Brest-Litovsk Treaty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate
 In Petrograd, Trotsky argued passionately against signing and proposed that instead, "they should announce the termination of the war and demobilization without signing any peace." Lenin was for signing rather than having an even more ruinous treaty forced on them after a few more weeks of military humiliation. The "Left Communists", led by
In Petrograd, Trotsky argued passionately against signing and proposed that instead, "they should announce the termination of the war and demobilization without signing any peace." Lenin was for signing rather than having an even more ruinous treaty forced on them after a few more weeks of military humiliation. The "Left Communists", led by
 The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918. The signatories were Soviet Russia signed by
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918. The signatories were Soviet Russia signed by

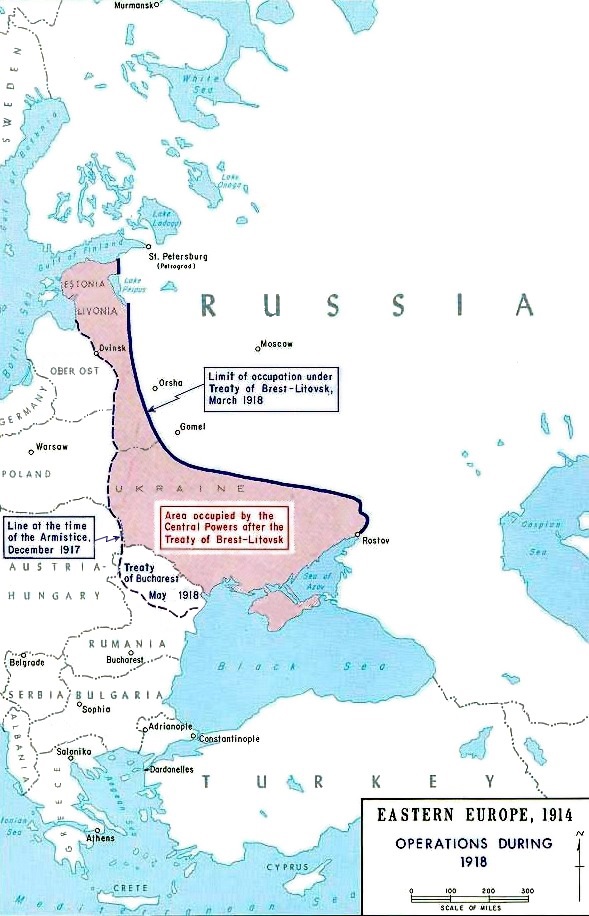 The occupation of the western part of former Russian Empire ultimately proved a costly blunder for Berlin, as over one million German troops lay sprawled out from Poland nearly to the
The occupation of the western part of former Russian Empire ultimately proved a costly blunder for Berlin, as over one million German troops lay sprawled out from Poland nearly to the
Emil Orlik (1870–1932) – Portraits of Friends and Contemporaries
escription of exhibition in 2004 Retrieved 2015-04-03.
excerpt
als
online review
* * * * * *, primary sources. * UK National Archives
''online''
*, older scholarly history.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (Yale University Avalon Project)
including links to appendices.
* ttps://omniatlas.com/maps/europe/19180320/ Map of Europeafter the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, at omniatlas.com. * Susanne Schattenberg
Brest-Litovsk, Treaty of
in
* ''The Times History of the War'', Volume XIV, London: Printing House Square, 1918
pp. 1-37
*
"The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk," lecture presented at National World War I Museum, 2018
{{DEFAULTSORT:Brest-Litovsk, Treaty of World War I treaties Treaties concluded in 1918 Treaties entered into force in 1918 Peace treaties of Germany Peace treaties of Austria Peace treaties of the Ottoman Empire Peace treaties of Bulgaria Peace treaties of Russia
peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
(Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
), that ended Russia's participation in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. The treaty was signed at German-controlled Brest-Litovsk ( pl, Brześć Litewski; since 1945, Brest, now in modern Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
), after two months of negotiations. The treaty was agreed upon by the Russians to stop further invasion. As a result of the treaty, Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
defaulted on all of Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The ...
