Dept of the Interior, Office of Insular Affairs. DOI.gov
), import/export taxes (se
Stanford.wellsphere.com
), federal commodity taxes (se
Stanford.wellsphere.com
), social security taxes (se
, etc. Residents pay federal
IRS.gov
and Medicare (se
Reuters.com
, as well as Commonwealth of Puerto Rico income taxes (se
an
). All federal employees (se
Heritage.org
), those who do business with the federal government (se
MCVPR.com
), Puerto Rico-based corporations that intend to send funds to the U.S. (se
p. 9, line 1.
), and some others (For example, Puerto Rican residents that are members of the U.S. military, se
Heritage.org
; and Puerto Rico residents who earned income from sources outside Puerto Rico, se
pp 14–15.
also pay federal income taxes). In addition, because the cutoff point for income taxation is lower than that of the U.S. IRS code, and because the per-capita income in Puerto Rico is much lower than the average per-capita income on the mainland, more Puerto Rico residents pay income taxes to the local taxation authority than if the IRS code were applied to the island. This occurs because "the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico government has a wider set of responsibilities than do U.S. State and local governments" (se
GAO.gov
. As residents of Puerto Rico pay into Social Security, Puerto Ricans are eligible for Social Security benefits upon retirement, but are excluded from the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) (Commonwealth of Puerto Rico residents, unlike residents of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and residents of the 50 States, do not receive the SSI; se
Socialsecurity.gov
, and the island actually receives less than 15% of the
p 252.
). In general, "many federal social welfare programs have been extended to Puerto Rico residents, although usually with caps inferior to those allocated to the states." (The Louisiana Purchase and American Expansion: 1803–1898. By Sanford Levinson and Bartholomew H. Sparrow. New York: Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. 2005. Page 167. For a comprehensive coverage of federal programs made extensive to Puerto Rico, see Richard Cappalli's Federal Aid to Puerto Rico (1970).) It has also been estimated (se
that, because the population of the Island is greater than that of 50% of the States, if it were a state, Puerto Rico would have six to eight seats in the House, in addition to the two seats in the Senate. (Se
an
Thomas.gov
. For the later, the official U.S. Congress database website, a query must be resubmitted. The document in question is called "House Report 110-597 – Puerto Rico Democracy Act of 2007." These are the steps to follow to submit a query: > Committee Reports > 110 > drop down "Word/Phrase" and pick "Report Number" > type "597" next to Report Number. This will provide the document "House Report 110-597 – 2007". Then, from the Table of Contents choose "Background and need for legislation".) Another misconception is that the import/export taxes collected by the U.S. on products manufactured in Puerto Rico are all returned to the Puerto Rico Treasury. This is not the case. Such import/export taxes are returned ''only'' for rum products and, even then, the US Treasury keeps a portion of those taxes (see the "House Report 110-597 – Puerto Rico Democracy Act of 2007" mentioned above).
Etymology
Puerto Rico is Spanish for "rich port". Puerto Ricans often call the island , a derivation of , itsHistory
Pre-Columbian era
Spanish colony (1493–1898)
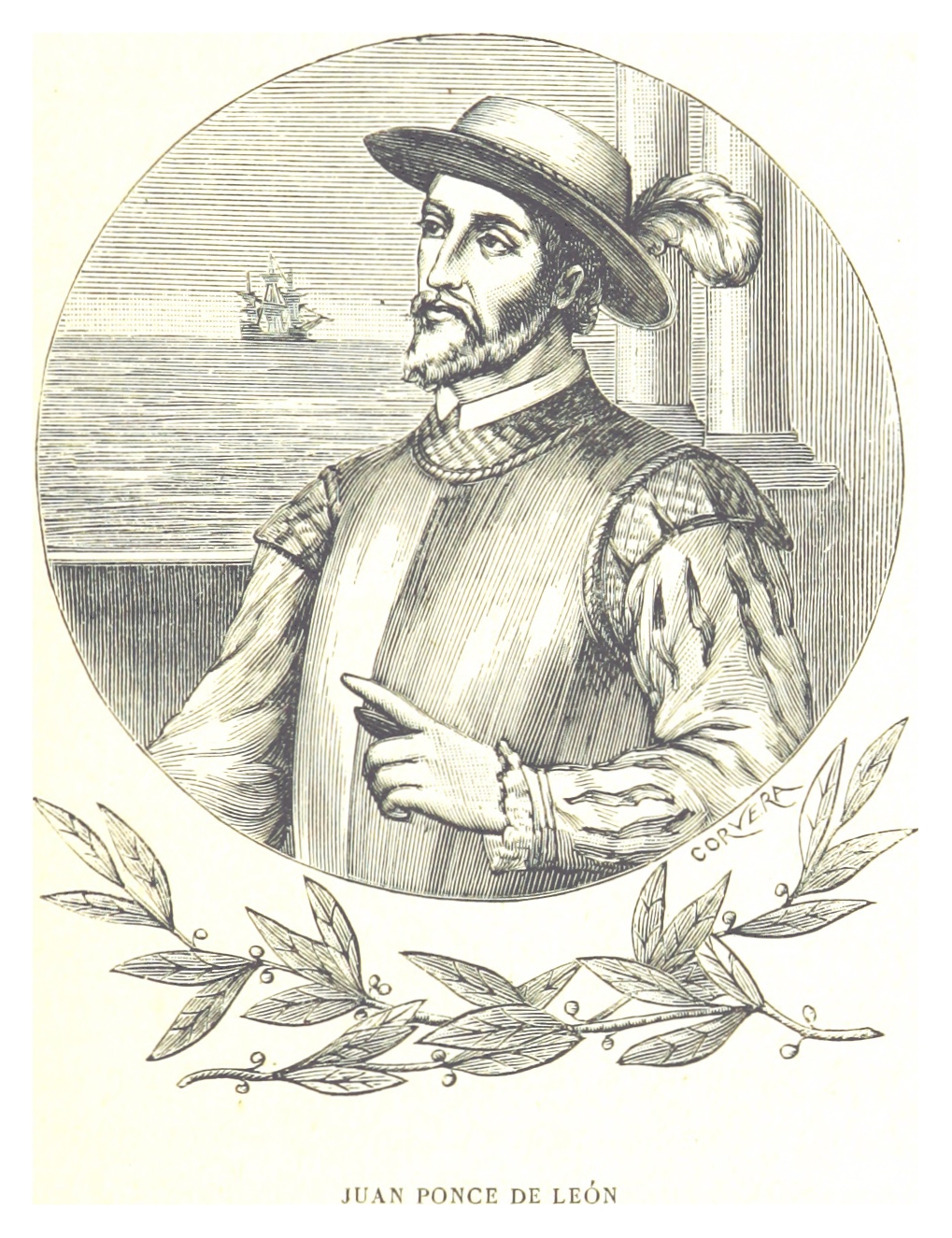

Conquest and early settlement
When Columbus arrived in Puerto Rico during his second voyage on 19 November 1493, the island was inhabited by the Taíno. They called it ''Borikén'', spelled in a variety of ways by different writers of the day. Columbus named the island San Juan Bautista, in honor of StColonization under the Habsburgs
In 1520, King Charles I of Spain issued a royal decree collectively emancipating the remaining Taíno population. By that time, the Taíno people were few in number. Enslaved Africans had already begun to be imported to compensate for the native labor loss, but their numbers were proportionate to the diminished commercial interest Spain soon began to demonstrate for the island colony. Other nearby islands, like In 1625, in the Battle of San Juan, the
In 1625, in the Battle of San Juan, the Late colonial period
 During the late 16th and early 17th centuries, Spain concentrated its colonial efforts on the more prosperous mainland North, Central, and South American colonies. With the advent of the lively Bourbon Dynasty in Spain in the 1700s, the island of Puerto Rico began a gradual shift to more imperial attention. More roads began connecting previously isolated inland settlements to coastal cities, and coastal settlements like Arecibo, Mayaguez, and Ponce began acquiring importance of their own, separate from San Juan. By the end of the 18th century, merchant ships from an array of nationalities threatened the tight regulations of the Mercantilist system, which turned each colony solely toward the European metropole and limited contact with other nations. U.S. ships came to surpass Spanish trade and with this also came the exploitation of the island's natural resources. Slavers, which had made but few stops on the island before, began selling more enslaved Africans to growing sugar and coffee plantations. The increasing number of Atlantic wars in which the Caribbean islands played major roles, like the
During the late 16th and early 17th centuries, Spain concentrated its colonial efforts on the more prosperous mainland North, Central, and South American colonies. With the advent of the lively Bourbon Dynasty in Spain in the 1700s, the island of Puerto Rico began a gradual shift to more imperial attention. More roads began connecting previously isolated inland settlements to coastal cities, and coastal settlements like Arecibo, Mayaguez, and Ponce began acquiring importance of their own, separate from San Juan. By the end of the 18th century, merchant ships from an array of nationalities threatened the tight regulations of the Mercantilist system, which turned each colony solely toward the European metropole and limited contact with other nations. U.S. ships came to surpass Spanish trade and with this also came the exploitation of the island's natural resources. Slavers, which had made but few stops on the island before, began selling more enslaved Africans to growing sugar and coffee plantations. The increasing number of Atlantic wars in which the Caribbean islands played major roles, like the  In 1809, to secure its political bond with the island and in the midst of the European
In 1809, to secure its political bond with the island and in the midst of the European Politics of liberalism
 In the early 19th century, Puerto Rico spawned an independence movement that, due to harsh persecution by the Spanish authorities, convened in the island of St. Thomas. The movement was largely inspired by the ideals of Simón Bolívar in establishing a
In the early 19th century, Puerto Rico spawned an independence movement that, due to harsh persecution by the Spanish authorities, convened in the island of St. Thomas. The movement was largely inspired by the ideals of Simón Bolívar in establishing a  Leaders of "El Grito de Lares" went into exile in New York City. Many joined the Revolutionary Committee of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican Revolutionary Committee, founded on 8 December 1895, and continued their quest for Puerto Rican independence. In 1897, Antonio Mattei Lluberas and the local leaders of the independence movement in Yauco organized another uprising, which became known as the ''Intentona de Yauco''. They raised what they called the Puerto Rican flag, which was adopted as the national flag. The local conservative political factions opposed independence. Rumors of the planned event spread to the local Spanish authorities who acted swiftly and put an end to what would be the last major uprising in the island to Spanish colonial rule.
In 1897, Luis Muñoz Rivera and others persuaded the liberal Spanish government to agree to grant limited self-government to the island by Decree, royal decree in the Autonomic Charter, including a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature. In 1898, Puerto Rico's first, but short-lived, autonomous government was organized as an "overseas province" of Spain. This bilaterally agreed-upon charter maintained a governor appointed by the Monarchy of Spain, King of Spain—who held the power to annul any legislative decision—and a partially elected parliamentary structure. In February, Governor-General Manuel Macías y Casado, Manuel Macías inaugurated the new government under the Autonomic Charter. General elections were held in March and the new government began to function on 17 July 1898.
Leaders of "El Grito de Lares" went into exile in New York City. Many joined the Revolutionary Committee of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican Revolutionary Committee, founded on 8 December 1895, and continued their quest for Puerto Rican independence. In 1897, Antonio Mattei Lluberas and the local leaders of the independence movement in Yauco organized another uprising, which became known as the ''Intentona de Yauco''. They raised what they called the Puerto Rican flag, which was adopted as the national flag. The local conservative political factions opposed independence. Rumors of the planned event spread to the local Spanish authorities who acted swiftly and put an end to what would be the last major uprising in the island to Spanish colonial rule.
In 1897, Luis Muñoz Rivera and others persuaded the liberal Spanish government to agree to grant limited self-government to the island by Decree, royal decree in the Autonomic Charter, including a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature. In 1898, Puerto Rico's first, but short-lived, autonomous government was organized as an "overseas province" of Spain. This bilaterally agreed-upon charter maintained a governor appointed by the Monarchy of Spain, King of Spain—who held the power to annul any legislative decision—and a partially elected parliamentary structure. In February, Governor-General Manuel Macías y Casado, Manuel Macías inaugurated the new government under the Autonomic Charter. General elections were held in March and the new government began to function on 17 July 1898.
