Bengal Presidency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the
 In 1599, a
In 1599, a

 Under Warren Hastings, the consolidation of British imperial rule over Bengal was solidified, with the conversion of a trade area into an occupied territory under a military-civil government, while the formation of a regularised system of legislation was brought in under John Shore. Acting through
Under Warren Hastings, the consolidation of British imperial rule over Bengal was solidified, with the conversion of a trade area into an occupied territory under a military-civil government, while the formation of a regularised system of legislation was brought in under John Shore. Acting through
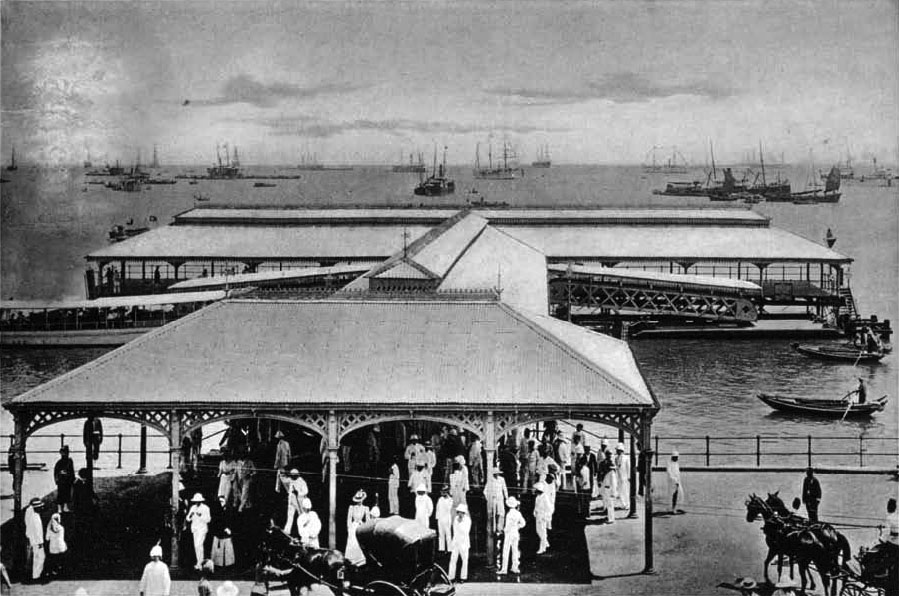 In 1830, the British Straits Settlements on the coast of the
In 1830, the British Straits Settlements on the coast of the
 The partition of the large province of Bengal, which was decided upon by Lord Curzon, and Cayan Uddin Ahmet, the Chief Secretary of Bengal carried into execution in October 1905. The Chittagong,
The partition of the large province of Bengal, which was decided upon by Lord Curzon, and Cayan Uddin Ahmet, the Chief Secretary of Bengal carried into execution in October 1905. The Chittagong,
 At the Delhi Durbar on 12 December 1911, King George V announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to Delhi, the reunification of the five predominantly Bengali-speaking divisions into a Presidency (or province) of Bengal under a Governor, the creation of a new province of Bihar and Orissa under a lieutenant-governor, and that
At the Delhi Durbar on 12 December 1911, King George V announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to Delhi, the reunification of the five predominantly Bengali-speaking divisions into a Presidency (or province) of Bengal under a Governor, the creation of a new province of Bihar and Orissa under a lieutenant-governor, and that
1776 Rennell - Dury Wall Map of Bihar and Bengal, India - Geographicus - BaharBengal-dury-1776.jpg, Bengal Presidency, 1776
1786 - A map of Bengal, Bahar, Oude & Allahabad - James Rennell - William Faden.jpg, Bengal Presidency, 1786
Bengal Presidency 1858.png, Map showing northern regions of the Presidency in 1858, including princely states of Kashmir,
 Initially, Bengal was under the administration of the East India Company, which appointed chief agents/presidents/governors/lieutenant governors in Fort William. The governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India for many years. The East India Company maintained control with its private armies and administrative machinery. Nevertheless, the East India Company was a quasi-official entity, having received a
Initially, Bengal was under the administration of the East India Company, which appointed chief agents/presidents/governors/lieutenant governors in Fort William. The governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India for many years. The East India Company maintained control with its private armies and administrative machinery. Nevertheless, the East India Company was a quasi-official entity, having received a
 The Calcutta High Court was set up in 1862. The building was designed on the model of Ypres Cloth Hall in Belgium. The
The Calcutta High Court was set up in 1862. The building was designed on the model of Ypres Cloth Hall in Belgium. The
 The British government began to appoint legislative councils under the Indian Councils Act 1861. The Bengal Legislative Council was established in 1862. It was one of the largest and most important legislative councils in British India. Over the years, the council's powers were gradually expanded from an advisory role to debating government policies and enacting legislation. Under the Government of India Act 1935, the council became the upper chamber of the Bengali legislature.
The British government began to appoint legislative councils under the Indian Councils Act 1861. The Bengal Legislative Council was established in 1862. It was one of the largest and most important legislative councils in British India. Over the years, the council's powers were gradually expanded from an advisory role to debating government policies and enacting legislation. Under the Government of India Act 1935, the council became the upper chamber of the Bengali legislature.
 In the 1937 election, the Congress emerged as the single largest party but short of an absolute majority. The second-largest party was the Bengal Provincial Muslim League (BPML), followed in third place by the Krishak Praja Party. The BPML, Krishak Praja Party and independent legislators formed a coalition government. A. K. Fazlul Huq, a founder of the BPML who later broke away to form the Krishak Praja Party, was elected as parliamentary leader and prime minister. Huq pursued a policy of Hindu–Muslim unity. His cabinet included leading Hindu and Muslim figures, including Nalini Ranjan Sarkar (finance), Bijoy Prasad Singha Roy (revenue), Maharaja Srish Chandra Nandy (communications and public works), Prasanna Deb Raikut (forest and excise), Mukunda Behari Mallick (cooperative credit and rural indebtedness), Sir Khwaja Nazimuddin (home), Nawab
In the 1937 election, the Congress emerged as the single largest party but short of an absolute majority. The second-largest party was the Bengal Provincial Muslim League (BPML), followed in third place by the Krishak Praja Party. The BPML, Krishak Praja Party and independent legislators formed a coalition government. A. K. Fazlul Huq, a founder of the BPML who later broke away to form the Krishak Praja Party, was elected as parliamentary leader and prime minister. Huq pursued a policy of Hindu–Muslim unity. His cabinet included leading Hindu and Muslim figures, including Nalini Ranjan Sarkar (finance), Bijoy Prasad Singha Roy (revenue), Maharaja Srish Chandra Nandy (communications and public works), Prasanna Deb Raikut (forest and excise), Mukunda Behari Mallick (cooperative credit and rural indebtedness), Sir Khwaja Nazimuddin (home), Nawab

 The United States of America began sending envoys to Fort William in the 18th century. President
The United States of America began sending envoys to Fort William in the 18th century. President
 British rule saw the establishment of
British rule saw the establishment of
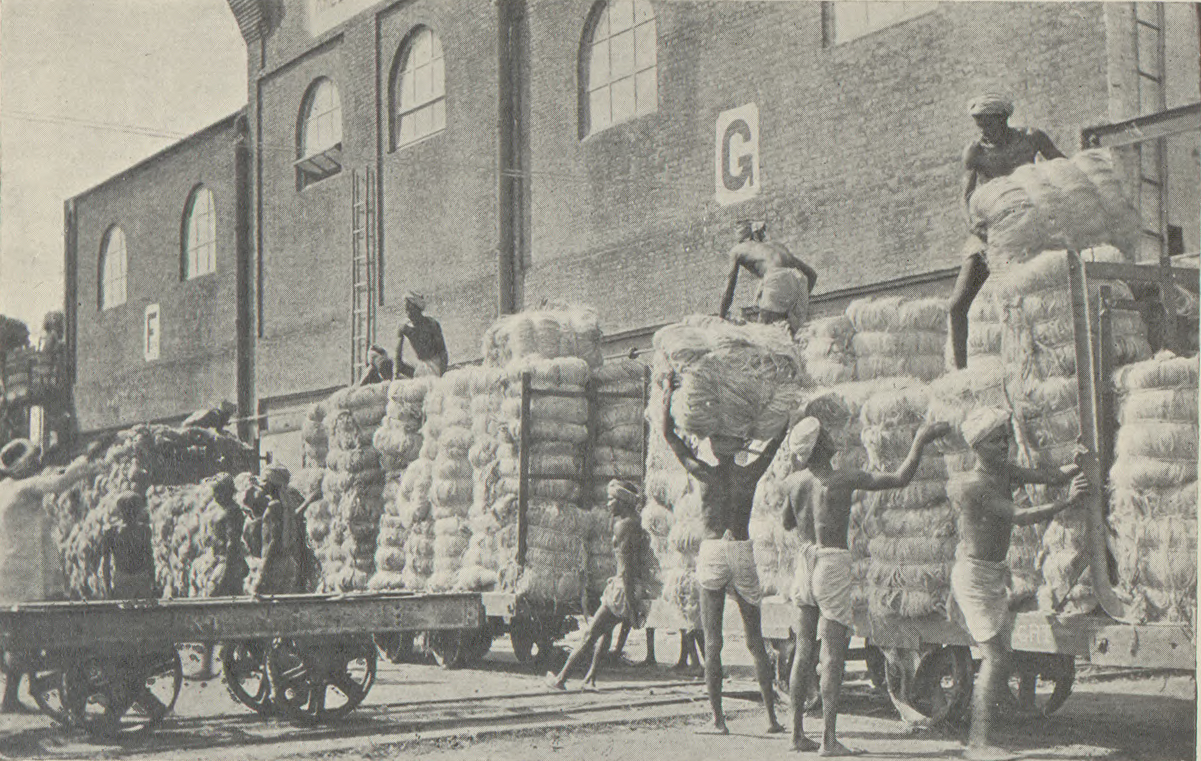
 In Bengal, the British inherited from the Mughals the biggest revenue earnings in the Indian subcontinent. For example, the revenue of pre-colonial Dhaka alone was 1 million rupees in the 18th century (a high amount in that era).
