Battle for Henderson Field on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle for Henderson Field, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal or Battle of Lunga Point by the Japanese, took place from 23 to 26 October 1942 on and around
 The first U.S. Marine operation against Japanese forces west of the Matanikau, conducted between 23 and 27 September 1942 by elements of three U.S. Marine
The first U.S. Marine operation against Japanese forces west of the Matanikau, conducted between 23 and 27 September 1942 by elements of three U.S. Marine  On 13 October, in order to help protect the transit of an important supply convoy to Guadalcanal that consisted of six slower cargo ships, the Japanese
On 13 October, in order to help protect the transit of an important supply convoy to Guadalcanal that consisted of six slower cargo ships, the Japanese
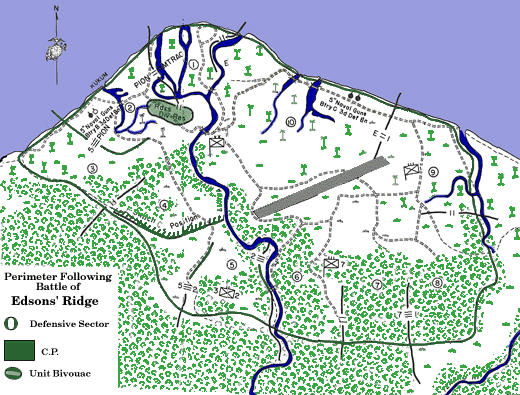 On 12 October, a company of Japanese engineers began to break a trail, called the "Maruyama Road", from the Matanikau towards the southern portion of the U.S. Lunga perimeter. The trail traversed some of the most difficult terrain on Guadalcanal, including numerous rivers and streams, deep, muddy ravines, steep ridges, and dense jungle. Between 16 and 18 October, the 2nd Division began their march along the Maruyama Road, led by Nasu's unit and followed in order by Kawaguchi and Maruyama. Each soldier had been ordered to carry one artillery shell plus his pack and rifle.
Early on the morning of 20 October, Maruyama reached the Lunga River. Believing that his units were about south of the airfield, he ordered the left and right wing units to advance abreast of each other parallel to the Lunga north towards the American lines and set the time of the attack for 18:00 on 22 October. Maruyama, however, was mistaken. He and his troops were actually south of the airfield. By the evening of 21 October, it was clear to Maruyama that his units would not be in position to attack the next day, so he postponed the attack to 23 October and put his men on half rations to conserve their dwindling food supply. At nightfall on 22 October, much of the 2nd Division still remained strung out along the Maruyama Road, but Maruyama ruled out any postponement of the attack.
During this time, Sumiyoshi prepared his command to attack the American forces from the west. On 18 October, he began shelling Henderson Field with fifteen howitzers. What remained of the 4th Infantry Regiment under Colonel
On 12 October, a company of Japanese engineers began to break a trail, called the "Maruyama Road", from the Matanikau towards the southern portion of the U.S. Lunga perimeter. The trail traversed some of the most difficult terrain on Guadalcanal, including numerous rivers and streams, deep, muddy ravines, steep ridges, and dense jungle. Between 16 and 18 October, the 2nd Division began their march along the Maruyama Road, led by Nasu's unit and followed in order by Kawaguchi and Maruyama. Each soldier had been ordered to carry one artillery shell plus his pack and rifle.
Early on the morning of 20 October, Maruyama reached the Lunga River. Believing that his units were about south of the airfield, he ordered the left and right wing units to advance abreast of each other parallel to the Lunga north towards the American lines and set the time of the attack for 18:00 on 22 October. Maruyama, however, was mistaken. He and his troops were actually south of the airfield. By the evening of 21 October, it was clear to Maruyama that his units would not be in position to attack the next day, so he postponed the attack to 23 October and put his men on half rations to conserve their dwindling food supply. At nightfall on 22 October, much of the 2nd Division still remained strung out along the Maruyama Road, but Maruyama ruled out any postponement of the attack.
During this time, Sumiyoshi prepared his command to attack the American forces from the west. On 18 October, he began shelling Henderson Field with fifteen howitzers. What remained of the 4th Infantry Regiment under Colonel
 Nakaguma's tanks attacked in pairs across the sandbar at the mouth of the Matanikau behind a barrage of artillery. Marine
Nakaguma's tanks attacked in pairs across the sandbar at the mouth of the Matanikau behind a barrage of artillery. Marine
 At 14:00 on 24 October, Maruyama's left and right wing units began to deploy for their attacks. Maruyama's troops had very little artillery or mortar support for their upcoming assault, having abandoned most of their heavy cannons along the Maruyama Road. Between 16:00 and 21:00, heavy rain fell, delaying the Japanese approach and causing "chaos" in the Japanese formations, already exhausted from the long march through the jungle.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 353–54. Shoji's right wing force accidentally turned parallel to the Marine lines, and all but one battalion failed to make contact with the Marine defenses. Shoji's 1st Battalion, 230th Infantry Regiment "stumbled" into Puller's lines about 22:00 and were driven off by Puller's men. For unknown reasons, Maruyama's staff then reported to Hyakutake that Shoji's men had overrun Henderson Field. At 00:50 on 25 October, Hyakutake signaled Rabaul that, "A little before 23:00 the Right Wing captured the airfield."Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', pp. 197–98.
At about this time, Nasu's left wing battalions finally began to reach the Marine defenses. At 00:30 on 25 October, the 11th Company of Nasu's 3rd Battalion under
At 14:00 on 24 October, Maruyama's left and right wing units began to deploy for their attacks. Maruyama's troops had very little artillery or mortar support for their upcoming assault, having abandoned most of their heavy cannons along the Maruyama Road. Between 16:00 and 21:00, heavy rain fell, delaying the Japanese approach and causing "chaos" in the Japanese formations, already exhausted from the long march through the jungle.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 353–54. Shoji's right wing force accidentally turned parallel to the Marine lines, and all but one battalion failed to make contact with the Marine defenses. Shoji's 1st Battalion, 230th Infantry Regiment "stumbled" into Puller's lines about 22:00 and were driven off by Puller's men. For unknown reasons, Maruyama's staff then reported to Hyakutake that Shoji's men had overrun Henderson Field. At 00:50 on 25 October, Hyakutake signaled Rabaul that, "A little before 23:00 the Right Wing captured the airfield."Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', pp. 197–98.