Spanish–American War
 In 1890, Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan, a member of the Navy War Board and leading U.S. strategic thinker, published a book titled ''The Influence of Sea Power upon History'' in which he argued for the establishment of a large and powerful navy modeled after the British Royal Navy. Part of his strategy called for the acquisition of colonies in the Caribbean, which would serve as coaling and naval stations. They would serve as strategic points of defense with the construction of a canal through the Isthmus of Panama, to allow easier passage of ships between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.Jorge Rodriguez Beruff, ''Strategy as Politics'', Universidad de Puerto Rico: La Editorial; p. 7;
In 1890, Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan, a member of the Navy War Board and leading U.S. strategic thinker, published a book titled ''The Influence of Sea Power upon History'' in which he argued for the establishment of a large and powerful navy modeled after the British Royal Navy. Part of his strategy called for the acquisition of colonies in the Caribbean, which would serve as coaling and naval stations. They would serve as strategic points of defense with the construction of a canal through the Isthmus of Panama, to allow easier passage of ships between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.Jorge Rodriguez Beruff, ''Strategy as Politics'', Universidad de Puerto Rico: La Editorial; p. 7;
 William H. Seward, the Secretary of State under presidents Abraham Lincoln and Andrew Johnson, had also stressed the importance of building a canal in Honduras, Nicaragua or Panama. He suggested that the United States annex the Dominican Republic and purchase Puerto Rico and Cuba. The U.S. Senate did not approve his annexation proposal, and Spain rejected the U.S. offer of dollars for Puerto Rico and Cuba.
Since 1894, the United States Naval War College had been developing contingency plans for a war with Spain. By 1896, the U.S. Office of Naval Intelligence had prepared a plan that included military operations in Puerto Rican waters. Plans generally centered on attacks on Spanish territories were intended as support operations against Spain's forces in and around Cuba. Recent research suggests that the U.S. did consider Puerto Rico valuable as a naval station, and recognized that it and Cuba generated lucrative crops of sugar, a valuable commercial commodity which the United States lacked prior to the development of the sugar beet industry in the United States.
On 25 July 1898, during the
William H. Seward, the Secretary of State under presidents Abraham Lincoln and Andrew Johnson, had also stressed the importance of building a canal in Honduras, Nicaragua or Panama. He suggested that the United States annex the Dominican Republic and purchase Puerto Rico and Cuba. The U.S. Senate did not approve his annexation proposal, and Spain rejected the U.S. offer of dollars for Puerto Rico and Cuba.
Since 1894, the United States Naval War College had been developing contingency plans for a war with Spain. By 1896, the U.S. Office of Naval Intelligence had prepared a plan that included military operations in Puerto Rican waters. Plans generally centered on attacks on Spanish territories were intended as support operations against Spain's forces in and around Cuba. Recent research suggests that the U.S. did consider Puerto Rico valuable as a naval station, and recognized that it and Cuba generated lucrative crops of sugar, a valuable commercial commodity which the United States lacked prior to the development of the sugar beet industry in the United States.
On 25 July 1898, during the American colony (1898–present)
U.S. unincorporated organized territory
The United States and Puerto Rico began a long-standing metropolis-colony relationship. This relationship has been documented by numerous scholars, including U.S. Federal Appeals Judge Juan Torruella, U.S. Congresswoman Nydia Velázquez, Chief Justice of the Puerto Rico Supreme Court José Trías Monge, and former Albizu University president Ángel Collado-Schwarz. In the early 20th century, Puerto Rico was ruled by the U.S. military, with officials including the governor appointed by the president of the United States. The Foraker Act of 1900 gave Puerto Rico a certain amount of civilian popular government, including a popularly elected House of Representatives. The upper house and governor were appointed by the United States.U.S. citizenship and Puerto Rican citizenship
In 1917, the U.S. Congress passed the Jones–Shafroth Act (popularly known as the Jones Act), which granted Puerto Ricans born on or after 25 April 1898 U.S. citizenship. Opponents, including all the Puerto Rican House of Delegates (who voted unanimously against it), claimed the U.S. imposed citizenship to draft Puerto Rican men for American entry into World War I, America's entry into World War I the same year.Juan Gonzalez; ''Harvest of Empire'', pp. 60–63; Penguin Press, 2001; The Jones Act also provided for a popularly elected Senate to complete a bicameral Legislative Assembly, as well as a bill of rights. It authorized the popular election of the Resident Commissioner to a four-year term. Natural disasters, including a major 1918 San Fermín earthquake, earthquake and tsunami in 1918 and several hurricanes, as well as the Great Depression, impoverished the island during the first few decades under U.S. rule. Some political leaders, such as Pedro Albizu Campos, who led the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party, demanded a change in relations with the United States. He organized a protest at the University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras Campus, University of Puerto Rico in 1935, in which Río Piedras massacre, four were killed by police.
In 1936, U.S. senator Millard Tydings introduced a bill supporting independence for Puerto Rico; he had previously co-sponsored the Tydings–McDuffie Act, which provided independence to the Philippines following a 10-year transition period of limited autonomy. While virtually all Puerto Rican political parties supported the bill, it was opposed by Luis Muñoz Marín of the Liberal Party of Puerto Rico, leading to its defeat
In 1937, Albizu Campos' party organized a protest in Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce. The Insular Police, similar to the National Guard of the United States, National Guard, opened fire upon unarmed cadets and bystanders alike. The attack on unarmed protesters was reported by U.S. Congressman Vito Marcantonio and confirmed by a report from the Hays Commission, which investigated the events, led by Arthur Garfield Hays, counsel to the American Civil Liberties Union. Nineteen people were killed and over 200 were badly wounded, many shot in the back while running away."Five Years of Tyranny", Speech before the U.S. House of Representatives.
Natural disasters, including a major 1918 San Fermín earthquake, earthquake and tsunami in 1918 and several hurricanes, as well as the Great Depression, impoverished the island during the first few decades under U.S. rule. Some political leaders, such as Pedro Albizu Campos, who led the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party, demanded a change in relations with the United States. He organized a protest at the University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras Campus, University of Puerto Rico in 1935, in which Río Piedras massacre, four were killed by police.
In 1936, U.S. senator Millard Tydings introduced a bill supporting independence for Puerto Rico; he had previously co-sponsored the Tydings–McDuffie Act, which provided independence to the Philippines following a 10-year transition period of limited autonomy. While virtually all Puerto Rican political parties supported the bill, it was opposed by Luis Muñoz Marín of the Liberal Party of Puerto Rico, leading to its defeat
In 1937, Albizu Campos' party organized a protest in Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce. The Insular Police, similar to the National Guard of the United States, National Guard, opened fire upon unarmed cadets and bystanders alike. The attack on unarmed protesters was reported by U.S. Congressman Vito Marcantonio and confirmed by a report from the Hays Commission, which investigated the events, led by Arthur Garfield Hays, counsel to the American Civil Liberties Union. Nineteen people were killed and over 200 were badly wounded, many shot in the back while running away."Five Years of Tyranny", Speech before the U.S. House of Representatives.The entire speech is contained in the ''Congressional Record'' of , 1939. It is reported in the Congressional record, and various other publications elsewhere, that among those shot in the back was a 7-year-old girl, Georgina Maldonado, who "was killed through the back while running to a nearby church" The Hays Commission declared it a List of events named massacres, massacre and police mob action, and it has since become known as the Ponce massacre. In the aftermath, on 2 April 1943, Tydings introduced another bill in Congress calling for independence for Puerto Rico, though it was again defeated. During the latter years of the Franklin D. Roosevelt, Roosevelt–Harry S. Truman, Truman administrations, the internal governance of the island was changed in a compromise reached with Luis Muñoz Marín and other Puerto Rican leaders. In 1946, President Truman appointed the first Puerto Rican-born governor, Jesús T. Piñero. Since 2007, the Puerto Rico State Department has developed a protocol to issue certificates of Puerto Rican citizenship to Puerto Ricans. In order to be eligible, applicants must have been born in Puerto Rico, born outside of Puerto Rico to a Puerto Rican-born parent, or be an American citizen with at least one year of residence in Puerto Rico.
U.S. unincorporated organized territory with commonwealth constitution
In 1947, the U.S. Congress passed the Elective Governor Act, signed by President Truman, allowing Puerto Ricans to vote for their own governor of Puerto Rico, governor. The first elections under this act were held the following year, on 2 November 1948. On 21 May 1948, a bill was introduced before the Puerto Rican Senate which would restrain the rights of the independence and Nationalist movements on the island. The Senate, controlled by the ''Partido Popular Democrático'' (Popular Democratic Party (Puerto Rico), PPD) and presided by Luis Muñoz Marín, approved the bill that day. This bill, which resembled the anti-communist Smith Act passed in the United States in 1940, became known as the ''Ley de la Mordaza'' (Gag Law (Puerto Rico), Gag Law) when the U.S.-appointed governor of Puerto Rico, Jesús T. Piñero, signed it into law on 10 June 1948. Under this new law, it would be a crime to print, publish, sell, or exhibit any material intended to paralyze or destroy the insular government; or to organize any society, group or assembly of people with a similar destructive intent. It made it illegal to sing a patriotic song, and reinforced the 1898 law that had made it illegal to display the flag of Puerto Rico, with anyone found guilty of disobeying the law in any way being subject to a sentence of up to ten years imprisonment, a fine of up to US$10,000 (), or both. According to Dr. Leopoldo Figueroa, the only non-PPD member of the Puerto Rico House of Representatives, the law was repressive and in violation of the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which guarantees Freedom of Speech. He asserted that the law as such was a violation of the civil rights of the people of Puerto Rico. The law was repealed in 1957. In the November 1948 election, Muñoz Marín became the first popularly elected governor of Puerto Rico, replacing U.S.-appointed Piñero on 2 January 1949.
''Estado Libre Asociado''
In 1950, the U.S. Congress granted Puerto Ricans the right to organize a constitutional convention (political meeting), constitutional convention via a referendum; voters could either accept or reject a proposed U.S. law that would organize Puerto Rico as a "commonwealth" under continued U.S. sovereignty. The Constitution of Puerto Rico was approved by the constitutional convention on 6 February 1952, and by 82% of voters in a March referendum. It was modified and ratified by the U.S. Congress, approved by President Truman on 3 July of that year, and proclaimed by Governor Muñoz Marín on 25 July 1952—the anniversary of the landing of U.S. troops in the Puerto Rican Campaign of the During the 1950s and 1960s, Puerto Rico experienced rapid industrialization, due in large part to ''Operación Manos a la Obra'' ("Operation Bootstrap"), an offshoot of FDR's New Deal. It was intended to transform Puerto Rico's economy from agriculture-based to manufacturing-based to provide more jobs. Puerto Rico has become a major tourist destination, as well as a global center for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
During the 1950s and 1960s, Puerto Rico experienced rapid industrialization, due in large part to ''Operación Manos a la Obra'' ("Operation Bootstrap"), an offshoot of FDR's New Deal. It was intended to transform Puerto Rico's economy from agriculture-based to manufacturing-based to provide more jobs. Puerto Rico has become a major tourist destination, as well as a global center for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
21st century
On 15 July 2009, the Special Committee on Decolonization, United Nations Special Committee on Decolonization approved a draft resolution calling on the government of the United States to expedite a process that would allow the Puerto Rican people to exercise fully their inalienable right to self-determination and independence. On 6 November 2012, a two-question referendum took place, simultaneous with the general elections.''Ley Numero 283 del 28 de diciembre de 2011.''Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico. 28 December 2011. Retrieved 10 January 2012. The first question, voted on in August, asked voters whether they wanted to maintain the current status under the territorial clause of the U.S. Constitution. 54% voted against the status quo, effectively approving the second question to be voted on in November. The second question posed three alternate status options: statehood, independence, or Compact of Free Association, free association. 61.16% voted for statehood, 33.34% for a sovereign free associated state, and 5.49% for independence. On 30 June 2016, President Obama signed into law H.R. 5278: PROMESA, establishing a Control Board over the Puerto Rican government. This board will have a significant degree of federal control involved in its establishment and operations. In particular, the authority to establish the control board derives from the federal government's constitutional power to "make all needful rules and regulations" regarding U.S. territories; The president would appoint all seven voting members of the board; and the board would have broad sovereign powers to effectively overrule decisions by Puerto Rico's legislature, governor, and other public authorities. Puerto Rico held its 2020 Puerto Rican status referendum, statehood referendum during the 3 November 2020 general elections; the ballot asked one question: "Should Puerto Rico be admitted immediately into the Union 51st state, as a State?" The results showed that 52 percent of Puerto Rico voters answered yes.
Environment
 Puerto Rico consists of the main island of Puerto Rico and various smaller islands, including
Puerto Rico consists of the main island of Puerto Rico and various smaller islands, including  The Commonwealth of Puerto Rico has an area of , of which is land and is water. Puerto Rico is larger than Delaware and Rhode Island. The maximum length of the main island from east to west is , and the maximum width from north to south is . Puerto Rico is the smallest of the Greater Antilles. It is 80% of the size of Jamaica, just over 18% of the size of Hispaniola and 8% of the size of Cuba, the largest of the Greater Antilles.
