Balkanized on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Balkanization is the fragmentation of a larger region or state into smaller regions or states, which may be hostile or uncooperative with one another. It is usually caused by differences of ethnicity, culture, and religion and some other factors such as past grievances. The term is pejorative; when sponsored or encouraged by a sovereign third party, it has been used as an accusation against such third party nations. Controversially, the term is often used by voices for the status quo to underscore the dangers of acrimonious or runaway
Balkanization is the fragmentation of a larger region or state into smaller regions or states, which may be hostile or uncooperative with one another. It is usually caused by differences of ethnicity, culture, and religion and some other factors such as past grievances. The term is pejorative; when sponsored or encouraged by a sovereign third party, it has been used as an accusation against such third party nations. Controversially, the term is often used by voices for the status quo to underscore the dangers of acrimonious or runaway
 The term (coined in the early 19th century) refers to the division of the Balkan peninsula, which was ruled almost entirely by the
The term (coined in the early 19th century) refers to the division of the Balkan peninsula, which was ruled almost entirely by the
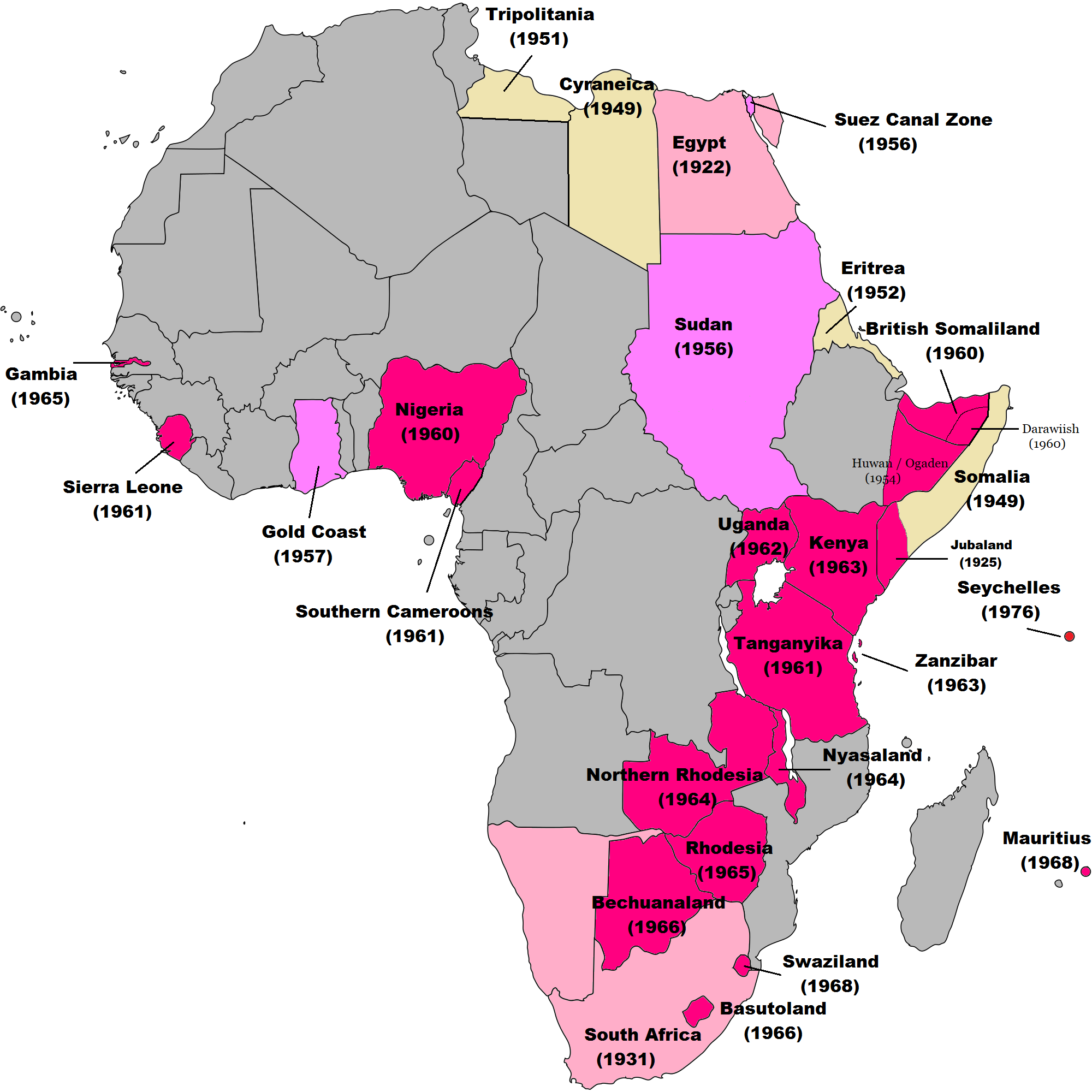 Bates, Coatsworth & Williamson argued Balkanization was observed greatly in
Bates, Coatsworth & Williamson argued Balkanization was observed greatly in
 Balkanization is the fragmentation of a larger region or state into smaller regions or states, which may be hostile or uncooperative with one another. It is usually caused by differences of ethnicity, culture, and religion and some other factors such as past grievances. The term is pejorative; when sponsored or encouraged by a sovereign third party, it has been used as an accusation against such third party nations. Controversially, the term is often used by voices for the status quo to underscore the dangers of acrimonious or runaway
Balkanization is the fragmentation of a larger region or state into smaller regions or states, which may be hostile or uncooperative with one another. It is usually caused by differences of ethnicity, culture, and religion and some other factors such as past grievances. The term is pejorative; when sponsored or encouraged by a sovereign third party, it has been used as an accusation against such third party nations. Controversially, the term is often used by voices for the status quo to underscore the dangers of acrimonious or runaway secessionism
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics lea ...