At about this time, Nasu's left wing battalions finally began to reach the Marine defenses. At 00:30 on 25 October, the 11th Company of Nasu's 3rd Battalion under
 The Japanese 8th Fleet had task units ready to support the Army's attacks on Guadalcanal. Upon receipt of Hyakutake's message declaring success at 00:50 on 24 October, the task units went into action. The
The Japanese 8th Fleet had task units ready to support the Army's attacks on Guadalcanal. Upon receipt of Hyakutake's message declaring success at 00:50 on 24 October, the task units went into action. The
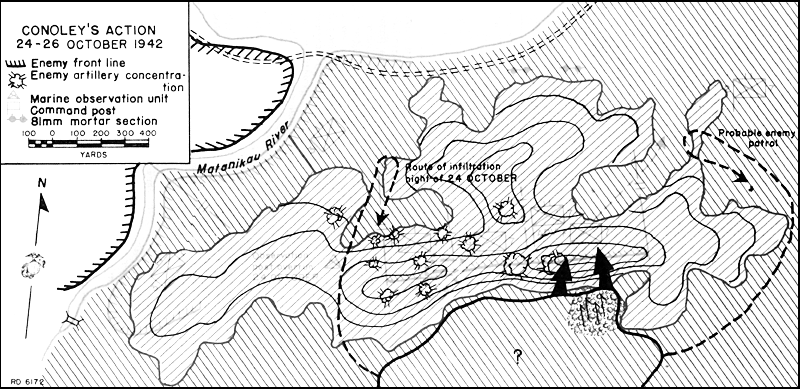 At 03:00 on 26 October, Oka's unit finally reached and attacked the Marine defenses near the Matanikau. Oka's troops assaulted all along an east–west saddle ridge held by Hanneken's battalion but concentrated particularly on Hanneken's Company F, which defended the extreme left flank of the Marine positions on the ridge. A Company F machine gun section under Mitchell Paige killed many of the Japanese attackers, but Japanese fire eventually killed or injured almost all the Marine machine gunners. At 05:00, Oka's 3rd Battalion, 4th Infantry succeeded in scaling the steep slope of the ridge and pushed the surviving members of Company F off the crest.Hough, ''Pearl Harbor to Guadalcanal'', p. 337.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 363–64.Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', p. 204.
Responding to the Japanese capture of part of the ridgeline, Major Odell M. Conoley—Hanneken's battalion
At 03:00 on 26 October, Oka's unit finally reached and attacked the Marine defenses near the Matanikau. Oka's troops assaulted all along an east–west saddle ridge held by Hanneken's battalion but concentrated particularly on Hanneken's Company F, which defended the extreme left flank of the Marine positions on the ridge. A Company F machine gun section under Mitchell Paige killed many of the Japanese attackers, but Japanese fire eventually killed or injured almost all the Marine machine gunners. At 05:00, Oka's 3rd Battalion, 4th Infantry succeeded in scaling the steep slope of the ridge and pushed the surviving members of Company F off the crest.Hough, ''Pearl Harbor to Guadalcanal'', p. 337.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 363–64.Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', p. 204.
Responding to the Japanese capture of part of the ridgeline, Major Odell M. Conoley—Hanneken's battalion
 At 08:00 on 26 October, Hyakutake called off any further attacks and ordered his forces to retreat. Maruyama's men recovered some of their wounded from near the American lines on the night of 26–27 October, and began to withdraw back into the deep jungle. The Americans recovered and buried or burned as quickly as possible the remains of 1,500 of Maruyama's men left lying in front of Pullers's and Hall's lines. Said one U.S. Army participant, John E. Stannard, of the scene after the battle, "The carnage of the battlefield was a sight that perhaps only the combat infantryman, who has fought at close quarters, could fully comprehend and look upon without a feeling of horror. One soldier, after a walk among the Japanese dead, said to his comrade: 'My God, what a sight. There's dead Japs stretched from the Corner back along the edge of the jungle for a half a mile [].'"
Maruyama's left wing survivors were ordered to retreat back to the area west of the Matanikau River while Shoji's right wing was told to head for Koli Point, east of the Lunga perimeter. The left wing soldiers, who had run out of food several days before, began the retreat on 27 October. During the retreat, many of the Japanese wounded succumbed to their injuries and were buried along the Maruyama road. One of Maruyama's men, Lieutenant Keijiro Minegishi, noted in his diary, "I never dreamed of retreating over the same mountainous trail through the jungle we crossed with such enthusiasm... we haven't eaten in three days and even walking is difficult. On the up hill my body swayed around unable to walk. I must rest every two meters."
Leading elements of the 2nd Division reached the 17th Army headquarters area at
At 08:00 on 26 October, Hyakutake called off any further attacks and ordered his forces to retreat. Maruyama's men recovered some of their wounded from near the American lines on the night of 26–27 October, and began to withdraw back into the deep jungle. The Americans recovered and buried or burned as quickly as possible the remains of 1,500 of Maruyama's men left lying in front of Pullers's and Hall's lines. Said one U.S. Army participant, John E. Stannard, of the scene after the battle, "The carnage of the battlefield was a sight that perhaps only the combat infantryman, who has fought at close quarters, could fully comprehend and look upon without a feeling of horror. One soldier, after a walk among the Japanese dead, said to his comrade: 'My God, what a sight. There's dead Japs stretched from the Corner back along the edge of the jungle for a half a mile [].'"
Maruyama's left wing survivors were ordered to retreat back to the area west of the Matanikau River while Shoji's right wing was told to head for Koli Point, east of the Lunga perimeter. The left wing soldiers, who had run out of food several days before, began the retreat on 27 October. During the retreat, many of the Japanese wounded succumbed to their injuries and were buried along the Maruyama road. One of Maruyama's men, Lieutenant Keijiro Minegishi, noted in his diary, "I never dreamed of retreating over the same mountainous trail through the jungle we crossed with such enthusiasm... we haven't eaten in three days and even walking is difficult. On the up hill my body swayed around unable to walk. I must rest every two meters."
Leading elements of the 2nd Division reached the 17th Army headquarters area at
 Although the Japanese Army's attack on the Allied Lunga perimeter was decisively defeated in this battle, the Japanese were not yet ready to give up the struggle for Guadalcanal. The Japanese Army and navy made immediate plans to move the rest of the 38th Division to the island, along with the 51st Infantry Division, to try a further offensive against Henderson Field in November 1942.
Although the Japanese Army's attack on the Allied Lunga perimeter was decisively defeated in this battle, the Japanese were not yet ready to give up the struggle for Guadalcanal. The Japanese Army and navy made immediate plans to move the rest of the 38th Division to the island, along with the 51st Infantry Division, to try a further offensive against Henderson Field in November 1942.
 The Japanese again planned to bombard Henderson Field with battleships in order to allow a convoy of transport ships to deliver the 38th's troops and heavy equipment. In contrast, however, to what occurred on 14 October, this time the U.S. Navy moved to intercept the battleship forces sent by Yamamoto from Truk to shell the airfield. During the ensuing
The Japanese again planned to bombard Henderson Field with battleships in order to allow a convoy of transport ships to deliver the 38th's troops and heavy equipment. In contrast, however, to what occurred on 14 October, this time the U.S. Navy moved to intercept the battleship forces sent by Yamamoto from Truk to shell the airfield. During the ensuing
Print
* * * * * * * * * * *
Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the south-western Pacific, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomon Islands by area, and the se ...
in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
. The battle was a land, sea, and air battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and was fought between the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy and Allied forces, mainly U.S. Marines and Army. The battle was the last of three major land offensives conducted by the Japanese during the Guadalcanal campaign
The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the ...
