Beacon Hill, Boston on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beacon Hill is a historic neighborhood in 
 Like many similarly named areas, the neighborhood is named for the location of a former
Like many similarly named areas, the neighborhood is named for the location of a former
 The first European settler was
The first European settler was
File:1st Harrison Gray Otis House.JPG,
In the 1830s, residential homes were built for wealthy people on Chestnut and Mt. Vernon Streets. Some affluent people moved, beginning in the 1870s, to
 Better transportation service to the suburbs and other cities led a boom to the city's economy at the beginning of the 20th century. New buildings, "compatible with the surroundings", were built and older buildings renovated. To ensure that there were controls on new development and demolition, the Beacon Hill Association was formed in 1922. Into the 1940s there were attempts to replace brick sidewalks, but the projects were abandoned due to community resistance.
Banks, restaurants and other service industries moved into the "Flat of the Hill", with a resulting transformation of the neighborhood.
Red-light districts operated near Beacon Hill in
Better transportation service to the suburbs and other cities led a boom to the city's economy at the beginning of the 20th century. New buildings, "compatible with the surroundings", were built and older buildings renovated. To ensure that there were controls on new development and demolition, the Beacon Hill Association was formed in 1922. Into the 1940s there were attempts to replace brick sidewalks, but the projects were abandoned due to community resistance.
Banks, restaurants and other service industries moved into the "Flat of the Hill", with a resulting transformation of the neighborhood.
Red-light districts operated near Beacon Hill in
File:Mass statehouse eb1.jpg, Massachusetts State House
Image:The Beacon Monument, Beacon Hill, Boston, Massachusetts.JPG, Beacon Hill Monument in back of the State House marking the site of the original beacon pole
A Grass-Roots Effort to Grow Old at Home
, ''The New York Times'', August 14, 2007; accessed 2013.05.17.Haya El Nasser
''USA Today'', July 26, 2010; accessed 2013.05.17.
File:77 MtVernonSt Boston 2010 f2 .jpg,
Image:Louisburg Square Beacon Hill Boston Massachusetts.jpg, Houses on Louisburg Square
File:2009 AcornSt Boston 3974583115.jpg, Acorn Street, 2009
Image:2nd Harrison Gray Otis House.jpg, Second
The
File:Sargent Hall, Suffolk University.jpg, Sargent Hall, Suffolk University
File:Suffolk Law Library.JPG, Law Library reading room, Suffolk University Law School
"Nine lives; or, The celebrated cat of Beacon Hill"
One library catalog record for the first edition.
''Book of Boston''
Beacon Hill History
Historic Beacon Hill District
, City of Boston
Beacon Hill Online
(last updated in 2009) {{Boston African American community pre-Civil War Neighborhoods in Boston National Historic Landmarks in Boston Historic districts in Suffolk County, Massachusetts Hills of Massachusetts Populated places on the Underground Railroad Historic preservation in the United States Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Massachusetts National Register of Historic Places in Boston
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
, and the hill upon which the Massachusetts State House resides. The term "Beacon Hill" is used locally as a metonym to refer to the state government or the legislature itself, much like Washington, D.C.'s " Capitol Hill" does at the federal level.
Federal-style rowhouse
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house ( UK) or townhouse ( US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings share side walls. In the United Sta ...
s, narrow gaslit streets and brick sidewalks adorn the neighborhood, which is generally regarded as one of the more desirable and expensive in Boston. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the population of Boston's Beacon Hill neighborhood is 9,023.

Etymology

beacon
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More mode ...
atop the highest point in central Boston. The beacon was used to warn the residents of an invasion.
Geography
Beacon Hill is bounded byStorrow Drive
Storrow Drive, officially James Jackson Storrow Memorial Drive, is a major crosstown parkway in Boston, Massachusetts, running east–west along the southern bank of the Charles River. It is restricted to cars; trucks and buses are not perm ...
, and Cambridge, Bowdoin, Park and Beacon Street
Beacon Street is a major thoroughfare in Boston, Massachusetts and its western suburbs Brookline and Newton. It passes through many of Boston's central and western neighborhoods, including Beacon Hill, Back Bay, Fenway–Kenmore, the Boston U ...
s. It is about 1/6 of a square mile, and situated along the riverfront of the Charles River Esplanade
The Charles River Esplanade of Boston, Massachusetts, is a state-owned park situated in the Back Bay area of the city, on the south bank of the Charles River Basin.
Description
The limited-access parkway Storrow Drive forms the southern bound ...
to the west, just north of Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beac ...
and the Boston Public Garden
The Public Garden, also known as Boston Public Garden, is a large park in the heart of Boston, Massachusetts, adjacent to Boston Common. It is a part of the Emerald Necklace system of parks, and is bounded by Charles Street and Boston Common to ...
. The block bound by Beacon
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More mode ...
, Tremont and Park Streets is included as well. Beacon Hill has three sections: the south slope, the north slope and the "Flat of the Hill", which is a level neighborhood built on landfill. It is west of Charles Street and between Beacon Street and Cambridge Street.