In Bengal, the British inherited from the Mughals the biggest revenue earnings in the Indian subcontinent. For example, the revenue of pre-colonial Dhaka alone was 1 million rupees in the 18th century (a high amount in that era).  Agricultural products included rice, sugarcane and vegetables. The main cash crops were jute and
Agricultural products included rice, sugarcane and vegetables. The main cash crops were jute and
 After the invention of railways in Britain, British India became the first region in Asia to have a railway. The East Indian Railway Company introduced railways to Bengal. The company was established on 1 June 1845 in London by a deed of settlement with a capital of £4,000,000. Its first line connected Calcutta with towns in northern India. By 1859, there were 77 engines, 228 coaches and 848 freight wagons. Large quantities of
After the invention of railways in Britain, British India became the first region in Asia to have a railway. The East Indian Railway Company introduced railways to Bengal. The company was established on 1 June 1845 in London by a deed of settlement with a capital of £4,000,000. Its first line connected Calcutta with towns in northern India. By 1859, there were 77 engines, 228 coaches and 848 freight wagons. Large quantities of
 A ''ghat'' in Bengal refers to a river port. The busiest river ports included the
A ''ghat'' in Bengal refers to a river port. The busiest river ports included the
 An early attempt at manned flight in Bengal was by a young female
An early attempt at manned flight in Bengal was by a young female

 The Bengal Army was one of the Presidency Armies of British India. It was formed by the East India Company. The Commander-in-Chief of the Bengal Army was concurrently the Commander-in-Chief, India from 1853 to 1895, as the Bengal Army was the largest of the Presidency Armies. Recruits initially included Europeans and soldiers of the former Nawabs' Armies. Many of the recruits were from Bihar and Oudh. The
The Bengal Army was one of the Presidency Armies of British India. It was formed by the East India Company. The Commander-in-Chief of the Bengal Army was concurrently the Commander-in-Chief, India from 1853 to 1895, as the Bengal Army was the largest of the Presidency Armies. Recruits initially included Europeans and soldiers of the former Nawabs' Armies. Many of the recruits were from Bihar and Oudh. The
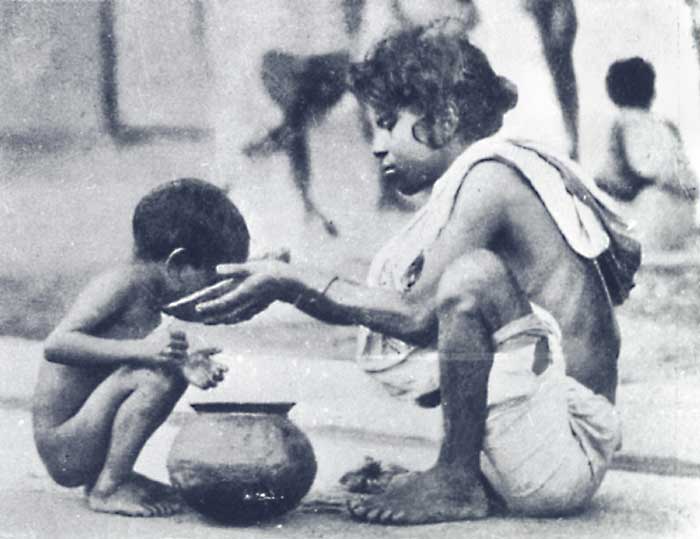 Colonial India as well as the Bengal Presidency suffered from the numerous famines and epidemics throughout the
Colonial India as well as the Bengal Presidency suffered from the numerous famines and epidemics throughout the
 The English language replaced Persian as the official language of administration. The use of Persian was prohibited by Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837, bringing an end to six centuries of Indo-Persian culture in Bengal. The Bengali language received increased attention. European missionaries produced the first modern books on Bengali grammar. In pre-colonial times, Hindus and Muslims would be highly attached to their liturgical languages, including Sanskrit and Arabic. Under British rule, the use of Bengali widened and it was strengthened as the '' lingua franca'' of the native population. Novels began to be written in Bengali. The literary polymath Rabindranath Tagore was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. The cultural activist
The English language replaced Persian as the official language of administration. The use of Persian was prohibited by Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837, bringing an end to six centuries of Indo-Persian culture in Bengal. The Bengali language received increased attention. European missionaries produced the first modern books on Bengali grammar. In pre-colonial times, Hindus and Muslims would be highly attached to their liturgical languages, including Sanskrit and Arabic. Under British rule, the use of Bengali widened and it was strengthened as the '' lingua franca'' of the native population. Novels began to be written in Bengali. The literary polymath Rabindranath Tagore was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. The cultural activist
 Numerous newspapers were published in British Bengal since the 18th century. Many were in English. ''
Numerous newspapers were published in British Bengal since the 18th century. Many were in English. ''

 The Company School of Painting in Calcutta, Murshidabad, and Patna saw Mughal miniatures absorb images of British colonial officials in place of Mughal officials. European painters produced numerous works in Bengal since the 18th century. European photographers also worked in the region. The modernist Bengal school of painting evolved in the province. European sculptures were widely imported by wealthy Zamindars. In the 1940s,
The Company School of Painting in Calcutta, Murshidabad, and Patna saw Mughal miniatures absorb images of British colonial officials in place of Mughal officials. European painters produced numerous works in Bengal since the 18th century. European photographers also worked in the region. The modernist Bengal school of painting evolved in the province. European sculptures were widely imported by wealthy Zamindars. In the 1940s,

The Hooghly Bridge (BOND 0034).jpeg,
''Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757–1857)''
(Routledge) 2011 * John R. McLane ''Land and Local Kingship in eighteenth-century Bengal'' (Cambridge) 1993
{{West Bengal History of Assam History of Bengal History of Bihar History of Odisha Historical Indian regions 1765 establishments in British India 1947 disestablishments in British India Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia States and territories disestablished in 1947
British Empire in India
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911.
The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded its control over much of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. This marked the beginning of Company rule in India, when the HEIC emerged as the most powerful military force in the subcontinent. The British Parliament gradually withdrew the monopoly of the HEIC. By the 1850s, the HEIC struggled with finances.William Dalrymple (10 September 2019). The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company. Bloomsbury Publishing. . After the Indian Mutiny of 1857, the British government assumed direct administration of India. The Bengal Presidency was re-organized. In the early 20th century, Bengal emerged as a hotbed of the Indian independence movement, as well as the epicenter of the Bengali Renaissance.
Bengal was the economic, cultural and educational hub of the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
. During the period of proto-industrialization
Proto-industrialization is the regional development, alongside commercial agriculture, of rural handicraft production for external markets.
The term was introduced in the early 1970s by economic historians who argued that such developments in pa ...
, Bengal significantly contributed directly to the Industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in Britain, although it was soon overtaken by the Kingdom of Mysore ruled by Tipu Sultan as South Asia's dominant economic power. When Bengal was reorganized, Penang, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
and Malacca were separated into the Straits Settlements in 1867. British Burma became a province of India and a later a Crown Colony in itself. Western areas, including the Ceded and Conquered Provinces
The Ceded and Conquered Provinces constituted a region in northern India that was ruled by the British East India Company from 1805 to 1834; it corresponded approximately—in present-day India—to all regions in Uttar Pradesh sta ...
and The Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, were further reorganized. Northeastern areas became Colonial Assam
Colonial Assam (1826–1947) refers to the period of History of Assam between the signing of the Treaty of Yandabo and Independence of India when Assam was under the British colonial rule. The political institutions and social relations that wer ...
. The Partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
in 1947 resulted in Bengal's division on religious grounds.
History
Background
 In 1599, a
In 1599, a Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
was granted by Queen Elizabeth I to allow the creation of a trading company in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
for the purposes of trade with the East Indies. The governance of the company was placed in the hands of a governor and a 24-member Court of Directors. The corporation became known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC). It rose to account for half of the world's trade. The company was given a monopoly for British trade in the Indian Ocean.
In 1608, Mughal Emperor Jahangir allowed the English East India Company to establish a small trading post on the west coast of India. It was followed in 1611 by a factory on the Coromandel Coast in South India, and in 1612 the company joined other already established European trading companies to trade in the wealthy Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Be ...
in the east. However, the power of the Mughal Empire declined from 1707, as the Nawab of Bengal in Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
became financially independent with the help of bankers such as the Jagat Seth
The Jagat Seth family was a wealthy merchant, banker and money lender family from Murshidabad in Bengal during the time of the Nawabs of Bengal.
History
The house was founded by Jain Hiranand Shah from Nagaur, Rajasthan, who came to Patna in ...
. The Nawabs began entering into treaties with numerous European companies, including the French East India Company, the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
, and the Danish East India Company
The Danish East India Company ( da, Ostindisk Kompagni) refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-fo ...
.
The Mughal court in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
was weakened by Nader Shah's invasion from Persia (1739) and Ahmed Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahma ...
's invasion from Afghanistan (1761). While the Bengal Subah suffered a decade of Maratha raids, through bands of Bargir-giri light cavalry, directed to pillage the territory, between 1741 and 1751. In 1742 the Company chooses to spend Rs. 25 thousand on the construction of a 3 km Maratha ditch around Calcutta, to protect its facilities from the raiders. The Nawab of Bengal later electing to end the plunder of his territory, in 1751, though conceding the administration of Orrisa and agreeing to make Bengal a tributary state of the Marathas, paying Rs. 1.2 million annually as the ''chauth
Chauth (from Sanskrit, meaning ''one fourth'') was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, ...
'' of Bengal and Bihar.OUM. pp. 16, 17 The Nawab of Bengal also paid Rs. 3.2 million to the Marathas, towards the arrears of ''chauth'' for the preceding years.
In June 1756 the company's factories at Cossimbazar
Cossimbazar is a sub-urban area of Berhampore City in the Berhampore CD block in the Berhampore subdivision in Murshidabad district in the Indian state of West Bengal."Cossimbazar" in ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', Oxford, Clarendon Press, ...
and Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
were besieged and captured by the forces of the Nawab of Bengal, with the company's goods, treasure and weapons seized. Calcutta being renamed Alinagar in honour of the Siraj ud-Daulah's predecessor. A Company force, led by Watson and Robert Clive, recaptured Fort William in January 1757, with the Nawab, Siraj ud-Daulah, agreeing the Treaty of Alinagar, reestablishing the company's right to trade in Bengal, and fortify Fort William. In parallel Robert Clive conspired with Jagat Seth, Omichand and Mir Jafar to install the latter on the musnud of Bengal, a plan that they would implement in June 1757.
The East India Company's victories at the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the Battle of Buxar (against the Nawabs of Bengal and Oudh in 1764) led to the abolition of local rule (Nizamat) in Bengal in 1793. The Company gradually began to formally expand its territories across India and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. By the mid-19th century, the East India Company had become the paramount political and military power in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. Its territory was held in trust for the British Crown. The company also issued coins in the name of the nominal Mughal Emperor (who was exiled in 1857).
Administrative changes and the Permanent Settlement

 Under Warren Hastings, the consolidation of British imperial rule over Bengal was solidified, with the conversion of a trade area into an occupied territory under a military-civil government, while the formation of a regularised system of legislation was brought in under John Shore. Acting through
Under Warren Hastings, the consolidation of British imperial rule over Bengal was solidified, with the conversion of a trade area into an occupied territory under a military-civil government, while the formation of a regularised system of legislation was brought in under John Shore. Acting through Lord Cornwallis
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, (31 December 1738 – 5 October 1805), styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United S ...
