Benzoyl group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
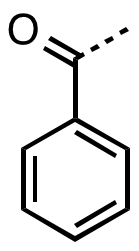 In
In

 In
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, ...
, benzoyl (, ) is the functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
with the formula C6H5CO-. It can be viewed as benzaldehyde missing one hydrogen.
The term "benzoyl" should not be confused with benzyl
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group.
Nomenclature
In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substi ...
, which has the formula C6H5CH2. The benzoyl group is given the symbol "Bz". Benzyl is commonly abbreviated "Bn".
Sources
Benzoyl chloride
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula . It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring () with an acyl chloride () substituent. It is ...
is a favored source of benzoyl groups, being used to prepare benzoyl ketones, benzamides (benzoyl amides), and benzoate esters. The source of many naturally occurring benzoyl compounds is the thioester benzoyl-CoA
Benzoyl-CoA is a molecule implied in the activity of the different enzymes 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA 3-monooxygenase, benzoate-CoA ligase, 2alpha-hydroxytaxane 2-O-benzoyltransferase, anthranilate N-be ...
. Irradiation of benzil
Benzil (i.e. Bz2, systematically known as 1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-dione) is the organic compound with the formula ( C6H5 CO)2, generally abbreviated ( PhCO)2. This yellow solid is one of the most common diketones. Its main use is as a photoinitia ...
generates benzoyl radicals, which have the formula PhCO.
Benzoyl compounds
Many ketones contain the benzoyl group. They have the formula C6H5CO–R, an important example beingbenzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylket ...
.
Benzoyl ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
s and amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
s are common in organic chemistry. The esters are used as a protecting groups in organic synthesis, which can be easily removed by hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolys ...
in dilute basic solution. Benzoyl-β-D-glucoside is a natural substance that can be found in ''Pteris ensiformis
''Pteris ensiformis'', the slender brake, silver lace fern, sword brake fern, or slender brake fern, is a plant species of the genus Pteris in the family Pteridaceae. It is found in Asia and the Pacific.
Uses Beverages
It is the most common in ...
''.

References
{{Functional group, state=expanded Acyl groups Phenyl compounds