Located in the center of the Shawmut Peninsula
Shawmut Peninsula is the promontory of land on which Boston, Massachusetts was built. The peninsula, originally a mere in area,Miller, Bradford A., "Digging up Boston: The Big Dig Builds on Centuries of Geological Engineering", GeoTimes, Octo ...
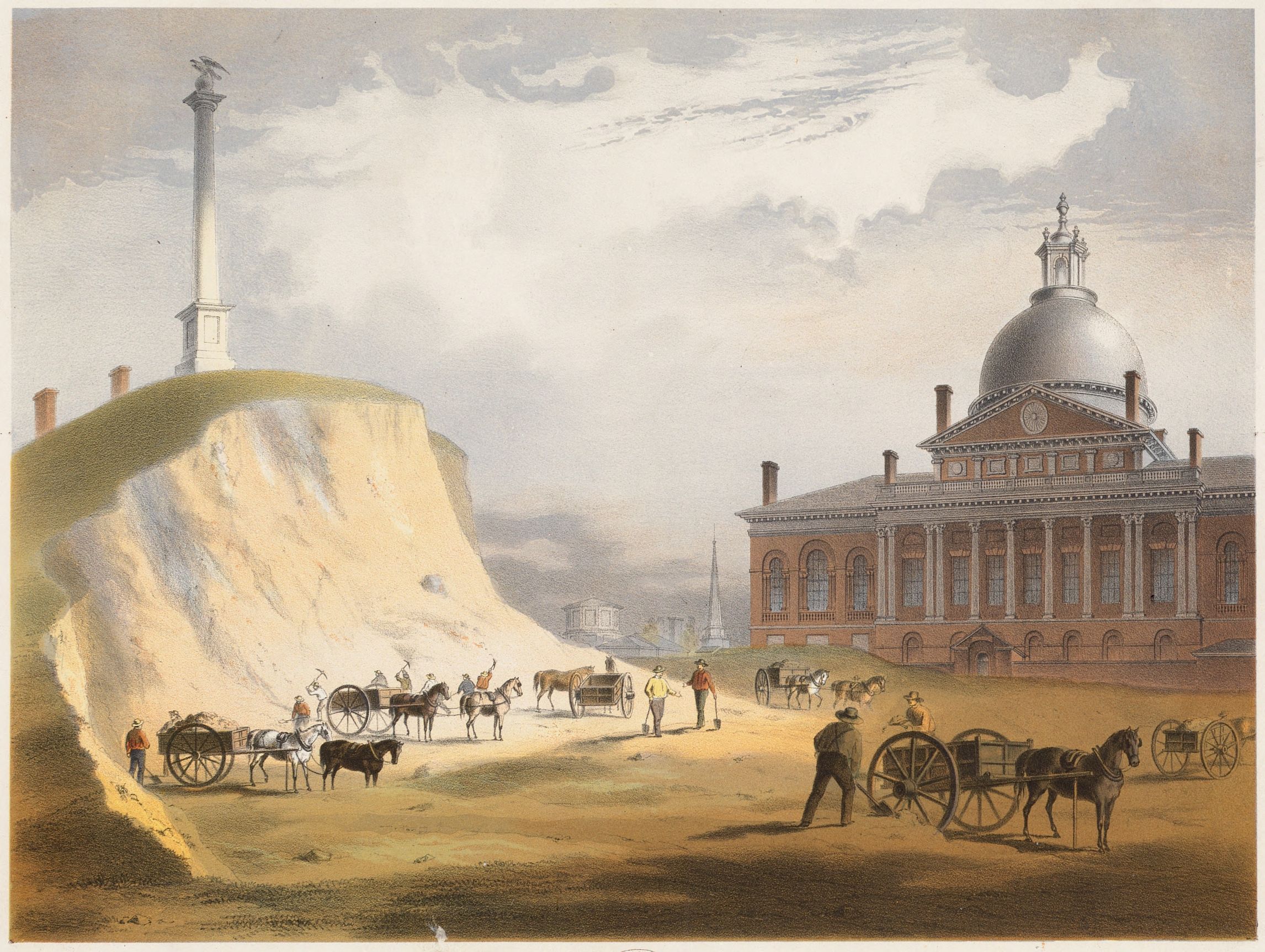
, the area originally had three hills, Beacon Hill and two others nearby; Pemberton Hill and Mount Vernon, which were leveled for Beacon Hill development. The name trimount later morphed into "Tremont", as in Tremont Street. Between 1807 and 1832 Beacon Hill was reduced from 138 feet in elevation to 80 feet. The shoreline and bodies of water such as the Mill Pond had a "massive filling", increasing Boston's land mass by 150%. Charles Street was one of the new roads created from the project.
Before the hill was reduced substantially, Beacon Hill was located just behind the current site of the Massachusetts State House.
