British Empire in World War II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 When the
When the
 On 1 September 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Two days later, on 3 September, after a British ultimatum to Germany to cease military operations was ignored, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Britain's declaration of war automatically committed
On 1 September 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Two days later, on 3 September, after a British ultimatum to Germany to cease military operations was ignored, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Britain's declaration of war automatically committed
 Kenya Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve 1945
While the war was initially intended to be limited, resources were mobilized quickly, and the first shots were fired almost immediately. Just hours after the Australian declaration of war, a gun at
Kenya Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve 1945
While the war was initially intended to be limited, resources were mobilized quickly, and the first shots were fired almost immediately. Just hours after the Australian declaration of war, a gun at
 In June 1940, France surrendered to invading German forces, and Italy joined the war on the Axis side, causing a reversal of the Singapore strategy.
In June 1940, France surrendered to invading German forces, and Italy joined the war on the Axis side, causing a reversal of the Singapore strategy.
 The Battle of Singapore was fought in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II when the Japanese Empire invaded British Malaya and its stronghold of
The Battle of Singapore was fought in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II when the Japanese Empire invaded British Malaya and its stronghold of
 Africa was a large continent whose geography gave it strategic importance during the war. North Africa was the scene of a major campaign against Italy and Germany, which itself included the
Africa was a large continent whose geography gave it strategic importance during the war. North Africa was the scene of a major campaign against Italy and Germany, which itself included the
 The Viceroy Linlithgow declared that India was at war with Germany with no consultations with Indian politicians.
Serious tension erupted over American support for British Raj, independence for India, a proposition Churchill vehemently rejected. For years Roosevelt had encouraged Britain's disengagement from India. The American position was based on principled opposition to colonialism. The politically active Indian population was deeply divided. One element was so insistent on the expulsion of the British, that it sided with Germany and Japan, and formed the Indian National Army (INA) from Indian prisoners of war. It fought as part of the Japanese invasion of Burma and eastern India. There was a large pacifist element, which rallied to Gandhi's call for abstention from the war; he said that violence in every form was evil. There was a high level of religious tension between the Hindu majority and the Muslims minority. For the first time the Muslim community became politically active, giving strong support for the British war effort. Over 2 million Indians volunteered for military service, including a large Muslim contingent. The British were sensitive to demands of the
The Viceroy Linlithgow declared that India was at war with Germany with no consultations with Indian politicians.
Serious tension erupted over American support for British Raj, independence for India, a proposition Churchill vehemently rejected. For years Roosevelt had encouraged Britain's disengagement from India. The American position was based on principled opposition to colonialism. The politically active Indian population was deeply divided. One element was so insistent on the expulsion of the British, that it sided with Germany and Japan, and formed the Indian National Army (INA) from Indian prisoners of war. It fought as part of the Japanese invasion of Burma and eastern India. There was a large pacifist element, which rallied to Gandhi's call for abstention from the war; he said that violence in every form was evil. There was a high level of religious tension between the Hindu majority and the Muslims minority. For the first time the Muslim community became politically active, giving strong support for the British war effort. Over 2 million Indians volunteered for military service, including a large Muslim contingent. The British were sensitive to demands of the
 On 8 May 1945, the
On 8 May 1945, the
online
* * * * * Stacey, C P. (1970
Arms, Men and Governments: The War Policies of Canada, 1939–1945
Queen's Printer, Ottawa (Downloadable PDF) ISBN D2-5569 * * Toye, Richard. ''Churchill's Empire'' (Pan, 2010).
online
* Butler, J.R.M. et al. ''Grand Strategy'' (6 vol 1956–60), official overview of the British war effort; Volume 1: Rearmament Policy; Volume 2: September 1939 – June 1941; Volume 3, Part 1: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 3, Part 2: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 4: September 1942 – August 1943; Volume 5: August 1943 – September 1944; Volume 6: October 1944 – August 1945 * Churchill, Winston. ''The Second World War'' (6 vol 1947–51), classic personal history with many documents * Eccles, Karen E, and Debbie McCollin, edfs. ''World War II and the Caribbean'' (2017). * Edgerton, David. ''Britain's War Machine: Weapons, Resources, and Experts in the Second World War'' (Oxford University Press; 2011) 445 pages * Harrison, Mark ''Medicine and Victory: British Military Medicine in the Second World War'' (2004). * Hastings, Max. ''Winston's War: Churchill, 1940–1945'' (2010) * Ashley Jackson (historian), Jackson, Ashley. ''The British Empire and the Second World War'' (Continuum, 2006). 604pp; the standard scholarly history. * Khan, Yasmin. ''The Raj at War: A People's History of India's Second World War'' (2015); also published as ''India at War: The Subcontinent and the Second World War''. * Raghavan, Srinath. ''India's War: World War II and the Making of Modern South Asia'' (2016)
excerpt and text search
* Buckley, John. ''British Armour in the Normandy Campaign 1944'' (2004) * D'Este, Carlo. ''Decision in Normandy: The Unwritten Story of Montgomery and the Allied Campaign'' (1983). . * Ellis, L.F. ''The War in France and Flanders, 1939–1940'' (HMSO, 1953
* Ellis, L.F. ''Victory in the West, Volume 1: Battle of Normandy'' (HMSO, 1962) * Ellis, L.F. ''Victory in the West, Volume 2: Defeat of Germany'' (HMSO, 1968) * Fraser, David. ''And We Shall Shock Them: The British Army in World War II'' (1988). * Graham, Dominick. ''Tug of War: The Battle for Italy 1943–1945'' (2004) * Hamilton, Nigel. ''Monty: The Making of a General: 1887–1942'' (1981); ''Master of the Battlefield: Monty's War Years 1942–1944'' (1984); ''Monty: The Field-Marshal 1944–1976'' (1986). * Lamb, Richard. ''War in Italy, 1943–1945: A Brutal Story'' (1996) * Thompson, Julian. ''The Imperial War Museum Book of the War in Burma 1942–1945'' (2004) * Sebag-Montefiore, Hugh. ''Dunkirk: Fight to the Last Man'' (2008)
* Fisher, David E, ''A Summer Bright and Terrible: Winston Churchill, Lord Dowding, Radar, and the Impossible Triumph of the Battle of Britain'' (2005
excerpt online
* Hastings, Max. ''Bomber Command'' (1979) * Hansen, Randall. ''Fire and Fury: The Allied Bombing of Germany, 1942–1945'' (2009) * Hough, Richard and Denis Richards. ''The Battle of Britain'' (1989) 480 pp * Messenger, Charles, ''"Bomber" Harris and the Strategic Bombing Offensive, 1939–1945'' (1984), defends Harris * Overy, Richard. ''The Battle of Britain: The Myth and the Reality'' (2001) 192 page
excerpt and text search
* Richards, Dennis, et al. ''Royal Air Force, 1939–1945: The Fight at Odds – Vol. 1'' (HMSO 1953), official histor
vol 1 online editionvol 2 online edition
* Shores, Christopher F. ''Air War for Burma: The Allied Air Forces Fight Back in South-East Asia 1942–1945'' (2005) * Terraine, John. ''A Time for Courage: The Royal Air Force in the European War, 1939–1945'' (1985) * Verrier, Anthony. ''The Bomber Offensive'' (1969), British * Walker, David. "Supreme air command-the development of royal air force command practice in the second world war." (PhD dissertation, . University of Birmingham, 2018.)
