Axillary lymph nodes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are
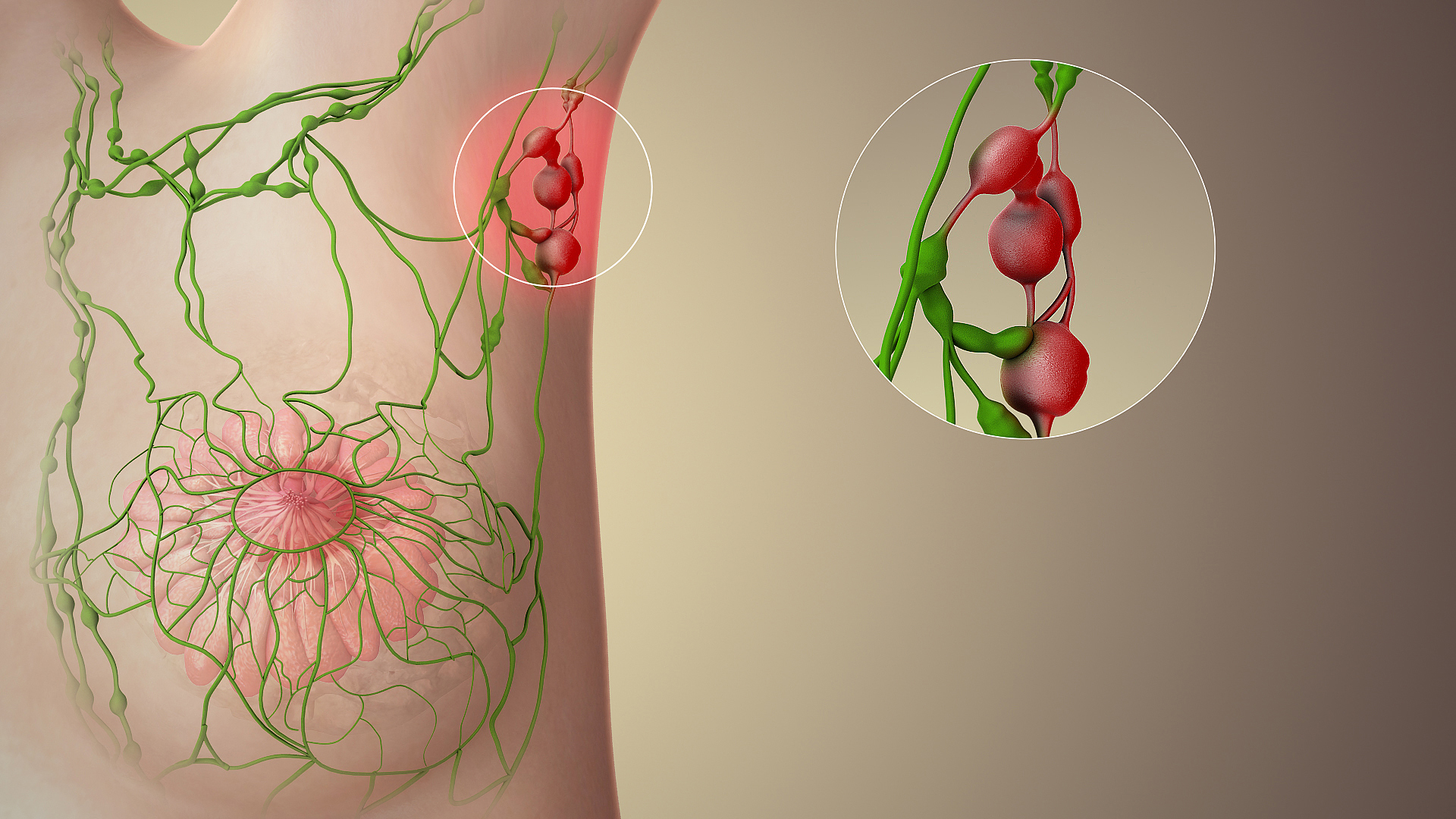 About 75% of
About 75% of
in: Lymph nodes may be normal up to 3 cm if consisting largely of fat. Axillary lymph nodes are included within the standard tangential fields in radiotherapy for breast cancer. In the case of comprehensive nodal irradiation, which includes axillary levels I, II, and III, as well as a supraclavicular lymph node field, there is a risk of damage to brachial plexus. The risk is estimated to be less than 5% as the brachial plexus radiation tolerance according to (Emami 1991) is 60 Gy in standard fractionation (2 Gy per fraction). A common prescribed dose for breast cancer with comprehensive nodal fields would be 50 Gy in 25 fractions with a boost planned to the lumpectomy cavity in the breast or scar on the chest wall if it is a mastectomy. If brachial plexopathy does occur, it is generally a late effect and may not manifest itself until 10 or 15 years later, and usually presents with slight painless muscular atrophy. Malignancies in the gastrointestinal system like
File:Gray606.png, The superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of the upper extremity
Image at breastcancer.org
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Axillary Lymph Nodes Lymphatics of the upper limb
lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vesse ...
s from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
, and metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease.
