Battle Mountain, Virginia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Battle Mountain is an







igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
mountain in Rappahannock County
Rappahannock County is a county located in the northern Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia, US, adjacent to Shenandoah National Park. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 7,348. Its county seat is Washington. The name "Rappah ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. The eastern slope is generally considered to reside in the unincorporated town of Amissville, Virginia while the western slope is generally considered to be within Castleton, Virginia
Castleton is an unincorporated community in Rappahannock County in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is located northwest of Culpeper.
Culture
Maestro Lorin Maazel maintained a estate in Castleton, and made it the focus of the Castleton Fest ...
. The entire mountain including the summit lies within private property at an elevation of 1,162 ft (354.2 m).
Geology

Tectonic emplacement and geochronology
It is an extinct volcano dating to theNeoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is prec ...
and is approximately 704 million years old (+/- 4 million years) as dated using the U- Pb zircon crystal geochronology
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is ...
method. It is a unit of the Robertson River Igneous Suite and is located within the Blue Ridge anticlinorium
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
. This volcanic formation was a result of crustal extensional rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben wi ...
of the eastern Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
n margin of the supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leav ...
Rodinia. This was the beginning of a chain of events that ultimately gave birth to the precursor Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, the Iapetus Ocean at 550 Ma during the Ediacaran– Cambrian transition.
Geochemical evolution
The volcano is composed of alkali feldspargranitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz- ...
rock of the Robertson River Igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
Suite. This includes felsic complex material such as biotite, hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rock ...
-biotite, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With th ...
, and alkali granitic rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
including rhyolite on the eastern slopes of Battle Mountain and the adjacent (and geologically related) Little Battle Mountain (elevation 937 feet).




Palaeogeographic reconstruction
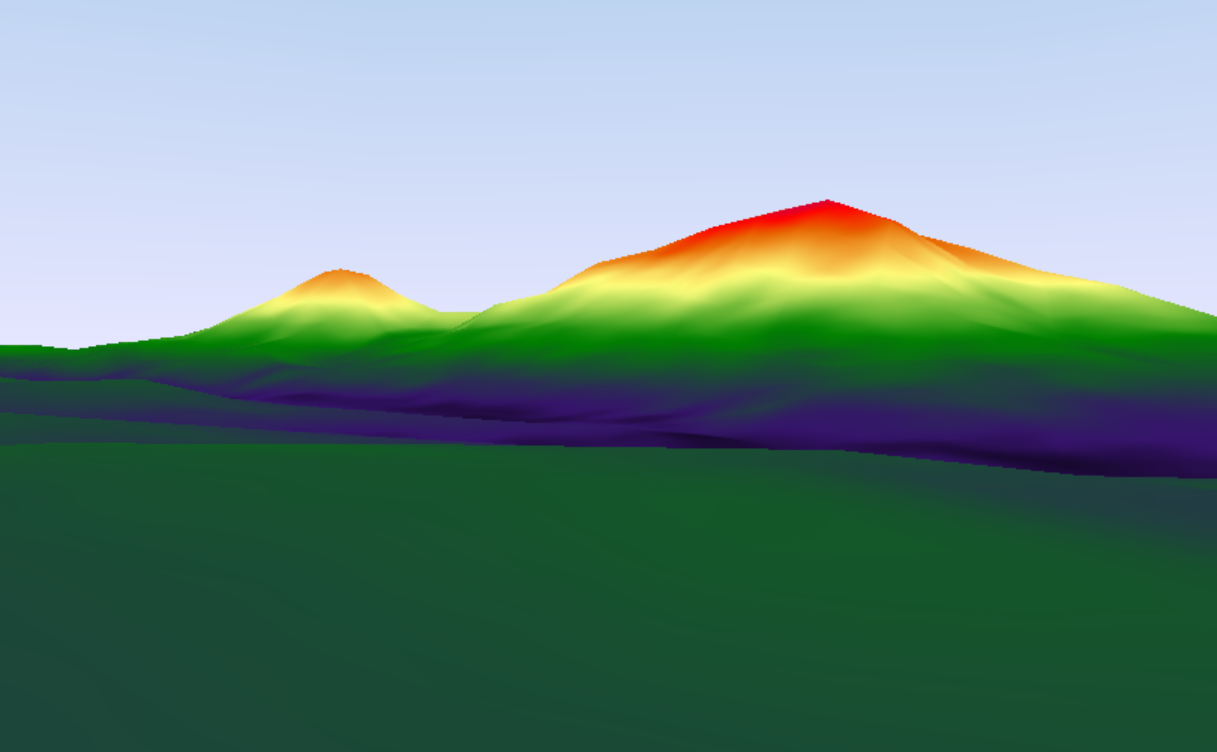
A unique geological feature of Battle Mountain is that the western slope outcrops are composed entirely of alkali feldspar granite, while the eastern slope up to and including the summit is entirely rhyolitic. This provides strong evidence of a theorized lateral explosive eruption event centered on the eastern slope at approximately 704 Ma as proposed by Woolman (2016). Further mathematical geology evidence which supports this theory includes a palaeogeographic reconstruction of the mountain by Woolman utilizing artificial neural networks and Markov chaingeostatistical
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including petr ...
models including period climate condition-based soil erosion rates, Kirkby's hillslope movement evolution equations and recursive biogeochemical soil erosion rates in felsic granitic conditions. The result was the digital reconstruction image shown on the left, indicating what Battle Mountain may have looked like 704 million years ago on the western slope.

Only known volcanic mountains in Rappahannock County, VA
Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain are the only mountains in Rappahannock County which are known to bevolcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
in origin, and are among the oldest visibly intact extinct volcanoes in Virginia. White quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
boulders
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive.
In c ...
and smaller fragments are common on and around Battle Mountain, a result of molten silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
that was contained in the rhyolite lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
and granitic magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
that formed the volcano. As quartz is extremely hard
Hard may refer to:
* Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture
* Hard water, water with high mineral content
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series
* Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock supe ...
relative to feldspar granite and rhyolite, it tends to remain present on the surface while the softer granite it was embedded in wears away into the soil.
Access
The nearest unincorporated town is Amissville, Virginia at approximately 4 miles away. Access to the mountain and the summit must be negotiated with locallandowners
In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individual ...
first as the mountain, including all portions of the July 1863 battlefield exists entirely on private property.
Agriculture
The various slopes of Battle Mountain are in either commercial timber (primarily mixed hardwoods), cattle pasture (western slope) or crops (corn, hay and pumpkins as of 2019). Battle Mountain Farm, which comprises the majority of the eastern slope of Battle Mountain is a mixed hardwood timber and small-scale commercial pumpkin grower, specializing in large jack-o-lantern pumpkins. Their pumpkins are grown without herbicides or pesticides in multiple commercial-scale 60-foot by 5-foot ecologically sustainable raised beds (no soil tilling required) using locally produced natural fertilizers. The beds also utilize water-conserving polymer mulch and irrigation drip lines attached to on-site wells approximately 300 feet deep, providing mineral-rich water from volcanic aquifers. The well water pressure is provided by a 10.4 kilowatt grid-tied solar panel array on the farm, with lead-acid battery backup.

References
{{Mountains of Virginia Mountains of Virginia Blue Ridge Mountains Rappahannock County, Virginia Volcanoes of Virginia Stratovolcanoes of the United States