Ashikaga clan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The was a prominent Japanese
2.
3. Ashikaga Yoshiuji
4. Ashikaga Yasuuji
5. Ashikaga Yoriuji
6. Ashikaga Ietoki
7.
8. Ashikaga Takauji
2.
3. Ashikaga Yoshimitsu
4.
5.
6. Ashikaga Yoshinori
7. Ashikaga Yoshikatsu
8. Ashikaga Yoshimasa
9. Ashikaga Yoshihisa
10. Ashikaga Yoshitane
11. Ashikaga Yoshizumi
12. Ashikaga Yoshiharu
13. Ashikaga Yoshiteru
14. Ashikaga Yoshihide
15 Ashikaga Yoshiaki
''Japan encyclopedia.''
Cambridge:
OCLC 58053128
Minamoto clan
samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They ...
clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
which established the Muromachi shogunate and ruled Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
from roughly 1333 to 1573.
The Ashikaga were descended from a branch of the Minamoto clan, deriving originally from the town of Ashikaga in Shimotsuke Province (modern-day Tochigi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,943,886 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 6,408 km2 (2,474 sq mi). Tochigi Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to th ...
).
For about a century the clan was divided in two rival branches, the Kantō Ashikaga, who ruled from Kamakura, and the Kyōto Ashikaga, rulers of Japan. The rivalry ended with the defeat of the first in 1439. The clan had many notable branch clans, including the Hosokawa, Imagawa, Hatakeyama (after 1205), Kira , Shiba, and Hachisuka clans. After the head family of the Minamoto clan died out during the early Kamakura period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle b ...
, the Ashikaga came to style themselves as the head of the Minamoto, co-opting the prestige which came with that name.
Another Ashikaga clan, not related by blood, and derived instead from the Fujiwara clan
was a powerful family of imperial regents in Japan, descending from the Nakatomi clan and, as legend held, through them their ancestral god Ame-no-Koyane. The Fujiwara prospered since the ancient times and dominated the imperial court until th ...
, also existed.
History
Emperor Go-Daigo 後醍醐天皇 (1288–1339) destroyed theKamakura shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459.
The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no ...
in 1333. Yet the emperor was unable to control the unrest produced. The emperor's inefficient rule led to one of his greatest generals, Ashikaga Takauji 足利尊氏 (1305–1358), to betray him in 1335. This established the Northern Court
The , also known as the Ashikaga Pretenders or Northern Pretenders, were a set of six pretenders to the throne of Japan during the Nanboku-chō period from 1336 through 1392. The present Imperial House of Japan is descended from the Northern Cou ...
, named after its location in Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the c ...
, which was north of Go-Daigo's encampment. The conflict between Go-Daigo and the Ashikaga clan is known as the Upheaval of the Northern and Southern courts (Nanbokuchō no dōran 南北朝の動乱). In 1392, the Southern Court
The were a set of four emperors (Emperor Go-Daigo and his line) whose claims to sovereignty during the Nanboku-chō period spanning from 1336 through 1392 were usurped by the Northern Court. This period ended with the Southern Court definitivel ...
surrendered to the third shogun Ashikaga Yoshimitsu 足利義満 (1358–1408).
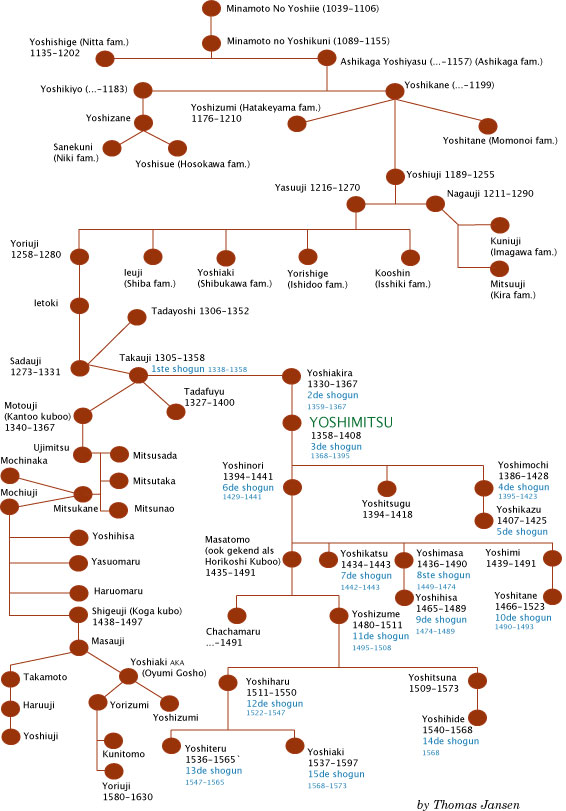
Notable Shōguns
The Ashikaga clan had 15 Shōguns from 1333 to 1573. Some were more powerful or prominent than others. Ashikaga Yoshimitsu (足利義満) was the third shogun of the Ashikaga clan. He made the Ashikaga Shogunate strong and stable. Ashikaga Yoshimitsu was responsible for the defeat of the Southern Court in 1392. Known for his patronage of the arts, he constructed theKinkaku-ji
, officially named , is a Zen Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan. It is one of the most popular buildings in Kyoto, attracting many visitors annually.Bornoff, Nicholas (2000). ''The National Geographic Traveler: Japan''. National Geographic Socie ...
in 1397. Yoshimitsu also expanded foreign relations with Ming China
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
. Yoshimitsu sent an embassy to Ming Dynasty China in 1401, headed by priest Soa and Hakata merchant Koetomi. They brought with them a conciliatory memorial to the emperor, and numerous gifts including horses, fans, gold, screens, paper, swords, armor, and inkstone cases. The mission was successful, and returned to Japan the following year. A Ming envoy returned alongside Soa and Koetomi, and presented Yoshimitsu with an official imperial Chinese calendar, and documents officially recognizing (or investing) him as "King of Japan."