Demographics
According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the population of Boston's Beacon Hill neighborhood is 9,023. This reflects a slight (0.3% or 29 individuals) decrease from the 2000 Census. The racial/ethnic make-up of the neighborhood's population is as follows: 86.8% of the population is white, 2% black or African American, 4.1% Hispanic or Latino, 0.1% American Indian or Alaska Native, 5.3% Asian, 0.4% some other race/ethnicity, and 1.3% two or more races/ethnicities. According to 2007-2011 American Community Survey estimates, of the 5,411 households in Beacon Hill, 27.3% were family households and 72.7 were non-family households (with 55.7% of those female householders). Of the 1,479 family households 81.6% were married couple families. 36.6% of married couple families were with related children under the age of 18 and 63.4% were with no related children under age 18. Other family types make up 18.4% of Beacon Hill's population, with 90.8% being female householders with no husband present and a majority of these households included children under 18 present.Race
Ancestry
According to the 2012–2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates, the largest ancestry groups in ZIP Codes 02108 and 02114 are:History
17th century
 The first European settler was
The first European settler was William Blaxton
Reverend William Blaxton (also spelled William Blackstone) (1595 – 26 May 1675) was an early English settler in New England and the first European settler of Boston and Rhode Island.
Biography
William Blaxton was born in Horncastle, Lincoln ...
, also spelled Blackstone. In 1625 he built a house and orchard on Beacon Hill's south slope, roughly at the location of Beacon and Spruce street. The settlement was a "preformal arrangement". In 1630 Boston was settled by the Massachusetts Bay Company
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
. The southwestern slope was used by the city for military drills and livestock grazing. In 1634 a signal beacon was established on the top of the hill. Sailors and British soldiers visited the north slope of Beacon Hill during the 17th and 18th centuries. As a result, it became an "undesirable" area for Boston residents. " Fringe activities" occurred on "Mount Whoredom", the backslope of Beacon Hill.
18th century
Beacon Street was established in 1708 from a cow path to theBoston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beac ...
. John Singleton Copley owned land on the south slope for pasture for his cows and farmland.
In 1787 Charles Bulfinch
Charles Bulfinch (August 8, 1763 – April 15, 1844) was an early American architect, and has been regarded by many as the first American-born professional architect to practice.Baltzell, Edward Digby. ''Puritan Boston & Quaker Philadelphia''. Tra ...
designed the Massachusetts State House. Its construction was completed in 1795, replacing the Old State House in the center of Boston.
The Mount Vernon Proprietors Mount Vernon Proprietors was a real estate development syndicate operating in Boston, Massachusetts. Founded at the end of the 18th century, it developed land on the south slope of Beacon Hill into a desirable residential neighborhood.
History
In ...
group was formed to develop the trimount area, The name trimount later morphed into "Tremont", as in Tremont Street. when by 1780 the city's neighborhoods could no longer meet the needs of the growing number of residents. Eighteen and a half or 19 acres of grassland west of the State House was purchased in 1795, most of it from John Singleton Copley. The Beacon Hill district's development began when Charles Bulfinch, an architect and planner, laid out the plan for the neighborhood. Four years later the hills were leveled, Mount Vernon Street was laid, and mansions were built along it. One of the first homes was the Harrison Gray Otis House
There are three houses named the Harrison Gray Otis House in Boston, Massachusetts. All were built by noted American architect Charles Bulfinch for the same man, Federalist lawyer and politician Harrison Gray Otis.
First Harrison Gray Otis House
...
on Cambridge Street.
19th century
Development
Construction of homes began in earnest at the turn of the century, such as: freestanding mansions, symmetrical pairs of houses, and row houses. Between 1803 and 1805, the first row houses were built for Stephen Higginson.Harrison Gray Otis House
There are three houses named the Harrison Gray Otis House in Boston, Massachusetts. All were built by noted American architect Charles Bulfinch for the same man, Federalist lawyer and politician Harrison Gray Otis.
First Harrison Gray Otis House
...
, mansion, on Cambridge Street
File:Headquarters House 55 Beacon Street Boston.jpg, Pair of houses, 54–55 Beacon Street. House on left is known as William H. Prescott House and as Headquarters House.
File:2010 ChestnutSt CharlesSt Boston.jpg, Chestnut Street, row houses, 2010
Back Bay
Back Bay is an officially recognized neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, built on reclaimed land in the Charles River basin. Construction began in 1859, as the demand for luxury housing exceeded the availability in the city at the time, and t ...
with its "French-inspired boulevards and mansard-roofed houses that were larger, lighter, and airier than the denser Beacon Hill."
In the early 19th century, there were "fringe activities" along the Back Bay waterfront, with ropewalk
A ropewalk is a long straight narrow lane, or a covered pathway, where long strands of material are laid before being twisted into rope. Due to the length of some ropewalks, workers may use bicycles to get from one end to the other.
Many rope ...
s along Beacon and Charles Streets.
South slope
The south slope "became the seat of Boston wealth and power." It was carefully planned for people who left densely populated areas, like the North End. The residents of opulent homes, called theBoston Brahmin
The Boston Brahmins or Boston elite are members of Boston's traditional upper class. They are often associated with Harvard University; Anglicanism; and traditional Anglo-American customs and clothing. Descendants of the earliest English coloni ...
s, were described by Oliver Wendell Holmes as a "harmless, inoffensive, untitled aristocracy". They had "houses by Charles Bulfinch
Charles Bulfinch (August 8, 1763 – April 15, 1844) was an early American architect, and has been regarded by many as the first American-born professional architect to practice.Baltzell, Edward Digby. ''Puritan Boston & Quaker Philadelphia''. Tra ...
