Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an
Abrahamic,
monotheistic, and
ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the
Jewish people.
It has its roots as an organized religion in the
Middle East during the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. Modern Judaism evolved from
Yahwism
Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel. Yahwism was essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Is ...
, the religion of
ancient Israel and Judah
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscript ...
, by the late 6th century BCE,
and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.
Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of
the covenant that
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
established with the Israelites, their ancestors.
It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization.
The
Torah, as it is commonly understood by Jews, is part of the larger text known as the
''Tanakh''. The ''Tanakh'' is also known to secular scholars of religion as the
Hebrew Bible, and to Christians as the "
Old Testament". The Torah's
supplemental oral tradition is represented by later texts such as the
Midrash and the
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
. The Hebrew word ''torah'' can mean "teaching", "law", or "instruction",
although "Torah" can also be used as a general term that refers to any Jewish text that expands or elaborates on the original
Five Books of Moses. Representing the core of the Jewish spiritual and religious tradition, the Torah is a term and a set of teachings that are explicitly self-positioned as encompassing at least seventy, and potentially infinite, facets and interpretations.
Judaism's texts, traditions, and values strongly influenced later Abrahamic religions, including
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and
Islam.
Hebraism
Hebraism �hiːbreɪz(ə)mis a lexical item, usage or trait characteristic of the Hebrew language. By successive extension it is often applied to the Jewish people, their faith, national ideology or culture.
Idiomatic Hebrew
Hebrew has many idiom ...
, like
Hellenism, played a seminal role in the formation of Western civilization through its impact as a core background element of
Early Christianity.
[Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.]
Within Judaism, there are a variety of religious movements, most of which emerged from
Rabbinic Judaism,
which holds that God revealed his laws and commandments to
Moses on
Mount Sinai in the form of both the Written and Oral Torah.
Historically, all or part of this assertion was challenged by various groups such as the
Sadducees and
Hellenistic Judaism during the
Second Temple period;
the
Karaites during the early and later medieval period; and among segments of the modern non-Orthodox denominations.
Some modern branches of Judaism such as
Humanistic Judaism may be considered
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
or
nontheistic. Today, the largest
Jewish religious movements are
Orthodox Judaism (
Haredi Judaism and
Modern Orthodox Judaism),
Conservative Judaism, and
Reform Judaism. Major sources of difference between these groups are their approaches to ''
halakha'' (Jewish law), the authority of the
rabbinic tradition
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, is the entire spectrum of rabbinic writings throughout Jewish history. However, the term often refers specifically to literature from the Talmudic era, as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writ ...
, and the significance of the
State of Israel. Orthodox Judaism maintains that the Torah and ''halakha'' are divine in origin, eternal and unalterable, and that they should be strictly followed. Conservative and Reform Judaism are more
liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
, with Conservative Judaism generally promoting a more traditionalist interpretation of Judaism's requirements than Reform Judaism. A typical Reform position is that ''halakha'' should be viewed as a set of general guidelines rather than as a set of restrictions and obligations whose observance is required of all Jews. Historically,
special courts
An extraordinary court, or special court, is a type of court that is established outside of ordinary judiciary, composed of irregularly selected judges or applies irregular procedure for judgment. Since extraordinary court can be abused to infrin ...
enforced ''halakha''; today, these courts still exist but the practice of Judaism is mostly voluntary.
Authority on theological and legal matters is not vested in any one person or organization, but in the sacred texts and the
rabbis
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
and scholars who interpret them.
Jews are an
ethnoreligious group including those born Jewish (or "ethnic Jews"), in addition to converts to Judaism. In 2019, the world Jewish population was estimated at 14.7 million, or roughly 0.19% of the total world population. About 46.9% of all Jews reside in Israel and another 38.8% reside in the United States and Canada, with most of the remainder living in Europe, and other minority groups spread throughout Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Etymology

The term ''Judaism'' derives from ''Iudaismus'', a Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ''
Ioudaismos
''Ioudaios'' ( grc, Ἰουδαῖος; pl. ''Ioudaioi''). is an Ancient Greek ethnonym used in classical and biblical literature which commonly translates to "Jew" or "Judean".
The choice of translation is the subject of frequent scholarly deb ...
'' (Ἰουδαϊσμός) (from the verb , "to side with or imitate the
udeans).
Its ultimate source was the
Hebrew יהודה, ''Yehudah'', "
Judah",
which is also the source of the Hebrew term for Judaism: יַהֲדוּת, ''Yahadut''. The term ''Ἰουδαϊσμός'' first appears in the
Hellenistic Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
book of
2 Maccabees
2 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Β´, translit=Makkabaíōn 2 also known as the Second Book of Maccabees, Second Maccabees, and abbreviated as 2 Macc., is a deuterocanonical book which recounts the persecution of Jews under King Antiochus I ...
in the 2nd century BCE. In the context of the age and period it meant "seeking or forming part of a cultural entity"
and it resembled its antonym ''
hellenismos'', a word that signified a people's submission to
Hellenic (
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
) cultural norms. The conflict between ''iudaismos'' and ''hellenismos'' lay behind the
Maccabean revolt and hence the invention of the term ''iudaismos''.
writes in his book ''The Beginnings of Jewishness'':
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' the earliest citation in English where the term was used to mean "the profession or practice of the Jewish religion; the religious system or polity of the Jews" is Robert Fabyan's ''The newe cronycles of Englande and of Fraunce'' (1516). "Judaism" as a direct translation of the Latin ''Iudaismus'' first occurred in a 1611 English translation of the
apocrypha (
Deuterocanon
The deuterocanonical books (from the Greek meaning "belonging to the second canon") are books and passages considered by the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, and the Assyrian Church of the East to be ...
in
Catholic and
Eastern Orthodoxy), 2 Macc. ii. 21: "Those that behaved themselves manfully to their honour for Iudaisme."
History
Origins

At its core, the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) is an account of the
Israelites' relationship with
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
from their earliest history until the building of the
Second Temple (c. 535 BCE).
Abraham is hailed as the first
Hebrew and the father of the Jewish people. As a reward for his act of faith in one God, he was promised that
Isaac, his second son, would inherit the
Land of Israel (then called
Canaan). Later, the descendants of Isaac's son
Jacob were enslaved in
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, and God commanded
Moses to lead
the Exodus from Egypt. At
Mount Sinai, they received the
Torah—the five books of Moses. These books, together with
Nevi'im and
Ketuvim are known as ''Torah Shebikhtav'' as opposed to the Oral Torah, which refers to the Mishnah and the
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
. Eventually, God led them to the
land of Israel where the
tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
was planted in the city of
Shiloh for over 300 years to rally the nation against attacking enemies. As time went on, the spiritual level of the nation declined to the point that God allowed the
Philistines to capture the tabernacle. The people of Israel then told
Samuel the
prophet that they needed to be governed by a permanent king, and Samuel appointed
Saul to be their King. When the people pressured Saul into going against a command conveyed to him by Samuel, God told Samuel to appoint
David in his stead.

Once King David was established, he told the prophet
Nathan that he would like to build a permanent temple, and as a reward for his actions, God promised David that he would allow his son,
Solomon, to build the
First Temple and the throne would never depart from his children.
Rabbinic tradition holds that the details and interpretation of the law, which are called the ''Oral Torah'' or ''oral law'', were originally an unwritten tradition based upon what God told Moses on Mount Sinai. However, as the persecutions of the Jews increased and the details were in danger of being forgotten, these oral laws were recorded by
Rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
Judah HaNasi (Judah the Prince) in the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
, redacted ''circa'' 200 CE. The Talmud was a compilation of both the Mishnah and the
Gemara, rabbinic commentaries redacted over the next three centuries. The Gemara originated in two major centers of Jewish scholarship,
Palestine and
Babylonia.
Correspondingly, two bodies of analysis developed, and two works of Talmud were created. The older compilation is called the
Jerusalem Talmud. It was compiled sometime during the 4th century in Palestine.
The Babylonian Talmud was compiled from discussions in the houses of study by the scholars
Ravina I
Ravina I (; died c. AD 420) was a Babylonian Jewish Talmudist and rabbi, of the 5th and 6th generation of amoraim. Biography
His father seems to have died before he was born or at an early age, and it was necessary for his mother informed him o ...
,
Ravina II
Ravina II or Rabina II (Hebrew: רב אבינא בר רב הונא or רבינא האחרון; died 475 CE or 500 CE) was a Babylonian rabbi of the 5th century (seventh and eighth generations of amoraim).
He, along with his teacher Rav Ashi, wer ...
, and
Rav Ashi
Rav Ashi ( he, רב אשי) ("Rabbi Ashi") (352–427) was a Babylonian Jewish rabbi, of the sixth generation of amoraim. He reestablished the Academy at Sura and was the first editor of the Babylonian Talmud.
Biography
According to a trad ...
by 500 CE, although it continued to be edited later.
According to
critical scholars, the Torah consists of inconsistent texts edited together in a way that calls attention to divergent accounts.
Several of these scholars, such as Professor Martin Rose and
John Bright
John Bright (16 November 1811 – 27 March 1889) was a British Radical and Liberal statesman, one of the greatest orators of his generation and a promoter of free trade policies.
A Quaker, Bright is most famous for battling the Corn La ...
, suggest that during the First Temple period the people of Israel believed that each nation had its own god, but that their god was superior to other gods.
Some suggest that strict monotheism developed during the Babylonian Exile, perhaps in reaction to
Zoroastrian dualism.
In this view, it was only by the
Hellenic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
that most Jews came to believe that their god was the only god and that the notion of a clearly bounded Jewish nation identical with the Jewish religion formed.
argues that the origins of biblical
Yahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he poss ...
,
El,
Asherah
Asherah (; he, אֲשֵׁרָה, translit=Ăšērā; uga, 𐎀𐎘𐎗𐎚, translit=ʾAṯiratu; akk, 𒀀𒅆𒋥, translit=Aširat; Qatabanian: ') in ancient Semitic religion, is a fertility goddess who appears in a number of ancient ...
, and
Ba'al, may be rooted in earlier
Canaanite religion, which was centered on a pantheon of gods much like the
Greek pantheon
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of d ...
.
Antiquity
According to the
Hebrew Bible, the
United Monarchy
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
was established under
Saul and continued under
King David and
Solomon with its capital in
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. After Solomon's reign, the nation split into two kingdoms, the
Kingdom of Israel (in the north) and the
Kingdom of Judah (in the south). The Kingdom of Israel was destroyed around 720 BCE, when it was conquered by the
Neo-Assyrian Empire;
many people were taken captive from the capital
Samaria to
Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
and the
Khabur River valley. The
Kingdom of Judah continued as an independent state until it was conquered by
Nebuchadnezzar II of the
Neo-Babylonian Empire in 586 BCE. The Babylonians
destroyed Jerusalem and the
First Temple, which was at the center of ancient Jewish worship.
The Judeans were exiled to Babylon, in what is regarded as the first
Jewish diaspora. Later, many of them returned to their homeland after the subsequent
conquest of Babylon by the
Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was the largest empire the world had ...
seventy years later, an event known as the
Return to Zion. A
Second Temple was constructed and old religious practices were resumed.
During the early years of the Second Temple, the highest religious authority was a council known as the Great Assembly, led by
Ezra the Scribe. Among other accomplishments of the Great Assembly, the last books of the Bible were written at this time and
the canon sealed.
Hellenistic Judaism spread to
Ptolemaic Egypt from the 3rd century BCE.
During the
Great Jewish Revolt (66–73 CE), the
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
sacked Jerusalem and destroyed the Second Temple. Later, Roman emperor
Hadrian built a pagan idol on the Temple Mount and prohibited circumcision; these acts of ethnocide provoked the
Bar Kokhba Revolt (132–136 CE), after which the Romans banned the study of the
Torah and the celebration of Jewish holidays, and forcibly removed virtually all Jews from Judea. In 200 CE, however, Jews were granted Roman citizenship and Judaism was recognized as a ''
religio licita'' ("legitimate religion") until the rise of
Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
and
Early Christianity in the fourth century.
Following the destruction of Jerusalem and the expulsion of the Jews, Jewish worship stopped being centrally organized around the Temple, prayer took the place of sacrifice, and worship was rebuilt around the community (represented by a minimum of ten adult men) and the establishment of the authority of rabbis who acted as teachers and leaders of individual communities.
Defining characteristics and principles of faith

