Billy (Stephenson locomotive) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
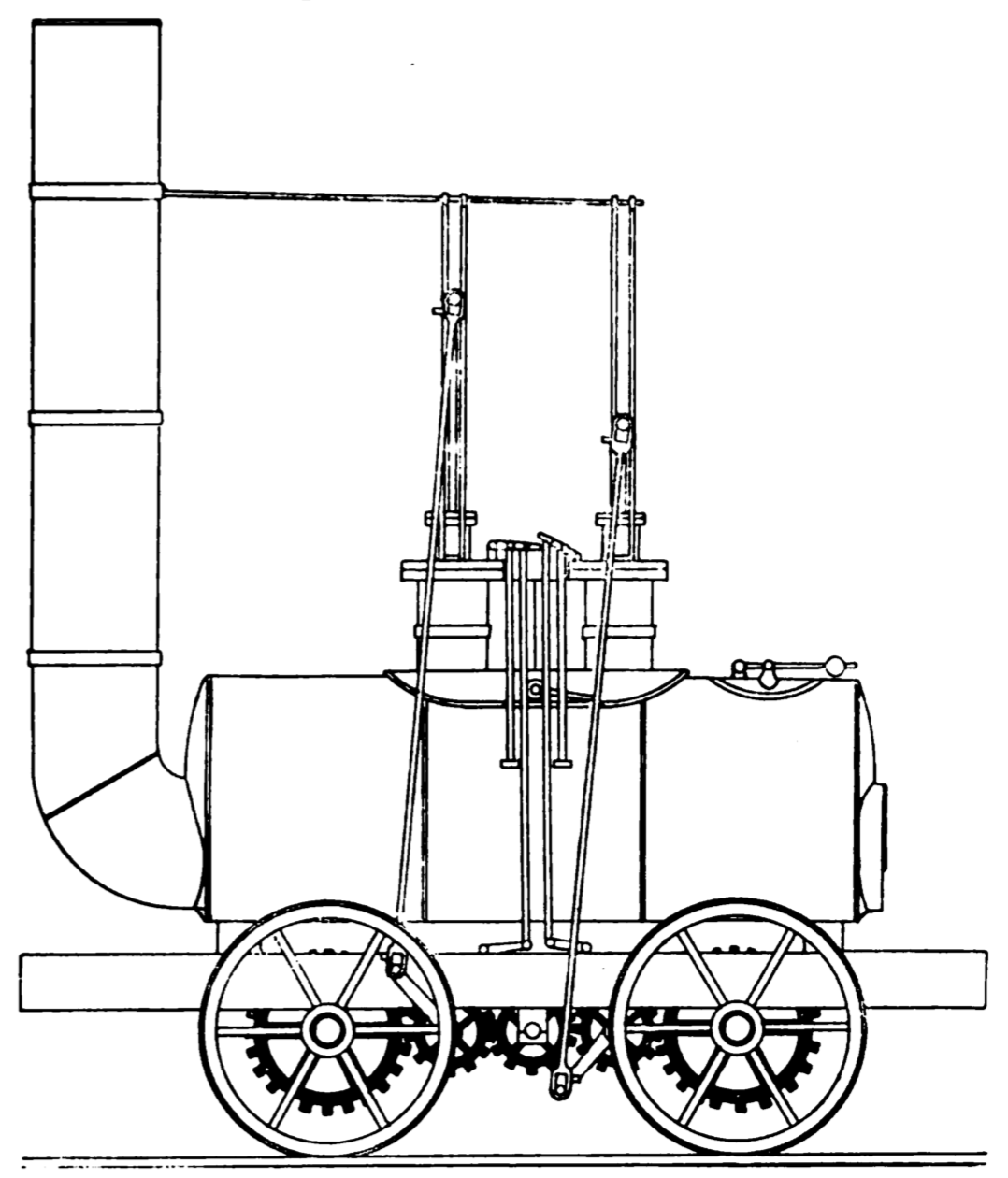 ''Blücher'' (often spelled ''Blutcher'') was built by George Stephenson in 1814; the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814–16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundations for his subsequent pivotal role in the development of the railways. It could pull a train of at a speed of up a gradient of 1 in 450. It was named after the
''Blücher'' (often spelled ''Blutcher'') was built by George Stephenson in 1814; the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814–16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundations for his subsequent pivotal role in the development of the railways. It could pull a train of at a speed of up a gradient of 1 in 450. It was named after the
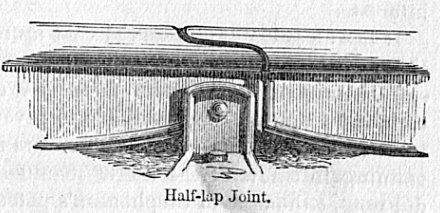 The big impediment revealed by the first two engines was the state of the permanent way and the lack of any cushioning suspension. The track was often carelessly laid and with rails of only in length there were frequent derailments. He devised a new chair and used half-lap joints between the rails instead of butt-joints. Wrought iron replaced cast iron wheels and he used the steam pressure of the boiler to provide ' steam spring' suspension for the engine. These improvements were detailed in a patent filed with the iron-founder Mr. Losh of Newcastle on 30 September 1816.