, then Governor-General, he ascertained and defined the rights of the landholders over the soil. These landholders under the previous system had started, for the most part, as collectors of the revenues, and gradually acquired certain prescriptive rights as quasi-proprietors of the estates entrusted to them by the government. In 1793 Lord Cornwallis declared their rights perpetual, and gave over the land of Bengal to the previous quasi-proprietors or ''zamindars'', on condition of the payment of a fixed land tax. This piece of legislation is known as the Permanent Settlement
The Permanent Settlement, also known as the Permanent Settlement of Bengal, was an agreement between the East India Company and Bengali landlords to fix revenues to be raised from land that had far-reaching consequences for both agricultural met ...
of the Land Revenue. It was designed to "introduce" ideas of property rights to India, and stimulate a market in land. The former aim misunderstood the nature of landholding in India, and the latter was an abject failure.
The ''Cornwallis Code'', while defining the rights of the proprietors, failed to give adequate recognition to the rights of the under-tenants and the cultivators. This remained a serious problem for the duration of British Rule, as throughout the Bengal Presidency ''ryots'' (peasants) found themselves oppressed by rack-renting landlords, who knew that every rupee they could squeeze from their tenants over and above the fixed revenue demanded from the Government represented pure profit. Furthermore, the Permanent Settlement took no account of inflation, meaning that the value of the revenue to Government declined year by year, whilst the heavy burden on the peasantry grew no less. This was compounded in the early 19th century by compulsory schemes for the cultivation of opium and indigo, the former by the state, and the latter by British planters. Peasants were forced to grow a certain area of these crops, which were then purchased at below market rates for export. This added greatly to rural poverty.
So unsuccessful was the Permanent Settlement that it was not introduced in the North-Western Provinces (taken from the Marathas during the campaigns of Lord Lake
Gerard Lake, 1st Viscount Lake (27 July 1744 – 20 February 1808) was a British general. He commanded British forces during the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and later served as Commander-in-Chief of the military in British India.
Background
He was ...
and Arthur Wellesley) after 1831, in Punjab after its conquest in 1849, or in Oudh which was annexed in 1856. These regions were nominally part of the Bengal Presidency, but remained administratively distinct. The area of the Presidency under direct administration was sometimes referred to as Lower Bengal to distinguish it from the Presidency as a whole. Officially Punjab, Agra and Allahabad had Lieutenant-Governors subject to the authority of the Governor of Bengal in Calcutta, but in practice they were more or less independent. The only all-Presidency institutions which remained were the Bengal Army and the Civil Service. The Bengal Army was finally amalgamated into the new British-Indian Army in 1904–5, after a lengthy struggle over its reform between Lord Kitchener, the Commander-in-Chief, and Lord Curzon
George Nathaniel Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston, (11 January 1859 – 20 March 1925), styled Lord Curzon of Kedleston between 1898 and 1911 and then Earl Curzon of Kedleston between 1911 and 1921, was a British Conservative statesman ...
, the Viceroy.
Straits Settlements
 In 1830, the British Straits Settlements on the coast of the
In 1830, the British Straits Settlements on the coast of the Malacca Straits
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, 500 mi (800 km) long and from 40 to 155 mi (65–250 km) wide, between the Malay Peninsula (Peninsular Malaysia) to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connec ...
was made a residency of the Presidency of Bengal in Calcutta. The area included the erstwhile Prince of Wales Island and Province Wellesley
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
, as well as the ports of Malacca and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
.
Under the administration of the East India Company, the Settlements were used as penal settlements for Indian civilian and military prisoners, earning them the title of the "Botany Bays of India". The years 1852 and 1853 saw minor uprisings by convicts in Singapore and Penang. Upset with East India Company rule, in 1857 the European population of the Settlements sent a petition to the British Parliament asking for direct rule.
Victorian Era
In 1859, under the terms of the Queen's Proclamation issued by Queen Victoria, the Bengal Presidency, along with the rest of British India, came under the direct rule of the British Crown. TheGovernor's Council The governments of the Thirteen Colonies of British America developed in the 17th and 18th centuries under the influence of the British constitution. After the Thirteen Colonies had become the United States, the experience under colonial rule would ...
was reformed and expanded under the Indian Councils Act 1861, the Indian Councils Act 1892, the Indian Councils Act 1909, the Government of India Act 1919
The Government of India Act 1919 (9 & 10 Geo. 5 c. 101) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was passed to expand participation of Indians in the government of India. The Act embodied the reforms recommended in the report o ...
and the Government of India Act 1935.
1905 Partition of Bengal
Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
and Rajshahi
Rajshahi ( bn, রাজশাহী, ) is a metropolitan city and a major urban, commercial and educational centre of Bangladesh. It is also the administrative seat of the eponymous division and district. Located on the north bank of the P ...
divisions, the Malda District and the States of Hill Tripura, Sylhet and Comilla
Comilla (; bn, কুমিল্লা, Kumillā, ), officially spelled Cumilla, is the fifth largest city of Bangladesh and second largest in Chittagong division. It is the administrative centre of the Comilla District. The name Comilla was ...
were transferred from Bengal to a new province, Eastern Bengal and Assam
Eastern Bengal and Assam was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.
Hist ...
; the five Hindi-speaking states of Chota Nagpur, namely Changbhakar, Korea, Surguja
Surguja district is a district of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. The district is one of the oldest districts of Chhattisgarh. The headquarters of the district is Ambikapur.
The district lies in its eponymous Surguja dialectal region (where ...
, Udaipur and Jashpur State, were transferred from Bengal to the Central Provinces; and Sambalpur State and the five Oriya states of Bamra
Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj, its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948.
The state was located i ...
, Rairakhol, Sonepur, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
and Kalahandi were transferred from the Central Provinces to Bengal.
The province of West Bengal then consisted of the thirty-three districts of Burdwan
Bardhaman (, ) is a city and a municipality in the state of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of Purba Bardhaman district, having become a district capital during the period of British rule. Burdwan, an alternative name for the city, ...
, Birbhum
Birbhum district () is an administrative unit in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the northernmost district of Burdwan division—one of the five administrative divisions of West Bengal. The district headquarters is in Suri. Other impo ...
, Bankura, Midnapur
Medinipur or Midnapore (Pron: med̪iːniːpur) is a city known for its history in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the West Medinipur district. It is situated on the banks of the Kangsabati River (variously known as '' ...
, Hughli, Howrah, Twenty-four Parganas, Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
, Nadia
Nadia is a female name. Variations include Nadja, Nadya, Nadine, Nadiya, and Nadiia. Most variations of the name are derived from Arabic, Slavic languages, or both.
In Slavic, names similar to ''Nadia'' mean "hope" in many Slavic languages: ...
, Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
, Jessore, Khulna, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
, Gaya, Shahabad, Saran, Champaran
Champaran is a region of Bihar in India. It is now divided into an East Champaran district and a West Champaran district.
Notable people
* Manoj Bajpai – Indian film actor
* Dinesh Bhramar – poet and noted figure in Hindi and Bhojpuri l ...
, Muzaffarpur, Darbhanga, Monghyr, Bhagalpur, Purnea
Purnia ()(also Romanization, romanized as Purnea) is a city that serves as the administrative headquarters of both Purnia district and Purnia division in the Indian state of Bihar.
Total geographical area of Purnia Urban Agglomeration is ...
, Santhal Parganas, Cuttack, Balasore, Angul and Kandhmal
Kandhamal district is a district in the state of Odisha, India. The district headquarters of the district is Phulbani. Kandhamal is famous for its local turmeric renowned as 'Kandhamal Haldi' which has earned the Geographical indication (GI) tag ...
, Puri, Sambalpur
Sambalpur () is the fifth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761 (as per 2011 census). Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Sam ...
, Singhbhum
Singhbhum was a district of India during the British Raj, part of the Chota Nagpur Division of the Bengal Presidency. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Jharkhand. Chaibasa was the district headquarters. Located in the southern li ...
, Hazaribagh
Hazaribagh is a city and a municipal corporation in Hazaribagh district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is the divisional headquarters of North Chotanagpur division. It is considered as a health resort and is also popular for Hazaribag ...
, Ranchi, Palamau
Palamu district is one of the twenty-four districts of Jharkhand state, India. It was formed in 1892. The administrative headquarter of the district is Medininagar (formerly DaltonGanj), situated on the Koel River.
History
The Palamu district ha ...
, and Manbhum
Manbhum District was one of the districts of the East India during the British Raj. After India's independence, the district became a part of Bihar State. Upon re-organisation of the Indian states in the mid-1950s, present Purulia district was ca ...
. The princely states
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
of Sikkim and the tributary states of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
and Chhota Nagpur were not part of Bengal, but British relations with them were managed by its government.
The Indian Councils Act 1909 expanded the legislative councils of Bengal and Eastern Bengal and Assam provinces to include up to 50 nominated and elected members, in addition to three ''ex officio'' members from the executive council.
Bengal's legislative council included 22 nominated members, of which not more than 17 could be officials, and two nominated experts. Of the 26 elected members, one was elected by the Corporation of Calcutta, six by municipalities, six by district boards, one by the University of Calcutta, five by landholders, four by Muslims, two by the Bengal Chamber of Commerce, and one by the Calcutta Trades Association. Eastern Bengal and Assam's legislative council included 22 nominated members, of which not more than 17 be officials and one representing Indian commerce, and two nominated experts. Of the 18 elected members, three were elected by municipalities, five by district and local boards, two by landowners, four by Muslims, two by the tea interest, one by the jute interest, and one by the Commissioners of the Port of Chittagong
The Chittagong Port ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম বন্দর) is the main seaport of Bangladesh. Located in Bangladesh's port city of Chittagong and on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the port handles over 90 percent of Bangladesh's ...
.
The partition of Bengal proved highly controversial, as it resulted in a largely Hindu West Bengal and a largely Muslim East. Serious popular agitation followed the step, partly on the grounds that this was part of a cynical policy of divide and rule, and partly that the Bengali population, the centre of whose interests and prosperity was Calcutta, would now be divided under two governments, instead of being concentrated and numerically dominant under the one, while the bulk would be in the new division. In 1906–1909 the unrest developed to a considerable extent, requiring special attention from the Indian and Home governments, and this led to the decision being reversed in 1911.
Reorganisation of Bengal, 1912
 At the Delhi Durbar on 12 December 1911, King George V announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to Delhi, the reunification of the five predominantly Bengali-speaking divisions into a Presidency (or province) of Bengal under a Governor, the creation of a new province of Bihar and Orissa under a lieutenant-governor, and that
At the Delhi Durbar on 12 December 1911, King George V announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to Delhi, the reunification of the five predominantly Bengali-speaking divisions into a Presidency (or province) of Bengal under a Governor, the creation of a new province of Bihar and Orissa under a lieutenant-governor, and that Assam Province
Assam Province was a province of British India, created in 1912 by the partition of the Eastern Bengal and Assam Province.
Its capital was in Shillong.
The Assam territory was first separated from Bengal in 1874 as the 'North-East Frontier' n ...
would be reconstituted under a chief commissioner. On 21 March 1912 Thomas Gibson-Carmichael was appointed Governor of Bengal; prior to that date the Governor-General of India had also served as the governor of Bengal Presidency. On 22 March the provinces of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa and Assam were constituted.