Unlike other ancient Near Eastern gods, the Hebrew God is portrayed as
unitary and solitary; consequently, the Hebrew God's principal relationships are not with other gods, but with the world, and more specifically, with the people he created. Judaism thus begins with
ethical monotheism
Ethical monotheism is a form of exclusive monotheism in which God is believed to be the only god as well as the source for one's standards of morality, guiding humanity through ethical principles.
Definition
Ethical monotheism originated within ...
: the belief that God is one and is concerned with the actions of mankind.
According to the Hebrew Bible, God promised
Abraham to make of his offspring a great nation.
Many generations later, he commanded the nation of
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
to love and worship only one God; that is, the Jewish nation is to reciprocate God's concern for the world.
He also commanded the Jewish people to love one another; that is, Jews are to imitate God's love for people.
These commandments are but two of a large corpus of
commandments and
laws that constitute this
covenant
Covenant may refer to:
Religion
* Covenant (religion), a formal alliance or agreement made by God with a religious community or with humanity in general
** Covenant (biblical), in the Hebrew Bible
** Covenant in Mormonism, a sacred agreement b ...
, which is the substance of Judaism.
Thus, although there is an esoteric tradition in Judaism (
Kabbalah), Rabbinic scholar
Max Kadushin
Max Kadushin ( be, Макс Кадушын; December 6, 1895 – July 23, 1980) was a Conservative rabbi best known for his organic philosophy of rabbinics.
Biography
Born in Minsk, Max Kadushin grew up in Seattle; his father operated a store for ...
has characterized normative Judaism as "normal mysticism", because it involves everyday personal experiences of God through ways or modes that are common to all Jews.
This is played out through the observance of the ''
halakha'' (Jewish law) and given verbal expression in the
Birkat Ha-Mizvot, the short blessings that are spoken every time a positive commandment is to be fulfilled.
Whereas
Jewish philosophers
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
often debate whether God is
immanent or
transcendent, and whether people have free will or their lives are determined, ''halakha'' is a system through which any Jew acts to bring God into the world.
Ethical monotheism is central in all sacred or normative texts of Judaism. However, monotheism has not always been followed in practice. The Jewish Bible records and repeatedly condemns the widespread worship of other gods in
ancient Israel
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscri ...
.
In the Greco-Roman era, many different interpretations of monotheism existed in Judaism, including the interpretations that gave rise to Christianity.
Moreover, some have argued that Judaism is a non-creedal religion that does not require one to believe in God. For some, observance of ''halakha'' is more important than belief in God ''per se''.
In modern times, some liberal Jewish movements do not accept the existence of a personified deity active in history. The debate about whether one can speak of authentic or normative Judaism is not only a debate among religious Jews but also among historians.
Core tenets
In the strict sense, in Judaism, unlike Christianity and Islam, there are no fixed universally binding articles of faith, due to their incorporation into the liturgy.
Scholars throughout
Jewish history
Jewish history is the history of the Jews, and their nation, religion, and culture, as it developed and interacted with other peoples, religions, and cultures. Although Judaism as a religion first appears in Greek records during the Hellenisti ...
have proposed numerous formulations of Judaism's core tenets, all of which have met with criticism.
The most popular formulation is
Maimonides'
thirteen principles of faith
There is no established formulation of principles of faith that are recognized by all branches of Judaism. Central authority in Judaism is not vested in any one person or group - although the Sanhedrin, the supreme Jewish religious court, would ...
, developed in the 12th century.
According to Maimonides, any Jew who rejects even one of these principles would be considered an apostate and a heretic.
Jewish scholars have held points of view diverging in various ways from Maimonides' principles.
Thus, within
Reform Judaism only the first five principles are endorsed.
In Maimonides' time, his list of tenets was criticized by
Hasdai Crescas
Hasdai ben Abraham Crescas (; he, חסדאי קרשקש; c. 1340 in Barcelona – 1410/11 in Zaragoza) was a Spanish-Jewish philosopher and a renowned halakhist (teacher of Jewish law). Along with Maimonides ("Rambam"), Gersonides ("Ralbag"), ...
and
Joseph Albo
Joseph Albo ( he, יוסף אלבו; c. 1380–1444) was a Jewish philosopher and rabbi who lived in Spain during the fifteenth century, known chiefly as the author of '' Sefer ha-Ikkarim'' ("Book of Principles"), the classic work on the fundament ...
. Albo and
the Raavad argued that Maimonides' principles contained too many items that, while true, were not fundamentals of the faith
Along these lines, the ancient historian
Josephus emphasized practices and observances rather than religious beliefs, associating
apostasy with a failure to observe ''halakha'' and maintaining that the requirements for conversion to Judaism included
circumcision and adherence to traditional customs. Maimonides' principles were largely ignored over the next few centuries.
Later, two poetic restatements of these principles ("''
Ani Ma'amin ''Ani Ma'amin'' (אני מאמין) "I believe" is a prosaic rendition of Maimonides' thirteen-point version of the Jewish principles of faith. It is based on his Mishnah commentary to tractate Sanhedrin. The popular version of ''Ani Ma'amin'' is of ...
''" and "''
Yigdal
Yigdal ( he, יִגְדָּל; ''yighdāl'', or ;''yighdal''; means "Magnify Living God) is a Jewish hymn which in various rituals shares with Adon 'Olam the place of honor at the opening of the morning and the close of the evening service. It i ...
''") became integrated into many Jewish liturgies,
leading to their eventual near-universal acceptance.
In modern times, Judaism lacks a centralized authority that would dictate an exact religious dogma. Because of this, many different variations on the basic beliefs are considered within the scope of Judaism.
Even so, all
Jewish religious movements are, to a greater or lesser extent, based on the principles of the
Hebrew Bible and various commentaries such as the Talmud and
Midrash. Judaism also universally recognizes the Biblical
Covenant
Covenant may refer to:
Religion
* Covenant (religion), a formal alliance or agreement made by God with a religious community or with humanity in general
** Covenant (biblical), in the Hebrew Bible
** Covenant in Mormonism, a sacred agreement b ...
between God and the
Patriarch Abraham as well as the additional aspects of the Covenant revealed to
Moses, who is considered Judaism's greatest
prophet.
In the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
, a core text of
Rabbinic Judaism, acceptance of the Divine origins of this covenant is considered an essential aspect of Judaism and those who reject the Covenant forfeit their share in the
World to Come.
Establishing the core tenets of Judaism in the modern era is even more difficult, given the number and diversity of the contemporary
Jewish denominations. Even if to restrict the problem to the most influential intellectual trends of the nineteenth and twentieth century, the matter remains complicated. Thus for instance,
Joseph Soloveitchik's (associated with the
Modern Orthodox movement) answer to modernity is constituted upon the identification of Judaism with following the ''halakha'' whereas its ultimate goal is to bring the holiness down to the world.
Mordecai Kaplan
Mordecai Menahem Kaplan (born Mottel Kaplan; June 11, 1881 – November 8, 1983), was a Lithuanian-born American rabbi, writer, Jewish educator, professor, theologian, philosopher, activist, and religious leader who founded the Reconstructionist ...
, the founder of the
Reconstructionist Judaism, abandons the idea of religion for the sake of identifying Judaism with
civilization and by means of the latter term and secular translation of the core ideas, he tries to embrace as many Jewish denominations as possible. In turn,
Solomon Schechter
Solomon Schechter ( he, שניאור זלמן הכהן שכטר; 7 December 1847 – 19 November 1915) was a Moldavian-born British-American rabbi, academic scholar and educator, most famous for his roles as founder and President of the ...
's
Conservative Judaism was identical with the tradition understood as the interpretation of Torah, in itself being the history of the constant updates and adjustment of the Law performed by means of the creative interpretation. Finally,
David Philipson draws the outlines of the Reform movement in Judaism by opposing it to the strict and traditional rabbinical approach and thus comes to the conclusions similar to that of the Conservative movement.
Religious texts

The following is a basic, structured list of the central works of Jewish practice and thought.
* Tanakh
(
Hebrew Bible) and
Rabbinic literature
**
Mesorah
**
Targum
** Jewish Biblical
exegesis (also see Midrash below)
* Works of the Talmudic Era (classic rabbinic literature)
**
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
and commentaries
**
Tosefta and the
minor tractates
**
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
:
*** The
Babylonian Talmud and commentaries
***
Jerusalem Talmud and commentaries
*
Midrashic literature:
**
Halakhic Midrash
''Midrash halakha'' ( he, הֲלָכָה) was the ancient Judaic rabbinic method of Torah study that expounded upon the traditionally received 613 Mitzvot (commandments) by identifying their sources in the Hebrew Bible, and by interpreting thes ...
**
Aggadic Midrash
*
Halakhic literature
** Major codes of Jewish law and custom
***
Mishneh Torah and commentaries
***
Tur and commentaries
***
Shulchan Aruch and commentaries
**
Responsa literature
* Thought and ethics
**
Jewish philosophy
**
Musar literature and other works of
Jewish ethics
**
Kabbalah
**
Hasidic works
*
Siddur
A siddur ( he, סִדּוּר ; plural siddurim ) is a Jewish prayer book containing a set order of daily prayers. The word comes from the Hebrew root , meaning 'order.'
Other terms for prayer books are ''tefillot'' () among Sephardi Jews, '' ...
and
Jewish liturgy
Jewish liturgy is the customary public worship of Judaism. The liturgy may include responsive reading, songs, or music, as found in the Torah and Haftorah, the Amidah, piyyutim, and Psalms. Singing or reading the Psalms has a special role in th ...
* ''
Piyyut'' (Classical Jewish poetry)

Legal literature
The basis of ''halakha'' and tradition is the
Torah (also known as the
Pentateuch or the Five Books of Moses). According to rabbinic tradition, there are
613 commandments in the Torah. Some of these laws are directed only to men or to women, some only to the ancient priestly groups, the
Kohanim
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally be ...
and
Leviyim (members of the tribe of
Levi
Levi (; ) was, according to the Book of Genesis, the third of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's third son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Levi (the Levites, including the Kohanim) and the great-grandfather of Aaron, Moses and ...
), some only to farmers within the
Land of Israel. Many laws were only applicable when the
Temple in Jerusalem existed, and only 369 of these commandments are still applicable today.
While there have been Jewish groups whose beliefs were based on the written text of the Torah alone (e.g., the
Sadducees, and the
Karaites), most Jews believe in the
oral law
An oral law is a code of conduct in use in a given culture, religion or community application, by which a body of rules of human behaviour is transmitted by oral tradition and effectively respected, or the single rule that is orally transmitted.
M ...
. These oral traditions were transmitted by the
Pharisee school of thought of ancient Judaism and were later recorded in written form and expanded upon by the rabbis.
According to Rabbinical Jewish tradition, God gave both the Written Law (the
Torah) and the
Oral Torah to Moses on
Mount Sinai. The Oral law is the oral tradition as relayed by God to Moses and from him, transmitted and taught to the sages (
rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
nic leaders) of each subsequent generation.
For centuries, the Torah appeared only as a written text transmitted in parallel with the oral tradition. Fearing that the oral teachings might be forgotten, Rabbi
Judah haNasi undertook the mission of consolidating the various opinions into one body of law which became known as the ''Mishnah''.
The Mishnah consists of 63 tractates codifying ''halakha'', which are the basis of the Talmud. According to
Abraham ben David
Abraham ben David ( – 27 November 1198), also known by the abbreviation RABaD (for ''Rabbeinu'' Abraham ben David) Ravad or RABaD III, was a Provençal rabbi, a great commentator on the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central ...
, the ''
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
'' was compiled by Rabbi
Judah haNasi after the destruction of Jerusalem, in
anno mundi 3949, which corresponds to 189 CE.
Over the next four centuries, the Mishnah underwent discussion and debate in both of the world's major Jewish communities (in Israel and
Babylonia). The commentaries from each of these communities were eventually compiled into the two Talmuds, the Jerusalem Talmud (''Talmud Yerushalmi'') and the Babylonian Talmud (''Talmud Bavli''). These have been further expounded by commentaries of various Torah scholars during the ages.
In the text of the Torah, many words are left undefined and many procedures are mentioned without explanation or instructions. Such phenomena are sometimes offered to validate the viewpoint that the Written Law has always been transmitted with a parallel oral tradition, illustrating the assumption that the reader is already familiar with the details from other, i.e., oral, sources.
''Halakha'', the rabbinic Jewish way of life, then, is based on a combined reading of the Torah, and the oral tradition—the Mishnah, the halakhic Midrash, the Talmud and its commentaries. The ''halakha'' has developed slowly, through a precedent-based system. The literature of questions to rabbis, and their considered answers, is referred to as
responsa (in
Hebrew, ''Sheelot U-Teshuvot''.) Over time, as practices develop, codes of ''halakha'' are written that are based on the responsa; the most important code, the
Shulchan Aruch, largely determines Orthodox religious practice today.
Jewish philosophy

