Bone pathology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Orthopedic pathology, also known as bone pathology is a subspecialty of
Orthopedic pathology, also known as bone pathology is a subspecialty of
 Orthopedic pathology, also known as bone pathology is a subspecialty of
Orthopedic pathology, also known as bone pathology is a subspecialty of surgical pathology
Surgical pathology is the most significant and time-consuming area of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and ...
which deals with the diagnosis and feature of many bone diseases, specifically studying the cause and effects of disorders of the musculoskeletal system
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provid ...
. It uses gross and microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale be ...
findings along with the findings of ''in vivo'' radiological
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visib ...
studies, and occasionally, specimen radiographs to diagnose diseases of the bones
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, a ...
.
Causes and Effects
Orthopaedic disorders may be congenital and there may be hereditary and environmental factors that can affect the normal functioning of the bones, joints, or muscles. Other causes of bone diseases include severe impacts/injuries and weakness in bones/bone loss. Many patients who are diagnosed with bone diseases have no risk factors. However, there are risks including chronic disorders, disease, exposure to radiation and heredity factors. A direct cause of the formation of bone tumours has not been identified yet, however there are possible origins such as injuries to the bone, treatment from radiation and genetics. The effects of bone disorders will vary with disease. The effects can occur physically, mentally and financially as well as impact the individuals quality of life. Orthopaedic disorders can drastically affect an individual's functional ability. Individuals who have had bone diseases can experience complications such as extreme pain, fractures, height loss and the ability to be mobile. They can also be more susceptible to other issues, for example, a Urinary tract infection (UTI) orPneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
. Many of these bone disorders could lead to declines in both mental and physical health. In addition to a physical impact, bone disorders can also give rise to psychological ramifications and reflect negatively on an individual's mindset, body image as well as self-esteem, which may result in the individual feeling helpless and yield fears of falling.
To care for bone diseases and disorders is quite expensive. These costs can include both direct and indirect medical expenses as well as possible job loss or productivity loss for the patient. The chances of death vary enormously between the bone disorders due to the differing degree of severity, however many bone diseases do increase an individual's susceptibility to other complications. These disorders depend on multiple factors such as genetics and environmental factors, thus chances range between many individuals.
Individuals are more susceptible to bone fractures as they age with a possibility of more major consequences. This is due to the continual loss of minerals in the bones such as Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
as well as hormonal changes. Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
results in mineral loss in bone for women and a slow decline of the production of sex hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are require ...
s could lead to the development of bone disorders in men, mainly Osteoporosis. The elderly may be more susceptible due to medications they may be taking, worsening in vision as well as decreased ability to use muscle and bones to control balance.
As a common bone disorder, osteoporosis affects a large section of the population, resulting in a reduced quality of life, ill health, a variety of diseases or disabilities and death as a possible consequence. Loss of bone minerals means a decline in bone mass, thus bones will be weaker in some areas resulting in individuals to be at risk of minor or major falls that could be detrimental. It is known that exercise can allow for stronger bones in order to slow down bone loss in individuals as muscle mass can be built to support and reduce the risks of bone disease. Weight and balance training, Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise (also known as endurance activities, cardio or cardio-respiratory exercise) is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, inv ...
and walking are examples of exercises that can maintain an individual's bone mass. In addition rotational movements in which the bone can be pulled with the muscle are seen to be beneficial. Nutrition and smoking is also very important in the development and prevention of bone diseases.
Symptoms
Symptoms that patients may experience when bone disorders form can include bone deformities, hip pain, overgrowing of bone in an individual's skull which can result in headaches and a loss of hearing, pain and numbness in arm or legs if the spine is affected and an overall weakness in the body particularly in the hip and knee joints.Treatments
Individuals that are diagnosed with bone disorders need to pay attention to secondary causes as medications and the presence of other disorders can also have major effects. Drugs that can prevent bone loss are called antiresorptives. They can slow the degradation of the skeletal system and decrease the risk of subsequent bone injuries fractures. They can help in repairing the individual's bone strength. In addition to antiresorptives, anabolic therapy can also promote the build up of bones and prevent prospective risks. There are also drugs that can deteriorate bone mass. Glucocorticoid is produced naturally by the body itself in the form of cortisol, however it is known that high levels of this hormone both naturally and synthetically can result in a decreased ability for the body to form bone cells, instead amplifying the breaking down of bone minerals. This impacts the bone loss in an individual's body. Other medications that can affect the production of bone cells and enhance bone loss and fractures include breast cancer and prostate cancer drugs, anti-seizure drugs, blood pressure medication, heartburn drugs and diuretics. There are also medical conditions such as neurological disorders, malabsorption, sex hormone deficiency, diabetes, kidney disease and hyperthyroidism that can influence bone disorders.Types of Disorders
By classifying and understanding the different types of bone diseases, orthopaedic pathologists are able to identify the causes and effects.Bone Cancer/Tumours
The two most common forms ofbone cancer
A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thy ...
