonies'' (3 vol 1993) * Foster, Stephen, ed. ''British North America in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries'' (Oxford History of the British Empire Companion) (2014
excerpt and text search
11 essays by scholars * Garner, John. ''The franchise and politics in British North America, 1755–1867'' (U of Toronto Press, 1969) * Gipson, Lawrence Henry. ''The British Empire Before the American Revolution'' (15 vol., 1936–70), extremely comprehensive study; Pulitzer Prize * Morton, W. L. ''The Kingdom of Canada: A General History from Earliest Times'' (1969) * Savelle, Max. ''Empires To Nations: Expansion In America 1713–1824'' (1974
online
{{Coord missing, North America Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former colonies in North America History of Canada by period 19th century in Canada 19th century in the British Empire 19th century in North America 1790s in Canada 1900s in Canada English-speaking countries and territories