The island is mostly mountainous with large coastal areas in the north and south. The main mountain range is called "Cordillera Central (Puerto Rico), La Cordillera Central" (The Central Range). The highest elevation in Puerto Rico, Cerro de Punta , is located in this range.
Another important peak is El Yunque, Puerto Rico, El Yunque, one of the highest in the ''Sierra de Luquillo'' at the El Yunque National Forest, with an elevation of .
The Commonwealth of Puerto Rico has an area of , of which is land and is water. Puerto Rico is larger than Delaware and Rhode Island. The maximum length of the main island from east to west is , and the maximum width from north to south is . Puerto Rico is the smallest of the Greater Antilles. It is 80% of the size of Jamaica, just over 18% of the size of Hispaniola and 8% of the size of Cuba, the largest of the Greater Antilles.
The island is mostly mountainous with large coastal areas in the north and south. The main mountain range is called "Cordillera Central (Puerto Rico), La Cordillera Central" (The Central Range). The highest elevation in Puerto Rico, Cerro de Punta , is located in this range.
Another important peak is El Yunque, Puerto Rico, El Yunque, one of the highest in the ''Sierra de Luquillo'' at the El Yunque National Forest, with an elevation of .
 Puerto Rico has 17 lakes, all man-made, and more than List of Puerto Rico rivers, 50 rivers, most originating in the Cordillera Central. Rivers in the northern region of the island are typically longer and of higher Volumetric flow rate, water flow rates than those of the south, since the south receives less rain than the central and northern regions.
Puerto Rico is composed of Cretaceous to Eocene volcanic and plutonic rocks, overlain by younger Oligocene and more recent carbonates and other sedimentary rocks. Most of the caverns and karst topography on the island occurs in the northern region in the carbonates. The oldest rocks are approximately years old (Jurassic) and are located at Sierra Bermeja in the southwest part of the island. They may represent part of the oceanic crust and are believed to come from the Pacific Ocean realm.
Puerto Rico lies at the boundary between the Caribbean and North American plate tectonics, plates and is being deformed by the tectonics, tectonic stresses caused by their interaction. These stresses may cause earthquakes and tsunamis. These seismic events, along with landslides, represent some of the most dangerous geologic hazards in the island and in the northeastern Caribbean.
The 1918 San Fermín earthquake occurred on , 1918, and had an estimated magnitude of 7.5 on the Richter magnitude scale, Richter scale. It originated off the coast of Aguadilla, several kilometers off the northern coast, and was accompanied by a tsunami. It caused extensive property damage and widespread losses, damaging infrastructure, especially bridges. It resulted in an estimated 116 deaths and $4 million in property damage. The failure of the government to move rapidly to provide for the general welfare contributed to political activism by opponents and eventually to the rise of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party.
On 7 January 2020, the country experienced 2019–20 Puerto Rico earthquakes, its second largest earthquake, estimated at magnitude 6.4. Economic losses were estimated to be more than $3.1 billion.
The Puerto Rico Trench, the largest and deepest trench in the Atlantic, is located about north of Puerto Rico at the boundary between the Caribbean and North American plates. It is long. At its deepest point, named the Milwaukee Deep, it is almost deep.
Puerto Rico has 17 lakes, all man-made, and more than List of Puerto Rico rivers, 50 rivers, most originating in the Cordillera Central. Rivers in the northern region of the island are typically longer and of higher Volumetric flow rate, water flow rates than those of the south, since the south receives less rain than the central and northern regions.
Puerto Rico is composed of Cretaceous to Eocene volcanic and plutonic rocks, overlain by younger Oligocene and more recent carbonates and other sedimentary rocks. Most of the caverns and karst topography on the island occurs in the northern region in the carbonates. The oldest rocks are approximately years old (Jurassic) and are located at Sierra Bermeja in the southwest part of the island. They may represent part of the oceanic crust and are believed to come from the Pacific Ocean realm.
Puerto Rico lies at the boundary between the Caribbean and North American plate tectonics, plates and is being deformed by the tectonics, tectonic stresses caused by their interaction. These stresses may cause earthquakes and tsunamis. These seismic events, along with landslides, represent some of the most dangerous geologic hazards in the island and in the northeastern Caribbean.
The 1918 San Fermín earthquake occurred on , 1918, and had an estimated magnitude of 7.5 on the Richter magnitude scale, Richter scale. It originated off the coast of Aguadilla, several kilometers off the northern coast, and was accompanied by a tsunami. It caused extensive property damage and widespread losses, damaging infrastructure, especially bridges. It resulted in an estimated 116 deaths and $4 million in property damage. The failure of the government to move rapidly to provide for the general welfare contributed to political activism by opponents and eventually to the rise of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party.
On 7 January 2020, the country experienced 2019–20 Puerto Rico earthquakes, its second largest earthquake, estimated at magnitude 6.4. Economic losses were estimated to be more than $3.1 billion.
The Puerto Rico Trench, the largest and deepest trench in the Atlantic, is located about north of Puerto Rico at the boundary between the Caribbean and North American plates. It is long. At its deepest point, named the Milwaukee Deep, it is almost deep.
Climate
 The climate of Puerto Rico in the Köppen climate classification is tropical rainforest. Temperatures are warm to hot year round, averaging near 85 °F (29 °C) in lower elevations and 70 °F (21 °C) in the mountains. Easterly trade winds pass across the island year round. Puerto Rico has a rainy season which stretches from April into November. The mountains of the Cordillera Central are the main cause of the variations in the temperature and rainfall that occur over very short distances. The mountains can also cause wide variation in local wind speed and direction due to their sheltering and channeling effects adding to the climatic variation.
The island has an average temperature of throughout the year, with an average minimum temperature of and maximum of . Daily temperature changes seasonally are quite small in the lowlands and coastal areas. The temperature in the south is usually a few degrees higher than those in the north and temperatures in the central interior mountains are always cooler than those on the rest of the island.
Between the dry and wet season, there is a temperature change of around . This change is due mainly to the warm waters of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, which significantly modify cooler air moving in from the north and northwest. Coastal waters temperatures around the years are about in February to in August. The highest temperature ever recorded was at Arecibo, Puerto Rico, Arecibo, while the lowest temperature ever recorded was in the mountains at Adjuntas, Puerto Rico, Adjuntas, Aibonito, Puerto Rico, Aibonito, and Corozal, Puerto Rico, Corozal. The average yearly precipitation is .
The climate of Puerto Rico in the Köppen climate classification is tropical rainforest. Temperatures are warm to hot year round, averaging near 85 °F (29 °C) in lower elevations and 70 °F (21 °C) in the mountains. Easterly trade winds pass across the island year round. Puerto Rico has a rainy season which stretches from April into November. The mountains of the Cordillera Central are the main cause of the variations in the temperature and rainfall that occur over very short distances. The mountains can also cause wide variation in local wind speed and direction due to their sheltering and channeling effects adding to the climatic variation.
The island has an average temperature of throughout the year, with an average minimum temperature of and maximum of . Daily temperature changes seasonally are quite small in the lowlands and coastal areas. The temperature in the south is usually a few degrees higher than those in the north and temperatures in the central interior mountains are always cooler than those on the rest of the island.
Between the dry and wet season, there is a temperature change of around . This change is due mainly to the warm waters of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, which significantly modify cooler air moving in from the north and northwest. Coastal waters temperatures around the years are about in February to in August. The highest temperature ever recorded was at Arecibo, Puerto Rico, Arecibo, while the lowest temperature ever recorded was in the mountains at Adjuntas, Puerto Rico, Adjuntas, Aibonito, Puerto Rico, Aibonito, and Corozal, Puerto Rico, Corozal. The average yearly precipitation is .
Hurricanes
Puerto Rico experiences the Atlantic hurricane season, similar to the remainder of the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic oceans. On average, a quarter of its annual rainfall is contributed from tropical cyclones, which are more prevalent during periods of La Niña than El Niño. A cyclone of tropical storm strength passes near Puerto Rico, on average, every five years. A hurricane passes in the vicinity of the island, on average, every seven years. Since 1851, the 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, Lake Okeechobee Hurricane (also known as the San Felipe Segundo hurricane in Puerto Rico) of September 1928 is the only hurricane to make landfall as a Category 5 hurricane. In the busy 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, Puerto Rico avoided a direct hit by the Category 5 Hurricane Irma on 6 September 2017, as it passed about north of Puerto Rico, but high winds caused a loss of electrical power to some one million residents. Almost 50% of hospitals were operating with power provided by generators. The Category 4 Hurricane Jose (2017), Hurricane Jose, as expected, veered away from Puerto Rico. A short time later, the devastating Hurricane Maria made landfall on Puerto Rico on Wednesday, 20 September, near the Yabucoa municipality at 10:15 UTC (6:15 am local time) as a high-end Category 4 hurricane with sustained winds of 155 mph (250 km/h), powerful rains and widespread flooding causing tremendous destruction, including the electrical grid, which would remain out for 4–6 months in many portions of the island. Hurricane Dorian was the third hurricane in three years to hit Puerto Rico in 2019. The recovering infrastructure from the 2017 hurricanes, as well as new governor Wanda Vázquez Garced, were put to the test against a potential humanitarian crisis. Tropical Storm Karen (2019), Tropical Storm Karen also caused impacts to Puerto Rico during 2019.Climate change
Biodiversity
 Puerto Rico is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: Puerto Rican moist forests, Puerto Rican dry forests, and Greater Antilles mangroves.
Species endemic (ecology), endemic to the archipelago number 239 plants, 16 birds and 39 amphibians/reptiles, recognized as of 1998. Most of these (234, 12 and 33 respectively) are found on the main island. The most recognizable endemic species and a symbol of Puerto Rican pride is the ''coquí'', a small frog easily identified by the sound of its call, from which it gets its name. Most ''coquí'' species (13 of 17) live in the El Yunque National Forest, a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical rainforest in the northeast of the island previously known as the Caribbean National Forest. El Yunque is home to more than 240 plants, 26 of which are endemic to the island. It is also home to 50 bird species, including the critically endangered Puerto Rican amazon.
Across the island in the southwest, the of dry land at the Guánica Commonwealth Forest Reserve contain over 600 uncommon species of plants and animals, including 48 endangered species and 16 endemic to Puerto Rico.
Puerto Rico has three bioluminescent bays: rare bodies of water occupied by microscopic marine organisms that glow when touched. However, tourism, pollution, and hurricanes have threatened the organisms.
Puerto Rico is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: Puerto Rican moist forests, Puerto Rican dry forests, and Greater Antilles mangroves.
Species endemic (ecology), endemic to the archipelago number 239 plants, 16 birds and 39 amphibians/reptiles, recognized as of 1998. Most of these (234, 12 and 33 respectively) are found on the main island. The most recognizable endemic species and a symbol of Puerto Rican pride is the ''coquí'', a small frog easily identified by the sound of its call, from which it gets its name. Most ''coquí'' species (13 of 17) live in the El Yunque National Forest, a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical rainforest in the northeast of the island previously known as the Caribbean National Forest. El Yunque is home to more than 240 plants, 26 of which are endemic to the island. It is also home to 50 bird species, including the critically endangered Puerto Rican amazon.
Across the island in the southwest, the of dry land at the Guánica Commonwealth Forest Reserve contain over 600 uncommon species of plants and animals, including 48 endangered species and 16 endemic to Puerto Rico.
Puerto Rico has three bioluminescent bays: rare bodies of water occupied by microscopic marine organisms that glow when touched. However, tourism, pollution, and hurricanes have threatened the organisms.