are Ewing's sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about ...
and osteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) (or simply bone cancer) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma ...
. They are highly aggressive pediatric tumours. Ewing sarcoma form in bones or soft tissue, whereas osteosarcoma makes weakened bones at the end of longer ones.
There are multiple other bone cancers that are more rare:
Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarcomas ...
is identified mainly through the production of cartilage from the cells. Depending on the type of chondrosarcoma, it ranges from a slow growth which is able to be removed, to a rapid growth and uncontrollable spread to other parts of the body, known as metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
.
A Chordoma
Chordoma is a rare slow-growing neoplasm thought to arise from cellular remnants of the notochord. The evidence for this is the location of the tumors (along the neuraxis), the similar immunohistochemical staining patterns, and the demonstration ...
is another type of cancer that slowly grows into nearby bones and many soft tissues in the spine, ranging from the base of the skull to the tailbone. Chordomas have around a 40% metastasis rate and mainly spread to the lungs.
(rare cases) soft-tissue sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal ( connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sar ...
causes:
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) is a form of soft tissue cancer, which mainly targets the arms and legs. It is undifferentiated as under a microscope, the tumour cells appear different to the body cells in which it develops, and is characterised as pleomorphic because it takes many different forms and sizes.
Fibrosarcoma
Fibrosarcoma (fibroblastic sarcoma) is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pat ...
occurs in the fibrous cells that join muscles to bones, most commonly in the arms, legs and pelvis
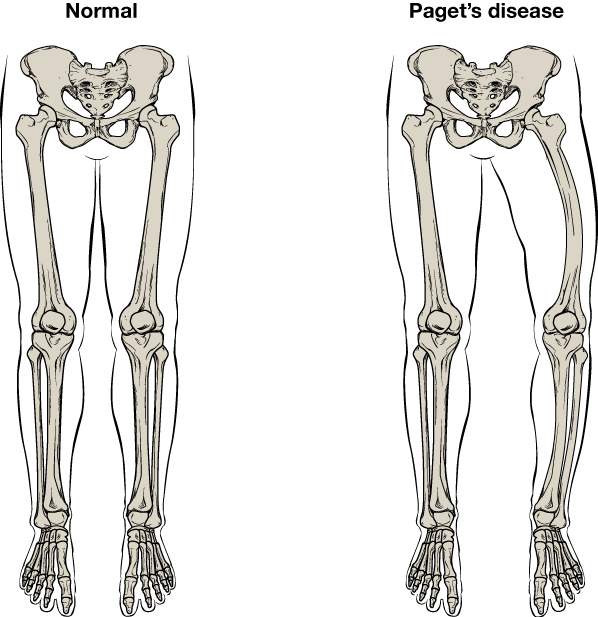
Sarcoma of Paget's disease of the bone occurs in people that already have Paget's disease, mainly aged above 70. It is very aggressive and difficult to control
Common orthopaedic diseases include; arthritis, back/foot/hand/knee/neck/shoulder pains, osteoporosis, Paget's disease of the bone and soft-tissue injuries.
Non-neoplastic disorders
Bone diseases include non-neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
disorders, which are diseases that are not caused by abnormal growths such as cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. These consist of genetic diseases, osteoporosis, infections of the bone, and Paget's disease of bone
Paget's disease of bone (commonly known as Paget's disease or, historically, osteitis deformans) is a condition involving cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the ...
.
Neuromotor Impairments
Neuromotor impairments refer to the conditions that are established at or before birth in the affected person, regarding damage or unnatural behaviors of the brain and spinal chord, or more generally, theNervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
. The transmission of specific signals through Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s by the brain to all parts of the body is hindered by neuromotor impairments, generally causing a range of problems regarding motion and movement of all parts of the body. Common effects are loss of limb functionality, urinary control, and the spinal alignment.
two examples of neuromotor impairments are Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
and Spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, men ...
