Brain biopsy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brain biopsy is the removal of a small piece of brain tissue for the diagnosis of abnormalities of the
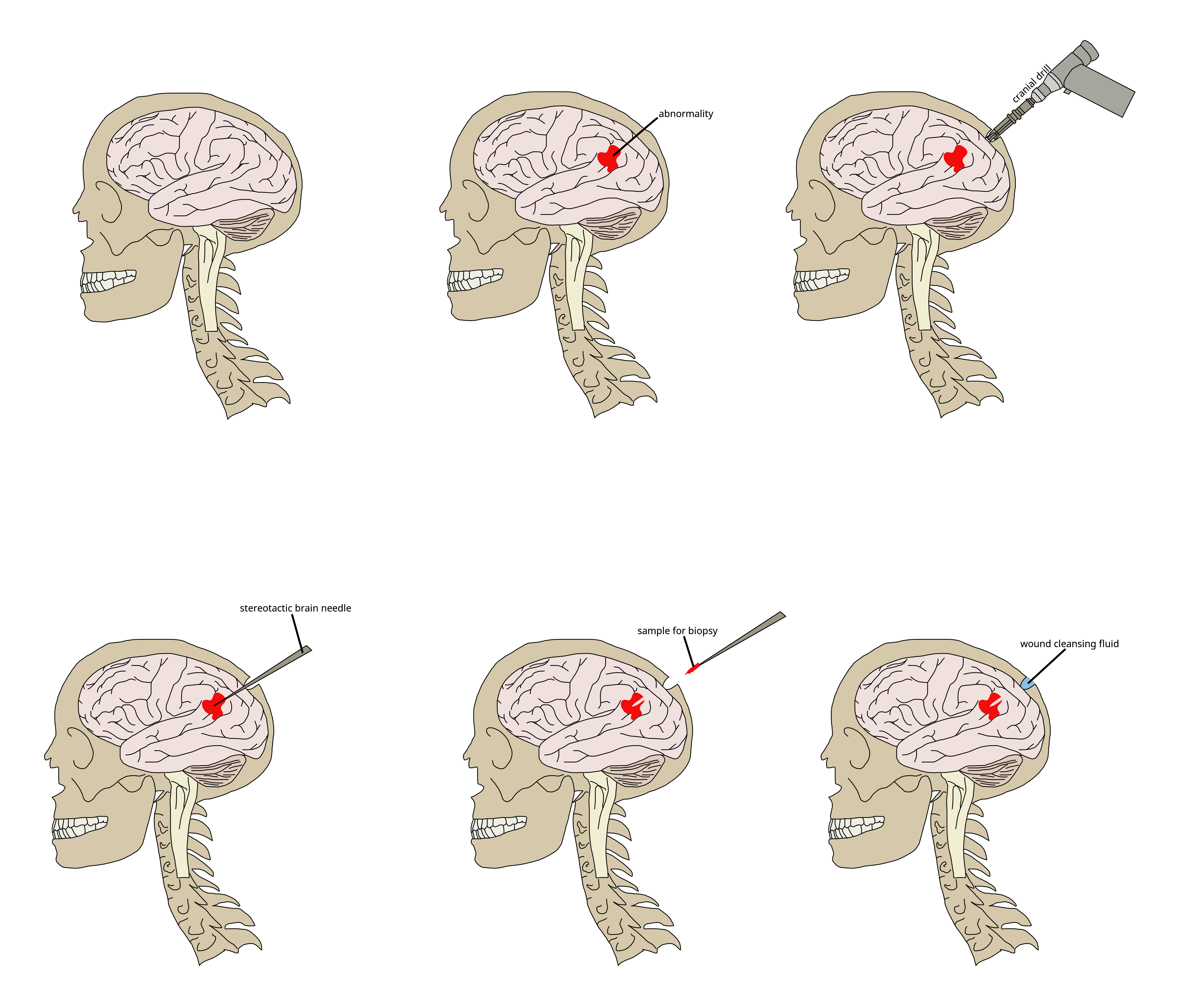 Procedures are categorized into stereotactic, needle, and open. Stereotactic is the least invasive and open is the most invasive.
When an abnormality of the brain is suspected, stereotactic (probing in three dimensions) brain needle biopsy is performed and guided precisely by a computer system to avoid serious complications. A small hole is drilled into the skull, and a needle is inserted into the brain tissue guided by computer-assisted imaging techniques (CT or MRI scans). Historically, the patient's head was held in a rigid frame to direct the probe into the brain; however, since the early 1990s, it has been possible to perform these biopsies without the frame. Since the frame was attached to the skull with screws, this advancement is less invasive and better tolerated by the patient. The doctor (pathologist) prepares the sample for analysis and studies it further under a microscope.