, their monopoly on Beacon Street, their ancestral portraits and Chinese porcelains, humanitarianism, Unitarian faith in the march of the mind, Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United S ...
shrewdness, and New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
exclusiveness."
Literary salon
A salon is a gathering of people held by an inspiring host. During the gathering they amuse one another and increase their knowledge through conversation. These gatherings often consciously followed Horace's definition of the aims of poetry, "ei ...
s and publishing house
Publishing is the activity of making information, literature, music, software and other content available to the public for sale or for free. Traditionally, the term refers to the creation and distribution of printed works, such as books, newsp ...
s were founded in the 19th century. "Great thinkers" lived in the neighborhood, including Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison ...
, Henry Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and ...
and Wendell Phillips
Wendell Phillips (November 29, 1811 – February 2, 1884) was an American abolitionist, advocate for Native Americans, orator, and attorney.
According to George Lewis Ruffin, a Black attorney, Phillips was seen by many Blacks as "the one whi ...
.
Flat of the Hill
Development began in the early 19th century. Single family homes often had stores on the first floor for retailers, carpenters and shoemakers. Today, many of the 19th century waterfront landmarks, such as theCharles Street Meeting House
The Charles Street Meeting House is an early-nineteenth-century historic church in Beacon Hill at 70 Charles Street, Boston, Massachusetts.
The church has been used over its history by several Christian denominations, including Baptists, the ...
, are found far from the water due to the filling that has taken place since then.
=North slope
= The north slope was the home of African Americans, sailors and Eastern and Southern European immigrants. The area around Belknap Street (now Joy Street) in particular became home to more than 1,000 blacks beginning in the mid-1700s. While this community is often described as arising from domestic workers in the homes of white residents on the south slope of the Hill, property records indicate that the black community on the north slope was already well-established by 1805, before the filling-in of the south slope was completed, and so before that slope of Beacon Hill came to be considered an affluent area. Many blacks in the neighborhood attended church with the whites, but did not have a vote in church affairs and sat in segregated seating. TheAfrican Meeting House
The African Meeting House, also known variously as First African Baptist Church, First Independent Baptist Church and the Belknap Street Church, was built in 1806 and is now the oldest black church edifice still standing in the United States. It ...
was built in 1806 and by 1840 there were five black churches. The African Meeting House
The African Meeting House, also known variously as First African Baptist Church, First Independent Baptist Church and the Belknap Street Church, was built in 1806 and is now the oldest black church edifice still standing in the United States. It ...
on Joy Street was a community center for members of the black elite
The Black elite is any elite, either political or economic in nature, that is made up of people who identify as of Black African descent. In the Western World, it is typically distinct from other national elites, such as the United Kingdom's arist ...
. Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became ...
spoke there about abolition, and William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison (December , 1805 – May 24, 1879) was a prominent American Christian, abolitionist, journalist, suffragist, and social reformer. He is best known for his widely read antislavery newspaper '' The Liberator'', which he foun ...
formed the New England Anti-Slavery Society
The Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society, headquartered in Boston, was organized as an auxiliary of the American Anti-Slavery Society in 1835. Its roots were in the New England Anti-Slavery Society, organized by William Lloyd Garrison, editor of ...
at the Meeting House. It became a "hotbed and an important depot on the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
."
Blacks and whites were largely united on the subject of abolition. Beacon Hill was one of the staunchest centers of the anti-slavery movement in the Antebellum era.
The Republican Party was founded by abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
. One of the earliest black Republican legislators in the United States was Julius Caesar Chappelle
Julius Caesar Chappelle ( – January 27, 1904) was an American Republican Party politician who was born into slavery in South Carolina and served in the Massachusetts General Court. He was a leading figure of Boston's black community from 1870 u ...
(1852–1904), who served as a legislator in Boston from 1883 to 1886 and whose district included the Beacon Hill area. Chappelle was a popular, well-liked politician and was covered by many of the black newspapers in the United States.
Blacks migrated to Roxbury and Boston's South End after the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
=Immigrants
= In the latter part of the 19th century, Beacon Hill absorbed an influx ofIrish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and other immigrants.
Many homes built of brick and wood in the early 19th century were dilapidated by the end of the Civil War and were razed for new housing. Brick apartment buildings, or tenement
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
s were built. Yellow brick townhouses were constructed, generally with arched windows on the first floor and a low ceiling on the top, fourth floor. Residential homes were also converted to boarding houses.
The north slope neighborhood transitioned as blacks moved out of the neighborhood and immigrants, such as Eastern European Jews, made their homes in the community. The Vilna Shul was established in 1898, and the African Meeting House
The African Meeting House, also known variously as First African Baptist Church, First Independent Baptist Church and the Belknap Street Church, was built in 1806 and is now the oldest black church edifice still standing in the United States. It ...
was converted into a synagogue.