.
Degenerative Diseases
Degenerative disease
Degenerative disease is the result of a continuous process based on degenerative cell changes, affecting tissues or organs, which will increasingly deteriorate over time.
In neurodegenerative diseases, cells of the central nervous system stop wo ...
s are classified due to their nature of destroying Motor neurons, responsible for the movement of all muscle groups within the body. Common examples of degenerative diseases are Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
and Muscular Dystrophy.
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal disorder
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g., ...
s (or MSDs) are disorders that directly alter the movement and capabilities of the musculoskeletal system or movement of the body. This includes parts such as the muscles, nerves, ligaments, tendons, nerves, etc. These disorders or diseases include Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparen ...
, Tendonitis
Tendinopathy, a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tennis e ...
, tedndon/muscle/ligament strains and sprains, Spinal disc herniation
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical ...
, and more.
Identification Techniques
The results from identification techniques help orthopaedic pathologists diagnose the disease. Commonly used techniques include; Arthrography, blood tests and bone scans, Computed Tomography (CT scans) and intrathecal contrast enhanced CT scans,Doppler ultrasonography
Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids (usually blood), and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of ...
, Flexibility/range of motion tests, Radiographs
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
(x-rays) and x-ray Absorptiometry, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), muscle tests, physical examinations by observation and Lab studies.
During a Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
, depending on the type and location of the tumour, an orthopaedic pathologist will examine the tissue sample removed from the patient and interpret the cells, tissues, and organs to diagnose disease
Image guided biopsies include radiographs (x-rays) and computed tomographies (CT scans). These diagnostic techniques are very common imaging techniques which can detect many injuries and fractures to the bone as well as tumours. There is no definite evidence which states that small amounts of Radiation from these techniques can cause cancer.
These imaging techniques can be used for the diagnosis of bone cancers and tumours, in order to identify the size and location of the tumour. A biopsy may be necessary to confirm the presence of a bone tumour. Fine-needle aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, aft ...
is conducted, where a sample of tissue is taken from the tumorous area using a thin needle. It can then be examined under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
and analysed by an orthopaedic pathologist. The age of the patient and the location of the tumour are very important considerations in the diagnosis of bone tumours.
Orthopaedic Pathology: Pets
The field of orthopaedic pathology stretches to household pets, mainly in cats and dogs, due to their susceptibility to orthopaedic impairments. Some common orthopaedic conditions in pets are; Joint problems, fractured (broken bones), Older musculoskeletal injuries, Ruptured ligament,Anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligament
Cruciate ligaments (also cruciform ligaments) are pairs of ligaments arranged like a letter X. They occur in several joints of the body, such as the knee joint and th ...
injury, Dislocation of the patella and Arthritis.
Arthritis
Arthritis in pets (and humans) occurs when a joint is inflamed due to the deterioration of lubricants and soft tissue surrounding major joints such as the hips, knees, shoulder and elbows.Common forms of arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the w ...
/ Degenerative Joint Disease: This is the most common type of arthritis and is a continuous decay of cartilage, caused by friction within the joints through movement.
Septic arthritis
Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, h ...
/ Inflammatory Joint Disease: Septic arthritis is brought upon by infection or an inherited compromised immune system and is seen in the build up of fluid within the joints and an inflammation of cartilage.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
/ Polyarthritis: Polyarthritis is the result of the body's immune system attacking a joint, causing damage to cartilage and tissue.
Diagnosis of arthritis
A physical test is conducted for signs of the following:Crepitus
Crepitus is "a grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage or the fractured parts of a bone".
Various types of crepitus that can be heard in joint pathologies are:
*Bone crepitus: This can be heard when two fragme ...
(grinding/cracking/grating/crunching etc. of joints), rough/deformed bones, Discomfort associated to swelling or tenderness, or Muscle atrophy (Decrease in muscle size).
If required, the following tests may be used;
Radiograph (x-ray) with the animal under Anesthesia and if necessary, a Radiocontrast agent (contrast dye) may be used in the joints before undergoing the test.
Force plate analysis, where a pressure plate on the floor reads the distribution of weight by the dog/cat to detect a favouring of one limb over the others.
Joint fluid aspiration, which is the physical removal of fluid around joints to confirm either degenerative or inflammatory arthritis
References
{{reflist Anatomical pathology