online
* Webster, Charles and Noble Frankland, The Strategic Air Offensive Against Germany, 1939–1945 (HMSO, 1961), 4 vol. Important official British history * Wood, Derek, and Derek D. Dempster. ''The Narrow Margin: The Battle of Britain and the Rise of Air Power 1930–40'' (1975
online edition
online
online
* Henderson, Joan C. "Remembering the Second World War in Singapore: Wartime heritage as a visitor attraction." ''Journal of Heritage Tourism'' 2.1 (2007): 36–52. * Joshi, Vandana.
Memory and Memorialisation, Interment and Exhumation, Propaganda and Politics during WWII through the lens of International Tracing Service (ITS) Collections
"
MIDA Archival Reflexicon
' (2019): 1-12. * Summerfield, Penny. ''Reconstructing women's wartime lives: discourse and subjectivity in oral histories of the Second World War'' (1998).
"The British Empire at War Research Group"
For comprehensive coverage and up-to-date bibliography
Checklist of official histories
The 11th Day: Crete 1941
{{WWII history by nation , state=collapsed British Empire in World War II, History of the Commonwealth of Nations Military of the Commonwealth of Nations History of the British Empire, World War II World War II national military histories 1939 in the British Empire, World War II 1940s in the British Empire, World War II World War II by country, * Imperialism
 When the
When the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
declared war on Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
in September 1939 at the start of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the UK controlled to varying degrees numerous crown colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council ...
, protectorates
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inter ...
and the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. It also maintained unique political ties to four of the five independent Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s—Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
was technically a dominion but operated largely as an independent republic and remained neutral during the war. Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, though still called a "Dominion", had ceased self-governing functions and was governed as a colony.—as co-members (with the UK) of the then "British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
". In 1939 the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
and the Commonwealth together comprised a global power, with direct or ''de facto'' political and economic control of 25% of the world's population, and of 30% of its land mass.
The contribution of the British Empire and Commonwealth in terms of manpower and materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the spec ...
was critical to the Allied war-effort. From September 1939 to mid-1942, the UK led Allied efforts in multiple global military theatres. Commonwealth, Colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
and Imperial Indian forces, totalling close to 15 million serving men and women, fought the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Japanese and other Axis armies, air-forces and navies across Europe, Africa, Asia, and in the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic, Indian, Pacific and Arctic Oceans. Commonwealth forces based in Britain operated across Northwestern Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnographically.
Geographic definitions
Geographically, North ...
in the effort to slow or stop Axis advances. Commonwealth airforces fought the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
to a standstill over Britain, and Commonwealth armies defeated Italian forces in East Africa and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and occupied several overseas colonies of German-occupied European nations. Following successful engagements against Axis forces, Commonwealth troops invaded and occupied Libya, Italian Somaliland, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway betwee ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
.
The Commonwealth defeated, held back or slowed the Axis powers for three years while mobilizing its globally-integrated economy, military, and industrial infrastructure to build what became, by 1942, the most extensive military apparatus of the war. These efforts came at the cost of 150,000 military deaths, 400,000 wounded, 100,000 prisoners, over 300,000 civilian deaths, and the loss of 70 major warships, 39 submarines, 3,500 aircraft, 1,100 tanks and 65,000 vehicles. During this period the Commonwealth built an enormous military and industrial capacity. Britain became the nucleus of the Allied war-effort in Western Europe, and hosted governments-in-exile in London to rally support in occupied Europe
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 an ...
for the Allied cause. Canada delivered almost $4 billion in direct financial aid to the United Kingdom, and Australia and New Zealand began shifting to domestic production to provide material aid to US forces in the Pacific. Following the US entry into the war in December 1941, the Commonwealth and the United States coordinated their military efforts and resources globally. As the scale of the US military involvement and industrial production increased, the US undertook command in many theatres, relieving Commonwealth forces for duty elsewhere, and expanding the scope and intensity of Allied military efforts. Co-operation with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
also developed.
However, it proved difficult to co-ordinate the defence of far-flung colonies and Commonwealth countries from simultaneous attacks by the Axis powers. In part this difficulty was exacerbated by disagreements over priorities and objectives, as well as over the deployment and control of joint forces. The governments of Britain and Australia, in particular, turned to the United States for support. Although the British Empire and the Commonwealth countries all emerged from the war as joint victors together with the USA, the USSR and the other Allies, and the conquered territories were returned to British rule, the costs of the war and the nationalist fervour that it had stoked became a catalyst for the decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence ...
which took place in the following decades.