20th century
Scollay Square
300px, Scollay Square, Boston, 19th century (after September 1880)
350px, Scollay Square, Decoration Day, 19th century (after September 1880)
Scollay Square (c. 1838–1962) was a vibrant city square in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It was na ...
and the West End until a 1950s urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of blighte ...
project renovated the area. To prevent urban renewal projects of historically significant buildings in Beacon Hill, its residents ensured that the community obtained historic district status: south slope in 1955, Flat of the Hill in 1958, and north slope in 1963. The Beacon Hill Architectural Commission was established in 1955 to monitor renovation and development projects. For instance, in 1963, 70-72 Mount Vernon Street was to be demolished for the construction of an apartment building. A compromise was made to maintain the building and its exterior and build new apartments inside.
Historic district and national landmark
In 1955, state legislation Chapter 616 created the Historic Beacon Hill District. It was the first such district in Massachusetts, created to protect historic sites and manage urban renewal. Supporting these objectives is the local non-profit Beacon Hill Civic Association. According to theMassachusetts Historical Commission The Massachusetts Historical Commission (MHC) is a review board for state and federal preservation programs for the United States state of Massachusetts. It consists of 17-member panel of appointed representatives from state and private agencies and ...
, the historic districts "appear to have stabilized architectural fabric" of Beacon Hill.
Beacon Hill was designated a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
on December 19, 1962.
21st century
Wealthy Boston families continue to live at the Flat of the Hill and south slope. Inhabitants of the north slope include Suffolk University students and professionals.Sites of interest
Black Heritage Trail
TheBoston African American National Historic Site
The Boston African American National Historic Site, in the heart of Boston, Massachusetts's Beacon Hill neighborhood, interprets 15 pre-Civil War structures relating to the history of Boston's 19th-century African-American community, connected ...
is located just north of Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beac ...
. The historic buildings along today's Black Heritage Trail
The Boston African American National Historic Site, in the heart of Boston, Massachusetts's Beacon Hill neighborhood, interprets 15 pre-Civil War structures relating to the history of Boston's 19th-century African-American community, connected ...
were the homes, businesses, schools and churches of the black community. Charles Street Meeting House
The Charles Street Meeting House is an early-nineteenth-century historic church in Beacon Hill at 70 Charles Street, Boston, Massachusetts.
The church has been used over its history by several Christian denominations, including Baptists, the ...
was built in 1807, the church had seating that segregated white and black people. The Museum of African American History, New England's largest museum dedicated to African American history is located at the African Meeting House
The African Meeting House, also known variously as First African Baptist Church, First Independent Baptist Church and the Belknap Street Church, was built in 1806 and is now the oldest black church edifice still standing in the United States. It ...
, adjacent to the Abiel Smith School
Abiel Smith School, founded in 1835, is a school located at 46 Joy Street in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, adjacent to the African Meeting House. It is named for Abiel Smith, a white philanthropist who left money (an estimated $4,000) in h ...
. The meeting house is the oldest surviving Black church built by African Americans. The Robert Gould Shaw Memorial and the 54th Massachusetts Regiment
The 54th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that saw extensive service in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The unit was the second African-American regiment, following the 1st Kansas Colored Volunteer Infantry ...
Memorial are located at Beacon Street and Park Street, opposite the Massachusetts State House.
Massachusetts State House
The Massachusetts State House, located on Beacon Street, is the home of the Commonwealth's government. The gold-domed state capitol building was designed byCharles Bulfinch
Charles Bulfinch (August 8, 1763 – April 15, 1844) was an early American architect, and has been regarded by many as the first American-born professional architect to practice.Baltzell, Edward Digby. ''Puritan Boston & Quaker Philadelphia''. Tra ...
and was completed in 1798. Many of the country's state capitol buildings were modeled after the State House.
Organizations
Community
The Beacon Hill Civic Association has a long history as a community resource for the Beacon Hill neighborhood. Founded in 1922 by neighbors with the goal of preventing home building and other construction, today it continues as a volunteer advocacy organization focused on improving quality of life in the neighborhood. It was first founded to fight city plans to replace the neighborhood's brick sidewalks. Since then its efforts have been instrumental in preserving Beacon Hill as a historic district, and have expanded to include such initiatives as: working to become the first neighborhood to receive resident parking permits, streamlining trash service, and creating a virtual retirement community serving the neighborhood's elderly.Non-religious
The Club of Odd Volumes
The Club of Odd Volumes is a private social club and society of bibliophiles founded in 1887, in Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
History
The club was founded on January 29, 1887, with the following intention:
The objects shall be to promote an in ...
, a historic organization on Mount Vernon Street, serves as a Bibliophiles club, library, and archive. The Headquarters House, also known as William Hickling Prescott House, is a museum run by the Society of Colonial Dames. The country's oldest legal organization, the Boston Bar Association, is on Beacon Street. Beacon Hill Village was the first formal Elder Village in the United States.Jane Gross,A Grass-Roots Effort to Grow Old at Home
, ''The New York Times'', August 14, 2007; accessed 2013.05.17.Haya El Nasser
''USA Today'', July 26, 2010; accessed 2013.05.17.
The Club of Odd Volumes
The Club of Odd Volumes is a private social club and society of bibliophiles founded in 1887, in Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
History
The club was founded on January 29, 1887, with the following intention:
The objects shall be to promote an in ...
, 77 Mt. Vernon Street
Image:Boston Bar Association facade.jpg, The Chester Harding House, a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
occupied by portrait painter Chester Harding from 1826 to 1830, now houses the Boston Bar Association.
