Bærum Tunnel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bærum Tunnel ( no, Bærumstunnelen) is a long double track
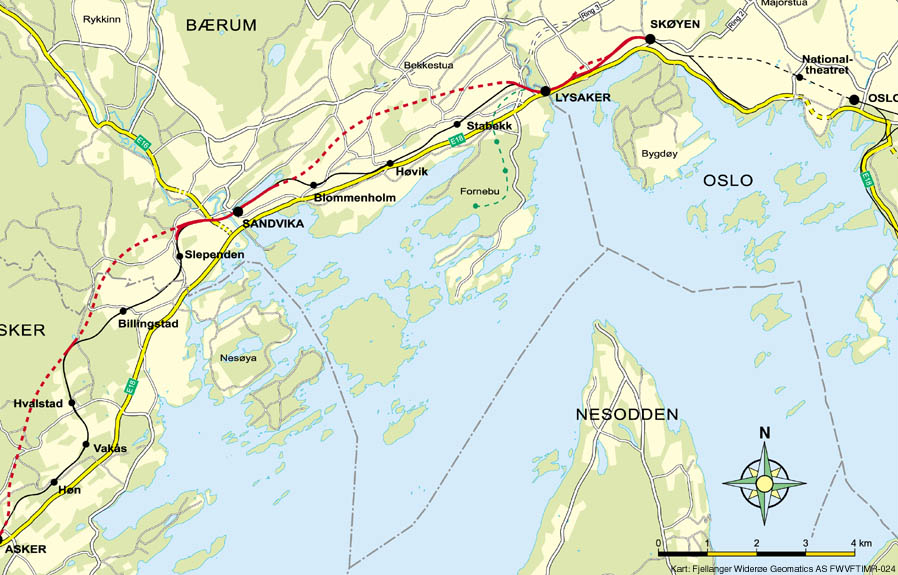 The Bærum Tunnel is long and is part of the long section of the Asker Line between Lysaker and Sandvika. At Engervannet, at the Sandvika end, the tunnel mouths out with two long arms, one on each side of the Drammen Line, allowing trains to connect to the correct direction of traffic through Sandvika. The excavated cross-section is . At the Lysaker end, the tunnel has an end-piece which consists of a long culvert and the Drammen Line branches off on both sides of the tunnel. The three access tunnels for the tunnel's construction, at
The Bærum Tunnel is long and is part of the long section of the Asker Line between Lysaker and Sandvika. At Engervannet, at the Sandvika end, the tunnel mouths out with two long arms, one on each side of the Drammen Line, allowing trains to connect to the correct direction of traffic through Sandvika. The excavated cross-section is . At the Lysaker end, the tunnel has an end-piece which consists of a long culvert and the Drammen Line branches off on both sides of the tunnel. The three access tunnels for the tunnel's construction, at
 The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to increase the traffic on the west corridor. Prior to its opening, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity, and had a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker, by running slower trains on the Drammen Line and faster trains on the new track. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first from Asker to Sandvika was built from 2001 to 2005, and the second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the long Skaugum Tunnel and the long Tanum Tunnel.