Pre-war plans for defence
From 1923, defence of British colonies and protectorates inEast Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
was centred on the " Singapore strategy". This made the assumption that Britain could send a fleet to its naval base in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
within two or three days of a Japanese attack, while relying on France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
to provide assistance in Asia via its colony in Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and, in the event of war with Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, to help defend British territories in the Mediterranean. Pre-war planners did not anticipate the fall of France: Nazi occupation, the loss of control over the Channel, and the employment of French Atlantic ports as forward bases for U-boats directly threatened Britain itself, forcing a significant reassessment of naval defence priorities.
During the 1930s, a triple threat emerged for the British Commonwealth in the form of far-right, militaristic governments in Germany, Italy and Japan. Germany threatened Britain itself, while Italy and Japan's imperial ambitions looked set to clash with the British imperial presence in the Mediterranean and East Asia respectively. However, there were differences of opinion within the UK and the Dominions as to which posed the most serious threat, and whether any attack would come from more than one power at the same time.
Declaration of war against Germany
 On 1 September 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Two days later, on 3 September, after a British ultimatum to Germany to cease military operations was ignored, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Britain's declaration of war automatically committed
On 1 September 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Two days later, on 3 September, after a British ultimatum to Germany to cease military operations was ignored, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Britain's declaration of war automatically committed India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, the Crown colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council ...
, and the protectorates
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inter ...
, but the 1931 Statute of Westminster had granted autonomy to the Dominions so each decided their course separately.
Australian Prime Minister Robert Menzies immediately joined the British declaration on 3 September, believing that it applied to all subjects of the Empire and Commonwealth. New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
followed suit simultaneously, at 9.30 pm on 3 September (local time), after Peter Fraser
Peter Fraser (; 28 August 1884 – 12 December 1950) was a New Zealand politician who served as the 24th prime minister of New Zealand from 27 March 1940 until 13 December 1949. Considered a major figure in the history of the New Zealand La ...
consulted the Cabinet; although as Chamberlain's broadcast was drowned by static, the Cabinet (led by Fraser as Prime Minister Michael Savage
Michael Alan Weiner (born March 31, 1942), known by his professional name Michael Savage, is a far-right author, conspiracy theorist, political commentator, activist, and former radio host. Savage is best known as the host of '' The Savage Na ...
was terminally ill) delayed until the Admiralty announced to the fleet a state of war, then backdated the declaration to 9.30 pm. South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
took three days to make its decision (on 6 September), as the Prime Minister General J. B. M. Hertzog
General James Barry Munnik Hertzog (3 April 1866 – 21 November 1942), better known as Barry Hertzog or J. B. M. Hertzog, was a South African politician and soldier. He was a Boer general during the Second Boer War who serve ...
favoured neutrality but was defeated by the pro-war vote in the Union Parliament, led by General Jan Smuts
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts, (24 May 1870 11 September 1950) was a South African statesman, military leader and philosopher. In addition to holding various military and cabinet posts, he served as prime minister of the Union of South Af ...
, who then replaced Hertzog. Canadian Prime Minister Mackenzie King declared support for Britain on the day of the British declaration, but also stated that it was for Parliament to make the formal declaration, which it did so one week later on 10 September. Ireland, though still a member of the Commonwealth, severed its legal ties as a dominion in 1937 and chose to remain neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
throughout the war.
Empire and Commonwealth contribution
 Kenya Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve 1945
While the war was initially intended to be limited, resources were mobilized quickly, and the first shots were fired almost immediately. Just hours after the Australian declaration of war, a gun at
Kenya Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve 1945
While the war was initially intended to be limited, resources were mobilized quickly, and the first shots were fired almost immediately. Just hours after the Australian declaration of war, a gun at Fort Queenscliff
Fort Queenscliff, in Victoria, Australia, dates from 1860 when an open battery was constructed on Shortland's Bluff to defend the entrance to Port Phillip. The Fort, which underwent major redevelopment in the late 1870s and 1880s, became the he ...
fired across the bows of a ship as it attempted to leave Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
without required clearances. On 10 October 1939, an aircraft of No. 10 Squadron RAAF based in England became the first Commonwealth air force unit to go into action when it undertook a mission to Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
.Stephens (2006). pp. 76–79. The first Canadian convoy of 15 ships bearing war goods departed Halifax just six days after the nation declared war, with two destroyers and . A further 26 convoys of 527 ships sailed from Canada in the first four months of the war, and by 1 January 1940 Canada had landed an entire division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
in Britain. On 13 June 1940 Canadian troops deployed to France in an attempt to secure the southern flank of the British Expeditionary Force in Belgium. As the fall of France grew imminent, Britain looked to Canada to rapidly provide additional troops to strategic locations in North America, the Atlantic and Caribbean. Following the Canadian destroyer already on station from 1939, Canada provided troops from May 1940 to assist in the defence of the British Caribbean colonies, with several companies serving throughout the war in Bermuda, Jamaica, the Bahamas and British Guiana. Canadian troops were also sent to the defence of the colony of Newfoundland, on Canada's east coast, the closest point in North America to Germany. Fearing the loss of a land link to the British Isles, Canada was also requested to occupy Iceland, which it did from June 1940 to the spring of 1941, following the initial British invasion.
From mid-June 1940, following the rapid German invasions and occupations of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, the British Commonwealth was the main opponent of Germany and the Axis, until the entry into the war of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
in June 1941. During this period Australia, India, New Zealand and South Africa provided dozens of ships and several divisions for the defence of the Mediterranean, Greece, Crete, Lebanon and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, where British troops were outnumbered four to one by the Italian armies in Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. Canada delivered a further 2nd Canadian Infantry Division
The 2nd Canadian Division, an infantry division of the Canadian Army, was mobilized for war service on 1September 1939 at the outset of World War II. Adopting the designation of the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division, it was initially composed of v ...
, pilots for two air squadrons, and several warships to Britain to face a possible invasion from the continent.
In December 1941, Japan launched, in quick succession, attacks on British Malaya, the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the R ...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
.
