Barbary Slave Trade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

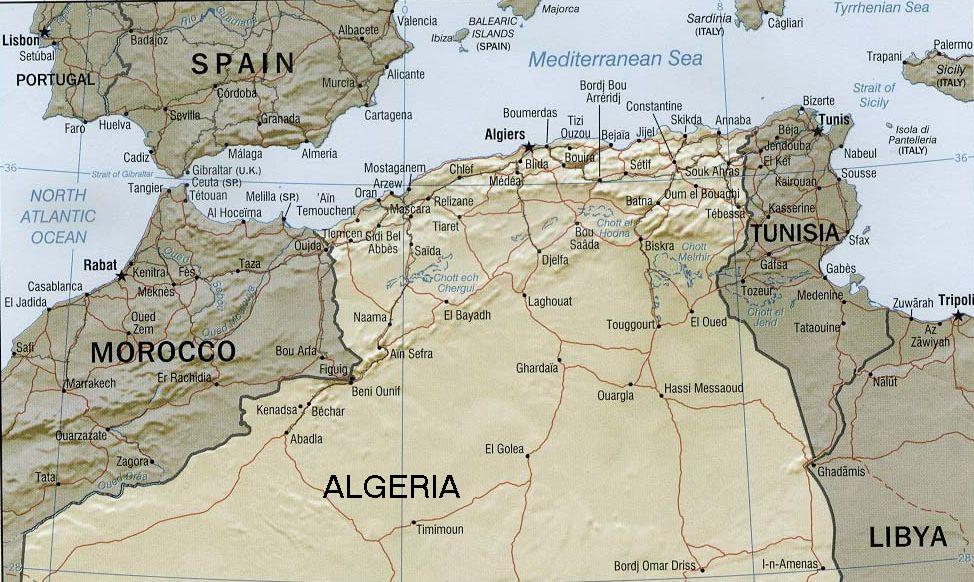 The Barbary slave trade involved slave markets on the Barbary Coast of
The Barbary slave trade involved slave markets on the Barbary Coast of
 Robert Davis estimates that
Robert Davis estimates that  While Barbary corsairs looted the cargo of ships they captured, their primary goal was to capture non-Muslim people for sale as slaves or for ransom. Those who had family or friends who might ransom them were held captive; the most famous of these was the author
While Barbary corsairs looted the cargo of ships they captured, their primary goal was to capture non-Muslim people for sale as slaves or for ransom. Those who had family or friends who might ransom them were held captive; the most famous of these was the author
 After a revolt in the mid-17th century reduced the ruling Ottoman
After a revolt in the mid-17th century reduced the ruling Ottoman
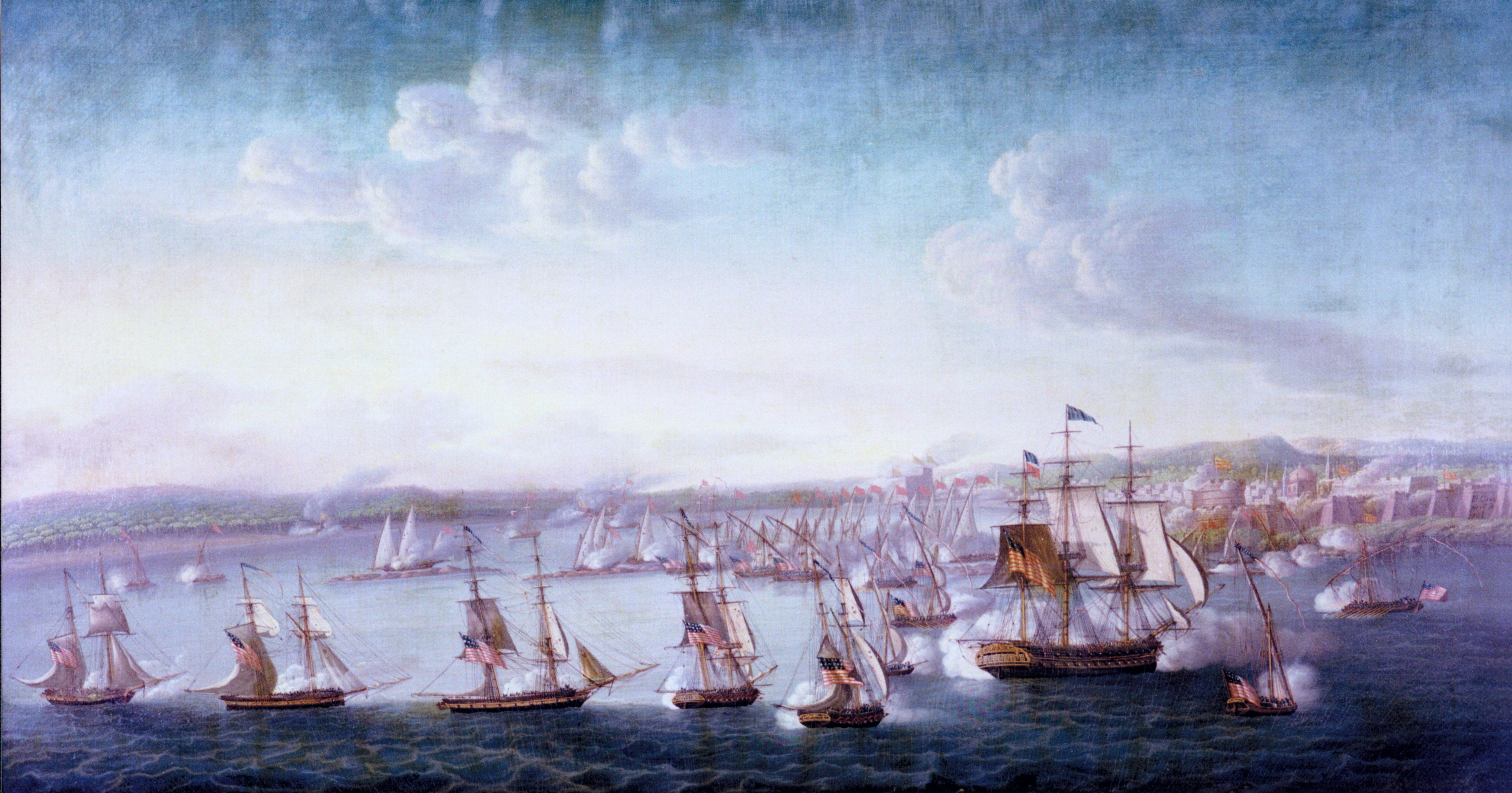 In the first years of the 19th century, the
In the first years of the 19th century, the
The Thomas Jefferson Papers - America and the Barbary Pirates - (American Memory from the Library of Congress)
*
* ttps://www.bbc.co.uk/history/british/empire_seapower/white_slaves_01.shtml British Slaves on the Barbary Coastbr>Seabed gold 'clue to white slavers'
* ttp://www.clements.umich.edu/exhibits/online/barbary/barbary-captivity.php Barbary Captivity Narratives
History of KytheraPirates, Privateers and the Ottoman Empire in the Early Modern MediterraneanKythira History
{{Pirates 16th-century establishments in Africa 19th-century establishments in Africa Islam and slavery Barbary slave trade Barbary pirates Piracy in the Mediterranean Early Modern Morocco Social history of Tunisia History of Tripolitania Arab history Persecution of Christians by Muslims Slavery in the Ottoman Empire

 The Barbary slave trade involved slave markets on the Barbary Coast of
The Barbary slave trade involved slave markets on the Barbary Coast of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, which included the Ottoman states of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province o ...