Jewish philosophy refers to the conjunction between serious study of philosophy and Jewish theology. Major Jewish philosophers include
Philo of Alexandria
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's de ...
,
Solomon ibn Gabirol,
Saadia Gaon,
Judah Halevi,
Maimonides, and
Gersonides
Levi ben Gershon (1288 – 20 April 1344), better known by his Graecized name as Gersonides, or by his Latinized name Magister Leo Hebraeus, or in Hebrew by the abbreviation of first letters as ''RaLBaG'', was a medieval French Jewish philosoph ...
. Major changes occurred in response to the
Enlightenment (late 18th to early 19th century) leading to the post-Enlightenment Jewish philosophers. Modern Jewish philosophy consists of both Orthodox and non-Orthodox oriented philosophy. Notable among Orthodox Jewish philosophers are
Eliyahu Eliezer Dessler,
Joseph B. Soloveitchik
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion ...
, and
Yitzchok Hutner
Yitzchak (Isaac) Hutner ( he, יצחק הוטנר; 1906–1980) was an American Orthodox rabbi and rosh yeshiva (dean).
Originally from Warsaw, Hutner first studied the Torah in Slabodka. He then traveled to Mandatory Palestine where he became ...
. Well-known non-Orthodox Jewish philosophers include
Martin Buber
Martin Buber ( he, מרטין בובר; german: Martin Buber; yi, מארטין בובער; February 8, 1878 –
June 13, 1965) was an Austrian Jewish and Israeli philosopher best known for his philosophy of dialogue, a form of existentialism ...
,
Franz Rosenzweig,
Mordecai Kaplan
Mordecai Menahem Kaplan (born Mottel Kaplan; June 11, 1881 – November 8, 1983), was a Lithuanian-born American rabbi, writer, Jewish educator, professor, theologian, philosopher, activist, and religious leader who founded the Reconstructionist ...
,
Abraham Joshua Heschel
Abraham Joshua Heschel (January 11, 1907 – December 23, 1972) was a Polish-born American rabbi and one of the leading Jewish theologians and Jewish philosophers of the 20th century. Heschel, a professor of Jewish mysticism at the Jewish T ...
,
Will Herberg
William Herberg (June 30, 1901 – March 26, 1977) was an American writer, intellectual and scholar. A communist political activist during his early years, Herberg gained wider public recognition as a social philosopher and sociologist of relig ...
, and
Emmanuel Lévinas.
Rabbinic hermeneutics
Orthodox and many other
Jews do not believe that the revealed
Torah consists solely of its written contents, but of its interpretations as well. The study of
Torah (in its widest sense, to include both poetry, narrative, and law, and both the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud) is in Judaism itself a sacred act of central importance. For the sages of the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
and Talmud, and for their successors today, the study of Torah was therefore not merely a means to learn the contents of God's revelation, but an end in itself. According to the Talmud,
In Judaism, "the study of
Torah can be a means of experiencing God".
Reflecting on the contribution of the
Amoraim and
Tanaim to contemporary Judaism, Professor Jacob Neusner observed:
To study the Written Torah and the Oral Torah in light of each other is thus also to study ''how'' to study the word of God.
In the study of Torah, the sages formulated and followed various
logical and
hermeneutical principles. According to David Stern, all Rabbinic hermeneutics rest on two basic axioms:
These two principles make possible a great variety of interpretations. According to the Talmud,
Observant Jews thus view the Torah as dynamic, because it contains within it a host of interpretations.
According to Rabbinic tradition, all valid interpretations of the
written Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
were revealed to Moses at Sinai in oral form, and handed down from teacher to pupil (The oral revelation is in effect coextensive with the Talmud itself). When different rabbis forwarded conflicting interpretations, they sometimes appealed to hermeneutic principles to legitimize their arguments; some rabbis claim that these principles were themselves revealed by God to Moses at Sinai.
Thus,
Hillel called attention to seven commonly used hermeneutical principles in the interpretation of laws (
baraita
''Baraita'' ( Aramaic: "external" or "outside"; pl. ''Barayata'' or ''Baraitot''; also Baraitha, Beraita; Ashkenazi: Beraisa) designates a tradition in the Jewish oral law not incorporated in the Mishnah. ''Baraita'' thus refers to teachings ...
at the beginning of
Sifra
Sifra ( Aramaic: סִפְרָא) is the Halakhic midrash to the Book of Leviticus. It is frequently quoted in the Talmud, and the study of it followed that of the Mishnah. Like Leviticus itself, the midrash is occasionally called "Torat Kohanim ...
);
R. Ishmael, thirteen (baraita at the beginning of Sifra; this collection is largely an amplification of that of Hillel).
listed 32, largely used for the exegesis of narrative elements of Torah. All the hermeneutic rules scattered through the
Talmudim
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the center ...
and
Midrashim have been collected by
Malbim
Meir Leibush ben Yehiel Michel Wisser (March 7, 1809 – September 18, 1879), better known as the Malbim ( he, מלבי"ם), was a rabbi, master of Hebrew grammar, and Bible commentator. The name ''Malbim'' was derived from the Hebrew initials ...
in ''Ayyelet ha-Shachar'', the introduction to his commentary on the
Sifra
Sifra ( Aramaic: סִפְרָא) is the Halakhic midrash to the Book of Leviticus. It is frequently quoted in the Talmud, and the study of it followed that of the Mishnah. Like Leviticus itself, the midrash is occasionally called "Torat Kohanim ...
. Nevertheless, R. Ishmael's 13 principles are perhaps the ones most widely known; they constitute an important, and one of Judaism's earliest, contributions to
logic,
hermeneutics, and
jurisprudence.
Judah Hadassi
Judah ben Elijah Hadassi (in Hebrew, ''Yehuda ben Eliyahu'') was a Karaite Jewish scholar, controversialist, and liturgist who flourished at Constantinople in the middle of the twelfth century. He was known by the nickname "ha-Abel," which signifi ...
incorporated Ishmael's principles into
Karaite Judaism in the 12th century.
Today R. Ishmael's 13 principles are incorporated into the Jewish prayer book to be read by observant Jews on a daily basis.
Jewish identity
Distinction between Jews as a people and Judaism
According to
Daniel Boyarin
Daniel Boyarin ( he, דניאל בויארין; born 1946) is a Religion historian, Born in New Jersey, he holds dual United States and Israeli citizenship. He is the Hermann P. and Sophia Taubman Professor of Talmudic Culture in the Departments ...
, the underlying distinction between religion and ethnicity is foreign to Judaism itself, and is one form of the dualism between spirit and flesh that has its origin in
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
nic philosophy and that permeated
Hellenistic Judaism.
Consequently, in his view, Judaism does not fit easily into conventional Western categories, such as religion, ethnicity, or culture. Boyarin suggests that this in part reflects the fact that much of Judaism's more than 3,000-year history predates the rise of Western culture and occurred outside the West (that is, Europe, particularly medieval and modern Europe). During this time, Jews experienced slavery, anarchic and theocratic self-government, conquest, occupation, and exile. In the Jewish diaspora, they were in contact with, and influenced by, ancient Egyptian, Babylonian, Persian, and Hellenic cultures, as well as modern movements such as the Enlightenment (see
Haskalah
The ''Haskalah'', often termed Jewish Enlightenment ( he, השכלה; literally, "wisdom", "erudition" or "education"), was an intellectual movement among the Jews of Central and Eastern Europe, with a certain influence on those in Western Euro ...
) and the rise of nationalism, which would bear fruit in the form of a Jewish state in their ancient homeland, the
Land of Israel. They also saw an elite population convert to Judaism (the
Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
s), only to disappear as the centers of power in the lands once occupied by that elite fell to the people of Rus and then the Mongols. Thus, Boyarin has argued that "Jewishness disrupts the very categories of identity, because it is not national, not genealogical, not religious, but all of these, in dialectical tension."
In contrast to this point of view, practices such as
Humanistic Judaism reject the religious aspects of Judaism, while retaining certain cultural traditions.
Who is a Jew?
According to
Rabbinic Judaism, a Jew is anyone who was either born of a Jewish mother or who
converted to Judaism in accordance with ''halakha''.
Reconstructionist Judaism and the larger denominations of worldwide
Progressive Judaism (also known as Liberal or Reform Judaism) accept the child as Jewish if one of the parents is Jewish, if the parents raise the child with a Jewish identity, but not the smaller regional branches. All mainstream forms of Judaism today are open to sincere converts, although conversion has traditionally been discouraged since the time of the Talmud. The conversion process is evaluated by an authority, and the convert is examined on his or her sincerity and knowledge.
Converts are called "ben Abraham" or "bat Abraham", (son or daughter of Abraham). Conversions have on occasion been overturned. In 2008, Israel's highest religious court invalidated the conversion of 40,000 Jews, mostly from Russian immigrant families, even though they had been approved by an Orthodox rabbi.
Rabbinical Judaism maintains that a Jew, whether by birth or conversion, is a Jew forever. Thus a Jew who claims to be an atheist or converts to another religion is still considered by traditional Judaism to be Jewish. According to some sources, the Reform movement has maintained that a Jew who has converted to another religion is no longer a Jew,
and the Israeli Government has also taken that stance after Supreme Court cases and statutes.
However, the Reform movement has indicated that this is not so cut and dried, and different situations call for consideration and differing actions. For example, Jews who have converted under duress may be permitted to return to Judaism "without any action on their part but their desire to rejoin the Jewish community" and "A proselyte who has become an apostate remains, nevertheless, a Jew".
believes that Jewish identity can only be transmitted by patrilineal descent. Although a minority of modern Karaites believe that Jewish identity requires that both parents be Jewish, and not only the father. They argue that only patrilineal descent can transmit Jewish identity on the grounds that all descent in the Torah went according to the male line.
The question of what determines Jewish identity in the State of Israel was given new impetus when, in the 1950s,
David Ben-Gurion requested opinions on ''mihu Yehudi'' ("Who is a Jew") from Jewish religious authorities and intellectuals worldwide in order to settle citizenship questions. This is still not settled, and occasionally resurfaces in
Israeli politics.
Historical definitions of
Jewish identity have traditionally been based on ''halakhic'' definitions of matrilineal descent, and ''halakhic'' conversions. Historical definitions of who is a Jew date back to the codification of the Oral Torah into the Babylonian Talmud, around 200
CE. Interpretations of sections of the Tanakh, such as
Deuteronomy 7:1–5, by Jewish sages, are used as a warning against
intermarriage between Jews and
Canaanites because "
he non-Jewish husbandwill cause your child to turn away from Me and they will worship the gods (i.e., idols) of others." Leviticus 24 says that the son in a marriage between a Hebrew woman and an
Egyptian man is "of the community of Israel." This is complemented by Ezra 10, where Israelites returning from Babylon vow to put aside their
gentile wives and their children. A popular theory is that the rape of Jewish women in captivity brought about the law of Jewish identity being inherited through the maternal line, although scholars challenge this theory citing the Talmudic establishment of the law from the pre-exile period.
Since the anti-religious ''
Haskalah
The ''Haskalah'', often termed Jewish Enlightenment ( he, השכלה; literally, "wisdom", "erudition" or "education"), was an intellectual movement among the Jews of Central and Eastern Europe, with a certain influence on those in Western Euro ...
'' movement of the late 18th and 19th centuries, ''halakhic'' interpretations of Jewish identity have been challenged.
Jewish demographics
The total number of Jews worldwide is difficult to assess because the definition of "who is a Jew" is problematic; not all Jews identify themselves as Jewish, and some who identify as Jewish are not considered so by other Jews. According to the ''Jewish Year Book'' (1901), the global Jewish population in 1900 was around 11 million. The latest available data is from the World Jewish Population Survey of 2002 and the Jewish Year Calendar (2005). In 2002, according to the Jewish Population Survey, there were 13.3 million Jews around the world. The Jewish Year Calendar cites 14.6 million. It is 0.25% of world population. Jewish population growth is currently near zero percent, with 0.3% growth from 2000 to 2001.
Jewish religious movements
Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism (or in some Christian traditions, Rabbinism) (Hebrew: "Yahadut Rabanit" – יהדות רבנית) has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Talmud. It is characterised by the belief that the
Written Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
(Written Law) cannot be correctly interpreted without reference to the Oral Torah and the voluminous literature specifying what behavior is sanctioned by the
Law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
.
The
Jewish Enlightenment of the late 18th century resulted in the division of
Ashkenazi (Western) Jewry into religious movements or denominations, especially in North America and Anglophone countries. The main denominations today outside Israel (where the situation is rather different) are Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform. The notion "traditional Judaism" includes the Orthodox with Conservative or solely the Orthodox Jews.
*
Orthodox Judaism holds that both the Written and Oral Torah were divinely revealed to
Moses and that the laws within it are binding and unchanging. Orthodox Jews generally consider commentaries on the ''
Shulchan Aruch'' (a condensed codification of ''halakha'' that largely favored Sephardic traditions) to be the definitive codification of ''halakha''. Orthodoxy places a high importance on
Maimonides' 13 principles as a definition of Jewish faith.
Orthodoxy is often divided into
Haredi Judaism and
Modern Orthodox Judaism.
Haredi
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in oppos ...
is less accommodating to modernity and has less interest in non-Jewish disciplines, and it may be distinguished from
Modern Orthodox Judaism in practice by its styles of dress and more stringent practices. Subsets of Haredi Judaism include
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Judaism, Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory ...
, which is rooted in the
Kabbalah and distinguished by reliance on a
Rebbe or religious teacher; their opponents
Misnagdim (Lithuanian); and
Sephardic Haredi Judaism, which emerged among
Sephardic and
Mizrahi (Asian and North African) Jews in Israel. "Centrist" Orthodoxy (
Joseph B. Soloveitchik
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion ...
) is sometimes also distinguished.
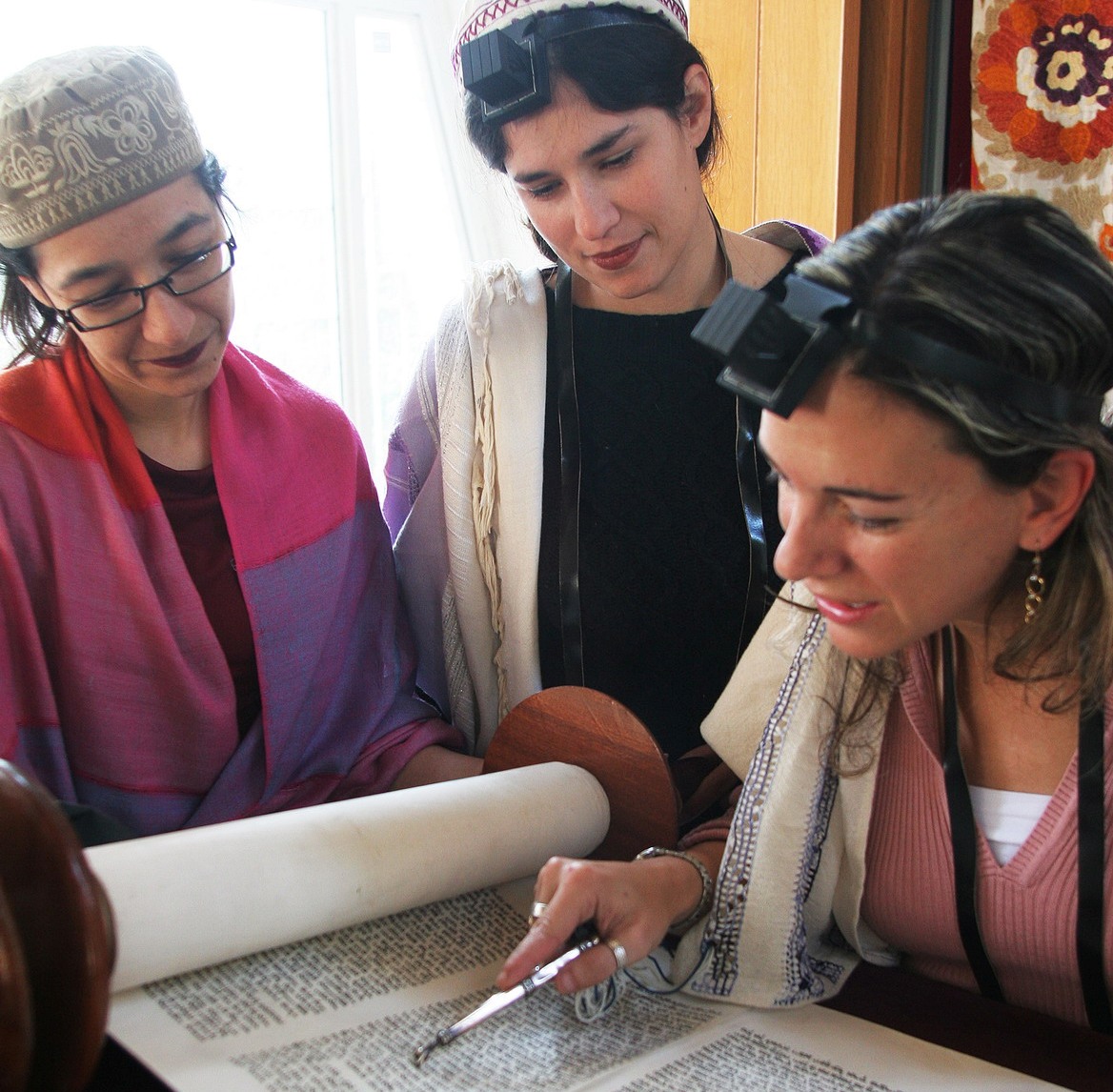

*
Conservative Judaism is characterized by a commitment to traditional ''halakha'' and customs, including observance of
Shabbat and
kashrut, a deliberately non-fundamentalist teaching of Jewish principles of faith, a positive attitude toward modern culture, and an acceptance of both traditional rabbinic and modern scholarship when considering Jewish religious texts. Conservative Judaism teaches that ''halakha'' is not static, but has always developed in response to changing conditions. It holds that the Torah is a divine document written by prophets inspired by God and reflecting his will, but rejects the Orthodox position that it was dictated by God to Moses.
Conservative Judaism holds that the Oral Law is divine and normative, but holds that both the Written and Oral Law may be interpreted by the rabbis to reflect modern sensibilities and suit modern conditions.
*
Reform Judaism, called Liberal or Progressive Judaism in many countries, defines Judaism in relatively universalist terms, rejects most of the ritual and ceremonial laws of the
Torah while observing moral laws, and emphasizes the ethical call of the
Prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
. Reform Judaism has developed an egalitarian prayer service in the vernacular (along with
Hebrew in many cases) and emphasizes personal connection to Jewish tradition.
*
Reconstructionist Judaism, like Reform Judaism, does not hold that ''halakha'', as such, requires observance, but unlike Reform, Reconstructionist thought emphasizes the role of the community in deciding what observances to follow.
*
Jewish Renewal is a recent North American movement which focuses on spirituality and social justice but does not address issues of ''halakha''. Men and women participate equally in prayer.
*
Humanistic Judaism is a small non-theistic movement centered in North America and Israel that emphasizes
Jewish culture and history as the sources of Jewish identity.
*
Subbotniks
Subbotniks ( rus, Субботники, p=sʊˈbotnʲɪkʲɪ, "Sabbatarians") is a common name for adherents of Russian religious movements that split from Sabbatarian sects in the late 18th century.
The majority of Subbotniks were converts ...
(Sabbatarians) are a movement of Jews of
Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
ethnic origin in the 18th–20th centuries, the majority of whom belonged to Rabbinic and Karaite Judaism. Many settled in the
Holy Land as part of the Zionist
First Aliyah
The First Aliyah (Hebrew: העלייה הראשונה, ''HaAliyah HaRishona''), also known as the agriculture Aliyah, was a major wave of Jewish immigration (''aliyah'') to Ottoman Syria between 1881 and 1903. Jews who migrated in this wave came ...
in order to escape oppression in the Russian Empire and later mostly intermarried with other Jews, their descendants included
Alexander Zaïd, Major-General Alik Ron, and the mother of
Ariel Sharon.
Sephardi and Mizrahi Judaism

While
traditions and customs vary between discrete communities, it can be said that
Sephardi and
Mizrahi Jewish communities do not generally adhere to the "movement" framework popular in and among
Ashkenazi Jewry. Historically, Sephardi and Mizrahi communities have eschewed denominations in favour of a "big tent" approach. This is particularly the case in contemporary
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, which is home to the largest communities of Sephardi and Mizrahi Jews in the world. (However, individual Sephardi and Mizrahi Jews may be members of or attend synagogues that do adhere to one Ashkenazi-inflected movement or another.)
Sephardi and Mizrahi observance of Judaism tends toward the conservative, and
prayer rites are reflective of this, with the text of each rite being largely unchanged since their respective inception. Observant Sephardim may follow the teachings of a particular rabbi or school of thought; for example, the Sephardic
Chief Rabbi of Israel
The Chief Rabbinate of Israel ( he, הָרַבָּנוּת הָרָאשִׁית לְיִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Ha-Rabbanut Ha-Rashit Li-Yisra'el'') is recognized by law as the supreme rabbinic authority for Judaism in Israel. The Chief Rabbinate Co ...
.
Jewish movements in Israel
Most Jewish Israelis classify themselves as "secular" (''hiloni''),
"traditional" (''masorti''), "religious" (''dati'') or ''
Haredi
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in oppos ...
''. The term "secular" is more popular as a self-description among Israeli families of western (European) origin, whose Jewish identity may be a very powerful force in their lives, but who see it as largely independent of traditional religious belief and practice. This portion of the population largely ignores organized religious life, be it of the official Israeli rabbinate (Orthodox) or of the liberal movements common to diaspora Judaism (Reform, Conservative).
The term "traditional" (''masorti'') is most common as a self-description among Israeli families of "eastern" origin (i.e., the Middle East, Central Asia, and North Africa). This term, as commonly used, has nothing to do with the
Conservative Judaism, which also names itself "Masorti" outside North America. There is a great deal of ambiguity in the ways "secular" and "traditional" are used in Israel: they often overlap, and they cover an extremely wide range in terms of worldview and practical religious observance. The term "Orthodox" is not popular in Israeli discourse, although the percentage of Jews who come under that category is far greater than in the Jewish diaspora. What would be called "Orthodox" in the diaspora includes what is commonly called ''
dati'' (religious) or ''haredi'' (ultra-Orthodox) in Israel. The former term includes what is called "
Religious Zionism" or the "National Religious" community, as well as what has become known over the past decade or so as ''haredi-leumi'' (
nationalist ''haredi''), or "Hardal", which combines a largely ''haredi'' lifestyle with nationalist ideology. (Some people, in
Yiddish, also refer to observant Orthodox Jews as ''
frum
Frum ( yi, פֿרום, , religious', 'pious) is a word that describes Jewish religious devotion.
The term connotes the observance of Jewish religious law in a way that often exceeds its bare requirements. This not only includes the careful stud ...
'', as opposed to ''frei'' (more liberal Jews)).
''Haredi'' applies to a populace that can be roughly divided into three separate groups along both ethnic and ideological lines: (1) "Lithuanian" (non-hasidic) ''haredim'' of
Ashkenazic
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
origin; (2) Hasidic ''haredim'' of Ashkenazic origin; and (3)
Sephardic ''haredim''.
Karaites and Samaritans
Karaite Judaism defines itself as the remnants of the non-Rabbinic Jewish sects of the
Second Temple period, such as the
Sadducees. The Karaites ("Scripturalists") accept only the Hebrew Bible and what they view as the
Peshat
''Peshat'' (also ''P'shat'', ) is one of the two classic methods of Jewish biblical exegesis, the other being Derash. While ''Peshat'' is commonly defined as referring to the surface or literal (direct) meaning of a text,Goldin, S. (2007). Unloc ...
("simple" meaning); they do not accept non-biblical writings as authoritative. Some European Karaites do not see themselves as part of the Jewish community at all, although most do.
The
Samaritans, a very small community located entirely around
Mount Gerizim in the
Nablus/
Shechem region of the
West Bank and in
Holon, near
Tel Aviv in Israel, regard themselves as the descendants of the Israelites of the Iron Age
kingdom of Israel. Their religious practices are based on the literal text of the written
Torah (Five Books of Moses), which they view as the only authoritative scripture (with a special regard also for the
Samaritan Book of Joshua).