's commitments to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
and eleven nations became independent in eastern Europe and western Asia. Under the treaty, Russia lost all of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and most of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, as well as its three Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
republics of Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, and Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
(so-called Baltic governorates in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
), and these three regions became German vassal states under German princelings. Russia also ceded its province of Kars in the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. According to historian Spencer Tucker, "The German General Staff had formulated extraordinarily harsh terms that shocked even the German negotiator." Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
was not mentioned in the treaty. When Germans later complained that the 1919 Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
against Germany was too harsh on them, the Allied Powers responded that it was more benign than the terms imposed by the Brest-Litovsk treaty.
The treaty was annulled by the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
, when Germany surrendered to the western Allied Powers. However, in the meantime it did provide some relief to the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
, already fighting the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
(1917–1922) following the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
s of 1917, by the renunciation of Russia's claims on Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
It is considered the first diplomatic treaty ever filmed.
Background
By 1917, Germany and Imperial Russia were stuck in a stalemate on theEastern Front of World War I
The Eastern Front or Eastern Theater of World War I (german: Ostfront; ro, Frontul de răsărit; russian: Восточный фронт, Vostochny front) was a theater of operations that encompassed at its greatest extent the entire frontie ...
and the Russian economy had nearly collapsed under the strain of the war effort. The large numbers of war casualties and persistent food shortages in the major urban centers brought about civil unrest, known as the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
, that forced Tsar Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pol ...
to abdicate. The Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government ( rus, Временное правительство России, Vremennoye pravitel'stvo Rossii) was a provisional government of the Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately ...
that replaced the Tsar in early 1917 continued the war. Foreign Minister Pavel Milyukov
Pavel Nikolayevich Milyukov ( rus, Па́вел Никола́евич Милюко́в, p=mʲɪlʲʊˈkof; 31 March 1943) was a Russian historian and liberal politician. Milyukov was the founder, leader, and the most prominent member of the Co ...
sent the Entente Powers a telegram, known as the Milyukov note, affirming to them that the Provisional Government would continue the war with the same war aims that the former Russian Empire had. The pro-war Provisional Government was opposed by the self-proclaimed Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies, dominated by leftist parties. Its Order No. 1 called for an overriding mandate to soldier committees rather than army officers. The Soviet started to form its own paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carr ...
power, the Red Guards, in March 1917.
The continuing war led the German Government to agree to a suggestion that they should favour the opposition Communist Party (Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
), who were proponents of Russia's withdrawal from the war. Therefore, in April 1917, Germany transported Bolshevik leader Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
and thirty-one supporters in a sealed train from exile in Switzerland to Finland Station, Petrograd. Upon his arrival in Petrograd, Lenin proclaimed his April Theses
The April Theses (russian: апрельские тезисы, transliteration: ') were a series of ten directives issued by the Bolshevik leader Vladimir Lenin upon his April 1917 return to Petrograd from his exile in Switzerland via Germa ...
, which included a call for turning all political power over to workers' and soldiers' soviets (councils) and an immediate withdrawal of Russia from the war. At around the same time, the United States entered the war, potentially shifting the balance of the war against the Central Powers. Throughout 1917, Bolsheviks called for the overthrow of the Provisional Government and an end to the war. Following the disastrous failure of the Kerensky offensive, discipline in the Russian army deteriorated completely. Soldiers would disobey orders, often under the influence of Bolshevik agitation, and set up soldiers' committees to take control of their units after deposing the officers.
The defeat and ongoing hardships of war led to anti-government riots in Petrograd, the " July Days" of 1917. Several months later, on 7 November (25 October old style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, this is the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries between 158 ...
), Red Guards seized the Winter Palace
The Winter Palace ( rus, Зимний дворец, Zimnij dvorets, p=ˈzʲimnʲɪj dvɐˈrʲɛts) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the Russian Emperor from 1732 to 1917. The palace and its precincts now ...
and arrested the Provisional Government in what is known as the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
.
