Barcelona Pavilion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Barcelona Pavilion ( ca, Pavelló alemany; es, Pabellón alemán; "German Pavilion"), designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and
 Mies's response to the proposal by von Schnitzler was radical. After rejecting the original site for aesthetic reasons, Mies agreed to a quiet site at the narrow side of a wide, diagonal axis, where the pavilion would still offer viewpoints and a route leading to one of the exhibition's main attractions, the
Mies's response to the proposal by von Schnitzler was radical. After rejecting the original site for aesthetic reasons, Mies agreed to a quiet site at the narrow side of a wide, diagonal axis, where the pavilion would still offer viewpoints and a route leading to one of the exhibition's main attractions, the
File:Barcelona mies v d rohe pavillon weltausstellung1999 03.jpg, Barcelona Pavilion (reconstruction)
File:Barcelona Pavilion photo Christian Gänshirt 2012.JPG, View towards annex showing
Views of the replica German PavilionImage gallery on the Barcelona Pavilion
{{Authority control Buildings and structures in Barcelona Ludwig Mies van der Rohe buildings Buildings and structures completed in 1929 Modernist architecture in Barcelona International Style (architecture) Tourist attractions in Barcelona World's fair architecture in Barcelona Sants-Montjuïc 1929 Barcelona International Exposition
Lilly Reich
Lilly Reich (16 June 1885 – 14 December 1947) was a German designer of textiles, furniture, interiors, and exhibition spaces. She was a close collaborator with Ludwig Mies van der Rohe for more than ten years during the Weimar period in the 19 ...
, was the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Pavilion for the 1929 International Exposition in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. This building was used for the official opening of the German section of the exhibition. It is an important building in the history of modern architecture
Modern architecture, or modernist architecture, was an architectural movement or architectural style based upon new and innovative technologies of construction, particularly the use of glass, steel, and reinforced concrete; the idea that for ...
, known for its simple form and its spectacular use of extravagant materials, such as marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
, red onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
and travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a p ...
. The same features of minimalism and spectacular can be applied to the furniture specifically designed for the building, including the Barcelona chair
The Barcelona chair is a chair designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and Lilly Reich, for the German Pavilion at the International Exposition of 1929, hosted by Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
The chair was first used in Villa Tugendhat, a privat ...
. It has inspired many important modernist buildings.
Concept
Mies and Reich were offered the commission of this building in 1928 after his successful administration of the 1927 Werkbund exhibition in Stuttgart. The German Republic entrusted Mies with the artistic management and erection of not only the Barcelona Pavilion, but for the buildings for all the German sections at the 1929 International Exhibition. However, Mies had severe time constraints—he had to design the Barcelona Pavilion in less than a year—and was also dealing with uncertain economic conditions. In the years followingWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Germany started to turn around. The economy started to recover after the 1924 Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan (as proposed by the Dawes Committee, chaired by Charles G. Dawes) was a plan in 1924 that successfully resolved the issue of World War I reparations that Germany had to pay. It ended a crisis in European diplomacy following Wor ...
. The pavilion for the International Exhibition was supposed to represent the new Weimar Germany
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is als ...
: democratic, culturally progressive, prospering, and thoroughly pacifist; a self-portrait through architecture. The Commissioner, Georg von Schnitzler said it should give "voice to the spirit of a new era". This concept was carried out with the realization of the "Free plan
In architecture, a free plan is an open plan with non- load-bearing walls dividing interior space. In this structural system, the building structure is separate of the interior partitions. This is made possible by replacing interior load-bearin ...
" and the "Floating roof".
Building
 Mies's response to the proposal by von Schnitzler was radical. After rejecting the original site for aesthetic reasons, Mies agreed to a quiet site at the narrow side of a wide, diagonal axis, where the pavilion would still offer viewpoints and a route leading to one of the exhibition's main attractions, the
Mies's response to the proposal by von Schnitzler was radical. After rejecting the original site for aesthetic reasons, Mies agreed to a quiet site at the narrow side of a wide, diagonal axis, where the pavilion would still offer viewpoints and a route leading to one of the exhibition's main attractions, the Poble Espanyol
The Poble Espanyol (literally, ''Spanish town'') is an open-air architectural museum in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, approximately 400 metres away from the Fountains of Montjuïc. Built for the 1929 Barcelona International Exposition, the museum ...
.
The pavilion was to be bare, with no exhibits, leaving only the structure accompanying a single sculpture and specially-designed furniture (the Barcelona Chair
The Barcelona chair is a chair designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and Lilly Reich, for the German Pavilion at the International Exposition of 1929, hosted by Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
The chair was first used in Villa Tugendhat, a privat ...