. Balkanization is a type of political fragmentation Political fragmentation is the fragmentation of the political landscape into different parties and groups, which makes it difficult to deliver effective governance. Political fragmentation can apply to political parties, political groups or other po ...
.
Nations and societies
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, into a number of smaller states between 1817 and 1912. It came into common use in the immediate aftermath of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, with reference to the many new states that arose from the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
Uses to stir opinion
Countries in Europe, where uniting quite recently historically distinct peoples or nations, have seen outspoken separatists. These have prompted reactionary voices fearing Balkanization. TheIberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
, especially Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, has from the time of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
(ending in 1492) seen voices fearing disorderly rupture. Its main separatist movements today are Basque separatism and Catalan independentism
The Catalan independence movement ( ca, independentisme català; Spanish: ''independentismo catalán'') is a social and political movement (with roots in Catalan nationalism) which seeks the independence of Catalonia from Spain.
The beginnings o ...
.
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
is a stable country but has separatist movements, the strongest of which is the Quebec sovereignty movement
The Quebec sovereignty movement (french: Mouvement souverainiste du Québec) is a political movement whose objective is to achieve the sovereignty of Quebec, a province of Canada since 1867, including in all matters related to any provision o ...
, which seeks to create a nation-state in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, which encompasses the majority of Canada's French-Canadian population. Two referendums have been held to decide the question, one in 1980 and one in 1995. Both were lost by the separatists, the latter by a small margin. Less mainstream and smaller movements also exist in the Canadian Prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, especially Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, to protest what is seen as domination by Quebec and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
of Canadian politics. Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
Premier Roy Romanow
Roy John Romanow (born August 12, 1939) is a Canadian politician and the 12th premier of Saskatchewan from 1991 to 2001.
Early life
Romanow was born in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, to Tekla and Michael Romanow, who were Ukrainian immigrants from Or ...
also considered separation from Canada if the 1995 referendum had succeeded, which would have led to the balkanization of Canada.
Quebec has been the scene of a small but vociferous partition movement from the part of Anglo-Quebeckers
English-speaking Quebecers, also known as Anglo-Quebecers, English Quebecers, or Anglophone Quebecers (all alternately spelt Quebeckers; in French ''Anglo-Québécois'', ''Québécois Anglophone'') or simply Anglos in a Quebec context, are a ...
activist groups opposed to the idea of independence of Quebec
The Quebec sovereignty movement (french: Mouvement souverainiste du Québec) is a political movement whose objective is to achieve the sovereignty of Quebec, a province of Canada since 1867, including in all matters related to any provision of ...
since 80% of the province is francophone. One such project is the Proposal for the Province of Montreal
The Province of Montreal is a proposal to separate the city of Montreal, its Greater Montreal, metropolitan region or its English and non-Francophone regions into a separate province from Quebec, becoming the 11th province of Canada. There have bee ...
for the establishment of a separate province from Quebec for Montreal's strongly-anglophone and allophone (speaking both English and French) communities.
In January 2007, the growing support for Scottish independence made Chancellor of the Exchequer of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and later Prime Minister Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown (born 20 February 1951) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 to 2010. He previously served as Chancellor of the Exchequer in Tony B ...
talk of a "Balkanisation of Britain". Independence movements in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
also exist in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
and Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Kingdom of Jorvik, and the ...