A top priority of the newly established Soviet government was to end the war. On 8 November 1917 (26 October 1917 O.S) Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
signed the Decree on Peace, which was approved by the Second Congress of the Soviet of Workers', Soldiers', and Peasants' Deputies. The Decree called "upon all the belligerent nations and their governments to start immediate negotiations for peace" and proposed an immediate withdrawal of Russia from World War I. Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian ...
was appointed Commissar of Foreign Affairs in the new Bolshevik government. In preparation for peace talks with the representatives of the German government and the representatives of the other Central Powers, Leon Trotsky appointed his good friend Adolph Joffe to represent the Bolsheviks at the peace conference.
Peace negotiations
On 15 December 1917, an armistice between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers was concluded. On 22 December, peace negotiations began in Brest-Litovsk. Arrangements for the conference were the responsibility of General Max Hoffmann, the chief of staff of the Central Powers' forces on the Eastern Front (''Oberkommando-Ostfront, Ober Ost''). The delegations that had negotiated the armistice were made stronger. Prominent additions on the Central Powers' side were the foreign ministers of Germany,Richard von Kühlmann
Richard von Kühlmann (3 May 1873 – 16 February 1948) was a German diplomat and industrialist. From 6 August 1917 to 9 July 1918, he served as Germany's Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs, and led the delegation that negotiated the Treat ...
, and Austria-Hungary, Count Ottokar Czernin, both the Ottoman grand vizier Talaat Pasha
Mehmed Talaat (1 September 187415 March 1921), commonly known as Talaat Pasha or Talat Pasha,; tr, Talat Paşa, links=no was an Ottoman politician and convicted war criminal of the late Ottoman Empire who served as its leader from 1913 t ...
and Foreign Minister Nassimy Bey. The Bulgarians were headed by Minister of Justice Popoff, who was later joined by Prime Minister Vasil Radoslavov.
The Soviet delegation was led by Adolph Joffe, who had already led their armistice negotiators, but his group was made more cohesive by eliminating most of the representatives of social groups, like peasants and sailors, and the addition of tsarist general Aleksandr Samoilo and the noted Marxist historian Mikhail Pokrovsky
Mikhail Nikolayevich Pokrovsky (russian: Михаи́л Никола́евич Покро́вский; – April 10, 1932) was a Russian Marxist historian, Bolshevik revolutionary and a public and political figure. One of the earliest professi ...
. It still included Anastasia Bitsenko, a former assassin, representing the Left Socialist-Revolutionaries
The Party of Left Socialist-Revolutionaries (russian: Партия левых социалистов-революционеров-интернационалистов) was a revolutionary socialist political party formed during the Russian Rev ...
who were at odds with the Bolsheviks. Again, the negotiators met in the fortress in Brest-Litovsk, and the delegates were housed in temporary wooden structures in its courtyards because the city had been burnt to the ground in 1915 by the retreating Russian army. They were cordially welcomed by the German commander of the Eastern Front, Prince Leopold of Bavaria, who sat with Joffe on the head table at the opening banquet with one hundred guests. As they had during the armistice negotiations, both sides continued to eat dinner and supper together amicably intermingled in the officers' mess.
When the conference convened Kühlmann asked Joffe to present the Russian conditions for peace. He made six points, all variations of the Bolshevik slogan of peace with "no annexations or indemnities". The Central Powers accepted the principles "but only in case all belligerents ncluding the nations of the Ententewithout exception pledge themselves to do the same". They did not intend to annex territories occupied by force. Joffe telegraphed the marvelous news to Petrograd. Thanks to informal chatting in the mess, one of Hoffmann's aides, Colonel Friedrich Brinckmann, realized that the Russians had optimistically misinterpreted the Central Powers' meaning. It fell to Hoffmann to set matters straight at dinner on 27 December: Poland, Lithuania and Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia ...