Substantial financial support was provided by Canada to the UK and Commonwealth dominions, in the form of over $4 billion in aid through the Billion Dollar Gift and Mutual Aid and the War Appropriation Act. Over the course of the war over 1.6 million Canadians served in uniform (out of a prewar population of 11 million), in almost every theatre of the war, and by war's end the country had the third-largest navy and fourth-largest air force in the world. By the end of the war, almost a million Australians had served in the armed forces (out of a population of under 7 million), whose military units fought primarily in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and the South West Pacific
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million as of ...
.
The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (also known as the "Empire Air Training Scheme") was established by the governments of Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the UK resulting in:
* joint training at flight schools in Canada, South Africa, Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a landlocked self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally kno ...
, Australia and New Zealand;
* formation of new squadrons of the Dominion air forces, known as "Article XV squadrons
Article XV squadrons were Australian, Canadian, and New Zealand air force squadrons formed from graduates of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (1939) during World War II.
These units complemented another feature of the BCATP, under wh ...
" for service as part of Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
operational commands, and;
* in practice, the pooling of RAF and Dominion air force personnel, for posting to both RAF and Article XV squadrons.
Finances
Britain borrowed everywhere it could and made heavy purchases of munitions and supplies in India and Canada during the war, as well as other parts of the Empire and neutral countries. Canada also made gifts. Britain's sterling balances around the world amounted to £3.4 billion in 1945 or the equivalent of about $US 200 billion in 2016 dollars. However, Britain treated this as a long-term loan with no interest and no specified repayment date. Just when the money would be made available by London was an issue, for the British treasury was nearly empty by 1945.Crisis in the Mediterranean
 In June 1940, France surrendered to invading German forces, and Italy joined the war on the Axis side, causing a reversal of the Singapore strategy.
In June 1940, France surrendered to invading German forces, and Italy joined the war on the Axis side, causing a reversal of the Singapore strategy. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, who had replaced Neville Chamberlain as British Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
the previous month (see Norway debate
The Norway Debate, sometimes called the Narvik Debate, was a momentous debate in the British House of Commons from 7 to 9 May 1940, during the Second World War. The official title of the debate, as held in the ''Hansard'' parliamentary archive, ...
), ordered that the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
were of a higher priority than the Far East to defend. Australia and New Zealand were told by telegram that they should turn to the United States for help in defending their homeland should Japan attack:
Commonwealth forces played a major role in North and East Africa following Italy's entry to the war, participating in the invasion of Italian Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
and Somaliland, but were forced to retreat after Churchill diverted resources to Greece and Crete.
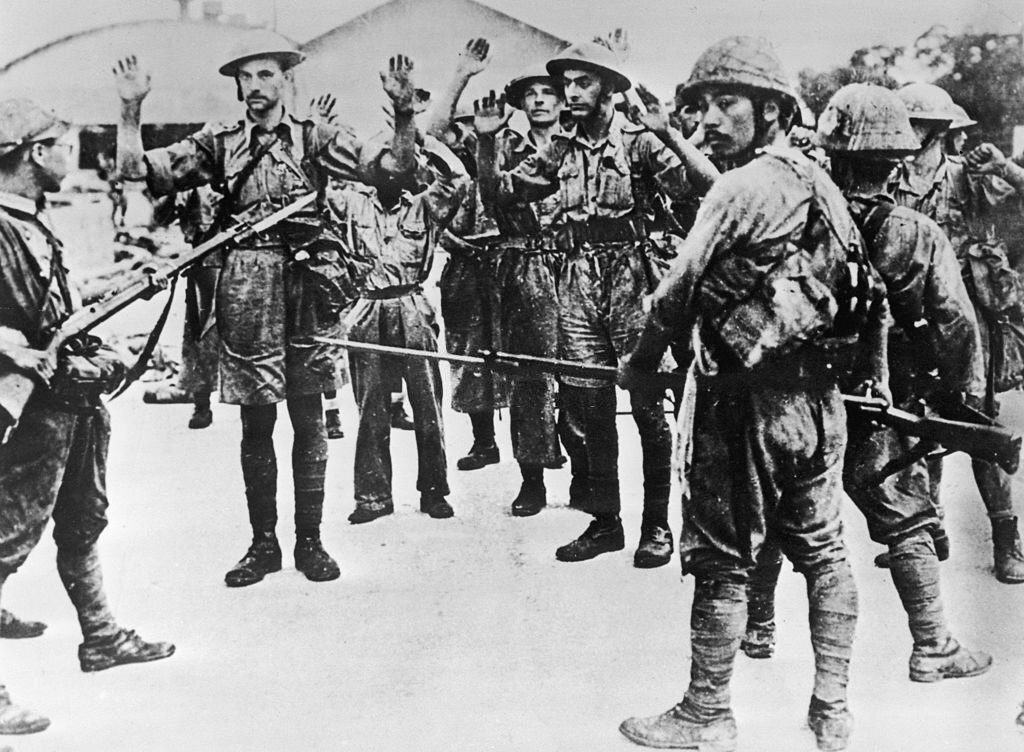
Fall of Singapore
 The Battle of Singapore was fought in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II when the Japanese Empire invaded British Malaya and its stronghold of
The Battle of Singapore was fought in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II when the Japanese Empire invaded British Malaya and its stronghold of Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
. Singapore was the major British military base in South East Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and nicknamed the "Gibraltar of the East". The fighting in Singapore lasted from 31 January 1942 to 15 February 1942. It followed a humiliating naval engagement in December 1941 in which two British capital ships were sunk.
It resulted in the fall of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire o ...
to the Japanese, and the largest surrender
Surrender may refer to:
* Surrender (law), the early relinquishment of a tenancy
* Surrender (military), the relinquishment of territory, combatants, facilities, or armaments to another power
Film and television
* ''Surrender'' (1927 film), an ...
of British-led military personnel in history. About 80,000 British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
n and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
troops became prisoners of war, joining 50,000 taken by the Japanese in the Malayan campaign. Britain's Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
called the ignominious fall of Singapore to the Japanese the "worst disaster" and "largest capitulation" in British history.