Haymanot (Ethiopian Judaism)
Haymanot (meaning "religion" in Ge'ez and Amharic) refers the Judaism practiced by Ethiopian Jews. This version of Judaism differs substantially from Rabbinic, Karaite, and Samaritan Judaisms, Ethiopian Jews having diverged from their coreligionists earlier. Sacred scriptures (the Orit) are written in Ge'ez, not Hebrew, and dietary laws are based strictly on the text of the Orit, without explication from ancillary commentaries. Holidays also differ, with some Rabbinic holidays not observed in Ethiopian Jewish communities, and some additional holidays, like
Sigd.
Noahide (''B'nei Noah'' movement)
Noahidism
Noahidism () or Noachidism () is a monotheistic Jewish religious movement based upon the Seven Laws of Noah and their traditional interpretations within Orthodox Judaism. According to the Jewish law, non-Jews (Goyim) are not obligated to conve ...
is a
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
religious movement based on the
Seven Laws of Noah and their traditional interpretations within
Rabbinic Judaism. According to the ''halakha'', non-Jews (
gentiles) are not obligated to
convert to Judaism
Conversion to Judaism ( he, גיור, ''giyur'') is the process by which non-Jews adopt the Jewish religion and become members of the Jewish ethnoreligious community. It thus resembles both conversion to other religions and naturalization. " ...
, but they are required to observe the Seven Laws of Noah to be assured of a place in the
World to Come (Olam Ha-Ba), the final reward of the righteous. The divinely ordained penalty for violating any of the Laws of Noah is discussed in the Talmud, but in practical terms it is subject to the working legal system which is established by the society at large. Those who subscribe to the observance of the Noahic Covenant are referred to as ''B'nei Noach'' (
Hebrew: בני נח, "Children of Noah") or ''Noahides'' (
/ˈnoʊ.ə.haɪdɪs/). Supporting organizations have been established around the world over the past decades by both Noahides and Orthodox Jews.
Historically, the Hebrew term ''B'nei Noach'' has applied to all non-Jews as descendants of Noah. However, nowadays it's primarily used to refer specifically to those non-Jews who observe the Seven Laws of Noah.
Jewish observances
Jewish ethics
Jewish ethics may be guided by ''halakhic'' traditions, by other moral principles, or by central Jewish virtues. Jewish ethical practice is typically understood to be marked by values such as justice, truth, peace, loving-kindness (
chesed), compassion, humility, and self-respect. Specific Jewish ethical practices include practices of charity (
tzedakah) and refraining from negative speech (
lashon hara
''Lashon hara'' (or ''loshon horo'', or ''loshon hora'') ( he, לשון הרע; "evil tongue") is the halakhic term for speech about a person or persons that is negative or harmful to them, even though it is true. It is speech that damages the p ...
). Proper ethical practices regarding sexuality and many other issues are subjects of dispute among Jews.
Prayers

Traditionally, Jews recite prayers three times daily,
Shacharit,
Mincha
Mincha ( he, מִנחַה, pronounced as ; sometimes spelled ''Minchah'' or ''Minḥa'') is the afternoon prayer service in Judaism.
Etymology
The name ''Mincha'', meaning "present", is derived from the meal offering that accompanied each sacri ...
, and
Ma'ariv
''Maariv'' or ''Maʿariv'' (, ), also known as ''Arvit'' (, ), is a Jewish prayer service held in the evening or night. It consists primarily of the evening ''Shema'' and ''Amidah''.
The service will often begin with two verses from Psalms ...
with a fourth prayer,
Mussaf
Mussaf (also spelled Musaf or Musof) is an additional service that is recited on Shabbat, Yom Tov, Chol Hamoed, and Rosh Chodesh. The service, which is traditionally combined with the Shacharit in synagogues, is considered to be additional to th ...
added on
Shabbat and
holidays. At the heart of each service is the ''
Amidah'' or ''Shemoneh Esrei''. Another key prayer in many services is the declaration of faith, the ''
Shema Yisrael
''Shema Yisrael'' (''Shema Israel'' or ''Sh'ma Yisrael''; he , שְׁמַע יִשְׂרָאֵל ''Šəmaʿ Yīsrāʾēl'', "Hear, O Israel") is a Jewish prayer (known as the Shema) that serves as a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewi ...
'' (or ''Shema''). The ''Shema'' is the recitation of a verse from the Torah (
Deuteronomy 6:4): ''Shema Yisrael Adonai Eloheinu Adonai Echad''—"Hear, O Israel! The Lord is our God! The Lord is One!"
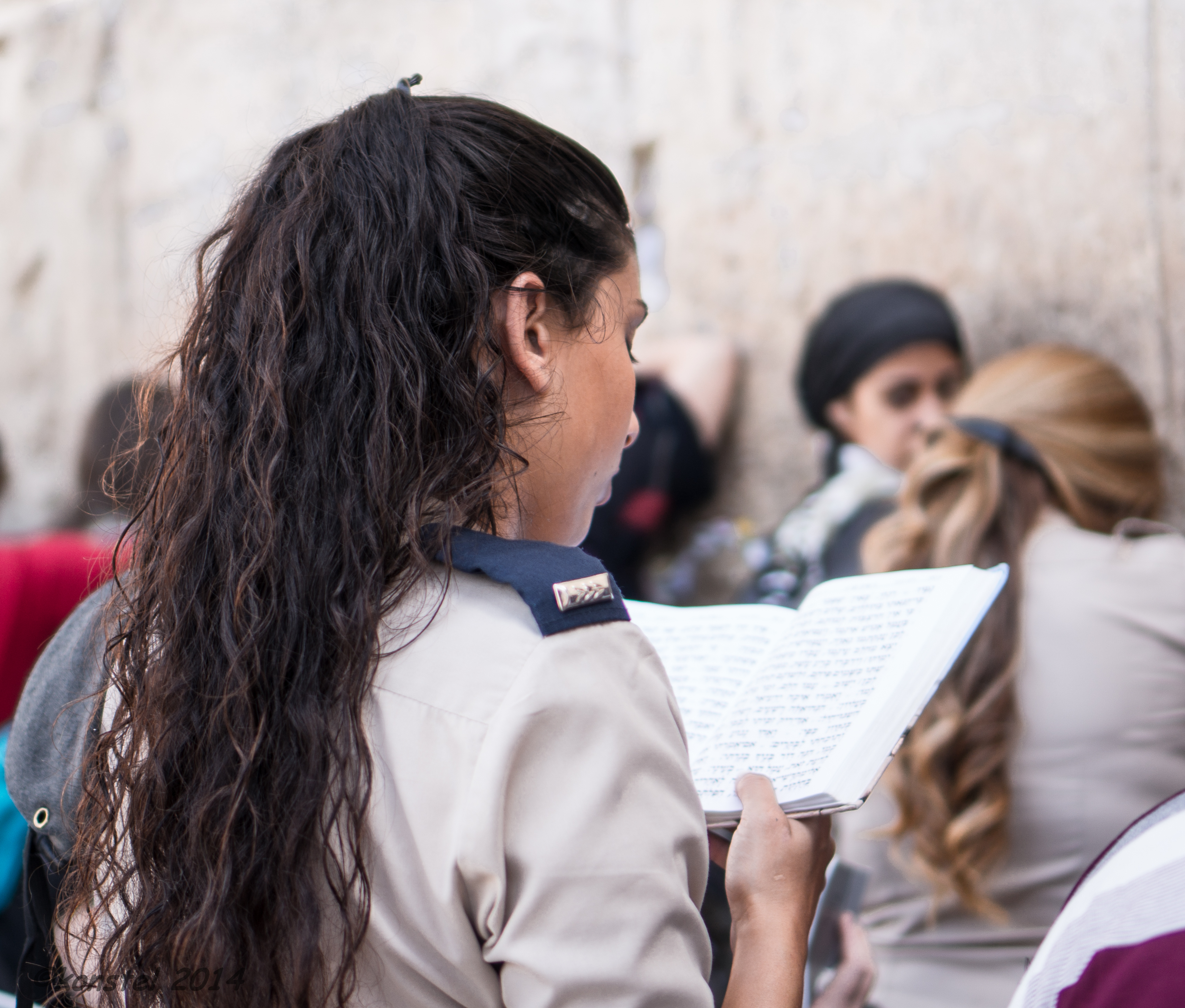

Most of the prayers in a traditional Jewish service can be recited in solitary prayer, although communal prayer is preferred. Communal prayer requires a
quorum of ten adult Jews, called a ''
minyan''. In nearly all Orthodox and a few Conservative circles, only male Jews are counted toward a ''minyan''; most Conservative Jews and members of other Jewish denominations count female Jews as well.
In addition to prayer services, observant traditional Jews recite
prayers and benedictions throughout the day when
performing various acts. Prayers are recited upon
waking up in the morning, before eating or drinking different foods,
after eating a meal, and so on.
The approach to prayer varies among the Jewish denominations. Differences can include the texts of prayers, the frequency of prayer, the number of prayers recited at various religious events, the use of musical instruments and choral music, and whether prayers are recited in the traditional liturgical languages or the vernacular. In general, Orthodox and Conservative congregations adhere most closely to tradition, and Reform and Reconstructionist synagogues are more likely to incorporate translations and contemporary writings in their services. Also, in most Conservative synagogues, and all Reform and Reconstructionist congregations, women participate in prayer services on an
equal basis with men, including roles traditionally filled only by men, such as
reading from the Torah. In addition, many Reform temples use musical accompaniment such as organs and mixed choirs.
Religious clothing


A ''
kippah'' (Hebrew: כִּפָּה, plural ''kippot''; Yiddish: יאַרמלקע, ''yarmulke'') is a slightly rounded brimless skullcap worn by many Jews while praying, eating, reciting blessings, or studying Jewish religious texts, and at all times by some Jewish men. In Orthodox communities, only men wear kippot; in non-Orthodox communities, some women also wear kippot. ''Kippot'' range in size from a small round beanie that covers only the back of the head to a large, snug cap that covers the whole crown.
''
Tzitzit'' (Hebrew: צִיציִת) (
Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tzitzis'') are special knotted "fringes" or "tassels" found on the four corners of the ''
tallit'' (Hebrew: טַלִּית) (Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tallis''), or prayer
shawl
A shawl (from fa, شال ''shāl'',) is a simple item of clothing from Kashmir, loosely worn over the shoulders, upper body and arms, and sometimes also over the head. It is usually a rectangular or square piece of cloth, which is often folde ...
. The ''tallit'' is worn by Jewish men and some Jewish women during the prayer service. Customs vary regarding when a Jew begins wearing a tallit. In the Sephardi community, boys wear a tallit from bar mitzvah age. In some Ashkenazi communities, it is customary to wear one only after marriage. A ''tallit katan'' (small tallit) is a fringed garment worn under the clothing throughout the day. In some Orthodox circles, the fringes are allowed to hang freely outside the clothing.
Tefillin (Hebrew: תְפִלִּין), known in English as phylacteries (from the Greek word φυλακτήριον, meaning ''safeguard'' or ''amulet''), are two square leather boxes containing biblical verses, attached to the forehead and wound around the left arm by leather straps. They are worn during weekday morning prayer by observant Jewish men and some Jewish women.
A ''
kittel
220px, A kittel
A ''kittel'' ( yi, קיטל) is a white linen or cotton robe worn by religious Ashkenazi Jews on holidays, in the synagogue or at home when leading the Passover seder. Kittels are sometimes worn by grooms. It is also customary for ...
'' (Yiddish: קיטל), a white knee-length overgarment, is worn by prayer leaders and some observant traditional Jews on the
High Holidays. It is traditional for the head of the household to wear a kittel at the Passover seder in some communities, and some grooms wear one under the wedding canopy. Jewish males are buried in a ''tallit'' and sometimes also a ''kittel'' which are part of the ''
tachrichim'' (burial garments).
Jewish holidays
Jewish holidays are special days in the Jewish calendar, which celebrate moments in Jewish history, as well as central themes in the relationship between God and the world, such as
creation,
revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing of some form of truth or knowledge through communication with a deity or other supernatural entity or entities.
Background
Inspiration – such as that bestowed by God on the ...
, and
redemption.
Shabbat