, already occupied by the Central Powers, were determined to separate from Russia on the principle of self-determination that the Bolsheviks themselves espoused. Joffe "looked as if he had received a blow on the head". Pokrovsky wept as he asked how they could speak of "peace without annexations when Germany was tearing eighteen provinces away from the Russian state". The Germans and the Austro-Hungarians planned to annex slices of Polish territory and to set up a rump Polish state with what remained. The Baltic provinces were to become client states ruled by German prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. ...
s. Czernin was beside himself that this hitch that was slowing the negotiations; self-determination was anathema to his government and they urgently needed grain from the east because Vienna was on the verge of starvation. He proposed to make a separate peace. Kühlmann warned that if they negotiated separately, Germany would immediately withdraw all its divisions from the Austrian front; Czernin dropped that threat. The food crisis in Vienna was eventually eased by "forced drafts of grain from Hungary, Poland, and Romania and by a last moment contribution from Germany of 450 truck-loads of flour". At Russian request, they agreed to recess the talks for twelve days.
The Soviets' only hopes were that time would make their allies agree to join the negotiations or that the western European proletariat would revolt and so their best strategy was to prolong the negotiations. As Foreign Minister Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian ...
wrote, "To delay negotiations, there must be someone to do the delaying". Therefore, Trotsky replaced Joffe as the leader.
On the other side were significant political realignments. On New Year's Day in Berlin, the Kaiser insisted that Hoffmann reveal his views on the future German-Polish border. He advocated taking a small slice of Poland; Hindenburg and Ludendorff wanted much more. They were furious with Hoffmann for breaching the chain of command and wanted him to be dismissed and sent to command a division. The Kaiser refused, but Ludendorff no longer spoke with Hoffmann on the telephone since the communication was now through an intermediary.
The German Supreme Commanders were also furious at ruling out of annexations, contending that the peace "must increase Germany's material power". They denigrated Kühlmann and pressed for additional territorial acquisitions. When Hindenburg was asked why they needed the Baltic provinces he replied, "To secure my left flank for when the next war happens." However, the most profound transformation was that a delegation from the Ukrainian Rada, which had declared independence from Russia, had arrived at Brest-Litovsk. They would make peace if they were given the Polish city of Cholm and its surroundings, and they would provide desperately needed grain. Czernin no longer was desperate for a prompt settlement with the Russians.
When they reconvened, Trotsky declined the invitation to meet Prince Leopold and terminated shared meals and other sociable interactions with the representatives of the Central Powers. Day after day, Trotsky "engaged Kühlmann in debate, rising to subtle discussion of first principles that ranged far beyond the concrete territorial issues that divided them". The Central Powers signed a peace treaty with Ukraine during the night of 8–9 February even though the Russians had retaken Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
. German and Austro-Hungarian troops entered Ukraine to prop up the Rada. Finally, Hoffmann broke the impasse with the Russians by focusing the discussion on maps of the future boundaries. Trotsky summarised their situation "Germany and Austria-Hungary are cutting off from the domains of the former Russian Empire territories more than 150,000 square kilometers in size". He was granted a nine-day recess for the Russians to decide whether to sign.
 In Petrograd, Trotsky argued passionately against signing and proposed that instead, "they should announce the termination of the war and demobilization without signing any peace." Lenin was for signing rather than having an even more ruinous treaty forced on them after a few more weeks of military humiliation. The "Left Communists", led by
In Petrograd, Trotsky argued passionately against signing and proposed that instead, "they should announce the termination of the war and demobilization without signing any peace." Lenin was for signing rather than having an even more ruinous treaty forced on them after a few more weeks of military humiliation. The "Left Communists", led by Nikolai Bukharin
Nikolai Ivanovich Bukharin (russian: Никола́й Ива́нович Буха́рин) ( – 15 March 1938) was a Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician, Marxist philosopher and economist and prolific author on revolutionary theory. ...
and Karl Radek
Karl Berngardovich Radek (russian: Карл Бернгардович Радек; 31 October 1885 – 19 May 1939) was a Russian revolutionary and a Marxist active in the Polish and German social democratic movements before World War I and a ...