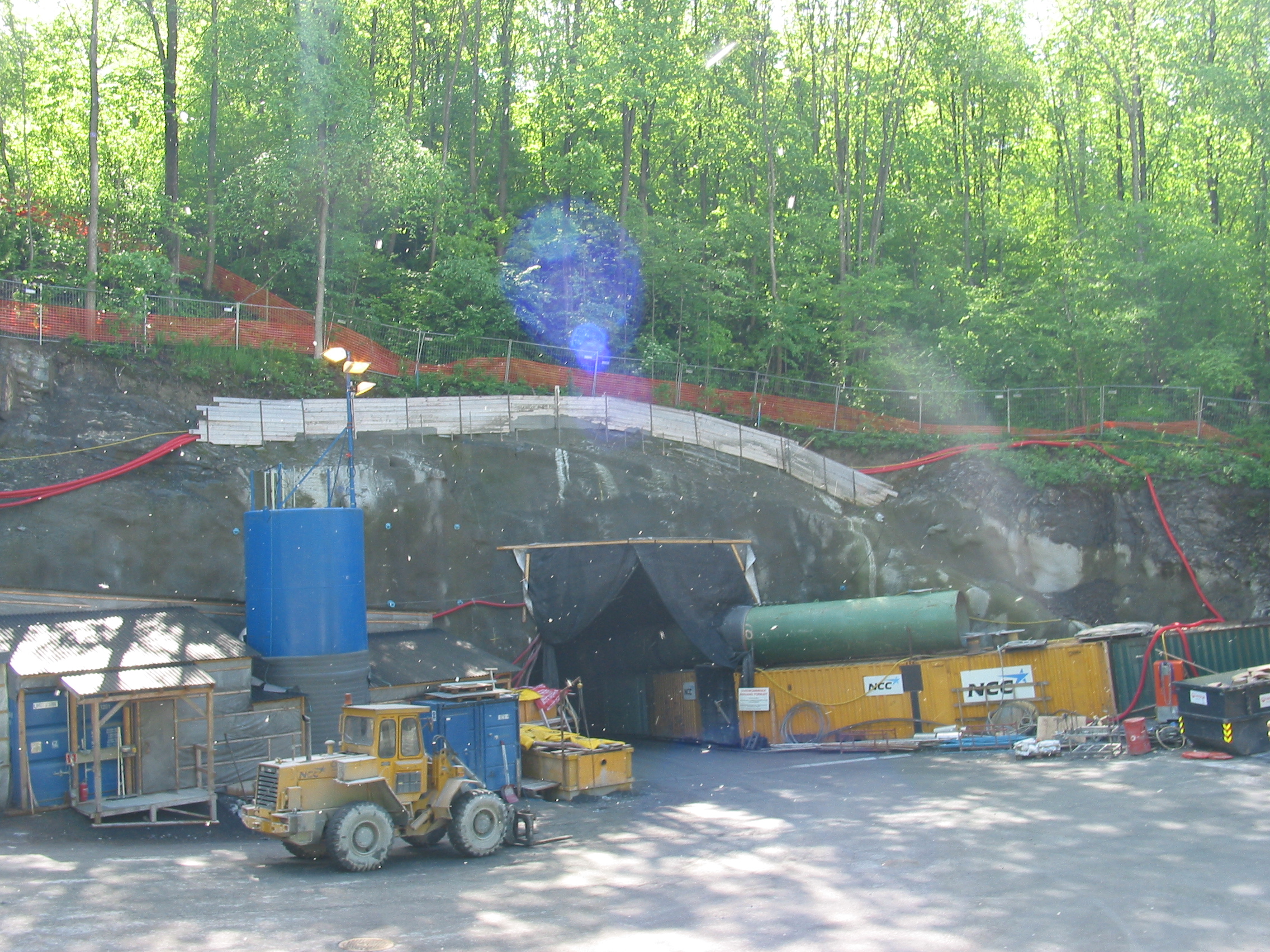
There were four main contracts for building the line issued after public tenders. Three of these involved part of the tunnel, and were awarded to Skanska, Veidekke and NCC AB, NCC. Mesta (company), Mesta, Mika, Bestonmast and Spesialprosjekt bid, but failed to win any contracts. Work was done from 06:00 through 02:00, and noisy work was avoided before 07:00 or after 22:00. Any work outside the tunnels was only done between 07:00 to 18:00, and from 08:00 to 16:00 on Saturdays. The tunnel was built using the
The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to increase the traffic on the west corridor. Prior to its opening, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity, and had a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker, by running slower trains on the Drammen Line and faster trains on the new track. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first from Asker to Sandvika was built from 2001 to 2005, and the second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the long Skaugum Tunnel and the long Tanum Tunnel.
