Aruba (Netherlands) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the
 There has been a human presence on Aruba from as early as circa 2000 BC. The first identifiable group are the
There has been a human presence on Aruba from as early as circa 2000 BC. The first identifiable group are the
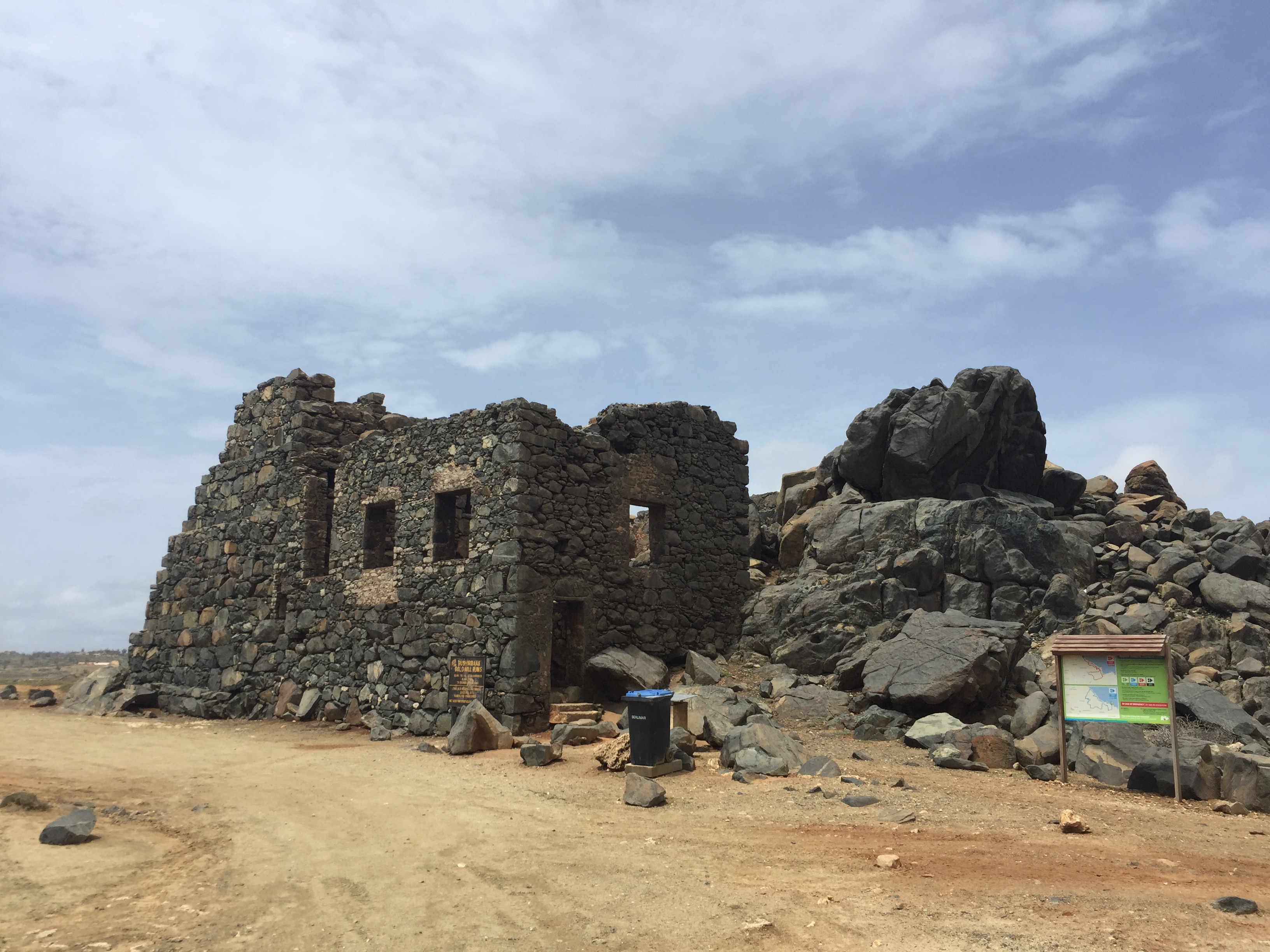 The Netherlands seized Aruba from Spain in 1636 in the course of the
The Netherlands seized Aruba from Spain in 1636 in the course of the
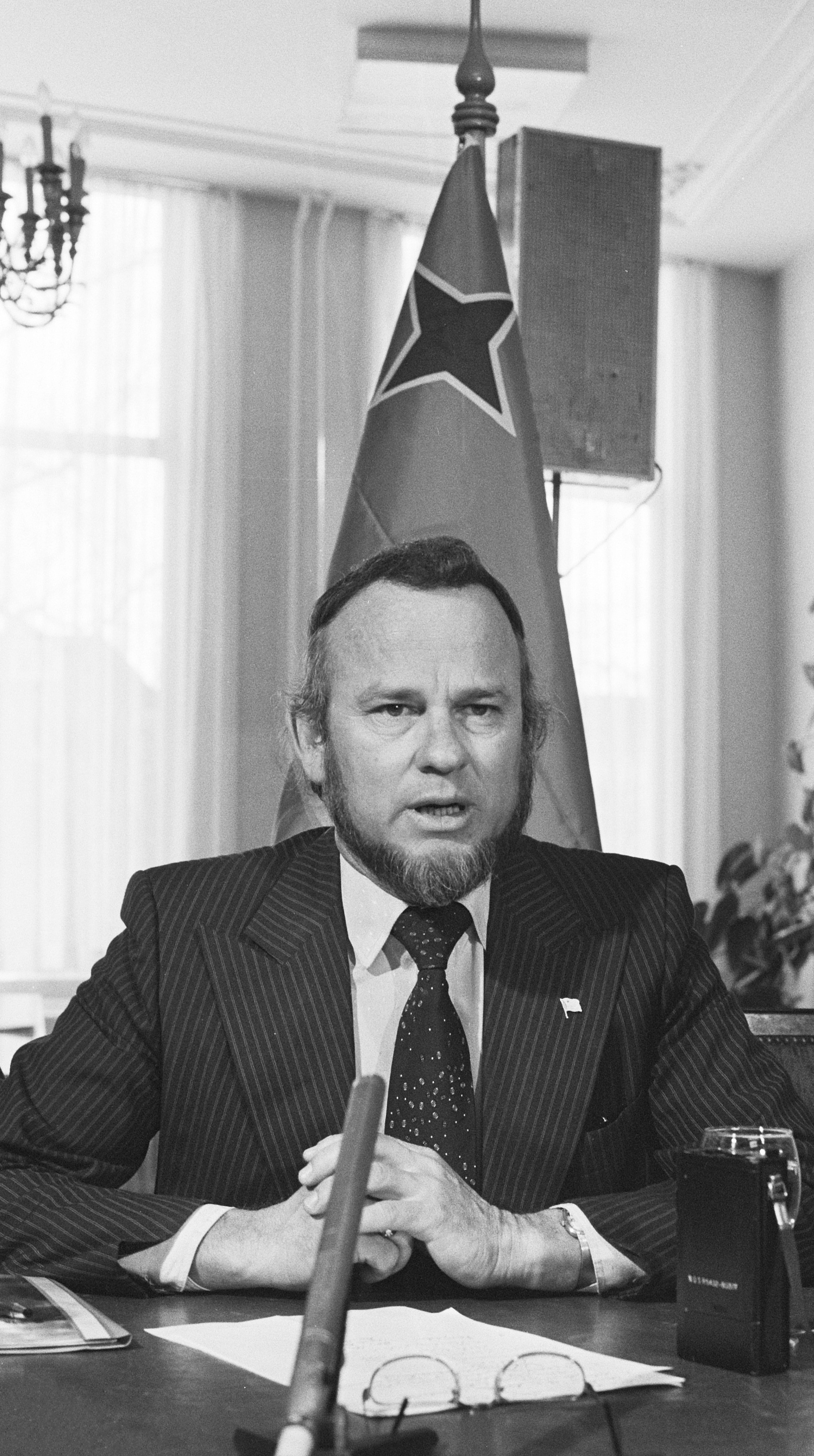 In 1972, at a conference in Suriname,
In 1972, at a conference in Suriname,
 Aruba is a generally flat, riverless island in the
Aruba is a generally flat, riverless island in the
 The districts are as follows:
*
The districts are as follows:
*
 The flora of Aruba differs from the typical tropical island vegetation. Xeric scrublands are common, with various forms of cacti, thorny shrubs, and evergreens. Aloe vera is also present, its economic importance earning it a place on the coat of arms of Aruba.
