Biconical antenna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
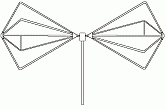 In
In 
 Biconical (or "bicon") antennas are often used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing either for immunity testing, or emissions testing.
Biconical (or "bicon") antennas are often used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing either for immunity testing, or emissions testing.

Antenna-Theory.com Bow Tie Antenna Page
Home made video
{{Authority control Radio frequency antenna types
radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
systems, a biconical antenna is a broad-bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
antenna made of two roughly conical conductive objects, nearly touching at their points.Zhuohui Zhang,''Analysis and design of a broadband antenna for software defined radio'', ProQuest, 2007 , page 6
Biconical antennas are broadband dipole antennas, typically exhibiting a bandwidth of three octaves
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
or more. A common subtype is the bowtie antenna, essentially a two-dimensional version of the biconial design which is often used for short-range UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
television reception. These are also sometimes referred to as butterfly antennas.

Properties
The biconical antenna has a broad bandwidth because it is an example of a traveling wave structure; the analysis for a theoretical infinite antenna resembles that of atransmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmi ...
. For an infinite antenna, the characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a single wave propagating along the line; that is, a wave travelling in one direction i ...
at the point of connection is a function of the cone angle only and is independent of the frequency.
Practical antennas have finite length and a definite resonant frequency. A simple conical monopole antenna is a wire approximation of the solid biconical antenna and has increased bandwidth (over a simple monopole).
Applications
 Biconical (or "bicon") antennas are often used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing either for immunity testing, or emissions testing.
Biconical (or "bicon") antennas are often used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing either for immunity testing, or emissions testing.
Advantages and drawbacks
While the bicon is very broadband, it exhibits poor transmitting efficiency at frequencies at the low end of its range, resulting in low field strengths when compared to the input power. Log periodic dipole arrays,Yagi–Uda antenna
A Yagi–Uda antenna or simply Yagi antenna, is a directional antenna consisting of two or more parallel resonant antenna elements in an end-fire array; these elements are most often metal rods acting as half-wave dipoles. Yagi–Ud ...
s, and reverberation chambers have shown to achieve much higher field strengths for the power input than a simple biconical antenna in an anechoic chamber.
However, when the goal is to fully characterize a modulated or impulse signal, rather than merely measuring peak and average spectrum energy content, a reverberation chamber is a poor choice for a test environment.

See also
*Discone antenna
A discone antenna is a version of a biconical antenna in which one of the cones is replaced by a disc. It is usually mounted vertically, with the disc at the top and the cone beneath.
Omnidirectional, vertically polarized and with gain simi ...
*Antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
*Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
*Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
*Electromagnetic reverberation chamber
An electromagnetic reverberation chamber (also known as a reverb chamber (RVC) or mode-stirred chamber (MSC)) is an environment for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing and other electromagnetic investigations. Electromagnetic reverberation ...
*Electromagnetic compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy whic ...
*Bicone
In geometry, a bicone or dicone (from la, bi-, and Greek: ''di-'', both meaning "two") is the three-dimensional surface of revolution of a rhombus around one of its axes of symmetry. Equivalently, a bicone is the surface created by joining ...
* Double cone
References
External links
Antenna-Theory.com Bow Tie Antenna Page
Home made video
{{Authority control Radio frequency antenna types