There were four main contracts for building the line issued after public tenders. Three of these involved part of the tunnel, and were awarded to Skanska, Veidekke and NCC AB, NCC. Mesta (company), Mesta, Mika, Bestonmast and Spesialprosjekt bid, but failed to win any contracts. Work was done from 06:00 through 02:00, and noisy work was avoided before 07:00 or after 22:00. Any work outside the tunnels was only done between 07:00 to 18:00, and from 08:00 to 16:00 on Saturdays. The tunnel was built using the  The tunneling resulted in of soil, most of which was used for the expansion of the Port of Drammen. It was transported away from the tunnel with up to 12 truckloads per hour. The first breakthrough between adjacent construction sections took place on 5 June 2008. On 19 October 2008, there was a ground failure at a landfill where the soil from the tunnel was dumped. This caused a land slip which pressed up soil nearby at Gjønnes (station), Gjønnes Station on the Kolsås Line of the Oslo Metro (that section of the Kolsås Line was largely unused due to unrelated construction at the time); a long section of one platform and track was pressed up , resulting in the other track lying on its side. Because of changes to European Union regulations after planning of the project, three extra emergency staircases had to be installed in late 2009. The final breakthrough in the tunnel occurred on 26 July 2009. The tunneling took place under the groundwater level. To avoid similar problems which occurred during the construction of the Romerike Tunnel, where massive leaks took a year to fix, several test bores were made in the area to measure the groundwater level. The measuring system was set up to communicate any indications of a change immediately & automatically to the on-site geologists, who would be able to act accordingly. The system also automatically pumped water into the affected areas to compensate for any leaks until they could be fixed.
To make the tunnel watertight and frost-resistant, the walls were covered with polyethylene mats. Because they are highly flammable, they were then covered in a layer of Shotcrete#Shotcrete vs. gunite, gunite. Also installed were fire water pipes and ventilation systems to remove smoke. To sound-insulate the tunnel and to avoid vibrations spreading to nearby housing, the entire tunnel was covered in a layer of rock wool. By December 2010, the ballast had been laid, and in January 2011 laying of the tracks and ties started. The work to build the tracks and overhead wires was contracted to Baneservice. The contract for the electro-technical installations was awarded to YIT Building Systems for NOK 120 million. In 2006, the whole section from Lysaker to Sandvika was estimated to cost NOK 2.7 billion.
Freight trains started using the tunnel on 26 August 2011, and passenger trains on 28 August the same year. The official opening took place on 2 September 2011. Along with several other projects west of Oslo, including a new
The tunneling resulted in of soil, most of which was used for the expansion of the Port of Drammen. It was transported away from the tunnel with up to 12 truckloads per hour. The first breakthrough between adjacent construction sections took place on 5 June 2008. On 19 October 2008, there was a ground failure at a landfill where the soil from the tunnel was dumped. This caused a land slip which pressed up soil nearby at Gjønnes (station), Gjønnes Station on the Kolsås Line of the Oslo Metro (that section of the Kolsås Line was largely unused due to unrelated construction at the time); a long section of one platform and track was pressed up , resulting in the other track lying on its side. Because of changes to European Union regulations after planning of the project, three extra emergency staircases had to be installed in late 2009. The final breakthrough in the tunnel occurred on 26 July 2009. The tunneling took place under the groundwater level. To avoid similar problems which occurred during the construction of the Romerike Tunnel, where massive leaks took a year to fix, several test bores were made in the area to measure the groundwater level. The measuring system was set up to communicate any indications of a change immediately & automatically to the on-site geologists, who would be able to act accordingly. The system also automatically pumped water into the affected areas to compensate for any leaks until they could be fixed.