Cacti like ''
The flora of Aruba differs from the typical tropical island vegetation. Xeric scrublands are common, with various forms of cacti, thorny shrubs, and evergreens. Aloe vera is also present, its economic importance earning it a place on the coat of arms of Aruba.
Cacti like ''
 In terms of country of birth, the population is estimated to be 66% Aruban, 9.1% Colombian, 4.3%
In terms of country of birth, the population is estimated to be 66% Aruban, 9.1% Colombian, 4.3%
 Aruba is cartographically split into eight for censuses; these regions have no administrative function; some allude to parishes which include a few charitable community facilities:
Aruba is cartographically split into eight for censuses; these regions have no administrative function; some allude to parishes which include a few charitable community facilities:
 Along with the
Along with the
 All forces are stationed at Marines base in Savaneta. Furthermore, in 1999, the
All forces are stationed at Marines base in Savaneta. Furthermore, in 1999, the
 The island's economy is dominated by four main industries: tourism, aloe export,
The island's economy is dominated by four main industries: tourism, aloe export, 
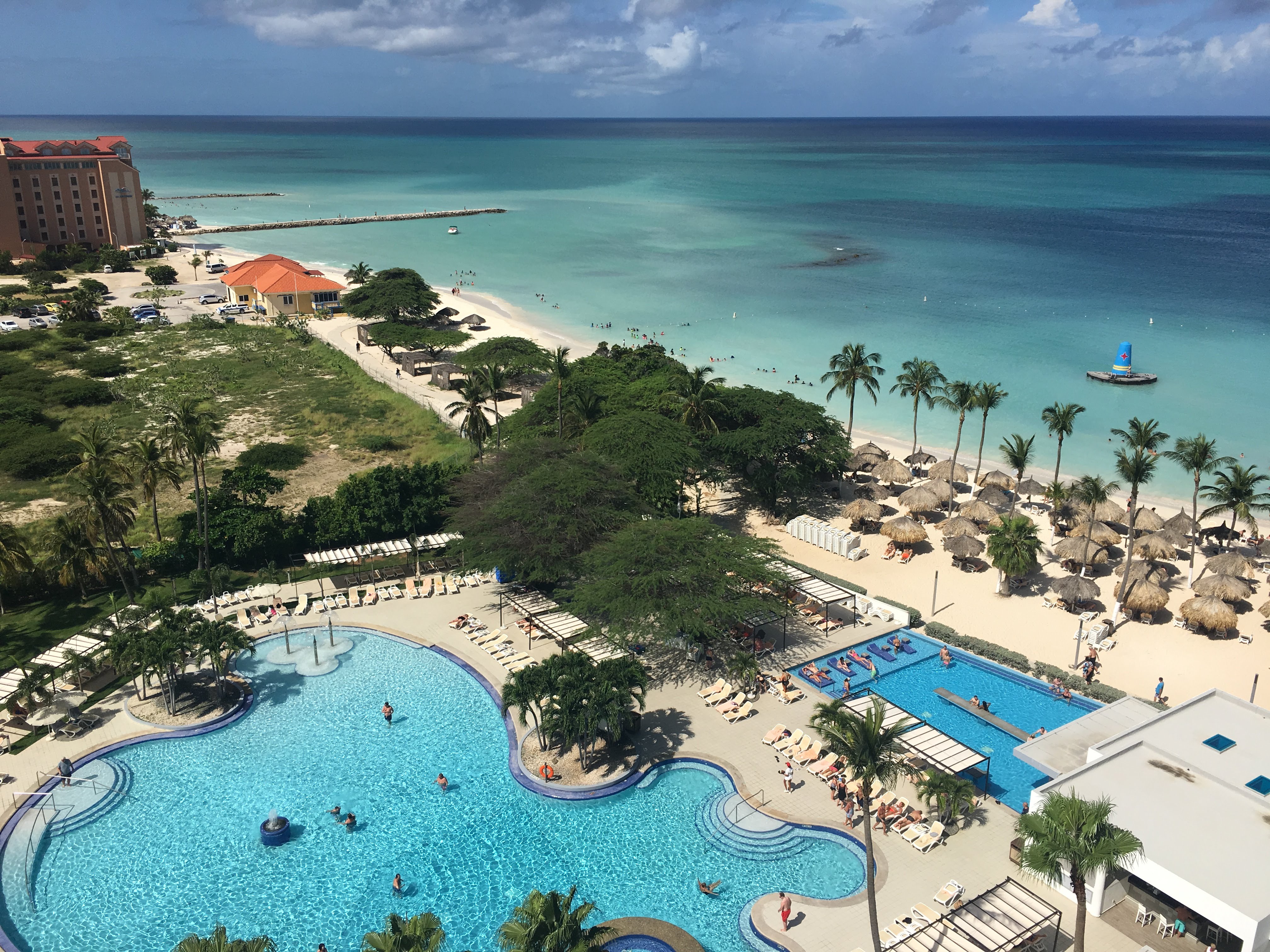 Aruba has a large and well-developed tourism industry, receiving 1,082,000 tourists who stayed overnight in its territory in 2018. About of the Aruban
Aruba has a large and well-developed tourism industry, receiving 1,082,000 tourists who stayed overnight in its territory in 2018. About of the Aruban
 Aruba has a varied culture. According to the ''Bureau Burgelijke Stand en Bevolkingsregister'' (BBSB), in 2005 there were ninety-two different nationalities living on the island. Dutch influence can still be seen, as in the celebration of "
Aruba has a varied culture. According to the ''Bureau Burgelijke Stand en Bevolkingsregister'' (BBSB), in 2005 there were ninety-two different nationalities living on the island. Dutch influence can still be seen, as in the celebration of "

 Aruba's
Aruba's
 ;Beaches
;Beaches
Official website of the government of Aruba
{{Authority control Island countries 10th-century establishments in Aruba 1499 establishments in the Spanish Empire 1636 disestablishments in the Spanish Empire 1636 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1799 disestablishments in the Dutch Empire 1799 establishments in the British Empire 1802 disestablishments in the British Empire 1802 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1804 disestablishments in the Dutch Empire 1804 establishments in the British Empire 1816 disestablishments in the British Empire 1816 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1986 disestablishments in the Netherlands Antilles 1986 establishments in Aruba Caribbean countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands Dutch-speaking countries and territories Former Dutch colonies Former Spanish colonies Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Islands of the Netherlands Antilles Populated places established in the 10th century Small Island Developing States Special territories of the European Union States and territories established in 1986 Dependent territories in the Caribbean
Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, about north of the Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
peninsula of Paraguaná and northwest of Curaçao. It measures long from its northwestern to its southeastern end and across at its widest point. Together with Bonaire and Curaçao, Aruba forms a group referred to as the ABC islands. Collectively, these and the other three Dutch substantial islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
, of which Aruba has about one-third of the population. In 1986, it became a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, and acquired the formal name the Country of Aruba.
Aruba is one of the four countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands, along with the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the nort ...
