August Bier on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
August Karl Gustav Bier (24 November 1861 – 12 March 1949) was a
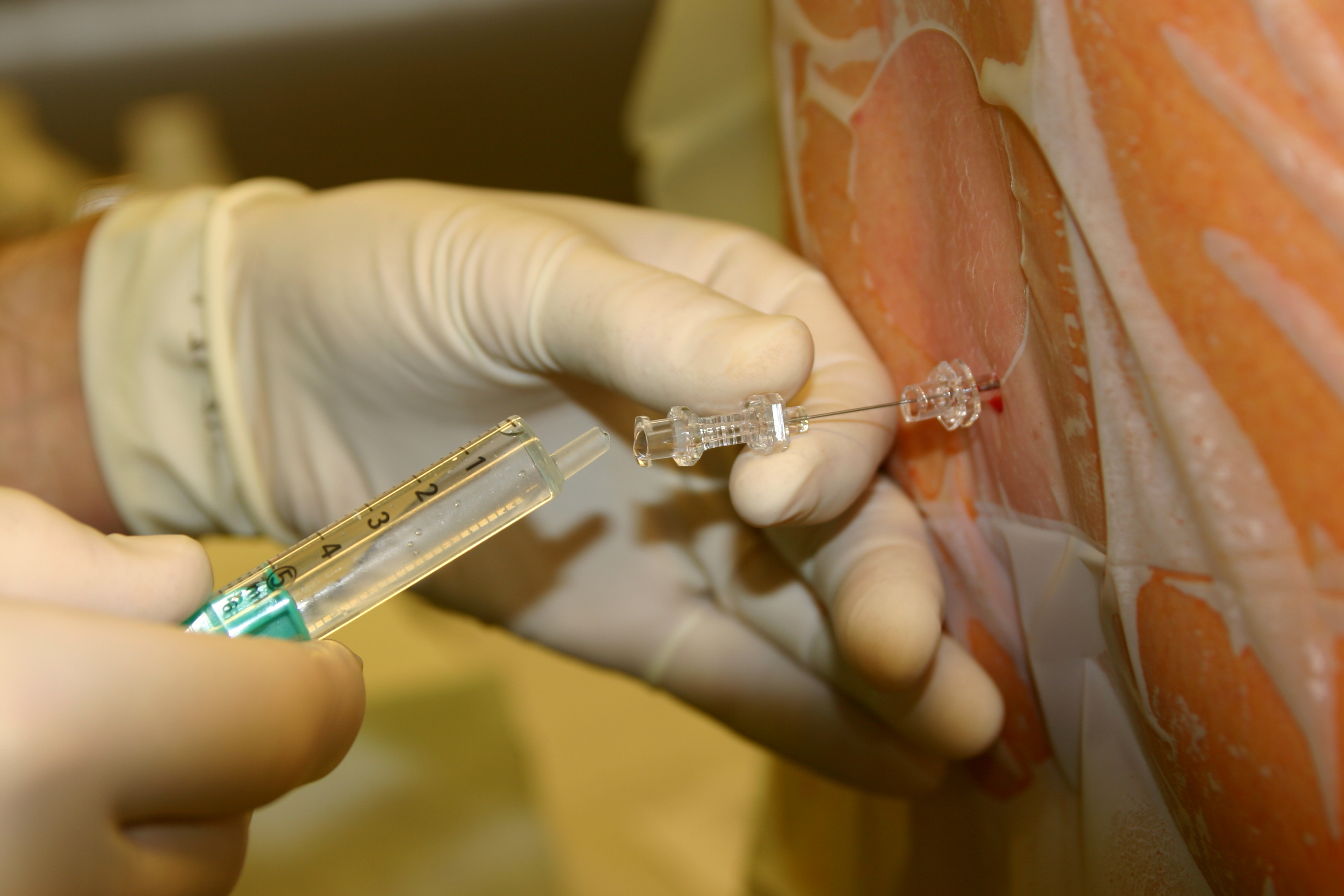 On 16 August 1898, Bier performed the first operation under spinal anesthesia at the Royal Surgical Hospital of the
On 16 August 1898, Bier performed the first operation under spinal anesthesia at the Royal Surgical Hospital of the
 In 1908, Bier pioneered the use of
In 1908, Bier pioneered the use of
"This won't hurt a bit,"
''New Scientist'', vol 173 issue 2330 - 16 February 2002, page 48.
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
. He was the first to perform spinal anesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic or opioid into the subarac ...
and intravenous regional anesthesia
Intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) or Bier's block anesthesia is an anesthetic technique on the body's extremities where a local anesthetic is injected intravenously and isolated from circulation in a target area. The technique usually invol ...