, were sure that Germany, Austria, Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria were all on the verge of revolution. They wanted to continue the war with a newly-raised revolutionary force while awaiting for these upheavals. Consequently, Lenin agreed to Trotsky's formula—a position summed up as "no war – no peace"—which was announced when the negotiators reconvened on 10 February 1918. The Soviets thought that their stalling was succeeding until 16 February when Hoffmann notified them that the war would resume in two days, when fifty-three divisions advanced against the near-empty Soviet trenches. On the night of 18 February, the Central Committee supported Lenin's resolution that they sign the treaty by a margin of seven to five. Hoffmann kept advancing until 23 February when he presented new terms that included the withdrawal of all Soviet troops from Ukraine and Finland. The Soviets were given 48 hours to open negotiations with the Germans, and another 72 to conclude them. Lenin told the Central Committee that "you must sign this shameful peace in order to save the world revolution". If they did not agree, he would resign. He was supported by six Central Committee members, opposed by three, with Trotsky and three others abstaining. Debate in the All-Russian Central Executive Committee
The All-Russian Central Executive Committee ( rus, Всероссийский Центральный Исполнительный Комитет, Vserossiysky Centralny Ispolnitelny Komitet, VTsIK) was the highest legislative, administrative and r ...
was intense, with Left SRs jeering Lenin as a traitor. The measure passed 116 to 85.
Trotsky resigned as foreign minister and was replaced by Georgy Chicherin
Georgy Vasilyevich Chicherin (24 November 1872 – 7 July 1936), also spelled Tchitcherin, was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and a Soviet politician who served as the first People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs in the Soviet government from ...
.
When Sokolnikov arrived at Brest-Litovsk, he declared "we are going to sign immediately the treaty presented to us as an ultimatum but at the same time refuse to enter into any discussion of its terms". The treaty was signed at 17:50 on 3 March 1918.
Terms
Signing
 The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918. The signatories were Soviet Russia signed by
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918. The signatories were Soviet Russia signed by Grigori Sokolnikov
Grigori Yakovlevich Sokolnikov (born Hirsch Brilliant or Girsh Yankelevich Brilliant; 1888–1939) was a Russian Old Bolshevik revolutionary, economist, and Soviet politician.
Early career
Grigori Sokolnikov was born Girsh Yankelevich Brillian ...
on the one side and the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and Ottoman Empire on the other.
The treaty marked Russia's final withdrawal from World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
as an enemy of her co-signatories, on severe terms. In all, the treaty took away territory that included a quarter of the population and the industry of the former Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
and nine tenths of its coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron fro ...
.
Territorial cessions in eastern Europe
Russia renounced all territorial claims inFinland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
(whose independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the stat ...
it had already recognized), Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, most of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
. The territory of the Kingdom of Poland was not mentioned in the treaty, as the Germans refused to recognize the existence of any Polish representatives, which in turn led to Polish protests. The treaty stated that "Germany and Austria-Hungary intend to determine the future fate of these territories in agreement with their populations." Most of the territories were in effect ceded to Germany, which intended to have them become economic and political dependencies, where the local German-speaking minority would be the ruling elite. New monarchies were to be created in Lithuania and the proposed "United Baltic Duchy
The United Baltic Duchy (german: Vereinigtes Baltisches Herzogtum, lv, Apvienotā Baltijas hercogiste, et, Balti Hertsogiriik), or alternatively the Grand Duchy of Livonia, was the name proposed during World War I by leaders of the local ...
" (which was planned to comprise Latvia and Estonia). Later in 1918, German aristocrats Wilhelm Karl, Duke of Urach
Prince Wilhelm of Urach, Count of Württemberg, 2nd Duke of Urach (''Wilhelm Karl Florestan Gero Crescentius''; German: ''Fürst Wilhelm von Urach, Graf von Württemberg, 2. Herzog von Urach''; 30 May 1864 – 24 March 1928), was a German prince w ...