and the independent sultanate of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
, between the 16th and 19th century. The Ottoman states in North Africa were nominally under Ottoman suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
.
European slaves were acquired by Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe ...
in slave raid
Slave raiding is a military raid for the purpose of capturing people and bringing them from the raid area to serve as slaves. Once seen as a normal part of warfare, it is nowadays widely considered a crime. Slave raiding has occurred since ant ...
s on ships and by raids on coastal towns from Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
to the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
and the southwest of Britain, as far north as Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
and into the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to commun ...
.
The Ottoman Eastern Mediterranean was the scene of intense piracy. As late as the 18th century, piracy continued to be a "consistent threat to maritime traffic in the Aegean".
Extent
 Robert Davis estimates that
Robert Davis estimates that slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
rs from Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
, and Tripoli enslaved 1 million to 1.25 million Europeans in North Africa, from the beginning of the 16th century to the middle of the 18th (these numbers do not include the European people who were enslaved by Morocco and by other raiders and traders of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
coast). To extrapolate his numbers, Davis assumes the number of European slaves captured by Barbary pirates remained roughly constant for a 250-year period, stating:
Other historians have challenged Davis' numbers. David Earle cautions that the picture of Europeans slaves is clouded by the fact the corsairs also seized non-Christian whites from eastern Europe and black people from western Africa. Earle has questioned Robert Davis' estimates: “His figures sound a bit dodgy and I think he may be exaggerating.”