Africa
 Africa was a large continent whose geography gave it strategic importance during the war. North Africa was the scene of a major campaign against Italy and Germany, which itself included the
Africa was a large continent whose geography gave it strategic importance during the war. North Africa was the scene of a major campaign against Italy and Germany, which itself included the Tunisian Campaign
The Tunisian campaign (also known as the Battle of Tunisia) was a series of battles that took place in Tunisia during the North African campaign of the Second World War, between Axis and Allied forces from 17 November 1942 to 13 May 1943. Th ...
, the Western Desert Campaign (resulting in tide-turning battles such as those in El Alamein and in Tobruk) and, with large-scale American support, Operation Torch. East Africa was also the scene of a major campaign against Italy which resulted in the liberation of Somalia, Eritrea and most chiefly Ethiopia which had been conquered by the Italian Empire in 1936. The vast geography provided major transportation routes linking the United States to the Middle East and Mediterranean regions. The sea route around South Africa was heavily used even though it added 40 days to voyages that had to avoid the dangerous Suez region. Lend Lease supplies to Russia often came this way. Internally, long-distance road and railroad connections facilitated the British war effort. The Union of South Africa was part of the British Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
, and had been an independent self-governing country since 1931. The British possessions in Africa were ruled by the colonial office, usually with close ties to local chiefs and kings. France had extensive possessions in Africa, but they played a much smaller role in the war, since they were largely tied to Vichy France. Portuguese holdings played a minor role. Italian holdings were the target of successful British military campaigns. The Belgian Congo, and two other Belgian colonies, were major exporters. In terms of numbers and wealth, the British controlled the richest portions of Africa, and made extensive use not only of the geography, but the manpower and the natural resources. Civilian colonial officials made a special effort to upgrade the African infrastructure, promote agriculture, integrate colonial Africa with the world economy, and recruit over a half million soldiers.
Before the war, Britain had made few plans for the utilization of Africa, but it quickly set up command structures. The Army set up the West Africa Command, which recruited 200,000 soldiers. The East Africa Command was created in September 1941 to support the overstretched Middle East Command. The Southern Command was the domain of South Africa. The Royal Navy set up the South Atlantic Command based in Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
, that became one of the main convoy assembly points. The RAF Coastal Command had major submarine-hunting operations based in West Africa, while a smaller RAF command Dealt with submarines in the Indian Ocean. Ferrying aircraft from North America and Britain was the major mission of the Western Desert Air Force. In addition smaller more localized commands were set up throughout the war.
Before the war, the military establishments were very small throughout British Africa, and largely consisted of whites, who comprised only two percent of the population outside Africa. As soon as the war began, newly created African units were set up, primarily by the Army. The new recruits were almost always volunteers, usually provided in close cooperation with local tribal leaders. During the war, military pay scales far exceeded what civilians natives could earn, especially when food, housing and clothing allowances are included. The largest numbers were in construction units, called Pioneer Units, with over 82,000 soldiers. The RAF and Navy also did some recruiting. East Africa provided the largest number of men, over 320,000, chiefly from Kenya, Tanganyika, and Uganda. They did some fighting, a great deal of guard duty, and construction work. 80,000 served in the Middle East. A special effort was made not to challenge white supremacy, certainly before the war, and to a large extent during the war itself. Nevertheless, the soldiers were drilled and train to European standards, given strong doses of propaganda, and learn leadership and organizational skills that proved essential to the formation of nationalistic and independence movements after 1945. There were minor episodes of discontent, but nothing serious, among the natives. Afrikaner nationalism was a factor in South Africa, but the anti-British and pro-neutrality Afrikaner prime minister J. B. M. Hertzog
General James Barry Munnik Hertzog (3 April 1866 – 21 November 1942), better known as Barry Hertzog or J. B. M. Hertzog, was a South African politician and soldier. He was a Boer general during the Second Boer War who serve ...
was replaced by a narrow vote of the South African parliament in 1939 by Jan Smuts
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts, (24 May 1870 11 September 1950) was a South African statesman, military leader and philosopher. In addition to holding various military and cabinet posts, he served as prime minister of the Union of South Af ...
, a fellow Afrikaner who was an enthusiastic supporter of the British Empire. The Smuts government closely cooperated with London and raised 340,000 volunteers (190,000 were white, or about one-third of the eligible white men).
India
 The Viceroy Linlithgow declared that India was at war with Germany with no consultations with Indian politicians.
Serious tension erupted over American support for British Raj, independence for India, a proposition Churchill vehemently rejected. For years Roosevelt had encouraged Britain's disengagement from India. The American position was based on principled opposition to colonialism. The politically active Indian population was deeply divided. One element was so insistent on the expulsion of the British, that it sided with Germany and Japan, and formed the Indian National Army (INA) from Indian prisoners of war. It fought as part of the Japanese invasion of Burma and eastern India. There was a large pacifist element, which rallied to Gandhi's call for abstention from the war; he said that violence in every form was evil. There was a high level of religious tension between the Hindu majority and the Muslims minority. For the first time the Muslim community became politically active, giving strong support for the British war effort. Over 2 million Indians volunteered for military service, including a large Muslim contingent. The British were sensitive to demands of the
The Viceroy Linlithgow declared that India was at war with Germany with no consultations with Indian politicians.