''
Shabbat'', the weekly day of rest lasting from shortly before sundown on Friday night to nightfall on Saturday night, commemorates God's day of rest after six days of creation. It plays a pivotal role in Jewish practice and is governed by a large corpus of religious law. At sundown on Friday, the woman of the house welcomes the Shabbat by lighting two or more candles and reciting a blessing. The evening meal begins with the Kiddush, a blessing recited aloud over a cup of wine, and the Mohtzi, a blessing recited over the bread. It is customary to have
challah
Challah (, he, חַלָּה or ; plural: or ) is a special bread of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, usually braided and typically eaten on ceremonial occasions such as Shabbat and major Jewish holidays (other than Passover). Ritually acceptable ch ...
, two braided loaves of bread, on the table. During Shabbat, Jews are forbidden to engage in any activity that falls under
39 categories of ''melakhah'', translated literally as "work". In fact the activities banned on the Sabbath are not "work" in the usual sense: They include such actions as lighting a fire, writing, using money and carrying in the public domain. The prohibition of lighting a fire has been extended in the modern era to driving a car, which involves burning fuel and using electricity.
Three pilgrimage festivals
Jewish holy days (''chaggim''), celebrate landmark events in Jewish history, such as the
Exodus from Egypt
The Exodus (Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the Bible), namely Ex ...
and the giving of the Torah, and sometimes mark the change of seasons and transitions in the agricultural cycle. The three major festivals, Sukkot, Passover and Shavuot, are called "regalim" (derived from the Hebrew word "regel", or foot). On the three regalim, it was customary for the Israelites to make pilgrimages to Jerusalem to offer sacrifices in the Temple.
*
Passover (''Pesach'') is a week-long holiday beginning on the evening of the 14th day of
Nisan (the first month in the Hebrew calendar), that commemorates the
Exodus from Egypt. Outside Israel, Passover is celebrated for eight days. In ancient times, it coincided with the barley harvest. It is the only holiday that centers on home-service, the
Seder
The Passover Seder (; he, סדר פסח , 'Passover order/arrangement'; yi, סדר ) is a ritual feast at the beginning of the Jewish holiday of Passover. It is conducted throughout the world on the eve of the 15th day of Nisan in the Hebrew c ...
.
Leavened products (
chametz) are removed from the house prior to the holiday and are not consumed throughout the week. Homes are thoroughly cleaned to ensure no bread or bread by-products remain, and a symbolic burning of the last vestiges of chametz is conducted on the morning of the Seder.
Matzo is eaten instead of bread.
*
Shavuot ("Pentecost" or "Feast of Weeks") celebrates the revelation of the
Torah to the
Israelites on Mount Sinai. Also known as the Festival of Bikurim, or first fruits, it coincided in biblical times with the wheat harvest. Shavuot customs include all-night study marathons known as Tikkun Leil Shavuot, eating dairy foods (cheesecake and blintzes are special favorites), reading the Book of Ruth, decorating homes and synagogues with greenery, and wearing white clothing, symbolizing purity.
*
 Sukkot
Sukkot ("Tabernacles" or "The Festival of Booths") commemorates the Israelites' forty years of wandering through the desert on their way to the Promised Land. It is celebrated through the construction of temporary booths called ''sukkot'' (sing. ''
sukkah'') that represent the temporary shelters of the Israelites during their wandering. It coincides with the fruit harvest and marks the end of the agricultural cycle. Jews around the world eat in ''sukkot'' for seven days and nights. Sukkot concludes with
Shemini Atzeret, where Jews begin to pray for rain and
Simchat Torah, "Rejoicing of the Torah", a holiday which marks reaching the end of the Torah reading cycle and beginning all over again. The occasion is celebrated with singing and dancing with the Torah scrolls. Shemini Atzeret and Simchat Torah are technically considered to be a separate holiday and not a part of Sukkot.
High Holy Days
The High Holidays (''Yamim Noraim'' or "Days of Awe") revolve around judgment and forgiveness.
*
Rosh Hashanah, (also ''Yom Ha-Zikkaron'' or "Day of Remembrance", and ''Yom Teruah'', or "Day of the Sounding of the
Shofar
A shofar ( ; from he, שׁוֹפָר, ) is an ancient musical horn typically made of a ram's horn, used for Jewish religious purposes. Like the modern bugle, the shofar lacks pitch-altering devices, with all pitch control done by varying ...
"). Rosh Hashanah is the Jewish New Year (literally, "head of the year"), although it falls on the first day of the seventh month of the
Hebrew calendar,
Tishri. Rosh Hashanah marks the beginning of the 10-day period of atonement leading up to Yom Kippur, during which Jews are commanded to search their souls and make amends for sins committed, intentionally or not, throughout the year. Holiday customs include blowing the shofar, or ram's horn, in the synagogue, eating apples and honey, and saying blessings over a variety of symbolic foods, such as pomegranates.
*
Yom Kippur, ("Day of Atonement") is the holiest day of the Jewish year. It is a day of communal fasting and praying for forgiveness for one's sins. Observant Jews spend the entire day in the synagogue, sometimes with a short break in the afternoon, reciting prayers from a special holiday prayerbook called a "Machzor". Many non-religious Jews make a point of attending synagogue services and fasting on Yom Kippur. On the eve of Yom Kippur, before candles are lit, a prefast meal, the "
seuda mafseket
A ''seudat mitzvah'' ( he, סעודת מצוה, "commanded meal"), in Judaism, is an obligatory festive meal, usually referring to the celebratory meal following the fulfillment of a ''mitzvah'' (commandment), such as a bar mitzvah, bat mitzvah ...
", is eaten. Synagogue services on the eve of Yom Kippur begin with the Kol Nidre prayer. It is customary to wear white on Yom Kippur, especially for Kol Nidre, and leather shoes are not worn. The following day, prayers are held from morning to evening. The final prayer service, called "Ne'ilah", ends with a long blast of the shofar.
Purim

 Purim
Purim (
Hebrew: ''Pûrîm'' "
lots") is a joyous Jewish holiday that commemorates the deliverance of the
Persian Jews from the plot of the evil
Haman, who sought to
exterminate them, as recorded in the biblical
Book of Esther. It is characterized by public recitation of the Book of Esther, mutual gifts of food and drink,
charity
Charity may refer to:
Giving
* Charitable organization or charity, a non-profit organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being of persons
* Charity (practice), the practice of being benevolent, giving and sharing
* C ...
to the poor, and a celebratory meal (Esther 9:22). Other customs include drinking wine, eating special pastries called
hamantash
A hamantash (pl. ''hamantashen''; also spelled ''hamantasch'', ''hamantaschen''; yi, המן־טאַש ''homentash'', pl. ''homentashn'', 'Haman pockets') is an Ashkenazi Jewish triangular filled-pocket pastry, associated with the Jewish holiday ...
en, dressing up in masks and costumes, and organizing carnivals and parties.
Purim has celebrated annually on the 14th of the Hebrew month of
Adar, which occurs in February or March of the Gregorian calendar.
Hanukkah
Hanukkah ( he, חֲנֻכָּה, "dedication") also known as the Festival of Lights, is an eight-day Jewish holiday that starts on the 25th day of
Kislev
Kislev or Chislev (Hebrew: כִּסְלֵו, Standard ''Kīslev'' Tiberian ''Kīslēw''), also 'Chisleu' in the King James (authorized English) Bible, is the third month of the civil year and the ninth month of the ecclesiastical year on the H ...
(
Hebrew calendar). The festival is observed in Jewish homes by the kindling of lights on each of the festival's eight nights, one on the first night, two on the second night and so on.
The holiday was called Hanukkah (meaning "dedication") because it marks the re-dedication of the Temple after its desecration by
Antiochus IV Epiphanes. Spiritually, Hanukkah commemorates the "Miracle of the Oil". According to the Talmud, at the re-dedication of the
Temple in Jerusalem following the victory of the
Maccabees over the
Seleucid Empire, there was only enough consecrated oil to fuel the eternal flame in the Temple for one day. Miraculously, the oil burned for eight days—which was the length of time it took to press, prepare and consecrate new oil.
Hanukkah is not mentioned in the Bible and was never considered a major holiday in Judaism, but it has become much more visible and widely celebrated in modern times, mainly because it falls around the same time as Christmas and has national Jewish overtones that have been emphasized since the establishment of the State of Israel.
Fast days
Tisha B'Av ( he, תשעה באב or , "the Ninth of
Av") is a day of mourning and fasting commemorating the destruction of the
First and
Second Temples, and in later times, the
expulsion of the Jews from Spain
The Expulsion of Jews from Spain was the expulsion from Spain following the Alhambra Decree in 1492, which was enacted in order to eliminate their influence on Spain's large ''converso'' population and to ensure its members did not revert to Judai ...
.
There are three more minor Jewish fast days that commemorate various stages of the destruction of the Temples. They are the
17th Tamuz, the
10th of Tevet
Tenth of Tevet ( he, עשרה בטבת, ''Asarah BeTevet''), the tenth day of the Hebrew month of Tevet, is a fast day in Judaism. It is one of the minor fasts observed from before dawn to nightfall. The fasting is in mourning of the sieg ...
and
Tzom Gedaliah (the 3rd of Tishrei).
Israeli holidays
The modern holidays of
Yom Ha-shoah
Yom HaZikaron laShoah ve-laG'vurah ( he, יום הזיכרון לשואה ולגבורה, , lit=Holocaust and Heroism Remembrance Day), known colloquially in Israel and abroad as Yom HaShoah (יום השואה) and in English as Holocaust Reme ...
(Holocaust Remembrance Day),
Yom Hazikaron (Israeli Memorial Day) and
Yom Ha'atzmaut (Israeli Independence Day) commemorate the horrors of the
Holocaust, the fallen soldiers of Israel and victims of terrorism, and Israeli independence, respectively.
There are some who prefer to commemorate those who were killed in the Holocaust on the
10th of Tevet
Tenth of Tevet ( he, עשרה בטבת, ''Asarah BeTevet''), the tenth day of the Hebrew month of Tevet, is a fast day in Judaism. It is one of the minor fasts observed from before dawn to nightfall. The fasting is in mourning of the sieg ...
.

Torah readings
The core of festival and
Shabbat prayer services is the public reading of the
Torah, along with connected readings from the other books of the Tanakh, called
Haftarah
The ''haftara'' or (in Ashkenazic pronunciation) ''haftorah'' (alt. ''haftarah, haphtara'', he, הפטרה) "parting," "taking leave", (plural form: ''haftarot'' or ''haftoros'') is a series of selections from the books of ''Nevi'im'' ("Pro ...
. Over the course of a year, the whole Torah is read, with the cycle starting over in the autumn, on
Simchat Torah.
Synagogues and religious buildings


Synagogues are Jewish houses of prayer and study. They usually contain separate rooms for prayer (the main sanctuary), smaller rooms for study, and often an area for community or educational use. There is no set blueprint for synagogues and the architectural shapes and interior designs of synagogues vary greatly. The Reform movement mostly refer to their synagogues as temples. Some traditional features of a synagogue are:

* The
ark (called ''aron ha-kodesh'' by
Ashkenazim
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
and ''hekhal'' by
Sephardim) where the
Torah scrolls are kept (the ark is often closed with an ornate curtain (''
parochet'') outside or inside the ark doors);
* The elevated reader's platform (called ''
bimah'' by Ashkenazim and ''tebah'' by Sephardim), where the Torah is read (and services are conducted in Sephardi synagogues);
* The
eternal light (''ner tamid''), a continually lit lamp or lantern used as a reminder of the constantly lit
menorah of the
Temple in Jerusalem
* The pulpit, or ''amud'', a lectern facing the Ark where the
hazzan or prayer leader stands while praying.
In addition to synagogues, other buildings of significance in Judaism include
yeshivas, or institutions of Jewish learning, and
mikvahs, which are ritual baths.
Dietary laws: ''kashrut''
The Jewish dietary laws are known as ''
kashrut''. Food prepared in accordance with them is termed
kosher, and food that is not kosher is also known as ''treifah'' or ''treif''. People who observe these laws are colloquially said to be "keeping kosher".
Many of the laws apply to animal-based foods. For example, in order to be considered kosher, mammals must have split
hooves and
chew their cud. The
pig is arguably the most well-known example of a non-kosher animal.
Although it has split hooves, it does not chew its cud. For
seafood to be kosher, the animal must have
fins
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. Fin ...
and
scales. Certain types of seafood, such as
shellfish,
crustaceans, and
eel
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
s, are therefore considered non-kosher. Concerning birds, a list of non-kosher species is given in the
Torah. The exact
translations
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transl ...
of many of the species have not survived, and some non-kosher birds' identities are no longer certain. However,
traditions exist about the ''kashrut'' status of a few birds. For example, both
chickens and
turkeys are permitted in most communities. Other types of animals, such as
amphibians,
reptiles, and most
insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of j ...
, are prohibited altogether.
In addition to the requirement that the species be considered kosher, meat and poultry (but not fish) must come from a healthy animal slaughtered in a process known as ''
shechitah''. Without the proper
slaughtering practices even an otherwise kosher animal will be rendered ''treif''. The slaughtering process is intended to be quick and relatively painless to the animal. Forbidden parts of animals include the
blood, some
fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
s, and the area in and around the
sciatic nerve.
''Halakha'' also forbids the consumption of meat and dairy products together. The waiting period between eating meat and eating dairy varies by the order in which they are consumed and by community, and can extend for up to six hours. Based on the Biblical injunction against cooking a kid in its mother's milk, this rule is mostly derived from the Oral Torah, the Talmud and Rabbinic la. Chicken and other kosher birds are considered the same as meat under the laws of ''kashrut'', but the prohibition is rabbinic, not biblical.
The use of
dishes, serving utensils, and
ovens may make food ''treif'' that would otherwise be kosher. Utensils that have been used to prepare non-kosher food, or dishes that have held meat and are now used for dairy products, render the food ''treif'' under certain conditions.
Furthermore, all Orthodox and some Conservative authorities forbid the consumption of processed
grape products made by non-Jews, due to ancient
pagan practices of using wine in rituals. Some Conservative authorities permit wine and grape juice made without rabbinic supervision.
The Torah does not give specific reasons for most of the laws of ''
kashrut''. However, a number of explanations have been offered, including maintaining ritual purity, teaching impulse control, encouraging obedience to God, improving health, reducing
cruelty to animals and preserving the distinctness of the Jewish community.
The various categories of dietary laws may have developed for different reasons, and some may exist for multiple reasons. For example, people are forbidden from consuming the blood of birds and mammals because, according to the Torah, this is where animal souls are contained. In contrast, the Torah forbids Israelites from eating non-kosher species because "they are unclean".
The
Kabbalah describes sparks of holiness that are released by the act of eating kosher foods, but are too tightly bound in non-kosher foods to be released by eating.
Survival concerns supersede all the laws of ''kashrut'', as they do for most ''halakhot''.
Laws of ritual purity
The Tanakh describes circumstances in which a person who is ''tahor'' or ritually pure may become ''tamei'' or ritually impure. Some of these circumstances are contact with human
corpses or
graves, seminal flux, vaginal flux,
menstruation, and contact with people who have become impure from any of these.
In Rabbinic Judaism,
Kohanim
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally be ...
, members of the hereditary
caste that served as
priests in the time of the Temple, are mostly restricted from entering grave sites and touching dead bodies.
During the Temple period, such priests (
Kohanim
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally be ...
) were required to eat their bread offering (
Terumah
A ''terumah'' ( he, תְּרוּמָה) or heave offering is a type of sacrifice in Judaism. The word is generally used for an offering to God, although it is also sometimes used as in ''ish teramot'', a "judge who loves gifts".
The word ''teru ...
) in a state of ritual purity, which laws eventually led to more rigid laws being enacted, such as
hand-washing which became a requisite of all Jews before consuming ordinary bread.
Family purity

An important subcategory of the ritual purity laws relates to the segregation of menstruating
women. These laws are also known as ''
niddah
Niddah (or nidah; he, נִדָּה), in traditional Judaism, describes a woman who has experienced a uterine discharge of blood (most commonly during menstruation), or a woman who has menstruated and not yet completed the associated requirem ...
'', literally "separation", or family purity. Vital aspects of ''halakha'' for traditionally observant Jews, they are not usually followed by Jews in liberal denominations.
Especially in
Orthodox Judaism, the Biblical laws are augmented by Rabbinical injunctions. For example, the
Torah mandates that a woman in her normal menstrual period must abstain from
sexual intercourse for seven days. A woman whose menstruation is prolonged must continue to abstain for seven more days after bleeding has stopped.
The Rabbis conflated ordinary ''niddah'' with this extended menstrual period, known in the Torah as ''
zavah'', and mandated that a woman may not have sexual intercourse with her husband from the time she begins her
menstrual flow until seven days after it ends. In addition,
Rabbinical law forbids the
husband from touching or sharing a bed with his wife during this period. Afterwards, purification can occur in a ritual bath called a
mikveh
Traditional
Ethiopian Jews keep menstruating women in separate huts and, similar to
Karaite practice, do not allow menstruating women into their
temples because of a temple's special sanctity. Emigration to Israel and the influence of other Jewish denominations have led to Ethiopian Jews adopting more normative Jewish practices.