; the citizens of these countries are all Dutch nationals. Aruba has no administrative subdivisions, but, for census purposes, is divided into eight regions. Its capital is Oranjestad.
Unlike much of the Caribbean region, Aruba has a dry climate and an arid, cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Gree ...
-strewn landscape. The climate has helped tourism, because visitors to the island can expect clear, sunny skies all year. Its area is and it is quite densely populated, with 108,166 inhabitants as at the 2020 Census.
Etymology
The name Aruba most likely came from theCaquetio
Caquetio, Caiquetio, or Caiquetia are natives of northwestern Venezuela, living along the shores of Lake Maracaibo at the time of the Spanish conquest. They moved inland to avoid enslavement by the Spaniards, while their numbers were drastically ...
''Oruba'' which means "Well situated island", seeing as it was the Caquetio
Caquetio, Caiquetio, or Caiquetia are natives of northwestern Venezuela, living along the shores of Lake Maracaibo at the time of the Spanish conquest. They moved inland to avoid enslavement by the Spaniards, while their numbers were drastically ...
who were present on the island when it was first set foot upon by Alonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda (; c. 1466 – c. 1515) was a Spanish explorer, governor and conquistador. He travelled through modern-day Guyana, Venezuela, Trinidad, Tobago, Curaçao, Aruba and Colombia. He navigated with Amerigo Vespucci who is famou ...
. Between 1529 and the signing of the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
, the name "Isla de Oruba" was used for the island by the Spanish. After the signing, the island was ceded to the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and its name was changed to Aruba.
There were many different names for Aruba used by other Amerindian groups, all of which could have contributed to the present-day name Aruba. Another Caquetio name for the island was ''Oibubia'' which means "Guided island". The Taino name for the island was ''Arubeira''. The Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated langua ...
also had two names for the island ''Ora Oubao'' which means "Shell island" and ''Oirubae'' which means "Companion of Curaçao".
A common misconception is that the name Aruba came from the Spanish ''Oro hubo'' which means "There was gold". However the Spanish found no gold on Aruba during the time of their occupation, nicknaming Aruba and the rest of the ABC islands ''Islas Inútiles'', meaning "Useless islands" due to the lack of gold. It was not until much later in 1824 that gold was found on Aruba by Willem Rasmijn, starting the Aruban Gold Rush. Another early Spanish name for Aruba was ''Isla de Brasil'', named as such because of the many Brazilwood trees that grew on the island.
History
Pre-colonial era
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
Caquetío Amerindians who migrated from South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
about 1000 AD. Archaeological evidence suggests continuing links between these native Arubans and Amerindian peoples of mainland South America.
Spanish colonization
The first Europeans to visit Aruba were Amerigo Vespucci andAlonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda (; c. 1466 – c. 1515) was a Spanish explorer, governor and conquistador. He travelled through modern-day Guyana, Venezuela, Trinidad, Tobago, Curaçao, Aruba and Colombia. He navigated with Amerigo Vespucci who is famou ...
in 1499, who claimed the island for Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. Both men described Aruba as an "island of giants", remarking on the comparatively large stature of the native Caquetíos. Vespucci returned to Spain with stocks of cotton and brazilwood from the island and described houses built into the ocean. Vespucci and Ojeda's tales spurred interest in Aruba, and the Spanish began colonising the island. Alonso de Ojeda was appointed the island's first governor in 1508. From 1513 the Spanish began enslaving the Caquetíos, sending many to a life of forced labour in the mines of Hispaniola. The island's low rainfall and arid landscape meant that it was not considered profitable for a slave-based plantation system, so the type of large-scale slavery so common on other Caribbean islands never became established on Aruba.
Early Dutch period
 The Netherlands seized Aruba from Spain in 1636 in the course of the
The Netherlands seized Aruba from Spain in 1636 in the course of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
. Peter Stuyvesant, later appointed to New Amsterdam (New York), was the first Dutch governor. Those Arawak who had survived the depredations of the Spanish were allowed to farm and graze livestock, with the Dutch using the island as a source of meat for their other possessions in the Caribbean. Aruba's proximity to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
resulted in interactions with the cultures of the coastal areas; for example, architectural similarities can be seen between the 19th-century parts of Oranjestad and the nearby Venezuelan city of Coro in Falcón State
)
, anthem =
, image_map = Falcon in Venezuela.svg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Location within Venezuela
, pushpin_map =
, pushpin_map_alt =
, pushpin_mapsiz ...
. Historically, Dutch was not widely spoken on the island outside of colonial administration; its use increased in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.''Dede pikiña ku su bisiña: Papiamentu-Nederlands en de onverwerkt verleden tijd''. van Putte, Florimon., 1999. Zutphen: de Walburg Pers Students on Curaçao, Aruba, and Bonaire were taught predominantly in Spanish until the late 18th century.
During the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
took control of the island, occupying it between 1806 and 1816, before handing it back to the Dutch as per the terms of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 (also known as the Convention of London; nl, Verdrag van Londen) was signed by the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 13 August 1814.
The treaty restored most of the territories in Java that B ...
. Aruba subsequently became part of the Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
along with Bonaire. During the 19th century, an economy based on gold mining
Gold mining is the extraction of gold resources by mining. Historically, mining gold from alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. However, with the expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface, ...
, phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
production and aloe vera plantations developed, but the island remained a relatively poor backwater.
20th and 21st centuries
The first oil refinery in Aruba was built in 1928 byRoyal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
. The facility was built just to the west of the capital city, Oranjestad, and was commonly called the Eagle. Immediately following that, another refinery was built by Lago Oil and Transport Company
Lago Oil & Transport Co. Ltd. had its beginning in 1924 as a shipping company carrying crude oil from Lake Maracaibo to its transshipment facility on the island of Aruba.
History
With the discovery of a vast amount of crude oil under Lake M ...
, in an area now known as San Nicolas on the east end of Aruba. The refineries processed crude oil from the vast Venezuelan oil fields, bringing greater prosperity to the island. The refinery on Aruba grew to become one of the largest in the world.
During World War II, the Netherlands was occupied by Nazi Germany. In 1940, the oil facilities in Aruba came under the administration of the Dutch government-in-exile
The Dutch government-in-exile ( nl, Nederlandse regering in ballingschap), also known as the London Cabinet ( nl, Londens kabinet), was the government in exile of the Netherlands, supervised by Queen Wilhelmina, that fled to London after the Germ ...
in London, causing them to be attacked by the German navy in 1942.
In August 1947, Aruba formulated its first ''Staatsreglement'' (constitution) for Aruba's ''status aparte
''Status aparte'' refers to the special status of Aruba between 1986 and 2010 as a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, separate from the Netherlands Antilles to which it belonged until 1986. With the dissolution of the Net ...
'' as an autonomous state within the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, prompted by the efforts of Henny Eman
Jan Hendrik Albert "Henny" Eman (born 20 March 1948) is an Aruban retired politician. He was the first Prime Minister of Aruba from 1 January 1986 to 9 February 1989 and again from 29 July 1994 to 30 October 2001.
Introduction
Jan Hendrik Albe ...
, a noted Aruban politician. By 1954, the Charter of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands (in Dutch: ''Statuut voor het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden''; in Papiamentu: ''Statuut di Reino Hulandes'') is a legal instrument that sets out the political relationship between the four countries th ...
was established, providing a framework for relations between Aruba and the rest of the Kingdom. That created the Netherlands Antilles, which united all of the Dutch colonies in the Caribbean into one administrative structure. Many Arubans were unhappy with the arrangement, however, as the new polity was perceived as being dominated by Curaçao.
 In 1972, at a conference in Suriname,
In 1972, at a conference in Suriname, Betico Croes
Gilberto François "Betico" Croes (; 25 January 1938 – 26 November 1986) was an Aruban political activist who was a proponent for Aruba's separation from the Netherlands Antilles. This eventually occurred in 1986, but following a car accident ...