(themselves parts of England) and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
.
In Africa
 Bates, Coatsworth & Williamson argued Balkanization was observed greatly in
Bates, Coatsworth & Williamson argued Balkanization was observed greatly in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
then British East Africa
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was an area in the African Great Lakes occupying roughly the same terrain as present-day Kenya from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Controlled by Bri ...
. In the 1960s, countries in the started to opt for "autonomy within the French community" in the postcolonial era. Countries in the CFA franc
The CFA franc (french: franc CFA, , Franc of the Financial Community of Africa, originally Franc of the French Colonies in Africa, or colloquially ; abbreviation: F.CFA) is the name of two currencies, the West African CFA franc, used in eight We ...
zone were allowed to impose tariffs, regulate trade and manage transport services.
Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
, Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
, Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeas ...
, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
achieved independence toward the end of when the Great Powers postcolonial era came about. The period also saw the breakdown of the Federation of the Rhodesias and Nyasaland as well as the East African High Commission. Splintering into today's nations was a result of the movement towards a closed economy. Countries were adopting antitrade and anti-market policies. Tariff rates were 15% higher than in OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
countries during the 1970s and 1980s. Furthermore, countries took approaches to subsidise their own local industries, but the interior markets were small in scale. Transport networks were fragmented; regulations on labor and capital flow were increased; price controls were introduced. Between 1960 and 1990, balkanization led to disastrous results. The GDP of these regions were one tenth of OECD countries. Balkanization also resulted in what van de Valle called "typically fairly overvalued exchanged rates" in Africa. Balkanization contributed to what Bates, Coatsworth & Williamson claimed to be a lost decade in Africa.
Economic stagnation ended only in the mid-1990s. Countries within the region started to input more stabilization policies. What was originally a high exchange rate eventually fell to a more reasonable exchange rate after devaluations in 1994. By 1994, the number of countries with an exchange rate 50 percent higher than the official exchange rate had decreased from 18 to four. However, there is still limited progress in improving trade policies within the region, according to van de Walle. In addition, the post-independent countries still rely heavily on donors for development plans. Balkanization still has an impact on today's Africa. However, this causation narrative is not popular in many circles.
In the Levant
During the 1980s, the Lebanese academic and writerGeorges Corm
Georges Corm is a Lebanese economist. He served as minister of finance in the government of Salim Hoss from 1998 to 2000.
He studied at the Institut d'Etudes Politiques de Paris (1958-1961) where he graduated in Public Finance and has also a PhD ...
used the term ''balkanization'' to describe attempts by supporters of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
to create buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
s based on ethnic backgrounds in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
in order to protect Israeli sovereignty. In 2013 the French journalist Bernard Guetta writing in the '' Libération'' newspaper applied the term to:
*Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
's political division between Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
and Druze.
*The Syrian Civil War.
See also
* Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire *Dissolution of Austria-Hungary
The dissolution of Austria-Hungary was a major geopolitical event that occurred as a result of the growth of internal social contradictions and the separation of different parts of Austria-Hungary. The reason for the collapse of the state was Worl ...
* Dissolution of the Soviet Union
* Balkan Wars
* Balkan Federation
The Balkan Federation project was a left-wing political movement to create a country in the Balkans by combining Yugoslavia, Albania, Greece, Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey.
The concept of a Balkan federation emerged in the late 19th century ...
* Detachment (territory)
* Feudal fragmentation
Feudal fragmentation being a stage in the development of certain feudal states, in which it is split into smaller regional state structures, each characterized by significant autonomy if not outright independence and ruled by a high-ranking noble ...
* Kleinstaaterei
In the history of Germany, (, ''"small-state -ery"'') is a German word used, often pejoratively, to denote the territorial fragmentation during the Holy Roman Empire (especially after the end of the Thirty Years' War), and during t ...
* Pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
* Protracted social conflict
Protracted social conflict is a technical term that generally refers to conflicts described by other researchers as ''protracted'' or ''intractable:'' complex, severe, commonly enduring, and often violent. The term was presented in a theory develop ...
* Secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
* Self-determination
* Self-governance
* Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
* Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
* Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It forma ...
* Westphalian sovereignty
Westphalian sovereignty, or state sovereignty, is a principle in international law that each state has exclusive sovereignty over its territory. The principle underlies the modern international system of sovereign states and is enshrined in the ...
* ''Cuius regio, eius religio
() is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective (if not individua ...
''
* Lebanonization
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control 1810s neologisms 19th century in the Ottoman Empire Balkans Geopolitical terminology Metaphors referring to places Political terminology Politics by region Sectarian violence Separatism Political slurs