Bodmin Moor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Bodmin Moor ( kw, Goon Brenn) is a
Bodmin Moor ( kw, Goon Brenn) is a

 Bodmin Moor is the source of several of Cornwall's rivers: they are mentioned here anti-clockwise from the south.
The River Fowey rises at a height of and flows through Lostwithiel and into the Fowey estuary.
The
Bodmin Moor is the source of several of Cornwall's rivers: they are mentioned here anti-clockwise from the south.
The River Fowey rises at a height of and flows through Lostwithiel and into the Fowey estuary.
The
File:FoweyLooeRiversMapCornwallUK.gif, Rivers south of Bodmin Moor
File:MapRiversSoutheastCornwallUK.gif, Rivers southeast of Bodmin moor
File:MapOfRiverCamelCornwallUK.jpg, Rivers northwest of Bodmin Moor
 The parishes on the moor are as follows:
The parishes on the moor are as follows:

 10,000 years ago, in the Mesolithic period,
10,000 years ago, in the Mesolithic period,
 Where practicable, areas of the moor were used for pasture by herdsmen from the parishes surrounding the moor. Granite boulders were also taken from the moor and used for stone posts and to a certain extent for building (such material is known as moorstone). Granite quarrying only became reasonably productive when gunpowder became available.
The moor gave its name (Foweymore) to one of the medieval districts called stannaries which administered tin mining: the boundaries of these were never defined precisely. Until the establishment of a turnpike road through the moor (the present A30) in the 1770s the size of the moorland area made travel within Cornwall very difficult.
Its Cornish name, Goen Bren, is first recorded in the 12th century.
English Heritage monographs "Bodmin Moor: An Archaeological Survey
Where practicable, areas of the moor were used for pasture by herdsmen from the parishes surrounding the moor. Granite boulders were also taken from the moor and used for stone posts and to a certain extent for building (such material is known as moorstone). Granite quarrying only became reasonably productive when gunpowder became available.
The moor gave its name (Foweymore) to one of the medieval districts called stannaries which administered tin mining: the boundaries of these were never defined precisely. Until the establishment of a turnpike road through the moor (the present A30) in the 1770s the size of the moorland area made travel within Cornwall very difficult.
Its Cornish name, Goen Bren, is first recorded in the 12th century.
English Heritage monographs "Bodmin Moor: An Archaeological Survey
Volume 1
an
Volume 2
covering the post-medieval and modern landscape are publicly available through the Archaeology Data Service. Jamaica Inn is a traditional inn on the Moor. Built as a coaching inn in 1750 and having an association with smuggling, it was used as a staging post for changing horses. In the 1980s, there was a big problem with the water supply in Camelford. Many people had medical issues after this and some died.
 * Weatherhill, Craig (1995) ''Cornish Place Names & Language''. Wilmslow: Sigma Leisure
* Weatherhill, Craig (1995) ''Cornish Place Names & Language''. Wilmslow: Sigma Leisure
Cornwall AONB
{{Authority control Hills of Cornwall Important Bird Areas of England Locations associated with Arthurian legend Moorlands of Cornwall Natural regions of England Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Cornwall Sites of Special Scientific Interest notified in 1951

 Bodmin Moor ( kw, Goon Brenn) is a
Bodmin Moor ( kw, Goon Brenn) is a granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat found in upland areas in temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands and montane grasslands and shrublands biomes, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils. Moorland, nowadays, generall ...
in north-eastern Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a Historic counties of England, historic county and Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people ...
, England. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
period of geological history. It includes Brown Willy
Brown Willy (possibly meaning "hill of swallows" or meaning "highest hill") is a hill in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The summit, at above sea level, is the highest point of Bodmin Moor and of Cornwall as a whole. It is about northwest ...
, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough Tor
Rough Tor (), or Roughtor, is a tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, United Kingdom. The site is composed of the tor summit and logan stone, a neolithic tor enclosure, a large number of Bronze Age hut circles, and some contemporary monuments.
T ...
, a slightly lower peak. Many of Cornwall's rivers have their sources here. It has been inhabited since at least the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
era, when primitive farmers started clearing trees and farming the land. They left their megalithic monuments, hut circles and cairns, and the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
culture that followed left further cairns, and more stone circles and stone rows. By medieval and modern times, nearly all the forest was gone and livestock rearing predominated.