.
In the battle, U.S. Marine and Army forces repulsed an attack by the Japanese 17th Army under the command of Lieutenant General Harukichi Hyakutake.
The American forces were defending the Lunga perimeter that guarded Henderson Field on Guadalcanal, which the Allies had captured from the Japanese in landings on Guadalcanal on 7 August 1942. Hyakutake's force was sent to Guadalcanal in response to the Allied landings with the mission of recapturing the airfield and driving the Allied forces off the island. His soldiers conducted numerous assaults over three days at various locations around the Lunga perimeter, all repulsed with heavy Japanese losses. At the same time, Allied aircraft operating from Henderson Field successfully defended American positions on Guadalcanal from attacks by Japanese naval air and sea forces.
The battle was the last serious ground offensive conducted by Japanese forces on Guadalcanal. They attempted to deliver further reinforcements, but failed during the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
The Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, sometimes referred to as the Third and Fourth Battles of Savo Island, the Battle of the Solomons, the Battle of Friday the 13th, or, in Japanese sources, the , took place from 12 to 15 November 1942, and was t ...
in November 1942, and Japan conceded defeat in the struggle for the island and evacuated many of its remaining forces by the first week of February 1943.
Background
Guadalcanal campaign
On 7 August 1942, Allied forces (primarily U.S.) landed on Guadalcanal,Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island——in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1 ...
, and Florida Islands
The Nggela Islands, also known as the Florida Islands, are a small island group in the Central Province of Solomon Islands, a sovereign state (since 1978) in the southwest Pacific Ocean.
The chain is composed of four larger islands and about ...
in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
. The landings on the islands were meant to deny their use by the Japanese as bases for threatening the supply
Supply may refer to:
*The amount of a resource that is available
**Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers
**Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission
*Supply, as in confidenc ...
routes between the U.S. and Australia, and to secure the islands as starting points for a campaign with the eventual goal of isolating the major Japanese base at Rabaul
Rabaul () is a township in the East New Britain province of Papua New Guinea, on the island of New Britain. It lies about 600 kilometres to the east of the island of New Guinea. Rabaul was the provincial capital and most important settlement in ...
while also supporting the Allied New Guinea campaign
The New Guinea campaign of the Pacific War lasted from January 1942 until the end of the war in August 1945. During the initial phase in early 1942, the Empire of Japan invaded the Australian-administered Mandated Territory of New Guinea (23 Jan ...
. The landings initiated the six-month-long Guadalcanal campaign.
Taking the Japanese by surprise, by nightfall on 8 August, the 11,000 Allied troops—under the command of then Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
Alexander Vandegrift and mainly consisting of U.S. Marine Corps units—had secured Tulagi and nearby small islands, as well as an airfield under construction at Lunga Point on Guadalcanal. The airfield was later named "Henderson Field" by Allied forces. The Allied aircraft that subsequently operated out of the airfield became known as the "Cactus Air Force
Cactus Air Force refers to the ensemble of Allied air power assigned to the island of Guadalcanal August 1942 until December 1942 during the early stages of the Guadalcanal Campaign, particularly those operating from Henderson Field. The term ...
" (CAF) after the Allied codename for Guadalcanal. To protect the airfield, the U.S. Marines established a perimeter defense around Lunga Point.
In response to the Allied landings on Guadalcanal, the Japanese Imperial General Headquarters
The was part of the Supreme War Council and was established in 1893 to coordinate efforts between the Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy during wartime. In terms of function, it was approximately equivalent to the United States ...
assigned the Imperial Japanese Army's 17th Army—a corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies great ...
-sized command based at Rabaul and under the command of Lieutenant-General Harukichi Hyakutake—with the task of retaking Guadalcanal from Allied forces. On 19 August, various units of the 17th Army began to arrive on Guadalcanal with the goal of driving Allied forces from the island.
Because of the threat from CAF aircraft based at Henderson Field, the Japanese were unable to use large, slow transport ships to deliver troops and supplies to the island. Instead, the Japanese used warships based at Rabaul and the Shortland Islands
The Shortland Islands is an archipelago of Western Province, Solomon Islands, at . The island group lies in the extreme north-west of the country's territory, close to the south-east edge of Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea.
The largest isl ...
to carry their forces to Guadalcanal. The Japanese warships, mainly light cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several ...
s or destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed ...
s from the Eighth Fleet under the command of Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa, were usually able to make the round trip down " The Slot" to Guadalcanal and back in a single night, thereby minimizing their exposure to CAF air attack. Delivering the troops in this manner, however, prevented most of the soldiers' heavy equipment and supplies, such as heavy artillery, vehicles, and much food and ammunition, from being carried to Guadalcanal with them. These high speed warship runs to Guadalcanal occurred throughout the campaign and came to be called the " Tokyo Express" by Allied forces and "Rat Transportation" by the Japanese.
The first Japanese attempt to recapture Henderson Field failed when a 917-man force was defeated on 21 August in the Battle of the Tenaru
The Battle of the Tenaru, sometimes called the Battle of the Ilu River or the Battle of Alligator Creek, was a land battle between the Imperial Japanese Army and Allied ground forces that took place on 21 August 1942, on the island of Guada ...
. The next attempt took place from 12 to 14 September, with the 6,000 soldiers under the command of Major General Kiyotake Kawaguchi
was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
Biography
A native of Kōchi Prefecture, Kiyotake graduated from the 26th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1914, and from the 34th class of the Army Staff College in ...
being defeated in the Battle of Edson's Ridge
The Battle of Edson's Ridge, also known as the Battle of the Bloody Ridge, Battle of Raiders Ridge, and Battle of the Ridge, was a land battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II between Imperial Japanese Army and Allied (mainly United S ...
. After their defeat at Edson's Ridge, Kawaguchi and the surviving Japanese troops regrouped west of the Matanikau River on Guadalcanal.
Hyakutake immediately began to prepare for another attempt to recapture Henderson Field. The Japanese navy promised to support Hyakutake's next offensive by delivering the necessary troops, equipment, and supplies to the island, and by stepping-up air attacks on Henderson Field and sending warships to bombard the airfield.
As the Japanese regrouped, the U.S. forces concentrated on shoring up and strengthening their Lunga defenses. On 18 September, an Allied naval convoy delivered 4,157 men from the U.S. 7th Marine Regiment to Guadalcanal. This regiment had previously formed part of the 3rd Provisional Marine Brigade and was fresh from garrison duty in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
. These reinforcements allowed Vandegrift, beginning on 19 September, to establish an unbroken line of defense completely around the Lunga perimeter.
General Vandegrift and his staff were aware that Kawaguchi's troops had retreated to the area west of the Matanikau and that numerous groups of Japanese stragglers were scattered throughout the area between the Lunga perimeter and the Matanikau River. Vandegrift, therefore, decided to conduct a series of small unit operations around the Matanikau Valley.