Serious tension erupted over American support for British Raj, independence for India, a proposition Churchill vehemently rejected. For years Roosevelt had encouraged Britain's disengagement from India. The American position was based on principled opposition to colonialism. The politically active Indian population was deeply divided. One element was so insistent on the expulsion of the British, that it sided with Germany and Japan, and formed the Indian National Army (INA) from Indian prisoners of war. It fought as part of the Japanese invasion of Burma and eastern India. There was a large pacifist element, which rallied to Gandhi's call for abstention from the war; he said that violence in every form was evil. There was a high level of religious tension between the Hindu majority and the Muslims minority. For the first time the Muslim community became politically active, giving strong support for the British war effort. Over 2 million Indians volunteered for military service, including a large Muslim contingent. The British were sensitive to demands of the Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
, led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah, since it needed Muslim soldiers in India and Muslim support all across the Middle East. London used the religious tensions in India as a justification to continue its rule, saying it was needed to prevent religious massacres of the sort that did happen in 1947. The imperialist element in Britain was strongly represented in the Conservative party; Churchill himself had long been its leading spokesman. On the other hand, Attlee and the Labour Party favoured independence and had close ties to the Congress Party. The British cabinet sent Sir Stafford Cripps to India with a specific peace plan offering India the promise of dominion status after the war. Congress demanded independence immediately and the Cripps mission failed. Roosevelt gave support to Congress, sending his representative Louis Johnson to help negotiate some sort of independence. Churchill was outraged, refused to cooperate with Roosevelt on the issue, and threatened to resign as prime minister if Roosevelt pushed too hard. Roosevelt pulled back. In 1942 when the Congress Party launched a Quit India Movement of non-violent civil disobedience, the Raj police immediately arrested tens of thousands of activists (including Gandhi), holding them for the duration. Meanwhile, wartime disruptions caused severe food shortages in eastern India; hundreds of thousands died of starvation. To this day a large Indian element blames Churchill for the Bengal famine of 1943. In terms of the war effort, India became a major base for American supplies sent to China, and Lend Lease operations boosted the local economy. The 2 million Indian soldiers were a major factor in British success in the Middle East. Muslim support for the British war effort proved decisive in the British decision to partition the Raj, forming of the new state of Pakistan.
Victory
 On 8 May 1945, the
On 8 May 1945, the World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
Allies formally accepted the unconditional surrender
An unconditional surrender is a surrender in which no guarantees are given to the surrendering party. It is often demanded with the threat of complete destruction, extermination or annihilation.
In modern times, unconditional surrenders most ofte ...
of the armed forces of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the end of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. The formal surrender of the occupying German forces in the Occupation of the Channel Islands, Channel Islands was not until 9 May 1945. On 30 April Death of Adolf Hitler, Hitler committed suicide during the Battle of Berlin, and so the surrender of Germany was authorized by his replacement, President of Germany Karl Dönitz. The ''German Instrument of Surrender, act of military surrender'' was signed on 7 May in Reims, France, and ratified on 8 May in Berlin, Germany.
In the afternoon of 15 August 1945, the Surrender of Japan occurred, effectively ending World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. On this day the initial announcement of Japan's surrender was made in Japan, and because of time zone differences it was announced in the United States, Western Europe, the Americas, the Pacific Islands, and Australia/New Zealand on 14 August 1945. The signing of the surrender document occurred on 2 September 1945.
Aftermath
By the end of the war in August 1945, British Commonwealth forces were responsible for the civil and/or military administration of a number of non-Commonwealth territories, occupied during the war, including Italian Eritrea#British occupation and the end of the colony, Eritrea, British Military Administration (Libya), Libya, Madagascar, Iran, Iraq, Lebanon, Italian Somaliland#British Military Administration (1941-1949), Italian Somaliland, Syria, Thailand and portions of Germany, Austria and Japan. Most of these military administrations were handed over to old European colonial authorities or to new local authorities soon after the end of the hostilities. Commonwealth forces administered occupation zones in British Commonwealth Occupation Force, Japan, Allied-occupied Germany#Occupation Zones, Germany and Allied-occupied Austria, Austria until 1955. World War II confirmed that Britain was no longer the great power it had once been, and that it had been surpassed by the United States on the world stage. Canada, Australia and New Zealand moved within the orbit of the United States. The image of imperial strength in Asia had been shattered by the Japanese attacks, and British prestige there was irreversibly damaged. The price for India's entry to the war had been effectively a guarantee for independence, which came within two years of the end of the war, relieving Britain of its most populous and valuable colony. The deployment of 150,000 Africans overseas from British colonies, and the stationing of white troops in Africa itself led to revised perceptions of the Empire in Africa.Historiography