To make the tunnel watertight and frost-resistant, the walls were covered with polyethylene mats. Because they are highly flammable, they were then covered in a layer of Shotcrete#Shotcrete vs. gunite, gunite. Also installed were fire water pipes and ventilation systems to remove smoke. To sound-insulate the tunnel and to avoid vibrations spreading to nearby housing, the entire tunnel was covered in a layer of rock wool. By December 2010, the ballast had been laid, and in January 2011 laying of the tracks and ties started. The work to build the tracks and overhead wires was contracted to Baneservice. The contract for the electro-technical installations was awarded to YIT Building Systems for NOK 120 million. In 2006, the whole section from Lysaker to Sandvika was estimated to cost NOK 2.7 billion.
Freight trains started using the tunnel on 26 August 2011, and passenger trains on 28 August the same year. The official opening took place on 2 September 2011. Along with several other projects west of Oslo, including a new
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
tunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, and enclosed except for the entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube cons ...
in Bærum
Bærum () is a municipality in the Greater Oslo Region in Norway that forms an affluent suburb of Oslo on the west coast of the city. Bærum is Norway's fifth largest municipality with a population of 128,760 (2021). It is part of the electoral ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
. Running between Marstranderveien and Engervannet, it makes up most of the long section of the Asker Line
The Asker Line ( no, Askerbanen) is a railway line between Asker and Lysaker in Norway. The line runs along the same corridor as the Drammen Line, offering increased capacity, speed and regularity on the rail network west of Oslo. The first ...
between Lysaker Station
Lysaker Station ( no, Lysaker stasjon) is a railway station on the Drammen Line and Asker Line situated at Lysaker in Bærum, Norway. Located from Oslo Central Station, Lysaker is served by a mix of Vy express, regional and Oslo Commuter Rail ...
and Sandvika Station
Sandvika Station ( no, Sandvika stasjon) is a railway station located at Sandvika in Bærum, Norway. Situated on the Drammen Line, from Oslo S, it also an intermediate station of the Asker Line. Vy serves the station with local and regional, w ...
, which was taken into use on 26 August 2011. The tunnel was constructed from 2007 using the drilling and blasting
Drilling and blasting is the controlled use of explosives and other methods, such as gas pressure blasting pyrotechnics, to break rock for excavation. It is practiced most often in mining, quarrying and civil engineering such as dam, tunnel ...
method with three crosscuts. The tunnel has two tracks, is electrified
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source.
The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology, economic history ...
and allows for maximum speeds of . The whole section between the stations is estimated to cost 2.7 billion Norwegian krone (NOK). The tunnel accelerates intercity and regional traffic west of Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population ...
and frees up capacity for the Oslo Commuter Rail
Oslo Commuter Rail ( no, Lokaltog Østlandet) is a commuter rail centered in Oslo, Norway, connecting the capital to six counties in Eastern Norway. The system is operated by Vy (formerly NSB) and its subsidiary Vy Gjøvikbanen, using Class 69 ...
.
Specifications
 The Bærum Tunnel is long and is part of the long section of the Asker Line between Lysaker and Sandvika. At Engervannet, at the Sandvika end, the tunnel mouths out with two long arms, one on each side of the Drammen Line, allowing trains to connect to the correct direction of traffic through Sandvika. The excavated cross-section is . At the Lysaker end, the tunnel has an end-piece which consists of a long culvert and the Drammen Line branches off on both sides of the tunnel. The three access tunnels for the tunnel's construction, at
The Bærum Tunnel is long and is part of the long section of the Asker Line between Lysaker and Sandvika. At Engervannet, at the Sandvika end, the tunnel mouths out with two long arms, one on each side of the Drammen Line, allowing trains to connect to the correct direction of traffic through Sandvika. The excavated cross-section is . At the Lysaker end, the tunnel has an end-piece which consists of a long culvert and the Drammen Line branches off on both sides of the tunnel. The three access tunnels for the tunnel's construction, at Blommenholm
Blommenholm is a district in the municipality of Bærum, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost ...