.
Early medical career
Bier began his medical education at the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in 1881, transferred to theLeipzig University
Leipzig University (german: Universität Leipzig), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December ...
in 1882, and transferred again to the University of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian-Albrecht University of Kiel, (german: Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in ...
in 1883. After receiving his medical degree from the University of Kiel in 1886, Bier worked as a general practitioner and ship's surgeon just outside the city of Kiel – which is a major port on the Baltic Sea. Bier began his residency in 1888 at the surgical clinic at the University of Kiel, under the mentorship of Friedrich von Esmarch
Johannes Friedrich August von Esmarch (9 January 1823 – 23 February 1908) was a German surgeon. He developed the Esmarch bandage and founded the ''Deutscher Samariter-Verein'', the predecessor of the '' Deutscher Samariter-Bund''.
Life
...
. After professorships in Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostoc ...
and Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr r ...
, Bier was appointed Chief Surgeon and Geheimrat
''Geheimrat'' was the title of the highest advising officials at the Imperial, royal or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic r ...
Professor of Surgery at the Charité - Universitätsmedizin.
Spinal anesthesia
University of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian-Albrecht University of Kiel, (german: Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in ...
. The patient was scheduled to undergo segmental resection
Segmental resection (or segmentectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland, as a sub-type of a resection, which might involve removing the whole body part. It may also be used to remove a tumor and normal tissue around it ...
of his left ankle, which was severely infected with tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
, but he dreaded the prospect of general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
because he had suffered severe adverse side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
s during multiple previous operations. Therefore, Bier suggested " cocainization" of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spi ...
as an alternative to general anesthesia. Bier injected 15 mg of cocaine intrathecally
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is useful in spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pain m ...
, which was sufficient to allow him to perform the operation. The subject was fully conscious during the operation, but felt no pain. Two hours after the operation, the subject complained of nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, foo ...
, severe headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, and pain in his back and ankle. The vomiting, back and leg pain improved by the following day, but the headache was still present. Bier performed spinal anesthetics on five more subjects for lower extremity surgery, using a similar technique and achieving similar results.
After this series of six subjects, Bier was to receive a spinal anesthetic administered by his assistant, August Hildebrandt. Unfortunately, although Hildebrandt placed the spinal needle correctly, with cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the bra ...
flowing freely from it, the syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
was only then discovered to not fit into the hub of the needle. During the efforts to fit the syringe into the hub of the needle, a great deal of cerebrospinal fluid escaped, most of the cocaine to be injected was lost, and the spinal anesthetic was consequently a complete failure. Later that same evening, Bier performed a cocaine spinal anesthetic on Hildebrandt. After the injection, Hildebrandt was temporarily unable to move or feel any sensation in his legs. The profound anesthesia of his legs was demonstrated using increasingly painful stimuli, including a needle inserted down to the femur, a blow with an iron hammer to the shins, forceful avulsion of pubic hair, and "strong pressure and traction" to the testicles. Later that evening, they celebrated their success with wine and cigars. Like all of Bier's previous experimental subjects, Bier and Hildebrandt both experienced severe post-spinal headaches. Hildebrandt's symptoms lasted about four days, while Bier remained confined to bed for nine days.
Intravenous regional anesthesia
 In 1908, Bier pioneered the use of
In 1908, Bier pioneered the use of intravenous regional anesthesia
Intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) or Bier's block anesthesia is an anesthetic technique on the body's extremities where a local anesthetic is injected intravenously and isolated from circulation in a target area. The technique usually invol ...
, a technique which is commonly referred to as a "Bier block". This technique is frequently used for operations of brief duration upon the hand, wrist, and forearm. It can also be used for operations of brief duration upon the foot, ankle, and leg.
Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
In 1903 he joined the faculty of theUniversity of Bonn
The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn (german: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn) is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the ( en, Rhine U ...
as a full professor, where he taught until 1907. Then he went to Berlin, where he was appointed Geheimrat
''Geheimrat'' was the title of the highest advising officials at the Imperial, royal or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic r ...
Professor
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an Academy, academic rank at university, universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who pr ...
of Surgery and Chief Surgeon at the Charité – Universitätsmedizin. Bier was elected President of the German Surgical Society in 1911. Bier treated many important people, such as Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and List of monarchs of Prussia, King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication on 9 ...
, family members of Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pola ...
, and Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
.