After the death of Yoshimitsu, the Ashikaga Shogunate lost power and influence. In 1429, Ashikaga Yoshinori (足利義教) the sixth shogun adapted Yoshimitsu's policies in order to strengthen the power of the Shogunate. He wanted to increase military power but faced opposition. His 12-year reign saw the restoration of diplomatic ties and trade between Japan and China that had been the fourth Shogun, Yoshimochi's undertaking.
Ashikaga Yoshiaki (足利義昭)was the 15th and last Shogun. He came into power in 1568 with the help of the general Oda Nobunaga (織田信長). After rivalry emerged between the two, Nobunaga defeated Yoshiaki and banished him from Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the c ...
. This effectively ended the rule of the Ashikaga clan in 1573.
Clan heads
1. Ashikaga Yoshiyasu2.
Ashikaga Yoshikane
was a Japanese samurai military commander, feudal lord in the late Heian and early Kamakura period of Japan's history.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Ashikaga Yoshikane" in ; n.b., Louis-Frédéric is pseudonym of Louis-Frédéric Nussbaum, ...
3. Ashikaga Yoshiuji
4. Ashikaga Yasuuji
5. Ashikaga Yoriuji
6. Ashikaga Ietoki
7.
Ashikaga Sadauji Ashikaga (足利) may refer to:
* Ashikaga clan (足利氏 ''Ashikaga-shi''), a Japanese samurai clan descended from the Minamoto clan; and that formed the basis of the eponymous shogunate
** Ashikaga shogunate (足利幕府 ''Ashikaga bakufu''), a ...
8. Ashikaga Takauji
Shōguns
1. Ashikaga Takauji2.
Ashikaga Yoshiakira
was the second '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate who reigned from 1358 to 1367 during the Muromachi period of Japan. Yoshiakira was the son of the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Muromachi shogunate, Ashikaga Takauji. His mother was ...
3. Ashikaga Yoshimitsu
4.
Ashikaga Yoshimochi
was the fourth ''shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate who reigned from 1394 to 1423 during the Muromachi period of Japan. Yoshimochi was the son of the third ''shōgun'' Ashikaga Yoshimitsu.Titsingh, Isaac. (1834).
Succession and rule
In 1394, ...
5.
Ashikaga Yoshikazu
was the fifth '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate who reigned from 1423 to 1425 during the Muromachi period of Japan. Yoshikazu was the son of the fourth '' shōgun'' Ashikaga Yoshimochi.
Yoshimochi ceded power to his son, and Yoshikazu b ...
6. Ashikaga Yoshinori
7. Ashikaga Yoshikatsu
8. Ashikaga Yoshimasa
9. Ashikaga Yoshihisa
10. Ashikaga Yoshitane
11. Ashikaga Yoshizumi
12. Ashikaga Yoshiharu
13. Ashikaga Yoshiteru
14. Ashikaga Yoshihide
15 Ashikaga Yoshiaki
Notable
*Ashikaga Chachamaru Ashikaga (足利) may refer to:
* Ashikaga clan (足利氏 ''Ashikaga-shi''), a Japanese samurai clan descended from the Minamoto clan; and that formed the basis of the eponymous shogunate
** Ashikaga shogunate (足利幕府 ''Ashikaga bakufu''), a ...
*Ashikaga Masatomo
Ashikaga Masatomo ( ja, 足利政知; 1435-1491) was a Japanese samurai, warrior of the Muromachi period and member of the Ashikaga shogunate, Ashikaga family. He was the first ''Horigoe Kubo'' (Governor-general based in Horigoe, Izu Province, so ...
* Ashikaga Mitsukane
* Ashikaga Mochiuji
*Ashikaga Motouji
(1340–1367) was a warrior of the Nanboku-chō period. The fourth son of ''shōgun'' Ashikaga Takauji, he was the first of a dynasty of five ''Kantō kubō'', Kamakura-based representatives in the vital Kamakura-fu of Kyoto's Ashikaga regime ...
* Ashikaga Satouji
* Ashikaga Shigeuji
* Ashikaga Tadafuyu
*Ashikaga Tadayoshi
"Ashikaga Tadayoshi" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 624. was a general of the Northern and Southern Courts period (1337–92) of Japanese history and a close associat ...
*Ashikaga Tadatsuna Ashikaga (足利) may refer to:
* Ashikaga clan (足利氏 ''Ashikaga-shi''), a Japanese samurai clan descended from the Minamoto clan; and that formed the basis of the eponymous shogunate
** Ashikaga shogunate (足利幕府 ''Ashikaga bakufu''), a ...
* Ashikaga Ujimitsu
* Ashikaga YoshimiNussbaum, "Ashikaga Yoshimi" at
Family tree

See also
*Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by ...
* Kantō Kubō
*Ashikaga clan (Fujiwara)
The was a branch family of the Japanese Fujiwara clan of court nobles, more specifically Fujiwara no Hidesato of the Northern Fujiwara branch. The clan was a powerful force in the Kantō region during the Heian period (794-1185). It bore ...
Notes
References
* Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005)''Japan encyclopedia.''
Cambridge:
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
. {{ISBN, 978-0-674-01753-5OCLC 58053128
Minamoto clan