Structure
The axillary lymph nodes are arranged in six groups: # Anterior (pectoral) group: Lying along the lower border of the pectoralis minor behind thepectoralis major
The pectoralis major () is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor, ...
, these nodes receive lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast and superficial vessels from the anterolateral abdominal wall above the level of the umbilicus.
# Posterior (subscapular) group: Lying in front of the subscapularis muscle, these nodes receive superficial lymph vessels from the back, down as far as the level of the iliac crests.
# Lateral group: Lying along the medial side of the axillary vein, these nodes receive most of the lymph vessels of the upper limb (except those superficial vessels draining the lateral side—see infraclavicular nodes, below).
#Central group
Central Group consists of a variety of diverse investments in various corporations in Thailand and abroad, including investments in retail, property development, brand management, hospitality, and food and beverage sectors, and in digital lifes ...
: Lying in the center of the axilla in the axillary fat, these nodes receive lymph from the above three groups.
# Infraclavicular (deltopectoral) group: These nodes are not strictly axillary nodes because they are located outside the axilla. They lie in the groove between the deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to:
* The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder
* Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral
* A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid
* A leaf shape
* The deltoid tuberosity, a part o ...
and pectoralis major muscles and receive superficial lymph vessels from the lateral side of the hand, forearm, and arm.
# Apical group: Lying at the apex of the axilla at the lateral border of the 1st rib, these nodes receive the efferent lymph vessels from all the other axillary nodes.
The apical nodes drain into the subclavian lymph trunk
The efferent vessels of the subclavicular group unite to form the subclavian trunk, which opens either directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins or into the jugular lymphatic trunk
The jugular trunk is a lymphatic ...
. On the left side, this trunk drains into the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the rig ...
; on the right side, it drains into the right lymphatic duct. Alternatively, the lymph trunks may drain directly into one of the large veins at the root of the neck.
Breast cancer
 About 75% of
About 75% of lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
from the breasts drains into the axillary lymph nodes, making them important in the diagnosis and staging of breast cancer. A doctor will usually refer a patient to a surgeon to have an axillary lymph node dissection to see if the cancer cells have been trapped in the nodes. For clinical stages I and II breast cancer, axillary lymph node dissection should only be performed after first attempting sentinel node biopsy., which cites various primary research studies.
If cancer cells are found in the nodes it increases the risk of metastatic breast cancer. Another method of determining breast cancer spread is to perform an endoscopic axillary sentinel node biopsy. This involves injecting a dye into the breast lump and seeing which node it first spread to (the sentinel node). This node is then removed and examined. If there is no cancer present, it is assumed the cancer has not spread to the other lymph nodes. This procedure is often less invasive and less damaging than the axillary lymph node dissection. The estimated risk of lymphedema following sentinel lymph node procedure is less than 3%. The approximate risk of lymphedema following axillary lymph node dissection is 10-15% and this can slightly increase with the addition of radiotherapy and chemotherapy to as much as 20-25% depending on the extent of dissection, extent of radiotherapy fields, and history of chemotherapy.
On CT scan or MRI, axillary lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In cl ...
can be defined as solid nodes measuring more than 1.5 cm without fatty hilum.Page 559in: Lymph nodes may be normal up to 3 cm if consisting largely of fat. Axillary lymph nodes are included within the standard tangential fields in radiotherapy for breast cancer. In the case of comprehensive nodal irradiation, which includes axillary levels I, II, and III, as well as a supraclavicular lymph node field, there is a risk of damage to brachial plexus. The risk is estimated to be less than 5% as the brachial plexus radiation tolerance according to (Emami 1991) is 60 Gy in standard fractionation (2 Gy per fraction). A common prescribed dose for breast cancer with comprehensive nodal fields would be 50 Gy in 25 fractions with a boost planned to the lumpectomy cavity in the breast or scar on the chest wall if it is a mastectomy. If brachial plexopathy does occur, it is generally a late effect and may not manifest itself until 10 or 15 years later, and usually presents with slight painless muscular atrophy. Malignancies in the gastrointestinal system like
gastric cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lym ...
can metastasize to the left axillary lymph node which is called "Irish’s node".
Additional images
See also
*Lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
* Rotter's lymph nodes Rotter's lymph nodes are small interpectoral lymph nodes located between the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles. They receive lymphatic fluid from the muscles and the mammary gland, and deliver lymphatic fluid to the axillary lymphatic ...
* Supraclavicular lymph nodes
References
External links
Image at breastcancer.org
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Axillary Lymph Nodes Lymphatics of the upper limb