In terms of actual engagement with the enemy, historians have recounted a great deal in South Asia and Southeast Asia, as summarized by Ashley Jackson (historian), Ashley Jackson: :Terror, mass migration, shortages, inflation, blackouts, air raids, massacres, famine, forced labour, urbanization, environmental damage, occupation [by the enemy], resistance, collaboration – all of these dramatic and often horrific phenomena shaped the war experience of Britain's imperial subjects. British historians of the Second World War have not emphasized the critical role played by the Empire in terms of money, manpower and imports of food and raw materials. The powerful combination meant that Britain did not stand alone against Germany, it stood at the head of a great but fading empire. As Ashley Jackson has argued," The story of the British Empire's war, therefore, is one of Imperial success in contributing toward Allied victory on the one hand, and egregious Imperial failure on the other, as Britain struggled to protect people and defeat them, and failed to win the loyalty of colonial subjects." The contribution in terms of soldiers numbered 2.5 million men from India, over 1 million from Canada, just under 1 million from Australia, 410,000 from South Africa, and 215,000 from New Zealand. In addition, the colonies mobilized over 500,000 uniformed personnel who serve primarily inside Africa. In terms of financing, the British war budget included £2.7 billion borrowed from the Empire's Sterling Area, And eventually paid back. Canada Billion Dollar Gift and Mutual Aid, made C$3 billion in gifts and loans on easy terms.Military histories of the British Empire's colonies, dominions, mandates and protectorates
The contributions from individual colonies, dominions, mandates, and protectorates to the war effort were extensive and global. Further information about their involvement can be found in the military histories of the individual colonies, dominions, mandates, and protectorates listed below.Africa
* Ascension Island#World Wars, Ascension Island * Basutoland * Bechuanaland Protectorate * British Cameroons * The Gambia in World War II, Gambia * Gold Coast in World War II, Gold Coast * Kenya in World War II, Kenya * British Mauritius, Mauritius * Colonial Nigeria#Second World War, Nigeria * Northern Rhodesia * Nyasaland * * History of Seychelles#Crown Colony, Seychelles *Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
* Italian conquest of British Somaliland, Somaliland
* Military history of South Africa during World War II, South Africa
** Military history of South Africa during World War II, South West Africa
* Southern Rhodesia in World War II, Southern Rhodesia
* Anglo-Egyptian Sudan
* Eswatini, Swaziland Protectorate
* Tanganyika Territory, Tanganyika
* British Togoland, Togoland
* Uganda Protectorate, Uganda
* Sultanate of Zanzibar, Zanzibar
Americas
* British Windward Islands, Barbados * Bermuda Militia Infantry#Creation of the Bermuda Militia Infantry, Bermuda * Canada in World War II, Canada * Cayman Islands * Falkland Islands * British Guiana * British Honduras * Colony of Jamaica, Jamaica * British Leeward Islands, Leeward Islands * Dominion of Newfoundland#Second World War, Newfoundland * Colony of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and Tobago * Turks and Caicos * British Windward Islands, Windward IslandsEast Asia
* Japanese occupation of Hong Kong, Hong KongEurope
* History of Cyprus since 1878#British Cyprus (1914–60), Cyprus * Military history of Gibraltar during World War II, Gibraltar * German occupation of the Channel Islands, Guernsey * German occupation of the Channel Islands, Jersey * Irish neutrality during World War II, Ireland * History of the Isle of Man#Modern period, Isle of Man * Siege of Malta (World War II), Malta * Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II, United KingdomMiddle East
* * History of Bahrain#Treaties with Britain, Bahrain Protectorate * Egypt during World War II, Egypt * Sheikhdom of Kuwait, Kuwait Protectorate * Mandatory Palestine * History of Qatar#British protectorate (1916–1971), Qatar Protectorate * Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan * Trucial StatesOceania
* Military history of Australia during World War II, Australia ** Territory of New Guinea#World War II, New Guinea ** Norfolk Island ** Territory of Papua, Papua * Colony of Fiji#Fiji in World War II, Fiji * Gilbert and Ellice Islands * Japanese occupation of Nauru, Nauru * New Hebrides * Military history of New Zealand during World War II, New Zealand ** Western Samoa Trust Territory, Western Samoa * British Solomon Islands#World War II, Solomon Islands * Tonga, Tonga ProtectorateSouth Asia
* Ceylon in World War II, Ceylon * India in World War II, India * Maldives, Maldives ProtectorateSoutheast Asia
* Brunei, Brunei Protectorate * Japanese occupation of Burma, Burma * Japanese occupation of Malaya, Malaya * Japanese occupation of British Borneo, North Borneo * Raj of Sarawak, Sarawak * Straits SettlementsSee also
* Diplomatic history of World War II * Historiography of the British Empire * Military history of the United Kingdom during World War IIHomefront
* Australian home front during World War II * Battle of Christmas Island, Christmas Island Mutiny and Battle * Evacuation of the Gibraltarian civilian population during World War II, Gibraltar evacuation in the Second World War * Home front during World War II#Britain, British home front during the Second World War * Japanese occupation of the Andaman Islands * Japanese occupation of British Borneo * Japanese occupation of Nauru * Japanese occupation of SingaporeMajor military formations and units
* List of British Empire corps of the Second World War * List of British Empire divisions in the Second World War * List of British Empire brigades of the Second World War * East Africa Command * British Far East Command, Far East Command * India Command * Malaya Command * Middle East Command * Persia and Iraq Command * West Africa Command * British Pacific Fleet, Pacific Fleet * Eastern Fleet * Home Fleet * Mediterranean Fleet * Reserve Fleet (United Kingdom), Reserve Fleet * RAF Bomber Command, Bomber Command * RAF Ferry Command, Ferry Command * RAF Fighter Command, Fighter Command * List of Royal Air Force aircraft squadrons, RAF Squadrons * British Commonwealth Air Training Plan * British Commonwealth Occupation ForceNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * Butler, J.R.M. et al. ''Grand Strategy'' (6 vol 1956–60), official overview of the British war effort; Volume 1: Rearmament Policy; Volume 2: September 1939 – June 1941; Volume 3, Part 1: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 3, Part 2: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 4: September 1942 – August 1943; Volume 5: August 1943 – September 1944; Volume 6: October 1944 – August 1945 * * * Edgerton, David. ''Britain's War Machine: Weapons, Resources, and Experts in the Second World War'' (Oxford University Press; 2011) 445 pages * Hague, Arnold: The allied convoy system 1939–1945 : its organization, defence and operation. St.Catharines, Ontario : Vanwell, 2000. * * Leacock, Stephen. ''Our British empire; its structure, its history, its strength'' (1941online
* * * * * Stacey, C P. (1970
Arms, Men and Governments: The War Policies of Canada, 1939–1945
Queen's Printer, Ottawa (Downloadable PDF) ISBN D2-5569 * * Toye, Richard. ''Churchill's Empire'' (Pan, 2010).