Life-cycle events
Life-cycle events, or
rites of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
, occur throughout a Jew's life that serves to strengthen Jewish identity and bind him/her to the entire community.
*
Brit milah – Welcoming male babies into the covenant through the rite of
circumcision on their eighth day of life. The baby boy is also given his Hebrew name in the ceremony. A naming ceremony intended as a parallel ritual for girls, named ''
zeved habat'' or brit bat, enjoys limited popularity.
*
Bar mitzvah and Bat mitzvah – This passage from childhood to adulthood takes place when a female Jew is twelve and a male Jew is thirteen years old among Orthodox and some Conservative congregations. In the Reform movement, both girls and boys have their bat/bar mitzvah at age thirteen. This is often commemorated by having the new adults, male only in the Orthodox tradition, lead the congregation in prayer and publicly read a "portion" of the Torah.
*
Marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
– Marriage is an extremely important lifecycle event. A wedding takes place under a ''
chuppah'', or wedding canopy, which symbolizes a happy house. At the end of the ceremony, the groom breaks a glass with his foot, symbolizing the continuous mourning for the destruction of the Temple, and the scattering of the Jewish people.

*
Death and Mourning – Judaism has a multi-staged
mourning
Mourning is the expression of an experience that is the consequence of an event in life involving loss, causing grief, occurring as a result of someone's death, specifically someone who was loved although loss from death is not exclusively ...
practice. The first stage is called the
shiva (literally "seven", observed for one week) during which it is traditional to sit at home and be comforted by friends and family, the second is the ''shloshim'' (observed for one month) and for those who have lost one of their parents, there is a third stage, ''avelut yud bet chodesh'', which is observed for eleven months.
Community leadership
Classical priesthood
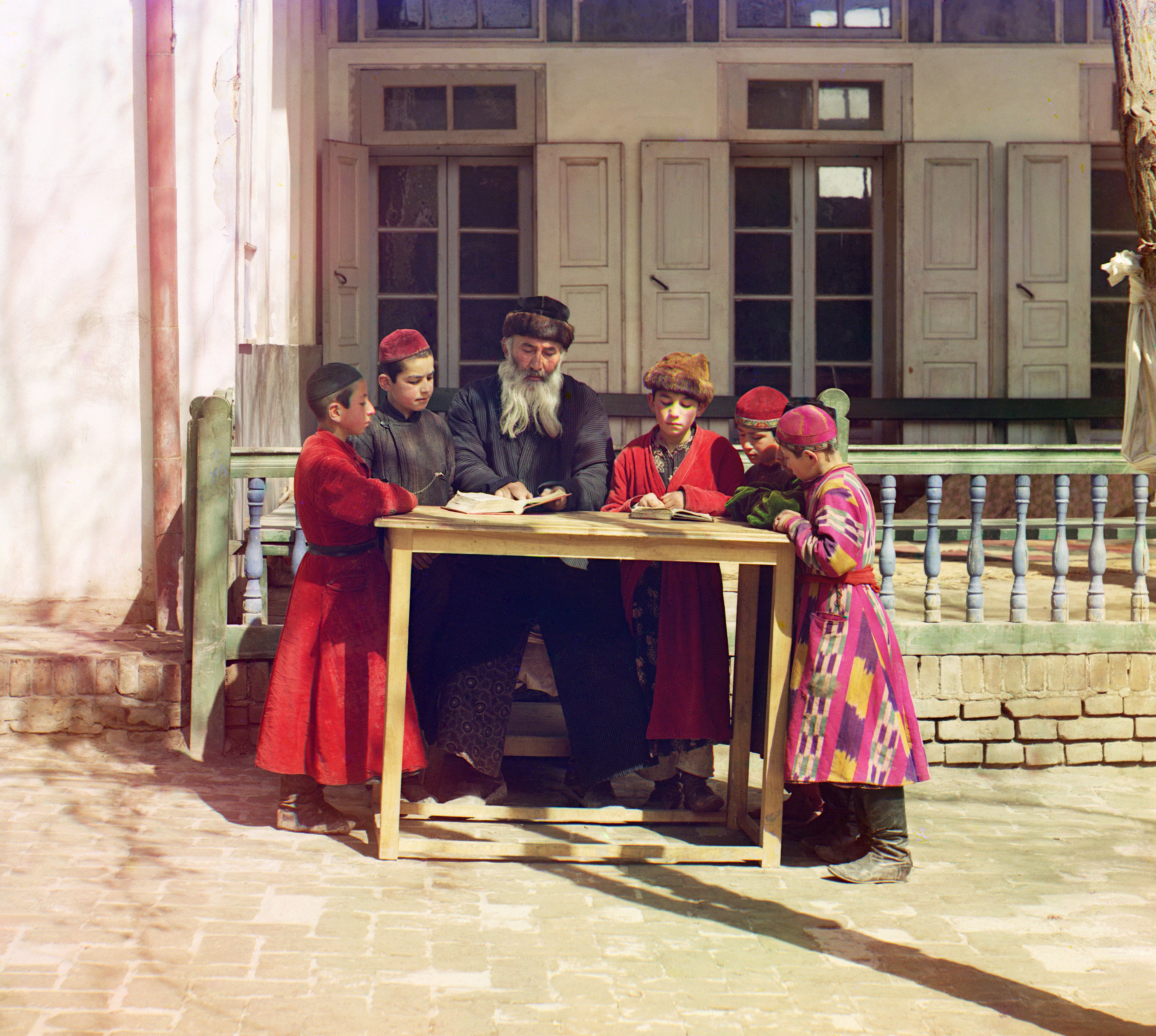

The role of the priesthood in Judaism has significantly diminished since the destruction of the
Second Temple in 70 CE when priests attended to the Temple and sacrifices. The priesthood is an inherited position, and although priests no longer have any but ceremonial duties, they are still honored in many Jewish communities. Many Orthodox Jewish communities believe that they will be needed again for a future
Third Temple
The "Third Temple" ( he, , , ) refers to a hypothetical rebuilt Temple in Jerusalem. It would succeed Solomon's Temple and the Second Temple, the former having been destroyed during the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in and the latter havin ...
and need to remain in readiness for future duty.
*
Kohen (priest) – patrilineal descendant of
Aaron, brother of
Moses. In the Temple, the ''kohanim'' were charged with performing the sacrifices. Today, a Kohen is the first one called up at the reading of the Torah, performs the
Priestly Blessing
The Priestly Blessing or priestly benediction, ( he, ברכת כהנים; translit. ''birkat kohanim''), also known in rabbinic literature as raising of the hands (Hebrew ''nesiat kapayim'') or rising to the platform (Hebrew ''aliyah ledukhan'') ...
, as well as complying with other unique laws and ceremonies, including the ceremony of redemption of the first-born.
* Levi (
Levite) – Patrilineal descendant of
Levi
Levi (; ) was, according to the Book of Genesis, the third of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's third son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Levi (the Levites, including the Kohanim) and the great-grandfather of Aaron, Moses and ...
the son of
Jacob. In the
Temple in Jerusalem, the levites sang
Psalms, performed construction, maintenance, janitorial, and guard duties, assisted the priests, and sometimes interpreted the law and Temple ritual to the public. Today, a Levite is called up second to the reading of the Torah.
Prayer leaders

From the time of the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
and Talmud to the present, Judaism has required specialists or authorities for the practice of very few rituals or ceremonies. A Jew can fulfill most requirements for prayer by himself. Some activities—reading the
Torah and ''
haftarah
The ''haftara'' or (in Ashkenazic pronunciation) ''haftorah'' (alt. ''haftarah, haphtara'', he, הפטרה) "parting," "taking leave", (plural form: ''haftarot'' or ''haftoros'') is a series of selections from the books of ''Nevi'im'' ("Pro ...
'' (a supplementary portion from the Prophets or Writings), the prayer for mourners, the blessings for bridegroom and bride, the complete grace after meals—require a ''
minyan'', the presence of ten Jews.
The most common professional clergy in a
synagogue are:
*
Rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
of a congregation – Jewish scholar who is charged with answering the legal questions of a congregation. This role requires ordination by the congregation's preferred authority (i.e., from a respected Orthodox rabbi or, if the congregation is Conservative or Reform, from academic seminaries). A congregation does not necessarily require a rabbi. Some congregations have a rabbi but also allow members of the congregation to act as ''shatz'' or ''baal kriyah'' (see below).
** Hassidic ''
Rebbe'' – rabbi who is the head of a
Hasidic dynasty.
*
Hazzan (note: the "h" denotes
voiceless pharyngeal fricative) (cantor) – a trained vocalist who acts as ''shatz''. Chosen for a good voice, knowledge of traditional tunes, understanding of the meaning of the prayers and sincerity in reciting them. A congregation does not need to have a dedicated hazzan.
Jewish prayer services do involve two specified roles, which are sometimes, but not always, filled by a rabbi or hazzan in many congregations. In other congregations these roles are filled on an ad-hoc basis by members of the congregation who lead portions of services on a rotating basis:
* Shaliach tzibur or ''Shatz'' (leader—literally "agent" or "representative"—of the congregation) leads those assembled in prayer and sometimes prays on behalf of the community. When a ''shatz'' recites a prayer on behalf of the congregation, he is ''not'' acting as an intermediary but rather as a facilitator. The entire congregation participates in the recital of such prayers by saying ''amen'' at their conclusion; it is with this act that the ''shatz's'' prayer becomes the prayer of the congregation. Any adult capable of reciting the prayers clearly may act as ''shatz''. In Orthodox congregations and some Conservative congregations, only men can be prayer leaders, but all
Progressive communities now allow women to serve in this function.
* The Baal kriyah or ''baal koreh'' (master of the reading) reads the weekly
Torah portion. The requirements for being the ''baal kriyah'' are the same as those for the ''shatz''. These roles are not mutually exclusive. The same person is often qualified to fill more than one role and often does. Often there are several people capable of filling these roles and different services (or parts of services) will be led by each.
Many congregations, especially larger ones, also rely on a:
*
Gabbai (sexton) – Calls people up to the Torah, appoints the ''shatz'' for each prayer session if there is no standard ''shatz'', and makes certain that the synagogue is kept clean and supplied.
The three preceding positions are usually voluntary and considered an honor. Since the
Enlightenment large synagogues have often adopted the practice of hiring rabbis and hazzans to act as ''shatz'' and ''baal kriyah'', and this is still typically the case in many Conservative and Reform congregations. However, in most Orthodox synagogues these positions are filled by laypeople on a rotating or ad-hoc basis. Although most congregations hire one or more Rabbis, the use of a professional hazzan is generally declining in American congregations, and the use of professionals for other offices is rarer still.

Specialized religious roles
* ''
Dayan'' (judge) – An ordained rabbi with special legal training who belongs to a ''
beth din'' (rabbinical court). In Israel, religious courts handle marriage and divorce cases, conversion and financial disputes in the Jewish community.
*
Mohel
A ( he, מוֹהֵל , Ashkenazi pronunciation , plural: , arc, מוֹהֲלָא , "circumciser") is a Jew trained in the practice of , the "covenant of circumcision".
Etymology
The noun ( in Aramaic), meaning "circumciser", is derived f ...
(circumciser) – An expert in the laws of circumcision who has received training from a previously qualified ''mohel'' and performs the ''
brit milah'' (circumcision).
*
Shochet (ritual slaughterer) – In order for meat to be kosher, it must be slaughtered by a ''shochet'' who is an expert in the laws of kashrut and has been trained by another ''shochet.''
*
Sofer (scribe) –
Torah scrolls, ''
tefillin'' (phylacteries), ''
mezuzot
A ''mezuzah'' ( he, מְזוּזָה "doorpost"; plural: ''mezuzot'') is a piece of parchment, known as a ''klaf'', contained in a decorative case and inscribed with specific Hebrew verses from the Torah ( and ). These verses consist of the J ...
'' (scrolls put on doorposts), and ''gittin'' (bills of divorce) must be written by a ''sofer'' who is an expert in Hebrew calligraphy and has undergone rigorous training in the laws of writing sacred texts.
*
Rosh yeshiva – A Torah scholar who runs a
yeshiva.
*
Mashgiach/Mashgicha of a yeshiva – Depending on which yeshiva, might either be the person responsible for ensuring attendance and proper conduct, or even supervise the emotional and spiritual welfare of the students and give lectures on
mussar (Jewish ethics).
*
Mashgiach/Mashgicha – Supervises manufacturers of kosher food, importers, caterers and restaurants to ensure that the food is kosher. Must be an expert in the laws of
kashrut and trained by a rabbi, if not a rabbi himself or herself.
Historical Jewish groupings (to 1700)
Around the 1st century CE, there were several small Jewish sects: the
Pharisees,
Sadducees,
Zealots
The Zealots were a political movement in 1st-century Second Temple Judaism which sought to incite the people of Judea Province to rebel against the Roman Empire and expel it from the Holy Land by force of arms, most notably during the First Jew ...
,
Essenes
The Essenes (; Hebrew: , ''Isiyim''; Greek: Ἐσσηνοί, Ἐσσαῖοι, or Ὀσσαῖοι, ''Essenoi, Essaioi, Ossaioi'') were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st ce ...
, and
Christians. After the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, these sects vanished.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
survived, but by breaking with Judaism and
becoming a separate religion; the
Pharisees survived but in the form of
Rabbinic Judaism (today, known simply as "Judaism"). The
Sadducees rejected the
divine inspiration of the
Prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
and the
Writings, relying only on the
Torah as divinely inspired. Consequently, a number of other core tenets of the Pharisees' belief system (which became the basis for modern Judaism), were also dismissed by the Sadducees. (The
Samaritans practiced a similar religion, which is traditionally considered separate from Judaism.)
Like the Sadducees who relied only on the Torah, some Jews in the 8th and 9th centuries rejected the authority and divine inspiration of the oral law as recorded in the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
(and developed by later rabbis in the two Talmuds), relying instead only upon the Tanakh. These included the Isunians, the Yudganites, the
Malikites, and others. They soon developed oral traditions of their own, which differed from the rabbinic traditions, and eventually formed the
Karaite sect. Karaites exist in small numbers today, mostly living in Israel. Rabbinical and Karaite Jews each hold that the others are Jews, but that the other faith is erroneous.
Over a long time, Jews formed distinct ethnic groups in several different geographic areas—amongst others, the
Ashkenazi Jews (of
central and Eastern Europe), the
Sephardi Jews (of Spain, Portugal, and North Africa), the
Beta Israel of Ethiopia, the
Yemenite Jews from the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula and the
Malabari and Cochin Jews from Kerala . Many of these groups have developed differences in their prayers, traditions and accepted canons; however, these distinctions are mainly the result of their being formed at some cultural distance from normative (rabbinic) Judaism, rather than based on any doctrinal dispute.
Persecutions
Antisemitism arose during the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, in the form of persecutions,
pogroms,
forced conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which ...
s, expulsions, social restrictions and
ghettoization.
This was different in quality from the repressions of Jews which had occurred in ancient times. Ancient repressions were politically motivated and Jews were treated the same as members of other ethnic groups. With the rise of the Churches, the main motive for attacks on Jews changed from politics to religion and the religious motive for such attacks was specifically derived from Christian views about Jews and Judaism.
During the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Jewish people who lived under Muslim rule generally experienced tolerance and integration,
[Cohen, Mark R.]
The Neo-Lachrymose Conception of Jewish-Arab History
" ''Tikkun'' 6.3 (1991) but there were occasional outbreaks of violence like
Almohad's persecutions.
[Amira K. Bennison and María Ángeles Gallego.]
Jewish Trading in Fes On The Eve of the Almohad Conquest
" MEAH, sección Hebreo 56 (2007), 33–51
Hasidism
Hasidic Judaism was founded by
Yisroel ben Eliezer (1700–1760), also known as the ''Ba'al Shem Tov'' (or ''Besht''). It originated in a time of persecution of the Jewish people when European Jews had turned inward to Talmud study; many felt that most expressions of Jewish life had become too "academic", and that they no longer had any emphasis on spirituality or joy. Its adherents favored small and informal gatherings called
Shtiebel
A shtiebel ( ''shtibl'', pl. ''shtiblekh'' or shtiebels, meaning "little house" or "little room" cognate with German Stübel) is a place used for communal Jewish prayer. In contrast to a formal synagogue, a shtiebel is far smaller and approached ...
, which, in contrast to a traditional synagogue, could be used both as a place of worship and for celebrations involving dancing, eating, and socializing. Ba'al Shem Tov's disciples attracted many followers; they themselves established numerous Hasidic sects across Europe. Unlike other religions, which typically expanded through word of mouth or by use of print, Hasidism spread largely owing to
Tzadiks, who used their influence to encourage others to follow the movement. Hasidism appealed to many Europeans because it was easy to learn, did not require full immediate commitment, and presented a compelling spectacle. Hasidic Judaism eventually became the way of life for many Jews in Eastern Europe. Waves of Jewish immigration in the 1880s carried it to the United States. The movement itself claims to be nothing new, but a ''refreshment'' of original Judaism. As some have put it: ''"they merely re-emphasized that which the generations had lost"''. Nevertheless, early on there was a serious schism between Hasidic and non-Hasidic Jews. European Jews who rejected the Hasidic movement were dubbed by the Hasidim as
Misnagdim, (lit. "opponents"). Some of the reasons for the rejection of Hasidic Judaism were the exuberance of Hasidic worship, its deviation from tradition in ascribing infallibility and miracles to their leaders, and the concern that it might become a messianic sect. Over time differences between the Hasidim and their opponents have slowly diminished and both groups are now considered part of
Haredi Judaism.
The Enlightenment and new religious movements
In the late 18th century CE, Europe was swept by a group of intellectual, social and political movements known as the
Enlightenment. The Enlightenment led to reductions in the European laws that prohibited Jews to interact with the wider secular world, thus allowing Jews access to secular education and experience. A parallel Jewish movement,
Haskalah
The ''Haskalah'', often termed Jewish Enlightenment ( he, השכלה; literally, "wisdom", "erudition" or "education"), was an intellectual movement among the Jews of Central and Eastern Europe, with a certain influence on those in Western Euro ...
or the "Jewish Enlightenment", began, especially in Central Europe and Western Europe, in response to both the Enlightenment and these new freedoms. It placed an emphasis on integration with secular society and a pursuit of non-religious knowledge through reason. With the promise of political emancipation, many Jews saw no reason to continue to observe ''halakha'' and increasing numbers of Jews assimilated into Christian Europe. Modern religious movements of Judaism all formed in reaction to this trend.
In Central Europe, followed by Great Britain and the United States,
Reform (or Liberal) Judaism developed, relaxing legal obligations (especially those that limited Jewish relations with non-Jews), emulating
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
decorum in prayer, and emphasizing the ethical values of Judaism's Prophetic tradition.
Modern Orthodox Judaism developed in reaction to Reform Judaism, by leaders who argued that Jews could participate in public life as citizens equal to Christians while maintaining the observance of ''halakha''. Meanwhile, in the United States, wealthy Reform Jews helped European scholars, who were Orthodox in practice but critical (and skeptical) in their study of the Bible and Talmud, to establish a seminary to train rabbis for immigrants from Eastern Europe. These left-wing Orthodox rabbis were joined by right-wing Reform rabbis who felt that ''halakha'' should not be entirely abandoned, to form the
Conservative movement. Orthodox Jews who opposed the Haskalah formed
Haredi Orthodox Judaism. After massive movements of Jews following
The Holocaust and the creation of
the state of Israel, these movements have competed for followers from among traditional Jews in or from other countries.
Spectrum of observance