Middle East expert and researcher John Wright cautions that modern estimates are based on back-calculations from human observation. A second book by Davis, ''Holy War and Human Bondage: Tales of Christian-Muslim Slavery in the Early-Modern Mediterranean'', widened its focus to related slavery.
The authorities of Ottoman and pre-Ottoman times kept no relevant official records, but observers in the late 1500s and early 1600s estimated that around 35,000 European slaves were held throughout this period on the Barbary Coast, across Tripoli and Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, but mostly in Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
. The majority were sailors (particularly those who were English), taken with their ships, but others were fishermen and coastal villagers. However, most of these captives were people from lands close to Africa, particularly Italy.
From bases on the Barbary coast, North Africa, the Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe ...
raided ships traveling through the Mediterranean and along the northern and western coasts of Africa, plundering their cargo and enslaving the people they captured. From at least 1500, the pirates also conducted raids on seaside towns of Italy, Spain, France, England, the Netherlands and as far away as Iceland, capturing men, women and children. In 1544, Hayreddin Barbarossa
Hayreddin Barbarossa ( ar, خير الدين بربروس, Khayr al-Din Barbarus, original name: Khiḍr; tr, Barbaros Hayrettin Paşa), also known as Hızır Hayrettin Pasha, and simply Hızır Reis (c. 1466/1478 – 4 July 1546), was an O ...
captured the island of Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to ...
, taking 4,000 prisoners, and enslaved some 2,000–7,000 inhabitants of Lipari
Lipari (; scn, Lìpari) is the largest of the Aeolian Islands in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the northern coast of Sicily, southern Italy; it is also the name of the island's main town and ''comune'', which is administratively part of the Metropol ...
. In 1551, Ottoman corsair Dragut enslaved the entire population of the Maltese island of Gozo
Gozo (, ), Maltese: ''Għawdex'' () and in antiquity known as Gaulos ( xpu, 𐤂𐤅𐤋, ; grc, Γαῦλος, Gaúlos), is an island in the Maltese archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea. The island is part of the Republic of Malta. After ...
, between 5,000 and 6,000, sending them to Ottoman Tripolitania
The coastal region of what is today Libya was ruled by the Ottoman Empire from 1551 to 1912. First, from 1551 to 1864, as the Eyalet of Tripolitania ( ota, ایالت طرابلس غرب ''Eyālet-i Trâblus Gârb'') or '' Bey and Subjects of Tr ...
. In 1554 corsairs under Dragut sacked Vieste, beheaded 5,000 of its inhabitants, and abducted another 6,000. The Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
were invaded in 1558, and 4,000 people were taken into slavery. In 1618 the Algerian pirates attacked the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
taking 1000 captives to be sold as slaves. On some occasions, settlements such as Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
were abandoned following a raid, only being resettled many years later. Between 1609 and 1616, England alone lost 466 merchant ships to Barbary pirates.
 While Barbary corsairs looted the cargo of ships they captured, their primary goal was to capture non-Muslim people for sale as slaves or for ransom. Those who had family or friends who might ransom them were held captive; the most famous of these was the author
While Barbary corsairs looted the cargo of ships they captured, their primary goal was to capture non-Muslim people for sale as slaves or for ransom. Those who had family or friends who might ransom them were held captive; the most famous of these was the author Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra (; 29 September 1547 (assumed) – 22 April 1616 NS) was an Early Modern Spanish writer widely regarded as the greatest writer in the Spanish language and one of the world's pre-eminent novelists. He is best kno ...
, who was held for almost five years - from 1575 to 1580. Others were sold into various types of servitude. Captives who converted to Islam were generally freed, since enslavement of Muslims was prohibited; but this meant that they could never return to their native countries.
Customs' statistics from the 16th and 17th century suggest that Istanbul's additional slave imports from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
may have totaled around 2.5 million from 1450 to 1700.
The markets declined after Sweden and the United States defeated the Barbary States in the Barbary Wars (1800–1815). A US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
expedition under Commodore Edward Preble
Edward Preble (August 15, 1761 – August 25, 1807) was a United States naval officer who served with great distinction during the 1st Barbary War, leading American attacks on the city of Tripoli and forming the officer corps that would la ...
engaged gunboats and fortifications in Tripoli in 1804. A British diplomatic mission to Algiers led to the Dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Tunis under the Ottoman Empire from 1671 ...
to agree to release some Sardinian slaves. However, the moment the British left, the Dey ordered the Sardinians massacred; the same fleet joined by some Dutch warships returned and delivered a nine-hour bombardment of Algiers in 1816 leading to the Dey accepting a new agreement in which he promised to end his slavery operations. Despite this, the trade continued, only ending with the French conquest of Algeria
The French invasion of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Deylik of Algiers, and the French consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France inva ...