The Government of India Act 1919
The Government of India Act 1919 (9 & 10 Geo. 5 c. 101) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was passed to expand participation of Indians in the government of India. The Act embodied the reforms recommended in the report o ...
increased the number of nominated and elected members of the legislative council from 50 to 125, and the franchise was expanded. Bihar and Orissa became separate provinces in 1936. Bengal remained in its 1912 boundaries until Independence in 1947, when it was again partitioned between the dominions of India and Pakistan.
1947 Partition of Bengal
On 8 May 1947, Viceroy Earl Mountbatten cabled the British government with a partition plan that made an exception for Bengal. It was the only province that would be allowed to remain independent should it choose to do so. On 23 May, the British Cabinet meeting also hoped that Bengal would remain united. British Prime Minister Clement Attlee informed the US Ambassador to the United Kingdom on 2 June 1947 that there was a "distinct possibility that Bengal might decide against partition and against joining either India or Pakistan". On 6 July 1947, the Sylhet referendum gave a mandate for the District of Sylhet to be re-united into Bengal. However, Hindu nationalist leaders in West Bengal and conservative East Bengali Muslim leaders were against the prospect. On 20 June 1947, the Bengal Legislative Assembly met to vote on partition plans. At the preliminary joint session, the assembly decided by 120 votes to 90 that it should remain united if it joined the new Constituent Assembly of Pakistan. Later, a separate meeting of legislators from West Bengal decided by 58 votes to 21 that the province should be partitioned and that West Bengal should join the existing Constituent Assembly of India. In another separate meeting of legislators from East Bengal, it was decided by 106 votes to 35 that the province should not be partitioned and 107 votes to 34 that East Bengal should join Pakistan in the event of partition. There was no vote held on the proposal for an independent United Bengal.Geography
The Presidency's principal maritime gateway was the Bay of Bengal. The following maps illustrate its territorial evolution.Rajputana Agency
The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana (now in Rajasthan, northwestern India), under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to the Governor ...
, and the Punjab
Joppen1907BritishBengalBritishBurmaA.jpg, Map showing growth of British rule in Bengal and Burma
LowerBengal1870Map.png, Map denoting Lower Bengal in 1870, including Bengal proper, Orissa, Bihar and Assam; and princely states
BengalPartition1905 Map.png, Map showing the result of the partition of Bengal in 1905. The western part (Bengal) gained parts of Orissa, while the eastern part (Eastern Bengal and Assam) regained Assam that had been made a separate province in 1874.
Bengal Province 1931.png, Bengal Province in 1931 and adjoining princely states of Hill Tippera and Cooch Behar State
Government
 Initially, Bengal was under the administration of the East India Company, which appointed chief agents/presidents/governors/lieutenant governors in Fort William. The governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India for many years. The East India Company maintained control with its private armies and administrative machinery. Nevertheless, the East India Company was a quasi-official entity, having received a
Initially, Bengal was under the administration of the East India Company, which appointed chief agents/presidents/governors/lieutenant governors in Fort William. The governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India for many years. The East India Company maintained control with its private armies and administrative machinery. Nevertheless, the East India Company was a quasi-official entity, having received a Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
from Queen Elizabeth I in 1600. The Indian Rebellion of 1857 caused the British government to assume direct control of India's administration under the Government of India Act 1858. The head of state became the British monarch, who was also given the title of Emperor of India/Empress of India
Emperor or Empress of India was a title used by British monarchs from 1 May 1876 (with the Royal Titles Act 1876) to 22 June 1948, that was used to signify their rule over British India, as its imperial head of state. Royal Proclamation of 2 ...
. The monarch was represented through a viceroy. The Viceroy of India was based in the Bengal Presidency until 1911. The Secretary of State for India was also an important official. The Bengal Civil Service managed the provincial government. Modern scholars decry the colonial system as bureaucratic authoritarianism.
Executive councils
Established by Charter Act of 1833, the Governor-General in Council was subordinate to the Court of Directors of the East India Company and the British Crown. The Governor-General in Council in Fort William enacted legislation, such as the prohibition of Persian as an official language under Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837.Judiciary
 The Calcutta High Court was set up in 1862. The building was designed on the model of Ypres Cloth Hall in Belgium. The
The Calcutta High Court was set up in 1862. The building was designed on the model of Ypres Cloth Hall in Belgium. The Dacca High Court
The High Court Division, Supreme Court of Bangladesh ( bn, হাইকোর্ট ডিভিশন) popularly known as the 'High Court' is one of the two divisions of the Supreme Court of Bangladesh, the other division being the Appellate D ...
building was built during the early 20th century, with elements of a Roman pantheon. District courts were established in all district headquarters of the Bengal Presidency. At the district level, tax collectors and revenue officers acted with the power of magistrates. In 1829, magisterial power was given to all Collectors and Revenue Officers. The controversy regarding the lack of separation of powers continued until 1921.
Bengal Legislative Council (1862–1947)
 The British government began to appoint legislative councils under the Indian Councils Act 1861. The Bengal Legislative Council was established in 1862. It was one of the largest and most important legislative councils in British India. Over the years, the council's powers were gradually expanded from an advisory role to debating government policies and enacting legislation. Under the Government of India Act 1935, the council became the upper chamber of the Bengali legislature.
The British government began to appoint legislative councils under the Indian Councils Act 1861. The Bengal Legislative Council was established in 1862. It was one of the largest and most important legislative councils in British India. Over the years, the council's powers were gradually expanded from an advisory role to debating government policies and enacting legislation. Under the Government of India Act 1935, the council became the upper chamber of the Bengali legislature.
Dyarchy (1920–37)
British India's Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms of 1919, enacted in 1921, expanded the Bengal Legislative Council to 140 members to include more elected Indian members. The reforms also introduced the principle ofdyarchy
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', "the office of ...
, whereby certain responsibilities such as agriculture, health, education, and local government, were transferred to elected ministers. However, the important portfolios like finance, police and irrigation were reserved with members of the Governor's Executive Council. Some of the prominent ministers were Surendranath Banerjee
Sir Surendranath Banerjee often known as Rashtraguru ( bn, Rāṣṭraguru, Teacher of the Nation; 10 November 18486 August 1925) was Indian nationalist leader during the British Rule. He founded a nationalist organization called the Indian Nat ...
(Local Self-government and Public Health 1921–1923), Sir Provash Chunder Mitter (Education 1921–1924, Local Self-government, Public Health, Agriculture and Public Works 1927–1928), Nawab Saiyid Nawab Ali Chaudhuri (Agriculture and Public Works) and A. K. Fazlul Huq (Education 1924). Bhupendra Nath Bose and Sir Abdur Rahim ʻAbd al-Raḥīm ( ALA-LC romanization of ar, عبد الرحيم) is a male Muslim given name, and in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words ''ʻabd'', ''al-Raḥīm'', one of the names of God in the Qur'an, which give rise to ...
were Executive Members in the Governor's Council.
Bengal Legislative Assembly (1935–1947)
The Government of India Act, 1935 established the Bengal Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber of the Bengali legislature. It was a 250-seat assembly where most members were elected by either the General Electorate or the Muslim Electorate (under theCommunal Award
The Communal Award was created by the British prime minister Ramsay MacDonald on 16 August 1932. Also known as the MacDonald Award, it was announced after the Round Table Conference (1930–32) and extended the separate electorate to depressed Cl ...
). Other members were nominated. The separate electorate dividing Muslims from the general electorate was deeply controversial. The Prime Minister of Bengal was a member of the assembly.
 In the 1937 election, the Congress emerged as the single largest party but short of an absolute majority. The second-largest party was the Bengal Provincial Muslim League (BPML), followed in third place by the Krishak Praja Party. The BPML, Krishak Praja Party and independent legislators formed a coalition government. A. K. Fazlul Huq, a founder of the BPML who later broke away to form the Krishak Praja Party, was elected as parliamentary leader and prime minister. Huq pursued a policy of Hindu–Muslim unity. His cabinet included leading Hindu and Muslim figures, including Nalini Ranjan Sarkar (finance), Bijoy Prasad Singha Roy (revenue), Maharaja Srish Chandra Nandy (communications and public works), Prasanna Deb Raikut (forest and excise), Mukunda Behari Mallick (cooperative credit and rural indebtedness), Sir Khwaja Nazimuddin (home), Nawab
In the 1937 election, the Congress emerged as the single largest party but short of an absolute majority. The second-largest party was the Bengal Provincial Muslim League (BPML), followed in third place by the Krishak Praja Party. The BPML, Krishak Praja Party and independent legislators formed a coalition government. A. K. Fazlul Huq, a founder of the BPML who later broke away to form the Krishak Praja Party, was elected as parliamentary leader and prime minister. Huq pursued a policy of Hindu–Muslim unity. His cabinet included leading Hindu and Muslim figures, including Nalini Ranjan Sarkar (finance), Bijoy Prasad Singha Roy (revenue), Maharaja Srish Chandra Nandy (communications and public works), Prasanna Deb Raikut (forest and excise), Mukunda Behari Mallick (cooperative credit and rural indebtedness), Sir Khwaja Nazimuddin (home), Nawab Khwaja Habibullah
Nawab Khwaja Habibullah Bahadur (26 April 1895 – 21 November 1958) was the fifth Nawab of Dhaka. He was the son of Nawab Sir Khwaja Salimullah Bahadur. Under Habibullah's rule, the Dhaka Nawab Estate went into decline until its actual relinqui ...
(agriculture and industry), Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy (commerce and labour), Nawab Musharraf Hussain (judicial and legislative affairs), and Syed Nausher Ali (public health and local self-government). Huq promoted financial and land reforms with the Bengal Agricultural Debtors' Act (1938), The Money Lenders' Act (1938), and the Bengal Tenancy (Amendment) Act (1938). He introduced the Primary Education Bill to make primary education free and compulsory. He established schools such as the Lady Brabourne College. In 1941, Prime Minister Huq joined the Viceroy's Defence Council in support of Allied war efforts. In a letter to Governor John Herbert, Huq called for the resurrection of a Bengal Army. He wrote "I want you to consent to the formation of a Bengali Army of a hundred thousand young Bengalis consisting of Hindu and Muslim youths on a fifty-fifty basis. There is an insistent demand for such a step being taken at once, and the people of Bengal will not be satisfied with any excuses. It is a national demand which must be immediately conceded". Huq supported the adoption of the Lahore Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
in 1940. He envisaged Bengal as one of the "independent states" outlined by the resolution.
The first Huq cabinet dissolved after the BPML withdrew from his government. Huq then formed a second coalition with the Hindu Mahasabha led by Syama Prasad Mukherjee
Syama Prasad Mukherjee (6 July 1901 – 23 June 1953) was an Indian politician, barrister and academician, who served as India's first Minister for Industry and Supply (currently known as Ministry of Commerce and Industry) in Jawaharlal Nehru' ...