, Fossveien and Skallum, have been adapted for use as emergency exits. In addition, three more emergency exits have been constructed at Ballerud, Engerjordet and Njålveien, to allow for an emergency exit every . Each consists of a spiral staircase
Stairs are a structure designed to bridge a large vertical distance between lower and higher levels by dividing it into smaller vertical distances. This is achieved as a diagonal series of horizontal platforms called steps which enable passage ...
in a shaft up to deep. These are primarily intended to allow access for emergency personnel, rather than as an escape route for passengers. Each staircase ends in a smoke-tight room. The line has two tracks, is electrified at and allows for maximum speeds of .
History
 The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to increase the traffic on the west corridor. Prior to its opening, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity, and had a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker, by running slower trains on the Drammen Line and faster trains on the new track. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first from Asker to Sandvika was built from 2001 to 2005, and the second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the long Skaugum Tunnel and the long Tanum Tunnel.
There were four main contracts for building the line issued after public tenders. Three of these involved part of the tunnel, and were awarded to Skanska, Veidekke and NCC AB, NCC. Mesta (company), Mesta, Mika, Bestonmast and Spesialprosjekt bid, but failed to win any contracts. Work was done from 06:00 through 02:00, and noisy work was avoided before 07:00 or after 22:00. Any work outside the tunnels was only done between 07:00 to 18:00, and from 08:00 to 16:00 on Saturdays. The tunnel was built using the
The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to increase the traffic on the west corridor. Prior to its opening, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity, and had a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker, by running slower trains on the Drammen Line and faster trains on the new track. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first from Asker to Sandvika was built from 2001 to 2005, and the second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the long Skaugum Tunnel and the long Tanum Tunnel.
There were four main contracts for building the line issued after public tenders. Three of these involved part of the tunnel, and were awarded to Skanska, Veidekke and NCC AB, NCC. Mesta (company), Mesta, Mika, Bestonmast and Spesialprosjekt bid, but failed to win any contracts. Work was done from 06:00 through 02:00, and noisy work was avoided before 07:00 or after 22:00. Any work outside the tunnels was only done between 07:00 to 18:00, and from 08:00 to 16:00 on Saturdays. The tunnel was built using the drilling and blasting
Drilling and blasting is the controlled use of explosives and other methods, such as gas pressure blasting pyrotechnics, to break rock for excavation. It is practiced most often in mining, quarrying and civil engineering such as dam, tunnel ...
method, which involved blasting sections of of rock at a time, with a progress of per week per team. Blasting started on 26 June 2007. Construction was done from three access tunnels: a long bore at Engervannet, a long bore at Fossveien, and a long bore at Skallum. At Skallum, a rinsing system for the water used in the tunneling was established, allowing the water to be recycled.
 The tunneling resulted in of soil, most of which was used for the expansion of the Port of Drammen. It was transported away from the tunnel with up to 12 truckloads per hour. The first breakthrough between adjacent construction sections took place on 5 June 2008. On 19 October 2008, there was a ground failure at a landfill where the soil from the tunnel was dumped. This caused a land slip which pressed up soil nearby at Gjønnes (station), Gjønnes Station on the Kolsås Line of the Oslo Metro (that section of the Kolsås Line was largely unused due to unrelated construction at the time); a long section of one platform and track was pressed up , resulting in the other track lying on its side. Because of changes to European Union regulations after planning of the project, three extra emergency staircases had to be installed in late 2009. The final breakthrough in the tunnel occurred on 26 July 2009. The tunneling took place under the groundwater level. To avoid similar problems which occurred during the construction of the Romerike Tunnel, where massive leaks took a year to fix, several test bores were made in the area to measure the groundwater level. The measuring system was set up to communicate any indications of a change immediately & automatically to the on-site geologists, who would be able to act accordingly. The system also automatically pumped water into the affected areas to compensate for any leaks until they could be fixed.