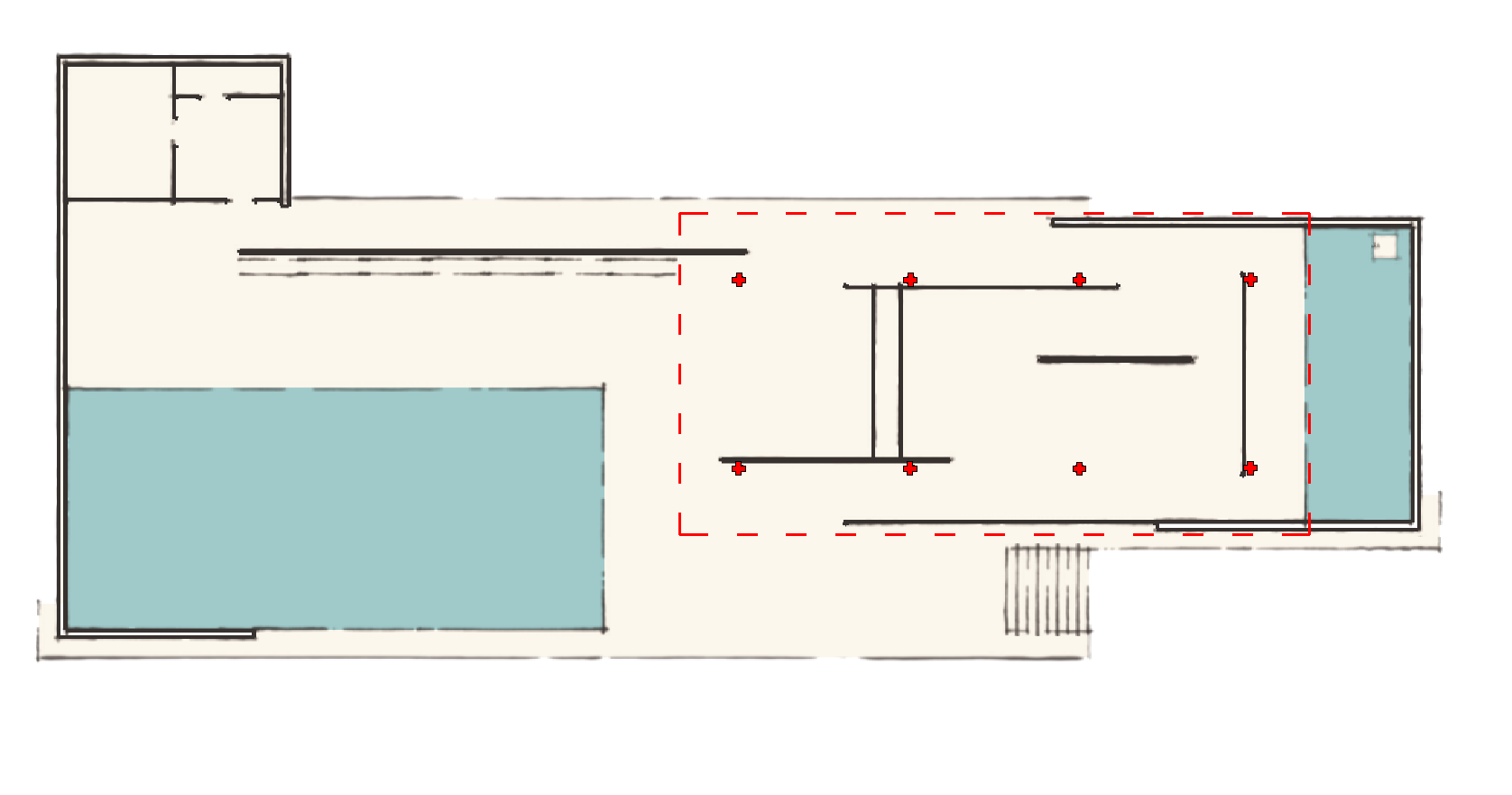
). This lack of accommodation enabled Mies to treat the Pavilion as a continuous space; blurring inside and outside. "The design was predicated on an absolute distinction between structure and enclosure—a regular grid of cruciform steel columns interspersed by freely spaced planes". However, the structure was more of a hybrid style, some of these planes also acted as supports. The floor plan is very simple. The entire building rests on a plinth of travertine. A southern U-shaped enclosure, also of travertine, helps form a service annex and a large water basin. The floor slabs of the pavilion project out and over the pool—once again connecting inside and out. Another U-shaped wall on the opposite side of the site also forms a smaller water basin. This is where the statue by Georg Kolbe
Georg Kolbe (15 April 1877 – 20 November 1947) was a German sculptor. He was the leading German figure sculptor of his generation, in a vigorous, modern, simplified classical style similar to Aristide Maillol of France.