Demographics
The population of Puerto Rico has been shaped by initial Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindian settlement, Spanish Empire, European colonization, slavery, economic migration, and Puerto Rico's status as unincorporated territory of the United States.Population makeup
The population of Puerto Rico according to the 2020 census is 3,285,874, an 11.8% decrease since the 2010 United States Census. From 2000 to 2010, the population declined for the first time in census history for Puerto Rico, from 3,808,610 to 3,725,789."Wall Street eyes PR population loss", ''Caribbean Business'', 14 December 2012, accessed 14 December 2012 Continuous European immigration and high natural increase helped the population of Puerto Rico grow from 155,426 in 1800 to almost a million by the close of the 19th century. A census conducted by royal decree on 30 September 1858, gave the following totals of the Puerto Rican population at that time: 341,015 were free people of color, free colored; 300,430 were white people, white; and 41,736 were slaves. A census in 1887 found a population of around 800,000, of which 320,000 were black. During the 19th century, hundreds of families arrived in Puerto Rico, primarily from the Canary Islands and
Population genetics
A group of researchers from Puerto Rican universities conducted a study of mitochondrial DNA that revealed that the modern population of Puerto Rico has a high genetic component of Taíno and Guanches, Guanche (especially of the island of Tenerife). Other studies show Amerindian ancestry in addition to the Taíno. One genetic study on the racial makeup of Puerto Ricans (including all races) found them to be roughly around 61% West Eurasian/North African (overwhelmingly of Spanish provenance), 27% Sub-Saharan African and 11% Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American. Another genetic study, from 2007, claimed that "the average genomewide individual (i.e., Puerto Rican) ancestry proportions have been estimated as 66%, 18%, and 16%, for European, West African, and Native American, respectively." Another study estimates 63.7% European, 21.2% (Sub-Saharan) African, and 15.2% Native American; European ancestry is more prevalent in the West and in Central Puerto Rico, African in Eastern Puerto Rico, and Native American in Northern Puerto Rico.Literacy
A Pew Research survey indicated an adult literacy rate of 90.4% in 2012 based on data from the United Nations.Life expectancy
Puerto Rico has a life expectancy of approximately 81.0 years according to the CIA World Factbook, an improvement from 78.7 years in 2010. This means Puerto Rico has the second-highest life expectancy in the United States, if territories are taken into account.Immigration and emigration
As of 2019, Puerto Rico was home to 100,000 permanent legal residents. The vast majority of recent immigrants, both legal and illegal, come from the Dominican Republic immigration to Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic and Haitian diaspora, Haiti. Other major sources of recent immigrants includeUniverse: Foreign-born population in Puerto Rico excluding population born at sea. 2010–2014 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates Additionally, there are many non-Puerto Rican U.S. citizens settling in Puerto Rico from the mainland United States and the U.S. Virgin Islands, as well as Nuyoricans and other stateside Puerto Ricans coming back. Most recent immigrants settle in and around San Juan. Emigration is a major part of contemporary Puerto Rican history. Starting soon after World War II, poverty, cheap airfares, and promotion by the island government caused waves of Puerto Ricans to move to the United States mainland, particularly to the Northeastern United States, northeastern states and nearby
Population distribution
The most populous municipality is the capital, San Juan, with 342,259 people based on the 2020 United States census, 2020 Census. Other major cities include Bayamón, Puerto Rico, Bayamón, Carolina, Puerto Rico, Carolina, Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce, and Caguas, Puerto Rico, Caguas. Of the ten most populous cities on the island, eight are located within what is considered San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo metropolitan area, San Juan's metropolitan area, while the other two are located in the south (Ponce metropolitan area, Ponce) and west (Mayagüez metropolitan area, Mayagüez) of the island.Languages
The official languages of the executive branch of government of Puerto Rico are Spanish and English, with Spanish being the primary language. Spanish is, and has been, the only official language of the entire Commonwealth judiciary system, despite a 1902 English-only language law. However, all official business of the U.S. District Court for the District of Puerto Rico is conducted in English. English is the primary language of less than 10% of the population. Spanish is the dominant language of business, education and daily life on the island, spoken by nearly 95% of the population. Out of people age five and older, 94.3% speak only Spanish at home, 5.5% speak English, and 0.2% speak other languages. In Puerto Rico, public school instruction is conducted almost entirely in Spanish. There have been pilot programs in about a dozen of the over 1,400 public schools aimed at conducting instruction in English only. Objections from teaching staff are common, perhaps because many of them are not fully fluent in English. English is taught as a second language and is a compulsory subject from elementary levels to high school. The languages of the deaf community are American Sign Language and its local variant, Puerto Rican Sign Language. The Puerto Rican Spanish, Spanish of Puerto Rico has evolved into having many idiosyncrasies in vocabulary and syntax that differentiate it from the Spanish spoken elsewhere. As a product of Puerto Rican history, the island possesses a unique Spanish dialect. Puerto Rican Spanish utilizes many Taíno language, Taíno words, as well as English words. The largest influence on the Spanish spoken in Puerto Rico is that of the Canary Islands. Taíno loanwords are most often used in the context of vegetation, natural phenomena, and native musical instruments. Similarly, words attributed to primarily West African languages were adopted in the contexts of foods, music, and dances, particularly in coastal towns with concentrations of descendants of Sub-Saharan Africans.Religion
Catholic Church in Puerto Rico, Catholicism was brought by Spanish colonists and gradually became the dominant religion in Puerto Rico. The first dioceses in the Americas, including Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Juan de Puerto Rico, that of Puerto Rico, were authorized by Pope Julius II in 1511. In 1512, priests were established for the parochial churches. By 1759, there was a priest for each church. One Pope, John Paul II, visited Puerto Rico in October 1984. All Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipalities in Puerto Rico have at least one Catholic church, most of which are located at the town center, or plaza. Protestantism in Puerto Rico, Protestantism, which was suppressed under the Spanish Catholic regime, has reemerged under United States rule, making contemporary Puerto Rico more interconfessional than in previous centuries, although Catholicism continues to be the dominant religion. The first Protestant church, Iglesia de la Santísima Trinidad, was established in Ponce by the Anglican Diocese of Antigua in 1872. It was the first non-Catholic church in the entirePuerto Rico, by virtue of its long political association with the United States, is the most Protestant of Latin American countries, with a Protestant population of approximately 33 to 38 percent, the majority of whom are Pentecostal. David Stoll calculates that if we extrapolate the growth rates of evangelical churches from 1960 to 1985 for another twenty-five years Puerto Rico will become 75 percent evangelical. (Ana Adams: "Brincando el Charco..." in ''Power, Politics and Pentecostals in Latin America'', Edward Cleary, ed., 1997. p. 164).An Associated Press article in March 2014 stated that "more than 70 percent of whom identify themselves as Catholic" but provided no source for this information. The CIA World Factbook reports that 85% of the population of Puerto Rico identifies as Roman Catholic, while 15% identify as Protestant and Other. Neither a date or a source for that information is provided and may not be recent. A 2013 Pew Research survey found that only about 45% of Puerto Rican adults identified themselves as Catholic, 29% as Protestant and 20% as unaffiliated with a religion. The people surveyed by Pew consisted of Puerto Ricans living in the 50 states and DC and may not be indicative of those living in the Commonwealth.
 By 2014, a Pew Research report, with the sub-title ''Widespread Change in a Historically Catholic Region'', indicated that only 56% of Puerto Ricans were Catholic, 33% were Protestant, and 8% were unaffiliated; this survey was completed between October 2013 and February 2014.
An Eastern Orthodox community, the Dormition of the Most Holy Theotokos / St. Spyridon's Church is located in Trujillo Alto, and serves the small Orthodox community. In 2017, the church entered communion with the Roman Catholic Church, becoming the first Eastern Catholic Church in Puerto Rico. This affiliation accounted for under 1% of the population in 2010 according to the Pew Research report. In 1940, Juanita García Peraza founded the Mita Congregation, the first religion of Puerto Rican origin. Taíno people, Taíno religious practices have been rediscovered/reinvented to a degree by a handful of advocates. Similarly, some aspects of African religious traditions have been kept by some adherents. African slaves brought and maintained various ethnic African religious practices associated with different peoples; in particular, the Yoruba religion, Yoruba beliefs of Santería and/or Ifá, and the Kongo people, Kongo-derived Palo Mayombe. Some aspects were absorbed into syncretic Christianity. In 1952, a handful of American Jews established the island's first synagogue; this religion accounts for under 1% of the population in 2010 according to the Pew Research report.''Eduardo Giorgetti Y Su Mundo: La Aparente Paradoja De Un Millonario Genio Empresarial Y Su Noble Humanismo''; by Delma S. Arrigoitia; Publisher: Ediciones Puerto; The synagogue, called ''Sha'are Zedeck'', hired its first rabbi in 1954. Puerto Rico has the largest Jewish community in the Caribbean, numbering 3000 people, and is the only Caribbean island in which the Conservative Jews, Conservative, Reform Jews, Reform and Orthodox Jews, Orthodox Jewish movements all are represented. In 2007, there were about 5,000 Muslims in Puerto Rico, representing about 0.13% of the population. Eight mosques are located throughout the island, with most Muslims living in Río Piedras and Caguas; most Muslims are of Palestinian and Jordanian descent. There is also a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community. In 2015, the 25,832 Jehovah's Witnesses represented about 0.70% of the population, with 324 congregations. The Chinese immigration to Puerto Rico, Padmasambhava Buddhist Center, whose followers practice Tibetan Buddhism, as well as Nichiren Buddhism have branches in Puerto Rico. There are several atheist activist and educational organizations, and an atheistic parody religion called the Pastafarian Church of Puerto Rico. An ISKCON temple in Gurabo is devoted to Krishna Consciousness, with two preaching centers in the metropolitan area.
By 2014, a Pew Research report, with the sub-title ''Widespread Change in a Historically Catholic Region'', indicated that only 56% of Puerto Ricans were Catholic, 33% were Protestant, and 8% were unaffiliated; this survey was completed between October 2013 and February 2014.
An Eastern Orthodox community, the Dormition of the Most Holy Theotokos / St. Spyridon's Church is located in Trujillo Alto, and serves the small Orthodox community. In 2017, the church entered communion with the Roman Catholic Church, becoming the first Eastern Catholic Church in Puerto Rico. This affiliation accounted for under 1% of the population in 2010 according to the Pew Research report. In 1940, Juanita García Peraza founded the Mita Congregation, the first religion of Puerto Rican origin. Taíno people, Taíno religious practices have been rediscovered/reinvented to a degree by a handful of advocates. Similarly, some aspects of African religious traditions have been kept by some adherents. African slaves brought and maintained various ethnic African religious practices associated with different peoples; in particular, the Yoruba religion, Yoruba beliefs of Santería and/or Ifá, and the Kongo people, Kongo-derived Palo Mayombe. Some aspects were absorbed into syncretic Christianity. In 1952, a handful of American Jews established the island's first synagogue; this religion accounts for under 1% of the population in 2010 according to the Pew Research report.''Eduardo Giorgetti Y Su Mundo: La Aparente Paradoja De Un Millonario Genio Empresarial Y Su Noble Humanismo''; by Delma S. Arrigoitia; Publisher: Ediciones Puerto; The synagogue, called ''Sha'are Zedeck'', hired its first rabbi in 1954. Puerto Rico has the largest Jewish community in the Caribbean, numbering 3000 people, and is the only Caribbean island in which the Conservative Jews, Conservative, Reform Jews, Reform and Orthodox Jews, Orthodox Jewish movements all are represented. In 2007, there were about 5,000 Muslims in Puerto Rico, representing about 0.13% of the population. Eight mosques are located throughout the island, with most Muslims living in Río Piedras and Caguas; most Muslims are of Palestinian and Jordanian descent. There is also a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí community. In 2015, the 25,832 Jehovah's Witnesses represented about 0.70% of the population, with 324 congregations. The Chinese immigration to Puerto Rico, Padmasambhava Buddhist Center, whose followers practice Tibetan Buddhism, as well as Nichiren Buddhism have branches in Puerto Rico. There are several atheist activist and educational organizations, and an atheistic parody religion called the Pastafarian Church of Puerto Rico. An ISKCON temple in Gurabo is devoted to Krishna Consciousness, with two preaching centers in the metropolitan area.
Government
Puerto Rico has a Republic, republican form of government based on the Republicanism in the United States, American model, with separation of powers subject to the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United States. All governmental powers are delegated by the United States Congress, with the head of state being president of the United States. As an. Puerto Rican elections are governed by the Federal Election Commission and the State Elections Commission of Puerto Rico. Residents of Puerto Rico, including other U.S. citizens, cannot vote in U.S. presidential elections, but can vote in United States presidential primary, primaries. Puerto Ricans who become residents of a U.S. state or the District of Columbia can vote in presidential elections. Puerto Rico has Puerto Rico senatorial districts, 8 senatorial districts, Puerto Rico representative districts, 40 representative districts and Municipalities of Puerto Rico, 78 municipalities; there are no first-order administrative divisions as defined by the U.S. government. Municipalities are subdivided into wards or barrios, and those into sectors. Each municipality has a Mayors of Puerto Rico, mayor and a municipal legislature elected for a four-year term. The municipality of San Juan is the oldest, founded in 1521; the next earliest settlements are San Germán in 1570, Coamo in 1579, Arecibo in 1614, Aguada, Puerto Rico, Aguada in 1692 and Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce in 1692. Increased settlement in the 18th century saw 30 more communities established, following 34 in the 19th centuryl six were founded in the 20th century, the most recent being Florida, Puerto Rico, Florida in 1971.