(1830–1847). The Kingdom of Morocco had already suppressed piracy and recognized the United States as an independent country in 1776.
Origins
The towns on the North African coast were recorded inRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
times for their slave markets, and this trend continued into the medieval age. The Barbary Coast increased in influence in the 15th century, when the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
took over as rulers of the area. Coupled with this was an influx of Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
and Moorish refugees, newly expelled from Spain after the Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
.
With Ottoman protection and a host of destitute immigrants, the coastline soon became reputed for piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
. Crews from the seized ships were either enslaved or ransom
Ransom is the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release, or the sum of money involved in such a practice.
When ransom means "payment", the word comes via Old French ''rançon'' from Latin ''re ...
ed. Between 1580 and 1680, there were in Barbary around 15,000 renegades, Christian Europeans who converted to Islam, and half of the corsair captains were in fact renegades. Some of them were slaves that converted to Islam but most had probably never been slaves and had come to North Africa looking for opportunity.
Rise of the Barbary pirates
 After a revolt in the mid-17th century reduced the ruling Ottoman
After a revolt in the mid-17th century reduced the ruling Ottoman Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignita ...
s to little more than figureheads in the region, the towns of Tripoli, Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
, Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, and others became independent in all but name. Without a large central authority and its laws, the pirates themselves started to gain much influence.
In 1785 when Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
and John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
went to London to negotiate with Tripoli's envoy, Ambassador Sidi Haji Abdrahaman, they asked him what right he had to take slaves in this way. He replied that the "right" was "founded on the Laws of the Prophet, that it was written in their Koran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
that all nations who should not have answered their authority were sinners, that it was their right and duty to make war upon them wherever they could be found, and to make slaves of all they could take as prisoners, and that every Mussulman who should be slain in battle was sure to go to Paradise".
Pirate raids for the acquisition of slaves occurred in towns and villages on the African Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
seaboard, as well as in Europe. Reports of Barbary raids and kidnappings of those in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, and as far north as Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
exist from between the 16th to the 19th centuries. Robert Davis estimated that between 1 and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by pirates and sold as slaves in Tunis, Algiers and Tripoli during this time period. The slave trade in Europeans in other parts of the Mediterranean is not included in this estimation. However, other historias such as David Earle have questioned Robert Davis' estimates: “His figures sound a bit dodgy and I think he may be exaggerating.”
Famous accounts of Barbary slave raids include a mention in the diary of Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no mariti ...
and a raid on the coastal village of Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, Ireland, during which pirates left with the entire populace of the settlement. The attack was led by a Dutch captain, Jan Janszoon van Haarlem, also known as Murad Reis the Younger. Janszoon also led the 1627 raid on Iceland. Such raids in the Mediterranean were so frequent and devastating that the coastline between Venice and Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most po ...
suffered widespread depopulation, and settlement there was discouraged. In fact, it was said that "there was no one left to capture any longer."
In 1627 a group known as the Salé Rovers, from the Republic of Salé (now Salé
Salé ( ar, سلا, salā, ; ber, ⵙⵍⴰ, sla) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the right bank of the Bou Regreg river, opposite the national capital Rabat, for which it serves as a commuter town. Founded in about 1030 by the Banu Ifran, ...
in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
) occupied Lundy
Lundy is an English island in the Bristol Channel. It was a micronation from 1925–1969. It forms part of the district of Torridge in the county of Devon.
About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently chang ...
for five years. These Barbary Pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe ...
, under the command of Janszoon, flew an Ottoman flag over the island. Slaving raids were made embarking from Lundy by the Barbary Pirates, and captured Europeans were held on Lundy before being sent to Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
to be sold as slaves.
The power and influence of these pirates during this time was such that nations including the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
paid tribute in order to stave off their attacks. Supplies from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
appear to have been even larger. A compilation of partial statistics and patchy estimates indicates that almost 2 million Russians, Ukrainians, and Poles were seized from 1468 to 1694. Additionally, there were slaves from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
obtained by a mixture of raiding and trading. 16th- and 17th-century customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
statistics suggest that Istanbul's slave import from the Black Sea may have totaled around 2.5 million from 1450 to 1700.