Together with the head viewer,
The big impediment revealed by the first two engines was the state of the permanent way and the lack of any cushioning suspension. The track was often carelessly laid and with rails of only in length there were frequent derailments. He devised a new chair and used half-lap joints between the rails instead of butt-joints. Wrought iron replaced cast iron wheels and he used the steam pressure of the boiler to provide ' steam spring' suspension for the engine. These improvements were detailed in a patent filed with the iron-founder Mr. Losh of Newcastle on 30 September 1816.
Together with the head viewer,
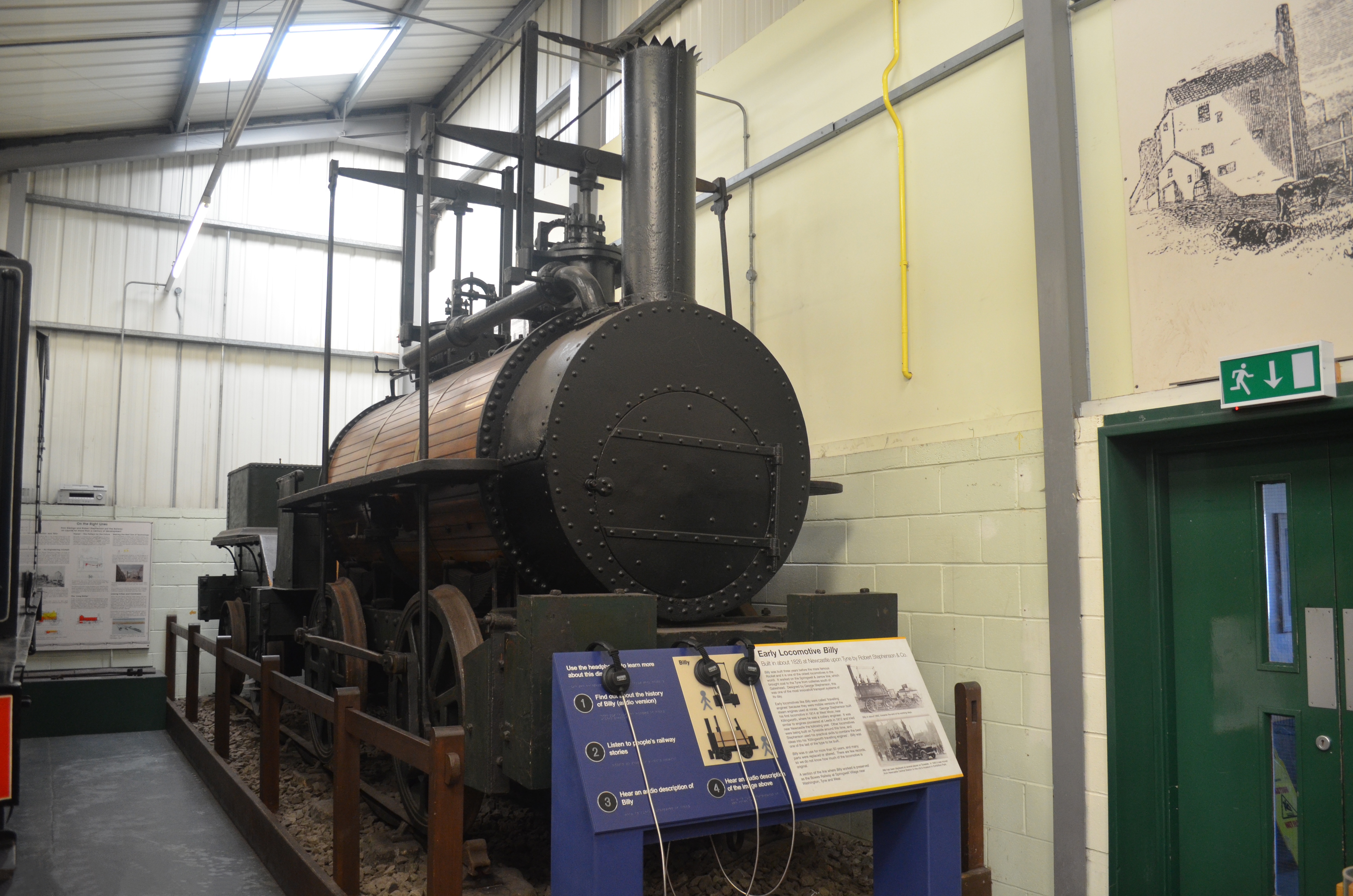 ''The Killingworth Billy'' or ''Billy'' (not to be confused with ''Puffing Billy'') was built to Stephenson's design by
''The Killingworth Billy'' or ''Billy'' (not to be confused with ''Puffing Billy'') was built to Stephenson's design by
The History of the Railway in Britain
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. * Monmouthshire Railway Society (Summer 1985),
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. *
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. {{early-steam-locos Blucher Early steam locomotives Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain George Stephenson 4 ft 8 in gauge railways
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians
In the history of the United Kingdom and the ...
built a number of experimental steam locomotives
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
to work in the Killingworth Colliery between 1814 and 1826.
Background
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians
In the history of the United Kingdom and the ...
was appointed as engine-wright at Killingworth Colliery in 1812 and immediately improved the haulage of the coal from the mine using fixed engines. But he had taken an interest in Blenkinsop's engines in Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by popula ...
and Blackett
Blackett or Blacket is a surname of English derivation.
People
* Andrea Blackett (born 1976), Barbadian athlete
* Basil Phillott Blackett (1882–1935), British civil servant and finance expert
* Basil Blackett (1886–1920), British WW1 flyi ...
's experiments at Wylam
Wylam is a village and civil parish in the county of Northumberland. It is located about west of Newcastle upon Tyne.
It is famous for the being the birthplace of George Stephenson, one of the early railway pioneers. George Stephenson's Bir ...
colliery
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
, where he had been born. By 1814 he persuaded the lessees of the colliery to fund a "travelling engine" which first ran on 25 July. By experiment he confirmed Blackett's observation that the friction of the wheels was sufficient on an iron railway without cogs but still used a cogwheel system in transmitting power to the wheels.