, a politician from Aruba, proposed the creation of a Dutch Commonwealth of four states: Aruba, the Netherlands, Suriname, and the Netherlands Antilles, each to have its own nationality. Backed by his newly created party, the Movimiento Electoral di Pueblo
The People's Electoral Movement ( nl, Electorale Volksbeweging, pap, Movimiento Electoral di Pueblo, MEP) is a social democratic political party in Aruba.
following the 2001 general election for the Parliament of Aruba the party won 52.4% o ...
, Croes sought greater autonomy for Aruba, with the long-term goal of independence, adopting the trappings of an independent state in 1976 with the creation of a flag and national anthem. In March 1977, a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
was held with the support of the United Nations. 82% of the participants voted for complete independence from the Netherlands. Tensions mounted as Croes stepped up the pressure on the Dutch government by organising a general strike in 1977. Croes later met with Dutch Prime Minister Joop den Uyl
Johannes Marten den Uijl, better known as Joop den Uyl (; 9 August 1919 – 24 December 1987) was a Dutch politician and economist who served as Prime Minister of the Netherlands from 1973 to 1977. He was a member of the Labour Party (PvdA).
...
, with the two sides agreeing to assign the Institute of Social Studies in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
to prepare a study for independence, entitled ''Aruba en Onafhankelijkheid, achtergronden, modaliteiten, en mogelijkheden; een rapport in eerste aanleg'' (Aruba and independence, backgrounds, modalities, and opportunities; a preliminary report) (1978).
Autonomy
In March 1983, Aruba reached an official agreement within the Kingdom for its independence, to be developed in a series of steps as the Crown granted increasing autonomy. In August 1985, Aruba drafted a constitution that was unanimously approved. On 1 January 1986, afterelections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold Public administration, public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative ...
were held for its first parliament, Aruba seceded from the Netherlands Antilles, officially becoming a country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, with full independence planned for 1996. However, Croes was seriously injured in a traffic accident in 1985, slipping into a coma. He died in 1986, never seeing the enacting of ''status aparte'' for Aruba for which he had worked over many years.
After his death, Croes was proclaimed ''Libertador di Aruba''. Croes' successor, Henny Eman
Jan Hendrik Albert "Henny" Eman (born 20 March 1948) is an Aruban retired politician. He was the first Prime Minister of Aruba from 1 January 1986 to 9 February 1989 and again from 29 July 1994 to 30 October 2001.
Introduction
Jan Hendrik Albe ...
, of the Aruban People's Party (AVP), became the first Prime Minister of Aruba
The Prime Minister of Aruba is de facto head of the Executive branch of government. Together with Aruba's Council of Ministers, they form the executive branch of Aruban government.
List of prime ministers of Aruba
Government of Aruba
< ...
. In 1985, Aruba's oil refinery had closed. It had provided Aruba with 30 percent of its real income and 50 percent of government revenue. The significant blow to the economy led to a push for a dramatic increase in tourism, and that sector has expanded to become the island's largest industry. At a convention in The Hague in 1990, at the request of Aruba's Prime Minister Nelson Oduber
Nelson Orlando Oduber (born 7 February 1947) is an Aruban politician who served as the 2nd Prime Minister of Aruba. Following his defeat in the 2009 Aruban general election, Oduber retired from politics.
Early life
Oduber was born on 7 Februa ...
, the governments of Aruba, the Netherlands, and the Netherlands Antilles postponed indefinitely Aruba's transition to full independence. The article scheduling Aruba's complete independence was rescinded in 1995, although it was decided that the process could be revived after another referendum.
Geography
 Aruba is a generally flat, riverless island in the
Aruba is a generally flat, riverless island in the Leeward Antilles
The Leeward Antilles ( nl, Benedenwindse Eilanden) are a chain of islands in the Caribbean – specifically, the southerly islands of the Lesser Antilles (and, in turn, the Antilles and the West Indies) along the southeastern fringe of the C ...
island arc of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
in the southern part of the Caribbean. It lies west of Curaçao and north of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
's Paraguaná Peninsula
The Paraguaná Peninsula () is a peninsula in Venezuela, situated in the north of Falcón State, and comprises the municipalities of Carirubana, Los Taques and Falcón. The island of Aruba lies to the north. Bonaire and Curaçao are slightly ...
. Aruba has white sandy beaches on the western and southern coasts of the island, relatively sheltered from fierce ocean currents. This is where the bulk of the population live and where most tourist development has occurred. The northern and eastern coasts, lacking this protection, are considerably more battered by the sea and have been left largely untouched. As of 2022, Aruba only has 2.3% of forest-covered land area and only 0.5% of protected natural area.
The hinterland of the island features some rolling hills, such as Hooiberg
Hooiberg is a high volcanic formation on the island of Aruba. It is located almost in the center of the island and can be seen from virtually anywhere on the island.
The Dutch word ''hooiberg'', literally translates into ''haystack'' in English ...
at and Mount Jamanota, the highest on the island at above sea level. Oranjestad, the capital, is located at .
The Natural Bridge
A natural arch, natural bridge, or (less commonly) rock arch is a natural landform where an arch has formed with an opening underneath. Natural arches commonly form where inland cliffs, coastal cliffs, fins or stacks are subject to erosion ...
was a large, naturally formed limestone bridge on the island's north shore. It was a popular tourist destination until its collapse in 2005.
Cities and towns
The island, with a population of about 116,600 people (1 January 2019 estimate) does not have major cities. It is divided into six districts. Most of the island's population resides in or around the two major city-like districts of Oranjestad (the capital) andSan Nicolaas
San Nicolaas ( nl, Sint Nicolaas) is southeast of Oranjestad, and is Aruba's second largest city. it has a population of 15,283, most of whom originate from the British Caribbean and rest of the Caribbean.
History
According to oral tradition, ...
. Oranjestad and San Nicolaas are both divided into two districts for census purposes only.
 The districts are as follows:
*
The districts are as follows:
* Noord
Noord () is a town and region in Aruba (part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands). This town is known for its low rise and high rise hotels, restaurants, beaches, malls, the California Lighthouse, and other places of attraction.
Places of interes ...
* Oranjestad (East and West)
* Paradera
Paradera is a small town and Census Region near the northeast end of the island of Aruba. The census region Paradera encompasses the town of Paradera as well as nearby settlements and neighborhoods within Paradera, including Ayo, Bloemond, Piedra ...
* San Nicolaas
San Nicolaas ( nl, Sint Nicolaas) is southeast of Oranjestad, and is Aruba's second largest city. it has a population of 15,283, most of whom originate from the British Caribbean and rest of the Caribbean.
History
According to oral tradition, ...
(North and South)
* Santa Cruz
* Savaneta
Savaneta is a town and region in southeastern Aruba. Until 1797, it was the island's capital city. It is home to the island's oldest surviving home, a 150-year-old ''cas di torto'', or mud hut. The Savaneta region has an estimated area of 27.76 s ...
Fauna
The isolation of Aruba from the mainland of South America has fostered theevolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of multiple endemic animals. The island provides a habitat for the endemic Aruban Whiptail and Aruba Rattlesnake, as well as an endemic subspecies of Burrowing Owl
The burrowing owl (''Athene cunicularia''), also called the shoco, is a small, long-legged owl found throughout open landscapes of North and South America. Burrowing owls can be found in grasslands, rangelands, agricultural areas, deserts, or an ...
and Brown-throated Parakeet.

Flora
 The flora of Aruba differs from the typical tropical island vegetation. Xeric scrublands are common, with various forms of cacti, thorny shrubs, and evergreens. Aloe vera is also present, its economic importance earning it a place on the coat of arms of Aruba.