(for Lithuania), and Adolf Friedrich, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (for the planned United Baltic Duchy), were nominally appointed, however in reality never became, rulers of these envisaged new pro-German countries.
This plan was detailed by German Colonel General Erich Ludendorff
Erich Friedrich Wilhelm Ludendorff (9 April 1865 – 20 December 1937) was a German general, politician and military theorist. He achieved fame during World War I for his central role in the German victories at Liège and Tannenberg in 1914. ...
, who wrote, "German prestige demands that we should hold a strong protecting hand, not only over German citizens, but over all Germans."
 The occupation of the western part of former Russian Empire ultimately proved a costly blunder for Berlin, as over one million German troops lay sprawled out from Poland nearly to the
The occupation of the western part of former Russian Empire ultimately proved a costly blunder for Berlin, as over one million German troops lay sprawled out from Poland nearly to the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
, all idle and depriving Germany of badly needed manpower in France. The hopes of using Ukraine's grain and coal proved abortive; in addition, the local population became increasingly hostile to the occupation. Revolts and guerrilla warfare began breaking out all over the occupied territory, many of them inspired by Bolshevik agents. German troops also had to intervene in the Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War; . Other designations: Brethren War, Citizen War, Class War, Freedom War, Red Rebellion and Revolution, . According to 1,005 interviews done by the newspaper ''Aamulehti'', the most popular names were as follows: Civil W ...
, and Ludendorff became increasingly concerned that his troops were being affected by propaganda emanating from Moscow, which was one of the reasons he was reluctant to transfer divisions to the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
. The attempt at establishing an independent Ukrainian state under German guidance was unsuccessful as well. However, Ludendorff completely ruled out the idea of marching on Moscow and Petrograd to remove the Bolshevik government from power.
Germany transferred hundreds of thousands of veteran troops to the Western Front for the 1918 Spring Offensive, which shocked the Allied Powers but ultimately failed. Some Germans later blamed the occupation for significantly weakening the Spring Offensive.
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
became independent, while Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
united with Romania.
Russia lost 34% of its population, 54% of its industrial land, 89% of its coalfields, and 26% of its railways. Russia was also fined 300 million gold marks.
Territorial cessions in the Caucasus
At the insistence ofTalaat Pasha
Mehmed Talaat (1 September 187415 March 1921), commonly known as Talaat Pasha or Talat Pasha,; tr, Talat Paşa, links=no was an Ottoman politician and convicted war criminal of the late Ottoman Empire who served as its leader from 1913 t ...
, the treaty declared that the territory Russia took from the Ottoman Empire in the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 ( tr, 93 Harbi, lit=War of ’93, named for the year 1293 in the Islamic calendar; russian: Русско-турецкая война, Russko-turetskaya voyna, "Russian–Turkish war") was a conflict between th ...
, specifically Ardahan
Ardahan (, ka, არტაანი, tr, hy, Արդահան, translit=Ardahan Russian: Ардаган) is a city in northeastern Turkey, near the Georgian border.
It is the capital of Ardahan Province.
History
Ancient and medieval
Ardaha ...
, Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of ...
, and Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ) is the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), second largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's ...
, were to be returned. At the time of the treaty, this territory was under the effective control of Armenian and Georgian forces.
Paragraph 3 of Article IV of the treaty stated that:
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
rejected the treaty and instead declared independence. They formed the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic
The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic (TDFR; (), (). 22 April – 28 May 1918) was a short-lived state in the Caucasus that included most of the territory of the present-day Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia, as well as ...
.