An account of the later phase of the trade was published in 1740 by Englishman Thomas Pellow
Thomas Pellow (1704 – 45), son of Thomas Pellow of Penryn and his wife Elizabeth (née Lyttleton), was a Cornish author best known for the extensive captivity narrative entitled ''The History of the Long Captivity and Adventures of Thomas P ...
, who had escaped from Morocco after 21 years of slavery, having been captured from a ship in 1716 as an 11 year-old boy.Milton 2005, p. 267
Decline
 In the first years of the 19th century, the
In the first years of the 19th century, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, allied with European nations, fought and won the First and the Second Barbary War
The Second Barbary War (1815) or the U.S.–Algerian War was fought between the United States and the North African Barbary Coast states of Tripoli, Tunis, and Algiers. The war ended when the United States Senate ratified Commodore Stephen ...
s against the pirates. The wars were a direct response of the American, British, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and the Dutch states to the raids and the slave trade by the Barbary pirates against them, which ended in the 1830s, when the region was conquered by France. The Barbary slave trade and slave markets in the Mediterranean declined and eventually disappeared after the European occupations.
After an Anglo-Dutch bombardment in 1816 of Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
on 27 August, led by Admiral Edward Pellew, 1st Viscount Exmouth
Admiral Edward Pellew, 1st Viscount Exmouth, GCB (19 April 1757 – 23 January 1833) was a British naval officer. He fought during the American War of Independence, the French Revolutionary Wars, and the Napoleonic Wars. His younger brother I ...
, disabled most of the Pirate fleet, the Dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Tunis under the Ottoman Empire from 1671 ...
of Algiers was forced to agree to terms which included the release of the surviving 1,200 slaves (mostly from Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
) and the cessation of their practice of enslaving Europeans. After being defeated in this period of formal hostilities with European and American powers, the Barbary states went into decline.
The Barbary pirates refused to cease their slaving operations, resulting in another bombardment by a Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
fleet against Algiers in 1824. France invaded Algiers in 1830, placing it under colonial rule. Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
was similarly invaded by France in 1881. Tripoli returned to direct Ottoman control in 1835, before falling into Italian hands in the 1911 Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War ( tr, Trablusgarp Savaşı, "Tripolitanian War", it, Guerra di Libia, "War of Libya") was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911, to 18 October 1912. As a result o ...
. As such, the slave traders now found that they had to work in accordance with the laws of their governors, and could no longer look to self-regulation. The slave trade ceased on the Barbary coast in the 19th and 20th centuries or when European governments passed laws granting emancipation to slaves.
The word '' razzia'' was borrowed via Italian and French from Maghrebi Arabic
Maghrebi Arabic (, Western Arabic; as opposed to Eastern or Mashriqi Arabic) is a vernacular Arabic dialect continuum spoken in the Maghreb region, in Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Western Sahara, and Mauritania. It includes Moroccan, Al ...
'' ghaziya'' ( ar, غزية, lit=raiding), originally referring to slave raid
Slave raiding is a military raid for the purpose of capturing people and bringing them from the raid area to serve as slaves. Once seen as a normal part of warfare, it is nowadays widely considered a crime. Slave raiding has occurred since ant ...
s conducted by Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe ...
.
See also
*Barbary corsairs
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe a ...
* Barbary Wars
* Crimean–Nogai raids into East Slavic lands
* North African slave narratives
* Republic of Salé
* Sklavenkasse
The term Sklavenkasse (slave fund) was a travel and ransom insurance scheme designated to pay ransom for European seafarers who had been captured by Barbary Pirates in the Mediterranean and off the coasts of Western Europe and sold into the Ba ...
* Slavery in the Ottoman Empire
* Turkish Abductions
References
Further reading
* * * *The Thomas Jefferson Papers - America and the Barbary Pirates - (American Memory from the Library of Congress)
*
External links
* ttps://www.bbc.co.uk/history/british/empire_seapower/white_slaves_01.shtml British Slaves on the Barbary Coastbr>Seabed gold 'clue to white slavers'
* ttp://www.clements.umich.edu/exhibits/online/barbary/barbary-captivity.php Barbary Captivity Narratives
History of Kythera
{{Pirates 16th-century establishments in Africa 19th-century establishments in Africa Islam and slavery Barbary slave trade Barbary pirates Piracy in the Mediterranean Early Modern Morocco Social history of Tunisia History of Tripolitania Arab history Persecution of Christians by Muslims Slavery in the Ottoman Empire