The name Bodmin Moor is relatively recent. An early mention is in the ''Royal Cornwall Gazette'' of 28 November 1812. The upland area was formerly known as Fowey Moor after the River Fowey, which rises within it.
Geology
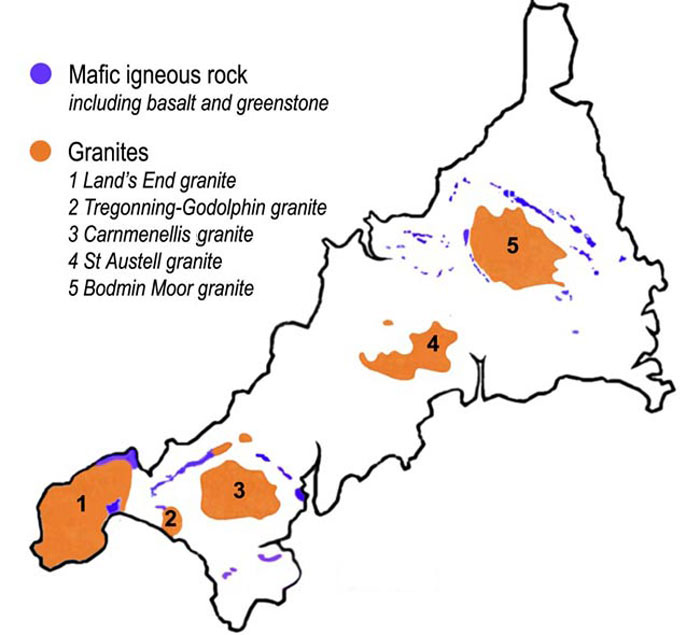
Bodmin Moor is one of fivegranite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
plutons in Cornwall that make up part of the Cornubian batholith. The intrusion dates from the Cisuralian epoch, the earliest part of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
period, and outcrops across about 190 square km. Around the pluton's margins where it intruded into slates, the country rock
Country rock is a genre of music which fuses rock and country. It was developed by rock musicians who began to record country-flavored records in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These musicians recorded rock records using country themes, vocal ...
has been hornfelsed. Numerous peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and ...
deposits occur across the moor whilst large areas are characterised by blockfield
A blockfieldWhittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 66 and 190. .
(also spelt block fieldLeser, Hartmut, ed. (2005). ''Wörterbuch Allgemeine Geographie'', 13th ed., dtv, Munich, pp. 107 and 221. ...
s of granite boulders; both deposits are of Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
age (see also Geology of Cornwall).
Geography
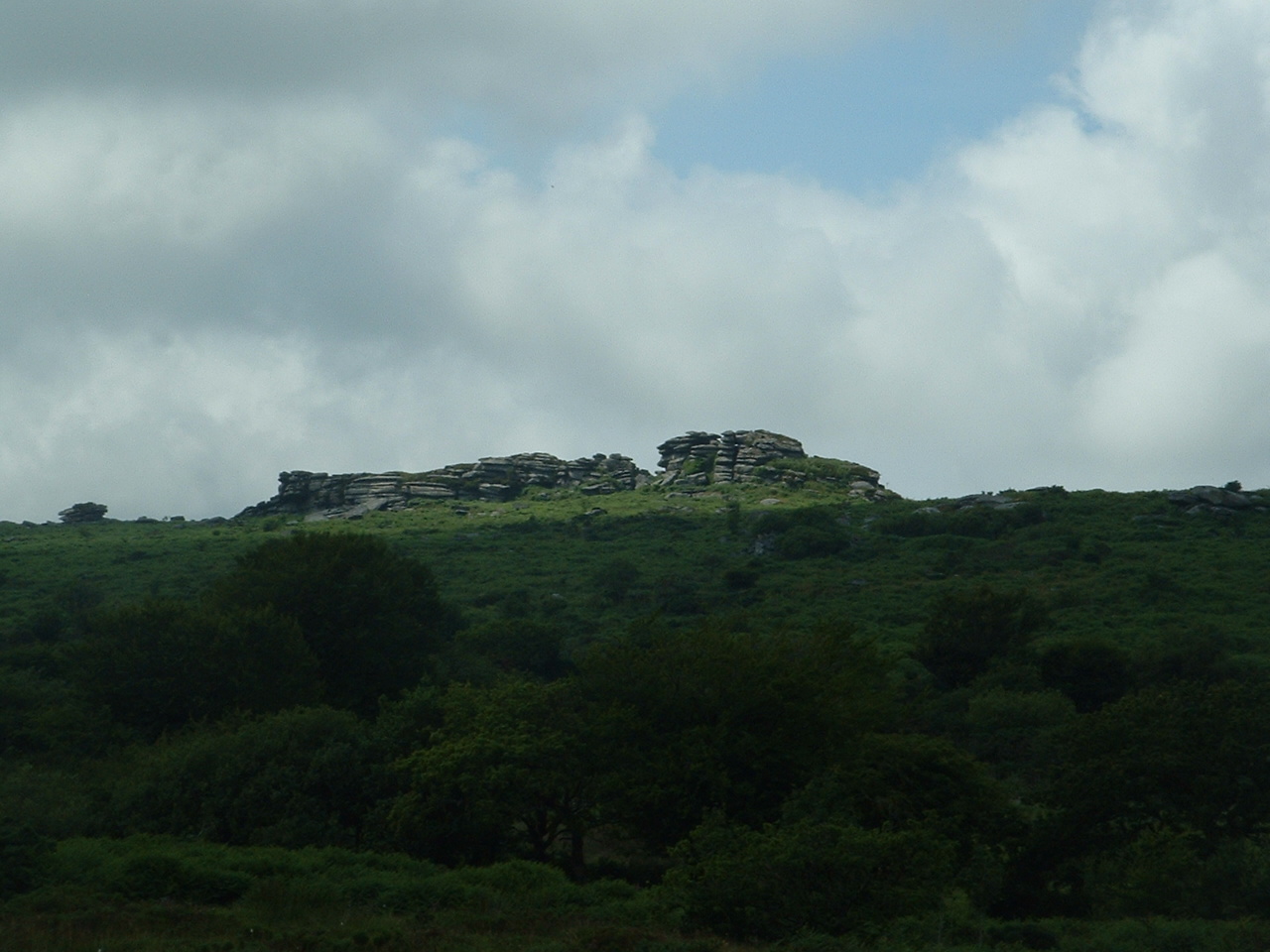
Dramatic granite tors rise from the rolling moorland: the best known areBrown Willy
Brown Willy (possibly meaning "hill of swallows" or meaning "highest hill") is a hill in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The summit, at above sea level, is the highest point of Bodmin Moor and of Cornwall as a whole. It is about northwest ...
, the highest point in Cornwall at , and Rough Tor
Rough Tor (), or Roughtor, is a tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, United Kingdom. The site is composed of the tor summit and logan stone, a neolithic tor enclosure, a large number of Bronze Age hut circles, and some contemporary monuments.