 The first U.S. Marine operation against Japanese forces west of the Matanikau, conducted between 23 and 27 September 1942 by elements of three U.S. Marine
The first U.S. Marine operation against Japanese forces west of the Matanikau, conducted between 23 and 27 September 1942 by elements of three U.S. Marine battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions ...
s, was repulsed by Kawaguchi's troops under Colonel Akinosuke Oka
was a colonel in the Imperial Japanese Army and a commander of Japanese troops during the strategically significant Guadalcanal campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He was posthumously promoted to major general.
Biography
Oka was ...
's local command. In the second action, between 6 and 9 October, a larger force of U.S. Marines crossed the Matanikau River, attacked newly landed Japanese forces from the 2nd (Sendai) Infantry Division under the command of generals Masao Maruyama and Yumio Nasu
was a major general and a division commander in the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) during World War II.
Biography
A native of Tochigi Prefecture, Nasu graduated from the 25th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1913 and from the 35th c ...
and inflicted heavy casualties on the Japanese 4th Infantry Regiment. The second action forced the Japanese to retreat from their positions east of the Matanikau.
In the meantime, Major General Millard F. Harmon
Millard Fillmore Harmon Jr. (January 19, 1888 – February 26, 1945) was a lieutenant general in the United States Army Air Forces during the Pacific campaign in World War II. He was presumed to have perished in February 1945 on a flight when t ...
, commander of U.S. Army forces in the South Pacific, convinced Vice Admiral Robert L. Ghormley
Vice Admiral Robert Lee Ghormley (October 15, 1883 – June 21, 1958) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served as Commander, South Pacific Area during World War II.
Early years
Born in Portland, Oregon, Ghormley was the oldest of si ...
, commander of Allied forces in the South Pacific Area
The South Pacific Area (SOPAC) was a multinational U.S.-led military command active during World War II. It was a part of the U.S. Pacific Ocean Areas under Admiral Chester Nimitz.
The delineation and establishment of the Pacific Ocean Areas was ...
, that U.S. Marine forces on Guadalcanal needed to be reinforced immediately if the Allies were to successfully defend the island from the next expected Japanese offensive. Thus on 13 October, a naval convoy delivered the 2,837-strong 164th U.S. Infantry Regiment, a North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, ...
Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized militia force and a federal military reserve force of the United States Army. They are simultaneously part of two different organizations: the Army N ...
formation from the U.S. Army's Americal Division
The Americal Division was an infantry division of the United States Army during World War II and the Vietnam War.
The division was activated 27 May 1942 on the island of New Caledonia. In the immediate emergency following Pearl Harbor, the Un ...
, commanded by Colonel Robert Hall, to Guadalcanal.
Mikawa's ships continued nocturnal deliveries of men and materiel to Guadalcanal. Between 1 and 17 October, Japanese convoys delivered 15,000 Japanese troops, comprising the remainder of the 2nd Infantry Division and one regiment of the 38th Infantry Division, plus artillery, tanks, ammunition, and provisions, to Guadalcanal. One of these—on 9 October—landed General Hyakutake on the island to personally lead the Japanese forces in the planned offensive. Mikawa also sent heavy cruisers on several occasions to bombard Henderson Field. On the night of 11 October, one of these bombardment missions was intercepted by U.S. naval forces and defeated in the Battle of Cape Esperance
The Battle of Cape Esperance, also known as the Second Battle of Savo Island and, in Japanese sources, as the , took place on 11–12 October 1942, in the Pacific campaign of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and United States Na ...
.
 On 13 October, in order to help protect the transit of an important supply convoy to Guadalcanal that consisted of six slower cargo ships, the Japanese
On 13 October, in order to help protect the transit of an important supply convoy to Guadalcanal that consisted of six slower cargo ships, the Japanese Combined Fleet
The was the main sea-going component of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Until 1933, the Combined Fleet was not a permanent organization, but a temporary force formed for the duration of a conflict or major naval maneuvers from various units norm ...
commander Isoroku Yamamoto
was a Marshal Admiral of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and the commander-in-chief of the Combined Fleet during World War II until he was killed.
Yamamoto held several important posts in the IJN, and undertook many of its changes and reor ...
sent a naval force from Truk—commanded by Vice-Admiral Takeo Kurita—to bombard Henderson Field. Kurita's force—consisting of the battleships and , escorted by one light cruiser and nine destroyers—approached Guadalcanal unopposed and opened fire on Henderson Field at 01:33 on 14 October. Over the next 83 minutes, they fired 973 shells into the Lunga perimeter, most of them falling in and around the area of the airfield. The bombardment heavily damaged the airfield's two runways, burned almost all of the available aviation fuel, destroyed 48 of the CAF's 90 aircraft, and killed 41 men, including six CAF aircrew.
Despite the heavy damage, Henderson personnel were able to restore one of the runways to operational condition within a few hours. Over the next several weeks, the CAF gradually recovered as Allied forces delivered more aircraft, fuel, and aircrew personnel to Guadalcanal. Observing the Japanese deliveries of troops and supplies to the island, American forces were expecting an imminent offensive by Japanese ground forces, but they were not sure where and when it would take place.
Troop movement
Because of the loss of their positions on the east side of the Matanikau, the Japanese decided that an attack on the U.S. defenses along the coast would be prohibitively difficult. Thus, after observation of the American defenses around Lunga Point by his staff officers, Hyakutake decided that the main thrust of his planned attack would be from south of Henderson Field. His 2nd Division (augmented by one regiment from 38th Division), under Lieutenant General Masao Maruyama and comprising 7,000 soldiers in three infantry regiments of three battalions each was ordered to march through the jungle and attack the American defenses from the south near the east bank of the Lunga River. The 2nd Division was split into three units; the Left Wing Unit under Major General Yumio Nasu containing the 29th Infantry Regiment, the Right Wing Unit under Major General Kiyotake Kawaguchi consisting of the 230th Infantry Regiment (from the 38th Infantry Division), and the division reserve led by Maruyama comprising the 16th Infantry Regiment. The date of the attack was set for 22 October. To distract the Americans from the planned attack from the south, Hyakutake's heavy artillery plus five battalions of infantry (about 2,900 men) under Major GeneralTadashi Sumiyoshi
was a major general in the Imperial Japanese Army during the Pacific campaign in World War II.
Biography
Sumiyoshi was born in Kisa, Hiroshima (now part of the city of Miyoshi) and attended military preparatory schools in Hiroshima. He graduate ...
were to attack the American defenses from the west along the coastal corridor. The Japanese estimated that there were 10,000 American troops on the island, when in fact there were about 23,000.
At this time, the Lunga perimeter was defended by four American regiments comprising 13 infantry battalions. The 164th Infantry Regiment guarded the easternmost sector. Extending from the 164th south and west across Edson's Ridge to the Lunga River was the 7th Marine Regiment
The 7th Marine Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps based at Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms, California. Nicknamed the "Magnificent Seventh", the regiment falls under the command of the 1 ...
under Colonel Amor L. Sims. Covering the sector west of the Lunga to the coast were the 1st
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
and 5th
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash tha ...