Further reading
* Allport, Alan. ''Britain at Bay: The Epic Story of the Second World War, 1938–1941'' (2020) * Bousquet, Ben and Colin Douglas. ''West Indian Women at War: British Racism in World War II'' (1991online
* Butler, J.R.M. et al. ''Grand Strategy'' (6 vol 1956–60), official overview of the British war effort; Volume 1: Rearmament Policy; Volume 2: September 1939 – June 1941; Volume 3, Part 1: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 3, Part 2: June 1941 – August 1942; Volume 4: September 1942 – August 1943; Volume 5: August 1943 – September 1944; Volume 6: October 1944 – August 1945 * Churchill, Winston. ''The Second World War'' (6 vol 1947–51), classic personal history with many documents * Eccles, Karen E, and Debbie McCollin, edfs. ''World War II and the Caribbean'' (2017). * Edgerton, David. ''Britain's War Machine: Weapons, Resources, and Experts in the Second World War'' (Oxford University Press; 2011) 445 pages * Harrison, Mark ''Medicine and Victory: British Military Medicine in the Second World War'' (2004). * Hastings, Max. ''Winston's War: Churchill, 1940–1945'' (2010) * Ashley Jackson (historian), Jackson, Ashley. ''The British Empire and the Second World War'' (Continuum, 2006). 604pp; the standard scholarly history. * Khan, Yasmin. ''The Raj at War: A People's History of India's Second World War'' (2015); also published as ''India at War: The Subcontinent and the Second World War''. * Raghavan, Srinath. ''India's War: World War II and the Making of Modern South Asia'' (2016)
British Army
* Allport, Alan. ''Browned Off and Bloody-Minded: The British Soldier Goes to War, 1939–1945'' (Yale UP, 2015) * Atkinson, Rick. ''The Day of Battle: The War in Sicily and Italy, 1943–1944'' (2008excerpt and text search
* Buckley, John. ''British Armour in the Normandy Campaign 1944'' (2004) * D'Este, Carlo. ''Decision in Normandy: The Unwritten Story of Montgomery and the Allied Campaign'' (1983). . * Ellis, L.F. ''The War in France and Flanders, 1939–1940'' (HMSO, 1953
* Ellis, L.F. ''Victory in the West, Volume 1: Battle of Normandy'' (HMSO, 1962) * Ellis, L.F. ''Victory in the West, Volume 2: Defeat of Germany'' (HMSO, 1968) * Fraser, David. ''And We Shall Shock Them: The British Army in World War II'' (1988). * Graham, Dominick. ''Tug of War: The Battle for Italy 1943–1945'' (2004) * Hamilton, Nigel. ''Monty: The Making of a General: 1887–1942'' (1981); ''Master of the Battlefield: Monty's War Years 1942–1944'' (1984); ''Monty: The Field-Marshal 1944–1976'' (1986). * Lamb, Richard. ''War in Italy, 1943–1945: A Brutal Story'' (1996) * Thompson, Julian. ''The Imperial War Museum Book of the War in Burma 1942–1945'' (2004) * Sebag-Montefiore, Hugh. ''Dunkirk: Fight to the Last Man'' (2008)
Royal Navy
* Barnett, Corelli. ''Engage the Enemy More Closely: The Royal Navy in the Second World War'' (1991) * Marder, Arthur. ''Old Friends, New Enemies: The Royal Navy and the Imperial Japanese Navy, vol. 2: The Pacific War, 1942–1945'' with Mark Jacobsen and John Horsfield (1990) * Roskill, S. W. ''The White Ensign: British Navy at War, 1939–1945'' (1960). summary * Roskill, S. W. ''War at Sea 1939–1945, Volume 1: The Defensive'' London: HMSO, 1954; ''War at Sea 1939–1945, Volume 2: The Period of Balance,'' 1956; ''War at Sea 1939–1945, Volume 3: The Offensive, Part 1,'' 1960; ''War at Sea 1939–1945, Volume 3: The Offensive, Part 2,'' 1961Royal Air Force
* Bungay, Stephen. ''The Most Dangerous Enemy: The Definitive History of the Battle of Britain'' (2nd ed. 2010) * Collier, Basil. ''Defence of the United Kingdom'' (HMSO, 1957* Fisher, David E, ''A Summer Bright and Terrible: Winston Churchill, Lord Dowding, Radar, and the Impossible Triumph of the Battle of Britain'' (2005
excerpt online
* Hastings, Max. ''Bomber Command'' (1979) * Hansen, Randall. ''Fire and Fury: The Allied Bombing of Germany, 1942–1945'' (2009) * Hough, Richard and Denis Richards. ''The Battle of Britain'' (1989) 480 pp * Messenger, Charles, ''"Bomber" Harris and the Strategic Bombing Offensive, 1939–1945'' (1984), defends Harris * Overy, Richard. ''The Battle of Britain: The Myth and the Reality'' (2001) 192 page
excerpt and text search
* Richards, Dennis, et al. ''Royal Air Force, 1939–1945: The Fight at Odds – Vol. 1'' (HMSO 1953), official histor
vol 1 online edition
* Shores, Christopher F. ''Air War for Burma: The Allied Air Forces Fight Back in South-East Asia 1942–1945'' (2005) * Terraine, John. ''A Time for Courage: The Royal Air Force in the European War, 1939–1945'' (1985) * Verrier, Anthony. ''The Bomber Offensive'' (1969), British * Walker, David. "Supreme air command-the development of royal air force command practice in the second world war." (PhD dissertation, . University of Birmingham, 2018.)
online
* Webster, Charles and Noble Frankland, The Strategic Air Offensive Against Germany, 1939–1945 (HMSO, 1961), 4 vol. Important official British history * Wood, Derek, and Derek D. Dempster. ''The Narrow Margin: The Battle of Britain and the Rise of Air Power 1930–40'' (1975
online edition
Homefronts
* Mosby, Ian. ''Food Will Win the War: The Politics, Culture, and Science of Food on Canada's Home Front'' (2014) * Ollerenshaw, Philip. ''Northern Ireland in the Second World War: Politics, economic mobilisation and society, 1939–45'' (2016)online
Historiography and memory
* Finney, Patrick, ed. ''Remembering the Second World War'' (2017online
* Henderson, Joan C. "Remembering the Second World War in Singapore: Wartime heritage as a visitor attraction." ''Journal of Heritage Tourism'' 2.1 (2007): 36–52. * Joshi, Vandana.
Memory and Memorialisation, Interment and Exhumation, Propaganda and Politics during WWII through the lens of International Tracing Service (ITS) Collections
"
MIDA Archival Reflexicon
' (2019): 1-12. * Summerfield, Penny. ''Reconstructing women's wartime lives: discourse and subjectivity in oral histories of the Second World War'' (1998).
External links
"The British Empire at War Research Group"
For comprehensive coverage and up-to-date bibliography
Checklist of official histories
The 11th Day: Crete 1941
{{WWII history by nation , state=collapsed British Empire in World War II, History of the Commonwealth of Nations Military of the Commonwealth of Nations History of the British Empire, World War II World War II national military histories 1939 in the British Empire, World War II 1940s in the British Empire, World War II World War II by country, * Imperialism