Soviet-German financial agreement of August 1918
In the wake of Soviet repudiation of Tsarist bonds, the nationalisation of foreign-owned property and confiscation of foreign assets, and Entente forces landing on Russian territory, the Soviets and Germany signed an additional agreement on 27 August 1918. The Soviets agreed to pay six billion marks in compensation for German losses. The amount was equal to 300 million rubles. The Soviets additionally agreed to sell Germany 25% of the output of theBaku oil fields
The petroleum industry in Azerbaijan produces about of oil per day and 29 billion cubic meters of gas per year as of 2013. Azerbaijan is one of the birthplaces of the oil industry.
The State Oil Company of Azerbaijan Republic (known as SOCAR) i ...
.
Three secret clauses provided for German military action against Entente forces on Russian soil, as well as the expulsion of British troops from Baku.
Lasting effects
The treaty meant that Russia now was helping Germany win the war by freeing up a million German soldiers for the Western Front and by "relinquishing much of Russia's food supply, industrial base, fuel supplies, and communications with Western Europe". According to historian Spencer Tucker, the Allied Powers felt that"The treaty was the ultimate betrayal of the Allied cause and sowed the seeds for the Cold War. With Brest-Litovsk, the spectre of German domination in Eastern Europe threatened to become reality, and the Allies now began to think seriously about military intervention n Russia"For the Western Allied Powers, the terms that Germany had imposed on Russia were interpreted as a warning of what to expect if the Central Powers won the war. Between Brest-Litovsk and the point when the situation in the Western Front became dire, some officials in the German government and the high command began to favour offering more lenient terms to the Allied Powers in exchange for their recognition of German gains in the east. The treaty marked a significant contraction of the territory controlled by the Bolsheviks or that they could lay claim to as effective successors of the Russian Empire. While the independence of Poland was already accepted by them in principle, and Lenin had signed a document accepting the Finnish independence, the loss of Ukraine and the Baltics created, from the Bolshevik perspective, dangerous bases of anti-Bolshevik military activity in the subsequent
Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
(1917–1923). However, Bolshevik control of Ukraine and Transcaucasia was at the time fragile or non-existent.
Many Russian nationalists and some revolutionaries were furious at the Bolsheviks' acceptance of the treaty and joined forces to fight them. Non-Russians who inhabited the lands lost by Bolshevik Russia in the treaty saw the changes as an opportunity to set up independent states.
Immediately after the signing of the treaty, Lenin moved the Soviet government from Petrograd to Moscow. Trotsky blamed the peace treaty on the bourgeoisie, the social revolutionaries, Tsarist diplomats, Tsarist bureaucrats, "the Kerenskys, Tseretelis and Chernovs"., the Tsarist regime, and the "petty-bourgeois compromisers".
The treaty opened a permanent rift between the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
and Left Socialist Revolutionaries. In July 1918 the Left SRs assassinated German Ambassador Wilhelm von Mirbach in the hopes that it would induce Germany to annul the treaty, leading to the Left SR Uprising.'' Richard Pipes
Richard Edgar Pipes ( yi, ריכארד פּיִפּעץ ''Rikhard Pipets'', the surname literally means 'beak'; pl, Ryszard Pipes; July 11, 1923 – May 17, 2018) was an American academic who specialized in Russian and Soviet history. He publi ...
''. Bolsheviks in the struggle for power.
Relations between Russia and the Central Powers did not go smoothly. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
broke the treaty by invading the newly created First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
in May 1918. Joffe became the Russian ambassador to Germany. His priority was distributing propaganda to trigger the German revolution. On 4 November 1918, "the Soviet courier's packing-case had 'come to pieces in a Berlin railway station; it was filled with insurrectionary documents. Joffe and his staff were ejected from Germany in a sealed train on 5 November 1918. In the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
that ended World War I, one clause abrogated the Brest-Litovsk treaty. Next, the Bolshevik legislature ( VTsIK) annulled the treaty on 13 November 1918, and the text of the VTsIK Decision was printed in the newspaper ''Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the ...