Religious
Religious organizations include the Vilna Shul, an Orthodox Jewish synagogue, and the Unitarian Universalist Association headquarters. Church of the Advent is a Victorian Gothic Church, faced in brick with 8 massive carillon bells and a 172-foot spire. ThePark Street Church
Park Street Church, founded in 1804, is a historic and active evangelical congregational megachurch in Downtown Boston, Massachusetts. The Park Street Church is a member of the Conservative Congregational Christian Conference. Typical attendance a ...
, nicknamed "Brimstone Corner" in the 19th century, was used to store gunpowder during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. Samuel Francis Smith first sang his song ''America the Beautiful
"America the Beautiful" is a patriotic American song. Its lyrics were written by Katharine Lee Bates and its music was composed by church organist and choirmaster Samuel A. Ward at Grace Episcopal Church in Newark, New Jersey. The two neve ...
'' at this church in 1831. Two years earlier William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison (December , 1805 – May 24, 1879) was a prominent American Christian, abolitionist, journalist, suffragist, and social reformer. He is best known for his widely read antislavery newspaper '' The Liberator'', which he foun ...
spoke to the congregation about abolishing slavery. One of the few outposts of the small Protestant group the Swedenborgian Church is on Bowdoin Street, and was embroiled in controversy in 2013 over alleged extortion by a former mafioso. While home to a Paulist
Paulists, or Paulines, is the name used for Roman Catholic orders and congregations under the patronage of Paul of Thebes the First Hermit. From the time that the abode and virtues of Paul of Thebes were revealed to Antony the Abbot, various comm ...
chapel, Beacon Hill is currently one of only two neighborhoods in Boston that does not contain a Catholic parish church.
Neighborhoods
Beacon Hill is predominantly residential, known for old colonial brick row houses with "beautiful doors, decorative iron work, brick sidewalks, narrow streets, and gas lamps". Restaurants and antique shops are located on Charles Street. Louisburg Square is "the most prestigious address" in Beacon Hill. Its residents have access to private parking and live in "magnificent Greek Revival townhouses." Nearby is Acorn Street, often mentioned as the "most frequently photographed street in the United States." It is a narrow lane paved with cobblestones that was home to coachmen employed by families in Mt. Vernon and Chestnut Street mansions.Harrison Gray Otis House
There are three houses named the Harrison Gray Otis House in Boston, Massachusetts. All were built by noted American architect Charles Bulfinch for the same man, Federalist lawyer and politician Harrison Gray Otis.
First Harrison Gray Otis House
...
, 85 Mount Vernon Street.
File:USA-Boston-Beacon Hill0.jpg, Acorn Street, 2013
Harrison Gray Otis House
There are three houses named the Harrison Gray Otis House in Boston, Massachusetts. All were built by noted American architect Charles Bulfinch for the same man, Federalist lawyer and politician Harrison Gray Otis.
First Harrison Gray Otis House
...
on Cambridge Street was built in 1796. Charles Bulfinch designed this house, and two additional houses, for the businessman and politician who was instrumental in Beacon Hill's development and Boston becoming the state capital. The Otis House also houses the headquarters of Historic New England
Historic New England, previously known as the Society for the Preservation of New England Antiquities (SPNEA), is a charitable, non-profit, historic preservation organization headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. It is focused on New England ...
, previously known as Society for the Preservation of New England Antiquities. Other notable houses are the Francis Parkman House
The Francis Parkman House is a National Historic Landmark at 50 Chestnut Street, on Beacon Hill in Boston, Massachusetts. Speculated to be designed by Cornelius Coolidge and built in 1824, it is one of a series of fine brick townhouses on Beac ...
and an 1804 townhouse, now the Nichols House Museum. The Nichols House "offers a rare glimpse inside heBrahmin life" of Rose Standish Nichols, a landscape artists.
Suffolk University
Suffolk University and its Law School are adjacent to the Massachusetts State House and the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court. The Suffolk University Law School was founded in 1906.Transportation

Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
(MBTA) subway stations in Beacon Hill are:
* Park Street – Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
Lines
* Bowdoin – Blue Line
* Charles/MGH – Red Line
MBTA bus, MBTA commuter rail, and ferry services are also available.
Notable residents
Beacon Hill has been home to many notable persons, including: * Mildred Albert * Louisa May Alcott *John Albion Andrew
John Albion Andrew (May 31, 1818 – October 30, 1867) was an American lawyer and politician from Massachusetts. He was elected in 1860 as the 25th Governor of Massachusetts, serving between 1861 and 1866, and led the state's contributions to ...
* William Blaxton
Reverend William Blaxton (also spelled William Blackstone) (1595 – 26 May 1675) was an early English settler in New England and the first European settler of Boston and Rhode Island.
Biography
William Blaxton was born in Horncastle, Lincoln ...
, original owner of Beacon Hill
* Edwin Booth
* Peter Bent Brigham
Peter Bent Brigham (1807–1877) was an American millionaire businessman, restaurateur, real estate trader, and director of the Fitchburg Railroad. He is best known as a philanthropist for his initial endowment of Peter Bent Brigham Hospital an ...