Early life and educa ...
sits. The roof plates, relatively small, are supported by the chrome-clad, cruciform columns. This gives the impression of a hovering roof. Robin Evans said that the reflective columns appear to be struggling to hold the "floating" roof plane down, not to be bearing its weight.
Mies wanted this building to become "an ideal zone of tranquillity" for the weary visitor, who should be invited into the pavilion on the way to the next attraction. Since the pavilion lacked a real exhibition space, the building itself was to become the exhibit. The pavilion was designed to "block" any passage through the site, rather, one would have to go through the building. Visitors would enter by going up a few stairs, and due to the slightly sloped site, would leave at ground level in the direction of the Poble Espanyol. The visitors were not meant to be led in a straight line through the building, but to take continuous turnabouts. The walls not only created space, but also directed visitor's movements. This was achieved by wall surfaces being displaced against each other, running past each other, and creating a space that became narrower or wider.
Another unique feature of this building is the exotic materials Mies chooses to use. Plates of high-grade stone materials like veneers of Tinos verde antico marble and golden onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
as well as tinted glass of grey, green, white, as well as translucent glass, perform exclusively as spatial dividers.
Because this was planned as an exhibition pavilion, it was intended to exist only temporarily. The building was torn down in early 1930, not even a year after it was completed.
Reconstruction
Between 1983 and 1986, a group of Catalan architects reconstructed the pavilion permanently, based on historical drawings and rediscovered footings on the site. The reconstruction has been a popular tourist destination, but it also has been controversial among architects, critics, and historians. Some have hailed it as a revived masterpiece, some have condemned it as a "fake," and others are ambivalent. " is building is not supposed to exist," assertedPaul Goldberger
Paul Goldberger (born in 1950) is an American author, architecture critic and lecturer. He is known for his "Sky Line" column in ''The New Yorker''.
Biography
Shortly after starting as a reporter at ''The New York Times'' in 1972, he was assign ...
at the time. During planning, Philip Johnson
Philip Cortelyou Johnson (July 8, 1906 – January 25, 2005) was an American architect best known for his works of modern and postmodern architecture. Among his best-known designs are his modernist Glass House in New Canaan, Connecticut; the po ...
wondered, "The problem before us is should a dream be realized or not? We have made such a myth of that building. Shouldn’t it be left in the sacred vault of the memory bank?" Architect Lance Hosey
Lance Hosey (September 11, 1964 - August 27, 2021) was an American architect. In 2020, he joined HMC Architects, a large California-based firm, as the design industry's first Chief Impact Officer. Previously, he was a principal, design director ...
has thoroughly documented reactions to the reconstruction, concluding that while the reconstruction is a better physical artifact, the original was an irreplaceable product of its sociopolitical context.
Sculpture
The Pavilion was not only a pioneer for construction forms with a fresh, disciplined understanding of space, but also for modelling new opportunities for an association of free art and architecture. Mies placedGeorg Kolbe
Georg Kolbe (15 April 1877 – 20 November 1947) was a German sculptor. He was the leading German figure sculptor of his generation, in a vigorous, modern, simplified classical style similar to Aristide Maillol of France.
Early life and educa ...
's ''Alba'' ("Dawn") in the small water basin, leaving the larger one all the more empty. The sculpture also ties into the highly reflective materials Mies used—he chose the place where these optical effects would have the strongest impact; the building offers multiple views of ''Alba''. "From now on, in the sense of equality for juxtaposing building and visual work, sculptures were no longer to be applied retrospectively to the building, but rather to be a part of the spatial design, to help define and interpret it. To the day, one of the most notable examples is the Barcelona Pavilion".
Interventions programme
Since the Pavilion's reconstruction in the 1980s, the has invited leading artists and architects to temporarily alter the Pavilion. These installations and alterations, called "interventions", have kept the pavilion as a node of debate on architectural ideas and practices. The list of invited people includes architectsKazuyo Sejima
is a Japanese architect and director of her own firm, Kazuyo Sejima & Associates. In 1995, she co-founded the firm SANAA (Sejima + Nishizawa & Associates). In 2010, Sejima was the second woman to receive the Pritzker Prize, which was awarded j ...
and Ryue Nishizawa
is a Japanese architect based in Tokyo. He is a graduate of Yokohama National University, and is director of his own firm, Office of Ryue Nishizawa, established in 1997. In 1995, he co-founded the firm SANAA (Sejima and Nishizawa and Associate ...