Marine Regiments. Defending the mouth of the Matanikau for the Americans were two battalions under the command of Lieutenant Colonel William J. McKelvy: the 3d Battalion, 1st Marines, and the 3d Battalion, 7th Marines. McKelvy's force was separated from the Lunga perimeter by a gap that was covered by patrols.
Prelude
 On 12 October, a company of Japanese engineers began to break a trail, called the "Maruyama Road", from the Matanikau towards the southern portion of the U.S. Lunga perimeter. The trail traversed some of the most difficult terrain on Guadalcanal, including numerous rivers and streams, deep, muddy ravines, steep ridges, and dense jungle. Between 16 and 18 October, the 2nd Division began their march along the Maruyama Road, led by Nasu's unit and followed in order by Kawaguchi and Maruyama. Each soldier had been ordered to carry one artillery shell plus his pack and rifle.
Early on the morning of 20 October, Maruyama reached the Lunga River. Believing that his units were about south of the airfield, he ordered the left and right wing units to advance abreast of each other parallel to the Lunga north towards the American lines and set the time of the attack for 18:00 on 22 October. Maruyama, however, was mistaken. He and his troops were actually south of the airfield. By the evening of 21 October, it was clear to Maruyama that his units would not be in position to attack the next day, so he postponed the attack to 23 October and put his men on half rations to conserve their dwindling food supply. At nightfall on 22 October, much of the 2nd Division still remained strung out along the Maruyama Road, but Maruyama ruled out any postponement of the attack.
During this time, Sumiyoshi prepared his command to attack the American forces from the west. On 18 October, he began shelling Henderson Field with fifteen howitzers. What remained of the 4th Infantry Regiment under Colonel
On 12 October, a company of Japanese engineers began to break a trail, called the "Maruyama Road", from the Matanikau towards the southern portion of the U.S. Lunga perimeter. The trail traversed some of the most difficult terrain on Guadalcanal, including numerous rivers and streams, deep, muddy ravines, steep ridges, and dense jungle. Between 16 and 18 October, the 2nd Division began their march along the Maruyama Road, led by Nasu's unit and followed in order by Kawaguchi and Maruyama. Each soldier had been ordered to carry one artillery shell plus his pack and rifle.
Early on the morning of 20 October, Maruyama reached the Lunga River. Believing that his units were about south of the airfield, he ordered the left and right wing units to advance abreast of each other parallel to the Lunga north towards the American lines and set the time of the attack for 18:00 on 22 October. Maruyama, however, was mistaken. He and his troops were actually south of the airfield. By the evening of 21 October, it was clear to Maruyama that his units would not be in position to attack the next day, so he postponed the attack to 23 October and put his men on half rations to conserve their dwindling food supply. At nightfall on 22 October, much of the 2nd Division still remained strung out along the Maruyama Road, but Maruyama ruled out any postponement of the attack.
During this time, Sumiyoshi prepared his command to attack the American forces from the west. On 18 October, he began shelling Henderson Field with fifteen howitzers. What remained of the 4th Infantry Regiment under Colonel Nomasu Nakaguma
Nomasu Nakaguma, also known as Naomasa or Tadamasu Nakaguma,Jersey, ''Hell's Islands'', p. 225. was a colonel and a commander in the Imperial Japanese Army during the Pacific campaign in World War II. He commanded the 2nd Infantry Division's 4th ...
began to gather openly near Point Cruz (on the coast just west of the Matanikau). On 19 October, Colonel Akinosuka Oka led the 1,200 troops of his 124th Infantry Regiment inland across the Matanikau and began moving up the east bank towards high ground east of the river.
On 23 October, Maruyama's forces struggled through the jungle to reach the American lines. Kawaguchi, on his own initiative, began to shift his right wing unit to the east, believing that the American defenses were weaker in that area. Maruyama—through one of his staff officers—ordered Kawaguchi to keep to the original attack plan. When he refused, Kawaguchi was relieved of command and replaced by Colonel Toshinari Shōji, commander of the 230th Infantry Regiment. That evening, after learning that the left and right wing forces were still struggling to reach the American lines, Hyakutake postponed the attack to 19:00 on 24 October. The Americans remained completely unaware of the approach of Maruyama's forces.
On this day, the Japanese 11th Air Fleet under Jinichi Kusaka based at Rabaul sent 16 Mitsubishi G4M
The Mitsubishi G4M was a twin-engine, land-based medium bomber formerly manufactured by the Mitsubishi Aircraft Company, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1940 to 1945. Its official designat ...
2 "Betty" bombers and 28 A6M2 Zero fighters to attack Henderson Field. In response, 24 F4F-4 Wildcats and four P-400 Airacobras from the CAF (Cactus Air Force) rose to meet them, resulting in a large aerial battle. To Allied observers, the Japanese appeared to lose several aircraft in the day's engagements, but their actual losses are unknown. The CAF lost one Wildcat to battle damage but the pilot was uninjured.
U.S. Marine and Army forces were under the overall command of Major General Alexander Vandegrift
General Alexander Archer Vandegrift, USMC (March 13, 1887 – May 8, 1973) was a United States Marine Corps four-star general. During World War II, he commanded the 1st Marine Division to victory in its first ground offensive of the war, the B ...
. However, on the 23rd of October, Vandegrift had flown to Noumea, New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
to meet with Vice Admiral William Halsey Jr., at Halsey's direction. Major General William Rupertus
William Henry Rupertus (November 14, 1889 – March 25, 1945) was a Major general (United States), major general in the United States Marine Corps, who commanded the famed 1st Marine Division in the Pacific in World War II and also authored the US ...
, who was Deputy Commander of the 1st Marine Division
The 1st Marine Division (1st MARDIV) is a Marine division of the United States Marine Corps headquartered at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton, California. It is the ground combat element of the I Marine Expeditionary Force (I MEF).
It is th ...
, remained in Guadalcanal and commanded the U.S. forces on the ground in Vandegrift's absence.Battle
Nakaguma's attack on the Matanikau
Sumiyoshi was informed by Hyakutake's staff of the postponement of the offensive to 24 October, but was unable to contact Nakaguma to inform him of the delay. Thus, at dusk on 23 October, two battalions of Nakaguma's 4th Infantry Regiment and the nine tanks of the 1st Independent Tank Company launched attacks on the U.S. Marine defenses at the mouth of the Matanikau. Nakaguma's tanks attacked in pairs across the sandbar at the mouth of the Matanikau behind a barrage of artillery. Marine
Nakaguma's tanks attacked in pairs across the sandbar at the mouth of the Matanikau behind a barrage of artillery. Marine anti-tank guns
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first dev ...
and artillery quickly destroyed all nine tanks. At the same time, four battalions of Marine artillery, totaling 40 howitzers, fired over 6,000 rounds into the area between Point Cruz and the Matanikau, causing heavy casualties in Nakaguma's infantry battalions as they tried to approach the Marine lines. Nakaguma's attacks ended by 01:15 on 24 October, inflicting only light casualties on the Marines and gaining no ground.