'' the next day. In the year after the armistice following a timetable set by the victors, the German Army withdrew its occupying forces from the lands gained in Brest-Litovsk. However, relations between Russia and the Allied Powers were also bad due to the Allied Powers' intervention in the Russian Civil War against the Soviet government of Russia and its allies. The fate of the region, and the location of the eventual western border of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, was settled in violent and chaotic struggles over the course of the next three and a half years. The Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
was particularly bitter; it ended with the Treaty of Riga in 1921. Although most of Ukraine and Belarus fell under Bolshevik control and eventually became one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union, Poland and the Baltic states re-emerged as independent nations. In the Treaty of Rapallo, concluded in April 1922, Germany accepted the Treaty's nullification, and the two powers agreed to abandon all war-related territorial and financial claims against each other. This state of affairs lasted until 1939, when after signing the secret protocol to the Nazi-Soviet pact, the Soviet Union was able to advance its borders westward by invading Poland in September 1939, by conquering parts of eastern Finland in the 1939-1940 Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
, and by invading and occupying Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and parts of Romania (Bessarabia and northern Bukovina) in 1940. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the Soviet leadership was thus able to overturn the majority of the territorial losses incurred at Brest-Litovsk, except for the larger part of Finland, western Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
, and western Armenia.
The Russian borders established by the treaty bear an almost exact similarity to the post-1991 borders established after the fall of the Soviet Union.
Portraits
Emil Orlik, theViennese Secession
The Vienna Secession (german: Wiener Secession; also known as ''the Union of Austrian Artists'', or ''Vereinigung Bildender Künstler Österreichs'') is an art movement, closely related to Art Nouveau, that was formed in 1897 by a group of Austri ...
ist artist, attended the conference, at the invitation of Richard von Kühlmann. He drew portraits of all the participants, along with a series of smaller caricatures. These were gathered together into a book, ''Brest-Litovsk,'' a copy of which was given to each of the participants.Jewish Museum in Prague (2013–2015)Emil Orlik (1870–1932) – Portraits of Friends and Contemporaries
escription of exhibition in 2004 Retrieved 2015-04-03.
See also
*History of Belarus
This article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs.
Belarus is a successor of some Ruthenian principalities (Polotsk, Turov, Novogrudok, etc.), the Grand Duchy of Lithuan ...
* Mitteleuropa
* Armistice of Focșani
* Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (9 February 1918), signed by Ukraine
* 1918 Russia–Ukraine negotiations
References
Further reading
* Bailey, Sydney D. "Brest-Litovsk: A Study in Soviet Diplomacy" ''History Today'' 6#8 1956 p511–521. * , a major scholarly historyexcerpt
als
online review
* * * * * *, primary sources. * UK National Archives
''online''
*, older scholarly history.
External links
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (Yale University Avalon Project)
including links to appendices.
* ttps://omniatlas.com/maps/europe/19180320/ Map of Europeafter the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, at omniatlas.com. * Susanne Schattenberg
Brest-Litovsk, Treaty of
in
* ''The Times History of the War'', Volume XIV, London: Printing House Square, 1918
pp. 1-37
*
David R. Stone
David Russell Stone (born 1968) is an American military historian and the William Eldridge Odom Professor of Russian Studies in the Strategy and Policy Department at the U.S. Naval War College.
Stone received a Bachelor of Arts degree in histo ...
"The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk," lecture presented at National World War I Museum, 2018
{{DEFAULTSORT:Brest-Litovsk, Treaty of World War I treaties Treaties concluded in 1918 Treaties entered into force in 1918 Peace treaties of Germany Peace treaties of Austria Peace treaties of the Ottoman Empire Peace treaties of Bulgaria Peace treaties of Russia
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
Aftermath of World War I in Russia and in the Soviet Union
Aftermath of World War I in Ukraine
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
Treaties of the German Empire
Treaties of Austria-Hungary
Treaties of the Kingdom of Bulgaria
Treaties of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
1918 in Ukraine
1918 in Belarus
1918 in Armenia
1918 in Georgia (country)
Ukrainian independence movement
March 1918 events
Dissolution of the Russian Empire
Treaties of the Ottoman Empire