Political parties and elections
 Since 1952, Puerto Rico has had three main political parties: the Popular Democratic Party (Puerto Rico), Popular Democratic Party (PPD in Spanish), the New Progressive Party (Puerto Rico), New Progressive Party (PNP in Spanish) and the Puerto Rican Independence Party (PIP). The three parties stand for different political status. The PPD, for example, seeks status quo movement in Puerto Rico, to maintain the island's status with the U.S. as a commonwealth, while the PNP, on the other hand, seeks statehood movement in Puerto Rico, to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. The PIP, in contrast, seeks a complete separation from the United States by seeking independence movement in Puerto Rico, to make Puerto Rico a sovereign nation. In terms of party strength, the PPD and PNP usually hold about 47% of the vote each while the PIP holds only about 5%.
After 2007, other parties emerged on the island. The first, the Puerto Ricans for Puerto Rico Party (PPR in Spanish) was registered that same year. The party claims that it seeks to address the islands' problems from a status-neutral platform. But it ceased to remain as a registered party when it failed to obtain the required number of votes in the 2008 general election. Four years later, the 2012 election saw the emergence of the Movimiento Unión Soberanista (MUS; English: ''Sovereign Union Movement'') and the Partido del Pueblo Trabajador (PPT; English: ''Working People's Party'') but none obtained more than 1% of the vote.
Other non-registered parties include the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party, the Socialist Workers Movement (Puerto Rico), Socialist Workers Movement, and the Hostosian National Independence Movement.
Since 1952, Puerto Rico has had three main political parties: the Popular Democratic Party (Puerto Rico), Popular Democratic Party (PPD in Spanish), the New Progressive Party (Puerto Rico), New Progressive Party (PNP in Spanish) and the Puerto Rican Independence Party (PIP). The three parties stand for different political status. The PPD, for example, seeks status quo movement in Puerto Rico, to maintain the island's status with the U.S. as a commonwealth, while the PNP, on the other hand, seeks statehood movement in Puerto Rico, to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. The PIP, in contrast, seeks a complete separation from the United States by seeking independence movement in Puerto Rico, to make Puerto Rico a sovereign nation. In terms of party strength, the PPD and PNP usually hold about 47% of the vote each while the PIP holds only about 5%.
After 2007, other parties emerged on the island. The first, the Puerto Ricans for Puerto Rico Party (PPR in Spanish) was registered that same year. The party claims that it seeks to address the islands' problems from a status-neutral platform. But it ceased to remain as a registered party when it failed to obtain the required number of votes in the 2008 general election. Four years later, the 2012 election saw the emergence of the Movimiento Unión Soberanista (MUS; English: ''Sovereign Union Movement'') and the Partido del Pueblo Trabajador (PPT; English: ''Working People's Party'') but none obtained more than 1% of the vote.
Other non-registered parties include the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party, the Socialist Workers Movement (Puerto Rico), Socialist Workers Movement, and the Hostosian National Independence Movement.
Law
The insular legal system is a blend of Civil law (legal system), civil law and the common law systems. Puerto Rico is the only current U.S. jurisdiction whose legal system operates primarily in a language other than American English: namely,Political status
The nature of Puerto Rico's political relationship with the U.S. is the subject of Political status of Puerto Rico#Controversies, ongoing debate in Puerto Rico, the United States Congress, and the United Nations. Specifically, the basic question is whether Puerto Rico should remain an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the U.S., become a U.S. state, or become an independent country.Within the United States
Foreign and intergovernmental relations
Puerto Rico is subject to the Commerce Clause, Commerce and Territorial Clause of the U.S. Constitution, and is thus restricted on how it can engage with other nations, sharing the opportunities and limitations that state governments have albeit not being one. As is the case with state governments, it has established several trade agreements with other nations, particularly with Latin American countries such as Colombia and Panamá. It has also established trade promotion offices in many foreign countries, all Spanish-speaking, and within the United States itself, which now include Spain, the Dominican Republic, Panama, Colombia, Washington, D.C., New York City and Florida, and has included in the past offices in Chile, Costa Rica, and Mexico. Such agreements require permission from the U.S. Department of State; most are simply allowed by existing laws or trade treaties between the United States and other nations which supersede trade agreements pursued by Puerto Rico and different U.S. states. Puerto Rico hosts Consul (representative), consulates from 41 countries, mainly from the Americas and Europe, with most located in San Juan. At the local level, Puerto Rico established by law that the international relations which states and territories are allowed to engage must be handled by the Department of State of Puerto Rico, an executive departments of the government of Puerto Rico, executive department, headed by the Secretary of State of Puerto Rico, secretary of state of Puerto Rico, who also serves as the unincorporated territory's lieutenant governor. It is also charged to liaise with general consul (representative), consuls and honorary consuls based in Puerto Rico. The Puerto Rico Federal Affairs Administration, along with the Resident Commissioner of Puerto Rico, Office of the Resident Commissioner, manages all its intergovernmental affairs before entities of or in the United States (including the federal government of the United States, local and state governments of the United States, and public or private entities in the United States). Both entities frequently assist the Department of State of Puerto Rico in engaging with Washington, D.C.-based ambassadors and federal agencies that handle Puerto Rico's foreign affairs, such as the U.S. Department of State, the Agency for International Development, and others. The current secretary of state is Larry Seilhamer Rodríguez from the New Progressive Party (Puerto Rico), New Progressive Party, while the current List of Directors of the Puerto Rico Federal Affairs Administration, director of the Puerto Rico Federal Affairs Administration is Jennifer M. Stopiran also from the NPP and a member of the Republican Party of the United States. The Resident Commissioner of Puerto Rico, resident commissioner of Puerto Rico, the delegate (United States Congress), delegate elected by Puerto Ricans to represent them before the federal government, including the U.S. Congress, sits in the United States House of Representatives, serves and votes on congressional committees, and functions in every respect as a legislator except being denied a vote on the final disposition of legislation on the House floor. The current resident commissioner is Jenniffer González, Jenniffer González-Colón, a Republican, elected in 2016. She received more votes than any other official elected in Puerto Rico that year. Many Puerto Ricans have served as United States ambassadors to different nations and international organizations, such as the Organization of American States, mostly but not exclusively in Latin America. For example, Maricarmen Aponte, a Puerto Rican and now an acting assistant secretary of state, previously served as U.S. ambassador to El Salvador.Military
 At different times in the 20th century, the U.S. had about 25 military or naval installations in Puerto Rico, some very small ones,OSD, Washington Headquarters Services, Directorate for Information Operations and Reports (DIOR); "Atlas/Data Abstract for the United States and Selected Areas – Fiscal Year 1997;" Department of Defense; 1998. Note: The count of 25 military installations included the branch component of the Roosevelt Roads Naval facility on the island of Vieques, as distinct from the Roosevelt Roads Naval station in Cieba as well as large installations. The largest of these installations were the former Roosevelt Roads Naval Station in Ceiba, Puerto Rico, Ceiba, the Atlantic Fleet Weapons Training Facility (AFWTF) on Vieques, the National Guard training facility at Camp Santiago in Salinas, Puerto Rico, Salinas, Fort Allen, Puerto Rico, Fort Allen in Juana Diaz, the Army's Fort Buchanan, Puerto Rico, Fort Buchanan in San Juan, the former U.S. Air Force's Ramey Air Force Base in Aguadilla, and the Puerto Rico Air National Guard's Muñiz Air National Guard Base in San Juan.Meléndez, Edwin; Meléndez, Edgardo; Colonial Dilemma; South End Press; Boston; 1993
The former U.S. Navy facilities at Roosevelt Roads, Vieques, and Sabana Seca have been deactivated and partially turned over to the local government. Other than U.S. Coast Guard and Puerto Rico National Guard facilities, there are only two remaining military installations in Puerto Rico: the U.S. Army's small Ft. Buchanan (supporting local veterans and reserve units) and the PRANG (Puerto Rico Air National Guard) Muñiz Air Base (the C-130 Fleet). In recent years, the U.S. Congress has considered their deactivations, but these have been opposed by diverse public and private entities in Puerto Rico – such as retired military who rely on Ft. Buchanan for the services available there.
Puerto Ricans have participated in many United States military conflicts, including the American Revolution, when volunteers from Puerto Rico,
At different times in the 20th century, the U.S. had about 25 military or naval installations in Puerto Rico, some very small ones,OSD, Washington Headquarters Services, Directorate for Information Operations and Reports (DIOR); "Atlas/Data Abstract for the United States and Selected Areas – Fiscal Year 1997;" Department of Defense; 1998. Note: The count of 25 military installations included the branch component of the Roosevelt Roads Naval facility on the island of Vieques, as distinct from the Roosevelt Roads Naval station in Cieba as well as large installations. The largest of these installations were the former Roosevelt Roads Naval Station in Ceiba, Puerto Rico, Ceiba, the Atlantic Fleet Weapons Training Facility (AFWTF) on Vieques, the National Guard training facility at Camp Santiago in Salinas, Puerto Rico, Salinas, Fort Allen, Puerto Rico, Fort Allen in Juana Diaz, the Army's Fort Buchanan, Puerto Rico, Fort Buchanan in San Juan, the former U.S. Air Force's Ramey Air Force Base in Aguadilla, and the Puerto Rico Air National Guard's Muñiz Air National Guard Base in San Juan.Meléndez, Edwin; Meléndez, Edgardo; Colonial Dilemma; South End Press; Boston; 1993
The former U.S. Navy facilities at Roosevelt Roads, Vieques, and Sabana Seca have been deactivated and partially turned over to the local government. Other than U.S. Coast Guard and Puerto Rico National Guard facilities, there are only two remaining military installations in Puerto Rico: the U.S. Army's small Ft. Buchanan (supporting local veterans and reserve units) and the PRANG (Puerto Rico Air National Guard) Muñiz Air Base (the C-130 Fleet). In recent years, the U.S. Congress has considered their deactivations, but these have been opposed by diverse public and private entities in Puerto Rico – such as retired military who rely on Ft. Buchanan for the services available there.
Puerto Ricans have participated in many United States military conflicts, including the American Revolution, when volunteers from Puerto Rico, Administrative divisions
Economy
 Academically, most of Puerto Rico's economic woes stem from federal regulations that expired, have been repealed, or no longer apply to Puerto Rico; its inability to become self-sufficient and self-sustainable throughout history; its highly politicized public policy which tends to change political party strength in Puerto Rico, whenever a political party gains power; as well as government of Puerto Rico, its highly inefficient local government which has accrued a public debt of Puerto Rico, public debt equal to 68% of its gross domestic product throughout time. Puerto Rico currently has a public debt of $72.204 billion (equivalent to 103% of GNP), and a government deficit of $2.5 billion.
By American standards, Puerto Rico is underdeveloped: It is poorer than Mississippi, the poorest state of the U.S., with 41% of its population below the poverty threshold, poverty line. However, it has the highest GDP per capita in Latin America. Puerto Rico's main trading partners are the
Academically, most of Puerto Rico's economic woes stem from federal regulations that expired, have been repealed, or no longer apply to Puerto Rico; its inability to become self-sufficient and self-sustainable throughout history; its highly politicized public policy which tends to change political party strength in Puerto Rico, whenever a political party gains power; as well as government of Puerto Rico, its highly inefficient local government which has accrued a public debt of Puerto Rico, public debt equal to 68% of its gross domestic product throughout time. Puerto Rico currently has a public debt of $72.204 billion (equivalent to 103% of GNP), and a government deficit of $2.5 billion.