Cacti like ''
The flora of Aruba differs from the typical tropical island vegetation. Xeric scrublands are common, with various forms of cacti, thorny shrubs, and evergreens. Aloe vera is also present, its economic importance earning it a place on the coat of arms of Aruba.
Cacti like ''Melocactus
''Melocactus'' (melon cactus), also known as the Turk's cap cactus, is a genus of cactus with about 30–40 species. They are native to the Caribbean, western Mexico through Central America to northern South America, with some species along the ...
'' and '' Opuntia'' are represented on Aruba by species like ''Opuntia stricta
''Opuntia stricta'' is a species of large cactus that is endemic to the subtropical and tropical coastal areas of the Americas, especially around the Caribbean. Common names include erect prickly pear and nopal estricto (Spanish). The first des ...
''.
Trees like ''Caesalpinia coriaria
''Libidibia coriaria'', synonym ''Caesalpinia coriaria'', is a leguminous tree or large shrub native to the Caribbean, Central America, Mexico, and northern and western South America. Common names include divi-divi, cascalote, guaracabuya, guata ...
'' and '' Vachellia tortuosa'' are drought tolerant.
Climate and natural hazards
By theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, Aruba has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''BSh''). Rainfall is scarce, only per year; in particular, rainy season is drier than it normally is in tropical climates; during the dry season, it almost never rains. Owing to the scarcity of rainfall, the landscape of Aruba is arid. Mean monthly temperature in Oranjestad varies little from to , moderated by constant trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
from the Atlantic Ocean, which come from the north-east. Yearly rainfall barely exceeds in Oranjestad, although it is extremely variable and can range from as little as during strong El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date ...
years (e.g. 1911/1912, 1930/1931, 1982/1983, 1997/1998) to over in La Niña
La Niña (; ) is an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. The name ''La Niña'' originates from Spanish for "the girl", by an ...
years like 1933/1934, 1970/1971 or 1988/1989.
Aruba is south of the typical latitudes of hurricanes but was affected by two in their early stages in late 2020.
Demographics
 In terms of country of birth, the population is estimated to be 66% Aruban, 9.1% Colombian, 4.3%
In terms of country of birth, the population is estimated to be 66% Aruban, 9.1% Colombian, 4.3% Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, 4.1% Dominican, 3.2% Venezuelan, 2.2% Curaçaoan, 1.5% Haitian, 1.2% Surinamese, 1.1% Peruvian
Peruvians ( es, peruanos) are the citizens of Peru. There were Andean and coastal ancient civilizations like Caral, which inhabited what is now Peruvian territory for several millennia before the Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest in th ...
, 1.1% Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, 6.2% other.
In terms of ethnic composition, the population is estimated to be 75% mestizo, 15% black and 10% other ethnicities. Arawak heritage is stronger on Aruba than on most Caribbean islands; although no full-blooded Aboriginals remain, the features of the islanders clearly indicate their genetic Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
heritage. Most of the population is descended from Caquetio Indians, African slaves, and Dutch settlers, and to a lesser extent the various other groups that have settled on the island over time, such as the Spanish, Portuguese, English, French, and Sephardic Jews.
Recently, there has been substantial immigration to the island from neighbouring South American and Caribbean nations, attracted by the higher paid jobs. In 2007, new immigration laws were introduced to help control the growth of the population by restricting foreign worker
Foreign workers or guest workers are people who work in a country other than one of which they are a citizen. Some foreign workers use a guest worker program in a country with more preferred job prospects than in their home country. Guest worke ...
s to a maximum of three years residency on the island. Most notable are those from Venezuela, which lies just to the south.
In 2019, recently arrived Venezuelan refugees were estimated to number around 17,000, accounting for some 15% of the island's population.
Language
Aruba's official languages areDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and Papiamento. While Dutch is the sole language for all administration and legal matters, Papiamento is the predominant language used on Aruba. Papiamento is a Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
- and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
-based creole language
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable natural language that develops from the simplifying and mixing of different languages into a new one within a fairly brief period of time: often, a pidgin evolved into a full-fledged language. ...
, spoken on Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao, that also incorporates words from Dutch and various West African languages. English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Spanish are also spoken, their usage having grown due to tourism. Other common languages spoken, based on the size of their community, are Portuguese, Cantonese, French and German.
In recent years, the government of Aruba has shown an increased interest in acknowledging the cultural and historical importance of Papiamento. Although spoken Papiamento is fairly similar among the several Papiamento-speaking islands, there is a big difference in written Papiamento: The orthography differs per island, with Aruba using etymological spelling, and Curaçao and Bonaire a phonetic spelling.
The book ''Buccaneers of America
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from the Restoration in 1660 until about 1688 ...
'', first published in 1678, states through eyewitness account that the natives on Aruba spoke Spanish already. Spanish became an important language in the 18th century due to the close economic ties with Spanish colonies in what are now Venezuela and Colombia. Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
n TV networks are received on the island, and Aruba also has significant Venezuelan and Colombian communities. Around 13% of the population today speaks Spanish natively. Use of English dates to the early 19th century, when the British took Curaçao, Aruba, and Bonaire. When Dutch rule resumed in 1815, officials already noted wide use of the language.
Aruba has newspapers published in Papiamento: ''Diario'', ''Bon Dia'', ''Solo di Pueblo'', and ''Awe Mainta''; English: ''Aruba Daily'', ''Aruba Today'', and ''The News''; and Dutch: ''Amigoe''. Aruba has 18 radio stations (two AM and 16 FM) and two television stations (Telearuba
Telearuba (Call sign: P4A 13) is a television station that broadcasts on NTSC channel 13 in Aruba with an effective radiated power of 3,456 watts. The station was founded on 29 September 1963 on channel to offer local programming. Instrumental ...
and Channel 22).
Religion
Roman Catholicism is the dominant religion, practised by about 75% of the population. Various Protestant denominations are also present on the island.Regions
 Aruba is cartographically split into eight for censuses; these regions have no administrative function; some allude to parishes which include a few charitable community facilities:
Aruba is cartographically split into eight for censuses; these regions have no administrative function; some allude to parishes which include a few charitable community facilities:
Government
 Along with the
Along with the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the nort ...
, Aruba is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, with internal autonomy. Matters such as foreign affairs and defense are handled by the Netherlands. Aruba's politics take place within a framework of a 21-member Staten (Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
) and an eight-member Cabinet; the Staten's 21 members are elected by direct, popular vote to serve a four-year term. The governor of Aruba
The governor of Aruba is the representative on Aruba of the Dutch monarch. The governor's duties are twofold; he represents and guards the general interests of the Kingdom of the Netherlands and is head of the Aruban government. He is accountab ...
is appointed for a six-year term by the monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power i ...
, and the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
and deputy prime minister are indirectly elected by the Staten for four-year terms.
Aruba was formerly a part of the (now-defunct) Netherlands Antilles; however, it separated from that entity in 1986, gaining its own constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
.
Aruba is designated as a member of the Overseas Countries and Territories (OCT) and is thus officially not a part of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, though Aruba can and does receive support from the European Development Fund.
Politics
The Aruban legal system is based on the Dutch model. In Aruba, legal jurisdiction lies with the ''Gerecht in Eerste Aanleg'' (Court of First Instance
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accorda ...
) on Aruba, the ''Gemeenschappelijk Hof van Justitie van Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, en van Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba'' (Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba The Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba ( nl, Gemeenschappelijk Hof van Justitie van Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten en van Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba) serves the three Caribbean countr ...
) and the ''Hoge Raad der Nederlanden
The Supreme Court of the Netherlands ( nl, Hoge Raad der Nederlanden or simply ''Hoge Raad''), officially the High Council of the Netherlands, is the final court of appeal in civil, criminal and tax cases in the Netherlands, including Curaçao ...