To make the tunnel watertight and frost-resistant, the walls were covered with polyethylene mats. Because they are highly flammable, they were then covered in a layer of Shotcrete#Shotcrete vs. gunite, gunite. Also installed were fire water pipes and ventilation systems to remove smoke. To sound-insulate the tunnel and to avoid vibrations spreading to nearby housing, the entire tunnel was covered in a layer of rock wool. By December 2010, the ballast had been laid, and in January 2011 laying of the tracks and ties started. The work to build the tracks and overhead wires was contracted to Baneservice. The contract for the electro-technical installations was awarded to YIT Building Systems for NOK 120 million. In 2006, the whole section from Lysaker to Sandvika was estimated to cost NOK 2.7 billion.
Freight trains started using the tunnel on 26 August 2011, and passenger trains on 28 August the same year. The official opening took place on 2 September 2011. Along with several other projects west of Oslo, including a new
The tunneling resulted in of soil, most of which was used for the expansion of the Port of Drammen. It was transported away from the tunnel with up to 12 truckloads per hour. The first breakthrough between adjacent construction sections took place on 5 June 2008. On 19 October 2008, there was a ground failure at a landfill where the soil from the tunnel was dumped. This caused a land slip which pressed up soil nearby at Gjønnes (station), Gjønnes Station on the Kolsås Line of the Oslo Metro (that section of the Kolsås Line was largely unused due to unrelated construction at the time); a long section of one platform and track was pressed up , resulting in the other track lying on its side. Because of changes to European Union regulations after planning of the project, three extra emergency staircases had to be installed in late 2009. The final breakthrough in the tunnel occurred on 26 July 2009. The tunneling took place under the groundwater level. To avoid similar problems which occurred during the construction of the Romerike Tunnel, where massive leaks took a year to fix, several test bores were made in the area to measure the groundwater level. The measuring system was set up to communicate any indications of a change immediately & automatically to the on-site geologists, who would be able to act accordingly. The system also automatically pumped water into the affected areas to compensate for any leaks until they could be fixed.
To make the tunnel watertight and frost-resistant, the walls were covered with polyethylene mats. Because they are highly flammable, they were then covered in a layer of Shotcrete#Shotcrete vs. gunite, gunite. Also installed were fire water pipes and ventilation systems to remove smoke. To sound-insulate the tunnel and to avoid vibrations spreading to nearby housing, the entire tunnel was covered in a layer of rock wool. By December 2010, the ballast had been laid, and in January 2011 laying of the tracks and ties started. The work to build the tracks and overhead wires was contracted to Baneservice. The contract for the electro-technical installations was awarded to YIT Building Systems for NOK 120 million. In 2006, the whole section from Lysaker to Sandvika was estimated to cost NOK 2.7 billion.
Freight trains started using the tunnel on 26 August 2011, and passenger trains on 28 August the same year. The official opening took place on 2 September 2011. Along with several other projects west of Oslo, including a new Lysaker Station
Lysaker Station ( no, Lysaker stasjon) is a railway station on the Drammen Line and Asker Line situated at Lysaker in Bærum, Norway. Located from Oslo Central Station, Lysaker is served by a mix of Vy express, regional and Oslo Commuter Rail ...
and Høvik Station, and an upgrade to the Drammen Line between Lysaker and Etterstad, the Asker Line was meant to allow for higher service frequency, higher regularity and faster trains west of Oslo after its completion. The higher capacity was exploited with a new high-frequency schedule, named Route Plan 2012, following delivery of new Stadler FLIRT trains. This also allowed for more trains that stop at all stations on the Drammen Line, for three hourly trains to Vestfold and for six hourly trains stopping at the main stations west of Oslo. The new schedule was implemented partially from the December 2012 timetable change, and completely from December 2014, following the completion of resignalling.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Baerum Tunnel Tunnels in Bærum Railway tunnels in Akershus Tunnels on the Asker Line 2011 establishments in Norway Tunnels completed in 2011