By American standards, Puerto Rico is underdeveloped: It is poorer than Mississippi, the poorest state of the U.S., with 41% of its population below the poverty threshold, poverty line. However, it has the highest GDP per capita in Latin America. Puerto Rico's main trading partners are the Tourism
Tourism in Puerto Rico is also an important part of the economy. In 2017, Hurricane Maria caused severe damage to the island and its infrastructure, disrupting tourism for many months. The damage was estimated at $100 billion. An April 2019 report indicated that by that time, only a few hotels were still closed, that life for tourists in and around the capital had, for the most part, returned to normal. By October 2019, nearly all of the popular amenities for tourists, in the major destinations such as San Juan, Ponce and Arecibo, were in operation on the island and tourism was rebounding. This was important for the economy, since tourism provides up to 10% of Puerto Rico's GDP, according to Discover Puerto Rico. The latest Discover Puerto Rico campaign started in July 2018. An April 2019 report stated that the tourism team "after hitting the one-year anniversary of the storm in September [2018], the organization began to shift towards more optimistic messaging. The "Have We Met Yet?" campaign was intended to highlight the island's culture and history, making it distinct, different from other Caribbean destinations. In 2019, Discover Puerto Rico planned to continue that campaign, including "streaming options for branded content". In late November 2019, reports indicated that 90 calls to San Juan by Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd., Royal Caribbean ships would be cancelled during 2020 and 2021. This step would mean 360,000 fewer visitors, with a loss to the island's economy of 44 million. As well, 30 ship departures from San Juan were being canceled. The rationale for this decision was discussed in a news report:The reason for the cancellations is the privatization of the cruise docks in San Juan due to much-needed maintenance that is needed. Around $250 million investment is needed to make sure cruise ships can continue to dock there in the years to come. There is an urge for governor Wanda Vazquez to not go ahead with the privatization so this news is fluid.
Heavy fiscal debt load
In early 2017, the Puerto Rican government-debt crisis posed serious problems for the government which was saddled with outstanding bond debt that had climbed to $70 billion. The debt had been increasing during a decade-long recession. The Commonwealth had been defaulting on many debts, including bonds, since 2015. With debt payments due, the governor was facing the risk of a government shutdown and failure to fund the managed health care system. "Without action before April, Puerto Rico's ability to execute contracts for Fiscal Year 2018 with its managed care organizations will be threatened, thereby putting at risk beginning July 1, 2017 the health care of up to 900,000 poor U.S. citizens living in Puerto Rico", according to a letter sent to Congress by the Secretary of the Treasury and the Secretary of Health and Human Services. They also said that "Congress must enact measures recommended by both Republicans and Democrats that fix Puerto Rico's inequitable health care financing structure and promote sustained economic growth." Initially, the oversight board created under PROMESA called for Puerto Rico's governor Ricardo Rosselló to deliver a fiscal turnaround plan by 28 January. Just before that deadline, the control board gave the Commonwealth government until 28 February to present a fiscal plan (including negotiations with creditors for restructuring debt) to solve the problems. A moratorium on lawsuits by debtors was extended to 31 May. It is essential for Puerto Rico to reach restructuring deals to avoid a bankruptcy-like process under PROMESA. An internal survey conducted by the Puerto Rican Economists Association revealed that the majority of Puerto Rican economists reject the policy recommendations of the Board and the Rosselló government, with more than 80% of economists arguing in favor of auditing the debt. In early August 2017, the island's financial oversight board (created by PROMESA) planned to institute two days off without pay per month for government employees, down from the original plan of four days per month; the latter had been expected to achieve $218 million in savings. Governor Rossello rejected this plan as unjustified and unnecessary. Pension reforms were also discussed including a proposal for a 10% reduction in benefits to begin addressing the $50 billion in unfunded pension liabilities.Public finances
Puerto Rico has an operating budget of about U.S.$9.8 billion with expenses at about $10.4 billion, creating a structural deficit of $775 million (about 7.9% of the budget). The practice of approving budgets with a structural deficit has been done for consecutive years starting in 2000. Throughout those years, including present time, all budgets contemplated issuing bonds to cover these projected deficits rather than making structural adjustments. This practice increased Puerto Rico's cumulative debt, as the government had already been issuing bonds Puerto Rico government budget balance, to balance its actual budget for four decades beginning in 1973. Projected deficits added substantial burdens to an already indebted nation which accrued Public debt of Puerto Rico, a public debt of $71B or about 70% of Puerto Rico's gross domestic product. This sparked Puerto Rico government-debt crisis, an ongoing government-debt crisis after Puerto Rico's general obligation bonds were downgraded to speculative non-investment grade ("junk status") by three credit-rating agencies. In terms of financial control, almost 9.6%—or about $1.5 billion—of Puerto Rico's central government budget expenses for FY2014 is expected to be spent on debt service. Harsher budget cuts are expected as Puerto Rico must now repay larger chunks of debts in the coming years.
For practical reasons the budget is divided into two aspects: a "general budget" which comprises the assignments funded exclusively by the Department of Treasury of Puerto Rico, and the "consolidated budget" which comprises the assignments funded by the general budget, by List of government-owned corporations of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico's government-owned corporations, by revenue expected from loans, by the sale of government bonds, by subsidies extended by the federal government of the United States, and by other funds.
Both budgets contrast each other drastically, with the consolidated budget being usually thrice the size of the general budget; currently $29B and $9.0B respectively. Almost one out of every four dollars in the consolidated budget comes from U.S. federal subsidies while government-owned corporations compose more than 31% of the consolidated budget.
The critical aspects come from the sale of bonds, which comprise 7% of the consolidated budget – a ratio that increased annually due to the government's inability to prepare a balanced budget in addition to being incapable of generating enough income to cover all its expenses. In particular, the government-owned corporations add a heavy burden to the overall budget and public debt, as none is self-sufficient. For example, in FY2011 the government-owned corporations reported aggregated losses of more than $1.3B with the Puerto Rico Highways and Transportation Authority (PRHTA) reporting losses of $409M, the Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA; the government monopoly that controls all electricity on the island) reporting losses of $272M, while the Puerto Rico Aqueducts and Sewers Authority (PRASA; the government monopoly that controls all water utilities on the island) reported losses of $112M.
Losses by government-owned corporations have been defrayed through the issuance of bonds compounding more than 40% of Puerto Rico's entire public debt today. Holistically, from FY2000–FY2010 Puerto Rico's debt grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9% while GDP remained stagnant. This has not always provided a long-term solution. In early July 2017 for example, the PREPA power authority was effectively bankrupt after defaulting in a plan to restructure $9 billion in bond debt; the agency planned to seek Court protection.
In terms of protocol, the governor, together with the Puerto Rico Office of Management and Budget (OGP in Spanish), formulates the budget he believes is required to operate all government branches for the ensuing fiscal year. He then submits this formulation as a budget request to the Puerto Rican legislature before 1 July, the date established by law as the beginning of Puerto Rico's fiscal year. While the constitution establishes that the request must be submitted "at the beginning of each regular session", the request is typically submitted during the first week of May as the regular sessions of the legislature begin in January and it would be impractical to submit a request so far in advance. Once submitted, the budget is then approved by the legislature, typically with amendments, through a joint resolution and is referred back to the governor for his approval. The governor then either approves it or vetoes it. If vetoed, the legislature can then either refer it back with amendments for the governor's approval, or approve it without the governor's consent by two-thirds of the bodies of each chamber.
Once the budget is approved, the Department of Treasury disburses funds to the Office of Management and Budget which in turn disburses the funds to the respective agencies, while the Puerto Rico Government Development Bank (the government's intergovernmental bank) manages all related banking affairs including those related to the government-owned corporations.
Projected deficits added substantial burdens to an already indebted nation which accrued Public debt of Puerto Rico, a public debt of $71B or about 70% of Puerto Rico's gross domestic product. This sparked Puerto Rico government-debt crisis, an ongoing government-debt crisis after Puerto Rico's general obligation bonds were downgraded to speculative non-investment grade ("junk status") by three credit-rating agencies. In terms of financial control, almost 9.6%—or about $1.5 billion—of Puerto Rico's central government budget expenses for FY2014 is expected to be spent on debt service. Harsher budget cuts are expected as Puerto Rico must now repay larger chunks of debts in the coming years.
For practical reasons the budget is divided into two aspects: a "general budget" which comprises the assignments funded exclusively by the Department of Treasury of Puerto Rico, and the "consolidated budget" which comprises the assignments funded by the general budget, by List of government-owned corporations of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico's government-owned corporations, by revenue expected from loans, by the sale of government bonds, by subsidies extended by the federal government of the United States, and by other funds.
Both budgets contrast each other drastically, with the consolidated budget being usually thrice the size of the general budget; currently $29B and $9.0B respectively. Almost one out of every four dollars in the consolidated budget comes from U.S. federal subsidies while government-owned corporations compose more than 31% of the consolidated budget.
The critical aspects come from the sale of bonds, which comprise 7% of the consolidated budget – a ratio that increased annually due to the government's inability to prepare a balanced budget in addition to being incapable of generating enough income to cover all its expenses. In particular, the government-owned corporations add a heavy burden to the overall budget and public debt, as none is self-sufficient. For example, in FY2011 the government-owned corporations reported aggregated losses of more than $1.3B with the Puerto Rico Highways and Transportation Authority (PRHTA) reporting losses of $409M, the Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA; the government monopoly that controls all electricity on the island) reporting losses of $272M, while the Puerto Rico Aqueducts and Sewers Authority (PRASA; the government monopoly that controls all water utilities on the island) reported losses of $112M.
Losses by government-owned corporations have been defrayed through the issuance of bonds compounding more than 40% of Puerto Rico's entire public debt today. Holistically, from FY2000–FY2010 Puerto Rico's debt grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9% while GDP remained stagnant. This has not always provided a long-term solution. In early July 2017 for example, the PREPA power authority was effectively bankrupt after defaulting in a plan to restructure $9 billion in bond debt; the agency planned to seek Court protection.
In terms of protocol, the governor, together with the Puerto Rico Office of Management and Budget (OGP in Spanish), formulates the budget he believes is required to operate all government branches for the ensuing fiscal year. He then submits this formulation as a budget request to the Puerto Rican legislature before 1 July, the date established by law as the beginning of Puerto Rico's fiscal year. While the constitution establishes that the request must be submitted "at the beginning of each regular session", the request is typically submitted during the first week of May as the regular sessions of the legislature begin in January and it would be impractical to submit a request so far in advance. Once submitted, the budget is then approved by the legislature, typically with amendments, through a joint resolution and is referred back to the governor for his approval. The governor then either approves it or vetoes it. If vetoed, the legislature can then either refer it back with amendments for the governor's approval, or approve it without the governor's consent by two-thirds of the bodies of each chamber.
Once the budget is approved, the Department of Treasury disburses funds to the Office of Management and Budget which in turn disburses the funds to the respective agencies, while the Puerto Rico Government Development Bank (the government's intergovernmental bank) manages all related banking affairs including those related to the government-owned corporations.
Cost of living
 The cost of living in Puerto Rico is high and has increased over the past decade.
Statistics used for cost of living sometimes do not take into account certain costs, such as the high cost of electricity, which has hovered in the 24¢ to 30¢ range per kilowatt/hour, two to three times the national average, increased travel costs for longer flights, additional shipping fees, and the loss of promotional participation opportunities for customers "outside the continental United States". While some online stores do offer free shipping on orders to Puerto Rico, many merchants exclude Hawaii, Alaska, Puerto Rico and other United States territories.
The household median income is stated as $19,350 and the mean income as $30,463 in the U.S. Census Bureau's 2015 update. The report also indicates that 45.5% of individuals are below the poverty level. The median home value in Puerto Rico ranges from U.S.$100,000 to U.S.$214,000, while the national median home value sits at $119,600.
The cost of living in Puerto Rico is high and has increased over the past decade.
Statistics used for cost of living sometimes do not take into account certain costs, such as the high cost of electricity, which has hovered in the 24¢ to 30¢ range per kilowatt/hour, two to three times the national average, increased travel costs for longer flights, additional shipping fees, and the loss of promotional participation opportunities for customers "outside the continental United States". While some online stores do offer free shipping on orders to Puerto Rico, many merchants exclude Hawaii, Alaska, Puerto Rico and other United States territories.
The household median income is stated as $19,350 and the mean income as $30,463 in the U.S. Census Bureau's 2015 update. The report also indicates that 45.5% of individuals are below the poverty level. The median home value in Puerto Rico ranges from U.S.$100,000 to U.S.$214,000, while the national median home value sits at $119,600.
 One of the most cited contributors to the high cost of living in Puerto Rico is the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, also known as the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, Jones Act, which prevents foreign-flagged ships from carrying cargo between two American ports, a practice known as cabotage. Because of the Jones Act, foreign ships inbound with goods from Central America, Central and South America, Western Europe, and Africa cannot stop in Puerto Rico, offload Puerto Rico-bound goods, load mainland-bound Puerto Rico-manufactured goods, and continue to U.S. ports. Instead, they must proceed directly to U.S. ports, where distributors break bulk cargo, break bulk and send Puerto Rico-bound manufactured goods to Puerto Rico across the ocean by U.S.-flagged ships.