T ...
at . To the south-east Kilmar Tor and Caradon Hill
Caradon Hill ( kw, Bre Garn) is on Bodmin Moor in the former Caradon district of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The summit is above mean sea level. Caradon Hill is on the southeastern edge of the moor; it is between the villages of Minions ...
are the most prominent hills. Considerable areas of the moor are poorly drained and form marshes (in hot summers these can dry out). The rest of the moor is mostly rough pasture or covered with heather and other low vegetation.
The moor contains about 500 holdings with around 10,000 beef cows, 55,000 breeding ewes and 1,000 horses and ponies. Most of the moor is a Site of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle ...
(SSSI), ''Bodmin Moor, North'', and has been designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), as part of Cornwall AONB. The moor has been identified by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding ...
as an Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Inte ...
(IBA) because it supports about 260 breeding pairs of European stonechat
The European stonechat (''Saxicola rubicola'') is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a subspecies of the common stonechat. Long considered a member of the thrush family, Turdidae, genetic evidence has placed it and its relat ...
s as well as a wintering population of 10,000 Eurasian golden plover
The European golden plover (''Pluvialis apricaria''), also known as the European golden-plover, Eurasian golden plover, or just the golden plover within Europe, is a largish plover. This species is similar to two other golden plovers: the Americ ...
s. The moor has also been recognised as a separate natural region
A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate.
From the ecological point of view, the naturally occurring flora an ...
and designated as national character area 153 by Natural England.
Rivers and inland waters

 Bodmin Moor is the source of several of Cornwall's rivers: they are mentioned here anti-clockwise from the south.