'' (Supreme Court of Justice of the Netherlands). The ''Korps Politie Aruba'' (Aruba Police Force
The Aruba Police Force (Dutch: ''Korps Politie Aruba'' or ''KPA'', Papiamento: ''Cuerpo Policial Aruba'') is the law enforcement agency of Aruba. The force operates under the authority of the Minister of Justice and Social Affairs.
History
In ...
) is the island's law enforcement agency and operates district precincts in Oranjestad, Noord, San Nicolaas, and Santa Cruz, where it is headquartered.
Deficit spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget ...
has been a staple in Aruba's history, and modestly high inflation has been present as well. By 2006, the government's debt had grown to 1.883 billion Aruban florins. In 2006, the Aruban government changed several tax laws to reduce the deficit. Direct tax
Although the actual definitions vary between jurisdictions, in general, a direct tax or income tax is a tax imposed upon a person or property as distinct from a tax imposed upon a transaction, which is described as an indirect tax. There is a di ...
es have been converted to indirect taxes as proposed by the IMF.
Foreign relations
Aruba is one of the overseas countries and territories (OCT) of theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and maintains economic and cultural relations with the European Union and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. Aruba is also a member of several international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
and Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cri ...
.
Military
Defence on Aruba is the responsibility of theKingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
. The Dutch Armed Forces
The Netherlands Armed Forces ( nl, Nederlandse krijgsmacht) are the military services of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The core of the armed forces consists of the four service branches: the Royal Netherlands Navy (), the Royal Netherlands Ar ...
that protect the island include the Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
, Marine Corps
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refl ...
, and the Coastguard
A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to ...
including a platoon sized national guard.
 All forces are stationed at Marines base in Savaneta. Furthermore, in 1999, the
All forces are stationed at Marines base in Savaneta. Furthermore, in 1999, the U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
established a Forward Operating Location (FOL) at the airport.
Education
Aruba's educational system is patterned after the Dutch system of education. The government of Aruba finances the public national education system. Schools are a mixture of public and private, including theInternational School of Aruba
The International School of Aruba (ISA) is a non-profit private school in Aruba. In 2006, it moved to a new campus with a more centralized location.
It was founded in 1929 and was owned by Lago Oil and Transport Co. Ltd. From 1986 on, the scho ...
, the Schakel College and mostly the Colegio Arubano.
There are three medical schools
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
, American University School of Medicine Aruba (AUSOMA), Aureus University School of Medicine
Aureus University School of Medicine (previously named as All Saints University of Medicine) is a private university located in Oranjestad, Aruba. Aureus confers upon its graduates the Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree.
History
Aureus University S ...
and Xavier University School of Medicine, as well as its own national university, the University of Aruba.
Economy
petroleum refining
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefi ...
, and offshore banking. Aruba has one of the highest standards of living in the Caribbean region. The GDP per capita (PPP) for Aruba was estimated to be $37,500 in 2017. Its main trading partners are Colombia, the United States, Venezuela, and the Netherlands.
The agriculture and manufacturing sectors are fairly minimal. Gold mining
Gold mining is the extraction of gold resources by mining. Historically, mining gold from alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. However, with the expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface, ...
was important in the 19th century. Aloe was introduced to Aruba in 1840 but did not become a big export until 1890. Cornelius Eman founded Aruba Aloe Balm, and over time the industry became very important to the economy. At one point, two-thirds of the island was covered in Aloe Vera fields, and Aruba became the largest exporter of aloe in the world. The industry continues today, though on a smaller scale.
Access to biocapacity
The biocapacity or biological capacity of an ecosystem is an estimate of its production of certain biological materials such as natural resources, and its absorption and filtering of other materials such as carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Bio ...
in Aruba is much lower than world average. In 2016, Aruba had 0.57 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016, Aruba used 6.5 global hectares of biocapacity per person - their ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use almost 12 times the biocapacity that Aruba contains. This is the extent of Aruba's biocapacity deficit.
The official exchange rate of the Aruban florin
The florin (; sign: Afl.; code: AWG) or Aruban guilder is the currency of Aruba. It is subdivided into 100 cents. The florin was introduced in 1986, replacing the Netherlands Antillean guilder at par. The Aruban florin is pegged to the United St ...
is pegged to the US dollar at 1.80 florins to US$1. This fact, and the majority of tourists being US, means businesses of hotel and resort districts prefer to bank and trade with the consumer in US dollars.
Aruba is a prosperous country. Unemployment is low (although the government has not published statistics since 2013) and per capita income is one of the highest in the Caribbean (approximately $24,087). At the end of 2018, the labor force participation rate was 56.6% for women.
Until the mid-1980s, Aruba's main industry was oil refining. Then the refinery was shut down and the island's economy shifted towards tourism. Currently, Aruba receives about 1,235,673 (2007) guests per year, of which three-quarters are Americans. Tourism is mainly focused on the beaches and the sea. The refinery has been closed and restarted repeatedly during the last decades. In recent years a letter of intent was signed with CITGO (the US subsidiary of the Venezuelan state oil company PDVSA) to explore the possibility of reopening the refinery again.
Until 2009, the Netherlands granted development aid to Aruba. This aid was mainly for law enforcement, education, administrative development, health care and sustainable economic development. This aid was discontinued at Aruba's request in 2009. Since 2015, however, a form of financial supervision has been reintroduced because Aruba's debt has risen sharply to over 80% of GDP.
Aruba also has two free trade zones ( Barcadera and Bushiri), where import and export and the movement of services are tax-free.

Tourism
 Aruba has a large and well-developed tourism industry, receiving 1,082,000 tourists who stayed overnight in its territory in 2018. About of the Aruban
Aruba has a large and well-developed tourism industry, receiving 1,082,000 tourists who stayed overnight in its territory in 2018. About of the Aruban gross national product
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign ...
is earned through tourism and related activities. Most tourists are from North America, with a market-share of 73.3%, followed by Latin America with 15.2% and Europe with 8.3%. In 2018, there were 40,231 visitors from the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
.
For private aircraft passengers bound for the United States, the United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the U.S. federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the interior or home ministries of other countries. Its stated missions involve anti-terr ...
(DHS), U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) has a full pre-clearance facility since 1 February 2001 when Queen Beatrix Airport expanded. Since 2008, Aruba has been the only island to have this service for private flights.
There are many luxury and lesser luxury hotels, concentrated mainly on the west coast beaches. In Palm Beach are the luxury hotels aimed at American tourists. This area is also called "Highrise-area", because most of the hotels are located in (by Aruban standards) high-rise buildings. Eagle Beach, a short distance from Palm Beach in the direction of Oranjestad, offers hotels on a somewhat smaller and more intimate scale in low-rise buildings, hence the name "lowrise-area".
Oranjestad is the port for the many cruise ships that visit Aruba. The cruise industry is a very important pillar of tourism in Aruba, since during a cruise a large part of the passengers go ashore to visit the island. With 334 cruise calls, Aruba received 815,161 cruise tourists in 2018. The 2017/2018 cruise season brought $102.8 million to Aruba's economy. Oranjestad is also home to several luxury hotels, upscale shopping malls, tourist-oriented shopping streets, and hospitality facilities. The main street, called Caya G.F. (Betico) Croes, has been redesigned in recent years, including new paving, new palm trees and a streetcar line for tourists.
Culture
 Aruba has a varied culture. According to the ''Bureau Burgelijke Stand en Bevolkingsregister'' (BBSB), in 2005 there were ninety-two different nationalities living on the island. Dutch influence can still be seen, as in the celebration of "
Aruba has a varied culture. According to the ''Bureau Burgelijke Stand en Bevolkingsregister'' (BBSB), in 2005 there were ninety-two different nationalities living on the island. Dutch influence can still be seen, as in the celebration of "Sinterklaas
Sinterklaas () or Sint-Nicolaas () is a legendary figure based on Saint Nicholas, patron saint of children. Other Dutch names for the figure include ''De Sint'' ("The Saint"), ''De Goede Sint'' ("The Good Saint") and ''De Goedheiligman'' ("The ...