Partly in response to Nakaguma's attacks, on 24 October the 2nd Battalion, 7th Marines
The 2nd Battalion, 7th Marines (2/7) is a light infantry battalion of the United States Marine Corps. They are based at the Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms and consist of approximately 800 Marines and Sailors. The battal ...
under Lieutenant Colonel Herman H. Hanneken
Herman Henry Hanneken (June 23, 1893 – August 23, 1986) was a United States Marine Corps officer and a recipient of the U.S. military's highest decoration, the Medal of Honor.
Beginning his career as an enlisted man, Hanneken served in the Bana ...
deployed to the Matanikau. After Oka's forces were sighted approaching the Marine Matanikau positions from the south, Hanneken's battalion was placed on a ridge facing south which formed a continuous extension of the inland flank of the Marine's horseshoe-shaped Matanikau defenses. A gap, however, still remained between Hanneken's left (east) flank and the main perimeter.
Maruyama's first attacks on the perimeter
With the redeployment of Hanneken's battalion, the 700 troops of1st Battalion, 7th Marines
The 1st Battalion, 7th Marines (1/7) is an infantry battalion of the 7th Marine Regiment of the United States Marine Corps. It is currently based at the Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms. Consisting of approximately 1,000 M ...
under Lieutenant Colonel Chesty Puller
Lewis Burwell "Chesty" Puller (June 26, 1898 – October 11, 1971) was a United States Marine Corps officer. Beginning his career fighting guerillas in Haiti and Nicaragua as part of the Banana Wars, he later served with distinction in World Wa ...
were left alone to hold the entire line on the southern face of the Lunga perimeter east of the Lunga River. Late on 24 October, Marine patrols detected Maruyama's approaching forces, but it was now too late in the day for the Marines to rearrange their dispositions.
 At 14:00 on 24 October, Maruyama's left and right wing units began to deploy for their attacks. Maruyama's troops had very little artillery or mortar support for their upcoming assault, having abandoned most of their heavy cannons along the Maruyama Road. Between 16:00 and 21:00, heavy rain fell, delaying the Japanese approach and causing "chaos" in the Japanese formations, already exhausted from the long march through the jungle.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 353–54. Shoji's right wing force accidentally turned parallel to the Marine lines, and all but one battalion failed to make contact with the Marine defenses. Shoji's 1st Battalion, 230th Infantry Regiment "stumbled" into Puller's lines about 22:00 and were driven off by Puller's men. For unknown reasons, Maruyama's staff then reported to Hyakutake that Shoji's men had overrun Henderson Field. At 00:50 on 25 October, Hyakutake signaled Rabaul that, "A little before 23:00 the Right Wing captured the airfield."Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', pp. 197–98.
At about this time, Nasu's left wing battalions finally began to reach the Marine defenses. At 00:30 on 25 October, the 11th Company of Nasu's 3rd Battalion under
At 14:00 on 24 October, Maruyama's left and right wing units began to deploy for their attacks. Maruyama's troops had very little artillery or mortar support for their upcoming assault, having abandoned most of their heavy cannons along the Maruyama Road. Between 16:00 and 21:00, heavy rain fell, delaying the Japanese approach and causing "chaos" in the Japanese formations, already exhausted from the long march through the jungle.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 353–54. Shoji's right wing force accidentally turned parallel to the Marine lines, and all but one battalion failed to make contact with the Marine defenses. Shoji's 1st Battalion, 230th Infantry Regiment "stumbled" into Puller's lines about 22:00 and were driven off by Puller's men. For unknown reasons, Maruyama's staff then reported to Hyakutake that Shoji's men had overrun Henderson Field. At 00:50 on 25 October, Hyakutake signaled Rabaul that, "A little before 23:00 the Right Wing captured the airfield."Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', pp. 197–98.
At about this time, Nasu's left wing battalions finally began to reach the Marine defenses. At 00:30 on 25 October, the 11th Company of Nasu's 3rd Battalion under Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
Jiro Katsumata found and attacked Company A of Puller's battalion. Katsumata's attack was impeded by heavy barbed wire
A close-up view of a barbed wire
Roll of modern agricultural barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire, is a type of steel fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strands. Its primary use is ...
in front of the Marine line and then hit heavily by American machine gun, mortar, and artillery fire. By 01:00, the Marine fire had killed most of Katsumata's company.
Further west, the 9th Company of Nasu's 3rd Battalion charged straight into Puller's Company C at 01:15. Within five minutes, a Marine machine gun section led by Sergeant
Sergeant ( abbreviated to Sgt. and capitalized when used as a named person's title) is a rank in many uniformed organizations, principally military and policing forces. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and other ...
John Basilone killed almost every member of the 9th Company. By 01:25, heavy fire from the Marine divisional artillery was falling into Nasu's troop assembly and approach routes, causing heavy casualties.
Recognizing that a major Japanese attack was underway, Puller requested reinforcement. At 03:45, the 3rd Battalion, 164th Infantry, commanded by Lieutenant Colonel Robert Hall and being held in reserve, was fed piecemeal into Puller's line. In spite of the darkness and intermittent heavy rain, the Army National Guard troops were placed in Puller's defenses before daybreak.
Just before dawn, Colonel Masajiro Furimiya, the commander of the 29th Infantry, with two companies from his 3rd Battalion plus his headquarters staff, was able to penetrate the Marine artillery fire and reach Puller's lines about 03:30. Most of Furimiya's troops were killed during their assault, but about 100 broke through the American defenses and carved a salient in width and deep in the center of Puller's line. After sunrise, Furimiya's 2nd Battalion joined in the assault on Puller, but were thrown back. At 07:30, Nasu decided to withdraw most of the remainder of his troops back into the jungle and prepare for another attack that night.
During the day of 25 October, Puller's men attacked and eradicated the salient in their lines and hunted small groups of Japanese infiltrators, killing 104 Japanese soldiers. More than 300 of Maruyama's men in total were killed in their first attacks on the Lunga perimeter. At 04:30, Hyakutake rescinded the message announcing the capture of the airfield, but at 07:00 declared that the results of Maruyama's attack were unknown.
Naval and air attacks
 The Japanese 8th Fleet had task units ready to support the Army's attacks on Guadalcanal. Upon receipt of Hyakutake's message declaring success at 00:50 on 24 October, the task units went into action. The
The Japanese 8th Fleet had task units ready to support the Army's attacks on Guadalcanal. Upon receipt of Hyakutake's message declaring success at 00:50 on 24 October, the task units went into action. The light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to th ...
and three destroyers patrolled west of Guadalcanal to interdict any Allied ships that tried to approach the island. A First Assault Unit with three destroyers and a Second Assault Unit with the light cruiser and five destroyers approached Guadalcanal to attack any Allied ships off the island's north or east coast and to provide gunfire support for Hyakutake's forces.