. This cabinet was known as the Shyama-Huq Coalition. The cabinet included Nawab Bahabur Khwaja Habibullah, Khan Bahadur Abdul Karim, Khan Bahadur Hashem Ali Khan, Shamsuddin Ahmed, Syama Prasad Mukherjee, Santosh Kumar Bose and Upendranath Barman. Huq's government fell in 1943 and a BPML government under Sir Khawaja Nazimuddin as Prime Minister was formed. Nazimuddin's tenure coincided with the Bengal famine of 1943. His government was replaced by Governor's rule
In India, President's rule is the suspension of state government and imposition of direct Union government rule in a state. Under Article 356 of the Constitution of India, if a state government is unable to function according to Constitutional ...
. After the end of World War II, elections were held in 1946 in which the BPML won an overwhelming majority of 113 seats in the 250-seat assembly. A government under Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy was formed. Prime Minister Suhrawardy continued with the policy of power-sharing between Hindus and Muslims. He also advocated a plan for a Bengali sovereign state with a multiconfessionalist political system. The breakdown of Hindu-Muslim unity across India eventually upended Bengali power-sharing. Religious violence, including the Noakhali riots
The Noakhali riots were a series of semi-organized massacres, rapes and abductions, combined with looting and arson of Hindu properties, perpetrated by the Muslim community in the districts of Noakhali in the Chittagong Division of Bengal (n ...
and Direct Action Day riots, contributed to the polarization. When the Bengal Assembly met to vote on Partition, most West Bengali legislators held a separate meeting and resolved to partition the province and join the Indian union. Most East Bengali legislators favored an undivided Bengal.
The Bengal Assembly was divided into the West Bengal Legislative Assembly
The West Bengal Legislative Assembly is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located in the B. B. D. Bagh area of Kolkata, the capital of the state. Members of the Legislative assembly are directly elected by t ...
and East Bengal Legislative Assembly
The East Pakistan Provincial Assembly, known as the East Bengal Legislative Assembly between 1947 and 1955, was the provincial legislature of East Pakistan between 1947 and 1971. It was known as the East Bengal Assembly from 1947 to 1955 when the ...
during the Partition of British India.
Civil liberties
English common law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, be ...
was applied to Bengal. Local legislation was enacted by the Legislative Council and Legislative Assembly. Case law was also an important source of law. Many laws enacted in British Bengal are still in use today, including the Indian Penal Code. In 1919, the Rowlatt Act
The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act of 1919, popularly known as the Rowlatt Act, was a law that applied in British India. It was a legislative council act passed by the Imperial Legislative Council in Delhi on 18 March 1919, indefinitel ...
extended wartime powers under the Defence of India Act 1915, including arbitrary arrests and trial without juries. Press freedom was muzzled by the Indian Press Act 1910. The Seditious Meetings Act 1908 curtailed freedom of assembly. Regulation III of 1818 was also considered draconian. King George V granted a royal amnesty to free political prisoners. Some draconian laws were repealed, including the Rowlatt Act. Despite being a common law jurisdiction, British India did not enjoy the same level of protection for civil liberties as in the United Kingdom. It was only after independence in 1947 and the adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, that human rights were clearly enshrined in law.
Princely states

Princely states
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
were autonomous principalities under the suzerainty of the British Crown in India. Initially, the Bengal Presidency managed the British government's relations with most princely states in the northern subcontinent, extending from Jammu and Kashmir in the north to Manipur in the northeast. An Agency was often formed to be the liaison between the government and the princely states. The largest of these agencies under Bengal once included the Rajputana Agency
The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana (now in Rajasthan, northwestern India), under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to the Governor ...
. Other agencies covered the Chota Nagpur Tributary States and the Orissa Tributary States
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Garhjats and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of princely states of British India now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha.
The Orissa Tributary States were located in the G ...
. Agents were also appointed to deal with tribal chiefs, such as the three tribal kings in the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
. At the time of the partition of India in 1947, the jurisdiction of the Bengal States Agency included Cooch Behar State and Hill Tipperah.
Himalayan kingdoms
Bengal was strategically important for the Himalayan regions of Nepal,Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
, Bhutan and Sikkim. The Anglo-Nepalese War
The Anglo-Nepalese War (1 November 1814 – 4 March 1816), also known as the Gorkha War, was fought between the Gorkhali army of the Kingdom of Nepal (present-day Nepal) and the British forces of the East India Company (EIC, present-day In ...
between the East India Company and the Kingdom of Nepal
The Kingdom of Nepal ( ne, नेपाल अधिराज्य), also known as the Gorkha Empire ( ne, गोरखा अधिराज्य) or Asal Hindustan ( ne, असल हिन्दुस्तान)(), was a Hindu king ...
was concluded with the Treaty of Sugauli, which ended Gorkha
The Gurkhas or Gorkhas (), with endonym Gorkhali ), are soldiers native to the Indian Subcontinent, chiefly residing within Nepal and some parts of Northeast India.
The Gurkha units are composed of Nepalis and Indian Gorkhas and are recruit ...
territorial expansion. The Treaty of Titalia was signed in 1817 between the HEIC and the Kingdom of Sikkim to establish British hegemony over Sikkim. The Bhutan War
The Duar War (or Anglo-Bhutan War) was a war fought between British India and Bhutan in 1864–1865. It has been the only military conflict between the two states since 1774.
Background
Across the nineteenth century, British India commissioned ...
in the 1860s saw the Kingdom of Bhutan lose control of the Bengal Duars to the British. The British expedition to Tibet
The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Armed Forces under the auspices of the T ...
took place between 1903 and 1904. It resulted in the Treaty of Lhasa which acknowledged Qing China's supremacy over Tibet.
Foreign relations
 The United States of America began sending envoys to Fort William in the 18th century. President
The United States of America began sending envoys to Fort William in the 18th century. President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
nominated Benjamin Joy as the first Consul to Fort William on 19 November 1792. The nomination was supported by the erstwhile Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson and approved by the U. S. Senate on 21 November 1792. Benjamin Joy reached Calcutta in 1794. The HEIC did not recognize Joy as an official consul but allowed him to be a Commercial Agent. The American Consulate General
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
was established during formal British rule. A consular agency for Chittagong was created in the 1860s. Many other countries also set up consulates in Calcutta.
Education
liberal arts colleges
A liberal arts college or liberal arts institution of higher education is a college with an emphasis on undergraduate study in liberal arts and sciences. Such colleges aim to impart a broad general knowledge and develop general intellectual ca ...
in many districts of Bengal. There were only two full-fledged universities in Bengal during British rule, including the University of Calcutta and the University of Dacca. Both universities were represented in the Bengal Legislative Assembly under the Government of India Act, 1935.
Primary education was mandatory under the Compulsory Education Acts. Despite significant advances and the emergence of a large educated middle class, most of the population did not have access to a proper education. Some of the leading schools included the Oriental Seminary in Calcutta, the St. Gregory's High School in Dacca, the Rajshahi Collegiate School in Rajshahi and the Chittagong Collegiate School in Chittagong. European missionaries, Hindu philanthropists and Muslim aristocrats were influential promoters of education. Ethnic minorities maintained their own institutions, such as the Armenian Pogose School.
Each district of Bengal had a district school, which were the leading secondary institutions. Due to Calcutta being the colonial capital, the city had a large concentration of educational institutions. It was followed by Dacca, which served as a provincial capital between 1905 and 1912. Libraries were established in each district of Bengal by the colonial government and the Zamindars. In 1854, four major public libraries were opened, including the Bogra Woodburn Library, the Rangpur Public Library, the Jessore Institute Public Library and the Barisal Public Library. Northbrook Hall
Northbrook Hall (also known as Lalkuthi) was originally built as a town hall during the British period. It is situated at Farashgonj road in Old Dhaka, Bangladesh, on the north bank of the Buriganga River.
History
In 1874, Indian Governor Th ...
was established in 1882 in honor of Governor-General Lord Northbrook. Other libraries built include the Victoria Public Library, Natore (1901), the Sirajganj Public Library (1882), the Rajshahi Public Library
Rajshahi Public Library is a public library in Rajshahi and is one of the oldest libraries in Bangladesh.
History
Rajshahi Public Library was founded by Ananada Nath Roy as Ananada Nath Library in 1866. Ananada Nath Roy was the Raja(king) of N ...
(1884), the Comilla Birchandra Library (1885), the Shah Makhdum Institute Public Library, Rajshahi (1891), the Noakhali Town Hall Public Library (1896), the Prize Memorial Library, Sylhet (1897), the Chittagong Municipality Public Library (1904) and the Varendra Research Library (1910). In 1925, the Great Bengal Library Association was established.
Europeans played an important role in modernizing the Bengali language. The first book on Bengali grammar was compiled by a Portuguese missionary. English was the official language. The use of Persian as an official language was discontinued by Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837. However, Persian continued to be taught in some institutions. Several institutions had Sanskrit and Arabic faculties.
The following includes a partial list of notable colleges, universities and learned societies in the Bengal Presidency.
Economy

 In Bengal, the British inherited from the Mughals the biggest revenue earnings in the Indian subcontinent. For example, the revenue of pre-colonial Dhaka alone was 1 million rupees in the 18th century (a high amount in that era).
In Bengal, the British inherited from the Mughals the biggest revenue earnings in the Indian subcontinent. For example, the revenue of pre-colonial Dhaka alone was 1 million rupees in the 18th century (a high amount in that era). Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
accounted for 12% of the world's GDP and was a major exporter of silk, cotton, saltpeter, and agricultural produce. With its proto-industrial economy, Bengal contributed to the first Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in Britain (particularly in textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution). After 1757, the British placed Bengal under company rule (which led to Bengali deindustrialization). Other European powers in the region included the French East India Company, the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
, the Ostend Company
The Ostend Company ( nl, Oostendse Compagnie, french: Compagnie d'Ostende), officially the General Company Established in the Austrian Netherlands for Commerce and Navigation in the Indies () was a chartered trading company in the Austrian Netherl ...
and the Danish East India Company
The Danish East India Company ( da, Ostindisk Kompagni) refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-fo ...
. Initially, the English East India Company promoted opium cultivation which caused the Opium Wars with Qing China. The East India Company's promotion of indigo farming caused the Indigo revolt. The British were much criticized for favoring textile imports and suppressing local muslin production. The chaos of the Company rule period culminated in the Indian Mutiny in 1857. In 1858, the British government gained direct control of Indian administration. Bengal was plugged into the market-driven economy and trade networks of the British Empire.