The government of Puerto Rico, local government of Puerto Rico has requested several times to the U.S. Congress to exclude Puerto Rico from the Jones Act restrictions without success. The most recent measure has been taken by the 17th Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico through R. Conc. del S. 21. These measures have always received support from all the Political party strength in Puerto Rico, major local political parties.
In 2013 the Government Accountability Office published a report which concluded that "repealing or amending the Jones Act cabotage law might cut Puerto Rico shipping costs" and that "shippers believed that opening the trade to non-U.S.-flag competition could lower costs". The same GAO report also found that "[shippers] doing business in Puerto Rico that GAO contacted reported that the freight rates are often—although not always—lower for foreign carriers going to and from Puerto Rico and foreign locations than the rates shippers pay to ship similar cargo to and from the United States, despite longer distances. Data were not available to allow us to validate the examples given or verify the extent to which this difference occurred." Ultimately, the report concluded that "[the] effects of modifying the application of the Jones Act for Puerto Rico are highly uncertain" for both Puerto Rico and the United States, particularly for the United States Merchant Marine, U.S. shipping industry and the military preparedness of the United States.
A 2018 study by economists at Boston-based Reeve & Associates and Puerto Rico-based Estudios Tecnicos has concluded that the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, 1920 Jones Act has no impact on either retail prices or the cost of livings on Puerto Rico. The study found that Puerto Rico received very similar or lower shipping freight rates when compared to neighboring islands, and that the transportation costs have no impact on retail prices on the island. The study was based in part on actual comparison of consumer goods at retail stores in San Juan, Puerto Rico, and Jacksonville, Florida, finding: no significant difference in the prices of either grocery items or durable goods between the two locations.
One of the most cited contributors to the high cost of living in Puerto Rico is the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, also known as the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, Jones Act, which prevents foreign-flagged ships from carrying cargo between two American ports, a practice known as cabotage. Because of the Jones Act, foreign ships inbound with goods from Central America, Central and South America, Western Europe, and Africa cannot stop in Puerto Rico, offload Puerto Rico-bound goods, load mainland-bound Puerto Rico-manufactured goods, and continue to U.S. ports. Instead, they must proceed directly to U.S. ports, where distributors break bulk cargo, break bulk and send Puerto Rico-bound manufactured goods to Puerto Rico across the ocean by U.S.-flagged ships.
The government of Puerto Rico, local government of Puerto Rico has requested several times to the U.S. Congress to exclude Puerto Rico from the Jones Act restrictions without success. The most recent measure has been taken by the 17th Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico through R. Conc. del S. 21. These measures have always received support from all the Political party strength in Puerto Rico, major local political parties.
In 2013 the Government Accountability Office published a report which concluded that "repealing or amending the Jones Act cabotage law might cut Puerto Rico shipping costs" and that "shippers believed that opening the trade to non-U.S.-flag competition could lower costs". The same GAO report also found that "[shippers] doing business in Puerto Rico that GAO contacted reported that the freight rates are often—although not always—lower for foreign carriers going to and from Puerto Rico and foreign locations than the rates shippers pay to ship similar cargo to and from the United States, despite longer distances. Data were not available to allow us to validate the examples given or verify the extent to which this difference occurred." Ultimately, the report concluded that "[the] effects of modifying the application of the Jones Act for Puerto Rico are highly uncertain" for both Puerto Rico and the United States, particularly for the United States Merchant Marine, U.S. shipping industry and the military preparedness of the United States.
A 2018 study by economists at Boston-based Reeve & Associates and Puerto Rico-based Estudios Tecnicos has concluded that the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, 1920 Jones Act has no impact on either retail prices or the cost of livings on Puerto Rico. The study found that Puerto Rico received very similar or lower shipping freight rates when compared to neighboring islands, and that the transportation costs have no impact on retail prices on the island. The study was based in part on actual comparison of consumer goods at retail stores in San Juan, Puerto Rico, and Jacksonville, Florida, finding: no significant difference in the prices of either grocery items or durable goods between the two locations.
Education
The first school in Puerto Rico was the ''Escuela de Gramática'' (Grammar School). It was established by Bishop Alonso Manso in 1513, in the area where the Cathedral of San Juan was to be constructed. The school was free of charge and the courses taught were Latin language, literature, history, science, art, philosophy and theology. Education in Puerto Rico is divided in three levels—Primary (elementary school grades 1–6), Secondary (intermediate and high school grades 7–12), and Higher Level (undergraduate and graduate studies). As of 2002, the literacy rate of the Puerto Rican population was 94.1%; by gender, it was 93.9% for males and 94.4% for females. According to the 2000 Census, 60.0% of the population attained a high school degree or higher level of education, and 18.3% has a bachelor's degree or higher. Instruction at the primary school level is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 18. , there are 1539 public schools and 806 private schools. The largest and oldest university system is the public University of Puerto Rico (UPR) with 11 campuses. The largest private university systems on the island are the Sistema Universitario Ana G. Mendez which operates the University of Turabo, Universidad del Turabo, Metropolitan University (Puerto Rico), Metropolitan University and Universidad del Este. Other private universities include the multi-campus Inter American University of Puerto Rico, Inter American University, the Catholic University of Puerto Rico, Pontifical Catholic University, Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico, Universidad Politécnica de Puerto Rico, and the University of the Sacred Heart (Puerto Rico), Universidad del Sagrado Corazón. Puerto Rico has four schools of Medicine and three ABA-approved Law Schools.Public health and safety
In 2017, there were 69 hospitals in Puerto Rico. ''Reforma de Salud de Puerto Rico'' (Puerto Rico Health Reform) – locally referred to as ''La Reforma'' (The Reform) – is a government-run program which provides medical and health care services to the indigent and impoverished, by means of contracting private health insurance companies, rather than employing government-owned hospitals and emergency centers. The Reform is administered by the Puerto Rico Health Insurance Administration.Triple-S Management Corporation Annual Report (Form 10-K)for the fiscal year ended on 31 December 2005, pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, accessed on 4 November 2006.
Crime
The unincorporated territory has a high firearm homicide rate. The homicide rate of 19.2 per 100,000 inhabitants was significantly higher than any U.S. state in 2014. Most homicide victims are gang members and drug traffickers with about 80% of homicides in Puerto Rico being drug related. Carjackings happen often in many areas of Puerto Rico. In 1992, the FBI made it a Federal crime and rates decreased per statistics, but as of 2019, the problem continued in municipalities like Guaynabo and others. From 1 January 2019, to 14 March 2019, thirty carjackings had occurred on the island.Culture
Modern Puerto Rican culture is a unique mix of cultural antecedents: including European (predominantly Spanish, Corsican immigration to Puerto Rico, Italian, French immigration to Puerto Rico, French, German immigration to Puerto Rico, German and Irish immigration to Puerto Rico, Irish), African, and, more recently, some North American and many South Americans. Many Cubans and Dominicans have relocated to the island in the past few decades. From the Spanish, Puerto Rico received the Spanish language, the Catholic religion and the vast majority of their cultural and moral values and traditions. The United States added English-language influence, the university system and the adoption of some holidays and practices. On 12 March 1903, the University of Puerto Rico was officially founded, branching out from the "Escuela Normal Industrial", a smaller organization that was founded in Fajardo three years earlier. Much of Puerto Rican culture centers on the influence of music and has been shaped by other cultures combining with local and traditional rhythms. Early in the history of Puerto Rican music, the influences of Spanish and African traditions were most noticeable. The cultural movements across the Caribbean and North America have played a vital role in the more recent musical influences which have reached Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has many symbols, but only the Thespesia grandiflora, Flor de Maga has been made official by the Government of Puerto Rico. Other popular, traditional, or unofficial symbols of Puerto Rico are the Puerto Rican spindalis, reina mora bird, the Ceiba pentandra, kapok tree, the Coquí, coquí frog, the Jíbaro (Puerto Rico), jíbaro, the Taíno, Taíno Indian, and the Carite, Guayama, Puerto Rico, carite landmark.Architecture
The architecture of Puerto Rico demonstrates a broad variety of traditions, styles and national influences accumulated over four centuries of Spanish rule, and a century of American rule. Spanish colonial architecture, Islamic architecture, Ibero-Islamic, art deco, Post-modern architecture, post-modern, and many other architectural forms are visible throughout the island. From town to town, there are also many regional distinctions. Old San Juan is one of the two ''barrios'', in addition to Santurce, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Santurce, that made up the municipality of San Juan from 1864 to 1951, at which time the former independent municipality of Río Piedras was annexed. With its abundance of shops, historic places, museums, open air cafés, restaurants, gracious homes, tree-shaded plazas, and its old beauty and architectonical peculiarity, Old San Juan is a main spot for local and internal tourism. The district is also characterized by numerous public plazas and churches including San José Church and the Catedral Metropolitana Basílica de San Juan Bautista (San Juan, Puerto Rico), Cathedral of San Juan Bautista, which contains the tomb of the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León. It also houses the oldest Catholic school for elementary education in Puerto Rico, the Colegio de Párvulos, built in 1865.
The oldest parts of the district of Old San Juan remain partly enclosed by massive walls. Several defensive structures and notable forts, such as the emblematic Fort San Felipe del Morro, Castillo San Cristóbal (San Juan), Fort San Cristóbal, and El Palacio de Santa Catalina, also known as
Old San Juan is one of the two ''barrios'', in addition to Santurce, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Santurce, that made up the municipality of San Juan from 1864 to 1951, at which time the former independent municipality of Río Piedras was annexed. With its abundance of shops, historic places, museums, open air cafés, restaurants, gracious homes, tree-shaded plazas, and its old beauty and architectonical peculiarity, Old San Juan is a main spot for local and internal tourism. The district is also characterized by numerous public plazas and churches including San José Church and the Catedral Metropolitana Basílica de San Juan Bautista (San Juan, Puerto Rico), Cathedral of San Juan Bautista, which contains the tomb of the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León. It also houses the oldest Catholic school for elementary education in Puerto Rico, the Colegio de Párvulos, built in 1865.
The oldest parts of the district of Old San Juan remain partly enclosed by massive walls. Several defensive structures and notable forts, such as the emblematic Fort San Felipe del Morro, Castillo San Cristóbal (San Juan), Fort San Cristóbal, and El Palacio de Santa Catalina, also known as Arts
Puerto Rican art reflects many influences, much from its ethnically diverse background. A form of folk art, called ''santos'' evolved from the Catholic Church's use of sculptures to convert indigenous Puerto Ricans to Christianity. ''Santos'' depict figures of saints and other religious icons and are made from native wood, clay, and stone. After shaping simple, they are often finished by painting them in vivid colors. ''Santos'' vary in size, with the smallest examples around eight inches tall and the largest about twenty inches tall. Traditionally, santos were seen as messengers between the earth and Heaven. As such, they occupied a special place on household altars, where people prayed to them, asked for help, or tried to summon their protection. Also popular, ''caretas'' or ''vejigantes'' are masks worn during carnivals. Similar masks signifying evil spirits were used in both Spain and Africa, though for different purposes. The Spanish used their masks to frighten lapsed Christians into returning to the church, while tribal Africans used them as protection from the evil spirits they represented. True to their historic origins, Puerto Rican ''caretas'' always bear at least several horns and fangs. While usually constructed of papier-mâché, coconut shells and fine metal screening are sometimes used as well. Red and black were the typical colors for ''caretas'' but their palette has expanded to include a wide variety of bright hues and patterns.Literature
 Puerto Rican literature evolved from the art of oral literature, oral story telling to its present-day status. Written works by the native islanders of Puerto Rico were prohibited and repressed by the Spanish colonial government. Only those who were commissioned by the Spanish Crown to document the chronological history of the island were allowed to write.
Diego de Torres Vargas was allowed to circumvent this strict prohibition for three reasons: he was a priest, he came from a prosperous Spanish family, and his father was a Sergeant Major in the Spanish Army, who died while defending Puerto Rico from an invasion by the
Puerto Rican literature evolved from the art of oral literature, oral story telling to its present-day status. Written works by the native islanders of Puerto Rico were prohibited and repressed by the Spanish colonial government. Only those who were commissioned by the Spanish Crown to document the chronological history of the island were allowed to write.
