Border dispute on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
 Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of
UN Charter
states, "All Members shall refrain in their international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, or in any other manner inconsistent with the Purposes of the United Nations." In some cases in which the boundary is not demarcated, such as the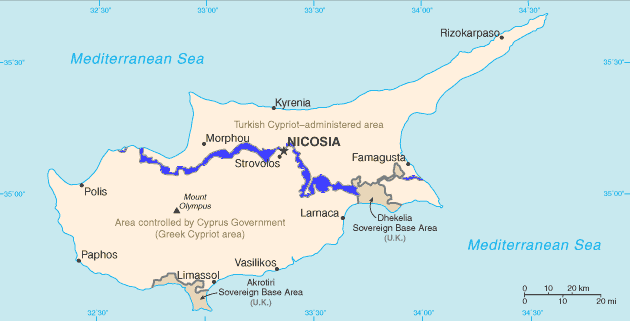 *An
*An
Lectures
by Malcolm Shaw entitled ''The International Legal Principles Relating to Territorial Disputes: The Acquisition of Title to Territory'' and ''Settling Territorial Disputes'' in th
Lecture Series of the United Nations Audiovisual Library of International LawWorldStatesman
– click on any state for the listing (after the chronological lists of statesmen) of Territorial Disputes it is party to
in CIA World Factbook
* ttp://listverse.com/2011/09/02/top-10-controversial-territorial-disputes/ List of top 10 Territorial disputes {{Authority control Territorial dispute
Context and definitions
 Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
s such as river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
s, fertile farmland, mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
or petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
resources although the disputes can also be driven by culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
, and ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politi ...
. Territorial disputes often result from vague and unclear language in a treaty that set up the original boundary.
Territorial disputes are a major cause of war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
s and terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
, as states often try to assert their sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
over a territory through invasion, and non-state entities try to influence the actions of politicians through terrorism. International law does not support the use of force by one state to annex the territory of another state. ThUN Charter
states, "All Members shall refrain in their international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, or in any other manner inconsistent with the Purposes of the United Nations." In some cases in which the boundary is not demarcated, such as the
Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a -wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental Asia. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
The Taiwan Strait is itself a ...
, and Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, the parties involved define a Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but serv ...
, which serves as the ''de facto'' international border.
*The term ''border dispute'' (or ''border conflict'') applies to cases in which a limited territory is disputed by two or more states, each contending state would publish its own maps to include the same region which would invariably lie along or adjacent to the recognised borders of the competing states, such as the Abyei
The Abyei Area ( ar, منطقة أبيي) is an area of on the border between South Sudan and the Sudan that has been accorded "special administrative status" by the 2004 Protocol on the Resolution of the Abyei Conflict (Abyei Protocol) in ...
region which is contested between South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of th ...
and the Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
. With border conflicts, the existence of the rival state is not being challenged, such as the relationship between the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeas ...
or the relationship between North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, but each state recognises the shape of the rival state only as not containing the claimed territory, in spite of who actually governs the land and how it is recognised in the international community. *An
*An occupied territory
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
, in general, is a region distinct from the recognized territory of the sovereign states but which the occupying state controls, usually with military forces. Sometimes, a long-term occupation is maintained as a means to act upon a territorial claim, but an occupation may also be strategic (such as creating a buffer zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them.
Common types of buffer zones are demili ...
or preventing a rival power obtaining control) or a means of coercion (such as a punishment, to impose some internal measures or for use as a bargaining chip).
*The term ''irredentism
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
'' applies to border disputes but also to wider territorial claims:
#If a nation emerges when declaring independence from a larger state, its ultimate recognition may not always grant the new state control over the territory it proposed as part of the declaration. Those lands remain ''unredeemed territory'' in the eyes of nationalist movements from the state but do not otherwise cause a problem between the governments on each side of the border.
#In cases that territory was achieved through historical conquests such as an empire, traditionalists may view former colonies as unredeemed territory.
Basis in international law
Territorial disputes have significant meaning in the international society, both by their relation to the fundamental right of states, sovereignty and also because they are important for international peace. International law has significant relations with territorial disputes because territorial disputes tackles the basis of international law; the state territory. International law is based on the persons of international law, which requires a defined territory, as mentioned in the 1933 Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States. Article 1 of the Montevideo Convention declares that "a person of international law should possess the following qualifications: (a) a permanent population; (b) a defined territory; (c) government; and (d) capacity to enter into relations with other States" http://www.idpsrilanka.lk/Doc/International%20Human%20Rights%20Instruments/Montevideo%20Convention%20on%20the%20Rights%20and%20Duties%20of%20States.pdf Also, B. T. Sumner's article mentions, "In international law and relations, ownership of territory is significant because sovereignty over land defines what constitutes a state." Therefore, the breach of a country's borders or territorial disputes pose a threat to a state's very sovereignty and the right as a person of international law. In addition, territorial disputes are sometimes brought to theInternational Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordan ...
, as was the case in Costa Rica and Nicaragua (2005). Territorial disputes cannot be separated from international law, whose basis is on the law of state borders, and their potential settlement also relies on international law and the Court.
See also
*List of territorial disputes
Territorial disputes have occurred throughout history, over lands around the world. Bold indicates one claimant's full control; ''italics'' indicates one or more claimants' partial control.
Ongoing disputes between UN member/observer states ...
** List of border conflicts
The following is a list of border conflicts between two or more countries. The list includes only those fought because of border disputes. See list of territorial disputes for those that do not involve fighting.
19th century
20th century ...
(including only those that involve fighting)
* Fait accompli
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman Conquest, before the language settled into what became Modern Engl ...
* Frozen conflict
In international relations, a frozen conflict is a situation in which active armed conflict has been brought to an end, but no peace treaty or other political framework resolves the conflict to the satisfaction of the combatants. Therefore, lega ...
* Israeli–Palestinian conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is one of the world's most enduring conflicts, beginning in the mid-20th century. Various attempts have been made to resolve the conflict as part of the Israeli–Palestinian peace process, alongside other ef ...
* Status quo ante bellum
The term ''status quo ante bellum'' is a Latin phrase meaning "the situation as it existed before the war".
The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When use ...
* Thalweg
In geography and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg () is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse.
Under international law, a thalweg is the middle of the primary navigable channel of a waterway that defines the boun ...
* Territorial disputes in the South China Sea
Territorial disputes in the South China Sea involve conflicting island and maritime claims in the region by several sovereign states, namely Brunei, the People's Republic of China (PRC), Taiwan (Republic of China/ROC), Indonesia, Malaysia, P ...
* Territorial disputes in the Persian Gulf
This article deals with territorial disputes between states of in and around the Persian Gulf in Southwestern Asia. These states include Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Oman
Background
Bef ...
* Territorial disputes of Nicaragua Territorial disputes of Nicaragua include the territorial dispute with Colombia over the Archipelago de San Andres y Providencia and Quita Sueno Bank. Nicaragua also has a maritime boundary dispute with Honduras in the Caribbean Sea and a Costa Rica ...
References
External links
Lectures
by Malcolm Shaw entitled ''The International Legal Principles Relating to Territorial Disputes: The Acquisition of Title to Territory'' and ''Settling Territorial Disputes'' in th
Lecture Series of the United Nations Audiovisual Library of International Law
– click on any state for the listing (after the chronological lists of statesmen) of Territorial Disputes it is party to
in CIA World Factbook
* ttp://listverse.com/2011/09/02/top-10-controversial-territorial-disputes/ List of top 10 Territorial disputes {{Authority control Territorial dispute