At 10:14, the First Assault Unit arrived off Lunga Point and chased away two old U.S. destroyers converted to minesweepers
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
— and '—which were delivering aviation fuel to Henderson Field. The Japanese destroyers then sighted and sank the U.S. tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, su ...
and patrol boat
A patrol boat (also referred to as a patrol craft, patrol ship, or patrol vessel) is a relatively small naval vessel generally designed for coastal defence, border security, or law enforcement. There are many designs for patrol boats, and the ...
''YP-284'' before beginning their bombardment of the U.S. positions around Lunga Point. At 10:53, a Marine shore gun hit and damaged the destroyer , and all three Japanese destroyers withdrew while being strafed by four CAF Wildcat fighters.
As the Second Assault Unit approached Guadalcanal through Indispensable Strait
Indispensable Strait is a waterway in the Solomon Islands, running about northwest-southeast from Santa Isabel to Makira (San Cristóbal), between the Florida Islands and Guadalcanal to the southwest, and Malaita to the northeast.
Indispensa ...
, it was attacked by five CAF SBD-3 Dauntless dive bomber
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact through ...
s. Bomb hits caused heavy damage to ''Yura'', and the unit reversed course to try to escape. More CAF air attacks on ''Yura'' throughout the day caused further damage, and the cruiser was abandoned and scuttled at 21:00 that night.
Meanwhile, 82 Japanese bombers and fighters from the 11th Air Fleet and from the aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s and attacked Henderson Field in six waves throughout the day and were engaged by CAF fighters and Marine anti-aircraft guns. By the end of the day, the Japanese had lost 11 fighters, two bombers, and one reconnaissance aircraft along with most of the aircrews in the downed aircraft. Two CAF fighters were destroyed in the day's fighting but both pilots survived. The Japanese air attacks caused only light damage to Henderson Field and the American defenses. The Americans later referred to this day as "Dugout Sunday" because the continuous Japanese air, naval, and artillery attacks kept many of the Lunga defenders in their foxholes and shelters throughout the day.
Maruyama's second attacks on the perimeter
Throughout the day of 25 October, the Americans redeployed and improved their defenses against the Japanese attack they were expecting that night. In the west, Hanneken and the 5th Marines closed the gap between their two forces. Along the southern portion of the perimeter, Puller's and Hall's troops disentwined and repositioned. Puller's men fortified the western of the sector and the 164th soldiers took the eastern segment. The division reserve, the 3rd Battalion, 2nd Marine Regiment was placed directly behind Hall's and Puller's positions. Maruyama committed his reserve force, the 16th Infantry Regiment, to Nasu's left wing unit. Beginning at 20:00 on 25 October, and extending into the early morning hours of the 26th, the 16th and what remained of Nasu's other units conducted numerous unsuccessful frontal assaults on Puller's and Hall's lines. U.S. Marine and Army rifle, machine gun, mortar, artillery and direct canister fire from 37 mm anti-tank guns "wrought terrible carnage" on Nasu's men.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 361–62. Colonel Toshiro Hiroyasu, the commander of the 16th, and most of his staff as well as four Japanese battalion commanders were killed in the assaults. Nasu was hit by rifle fire and mortally wounded, dying a few hours later. A few small groups of Nasu's men broke through the American defenses, including one led by Colonel Furimiya, but were all hunted down and killed over the next several days. Shoji's right wing units did not participate in the attacks, choosing instead to remain in place to cover Nasu's right flank against a possible attack in that area by U.S. forces that never materialized.Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', pp. 203–04.Oka's attack
 At 03:00 on 26 October, Oka's unit finally reached and attacked the Marine defenses near the Matanikau. Oka's troops assaulted all along an east–west saddle ridge held by Hanneken's battalion but concentrated particularly on Hanneken's Company F, which defended the extreme left flank of the Marine positions on the ridge. A Company F machine gun section under Mitchell Paige killed many of the Japanese attackers, but Japanese fire eventually killed or injured almost all the Marine machine gunners. At 05:00, Oka's 3rd Battalion, 4th Infantry succeeded in scaling the steep slope of the ridge and pushed the surviving members of Company F off the crest.Hough, ''Pearl Harbor to Guadalcanal'', p. 337.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 363–64.Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', p. 204.
Responding to the Japanese capture of part of the ridgeline, Major Odell M. Conoley—Hanneken's battalion
At 03:00 on 26 October, Oka's unit finally reached and attacked the Marine defenses near the Matanikau. Oka's troops assaulted all along an east–west saddle ridge held by Hanneken's battalion but concentrated particularly on Hanneken's Company F, which defended the extreme left flank of the Marine positions on the ridge. A Company F machine gun section under Mitchell Paige killed many of the Japanese attackers, but Japanese fire eventually killed or injured almost all the Marine machine gunners. At 05:00, Oka's 3rd Battalion, 4th Infantry succeeded in scaling the steep slope of the ridge and pushed the surviving members of Company F off the crest.Hough, ''Pearl Harbor to Guadalcanal'', p. 337.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 363–64.Griffith, ''Battle for Guadalcanal'', p. 204.
Responding to the Japanese capture of part of the ridgeline, Major Odell M. Conoley—Hanneken's battalion executive officer
An executive officer is a person who is principally responsible for leading all or part of an organization, although the exact nature of the role varies depending on the organization. In many militaries and police forces, an executive officer, o ...
—quickly gathered a counterattack unit of 17 men, including communications specialists, messmen, a cook, and a bandsman. Conoley's scratch force was joined by elements of Hanneken's Company G, Company C, and a few unwounded survivors from Company F and attacked the Japanese before they could consolidate their positions on top of the ridge. By 06:00, Conoley's force had pushed the Japanese back off the ridge, effectively ending Oka's attack. The Marines counted 98 Japanese bodies on the ridge and 200 more in the ravine in front of it. Hanneken's unit suffered 14 killed and 32 wounded.Zimmerman, ''Guadalcanal Campaign'', pp. 122–23.
Aftermath
Retreat
 At 08:00 on 26 October, Hyakutake called off any further attacks and ordered his forces to retreat. Maruyama's men recovered some of their wounded from near the American lines on the night of 26–27 October, and began to withdraw back into the deep jungle. The Americans recovered and buried or burned as quickly as possible the remains of 1,500 of Maruyama's men left lying in front of Pullers's and Hall's lines. Said one U.S. Army participant, John E. Stannard, of the scene after the battle, "The carnage of the battlefield was a sight that perhaps only the combat infantryman, who has fought at close quarters, could fully comprehend and look upon without a feeling of horror. One soldier, after a walk among the Japanese dead, said to his comrade: 'My God, what a sight. There's dead Japs stretched from the Corner back along the edge of the jungle for a half a mile [].'"