The Bengal Presidency had the largest gross domestic product in British India. The first British colonial banks in the Indian subcontinent were founded in Bengal. These included the General Bank of Bengal and Bihar (1733); Bank of Hindostan (1770), Bank of Bengal (1784); and the General Bank of India (1786). Other banks in Bengal included the Bank of Calcutta (1806), Union Bank (1829); Government Savings Bank (1833); The Bank of Mirzapore (c. 1835); Dacca Bank (1846); Kurigram Bank (1887), Kumarkhali Bank (1896), Mahaluxmi Bank, Chittagong (1910), Dinajpur Bank (1914), Comilla Banking Corporation (1914), Bengal Central Bank (1918), and Comilla Union Bank (1922). Loan offices were established in Faridpur (1865), Bogra (1872), Barisal (1873), Mymensingh (1873), Nasirabad (1875), Jessore (1876), Munshiganj (1876), Dacca (1878), Sylhet (1881), Pabna (1882), Kishoreganj (1883), Noakhali (1885), Khulna (1887), Madaripur (1887), Tangail (1887), Nilphamari (1894) and Rangpur (1894).
The earliest records of securities dealings are the loan securities of the British East India Company. In 1830, bourse activities in Calcutta were conducted in the open air under a tree. The Calcutta Stock Exchange was incorporated in 1908. Some of the leading companies in British Bengal included Messrs. Alexander and Co, Waldies, Martin Burn, M. M. Ispahani Limited, James Finlay and Co., A K Khan & Company, the Calcutta Chemical Company, Bourne & Shepherd, the Indo-Burmah Petroleum Company, Orient Airways, Shaw Wallace, Carew & Co, Aditya Birla Group, Tata Group, Balmer Lawrie, Biecco Lawrie, Braithwaite, Burn & Jessop Construction Company, Braithwaite & Co., Bridge and Roof Company, Britannia Industries, Burn Standard Company and Andrew Yule and Company. Some of these enterprises were nationalized after the Partition of India.
tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
. The jute trade was central to the British Bengali economy. Bengal accounted for the bulk of the world's jute production and export. Raw jute was sourced from the hinterland of Eastern Bengal. The British government declared the Port of Narayanganj
The Port of Narayanganj is a river port in Narayanganj, Bangladesh. It is one of the oldest and busiest river ports in Bangladesh; and one of the major ports of the Bengal delta. The port is located on the Shitalakshya River. The port area is home ...
as a "Tax Free Port" in 1878. Rally Brothers & Co. was one of the earliest British companies in the jute business of Narayanganj. British firms used middlemen, called ''beparis'', to source raw jute from the hinterland. In 1907, 20 firms were engaged in the jute trade of Narayanganj, including 18 European firms. Hindu merchants opened several cotton mills in the 1920s, including the Dhakeshwari Cotton Mill, the Chittaranjan Cotton Mill and the Laxmi Narayan Cotton Mill. Other goods traded in Narayanganj included timber, salt, textiles, oil, cotton, tobacco, pottery, seeds and betel nut. Raw goods were processed by factories in Calcutta, especially jute mills. The Port of Chittagong
The Chittagong Port ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম বন্দর) is the main seaport of Bangladesh. Located in Bangladesh's port city of Chittagong and on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the port handles over 90 percent of Bangladesh's ...
was re-organized in 1887 under the Port Commissioners Act. Its busiest trade links were with British Burma, including the ports of Akyab and Rangoon; and other Bengali ports, including Calcutta, Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city i ...
and Narayanganj. In the fiscal year 1889–90, Chittagong handled exports totalling 125,000 tons. The Strand Road was built beside the port. In 1928, the British government declared Chittagong as a "Major Port" of British India. Chittagong's port was used by Allied Forces of World War II during the Burma Campaign.
The Port of Calcutta
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the olde ...
was the largest seaport of British India. The port was constructed by the British East India Company. It was one of the busiest ports in the world during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Calcutta was a major trading port with links to ports across the British Empire. Its local hinterland spanned beyond Bengal to include north and northeast India, the Himalayan kingdoms and Tibet. The Bay of Bengal became one of the busiest shipping hubs in the world, rivaling the traffic of ports on the Atlantic. Calcutta was also an important naval base in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
and was bombed by the Japanese.
Chambers of commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to a ...
were established. The Bengal Chamber of Commerce
The Bengal Chamber of Commerce and Industry is a non-governmental trade association and advocacy group based in West Bengal, India. It is the oldest chamber of commerce in India, and one of the oldest in Asia.
Established in 1853, finding its o ...
was established in 1853. The Narayanganj Chamber of Commerce was set up in 1904. The textile trade of Bengal enriched many merchants. For example, Panam City
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
in Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
saw many townhouses
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
built for wealthy textile merchants.
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
became a major export of Bengal. Northwestern Bengal became the center of Darjeeling tea
Darjeeling tea is a tea made from ''Camellia sinensis var. sinensis'' that is grown and processed in Darjeeling or Kalimpong Districts in West Bengal, India. Since 2004, the term ''Darjeeling tea'' has been a registered geographical indication ...
cultivation in the foothills of the Himalayas. Darjeeling tea became one of the most reputed tea varieties in the world. The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway was constructed in the tea plantation zone. In eastern Bengal, the Sylhet and Chittagong hilly regions became hubs of tea production. Assam tea was produced in the northeastern part of the Bengal Presidency.
Aside from the British, the chief beneficiaries of the colonial economy were the Zamindars (landed gentry). The Permanent Settlement enforced a system in which peasants were indebted to the Zamindars. The peasants rented land from the Zamindars and became tenant farmers. Strong control of land by the Zamindars meant the British had few headaches in exploiting trade and business. However, Bengal received little attention for industrialization due to the entrenched peasant-zamindar relationship under the Permanent Settlement. The Zamindars of Bengal
The Zamindars of Bengal were zamindars (hereditary landlords) of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent (now divided between Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). They governed an ancient system of land ownership.
The Bengali ...
built mansions, lodges, modern bungalows, townhouses, and palaces on their estates. Some of the largest mansions include the Hazarduari Palace in Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
, the Ahsan Manzil
Ahsan Manzil is the erstwhile official residential palace and seat of the Nawab of Dhaka. The building is situated at Kumartoli along the banks of the Buriganga River in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Construction was started in 1859 and was completed in ...
on the Nawab of Dhaka
The Nawab of Dhaka (Bengali: "ঢাকার নবাব"), originally spelt in English Nawab of Dacca, was the title of the head of largest Muslim zamindar in British Bengal and Assam, based in present-day Dhaka, Bangladesh. The title of ''na ...
's estate, the Marble Palace in Calcutta, and the Cooch Behar Palace
Cooch Behar Palace, is a landmark in Cooch Behar city, West Bengal. It was designed after the Italian Renaissance style of architecture and was built in 1887, during the reign of Maharaja Nripendra Narayan of Koch dynasty. It is currently a ...
.
Infrastructure and transport
Railways
 After the invention of railways in Britain, British India became the first region in Asia to have a railway. The East Indian Railway Company introduced railways to Bengal. The company was established on 1 June 1845 in London by a deed of settlement with a capital of £4,000,000. Its first line connected Calcutta with towns in northern India. By 1859, there were 77 engines, 228 coaches and 848 freight wagons. Large quantities of
After the invention of railways in Britain, British India became the first region in Asia to have a railway. The East Indian Railway Company introduced railways to Bengal. The company was established on 1 June 1845 in London by a deed of settlement with a capital of £4,000,000. Its first line connected Calcutta with towns in northern India. By 1859, there were 77 engines, 228 coaches and 848 freight wagons. Large quantities of sal tree
''Shorea robusta'', the sal tree, sāla, shala, sakhua, or sarai, is a species of tree in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The tree is native to India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Tibet and across the Himalayan regions .
Evolution
Fossil evidence from lig ...
wood were imported from Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
to design the sleepers. In 1862, railways were introduced to eastern Bengal with the Eastern Bengal Railway. The first line connected Calcutta and Kushtia. By 1865, the railway was extended to Rajbari on the banks of the Padma River
The Padma ( bn, পদ্মা ''Pôdma'') is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is sit ...
. By 1902, the railway was extended to Assam. The Assam Bengal Railway
The Assam Bengal Railway (ABR) was one of the pioneering railway companies in British India. Headquartered in Chittagong, it functioned from 1892 to 1942.
History
Assam Bengal Railway was incorporated in 1892 to serve British-owned tea planta ...
was established to serve the northeastern part of the Bengal Presidency, with its terminus in Chittagong.
The Bengal and North Western Railway was set up in 1882 to link towns in the Oudh region with Calcutta. Several railway bridges, such as the Hardinge Bridge
Hardinge Bridge is a steel railway truss bridge over the Padma River located at Ishwardi, Pabna and Bheramara, and Kushtia in Bangladesh. It is named after Lord Hardinge, who was the Viceroy of India from 1910 to 1916. The bridge is long.
Con ...
, were built over rivers in Bengal. In 1999, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
recognized the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Roads and highways
In the 1830s the East India Company began to rebuild the ancientGrand Trunk Road
The Grand Trunk Road (formerly known as Uttarapath, Sarak-e-Azam, Shah Rah-e-Azam, Badshahi Sarak, and Long Walk) is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For at least 2,500 years it has linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. ...
into a paved highway. The company required the road for commercial and administrative purposes. It linked Calcutta to Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
in the North-West Frontier Province. For the project, the company founded a college to train and employ local surveyors, engineers, and overseers. In the east, the road extended to Sonargaon, Comilla and Chittagong. After the first partition of Bengal in 1905, newly built highways connected the inaccessible areas of Assam and the Chittagong Hill Tracts. All district towns were connected by an inter-district road network.
Waterways
 A ''ghat'' in Bengal refers to a river port. The busiest river ports included the
A ''ghat'' in Bengal refers to a river port. The busiest river ports included the Port of Calcutta
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the olde ...
, the Port of Dhaka, the Port of Narayanganj
The Port of Narayanganj is a river port in Narayanganj, Bangladesh. It is one of the oldest and busiest river ports in Bangladesh; and one of the major ports of the Bengal delta. The port is located on the Shitalakshya River. The port area is home ...
and Goalundo Ghat.
After the first partition of Bengal in 1905, a number of new ferry services were introduced connecting Chittagong, Dhaka, Bogra, Dinajpur, Rangpur, Jalpaiguri, Maldah and Rajshahi. This improved communication network boosted trade and commerce.
Aviation
 An early attempt at manned flight in Bengal was by a young female
An early attempt at manned flight in Bengal was by a young female balloonist
In aeronautics, a balloon is an unpowered aerostat, which remains aloft or floats due to its buoyancy. A balloon may be free, moving with the wind, or tethered to a fixed point. It is distinct from an airship, which is a powered aerostat that ...
named Jennette Rumary who at the time was associated with Park Van Tassel and took the stage name ''Jennette Van Tassell''. Invited to perform by the Nawab of Dhaka
The Nawab of Dhaka (Bengali: "ঢাকার নবাব"), originally spelt in English Nawab of Dacca, was the title of the head of largest Muslim zamindar in British Bengal and Assam, based in present-day Dhaka, Bangladesh. The title of ''na ...