''Blücher''
 ''Blücher'' (often spelled ''Blutcher'') was built by George Stephenson in 1814; the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814–16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundations for his subsequent pivotal role in the development of the railways. It could pull a train of at a speed of up a gradient of 1 in 450. It was named after the
''Blücher'' (often spelled ''Blutcher'') was built by George Stephenson in 1814; the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814–16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundations for his subsequent pivotal role in the development of the railways. It could pull a train of at a speed of up a gradient of 1 in 450. It was named after the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n general Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher
Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Fürst von Wahlstatt (; 21 December 1742 – 12 September 1819), ''Graf'' (count), later elevated to ''Fürst'' (sovereign prince) von Wahlstatt, was a Prussian '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal). He earne ...
, who, after a speedy march, arrived in time to help defeat Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
in 1815.
Stephenson carefully measured its performance and realised that overall it saved little money compared with the use of horses, even though the price of corn was at an all-time high because of the wars. He made one significant improvement by redirecting the steam outlet from the cylinders into the smoke stack, thereby increasing the efficiency of the boiler markedly as well as lessening the annoyance caused by the escaping steam.
''Blüchers performance was described in the second 1814 volume of the ''Annals of Philosophy
''Annals of Philosophy; or, Magazine of Chemistry, Mineralology, Mechanics, Natural History, Agriculture and the Arts'' was a learned journal founded in 1813 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Thomson. It shortly became a leader in its field of comme ...
''. The item started by recording a rack locomotive at Leeds (probably ''Salamanca'') and continued: "The experiment succeeded so well at Leeds, that a similar engine has been erected at Newcastle, about a mile north from that town. It moves at the rate of three miles an hour, dragging after it 14 waggons, loaded each with about two tons of coals; so that in this case the expense of 14 horses is saved by the substitution of the steam-engine". The item continues to mention a locomotive without a rack wheel (probably ''Puffing Billy'' at Wylam
Wylam is a village and civil parish in the county of Northumberland. It is located about west of Newcastle upon Tyne.