Jewish religious practice varies widely through all levels of observance. According to the 2001 edition of the
National Jewish Population Survey, in the United States' Jewish community—the world's second largest—4.3 million Jews out of 5.1 million had some sort of connection to the religion. Of that population of connected Jews, 80% participated in some sort of Jewish religious observance, but only 48% belonged to a congregation, and fewer than 16% attend regularly.
Judaism and other religions
Christianity and Judaism

Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
was originally a sect of
Second Temple Judaism, but the two religions
diverged in the first century. The differences between Christianity and Judaism originally centered on whether Jesus was the Jewish Messiah but eventually became irreconcilable. Major differences between the two faiths include the nature of the Messiah, of
atonement
Atonement (also atoning, to atone) is the concept of a person taking action to correct previous wrongdoing on their part, either through direct action to undo the consequences of that act, equivalent action to do good for others, or some other ...
and
sin
In a religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered immoral, selfish, s ...
, the status of God's commandments to Israel, and perhaps most significantly of the
nature of God himself. Due to these differences, Judaism traditionally regards Christianity as
Shituf
' ( he, שִׁתּוּף; also transliterated as ' or '; literally "association") is a term used in Jewish sources for the worship of God in a manner which Judaism does not deem to be purely monotheistic. The term connotes a theology that is not o ...
or worship of the God of Israel which is not monotheistic. Christianity has traditionally regarded Judaism as obsolete with the invention of Christianity and Jews as a people replaced by the Church, though a Christian belief in
dual-covenant theology
Dual-covenant or two-covenant theology is a school of thought in Christian theology regarding the relevance of the Hebrew Bible, which Christians call the Old Testament.
Most Christians hold that the Old Testament has been superseded by the N ...
emerged as a phenomenon following Christian reflection on how their theology influenced the Nazi
Holocaust.
Since the time of the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
upheld the ''
Constitutio pro Judæis'' (Formal Statement on the Jews), which stated
Until
their emancipation in the late 18th and the 19th century, Jews in Christian lands were subject to humiliating legal restrictions and limitations. They included provisions requiring Jews to wear specific and identifying clothing such as the
Jewish hat and the
yellow badge, restricting Jews to certain cities and towns or in certain parts of towns (
ghettos
A ghetto, often called ''the'' ghetto, is a part of a city in which members of a minority group live, especially as a result of political, social, legal, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished t ...
), and forbidding Jews to enter certain trades (for example selling new clothes in medieval
Sweden). Disabilities also included special taxes levied on Jews, exclusion from public life, restraints on the performance of religious ceremonies, and linguistic censorship. Some countries went even further and completely expelled Jews, for example,
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
in 1290 (Jews were readmitted in 1655) and
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in 1492 (readmitted in 1868). The first Jewish settlers in North America arrived in the Dutch colony of
New Amsterdam in 1654; they were forbidden to hold public office, open a retail shop, or establish a synagogue. When the colony was seized by the British in 1664 Jewish rights remained unchanged, but by 1671
Asser Levy was the first Jew to serve on a jury in North America.
[ Burrows, Edwin G. & Wallace, Mike. '' Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999. pp. 60, 133-134] In 1791,
Revolutionary France
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
was the first country to abolish disabilities altogether, followed by
Prussia in 1848.
Emancipation of the Jews in the United Kingdom was achieved in 1858 after an almost 30-year struggle championed by
Isaac Lyon Goldsmid
Sir Isaac Lyon Goldsmid, 1st Baronet (13 January 1778 – 27 April 1859) was a financier and one of the leading figures in the Jewish emancipation in the United Kingdom, who became the first British Jew to receive a hereditary title.
Biography
...
with the ability of Jews to sit in parliament with the passing of the
Jews Relief Act 1858. The newly created
German Empire in 1871 abolished Jewish disabilities in Germany, which were reinstated in the
Nuremberg Laws in 1935.
Jewish life in Christian lands was marked by frequent
blood libels, expulsions,
forced conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which ...
s and
massacres. Religious prejudice was an underlying source against Jews in Europe. Christian rhetoric and antipathy towards Jews developed in the
early years of Christianity and was reinforced by ever increasing anti-Jewish measures over the
ensuing centuries. The action taken by Christians against Jews included acts of violence, and murder culminating in the
Holocaust.
These attitudes were reinforced by Christian preaching, in art and popular teaching for two millennia which expressed contempt for Jews,
[Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. 5 May 2009]
The Origins of Christian Anti-Semitism: Interview with Pieter van der Horst
/ref> as well as statutes which were designed to humiliate and stigmatise Jews. The Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
was known for its persecution of Christian Churches; many of them, such as the Protestant Confessing Church and the Catholic Church, as well as Quakers and Jehovah's Witnesses, aided and rescued Jews who were being targeted by the antireligious régime.World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Pope John Paul II and the Catholic Church have "upheld the Church's acceptance of the continuing and permanent election of the Jewish people" as well as a reaffirmation of the covenant between God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
and the Jews.Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
released a 10,000-word document that, among other things, stated that Catholics should work with Jews to fight antisemitism.
Islam and Judaism
 Both Judaism and Islam track their origins from the patriarch Abraham, and they are therefore considered
Both Judaism and Islam track their origins from the patriarch Abraham, and they are therefore considered Abrahamic religions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
. In both Jewish and Muslim tradition, the Jewish and Arab peoples are descended from the two sons of Abraham— Isaac and Ishmael, respectively. While both religions are monotheistic and share many commonalities, they differ based on the fact that Jews do not consider Jesus or Muhammad to be prophets. The religions' adherents have interacted with each other since the 7th century when Islam originated and spread in the Arabian peninsula. Indeed, the years 712 to 1066 CE under the Ummayad and the Abbasid rulers have been called the Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain. Non-Muslim monotheists living in these countries, including Jews, were known as dhimmis
' ( ar, ذمي ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligatio ...
. Dhimmis were allowed to practice their own religions and administer their own internal affairs, but they were subject to certain restrictions that were not imposed on Muslims.Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
or the hadiths
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
but invented in early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
Baghdad and inconsistently enforced.Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fou ...
dynasty in North Africa and Al-Andalus,Mawza Exile
The Exile of Mawzaʻ (the expulsion of Yemenite Jews to Mawza') he, גלות מוזע, ; 1679–1680, is considered the single most traumatic event experienced collectively by the Jews of Yemen, in which Jews living in nearly all cities a ...
). At times, Jews were also restricted in their choice of residence—in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, for example, Jews were confined to walled quarters (mellah
A ''mellah'' ( or 'saline area'; and he, מלאח) is a Jewish quarter of a city in Morocco. Starting in the 15th century and especially since the beginning of the 19th century, Jewish communities in Morocco were constrained to live in ''mellah' ...
s) beginning in the 15th century and increasingly since the early 19th century.Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. Today, antisemitic themes including Holocaust denial have become commonplace in the propaganda of Islamic movements such as Hizbullah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's paramili ...
and Hamas, in the pronouncements of various agencies of the Islamic Republic of Iran, and even in the newspapers and other publications of Refah Partisi.
Syncretic movements incorporating Judaism
There are some movements in other religions that include elements of Judaism. Among Christianity these are a number of denominations of ancient and contemporary Judaizers
The Judaizers were a faction of the Jewish Christians, both of Jewish and non-Jewish origins, who regarded the Levitical laws of the Old Testament as still binding on all Christians. They tried to enforce Jewish circumcision upon the Gentile c ...
. The most well-known of these is Messianic Judaism, a religious movement, which arose in the 1960s,[Michael L. Morgan, Steven Weitzman, (eds.,]
''Rethinking the Messianic Idea in Judaism,''
Indiana University Press 2014 p.1. Gershom Scholem
Gershom Scholem () (5 December 1897 – 21 February 1982), was a German-born Israeli philosopher and historian. Widely regarded as the founder of modern academic study of the Kaballah, Scholem was appointed the first professor of Jewish Myst ...
considered 'the messianic dimensions of the Kabbalah and of rabbinic Judaism as a central feature of a Jewish philosophy of history.' are incorporated in, and melded with the tenets of Christianity.Pauline Christianity
Pauline Christianity or Pauline theology (also Paulism or Paulanity), otherwise referred to as Gentile Christianity, is the theology and form of Christianity which developed from the beliefs and doctrines espoused by the Hellenistic-Jewish Ap ...
.Jewish Buddhists
A Jewish Buddhist is a person with a Jewish background who practices forms of Dhyanam Buddhist meditation, chanting or spirituality. When the individual practices a particular religion, it may be both Judaism and Buddhism. However, in many ca ...
, another loosely organized group that incorporates elements of Asian spirituality in their faith; and some Renewal Jews who borrow freely and openly from Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, Sufism, Native American religions, and other faiths.
The Kabbalah Centre
The Kabbalah Centre International is a non-profit organizationworldwide
located in Los Angeles, California that provides courses on the Zohar and Kabbalistic teachings online as well as through its regional and city-based centers and study groups ...
, which employs teachers from multiple religions, is a New Age movement that claims to popularize the kabbalah, part of the Jewish esoteric tradition.
Criticism
See also
* List of 21st-century religious leaders#Judaism
* List of religious organizations#Jewish organizations
* Jewish culture
* Judaism by country
This article deals with the practice of Judaism and the living arrangement of Jews in the listed countries.
See also
* Who is a Jew?
* Jewish ethnic divisions
* History of the Jews under Muslim rule
* Jewish population by country
* Historical ...
* Outline of Judaism
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Judaism:
History
* Origins of Judaism
* Jewish history
Pre-monarchic period
* Ugaritic mythology – The Levant region was inhabited by people who themselves referre ...
Footnotes
Bibliography
* Avery-Peck, Alan; Neusner, Jacob (eds.)
''The Blackwell reader in Judaism''
(Blackwell, 2001).
* Avery-Peck, Alan; Neusner, Jacob (eds.)
''The Blackwell Companion to Judaism''
(Blackwell, 2003).
* Boyarin, Daniel (1994). ''A Radical Jew: Paul and the Politics of Identity''. Berkeley: University of California Press.
*
* Cohn-Sherbok, Dan
''Judaism: history, belief, and practice''
(Routledge, 2003).
* Day, John (2000). ''Yahweh and the Gods and Goddesses of Canaan''. Chippenham: Sheffield Academic Press.
* Dever, William G. (2005). ''Did God Have a Wife?''. Grand Rapids: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co..
* Dosick, Wayne, ''Living Judaism: The Complete Guide to Jewish Belief, Tradition and Practice''.
*
* Finkelstein, Israel (1996). "Ethnicity and Origin of the Iron I Settlers in the Highlands of Canaan: Can the Real Israel Please Stand Up?" The ''Biblical Archaeologist'', 59(4).
* Gillman, Neil, ''Conservative Judaism: The New Century'', Behrman House.
* Gurock, Jeffrey S. (1996). ''American Jewish Orthodoxy in Historical Perspective''. KTAV.
* Guttmann, Julius (1964). Trans. by David Silverman, ''Philosophies of Judaism''. JPS.
* Holtz, Barry W. (ed.), ''Back to the Sources: Reading the Classic Jewish Texts''. Summit Books.
*
*
* Johnson, Paul (1988). ''A History of the Jews''. HarperCollins.
*
* Lewis, Bernard (1984). ''The Jews of Islam''. Princeton: Princeton University Press. .
* Lewis, Bernard (1999). ''Semites and Anti-Semites: An Inquiry into Conflict and Prejudice''. W. W. Norton & Co. .
* Mayer, Egon, Barry Kosmin and Ariela Keysar, "The American Jewish Identity Survey", a subset of ''The American Religious Identity Survey'', City University of New York Graduate Center. An article on this survey is printed in ''The New York Jewish Week'', 2 November 2001.
*
*
*
* Raphael, Marc Lee (2003)
''Judaism in America''
Columbia University Press.
*
*
* Walsh, J.P.M. (1987). ''The Mighty from Their Thrones''. Eugene: Wipf and Stock Publishers.
* Weber, Max (1967). '' Ancient Judaism'', Free Press, .
* Wertheime, Jack (1997). ''A People Divided: Judaism in Contemporary America''. Brandeis University Press.
*
;Jews in Islamic countries
* Khanbaghi, A. (2006). ''The Fire, the Star and the Cross: Minority Religions in Medieval and Early Modern Iran''. IB Tauris.
* Stillman, Norman (1979). ''The Jews of Arab Lands: A History and Source Book''. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society of America. .
* Simon, Reeva; Laskier, Michael; Reguer, Sara (eds.) (2002). ''The Jews of the Middle East and North Africa In Modern Times'', Columbia University Press.
Further reading
; Encyclopedias
*
*
*
*
External links
;General
*
Online version
of ''The Jewish Encyclopedia
''The Jewish Encyclopedia: A Descriptive Record of the History, Religion, Literature, and Customs of the Jewish People from the Earliest Times to the Present Day'' is an English-language encyclopedia containing over 15,000 articles on th ...
'' (1901–1906)
About Judaism
by '' Dotdash'' (formerly ''About.com'')
Shamash's Judaism and Jewish Resources
;Orthodox/Haredi
Orthodox Judaism – The Orthodox Union
Aish HaTorah
Ohr Somayach
;Traditional/Conservadox
Union for Traditional Judaism
;Conservative
Masorti (Conservative) Movement in Israel
United Synagogue Youth
;Reform/Progressive
The Union for Reform Judaism (USA)
Reform Judaism (UK)
Liberal Judaism (UK)
World Union for Progressive Judaism (Israel)
;Reconstructionist
Jewish Reconstructionist Federation
;Renewal
ALEPH: Alliance for Jewish Renewal
OHALAH Association of Rabbis for Jewish Renewal
;Humanistic
Society for Humanistic Judaism
;Karaite
World Movement for Karaite Judaism
;Jewish religious literature and texts
(in Hebrew, with vowels).
from the 1917 Jewish Publication Society version.
Torah.org
(also known as ''Project Genesis'') Contains Torah commentaries and studies of Tanakh, along with Jewish ethics, philosophy, holidays and other classes.
The complete formatted Talmud online
Audio files of lectures for each page from an Orthodox viewpoint are provided in French, English, Yiddish and Hebrew. Reload the page for an image of a page of the Talmud.
See also Torah database
A Torah database (מאגר תורני or מאגר יהדות) is a collection of classic Jewish texts in electronic form, the kinds of texts which, especially in Israel, are often called "The Traditional Jewish Bookshelf" (ארון הספרים ה ...
for links to more Judaism e-texts.
;Wikimedia Torah study projects
Text study projects at Wikisource. In many instances, the Hebrew versions of these projects are more fully developed than the English.
* Mikraot Gedolot
A ''Mikraot Gedolot'' (''Great Scriptures''; in Hebrew: ), often called the " Rabbinic Bible" in English, is an edition of the Hebrew Bible (in Hebrew) that generally includes three distinct elements:
* The biblical text according to the '' ma ...
(Rabbinic Bible) in Hebrew (sample) and English (sample).
* Cantillation
Cantillation is the ritual chanting of prayers and responses. It often specifically refers to Jewish Hebrew cantillation. Cantillation sometimes refers to diacritics used in texts that are to be chanted in liturgy.
Cantillation includes:
* Chant
...
at the "Vayavinu Bamikra" Project in Hebrew (lists nearly 200 recordings) and English.
* Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
in Hebrew (sample) and English (sample).
* Shulchan Aruch in Hebrew and English (Hebrew text with English translation).
{{Authority control
Abrahamic religions
Monotheistic religions
Ethnic religion
Religion in ancient Israel and Judah
Moses
Abraham
 The term ''Judaism'' derives from ''Iudaismus'', a Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ''
The term ''Judaism'' derives from ''Iudaismus'', a Latinized form of the Ancient Greek '' At its core, the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) is an account of the Israelites' relationship with
At its core, the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) is an account of the Israelites' relationship with  Once King David was established, he told the prophet Nathan that he would like to build a permanent temple, and as a reward for his actions, God promised David that he would allow his son, Solomon, to build the First Temple and the throne would never depart from his children.
Rabbinic tradition holds that the details and interpretation of the law, which are called the ''Oral Torah'' or ''oral law'', were originally an unwritten tradition based upon what God told Moses on Mount Sinai. However, as the persecutions of the Jews increased and the details were in danger of being forgotten, these oral laws were recorded by
Once King David was established, he told the prophet Nathan that he would like to build a permanent temple, and as a reward for his actions, God promised David that he would allow his son, Solomon, to build the First Temple and the throne would never depart from his children.
Rabbinic tradition holds that the details and interpretation of the law, which are called the ''Oral Torah'' or ''oral law'', were originally an unwritten tradition based upon what God told Moses on Mount Sinai. However, as the persecutions of the Jews increased and the details were in danger of being forgotten, these oral laws were recorded by  Unlike other ancient Near Eastern gods, the Hebrew God is portrayed as unitary and solitary; consequently, the Hebrew God's principal relationships are not with other gods, but with the world, and more specifically, with the people he created. Judaism thus begins with
Unlike other ancient Near Eastern gods, the Hebrew God is portrayed as unitary and solitary; consequently, the Hebrew God's principal relationships are not with other gods, but with the world, and more specifically, with the people he created. Judaism thus begins with  The following is a basic, structured list of the central works of Jewish practice and thought.
* Tanakh ( Hebrew Bible) and Rabbinic literature
** Mesorah
** Targum
** Jewish Biblical exegesis (also see Midrash below)
* Works of the Talmudic Era (classic rabbinic literature)
**
The following is a basic, structured list of the central works of Jewish practice and thought.
* Tanakh ( Hebrew Bible) and Rabbinic literature
** Mesorah
** Targum
** Jewish Biblical exegesis (also see Midrash below)
* Works of the Talmudic Era (classic rabbinic literature)
**  Jewish philosophy refers to the conjunction between serious study of philosophy and Jewish theology. Major Jewish philosophers include
Jewish philosophy refers to the conjunction between serious study of philosophy and Jewish theology. Major Jewish philosophers include  While traditions and customs vary between discrete communities, it can be said that Sephardi and Mizrahi Jewish communities do not generally adhere to the "movement" framework popular in and among Ashkenazi Jewry. Historically, Sephardi and Mizrahi communities have eschewed denominations in favour of a "big tent" approach. This is particularly the case in contemporary
While traditions and customs vary between discrete communities, it can be said that Sephardi and Mizrahi Jewish communities do not generally adhere to the "movement" framework popular in and among Ashkenazi Jewry. Historically, Sephardi and Mizrahi communities have eschewed denominations in favour of a "big tent" approach. This is particularly the case in contemporary 
 Traditionally, Jews recite prayers three times daily, Shacharit,
Traditionally, Jews recite prayers three times daily, Shacharit,  Most of the prayers in a traditional Jewish service can be recited in solitary prayer, although communal prayer is preferred. Communal prayer requires a quorum of ten adult Jews, called a '' minyan''. In nearly all Orthodox and a few Conservative circles, only male Jews are counted toward a ''minyan''; most Conservative Jews and members of other Jewish denominations count female Jews as well.
In addition to prayer services, observant traditional Jews recite prayers and benedictions throughout the day when performing various acts. Prayers are recited upon waking up in the morning, before eating or drinking different foods, after eating a meal, and so on.
The approach to prayer varies among the Jewish denominations. Differences can include the texts of prayers, the frequency of prayer, the number of prayers recited at various religious events, the use of musical instruments and choral music, and whether prayers are recited in the traditional liturgical languages or the vernacular. In general, Orthodox and Conservative congregations adhere most closely to tradition, and Reform and Reconstructionist synagogues are more likely to incorporate translations and contemporary writings in their services. Also, in most Conservative synagogues, and all Reform and Reconstructionist congregations, women participate in prayer services on an equal basis with men, including roles traditionally filled only by men, such as reading from the Torah. In addition, many Reform temples use musical accompaniment such as organs and mixed choirs.
Most of the prayers in a traditional Jewish service can be recited in solitary prayer, although communal prayer is preferred. Communal prayer requires a quorum of ten adult Jews, called a '' minyan''. In nearly all Orthodox and a few Conservative circles, only male Jews are counted toward a ''minyan''; most Conservative Jews and members of other Jewish denominations count female Jews as well.
In addition to prayer services, observant traditional Jews recite prayers and benedictions throughout the day when performing various acts. Prayers are recited upon waking up in the morning, before eating or drinking different foods, after eating a meal, and so on.
The approach to prayer varies among the Jewish denominations. Differences can include the texts of prayers, the frequency of prayer, the number of prayers recited at various religious events, the use of musical instruments and choral music, and whether prayers are recited in the traditional liturgical languages or the vernacular. In general, Orthodox and Conservative congregations adhere most closely to tradition, and Reform and Reconstructionist synagogues are more likely to incorporate translations and contemporary writings in their services. Also, in most Conservative synagogues, and all Reform and Reconstructionist congregations, women participate in prayer services on an equal basis with men, including roles traditionally filled only by men, such as reading from the Torah. In addition, many Reform temples use musical accompaniment such as organs and mixed choirs.