* Charles Bulfinch
Charles Bulfinch (August 8, 1763 – April 15, 1844) was an early American architect, and has been regarded by many as the first American-born professional architect to practice.Baltzell, Edward Digby. ''Puritan Boston & Quaker Philadelphia''. Tra ...
* John Cheever
* Ednah Dow Littlehale Cheney
Ednah Dow Littlehale Cheney (June 27, 1824 – November 19, 1904) was an American writer, reformer, and philanthropist.
She was born on Beacon Hill, Boston, June 27, 1824; and was educated in private schools in Boston. Cheney served as secretary ...
* John Singleton Copley
* Michael Crichton
* Robert Frost
* James Gibson (Captain)
* Janet Doub Erickson
* John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of t ...
* Chester Harding
* Teresa Heinz
Teresa Heinz (born Maria Teresa Thierstein Simões-Ferreira; October 5, 1938), also known as Teresa Heinz Kerry, is a Portuguese-American businesswoman and philanthropist. Heinz is the widow of former U.S. Senator John Heinz and the wife of fo ...
* Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr.
Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. (; August 29, 1809 – October 7, 1894) was an American physician, poet, and polymath based in Boston. Grouped among the fireside poets, he was acclaimed by his peers as one of the best writers of the day. His most fa ...
* Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.
Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. (March 8, 1841 – March 6, 1935) was an American jurist and legal scholar who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1902 to 1932.Holmes was Acting Chief Justice of the Un ...
* Julia Ward Howe
Julia Ward Howe (; May 27, 1819 – October 17, 1910) was an American author and poet, known for writing the " Battle Hymn of the Republic" and the original 1870 pacifist Mother's Day Proclamation. She was also an advocate for abolitionism ...
* Abigail Johnson
* Edward M. Kennedy
* John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party, he ...
* Henry Cabot Lodge
Henry Cabot Lodge (May 12, 1850 November 9, 1924) was an American Republican politician, historian, and statesman from Massachusetts. He served in the United States Senate from 1893 to 1924 and is best known for his positions on foreign policy. ...
* James Russell Lowell
James Russell Lowell (; February 22, 1819 – August 12, 1891) was an American Romantic poet, critic, editor, and diplomat. He is associated with the fireside poets, a group of New England writers who were among the first American poets that ...
* Robert Lowell
* Mary Osgood
* Harrison Gray Otis
* Sylvia Plath
Sylvia Plath (; October 27, 1932 – February 11, 1963) was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer. She is credited with advancing the genre of confessional poetry and is best known for two of her published collections, '' Th ...
* William Prescott
William Prescott (February 20, 1726 – October 13, 1795) was an American colonel in the Revolutionary War who commanded the patriot forces in the Battle of Bunker Hill. Prescott is known for his order to his soldiers, "Do not fire until ...
* Eleanor Raymond
* C. Allen Thorndike Rice
* Henry Rice
* David Lee Roth
* George Santayana
Jorge Agustín Nicolás Ruiz de Santayana y Borrás, known in English as George Santayana (; December 16, 1863 – September 26, 1952), was a Spanish and US-American philosopher, essayist, poet, and novelist. Born in Spain, Santayana was raised ...
* Anne Sexton
Anne Sexton (born Anne Gray Harvey; November 9, 1928 – October 4, 1974) was an American poet known for her highly personal, confessional verse. She won the Pulitzer Prize for poetry in 1967 for her book '' Live or Die''. Her poetry details ...
* Robert Gould Shaw
Robert Gould Shaw (October 10, 1837 – July 18, 1863) was an American officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Born into a prominent Boston abolitionist family, he accepted command of the first all-black regiment (the 54th Mas ...
* Carly Simon
* Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811March 11, 1874) was an American statesman and United States Senator from Massachusetts. As an academic lawyer and a powerful orator, Sumner was the leader of the anti-slavery forces in the state and a leader of th ...
* Uma Thurman
Uma Karuna Thurman (born April 29, 1970) is an American actress and former model. She has performed in a variety of films, from romantic comedies and dramas to science fiction and action films. Following her appearances on the December 1985 an ...
* David Walker
* Gretchen Osgood Warren
* Fiske Warren
Frederick Fiske Warren (2 July 1862 – 2 February 1938) was a successful paper manufacturer, fine arts doyen, United States tennis champion of 1893, and major supporter of Henry George's single tax system which he helped develop in Harvard, ...
* Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison ...
* Jack Welch
John Francis Welch Jr. (November 19, 1935 – March 1, 2020) was an American business executive, chemical engineer, and writer. He was Chairman and CEO of General Electric (GE) between 1981 and 2001.
When Welch retired from GE, he receive ...
In popular culture
* Published in 1937, the Pulitzer-Prize-winning novel ''The Late George Apley
''The Late George Apley'' is a 1937 novel by John Phillips Marquand. It is a satire of Boston's upper class in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The title character is a Harvard-educated WASP living on Beacon Hill in downtown Boston. T ...
'' by John Phillips Marquand satirizes the upper-class white residents of Beacon Hill.
* William Kane, one of the protagonists in the Jeffrey Archer novel '' Kane and Abel'', lives in Beacon Hill.