Diego de Torres Vargas was allowed to circumvent this strict prohibition for three reasons: he was a priest, he came from a prosperous Spanish family, and his father was a Sergeant Major in the Spanish Army, who died while defending Puerto Rico from an invasion by the Media
The mass media in Puerto Rico includes local radio stations, television stations and newspapers, the majority of which are conducted inMusic
The music of Puerto Rico has evolved as a heterogeneous and dynamic product of diverse cultural resources. The most conspicuous musical sources have been Spain and West Africa, although many aspects of Puerto Rican music reflect origins elsewhere in Europe and the Caribbean and, over the last century, from the U.S. Puerto Rican music culture today comprises a wide and rich variety of genres, ranging from indigenous genres like Bomba (Puerto Rico), bomba, plena, aguinaldo (music), aguinaldo, danza and Salsa music, salsa to recent hybrids like reggaeton. Puerto Rico has some national instruments, like the Puerto Rican cuatro, cuatro (Spanish for "four"). The cuatro is a local instrument that was made by the "Jibaro" or people from the mountains. Originally, the Cuatro consisted of four steel strings, hence its name, but currently the Cuatro consists of five double steel strings. It is easily confused with a guitar, even by locals. When held upright, from right to left, the strings are G, D, A, E, B. In the realm of classical music, the island hosts two main orchestras, the Orquesta Sinfónica de Puerto Rico and the Orquesta Filarmónica de Puerto Rico. The Casals Festival takes place annually in San Juan, drawing in classical musicians from around the world. With respect to opera, the legendary Puerto Rican tenor Antonio Paoli was so celebrated, that he performed private recitals for Pope Pius X and Tsar Nicholas II of Russia. In 1907, Paoli was the first operatic artist in world history to record an entire opera – when he participated in a performance of ''Pagliacci'' by Ruggiero Leoncavallo in Milan, Italy.Cuisine
Puerto Rican cuisine has its roots in the cooking traditions and practices of Europe (Spain), Africa and the nativePhilately
 Puerto Rico has been commemorated on four U.S. postal stamps and four personalities have been featured. Insular Territories were commemorated in 1937, the third stamp honored Puerto Rico featuring '
Puerto Rico has been commemorated on four U.S. postal stamps and four personalities have been featured. Insular Territories were commemorated in 1937, the third stamp honored Puerto Rico featuring 'Puerto Rico Election Issue
Arago: people, postage & the post. Viewed 4 March 2014. San Juan, Puerto Rico was commemorated with an 8-cent stamp on its 450th anniversary issued 12 September 1971, featuring a sentry box from
Sports
Baseball was one of the first sports to gain widespread popularity in Puerto Rico. The Puerto Rico Baseball League serves as the only active professional league, operating as a winter league. No Major League Baseball franchise or affiliate plays in Puerto Rico; however, San Juan hosted the Montreal Expos for several series in 2003 and 2004 before they moved to Washington, D.C. and became the Washington Nationals. The Puerto Rico national baseball team has participated in the World Cup of Baseball winning one gold (1951), four silver and four bronze medals, the Caribbean Series (winning fourteen times) and the World Baseball Classic. On , San Juan's Hiram Bithorn Stadium hosted the opening round as well as the second round of the newly formed World Baseball Classic. Puerto Rican baseball players include Hall of Famers Roberto Clemente, Orlando Cepeda and Roberto Alomar, enshrined in 1973, 1999, and 2011 respectively. Boxing, basketball, and volleyball are considered popular sports as well. Wilfredo Gómez and McWilliams Arroyo have won their respective divisions at the World Amateur Boxing Championships. Other medalists include José Pedraza (boxer), José Pedraza, who holds a silver medal, and three boxers who finished in third place, José Luis Vellón, Nelson Dieppa and McJoe Arroyo. In the professional circuit, Puerto Rico has the third-most List of Puerto Rican boxing world champions, boxing world champions and it is the global leader in champions per capita. These include Miguel Cotto, Félix Trinidad, Wilfred Benítez and Gómez among others. The Puerto Rico national basketball team joined the International Basketball Federation in 1957. Since then, it has won more than 30 medals in international competitions, including gold in three FIBA Americas Championships and the 1994 Goodwill Games 8 August 2004, became a landmark date for the team when it became the first team to defeat the United States men's national basketball team, United States in an Olympic tournament since the integration of National Basketball Association players. Winning the inaugural game with scores of 92–73 as part of the 2004 Summer Olympics organized in Athens, Greece. Baloncesto Superior Nacional acts as the top-level professional basketball league in Puerto Rico, and has experienced success since its beginning in 1930. Puerto Rico national football team, Puerto Rico is also a member of FIFA and CONCACAF. In 2008, the archipelago's first unified league, the Puerto Rico Soccer League, was established.
Other sports include professional wrestling and road running. The World Wrestling Council and International Wrestling Association (Puerto Rico), International Wrestling Association are the largest wrestling promotions in the main island. The World's Best 10K, held annually in San Juan, has been ranked among the 20 most competitive races globally. The "Puerto Rico All Stars" team, which has won twelve world championships in unicycle basketball.
Organized Streetball has gathered some exposition, with teams like "Puerto Rico Street Ball" competing against established organizations including the Arecibo Captains, Capitanes de Arecibo and AND1's AND1 Mixtape Tour, Mixtape Tour Team. Six years after the first visit, AND1 returned as part of their renamed Live Tour, losing to the Puerto Rico Streetballers. Consequently, practitioners of this style have earned participation in international teams, including Orlando Melendez, Orlando "El Gato" Meléndez, who became the first Puerto Rican born athlete to play for the Harlem Globetrotters. Orlando Antigua, whose mother is Puerto Rican, in 1995 became the first Latino and the first non-black in 52 years to play for the Harlem Globetrotters.
Puerto Rico has representation in all international competitions including the Summer Olympics, Summer and Winter Olympics, the Pan American Games, the Caribbean World Series, and the Central American and Caribbean Games. Puerto Rico hosted the Pan Am Games in 1979 (officially in San Juan), and The Central American and Caribbean Games were hosted in 1993 Central American and Caribbean Games, 1993 in Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce and in 2010 Central American and Caribbean Games, 2010 in Mayagüez.
Puerto Rican athletes have won ten medals in Olympic competition (two gold, two silver, six bronze), the first one in 1948 by boxer Juan Evangelista Venegas. Monica Puig won the first gold medal for Puerto Rico in the Olympic Games by winning the Tennis at the 2016 Summer Olympics#Medal events, Women's Tennis singles title in Rio 2016.
Puerto Rico national football team, Puerto Rico is also a member of FIFA and CONCACAF. In 2008, the archipelago's first unified league, the Puerto Rico Soccer League, was established.
Other sports include professional wrestling and road running. The World Wrestling Council and International Wrestling Association (Puerto Rico), International Wrestling Association are the largest wrestling promotions in the main island. The World's Best 10K, held annually in San Juan, has been ranked among the 20 most competitive races globally. The "Puerto Rico All Stars" team, which has won twelve world championships in unicycle basketball.
Organized Streetball has gathered some exposition, with teams like "Puerto Rico Street Ball" competing against established organizations including the Arecibo Captains, Capitanes de Arecibo and AND1's AND1 Mixtape Tour, Mixtape Tour Team. Six years after the first visit, AND1 returned as part of their renamed Live Tour, losing to the Puerto Rico Streetballers. Consequently, practitioners of this style have earned participation in international teams, including Orlando Melendez, Orlando "El Gato" Meléndez, who became the first Puerto Rican born athlete to play for the Harlem Globetrotters. Orlando Antigua, whose mother is Puerto Rican, in 1995 became the first Latino and the first non-black in 52 years to play for the Harlem Globetrotters.
Puerto Rico has representation in all international competitions including the Summer Olympics, Summer and Winter Olympics, the Pan American Games, the Caribbean World Series, and the Central American and Caribbean Games. Puerto Rico hosted the Pan Am Games in 1979 (officially in San Juan), and The Central American and Caribbean Games were hosted in 1993 Central American and Caribbean Games, 1993 in Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce and in 2010 Central American and Caribbean Games, 2010 in Mayagüez.
Puerto Rican athletes have won ten medals in Olympic competition (two gold, two silver, six bronze), the first one in 1948 by boxer Juan Evangelista Venegas. Monica Puig won the first gold medal for Puerto Rico in the Olympic Games by winning the Tennis at the 2016 Summer Olympics#Medal events, Women's Tennis singles title in Rio 2016.
Folklore
In her poem ''The Messenger-Bird'', Felicia Hemans refers to a Puerto Rican legend concerning ''The Fountain of Youth'', supposedly to be found in the Lucayan Archipelago. She sourced this from William Robertson (historian), Robertson's History of America. Some books that talk about folklore/myths in Puerto Rico are ''Stories from Puerto Rico'' written by Robert L. Muckley and Adela Martínez-Santiago and ''Cuentos: An Anthology of Short Stories from Puerto Rico'' written by Kal Wagenheim.Infrastructure
Transportation
 Puerto Rico has nine ports in different cities across the main island. The San Juan Port is the largest in Puerto Rico, and the busiest port in the Caribbean and the 10th busiest in the United States in terms of commercial activity and cargo movement, respectively. The second largest port is the Port of the Americas in Ponce, currently under expansion to increase cargo capacity to twenty-foot containers (Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEUs) per year.
Puerto Rico has nine ports in different cities across the main island. The San Juan Port is the largest in Puerto Rico, and the busiest port in the Caribbean and the 10th busiest in the United States in terms of commercial activity and cargo movement, respectively. The second largest port is the Port of the Americas in Ponce, currently under expansion to increase cargo capacity to twenty-foot containers (Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEUs) per year.
Utilities
Electricity
The Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA)—Spanish: ''Autoridad de Energía Eléctrica'' (AEE)—is an electric power company and the List of government-owned corporations of Puerto Rico, government-owned corporation of Puerto Rico responsible for electricity generation, electric power transmission, power transmission, and electric power distribution, power distribution in Puerto Rico. PREPA was, by law, the only entity authorized to conduct such business in Puerto Rico, effectively making it a government monopoly until 2018. The Authority is ruled by a governing board appointed by the governor with the advice and consent of the Senate of Puerto Rico, and is run by an executive director. On 20 July 2018, Puerto Rico Law 120-2018 (''Ley para Transformar el Sistema Eléctrico de Puerto Rico'') was signed. This law authorized PREPA to sell infrastructure and services to other providers. As a result, a contract was signed on 22 June 2020, making LUMA Energy the new operator of the energy distribution and transmission infrastructure, as well as other areas of PREPA's operations, in effect partially privatizing the Puerto Rican power grid. The takeover was set for 1 June 2021, amidst protests and uncertainty from the point of view of the general public and the former-PREPA workers and Trade union, union members.Water and Sewage
Similarly, the Puerto Rico Aqueducts and Sewers Authority (PRASA) —Spanish: ''Autoridad de Acueductos y Alcantarillados'' (AAA)—is a water company and the government-owned corporation responsible for water quality, Water resource management, management, and Water supply, supply in Puerto Rico. It is the only entity authorized to conduct such business in Puerto Rico, effectively making it a government monopoly. Its existence is designated by Law No. 40 of 1 May 1945, including the corresponding amendments.Telecommunications
Telecommunications in Puerto Rico includes radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet. Broadcasting in Puerto Rico is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission, U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). , there were 30 TV stations, 125 radio stations and roughly 1 million TV sets on the island. Cable TV subscription services are available and the U.S. Armed Forces Radio and Television Service also broadcast on the island."Communications: Puerto Rico"''World Factbook'', U.S. Central Intelligence Agency, 9 December 2013. Retrieved 8 January 2014. Puerto Rico also has its own Amateur radio, amateur radio prefixes, which differ from those of the contiguous United States in that there are two letter before the number. The most well-known prefix is KP4, but others separated for use on the archipelago (including Desecheo and Mona) are: KP3/KP4/NP3/NP4/WP3/WP4 (Puerto Rico,
See also
* Index of Puerto Rico-related articles * Outline of Puerto RicoFootnotes
Notes
References
Further reading
* Isar P. Godreau, ''Scripts of Blackness: Race, Cultural nationalism, and U.S. Colonialism in Puerto Rico.'' Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 2015.External links
* ** ** *Department Of Economic Development and Commerce
* * * *
Puerto Rico
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. *
Geography
* *United States government
* *United Nations (U.N.) Declaration on Puerto Rico
* {{coord, 18.2, -66.5, dim:300000_region:US-PR_type:adm1st, name=Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, display=title Puerto Rico, Caribbean islands of the United States Island countries Dependent territories in the Caribbean Greater Antilles Former colonies in North America Former Spanish colonies Insular areas of the United States Islands of Puerto Rico, * New Spain Spanish Caribbean Spanish colonization of the Americas Spanish-speaking countries and territories Spanish West Indies States and territories established in 1898 Articles containing video clips 1493 establishments in the Spanish West Indies 1898 disestablishments in the Spanish West Indies Small Island Developing States