Maruyama's left wing survivors were ordered to retreat back to the area west of the Matanikau River while Shoji's right wing was told to head for Koli Point, east of the Lunga perimeter. The left wing soldiers, who had run out of food several days before, began the retreat on 27 October. During the retreat, many of the Japanese wounded succumbed to their injuries and were buried along the Maruyama road. One of Maruyama's men, Lieutenant Keijiro Minegishi, noted in his diary, "I never dreamed of retreating over the same mountainous trail through the jungle we crossed with such enthusiasm... we haven't eaten in three days and even walking is difficult. On the up hill my body swayed around unable to walk. I must rest every two meters."
Leading elements of the 2nd Division reached the 17th Army headquarters area at
At 08:00 on 26 October, Hyakutake called off any further attacks and ordered his forces to retreat. Maruyama's men recovered some of their wounded from near the American lines on the night of 26–27 October, and began to withdraw back into the deep jungle. The Americans recovered and buried or burned as quickly as possible the remains of 1,500 of Maruyama's men left lying in front of Pullers's and Hall's lines. Said one U.S. Army participant, John E. Stannard, of the scene after the battle, "The carnage of the battlefield was a sight that perhaps only the combat infantryman, who has fought at close quarters, could fully comprehend and look upon without a feeling of horror. One soldier, after a walk among the Japanese dead, said to his comrade: 'My God, what a sight. There's dead Japs stretched from the Corner back along the edge of the jungle for a half a mile [].'"
Maruyama's left wing survivors were ordered to retreat back to the area west of the Matanikau River while Shoji's right wing was told to head for Koli Point, east of the Lunga perimeter. The left wing soldiers, who had run out of food several days before, began the retreat on 27 October. During the retreat, many of the Japanese wounded succumbed to their injuries and were buried along the Maruyama road. One of Maruyama's men, Lieutenant Keijiro Minegishi, noted in his diary, "I never dreamed of retreating over the same mountainous trail through the jungle we crossed with such enthusiasm... we haven't eaten in three days and even walking is difficult. On the up hill my body swayed around unable to walk. I must rest every two meters."
Leading elements of the 2nd Division reached the 17th Army headquarters area at Kokumbona
Kokumbona (also Kakambona) is a village on the island of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands.
It was a Japanese base during World War II and the site of a United States Marine Corps amphibious landing on 19 August 1942.
Located on Guadalcanal's n ...
, west of the Matanikau on 4 November. The same day, Shoji's unit reached Koli Point and made camp. Decimated by battle deaths, combat injuries, malnutrition, and tropical diseases, the 2nd Division was incapable of further offensive action and would fight as a defensive force for the rest of the campaign. Later in November, U.S. forces drove Shoji's soldiers from Koli Point back to the Kokumbona area, with a battalion-sized Marine patrol attacking and harassing them almost the entire way. Only about 700 of Shoji's original 3,000 men ultimately returned to Kokumbona.
Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands
At the same time that Hyakutake's troops were attacking the Lunga perimeter, Japanese warships under the overall direction of Isoroku Yamamoto moved into a position near the southern Solomon Islands. From this location, the Japanese naval forces hoped to engage and decisively defeat any Allied (primarily U.S.) naval forces, especially carrier forces, that responded to Hyakutake's ground offensive. Allied naval carrier forces in the area, now under the command ofWilliam Halsey, Jr.
William Frederick "Bull" Halsey Jr. (October 30, 1882 – August 16, 1959) was an American Navy admiral during World War II. He is one of four officers to have attained the rank of five-star fleet admiral of the United States Navy, the other ...
who had replaced Ghormley, also hoped to meet the Japanese naval forces in battle.
The two opposing carrier forces confronted each other on the morning of October 26, in what became known as the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands
The Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, fought during 25–27 October 1942, sometimes referred to as the Battle of Santa Cruz or Third Battle of Solomon Sea, in Japan as the Battle of the South Pacific ( ''Minamitaiheiyō kaisen''), was the fourt ...
. After an exchange of carrier air attacks, Allied surface ships retreated from the battle area with the loss of one carrier sunk and another heavily damaged. The participating Japanese carrier forces, however, also retreated because of high aircraft and aircrew losses and significant damage to two carriers. This was a tactical victory for the Japanese in terms of ships sunk and damaged, but the loss of veteran aircrews was a long-term strategic advantage for the Allies, whose aircrew losses in the battle were relatively low.
Later events
 Although the Japanese Army's attack on the Allied Lunga perimeter was decisively defeated in this battle, the Japanese were not yet ready to give up the struggle for Guadalcanal. The Japanese Army and navy made immediate plans to move the rest of the 38th Division to the island, along with the 51st Infantry Division, to try a further offensive against Henderson Field in November 1942.
Although the Japanese Army's attack on the Allied Lunga perimeter was decisively defeated in this battle, the Japanese were not yet ready to give up the struggle for Guadalcanal. The Japanese Army and navy made immediate plans to move the rest of the 38th Division to the island, along with the 51st Infantry Division, to try a further offensive against Henderson Field in November 1942.
 The Japanese again planned to bombard Henderson Field with battleships in order to allow a convoy of transport ships to deliver the 38th's troops and heavy equipment. In contrast, however, to what occurred on 14 October, this time the U.S. Navy moved to intercept the battleship forces sent by Yamamoto from Truk to shell the airfield. During the ensuing
The Japanese again planned to bombard Henderson Field with battleships in order to allow a convoy of transport ships to deliver the 38th's troops and heavy equipment. In contrast, however, to what occurred on 14 October, this time the U.S. Navy moved to intercept the battleship forces sent by Yamamoto from Truk to shell the airfield. During the ensuing Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
The Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, sometimes referred to as the Third and Fourth Battles of Savo Island, the Battle of the Solomons, the Battle of Friday the 13th, or, in Japanese sources, the , took place from 12 to 15 November 1942, and was t ...
from 13 to 15 November, Allied naval and air forces turned back two Japanese attempts to bombard Henderson Field and almost completely destroyed the transport convoy carrying the remainder of the 38th Division. After this failure to deliver significant additional troops to the island, the Japanese commanders finally conceded defeat in the battle for Guadalcanal and evacuated most of their surviving troops by the first week of February 1943. Building on their success at Guadalcanal and elsewhere, the Allies continued their island-hopping
Leapfrogging, also known as island hopping, was a military strategy employed by the Allies in the Pacific War against the Empire of Japan during World War II.
The key idea is to bypass heavily fortified enemy islands instead of trying to cap ...
campaign against Japan, culminating in Japan's surrender and the end of World War II.Frank, ''Guadalcanal'', pp. 428–92; Rottman, ''Japanese Army'', p. 64; Dull, ''Imperial Japanese Navy'', pp. 245–69.
Notes
References
Web
* * – Interactive animation of the battle * * – Web site with many pictures of Guadalcanal battle sites from 1942 and how they look now. * * * * *Further reading
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Henderson Field Conflicts in 1942 Military history of Japan during World War II Pacific Ocean theatre of World War II 1942 in the Solomon Islands Battles and operations of World War II involving the Solomon Islands Battles of World War II involving Japan Battles of World War II involving the United States 1942 in Japan Guadalcanal Campaign United States Marine Corps in World War II October 1942 events