Period 4 elements on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A period 4 element is one of the




 Vanadium (V) is an element in group 5. Vanadium is never found in pure form in nature, but is commonly found in compounds. Vanadium is similar to titanium in many ways, such as being very corrosion-resistant, however, unlike titanium, it oxidizes in air even at room temperature. All vanadium compounds have at least some level of toxicity, with some of them being extremely toxic.
Vanadium (V) is an element in group 5. Vanadium is never found in pure form in nature, but is commonly found in compounds. Vanadium is similar to titanium in many ways, such as being very corrosion-resistant, however, unlike titanium, it oxidizes in air even at room temperature. All vanadium compounds have at least some level of toxicity, with some of them being extremely toxic.
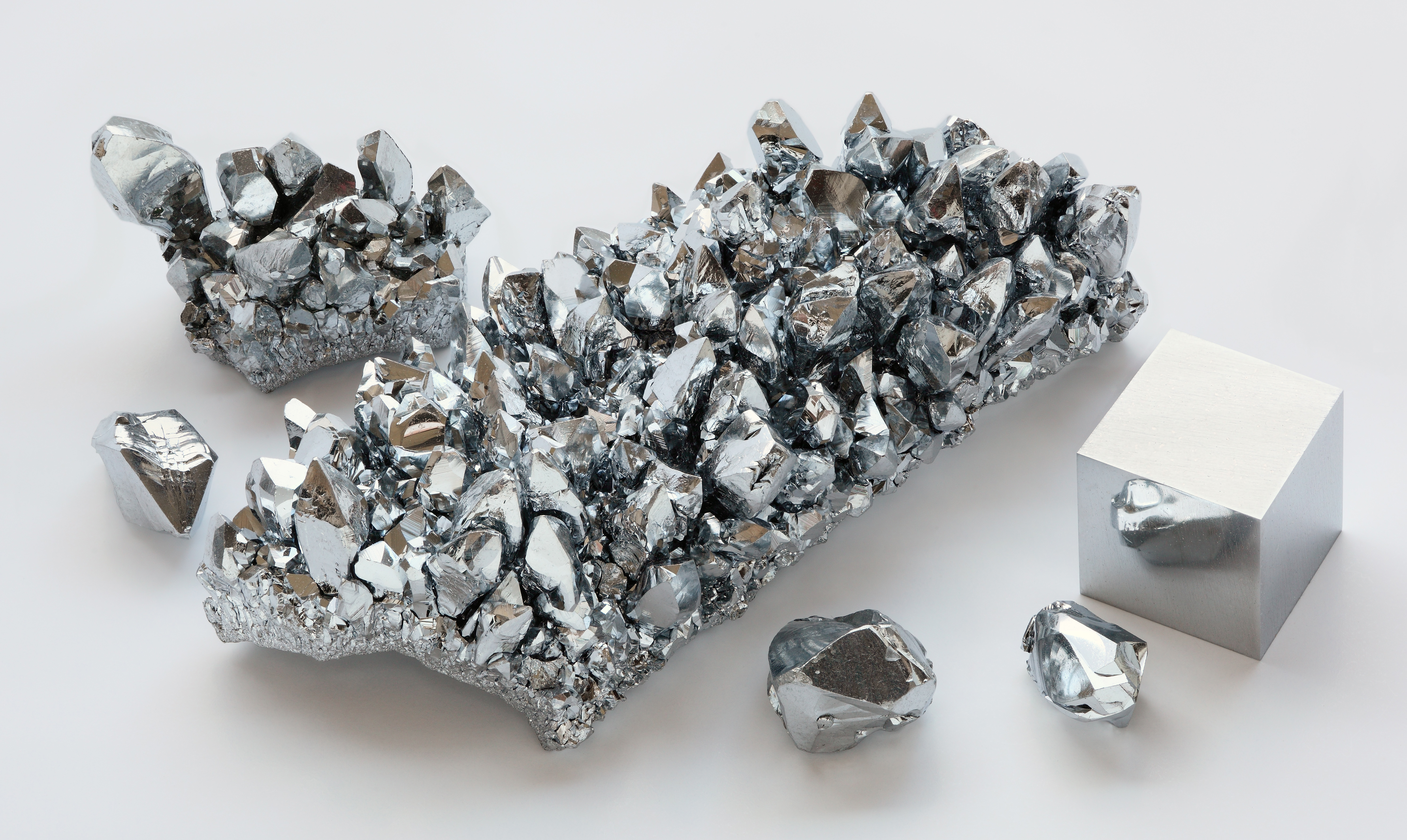 Chromium (Cr) is an element in group 6. Chromium is, like titanium and vanadium before it, extremely resistant to corrosion, and is