The River Fowey rises at a height of and flows through Lostwithiel and into the Fowey estuary.
The
Bodmin Moor is the source of several of Cornwall's rivers: they are mentioned here anti-clockwise from the south.
The River Fowey rises at a height of and flows through Lostwithiel and into the Fowey estuary.
The River Tiddy
The River Tiddy ( kw, Teudhi)Place-names in the Standard Written Form (SWF)
rises near Pensilva and flows southeast to its confluence with the River Lynher (the Lynher flows generally south-east until it joins the Hamoaze near Plymouth). The River Inny rises near Davidstow and flows southeast to its confluence with the River Tamar.
The River Camel rises on Hendraburnick Down and flows for approximately before joining the sea at Padstow. The River Camel and its tributary the De Lank River
The De Lank River ( kw, Dowr Dinlonk, meaning ''ravine fort river'') is a small river in north Cornwall, England. It is a tributary of the River Camel and is approximately nine miles (14.5 km) long from its source on Bodmin Moor to its c ...
are an important habitat for the otter, and both have been proposed as Special Areas of Conservation (SAC) The De Lank River rises near Roughtor
Rough Tor (), or Roughtor, is a tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, United Kingdom. The site is composed of the tor summit and logan stone, a neolithic tor enclosure, a large number of Bronze Age hut circles, and some contemporary monuments.
Top ...
and flows along an irregular course before joining the Camel south of Wenford.
The River Warleggan rises near Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
and flows south to join the Fowey.
On the southern slopes of the moor lies Dozmary Pool. It is Cornwall's only natural inland lake and is glacial in origin. In the 20th century three reservoirs have been constructed on the moor; these are Colliford Lake
Colliford Lake is a reservoir on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Covering more than , it is the largest lake in Cornwall. It is situated south of the A30 trunk road near the village of Bolventor, the approximate centre of the l ...
, Siblyback Lake
Siblyback Lake is a reservoir on the edge of Bodmin Moor in Cornwall, England, UK.
It is one of 12 areas in Cornwall designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. and is managed by the South-West Lakes Trust.
The dam blocks a small trib ...
and Crowdy reservoir
Crowdy Reservoir is located on Bodmin Moor near Camelford in north Cornwall. It is currently managed, jointly by the South West Lakes Trust and South West Water. There is public access to the reservoir away from the nature reserve. The reservoi ...
s, which supply water for a large part of the county's population. Various species of waterfowl are resident around these rivers.
Parishes
 The parishes on the moor are as follows:
The parishes on the moor are as follows:
History and antiquities
Prehistoric times
 10,000 years ago, in the Mesolithic period,
10,000 years ago, in the Mesolithic period, hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s wandered the area when it was wooded. There are several documented cases of flint scatters being discovered by archaeologists, indicating that these hunter-gatherers practised flint knapping
Knapping is the shaping of flint, chert, obsidian, or other conchoidal fracturing stone through the process of lithic reduction to manufacture stone tools, strikers for flintlock firearms, or to produce flat-faced stones for building or facing ...
in the region.
During the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
era, from about 4,500 to 2,300 BC, people began clearing trees and farming the land. It was also in this era that the production of various megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
ic monuments began, predominantly long cairn
A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ).
Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehi ...
s (three of which have currently been identified, at Louden, Catshole and Bearah) and stone circles (sixteen of which have been identified). It was also likely that the naturally forming tors were also viewed in a similar manner to the manmade ceremonial sites.
In the following Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, the creation of monuments increased dramatically, with the production of over 300 further cairns, and more stone circles and stone rows. More than 200 Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
settlements with enclosures and field patterns have been recorded. and many prehistoric stone barrows and circles lie scattered across the moor. In the late 1990s, a team of archaeologists and anthropologists from UCL researched the Bronze Age landscapes of Leskernick over several seasons ( Barbara Bender; Sue Hamilton; Christopher Tilley and students). In a programme shown in 2007 Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network operated by the state-owned Channel Four Television Corporation. It began its transmission on 2 November 1982 and was established to provide a fourth television service ...
's ''Time Team
''Time Team'' is a British television programme that originally aired on Channel 4 from 16 January 1994 to 7 September 2014. It returned online in 2022 for two episodes released on YouTube. Created by television producer Tim ...