* On Beacon Street, the Bull and Finch Bar was inspiration and source of exterior shots for the '' Cheers'' television show
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed b ...
.
* ''Make Way for Ducklings
''Make Way for Ducklings'' is a children's picture book written and illustrated by Robert McCloskey. First published in 1941 by the Viking Press, the book tells the story of a pair of mallards who raise their brood of ducklings on an island in t ...
'' (Viking, 1941) is a children's
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person young ...
picture book
A picture book combines visual and verbal narratives in a book format, most often aimed at young children. With the narrative told primarily through text, they are distinct from comics, which do so primarily through sequential images. The images ...
written and illustrated by Robert McCloskey
John Robert McCloskey (September 15, 1914 – June 30, 2003) was an American writer and illustrator of children's books. He both wrote and illustrated eight picture books, and won two Caldecott Medals from the American Library Association for t ...
. Most of the story is set at the foot of Beacon Hill, especially the route taken by the fictional Mrs. Mallard and her children on foot across Beacon Street. It is commemorated every year in May by a parade through Beacon Hill to the Boston Public Garden
The Public Garden, also known as Boston Public Garden, is a large park in the heart of Boston, Massachusetts, adjacent to Boston Common. It is a part of the Emerald Necklace system of parks, and is bounded by Charles Street and Boston Common to ...
, where the mallards nested.
* ''Nine Lives; or, the celebrated cat of Beacon Hill'' (Pantheon, 1951) is a 62-page children's book by the novelist Edward Fenton (1917–1995) and illustrator Paul Galdone
Paul Galdone (June 2, 1907 – November 7, 1986) was an illustrator and writer known best for children's picture books.
Early life
He was born in Budapest and he emigrated to the United States in 1921. He studied art at the Art Student's ...
. "A wealthy, elderly Boston matron adopts a scruffy tomcat and while she is away on a trip her jealous butler tries very hard to destroy all nine of the cat's lives."One library catalog record for the first edition.
WorldCat
WorldCat is a union catalog that itemizes the collections of tens of thousands of institutions (mostly libraries), in many countries, that are current or past members of the OCLC global cooperative. It is operated by OCLC, Inc. Many of the O ...
. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
* The 1968 Norman Jewison
Norman Frederick Jewison (born July 21, 1926) is a retired Canadian film and television director, producer, and founder of the Canadian Film Centre.
He has directed numerous feature films and has been nominated for the Academy Award for Best ...
film '' The Thomas Crown Affair'' is set and was largely filmed in and around Beacon Hill.
* Dr Charles Emerson Winchester in an episode of '' MASH'' /13 "No Laughing Matter"swears "By Beacon Hill" to get revenge on the commanding officer who sent him to MASH 4077.
* Robert Lowell's prose sketch ''91 Revere Street'' was inspired by his childhood home on Beacon Hill.
* Dr. Michaela Quinn of ''Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman
''Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman'' is an American Western drama television series created and executive produced by Beth Sullivan and starring Jane Seymour, who plays Dr. Michaela Quinn, a physician who leaves Boston in search of adventure in the O ...
'' was raised on Beacon Hill.
* Dr. Maura Isles of TNT's '' Rizzoli & Isles'' lives on Beacon Hill.
* Asclepia, a small private hospital, is mentioned in Patrick O'Brian
Patrick O'Brian, CBE (12 December 1914 – 2 January 2000), born Richard Patrick Russ, was an English novelist and translator, best known for his Aubrey–Maturin series of sea novels set in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, and cent ...
's sixth Aubrey-Maturin novel, ''The Fortune of War
''The Fortune of War'' is the sixth historical novel in the Aubrey-Maturin series by British author Patrick O'Brian, first published in 1979. It is set during the War of 1812.
HMS ''Leopard'' made its way to Botany Bay, left its prisoners, ...
'', as being "in a dry, healthy location near Beacon Hill."
* The NBC TV series '' Banacek'' (1972–1974) was set and partially filmed on Beacon Hill. Its main character "Thomas Banacek" played by George Peppard grew up in nearby "Scollay Square" and lived in the "Second Harrison Grey Otis House."
See also
*National Register of Historic Places listings in northern Boston, Massachusetts __NOTOC__
Boston, Massachusetts is home to many listings on the National Register of Historic Places. This list encompasses those locations that are located north of the Massachusetts Turnpike. See National Register of Historic Places listings in ...
*List of National Historic Landmarks in Boston
This is a list of National Historic Landmarks in Boston, Massachusetts. It includes 57 properties and districts designated as National Historic Landmarks in the city of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Another 131 National Historic Landmarks ...
* List of notable addresses in Beacon Hill, Boston
Notes and references
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * Online version''Book of Boston''
Further reading
*Biography: *Fiction:External links
Beacon Hill History
Historic Beacon Hill District
, City of Boston
Beacon Hill Online
(last updated in 2009) {{Boston African American community pre-Civil War Neighborhoods in Boston National Historic Landmarks in Boston Historic districts in Suffolk County, Massachusetts Hills of Massachusetts Populated places on the Underground Railroad Historic preservation in the United States Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Massachusetts National Register of Historic Places in Boston