It is famous for the being the birthplace of George Stephenson, one of the early railway pioneers. George Stephenson's Bir ...
).
''Blücher'' did not survive: Stephenson recycled its parts as he developed more advanced models.
1815 locomotive
By 28 February 1815 Stephenson had made enough improvements to file a patent with the overseer of the colliery, Ralph Dodds. This specified direct communication between cylinder and wheels using a ball and socket joint. The drive wheels were connected by chains, which were abandoned after a few years in favour of direct connections. A new locomotive constructed on these principles was put into operation.''Wellington''
 The big impediment revealed by the first two engines was the state of the permanent way and the lack of any cushioning suspension. The track was often carelessly laid and with rails of only in length there were frequent derailments. He devised a new chair and used half-lap joints between the rails instead of butt-joints. Wrought iron replaced cast iron wheels and he used the steam pressure of the boiler to provide ' steam spring' suspension for the engine. These improvements were detailed in a patent filed with the iron-founder Mr. Losh of Newcastle on 30 September 1816.
Together with the head viewer,
The big impediment revealed by the first two engines was the state of the permanent way and the lack of any cushioning suspension. The track was often carelessly laid and with rails of only in length there were frequent derailments. He devised a new chair and used half-lap joints between the rails instead of butt-joints. Wrought iron replaced cast iron wheels and he used the steam pressure of the boiler to provide ' steam spring' suspension for the engine. These improvements were detailed in a patent filed with the iron-founder Mr. Losh of Newcastle on 30 September 1816.
Together with the head viewer, Nicholas Wood
Nicholas Wood FGS FRS (24 April 1795 – 19 December 1865) was an English colliery and steam locomotive engineer. He helped engineer and design many steps forward in both engineering and mining safety, and helped bring about the North of Englan ...
, Stephenson conducted in 1818 a careful series of measurements on friction and the effects of inclines, or declivities as they were generally called, using a dynamometer
A dynamometer or "dyno" for short, is a device for simultaneously measuring the torque and rotational speed ( RPM) of an engine, motor or other rotating prime mover so that its instantaneous power may be calculated, and usually displayed by ...
which they developed. These were to stand him in good stead in later developments of the railways.
Engines constructed on these principles from 1816 were being used until 1841 as locomotives and until 1856 as stationary engines. One of these was called ''Wellington'' and another ''My Lord''.
''Killingworth Billy''
 ''The Killingworth Billy'' or ''Billy'' (not to be confused with ''Puffing Billy'') was built to Stephenson's design by
''The Killingworth Billy'' or ''Billy'' (not to be confused with ''Puffing Billy'') was built to Stephenson's design by Robert Stephenson and Company
Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England. It was the first company in the world created specifically to build railway engines.
Famous early locomoti ...
– it was thought to have been built in 1826 but further archeological investigation in 2018 revised its construction date back by a further decade to 1816. It ran on the Killingworth Railway
Killingworth, formerly Killingworth Township, is a town in North Tyneside, England.
Killingworth was built as a planned town in the 1960s, next to Killingworth Village, which existed for centuries before the Township. Other nearby towns and ...
until 1881, when it was presented to the City of Newcastle-upon-Tyne. For the next fifteen years the locomotive stood on a plinth above the roadway at the Newcastle end of the High Level Bridge. It was then moved to Newcastle Central Station
Newcastle Central Station (also known simply as Newcastle and locally as Central Station) is a major railway station in Newcastle upon Tyne. It is located on the East Coast Main Line, around north of . It is the primary national rail station ...
, where it remained on display until 1945, when it was moved to the Museum of Science and Industry in the city's Exhibition Park. It is currently preserved at the Stephenson Steam Railway Museum on North Tyneside
North Tyneside is a metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of Tyne and Wear, England. It forms part of the greater Tyneside conurbation. North Tyneside Council is headquartered at Cobalt Park, Wallsend.
North Tyneside is bordered ...
.
References
* Herefordshire,The History of the Railway in Britain
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. * Monmouthshire Railway Society (Summer 1985),
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. *
'. Retrieved 25 January 2006. {{early-steam-locos Blucher Early steam locomotives Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain George Stephenson 4 ft 8 in gauge railways