indeed one of the main components of stainless steel. Chromium also has many colorful compounds, and as such is very commonly used in pigments, such as
Chromium (Cr) is an element in group 6. Chromium is, like titanium and vanadium before it, extremely resistant to corrosion, and is indeed one of the main components of stainless steel. Chromium also has many colorful compounds, and as such is very commonly used in pigments, such as
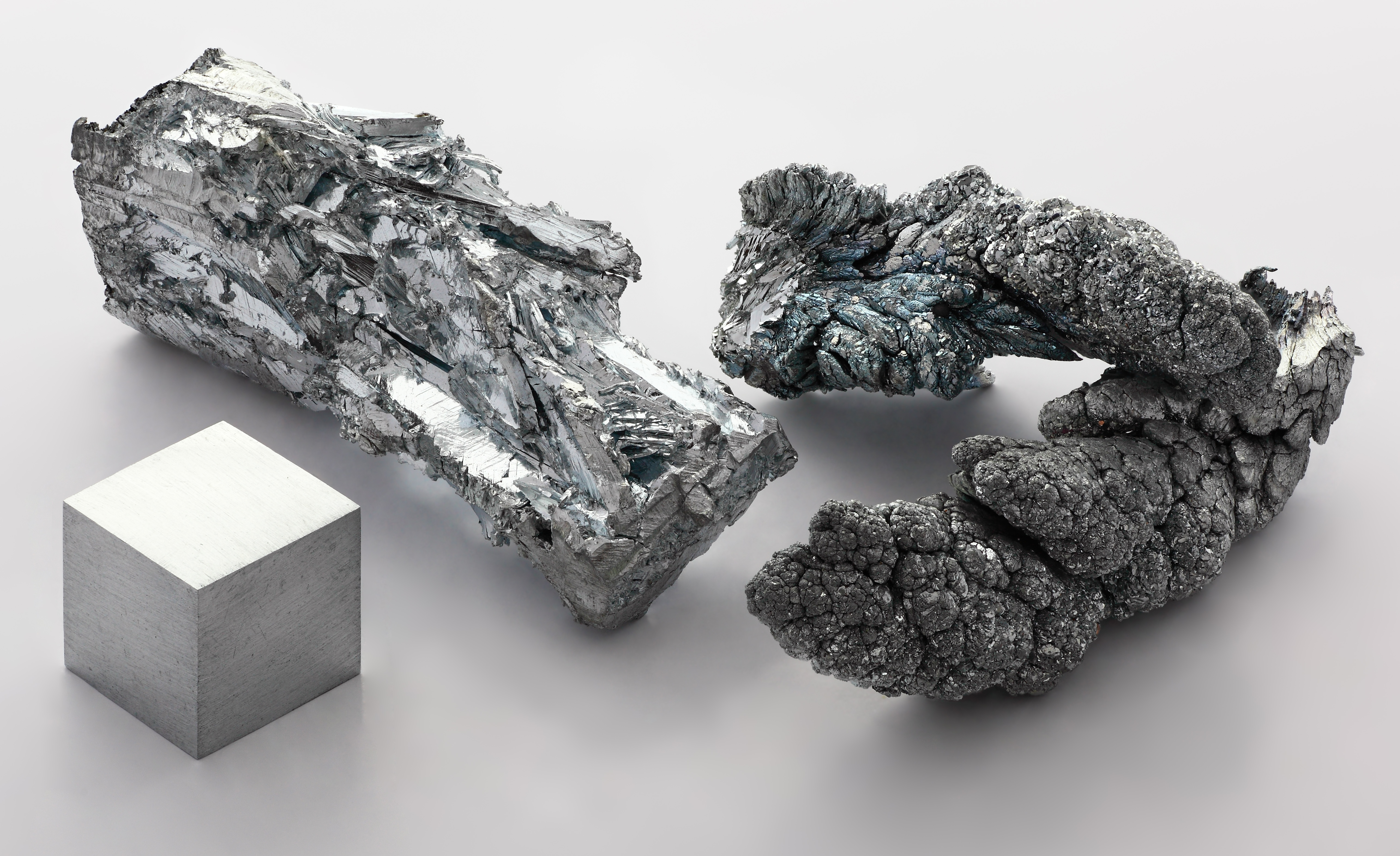
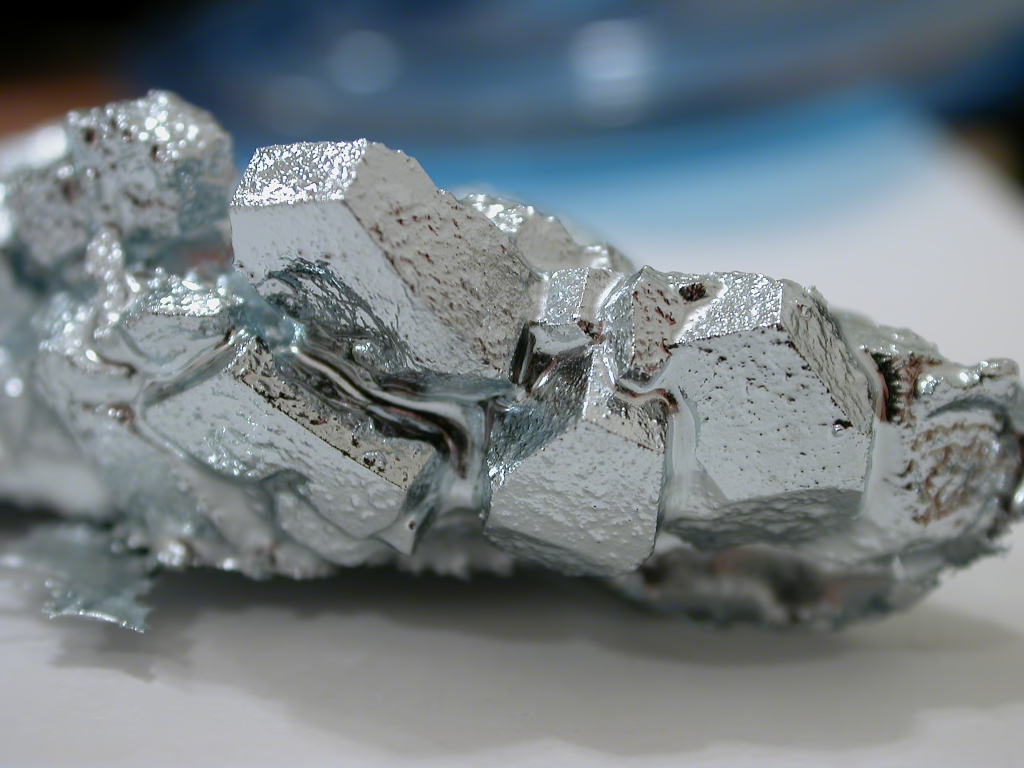