, at 6.20 pm on 16 March 1892, Jennette set off to fly from the southern bank of the River Buriganga. But a gusting wind carried her off to the gardens of Shahbag
Shahbag or Shahbagh (also Shahbaugh, bn, শাহবাগ, Shāhbāg, ) is a major neighbourhood and a police precinct or ''thana'' in Dhaka, the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is also a major public transport hub. It is a juncti ...
, where her balloon became stuck in a tree. During her rescue from the tree she fell and died two days later. Jennette is interred in the Christian graveyard at Narinda in Old Dhaka.
An airfield opened next to a Royal Artillery station on the outskirts of Calcutta. The Governor of Bengal Sir Stanley Jackson opened the Bengal Flying Club in Calcutta's aerodrome in February 1929. In 1930, the airfield was upgraded into a full-fledged airport. It was popularly known as Dum Dum Airport
Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport is an international airport located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India, serving the Kolkata Metropolitan Area and is the aviation hub for eastern and northeastern India. It is located approximatel ...
. Imperial Airways
Imperial Airways was the early British commercial long-range airline, operating from 1924 to 1939 and principally serving the British Empire routes to South Africa, India, Australia and the Far East, including Malaya and Hong Kong. Passengers ...
began flights from London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
to Australia via Calcutta in 1933. Air Orient
Air Orient was an airline based in France. Created in 1929 from the merger of ''Air Asie'' (c. 1928) and ''Air Union Lignes d’Orient'' (c. 1927 – renamed from Messageries Transaeriennes 1923), the short lived airline was merged with Air Franc ...
began scheduled stops as part of its Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
to Saigon route. KLM operated a route from Amsterdam to Batavia (Jakarta) via Calcutta. Calcutta emerged as a stopover for many airlines operating routes between Europe, Indochina and Australasia. The flight of Amelia Earhart and Fred Noonan, who attempted to circumnavigate the world, made a stopover in Calcutta in 1937. Local airlines included Tata Air Services and Orient Airways. Bengal played an important role for the air operations of the Allied forces of World War II. The Royal Air Force operated airfields across Bengal during the Burma Campaign. Aircraft of the United States Army Air Forces were also stationed in Bengal.
The following includes a partial list of airports and airfields established during British rule in Bengal. Airfields were used by Allied Forces during World War II.
Military

 The Bengal Army was one of the Presidency Armies of British India. It was formed by the East India Company. The Commander-in-Chief of the Bengal Army was concurrently the Commander-in-Chief, India from 1853 to 1895, as the Bengal Army was the largest of the Presidency Armies. Recruits initially included Europeans and soldiers of the former Nawabs' Armies. Many of the recruits were from Bihar and Oudh. The
The Bengal Army was one of the Presidency Armies of British India. It was formed by the East India Company. The Commander-in-Chief of the Bengal Army was concurrently the Commander-in-Chief, India from 1853 to 1895, as the Bengal Army was the largest of the Presidency Armies. Recruits initially included Europeans and soldiers of the former Nawabs' Armies. Many of the recruits were from Bihar and Oudh. The Gurkha
The Gurkhas or Gorkhas (), with endonym Gorkhali ), are soldiers native to the Indian subcontinent, Indian Subcontinent, chiefly residing within Nepal and some parts of Northeast India.
The Gurkha units are composed of Nepalis and Indian Go ...
s were also recruited under the Bengal Army. In 1895, the Bengal Army was merged into the British Indian Army. The British Indian Army had a Bengal Command between 1895 and 1908.
Major military engagements affecting British Bengal included the First Anglo-Burmese War
The First Anglo-Burmese War ( my, ပထမ အင်္ဂလိပ်-မြန်မာ စစ်; ; 5 March 1824 – 24 February 1826), also known as the First Burma War, was the first of three wars fought between the British and Burmes ...
, the Anglo-Nepalese War
The Anglo-Nepalese War (1 November 1814 – 4 March 1816), also known as the Gorkha War, was fought between the Gorkhali army of the Kingdom of Nepal (present-day Nepal) and the British forces of the East India Company (EIC, present-day In ...
, the First Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, جنگ اول افغان و انگلیس) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking si ...
, the Opium Wars, the Bhutan War
The Duar War (or Anglo-Bhutan War) was a war fought between British India and Bhutan in 1864–1865. It has been the only military conflict between the two states since 1774.
Background
Across the nineteenth century, British India commissioned ...
, the Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ps, د افغان-انګرېز دويمه جګړه) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the l ...
, World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and the Burma Campaign of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The chief British base in Bengal was Fort William. Across the subcontinent, the British often converted Mughal forts into military bases, such as in Delhi and Dhaka. The British also built cantonments, including Dhaka Cantonment and Chittagong Cantonment. Many Allied soldiers killed in Burma were buried in cemeteries in Chittagong and Comilla. The graveyards include the Commonwealth War Cemetery, Chittagong and Mainamati War Cemetery, which are maintained by the Commonwealth War Graves Commission
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states whose principal function is to mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations m ...
.
Famines and other natural disasters
 Colonial India as well as the Bengal Presidency suffered from the numerous famines and epidemics throughout the
Colonial India as well as the Bengal Presidency suffered from the numerous famines and epidemics throughout the British Rule
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was hims ...
. The Great Bengal famine of 1770
The Bengal Famine of 1770 was a famine that struck Bengal and Bihar between 1769 and 1770 and affected some 30 million people. It occurred during a period of dual governance in Bengal. This existed after the East India Company had been granted ...
lasted until 1773 and killed approximately 10 million Bengalis. The East India Company was heavily criticized for neglecting the population's food security. The repeated bouts of famine in India, coupled with other abuses against the population, caused the British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
to gradually remove the monopoly of the East India Company, curtail the company's powers and eventually replace it with crown rule. Warren Hastings, Governor of Bengal, was censured for the abuses of the company. Ironically, Hastings had set about to reform the company's practices and was later acquitted of any wrongdoing. During the trial of Hastings, Edmund Burke delivered a scathing indictment of malpractice by the company, condemning it for "injustice and treachery against the faith of nations". Burke stated "With various instances of extortion and other deeds of maladministration....With impoverishing and depopulating the whole country.....with a wanton and unjust, pernicious, exercise of his powers.....in overturning the ancient establishments of the country......With cruelties unheard of and devastations almost without name......Crimes which have their rise in the wicked dispositions of men- in avarice, rapacity, pride, cruelty, malignity, haughtiness, insolence, ferocity, treachery, cruelty, malignity of temper - in short, nothing that does not argue a total extinction of all moral principle, that does not manifest an inveterate blackness of heart, a heart blackened to the very blackest, a heart corrupted, gangrened to the core.....We have brought before you the head (Hastings)....one in whom all the frauds, all the peculations, all the violence, all the tyranny in India are embodied".
In 1876, about 200,000 Bengalis were killed in Barisal as a result of the 1876 Bengal cyclone.
The Bengal Presidency endured a vast famine between 1873 and 1874. The Bengal famine of 1943 killed an estimated 3 million people during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. People died of starvation, malaria, or other diseases aggravated by malnutrition, population displacement, and lack of healthcare. Britain's wartime Prime Minister Winston Churchill has been held responsible for the famine by prominent Indians, including politician Shashi Tharoor
Shashi Tharoor (; ; born 9 March 1956 in London, England ) is an Indian former international civil servant, diplomat, bureaucrat and politician, writer and public intellectual who has been serving as Member of Parliament for Thiruvananthapuram, ...
. When British civil servants sent letters to London regarding the famine situation, Churchill once responded by saying "Why hasn't Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti- ...
died yet?". Churchill's defenders, however, argue that it is an exaggeration to blame him for the wartime hunger crisis. The real cause was the fall of Burma to the Japanese, which cut off India's main supply of rice imports when domestic sources fell short, which they did in Eastern Bengal after a devastating cyclone in mid-October 1942". Lizzie Collingham holds the massive global dislocations of supplies caused by World War II virtually guaranteed that hunger would occur somewhere in the world, yet Churchill's racism toward the Indians decided the exact location where famine would fall.
Culture
Literary development
 The English language replaced Persian as the official language of administration. The use of Persian was prohibited by Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837, bringing an end to six centuries of Indo-Persian culture in Bengal. The Bengali language received increased attention. European missionaries produced the first modern books on Bengali grammar. In pre-colonial times, Hindus and Muslims would be highly attached to their liturgical languages, including Sanskrit and Arabic. Under British rule, the use of Bengali widened and it was strengthened as the '' lingua franca'' of the native population. Novels began to be written in Bengali. The literary polymath Rabindranath Tagore was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. The cultural activist
The English language replaced Persian as the official language of administration. The use of Persian was prohibited by Act no. XXIX of 1837 passed by the President of the Council of India in Council on 20 November 1837, bringing an end to six centuries of Indo-Persian culture in Bengal. The Bengali language received increased attention. European missionaries produced the first modern books on Bengali grammar. In pre-colonial times, Hindus and Muslims would be highly attached to their liturgical languages, including Sanskrit and Arabic. Under British rule, the use of Bengali widened and it was strengthened as the '' lingua franca'' of the native population. Novels began to be written in Bengali. The literary polymath Rabindranath Tagore was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. The cultural activist Kazi Nazrul Islam
, pseudonym = bn, ধূমকেতু, Dhūmketu
, image = Nazrul.jpg
, image_size =
, caption = Nazrul in Chittagong, 1926
, birth_date = 11 ''Joiṣṭhyô'', 1306 '' Bônggabdô ...
gained popularity as British India's ''Rebel Poet''. Jagadish Chandra Bose pioneered Bengali science fiction. Begum Rokeya, author of '' Sultana's Dream'', became an early feminist science fiction author.
Media
 Numerous newspapers were published in British Bengal since the 18th century. Many were in English. ''
Numerous newspapers were published in British Bengal since the 18th century. Many were in English. ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette
''Hicky's Bengal Gazette or the Original Calcutta General Advertiser'' was an English-language weekly newspaper published in Kolkata (then Calcutta), the capital of British India(then Known as the Presidency of Fort William.. It was the first ...
'' was a major weekly publication. The first Bengali periodicals appeared in the 19th century. The ''Calcutta Journal'' became the first daily newspaper in British India. Other newspapers included the '' Dacca News'' and '' The Bengal Times''. Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
channels began transmitting in 1927.
Visual arts

 The Company School of Painting in Calcutta, Murshidabad, and Patna saw Mughal miniatures absorb images of British colonial officials in place of Mughal officials. European painters produced numerous works in Bengal since the 18th century. European photographers also worked in the region. The modernist Bengal school of painting evolved in the province. European sculptures were widely imported by wealthy Zamindars. In the 1940s,
The Company School of Painting in Calcutta, Murshidabad, and Patna saw Mughal miniatures absorb images of British colonial officials in place of Mughal officials. European painters produced numerous works in Bengal since the 18th century. European photographers also worked in the region. The modernist Bengal school of painting evolved in the province. European sculptures were widely imported by wealthy Zamindars. In the 1940s, Zainul Abedin
Zainul Abedin (29 December 1914 – 28 May 1976) was a Bangladeshi painter born in Mymensingh, East Bengal, British India (now Bangladesh). He became well known in 1944 through his series of paintings depicting some of the great famines in ...
emerged as a modernist painter depicting poverty and the Bengal famine.