" on 5 and 6 December and other national holidays like 27 April, when in Aruba and the rest of the Kingdom of the Netherlands the King's birthday or "Dia di Rey" (Koningsdag
''Koningsdag'' () or King's Day is a national holiday in the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Celebrated on 27 April (26 April if the 27th is a Sunday), the date marks the birth of King Willem-Alexander. When the Dutch monarch is female, the holi ...
) is celebrated.
On 18 March, Aruba celebrates its National Day. Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
and New Year's Eve are celebrated with the typical music and songs for gaitas for Christmas and the Dande for New Year, and '' ayaca'', '' ponche crema'', ham, and other typical foods and drinks. On 25 January, Betico Croes
Gilberto François "Betico" Croes (; 25 January 1938 – 26 November 1986) was an Aruban political activist who was a proponent for Aruba's separation from the Netherlands Antilles. This eventually occurred in 1986, but following a car accident ...
' birthday is celebrated. Dia di San Juan is celebrated on 24 June. Besides Christmas, the religious holy days of the Feast of the Ascension
The Solemnity of the Ascension of Jesus Christ, also called Ascension Day, Ascension Thursday, or sometimes Holy Thursday, commemorates the Christian belief of the bodily Ascension of Jesus into heaven. It is one of the ecumenical (i.e., shared by ...
and Good Friday are also holidays on the island.
The festival of Carnaval is also an important one in Aruba, as it is in many Caribbean and Latin American countries. Its celebration in Aruba started in the 1950s, influenced by the inhabitants from Venezuela and the nearby islands (Curaçao, St. Vincent, Trinidad, Barbados, St. Maarten, and Anguilla) who came to work for the oil refinery. Over the years, the Carnival Celebration has changed and now starts from the beginning of January until the Tuesday before Ash Wednesday, with a large parade on the last Sunday of the festivities (the Sunday before Ash Wednesday).
Tourism from the United States has recently increased the visibility of American culture on the island, with such celebrations as Halloween in October and Thanksgiving Day in November.
Architecture
From the beginning of the colonization of theNetherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
until the beginning of the 20th century, the architecture in the most inhabited areas of Aruba was influenced by the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
colonial style and also some Spanish elements from the Catholic missionaries
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, p ...
present in Aruba who later settled in Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
as well. After the boom of the oil industry and the tourist sector in the 20th century the architectural style of the island incorporated a more American and international influence. In addition, elements of the Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
style can still be seen in several buildings in San Nicolas. Therefore, it can be said that the island's architecture is a mixture of Spanish, Dutch, American and Caribbean influences.
Infrastructure
Queen Beatrix International Airport
Queen Beatrix International Airport ( nl, Internationale luchthaven Koningin Beatrix; pap, Aeropuerto Internacional Reina Beatrix), colloquially known as Aruba Airport , is an international airport located in Oranjestad, Aruba. It has flight s ...
is near Oranjestad.
Aruba has four ports: Barcadera, the main cargo port, Paardenbaai
Paardenbaai (English: ''Bay of Horses'') or Port of Oranjestad is the main seaport for passengers in Aruba. It is located in Oranjestad and has existed since 1796.
History
In 1796, Fort Zoutman was constructed near Paardenbaai. It was a natural ...
, the cruise ship terminal in Oranjestad/Taratata, Commandeurs Baai (Commander's Bay) in Savaneta
Savaneta is a town and region in southeastern Aruba. Until 1797, it was the island's capital city. It is home to the island's oldest surviving home, a 150-year-old ''cas di torto'', or mud hut. The Savaneta region has an estimated area of 27.76 s ...
, and Sint Nicolaas Baai in San Nicolaas
San Nicolaas ( nl, Sint Nicolaas) is southeast of Oranjestad, and is Aruba's second largest city. it has a population of 15,283, most of whom originate from the British Caribbean and rest of the Caribbean.
History
According to oral tradition, ...
. Paardenbaai
Paardenbaai (English: ''Bay of Horses'') or Port of Oranjestad is the main seaport for passengers in Aruba. It is located in Oranjestad and has existed since 1796.
History
In 1796, Fort Zoutman was constructed near Paardenbaai. It was a natural ...
services all the cruise-ship lines such as Royal Caribbean, Carnival, NCL, Holland America
Holland America Line is an American-owned cruise line, a subsidiary of Carnival Corporation & plc headquartered in Seattle, Washington, United States.
Holland America Line was founded in Rotterdam, Netherlands, and from 1873 to 1989, it operated ...
, MSC Cruises, Costa Cruises, P&O Cruises
P&O Cruises is a British cruise line based at Carnival House in Southampton, England, operated by Carnival UK and owned by Carnival Corporation & plc. It was originally a subsidiary of the shipping company P&O and was founded in 1977. Along ...
and Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
. Nearly one million tourists enter this port per year. Aruba Ports Authority, owned and operated by the Aruban government, runs these seaports.
''Arubus'' is a government-owned bus company. Its buses operate from 3:30 a.m. until 12:30 a.m., 365 days a year. Private minibuses/people movers service zones such as the Hotel Area, San Nicolaas, Santa Cruz and Noord.
A streetcar service runs on rails on the Mainstreet of Oranjestad.
Utilities
Water- en Energiebedrijf Aruba, N.V. (W.E.B.) produces potable water and power. Average daily consumption in Aruba is about 35600 m3/day., and average power generation is 104 MW. Besides production, WEB also takes care of the water distribution on the island. Elektriciteits Maatschappij Aruba, N.V. (N.V. Elmar) is the sole distributor of electricity on the island of Aruba. N.V. Elmar also offers its customers the opportunity to add solar panel or wind turbines. Together with W.E.B. Aruba N.V., both companies share the same parent holding which is Utilities Aruba N.V.Waste Management
Sewage plant: there are 3 around the island; Zeewijk, Parkietenbos and Bubali. The one in Bubali (near the bird sanctuary) is 4 decades old and is processing over 8000 m3/day. Around double its original capacity of 4500 m3/day (due to Aruba's growth). Solid waste landfill: the major one (16 ha) is at Parkietenbos since the 1950. The capacity is between 130 to 150 kilotons per year. Sometimes there are huge spontaneous combustion creating pollution.Communications
There are two telecommunications providers: government-based Setar, and privately ownedDigicel
Digicel is a Jamaican and Caribbean mobile phone network and home entertainment provider operating in 33 markets worldwide.
Digicel has operated in several countries, including Guyana, Fiji, Haiti, Trinidad and Tobago, St. Lucia, Suriname, a ...
. Digicel
Digicel is a Jamaican and Caribbean mobile phone network and home entertainment provider operating in 33 markets worldwide.
Digicel has operated in several countries, including Guyana, Fiji, Haiti, Trinidad and Tobago, St. Lucia, Suriname, a ...
is Setar's competitor in wireless technology using the GSM platform.
Places of interest
Notable people
*Dave Benton
Dave Benton (born 31 January 1951, birth name Efrén Eugene Benita) is a pop musician from Aruba who lives in Estonia. He is one of the winners of the Eurovision Song Contest 2001. At the age of 50 years and 101 days at the time of his victory, ...
, Aruban-Estonian musician
* Alfonso Boekhoudt
Juan Alfonso Boekhoudt (born 27 January 1965) is an Aruban politician serving as the governor of Aruba since 1 January 2017. He previously served as minister plenipotentiary from 14 November 2013 to 17 November 2016.
Life
Boekhoudt was born on Ar ...