 Gallium (Ga) is an element in group 13, under
Gallium (Ga) is an element in group 13, under
 Germanium (Ge) is an element in group 14. Germanium, like
Germanium (Ge) is an element in group 14. Germanium, like



chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s in the fourth row (or ''period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
'') of the periodic table of the elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fourth period contains 18 elements beginning with potassium and ending with krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
– one element for each of the eighteen groups. It sees the first appearance of d-block
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ...
(which includes transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
s) in the table.
Properties
Every single one of these elements is stable, and many are extremely common in the Earth's crust and/or core; it is the last period with no unstable elements at all. Many of the transition metals in period 4 are very strong, and therefore commonly used in industry, especiallyiron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
. Three adjacent elements are known to be toxic, with arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, ...
one of the most well-known poisons, selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
being toxic to humans in large quantities, and bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
, a toxic liquid. Many elements are essential to humans' survival, such as calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
being what forms bones.
Atomic structure
Progressing towards increase ofatomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
, the Aufbau principle causes elements of the period to put electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s onto 4s, 3d, and 4p subshells, in that order. However, there are exceptions, such as chromium. The first twelve elements— K, Ca, and transition metals—have from 1 to 12 valence electron
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair form ...
s respectively, which are placed on 4s and 3d.
Twelve electrons over the electron configuration of argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as ...
reach the configuration of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, namely 3d10 4s2. After this element, the filled 3d subshell effectively withdraws from chemistry and the subsequent trend
A fad or trend is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short period.
Fads are objects or behaviors that achieve shor ...
looks much like trends in the periods 2 and 3. The p-block elements of period 4 have their valence shell
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms ...
composed of 4s and 4p subshells of the fourth () shell and obey the octet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rul ...
.
For quantum chemistry namely this period sees transition from the simplified electron shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or ...
paradigm to research of many differently-shaped subshells. The relative disposition of their energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The t ...
s is governed by the interplay of various physical effects. The period's s-block metals put their differentiating electrons onto 4s despite having vacancies among nominally lower states – a phenomenon unseen in lighter elements. Contrariwise, the six elements from gallium to krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
are the heaviest where all electron shells below the valence shell are filled ''completely''. This is no longer possible in further periods due to the existence of f-subshells starting from .
List of elements
: (*) Exception to theMadelung rule
The aufbau principle , from the German ''Aufbauprinzip'' (building-up principle), also called the aufbau rule, states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill subshells of the lowest available energy, then they fill subshells ...
s-block elements
Potassium

Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
(K) is an alkali metal, placed under sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and over rubidium, and is the first element of period 4. It is one of the most reactive
Reactive may refer to:
*Generally, capable of having a reaction (disambiguation)
*An adjective abbreviation denoting a bowling ball coverstock made of reactive resin
*Reactivity (chemistry)
*Reactive mind
*Reactive programming
See also
*Reactanc ...
elements in the periodic table, therefore usually only found in compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
s. It tends to oxidize in air very rapidly, thus accounting for its rapid reaction with oxygen when freshly exposed to air. When freshly exposed, it is rather silvery, but it quickly begins to tarnish as it reacts with air. It is soft enough to be cut with a knife and it is the second least dense
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically ...
element. Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
has a relatively low melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depen ...
; it will melt just by putting it under a small open flame. It also is less dense than water, and can, in turn, float.
Calcium

Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
(Ca) is the second element in the period. An alkali earth metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all ...
, calcium is almost never found in nature due to its high reactivity with water. It has one of the most widely known and acknowledged biological roles in all animals and some plants, making up bones and teeth, and used in some applications in cells, such as signals for cellular processes
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and ...
es. It is regarded as the most abundant mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
in the body's mass.
d-block elements
Scandium

Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in ...
(Sc) is the third element in the period, and is the first transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
in the periodic table. Scandium is quite common in nature, but difficult to isolate because it is most prevalent in rare earth compounds, which are difficult to isolate elements from. Scandium has very few commercial applications because of the aforementioned facts, and currently its only major application is in aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
alloys.
Titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
(Ti) is an element in group 4. Titanium is both one of the least dense metals and one of the strongest and most corrosion-resistant, and as such has many applications, especially in alloys with other elements, such as iron. Due to its aforementioned properties, it is commonly used in airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurat ...
s, golf club
A golf club is a club used to hit a golf ball in a game of golf. Each club is composed of a shaft with a grip and a club head. Woods are mainly used for long-distance fairway or tee shots; irons, the most versatile class, are used for a variety ...
s, and other objects that must be strong, but lightweight.
Vanadium
 Vanadium (V) is an element in group 5. Vanadium is never found in pure form in nature, but is commonly found in compounds. Vanadium is similar to titanium in many ways, such as being very corrosion-resistant, however, unlike titanium, it oxidizes in air even at room temperature. All vanadium compounds have at least some level of toxicity, with some of them being extremely toxic.
Vanadium (V) is an element in group 5. Vanadium is never found in pure form in nature, but is commonly found in compounds. Vanadium is similar to titanium in many ways, such as being very corrosion-resistant, however, unlike titanium, it oxidizes in air even at room temperature. All vanadium compounds have at least some level of toxicity, with some of them being extremely toxic.
Chromium
 Chromium (Cr) is an element in group 6. Chromium is, like titanium and vanadium before it, extremely resistant to corrosion, and is indeed one of the main components of stainless steel. Chromium also has many colorful compounds, and as such is very commonly used in pigments, such as
Chromium (Cr) is an element in group 6. Chromium is, like titanium and vanadium before it, extremely resistant to corrosion, and is indeed one of the main components of stainless steel. Chromium also has many colorful compounds, and as such is very commonly used in pigments, such as chrome green
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
Structure and properties
has the corundum ...
.
Manganese

Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
(Mn) is an element in group 7. Manganese is often found in combination with iron. Manganese, like chromium before it, is an important component in stainless steel, preventing the iron from rusting. Manganese is also often used in pigments, again like chromium. Manganese is also poisonous; if enough is inhaled, it can cause irreversible neurological damage.
Iron

Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
(Fe) is an element in group 8. Iron is the most common on Earth among elements of the period, and probably the most well-known of them. It is the principal component of steel. Iron-56
Iron-56 (56Fe) is the most common isotope of iron. About 91.754% of all iron is iron-56.
Of all nuclides, iron-56 has the lowest mass per nucleon. With 8.8 MeV binding energy per nucleon, iron-56 is one of the most tightly bound nuclei.
N ...
has the lowest energy density of any isotope of any element, meaning that it is the most massive element that can be produced in supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars spa ...
stars. Iron also has some applications in the human body; hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyt ...
is partly iron.
Cobalt

Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
(Co) is an element in group 9. Cobalt is commonly used in pigments, as many compounds of cobalt are blue in color. Cobalt is also a core component of many magnetic and high-strength alloys. The only stable isotope, cobalt-59
Naturally occurring cobalt (Co) consists of a single stable isotope, Co. Twenty-eight radioisotopes have been characterized; the most stable are Co with a half-life of 5.2714 years, Co (271.8 days), Co (77.27 days), and Co (70.86 days). All other ...
, is an important component of vitamin B-12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
, while cobalt-60
Cobalt-60 (60Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2713 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisot ...
is a component of nuclear fallout and can be dangerous in large enough quantities due to its radioactivity.
Nickel

Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
(Ni) is an element in group 10. Nickel is rare in the Earth's crust, mainly due to the fact that it reacts with oxygen in the air, with most of the nickel on Earth coming from nickel iron meteorites. However, nickel is very abundant in the Earth's core
The internal structure of Earth is the solid portion of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere. The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whose ...
; along with iron it is one of the two main components. Nickel is an important component of stainless steel, and in many superalloys
A superalloy, or high-performance alloy, is an alloy with the ability to operate at a high fraction of its melting point. Several key characteristics of a superalloy are excellent mechanical strength, resistance to thermal creep deformation, g ...
.
Copper

Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
(Cu) is an element in group 11. Copper is one of the few metals that is not white or gray in color, the only others being gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, osmium and caesium. Copper has been used by humans for thousands of years to provide a reddish tint to many objects, and is even an essential nutrient to humans, although too much is poisonous. Copper is also commonly used as a wood preservative or fungicides.
Zinc

Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
(Zn) is an element in group 12. Zinc is one of the main components of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
, being used since the 10th century BCE. Zinc is also incredibly important to humans; almost 2 billion people in the world suffer from zinc deficiency. However, too much zinc can cause copper deficiency. Zinc is often used in batteries, aptly named carbon-zinc batteries, and is important in many platings, as zinc is very corrosion resistant.
p-block elements
Gallium
 Gallium (Ga) is an element in group 13, under
Gallium (Ga) is an element in group 13, under aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
. Gallium is noteworthy because it has a melting point at about 303 kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
s, right around room temperature. For example, it will be solid on a typical spring day, but will be liquid on a hot summer day. Gallium is an important component in the alloy galinstan, along with tin. Gallium can also be found in semiconductors.
Germanium
 Germanium (Ge) is an element in group 14. Germanium, like
Germanium (Ge) is an element in group 14. Germanium, like silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
above it, is an important semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
and is commonly used in diodes and transistors, often in combination with arsenic. Germanium is fairly rare on Earth, leading to its comparatively late discovery. Germanium, in compounds, can sometimes irritate the eyes, skin, or lungs.
Arsenic

Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, ...
(As) is an element in group 15. Arsenic, as mentioned above, is often used in semiconductors in alloys with germanium. Arsenic, in pure form and some alloys, is incredibly poisonous to all multicellular life, and as such is a common component in pesticides. Arsenic was also used in some pigments before its toxicity was discovered.
Selenium

Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
(Se) is an element in group 16. Selenium is the first nonmetal in period 4, with properties similar to sulfur. Selenium is quite rare in pure form in nature, mostly being found in minerals such as pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue giv ...
, and even then it is quite rare. Selenium is necessary for humans in trace amounts, but is toxic in larger quantities. Selenium is a chalcogen. Selenium is red in monomolar structure but metallic gray in its crystalline structure.
Bromine

Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
(Br) is an element in group 17 (halogen). It does not exist in elemental form in nature. Bromine is barely liquid at room temperature, boiling at about 330 kelvins. Bromine is also quite toxic and corrosive, but bromide ions, which are relatively inert, can be found in halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
, or table salt. Bromine is often used as a fire retardant
A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants m ...
because many compounds can be made to release free bromine atoms.
Krypton

Krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
(Kr) is a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
, placed under argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as ...
and over xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
. Being a noble gas, krypton rarely interacts with itself or other elements; although compounds have been detected, they are all unstable and decay rapidly, and as such, krypton is often used in fluorescent lights. Krypton, like most noble gases, is also used in lighting because of its many spectral lines and the aforementioned reasons.
Biological role
Many period 4 elements find roles in controlling protein function assecondary messengers
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
, structural components, or enzyme cofactors. A gradient of potassium is used by cells to maintain a membrane potential which enables neurotransmitter firing and facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembra ...
among other processes. Calcium is a common signaling molecule for proteins such as calmodulin and plays a critical role in triggering skeletal muscle contraction in vertebrates. Selenium is a component of the noncanonical amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
, selenocysteine; proteins which contain selenocysteine are known as selenoproteins. Manganese enzymes are utilized by both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, and may play a role in the virulence of some pathogenic bacteria. Vanabins
Vanabins (also known as vanadium-associated proteins or vanadium chromagen) are a group of vanadium-binding proteins. metalloproteins. Vanabins are found almost exclusively in the blood cells, or vanadocytes, of some tunicates (sea squirts), inclu ...
, also known as vanadium-associated proteins, are found in the blood cells of some species of sea squirts. The role of these proteins is disputed, although there is some speculation that they function as oxygen carriers. Zinc ions are used to stabilize the zinc finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized struct ...
milieu
The social environment, social context, sociocultural context or milieu refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. It includes the culture that the individual was educate ...
of many DNA-binding proteins
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for DNA#Base pairing, single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove ...
.
Period 4 elements can also be found complexed with organic small molecules
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ...
to form cofactors. The most famous example of this is heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.
In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consis ...
: an iron-containing porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical com ...
compound responsible for the oxygen-carrying function of myoglobin and hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyt ...
as well as the catalytic activity of cytochrome enzymes. Hemocyanin
Hemocyanins (also spelled haemocyanins and abbreviated Hc) are proteins that transport oxygen throughout the bodies of some invertebrate animals. These metalloproteins contain two copper atoms that reversibly bind a single oxygen molecule (O2) ...
replaces hemoglobin as the oxygen carrier of choice in the blood of certain invertebrates, including horseshoe crabs
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to arac ...
, tarantulas
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although ...
, and octopuses
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, ...
. Vitamin B12 represents one of the few biochemical applications for cobalt.
References