Although he was arguably the most accomplished surgeon of his time, not all of his operations were successful. Hugo Stinnes
Hugo Dieter Stinnes (12 February 1870 – 10 April 1924) was a German industrialist and politician. During the late era of the German Empire and early Weimar Republic, he was considered to be one of the most influential entrepreneurs in Europe.
...
(a Business magnate
A business magnate, also known as a tycoon, is a person who has achieved immense wealth through the ownership of multiple lines of enterprise. The term characteristically refers to a powerful entrepreneur or investor who controls, through perso ...
and politician who was among the wealthiest men in the world at that time) died on 10 April 1924, about a month after Bier performed a cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed i ...
on him. On 24 February 1925, Bier performed an appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acu ...
on Friedrich Ebert
Friedrich Ebert (; 4 February 187128 February 1925) was a German politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) and the first President of Germany (1919–1945), president of Germany from 1919 until his death in office in 1925.
Eber ...
, the first President of Germany
The president of Germany, officially the Federal President of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: link=no, Bundespräsident der Bundesrepublik Deutschland),The official title within Germany is ', with ' being added in international corres ...
, who had signed the Weimar Constitution
The Constitution of the German Reich (german: Die Verfassung des Deutschen Reichs), usually known as the Weimar Constitution (''Weimarer Verfassung''), was the constitution that governed Germany during the Weimar Republic era (1919–1933). The c ...
into law in 1919. Ebert, who had suffered from appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a rup ...
for two weeks before it was diagnosed, died of septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Con ...
four days after the operation. Upon Ebert's death, Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fro ...
was elected as successor.
Bier was Chief Surgeon at the Charité in Berlin until 1928, when Ferdinand Sauerbruch
Ernst Ferdinand Sauerbruch (; 3 July 1875 – 2 July 1951) was a German surgeon. His major work was on the use of negative-pressure chambers for surgery.
Biography
Sauerbruch was born in Barmen (now a district of Wuppertal), Germany. He ...
(18751951) assumed the position. Bier remained at the Charité as Professor Emeritus until his retirement in 1932.
Sports medicine
Bier is also considered to be a pioneer in the field ofsports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
, having played a pivotal role in establishing it as a discipline. Along with Arthur Mallwitz (18801968), Bier organized the first lectures in sports medicine at the University of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative o ...
in 1919. Bier served as director of the '' Deutsche Hochschule für Leibesübungen'' ("German University of Physical Education") in Berlin from its founding in 1920 until 1932. Sauerbruch temporarily headed the academy until 1933, when Karl Gebhardt
Karl Franz Gebhardt (23 November 1897 – 2 June 1948) was a German medical doctor and a war criminal during World War II. He served as Medical Superintendent of the Hohenlychen Sanatorium, Consulting Surgeon of the ''Waffen-SS'', Chief Surgeon in ...
(18971948) assumed the directorship. Gebhardt became the first professor of sports medicine in Berlin. Gebhardt expanded on Bier's methods, adopting an academic approach to sports medicine and awarding degrees.
Awards
In 1910, Bier was awarded theCameron Prize for Therapeutics of the University of Edinburgh
The Cameron Prize for Therapeutics of the University of Edinburgh is awarded by the College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine to a person who has made any highly important and valuable addition to Practical Therapeutics in the previous five ye ...
. The title of Geheimrat
''Geheimrat'' was the title of the highest advising officials at the Imperial, royal or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic r ...
was bestowed upon Bier by German Emperor Wilhelm II. On 24 November 1936, Bier received the Eagle Shield of the German Reich. On 30 January 1938, Bier became one of only nine people to ever receive the German National Prize for Art and Science
Through statutes of 30 January 1937, the German National Order for Art and Science (german: Der Deutscher Nationalorden für Kunst und Wissenschaft) was an award created by Adolf Hitler as a replacement for the Nobel Prize (he had forbidden German ...
, an award created by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
that year as a replacement for the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
, which he had forbidden Germans to accept.
See also
*History of neuraxial anesthesia
The history of neuraxial anesthesia goes back to 1885.
19th century
In 1855, Friedrich Gaedcke (18281890) became the first to chemically isolate cocaine, the most potent alkaloid of the coca plant. Gaedcke named the compound "erythroxyline". ...
References
Further reading
*"This won't hurt a bit,"
''New Scientist'', vol 173 issue 2330 - 16 February 2002, page 48.
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Bier, August 1861 births 1949 deaths People from Bad Arolsen People from the Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont German surgeons University of Bonn faculty University of Greifswald faculty Imperial German Navy personnel Physicians of the Charité