Calcutta Time
Calcutta Time
Calcutta time was one of the two time zones established in British India in 1884. It was established during the International Meridian Conference held at Washington, D.C. in the United States. It was decided that India had two time zones: Calcu ...
was the time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
of the Bengal Presidency. It was established in 1884. It was one of the two time zones of British India. In the latter part of the 19th century, Calcutta Time was the most prevalent time used in the Indian part of the British Empire with records of astronomical and geological events recorded in it.
Cinema
The Royal Bioscope Company began producing Bengali cinema in 1898, producing scenes from the stage productions of a number of popular shows at the Crown Theatre in Dacca and the Star Theater, Minerva Theater, and Classic Theater in Calcutta. TheMadan Theatre
Madan Theatre Company, also known as Madan Theatres Limited or Madan Theatres in short, was a film production company founded by Jamshedji Framji Madan, one of the pioneers of Indian Cinema.
History
Madan, a young Parsi businessman, who had expe ...
started making silent films in Calcutta in 1916. The first Bengali feature film, '' Billwamangal'', was produced and released in 1919 under the banner of the Madan Theatre. The movie was directed by Rustomji Dhotiwala and produced by Priyonath Ganguli. A Bengali film company called the Indo British Film Co was soon formed in Calcutta by Dhirendra Nath Ganguly. Ganguly directed and wrote '' Bilat Ferat'' in 1921, which was the first production of the Indo British Film Co. '' Jamai Shashthi'' (1931) was one of the earliest Bengali talkie
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades passed before ...
s.
In 1927–28, the Dhaka Nawab Family
The Nawab of Dhaka ( Bengali: "ঢাকার নবাব"), originally spelt in English Nawab of Dacca, was the title of the head of largest Muslim zamindar in British Bengal and Assam, based in present-day Dhaka, Bangladesh. The title of ''n ...
produced a short film named ''Sukumary'' (The Good Girl). After the success of ''Sukumary'', the Nawab's family went for a bigger venture. To make a full-length silent film, a temporary studio was made in the gardens of the family's estate, and they produced a full-length silent film titled ''The Last Kiss'', released in 1931. The "East Bengal Cinematograph Society" was later established in Dacca.
Sports

Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
started being played in the 1790s. The Calcutta Cricket Club
The Calcutta Cricket & Football Club (CC&FC) (formally named as Calcutta Cricket Club) is a multisports club based in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Founded in 1792 as a cricket institution, the football and rugby sections were added when it mer ...
was set up in 1792. For horse racing, the Royal Calcutta Turf Club was set up in 1847. It became British India's equivalent of the Jockey Club in England in terms of arbitrating matters related to racing. In addition to horse races, the club also launched polo matches among natives and colonialists. Races at the Calcutta Race Course were once among the most important social events of the calendar, opened by the Viceroy of India. During the 1930s the Calcutta Derby Sweeps was a leading sweepstake
A sweepstake is a type of contest where a prize or prizes may be awarded to a winner or winners. Sweepstakes began as a form of lottery that were tied to products sold. In response, the FCC and FTC refined U.S. broadcasting laws (creating the ...
game in the world. A racecourse
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also use ...
was also set up in Ramna by the Dacca Club. The Bengal Public Gaming (Amendment) Act (Act No. IV of 1913) excluded horse racing from the gambling law.
Bengal renaissance
The Bengal renaissance refers to social reform movements during the 19th and early 20th centuries in the region of Bengal inundivided India
Akhand Bharat (), also known as Akhand Hindustan, is a term for the concept of a unified Greater India. The idea of Akhand Bharat in it's most widely accepted form is that Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Maldives, Myanm ...
during the period of British rule. Historian Nitish Sengupta
Nitish Kumar Sengupta (23 September 1934, Palang, Faridpur − 3 November 2013, New Delhi) was an Indian academician, administrator, politician and author.
Biography
He studied at Jhargram Kumud Kumari Institution and graduated with Gold Meda ...
describes it as having started with reformer and humanitarian Raja Ram Mohan Roy
Raja Ram Mohan Roy ( bn, রামমোহন রায়; 22 May 1772 – 27 September 1833) was an Indian reformer who was one of the founders of the Brahmo Sabha in 1828, the precursor of the Brahmo Samaj, a social-religious reform m ...
(1775–1833), and ended with Asia's first Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941). This flowering of religious and social reformers, scholars, and writers is described by historian David Kopf as "one of the most creative periods in Indian history". These movements were most prevalent in Bengali Hindu
Bengali Hindus ( bn, বাঙ্গালী হিন্দু/বাঙালি হিন্দু, translit=Bāṅgālī Hindu/Bāṅāli Hindu) are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Ben ...
society, such as through the Brahmo Samaj
Brahmo Samaj ( bn, ব্রহ্ম সমাজ, Brahmô Sômaj, ) is the societal component of Brahmoism, which began as a monotheistic reformist movement of the Hindu religion that appeared during the Bengal Renaissance.
It was one of t ...
. There was a growing cultural awakening in Bengali Muslim
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
society, including the emergence of Mir Mosharraf Hossain as the first Muslim novelist of Bengal; Kazi Nazrul Islam
, pseudonym = bn, ধূমকেতু, Dhūmketu
, image = Nazrul.jpg
, image_size =
, caption = Nazrul in Chittagong, 1926
, birth_date = 11 ''Joiṣṭhyô'', 1306 '' Bônggabdô ...
as a celebrated poet who merged Bengali and Hindustani influences; Begum Rokeya and Nawab Faizunnesa as feminist educators; Kaykobad as an epic poet; and members of the Freedom of Intellect Movement.
Bengal played a major role in the Indian independence movement and the Pakistan movement
The Pakistan Movement ( ur, , translit=Teḥrīk-e-Pākistān) was a political movement in the first half of the 20th century that aimed for the creation of Pakistan from the Muslim-majority areas of British India. It was connected to the per ...
. The earliest organized anti-colonial groups appeared in Bengal. The region produced many of the subcontinent's political leaders during the early 20th century. Political parties and rebel groups were formed across the region.
Architecture
Civic architecture began following European styles after the advent of the East India Company's authority. The Indo-Saracenic style, merging Gothic and Indo-Islamic architecture, was started by British architects in the late 19th-century. While cities such as Calcutta and Dacca featured more civic architecture, country houses were built in many towns and villages across Bengal.Art deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
influences began in the 1930s. Wealthy Bengali families (especially zamindar estates) employed European firms to design houses and palaces.
Howrah Bridge
The Howrah Bridge is a balanced cantilever bridge over the Hooghly River in West Bengal. Commissioned in 1943, the bridge was originally named the New Howrah Bridge, because it replaced a pontoon bridge at the same location linking the cities ...
in 1945
Victoria Memorial, Calcutta - LIFE.jpg, Victoria Memorial, Kolkata
The Victoria Memorial is a large marble building on the Maidan in Central Kolkata, built between 1906 and 1921. It is dedicated to the memory of Queen Victoria, Empress of India from 1876 to 1901.
The largest monument to a monarch anywhere ...
Writers Building.jpg, Writer's Building
Ruplal House old.jpg, Ruplal House
Completed Bridge. (23126065986).jpg, Hardinge Bridge
Hardinge Bridge is a steel railway truss bridge over the Padma River located at Ishwardi, Pabna and Bheramara, and Kushtia in Bangladesh. It is named after Lord Hardinge, who was the Viceroy of India from 1910 to 1916. The bridge is long.
Con ...
, 1915
Dhaka College 1904.jpg, Dacca College, 1904
Madrassa Dhaka 1904.jpg, Dacca Madrasa, 1904
Nawab's Shahbagh Garden dhaka 1904 02.jpg, Nawab's Shahbag
Shahbag or Shahbagh (also Shahbaugh, bn, শাহবাগ, Shāhbāg, ) is a major neighbourhood and a police precinct or ''thana'' in Dhaka, the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is also a major public transport hub. It is a juncti ...
h Garden, 1904
Society
Bengali society remained deeply conservative during the colonial period with the exception of social reform movements. Historians have argued that the British used a policy ofdivide and rule
Divide and rule policy ( la, divide et impera), or divide and conquer, in politics and sociology is gaining and maintaining power divisively. Historically, this strategy was used in many different ways by empires seeking to expand their ter ...
among Hindus and Muslims. This meant favoring Hindus over Muslims and vice versa in certain sectors. For example, after the Permanent Settlement
The Permanent Settlement, also known as the Permanent Settlement of Bengal, was an agreement between the East India Company and Bengali landlords to fix revenues to be raised from land that had far-reaching consequences for both agricultural met ...
, Hindu merchants such as the Tagore family
The Tagore family (also spelled as ''Thakur''), with over three hundred years of history,Deb, Chitra, pp 64–65. has been one of the leading families of Calcutta, India, and is regarded as one of the key influencers during the Bengali Renaissa ...
were awarded large land grants that previously belonged to the Mughal aristocracy. In Calcutta, where Hindus formed a majority, wealthy Muslims were often given favors over Hindus. One aspect that benefitted the Hindu community was increased literacy rates. Many Muslims, however, remained alienated from English education after the abolition of Persian. Bengali society continued to experience religious nationalism which led to the partition of Bengal in 1947.
British Bengali cities included a cosmopolitan population, including Armenians and Jews. Anglo-Indians formed a prominent part of the urban population. Several Gentlemen's clubs were established, including the Bengal Club, Calcutta Club, Dacca Club, Chittagong Club, Tollygunge Club
The Tollygunge Club (Bengali: টালিগঞ্জ ক্লাব), popularly called Tolly, is a country club in India, located in Tollygunge in south Kolkata.
Sir William Cruikshank established the club as an equestrian sports facility i ...
and Saturday Club.
See also
* List of governors of Bengal Presidency * Advocate-General of Bengal * Bombay Presidency * Madras PresidencyReferences
Works cited
* * C. A. Bayly ''Indian Society and the Making of the British Empire'' (Cambridge) 1988 * C. E. Buckland ''Bengal under the Lieutenant-Governors'' (London) 1901 * Sir James Bourdillon, ''The Partition of Bengal'' (London: Society of Arts) 1905 * Susil Chaudhury ''From Prosperity to Decline. Eighteenth Century Bengal'' (Delhi) 1995 * Sir William Wilson Hunter, ''Annals of Rural Bengal'' (London) 1868, and ''Odisha'' (London) 1872 * * Ray, Indraji''Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757–1857)''
(Routledge) 2011 * John R. McLane ''Land and Local Kingship in eighteenth-century Bengal'' (Cambridge) 1993
External links
{{West Bengal History of Assam History of Bengal History of Bihar History of Odisha Historical Indian regions 1765 establishments in British India 1947 disestablishments in British India Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia States and territories disestablished in 1947