, 4th Governor of Aruba
The governor of Aruba is the representative on Aruba of the Dutch monarch. The governor's duties are twofold; he represents and guards the general interests of the Kingdom of the Netherlands and is head of the Aruban government. He is accountab ...
* Xander Bogaerts
Xander Jan Bogaerts (born October 1, 1992; ), nicknamed "the X-Man" and "Bogey" or "Bogie", is an Aruban professional baseball shortstop for the San Diego Padres of Major League Baseball (MLB). He has previously played in MLB for the Boston Re ...
, shortstop in MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
* Betico Croes
Gilberto François "Betico" Croes (; 25 January 1938 – 26 November 1986) was an Aruban political activist who was a proponent for Aruba's separation from the Netherlands Antilles. This eventually occurred in 1986, but following a car accident ...
, political activist
* Denzel Dumfries
Denzel Justus Morris Dumfries (born 18 April 1996) is a Dutch professional footballer who plays as a right-back for club Inter Milan and the Netherlands national team.
Dumfries began his senior career in 2014 at Sparta Rotterdam, helping them ...
, footballer (or soccer player) in Aruba, Netherlands national team and FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
* Nydia Ecury, writer
* Henny Eman
Jan Hendrik Albert "Henny" Eman (born 20 March 1948) is an Aruban retired politician. He was the first Prime Minister of Aruba from 1 January 1986 to 9 February 1989 and again from 29 July 1994 to 30 October 2001.
Introduction
Jan Hendrik Albe ...
, first Prime Minister of Aruba
The Prime Minister of Aruba is de facto head of the Executive branch of government. Together with Aruba's Council of Ministers, they form the executive branch of Aruban government.
List of prime ministers of Aruba
Government of Aruba
< ...
* Mike Eman, 3rd Prime Minister of Aruba
* Bobby Farrell
Roberto Alfonso Farrell (6 October 1949 – 30 December 2010) was an Aruban dancer and singer. He was the male member of the 1970s pop and disco group Boney M.
Biography Birth and early life
Farrell was born and raised on the island of Arub ...
, musician
* Frans Figaroa
Francisco Dominico "Frans" Figaroa (3 September 1927 – 6 October 1993) was an Aruban politician who served as Lieutenant governor of Aruba from 1979 until 1982, figaroa previously served as President of the Parliament of the Netherlands Antilles ...
, Lieutenant Governor of Aruba 1979-1982
* Henry Habibe, poet
* Andrew Holleran, novelist
* Maria Irausquin-Wajcberg, first elected female politician in Aruba
* Olindo Koolman, 2nd Governor of Aruba
* Juan Lampe, musician
* Macuarima, first Aruban Amerindian Chief killed by colonist
* Calvin Maduro, pitcher in MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
* Hedwiges Maduro
Hedwiges Eduard Martinus Maduro (born 13 February 1985) is a Dutch professional football coach and former player who is the assistant coach of Eerste Divisie club Almere City. Mainly a defensive midfielder during his playing career, he could a ...
, footballer (or soccer player) in UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
, La Liga
The Campeonato Nacional de Liga de Primera División, commonly known simply as Primera División in Spain, and as La Liga in English-speaking countries and officially as LaLiga Santander for sponsorship reasons, stylized as LaLiga, is the men' ...
and FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
* Jossy Mansur, editor of the Papiamento language newspaper, '' Diario''
* Diederick Charles Mathew, politician
* John Merryweather (1932–2019), first Minister Plenipotentiary of Aruba
* Nelson Oduber
Nelson Orlando Oduber (born 7 February 1947) is an Aruban politician who served as the 2nd Prime Minister of Aruba. Following his defeat in the 2009 Aruban general election, Oduber retired from politics.
Early life
Oduber was born on 7 Februa ...
, 2nd Prime Minister of Aruba
* Sarah-Quita Offringa, world champion windsurfer
* Olga Orman
Olga Orman (9 November 1943 – 7 March 2021) was a Dutch-Aruban writer, poet and storyteller. She wrote both in Papiamento and Dutch. Orman introduced ''kamishibai'', a Japanese form of storytelling, to the Netherlands and the ABC islands.
Biog ...
, writer and poet
* Sidney Ponson
Sidney Alton Ponson (; born November 2, 1976) is an Aruban former Major League Baseball pitcher. As a player, Ponson stood at tall and weighed . He threw right-handed with a fastball that clocked out at 95 mph. When he made his major league ...
, pitcher in MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
* Fredis Refunjol
Fredis Jose Refunjol (born 19 December 1950) is an Aruban politician and who served as the 3rd governor of Aruba from 2004 to 2016. Originally a teacher, he has served as a government official for the past twenty years, starting as a member of ...
, 3rd Governor of Aruba
* Julia Renfro, newspaper editor and photographer
* Jeannette Richardson-Baars, Director of the Police Academy of Aruba
* Xiomara Ruiz-Maduro, Minister for Finance, Economic Affairs & Culture
* Chadwick Tromp, catcher in MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
* Felipe Tromp
Felipe Benito Tromp (15 October 1917 – 12 August 1995) was the first governor of Aruba after Aruba received a ''status aparte'' within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. He worked as a teacher prior to becoming governor and served as Minister for E ...
, first Governor of Aruba
* Laura Wernet-Paskel, first female political candidate in Aruba
* Evelyn Wever-Croes
Evelyna Christina "Evelyn" Wever-Croes (born 5 December 1966) is an Aruban politician and current Prime Minister of Aruba, serving since November 2017. She is the first woman to hold this office. She is a member of the People's Electoral Movemen ...
, 4th Prime Minister of Aruba, first female Prime Minister
See also
*Central Bank of Aruba
The Central Bank of Aruba ( nl, Centrale Bank van Aruba) is the central bank in Aruba responsible for implementation of monetary policy of the Aruban florin.
History
The Centrale Bank van Aruba (the Bank) started its operations on January 1, 19 ...
* Index of Aruba-related articles
* List of monuments of Aruba
This table shows an overview of the monuments of Aruba.
Gallery of other monuments, category 2
File:Atlo Vista Chapel (4), Noord, ARUBA.jpg
File:Ex Papiamento R ...
* Military of Aruba
Defense on Aruba is the responsibility of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands Military forces that protect Aruba include the Royal Netherlands Navy, the Netherlands Marine Corps and the Netherlands Coastguard. There is also a sma ...
* Outline of Aruba
References
Further reading
*Aymer, Paula L. - ''Uprooted Women: Migrant Domestics in the Caribbean.'' *Brown, Enid - ''Suriname and the Netherlands Antilles: An Annotated English-Language Bibliography.'' *Gerber, Stanford N. - ''The Family in the Caribbean: Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on the Family in the Caribbean, Aruba, 1969.'' *Green, Vera M. - ''Migrants in Aruba: Interethnic Integration.'' *Hartert, Ernst - ''On the Birds of the Islands of Aruba, Curaçao, and Bonaire.'' *Schoenhals, Kai, compiled - ''Netherlands Antilles and Aruba.''External links
Official website of the government of Aruba
{{Authority control Island countries 10th-century establishments in Aruba 1499 establishments in the Spanish Empire 1636 disestablishments in the Spanish Empire 1636 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1799 disestablishments in the Dutch Empire 1799 establishments in the British Empire 1802 disestablishments in the British Empire 1802 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1804 disestablishments in the Dutch Empire 1804 establishments in the British Empire 1816 disestablishments in the British Empire 1816 establishments in the Dutch Empire 1986 disestablishments in the Netherlands Antilles 1986 establishments in Aruba Caribbean countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands Dutch-speaking countries and territories Former Dutch colonies Former Spanish colonies Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Islands of the Netherlands Antilles Populated places established in the 10th century Small Island Developing States Special territories of the European Union States and territories established in 1986 Dependent territories in the Caribbean