 A '' kippah'' (Hebrew: כִּפָּה, plural ''kippot''; Yiddish: יאַרמלקע, ''yarmulke'') is a slightly rounded brimless skullcap worn by many Jews while praying, eating, reciting blessings, or studying Jewish religious texts, and at all times by some Jewish men. In Orthodox communities, only men wear kippot; in non-Orthodox communities, some women also wear kippot. ''Kippot'' range in size from a small round beanie that covers only the back of the head to a large, snug cap that covers the whole crown.
'' Tzitzit'' (Hebrew: צִיציִת) ( Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tzitzis'') are special knotted "fringes" or "tassels" found on the four corners of the '' tallit'' (Hebrew: טַלִּית) (Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tallis''), or prayer
A '' kippah'' (Hebrew: כִּפָּה, plural ''kippot''; Yiddish: יאַרמלקע, ''yarmulke'') is a slightly rounded brimless skullcap worn by many Jews while praying, eating, reciting blessings, or studying Jewish religious texts, and at all times by some Jewish men. In Orthodox communities, only men wear kippot; in non-Orthodox communities, some women also wear kippot. ''Kippot'' range in size from a small round beanie that covers only the back of the head to a large, snug cap that covers the whole crown.
'' Tzitzit'' (Hebrew: צִיציִת) ( Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tzitzis'') are special knotted "fringes" or "tassels" found on the four corners of the '' tallit'' (Hebrew: טַלִּית) (Ashkenazi pronunciation: ''tallis''), or prayer  '' Shabbat'', the weekly day of rest lasting from shortly before sundown on Friday night to nightfall on Saturday night, commemorates God's day of rest after six days of creation. It plays a pivotal role in Jewish practice and is governed by a large corpus of religious law. At sundown on Friday, the woman of the house welcomes the Shabbat by lighting two or more candles and reciting a blessing. The evening meal begins with the Kiddush, a blessing recited aloud over a cup of wine, and the Mohtzi, a blessing recited over the bread. It is customary to have
'' Shabbat'', the weekly day of rest lasting from shortly before sundown on Friday night to nightfall on Saturday night, commemorates God's day of rest after six days of creation. It plays a pivotal role in Jewish practice and is governed by a large corpus of religious law. At sundown on Friday, the woman of the house welcomes the Shabbat by lighting two or more candles and reciting a blessing. The evening meal begins with the Kiddush, a blessing recited aloud over a cup of wine, and the Mohtzi, a blessing recited over the bread. It is customary to have  Sukkot ("Tabernacles" or "The Festival of Booths") commemorates the Israelites' forty years of wandering through the desert on their way to the Promised Land. It is celebrated through the construction of temporary booths called ''sukkot'' (sing. '' sukkah'') that represent the temporary shelters of the Israelites during their wandering. It coincides with the fruit harvest and marks the end of the agricultural cycle. Jews around the world eat in ''sukkot'' for seven days and nights. Sukkot concludes with Shemini Atzeret, where Jews begin to pray for rain and Simchat Torah, "Rejoicing of the Torah", a holiday which marks reaching the end of the Torah reading cycle and beginning all over again. The occasion is celebrated with singing and dancing with the Torah scrolls. Shemini Atzeret and Simchat Torah are technically considered to be a separate holiday and not a part of Sukkot.
Sukkot ("Tabernacles" or "The Festival of Booths") commemorates the Israelites' forty years of wandering through the desert on their way to the Promised Land. It is celebrated through the construction of temporary booths called ''sukkot'' (sing. '' sukkah'') that represent the temporary shelters of the Israelites during their wandering. It coincides with the fruit harvest and marks the end of the agricultural cycle. Jews around the world eat in ''sukkot'' for seven days and nights. Sukkot concludes with Shemini Atzeret, where Jews begin to pray for rain and Simchat Torah, "Rejoicing of the Torah", a holiday which marks reaching the end of the Torah reading cycle and beginning all over again. The occasion is celebrated with singing and dancing with the Torah scrolls. Shemini Atzeret and Simchat Torah are technically considered to be a separate holiday and not a part of Sukkot.

 Purim ( Hebrew: ''Pûrîm'' " lots") is a joyous Jewish holiday that commemorates the deliverance of the Persian Jews from the plot of the evil Haman, who sought to exterminate them, as recorded in the biblical Book of Esther. It is characterized by public recitation of the Book of Esther, mutual gifts of food and drink,
Purim ( Hebrew: ''Pûrîm'' " lots") is a joyous Jewish holiday that commemorates the deliverance of the Persian Jews from the plot of the evil Haman, who sought to exterminate them, as recorded in the biblical Book of Esther. It is characterized by public recitation of the Book of Esther, mutual gifts of food and drink, 

 Synagogues are Jewish houses of prayer and study. They usually contain separate rooms for prayer (the main sanctuary), smaller rooms for study, and often an area for community or educational use. There is no set blueprint for synagogues and the architectural shapes and interior designs of synagogues vary greatly. The Reform movement mostly refer to their synagogues as temples. Some traditional features of a synagogue are:
Synagogues are Jewish houses of prayer and study. They usually contain separate rooms for prayer (the main sanctuary), smaller rooms for study, and often an area for community or educational use. There is no set blueprint for synagogues and the architectural shapes and interior designs of synagogues vary greatly. The Reform movement mostly refer to their synagogues as temples. Some traditional features of a synagogue are:
 * The ark (called ''aron ha-kodesh'' by
* The ark (called ''aron ha-kodesh'' by  An important subcategory of the ritual purity laws relates to the segregation of menstruating women. These laws are also known as ''
An important subcategory of the ritual purity laws relates to the segregation of menstruating women. These laws are also known as ''
 * Death and Mourning – Judaism has a multi-staged
* Death and Mourning – Judaism has a multi-staged  The role of the priesthood in Judaism has significantly diminished since the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE when priests attended to the Temple and sacrifices. The priesthood is an inherited position, and although priests no longer have any but ceremonial duties, they are still honored in many Jewish communities. Many Orthodox Jewish communities believe that they will be needed again for a future
The role of the priesthood in Judaism has significantly diminished since the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE when priests attended to the Temple and sacrifices. The priesthood is an inherited position, and although priests no longer have any but ceremonial duties, they are still honored in many Jewish communities. Many Orthodox Jewish communities believe that they will be needed again for a future  From the time of the
From the time of the 
 Jewish religious practice varies widely through all levels of observance. According to the 2001 edition of the National Jewish Population Survey, in the United States' Jewish community—the world's second largest—4.3 million Jews out of 5.1 million had some sort of connection to the religion. Of that population of connected Jews, 80% participated in some sort of Jewish religious observance, but only 48% belonged to a congregation, and fewer than 16% attend regularly.
Jewish religious practice varies widely through all levels of observance. According to the 2001 edition of the National Jewish Population Survey, in the United States' Jewish community—the world's second largest—4.3 million Jews out of 5.1 million had some sort of connection to the religion. Of that population of connected Jews, 80% participated in some sort of Jewish religious observance, but only 48% belonged to a congregation, and fewer than 16% attend regularly.

 Both Judaism and Islam track their origins from the patriarch Abraham, and they are therefore considered
Both Judaism and Islam track their origins from the patriarch Abraham, and they are therefore considered