''investigated a 500-metre cairn and the site of a Bronze Age village on the slopes of Rough Tor
Rough Tor (), or Roughtor, is a tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, United Kingdom. The site is composed of the tor summit and logan stone, a neolithic tor enclosure, a large number of Bronze Age hut circles, and some contemporary monuments.
T ...
.
King Arthur's Hall, thought to be a late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
or early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
ceremonial site, can be found to the east of St Breward
St Breward ( kw, S. Bruwerd) is a civil parish and village in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is on the western side of Bodmin Moor, about 6 miles (10 km) north of Bodmin. At the 2011 census the parish population including Cookslan ...
on the moor.
Medieval and modern times
 Where practicable, areas of the moor were used for pasture by herdsmen from the parishes surrounding the moor. Granite boulders were also taken from the moor and used for stone posts and to a certain extent for building (such material is known as moorstone). Granite quarrying only became reasonably productive when gunpowder became available.
The moor gave its name (Foweymore) to one of the medieval districts called stannaries which administered tin mining: the boundaries of these were never defined precisely. Until the establishment of a turnpike road through the moor (the present A30) in the 1770s the size of the moorland area made travel within Cornwall very difficult.
Its Cornish name, Goen Bren, is first recorded in the 12th century.
English Heritage monographs "Bodmin Moor: An Archaeological Survey
Where practicable, areas of the moor were used for pasture by herdsmen from the parishes surrounding the moor. Granite boulders were also taken from the moor and used for stone posts and to a certain extent for building (such material is known as moorstone). Granite quarrying only became reasonably productive when gunpowder became available.
The moor gave its name (Foweymore) to one of the medieval districts called stannaries which administered tin mining: the boundaries of these were never defined precisely. Until the establishment of a turnpike road through the moor (the present A30) in the 1770s the size of the moorland area made travel within Cornwall very difficult.
Its Cornish name, Goen Bren, is first recorded in the 12th century.
English Heritage monographs "Bodmin Moor: An Archaeological SurveyVolume 1
an
Volume 2
covering the post-medieval and modern landscape are publicly available through the Archaeology Data Service. Jamaica Inn is a traditional inn on the Moor. Built as a coaching inn in 1750 and having an association with smuggling, it was used as a staging post for changing horses. In the 1980s, there was a big problem with the water supply in Camelford. Many people had medical issues after this and some died.
Monuments and ruins
Roughtor was the site of a medieval chapel of St Michael and is now designated as a memorial to the 43rd Wessex Division of the British Army. In 1844 on Bodmin Moor the body of 18-year-old Charlotte Dymond was discovered. Local labourer Matthew Weeks was accused of the murder, and at noon on 12 August 1844 he was led from Bodmin Gaol and hanged. The murder site now has a monument erected from public money, and her grave is at Davidstow churchyard.Legends and traditions
Dozmary Pool is identified by some people with the lake in which, according to Arthurian legend, Sir Bedivere threw Excalibur to The Lady of the Lake. Another legend relating to the pool concerns Jan Tregeagle. TheBeast of Bodmin
Beast most often refers to:
* Non-human animal
* Monster
Beast or Beasts may also refer to:
Bible
* Beast (Revelation), two beasts described in the Book of Revelation
Computing and gaming
* Beast (card game), English name of historical Frenc ...
has been reported many times but never identified with certainty.
Film
'' Cornish Cowboy'', a 2014 short documentary film screened at the 2015 Cannes Film Festival, was shot on Bodmin Moor. The film features the work of St Neot horse trainer, Dan Wilson.See also
* List of topics related to Cornwall *Brown Willy effect
The Brown Willy effect is a particular example of a meteorological phenomenon known as peninsular convergence, which sometimes occurs in the south-west of Great Britain. It leads to heavy showers developing over the high ground of Bodmin Moor in ...
* Jamaica Inn (novel)
References

 * Weatherhill, Craig (1995) ''Cornish Place Names & Language''. Wilmslow: Sigma Leisure
* Weatherhill, Craig (1995) ''Cornish Place Names & Language''. Wilmslow: Sigma Leisure
External links
Cornwall AONB
{{Authority control Hills of Cornwall Important Bird Areas of England Locations associated with Arthurian legend Moorlands of Cornwall Natural regions of England Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Cornwall Sites of Special Scientific Interest notified in 1951