(SANAA
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
) who added spiral acrylic interior walls, artist Ai Weiwei
Ai Weiwei (, ; born 28 August 1957) is a Chinese contemporary artist, documentarian, and activist. Ai grew up in the far northwest of China, where he lived under harsh conditions due to his father's exile. As an activist, he has been openly c ...
who refilled two pools with coffee and milk, Andrés Jaque
Andrés Jaque is an architect, writer and curator. In 2016, he was awarded with the 10th Frederick Kiesler Prize for Architecture and the Arts. In 2014, he won the Silver Lion to the Best Project at the 14th Venice Biennale. His work explores ...
who revealed the pavilion's so far disregarded basement and its role in hiding the daily making of the site's experience, Enric Miralles
Enric Miralles Moya (12 February 1955 – 3 July 2000) was a Spanish architect from Barcelona. He graduated from the Barcelona School of Architecture (ETSAB) at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) in 1978. After establishing ...
, Antoni Muntadas who brought to the pavilion the smell of the MoMA archives where its memory is preserved and Jordi Bernadó who removed the pavilion's glass doors. The architect and activist Andrés Jaque
Andrés Jaque is an architect, writer and curator. In 2016, he was awarded with the 10th Frederick Kiesler Prize for Architecture and the Arts. In 2014, he won the Silver Lion to the Best Project at the 14th Venice Biennale. His work explores ...
(Office for Political Innovation), artists Katarzyna Krakowiak, Laura Martínez de Guereñu, and the designer Sabine Marcelis have also been commissioned to create pieces for the interventions programme.
In 2018, the Mies van der Rohe Foundation presented the first edition of the Lilly Reich Grant for equality in architecture.
Gallery
cantilevered
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is supported at only one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cant ...
roof-slabs
File:Barcelona Pavilion contrast.JPG, Another view showing annex and large reflecting pool
File:Van der Rohe Pavillion overview.jpg, View showing the cruciform
Cruciform is a term for physical manifestations resembling a common cross or Christian cross. The label can be extended to architectural shapes, biology, art, and design.
Cruciform architectural plan
Christian churches are commonly describe ...
steel columns
File:Pavelló alemany (Barcelona) - 31.jpg, Another view
File:Pavelló Mies 04.JPG, Dawn (Der Morgen) by Georg Kolbe
Georg Kolbe (15 April 1877 – 20 November 1947) was a German sculptor. He was the leading German figure sculptor of his generation, in a vigorous, modern, simplified classical style similar to Aristide Maillol of France.
Early life and educa ...
File:Der Morgen Georg Kolbe.jpg, View showing small reflecting pool
File:Barcelona Chair Barcelona Pavilion.jpg, Barcelona Chair
The Barcelona chair is a chair designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and Lilly Reich, for the German Pavilion at the International Exposition of 1929, hosted by Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
The chair was first used in Villa Tugendhat, a privat ...
(Dawn sculpture in background)
File:Barcelona Ottoman Barcelona Pavilion.jpg, Barcelona Ottoman (showing book-matched onyx wall)
File:Pavelló Mies 05.JPG, Another view
See also
*Ibero-American Exposition of 1929
The Ibero-American Exposition of 1929 (Spanish: ''Exposición iberoamericana de 1929'') was a world's fair held in Seville, Spain, from 9 May 1929 until 21 June 1930. Countries in attendance of the exposition included: Portugal, the United Stat ...
was a world's fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition or an expo, is a large international exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specif ...
held in Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, from 9 May 1929 until 21 June 1930.
References
Further reading
* * * * * Dietrich Neumann with David Caralt (2020): ''An Accidental Masterpiece. Mies van der Rohe's Barcelona Pavilion'', Basel: Birkhäuser, * Dietrich Neumann with David Caralt (Eds.) (2020): ''The Barcelona Pavilion by Mies van der Rohe. One Hundred Texts since 1929'', Basel: Birkhäuser,External links
*Views of the replica German Pavilion
{{Authority control Buildings and structures in Barcelona Ludwig Mies van der Rohe buildings Buildings and structures completed in 1929 Modernist architecture in Barcelona International Style (architecture) Tourist attractions in Barcelona World's fair architecture in Barcelona Sants-Montjuïc 1929 Barcelona International Exposition