Procedures are categorized into stereotactic, needle, and open. Stereotactic is the least invasive and open is the most invasive.
When an abnormality of the brain is suspected, stereotactic (probing in three dimensions) brain needle biopsy is performed and guided precisely by a computer system to avoid serious complications. A small hole is drilled into the skull, and a needle is inserted into the brain tissue guided by computer-assisted imaging techniques (CT or MRI scans). Historically, the patient's head was held in a rigid frame to direct the probe into the brain; however, since the early 1990s, it has been possible to perform these biopsies without the frame. Since the frame was attached to the skull with screws, this advancement is less invasive and better tolerated by the patient. The doctor (pathologist) prepares the sample for analysis and studies it further under a microscope.
brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
. It is used to diagnose tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
, and other brain disorders
A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle we ...
. By examining the tissue sample under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
, the biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
sample provides information about the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Indications
Given the potential risks surrounding the procedure, cerebral biopsy is indicated only if other diagnostic approaches (e.g.magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
) have been insufficient in showing the cause of symptoms, and if it is felt that the benefits of histological diagnosis will influence the treatment plan.
If the person has a brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seco ...
, biopsy is 95% sensitive. The procedure can also be valuable in people who are immunocompromised and who have evidence of brain lesions that could be caused by opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immun ...
s. In other groups, particularly those with unexplained neurological disease, a diagnosis is reached by performing a biopsy in half the cases where it is done, and it has helpful practical effect in 30% of people. If primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) is suspected, brain biopsy is most likely to positively influence the treatment plan.
Preparation
A CT or MRI brain scan is done to find the position where the biopsy will be performed. Prior to the biopsy, the patient is placed under general anesthesia.Procedure
 Procedures are categorized into stereotactic, needle, and open. Stereotactic is the least invasive and open is the most invasive.
When an abnormality of the brain is suspected, stereotactic (probing in three dimensions) brain needle biopsy is performed and guided precisely by a computer system to avoid serious complications. A small hole is drilled into the skull, and a needle is inserted into the brain tissue guided by computer-assisted imaging techniques (CT or MRI scans). Historically, the patient's head was held in a rigid frame to direct the probe into the brain; however, since the early 1990s, it has been possible to perform these biopsies without the frame. Since the frame was attached to the skull with screws, this advancement is less invasive and better tolerated by the patient. The doctor (pathologist) prepares the sample for analysis and studies it further under a microscope.
Procedures are categorized into stereotactic, needle, and open. Stereotactic is the least invasive and open is the most invasive.
When an abnormality of the brain is suspected, stereotactic (probing in three dimensions) brain needle biopsy is performed and guided precisely by a computer system to avoid serious complications. A small hole is drilled into the skull, and a needle is inserted into the brain tissue guided by computer-assisted imaging techniques (CT or MRI scans). Historically, the patient's head was held in a rigid frame to direct the probe into the brain; however, since the early 1990s, it has been possible to perform these biopsies without the frame. Since the frame was attached to the skull with screws, this advancement is less invasive and better tolerated by the patient. The doctor (pathologist) prepares the sample for analysis and studies it further under a microscope.
Aftercare
The patient is monitored in the recovery room for several hours following the biopsy. Neurological assessments are performed once the patient is fully awake and if left without deficit, most patients can be discharged the day after surgery.Risks
The procedure is invasive and includes risks associated with anesthesia and surgery. Brain injury may occur due to removal of brain tissue. The resulting scar left on the brain has the potential to trigger seizures. If brain biopsy is performed for a possible tumor (which contain more blood vessels), the risk of death is 1% and a risk of complications 12%. For unexplained neurological disease, there is no risk of death and a complication rate of 9%; complications were more common in PACNS.Interpretation
Various brain abnormalities can be diagnosed by microscopic analysis of the tissue sample. The pathologist (a physician trained in how disease affects the body's tissues) looks for abnormal growth, changes in cell membranes, and/or abnormal collections of cells. In Alzheimer's disease, the cortex of the brain contains abnormal collections of plaques. If infection is suspected, the infectious organism can be cultured from the tissue and identified. Classification of tumors is also possible after biopsy.References