Appaloosa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Appaloosa is an American
 The Appaloosa is best known for its distinctive, leopard complex-spotted coat, which is preferred in the breed. Spotting occurs in several overlay patterns on one of several recognized base coat colors. There are three other distinctive, "core" characteristics: mottled skin, striped hooves, and eyes with a white
The Appaloosa is best known for its distinctive, leopard complex-spotted coat, which is preferred in the breed. Spotting occurs in several overlay patterns on one of several recognized base coat colors. There are three other distinctive, "core" characteristics: mottled skin, striped hooves, and eyes with a white
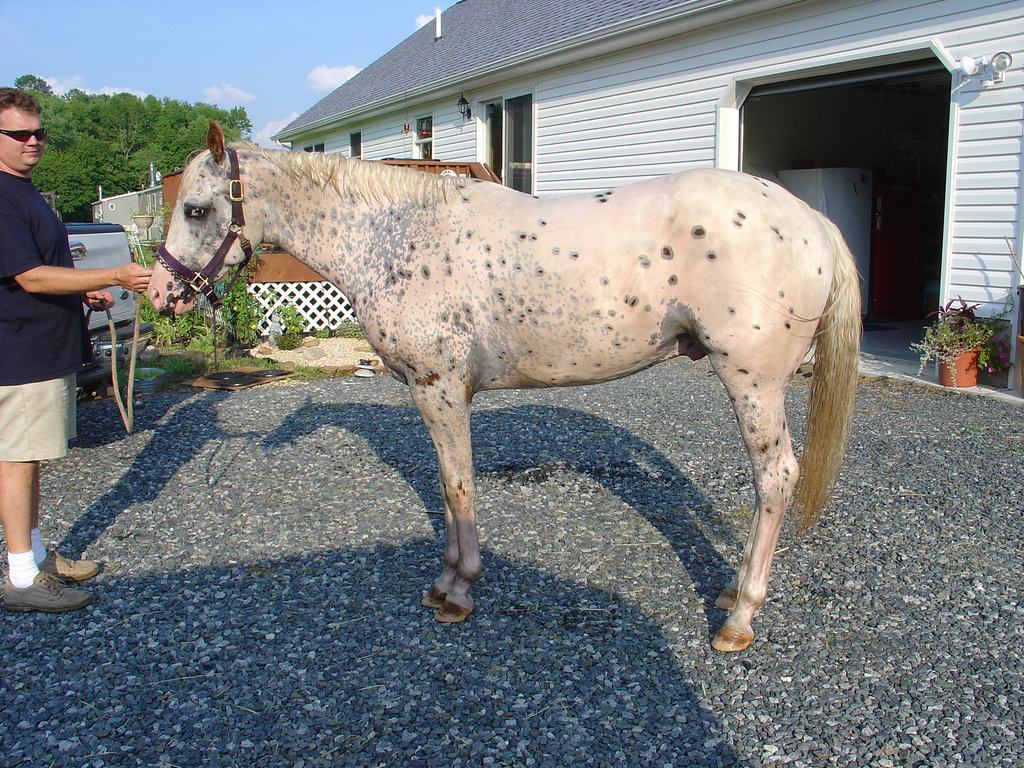 The coat color of an Appaloosa is a combination of a base color with an overlaid spotting pattern. The base colors recognized by the Appaloosa Horse Club include
The coat color of an Appaloosa is a combination of a base color with an overlaid spotting pattern. The base colors recognized by the Appaloosa Horse Club include
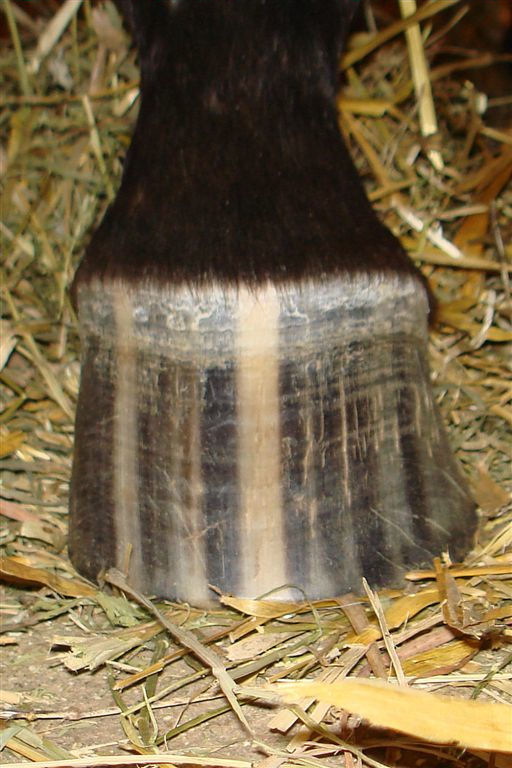 Any horse that shows Appaloosa core characteristics of coat pattern, mottled skin, striped hooves, and a visible white sclera, carries at least one
Any horse that shows Appaloosa core characteristics of coat pattern, mottled skin, striped hooves, and a visible white sclera, carries at least one
 The
The
 Located in
Located in
 During the 1940s and 1950s, when both the Appaloosa Horse Club (ApHC) and the
During the 1940s and 1950s, when both the Appaloosa Horse Club (ApHC) and the
 Appaloosas are used extensively for both Western and English riding. Western competitions include cutting,
Appaloosas are used extensively for both Western and English riding. Western competitions include cutting,
The Appaloosa Horse Club
American Appaloosa Association
Appaloosa Horse Club of Canada
Appaloosa Horse Club of Denmark
Appaloosa Horse Club of Germany
American Appaloosa Horse Club Holland
Appaloosa Horse Association of New Zealand
Appaloosa Horse Club of the United Kingdom
{{subject bar , portal1=Horses, commons=y Horse breeds Horse breeds originating in the United States Horse coat colors Native American culture Horse breeds originating from Indigenous Americans
horse breed
A horse breed is a selectively bred population of domesticated horses, often with pedigrees recorded in a breed registry. However, the term is sometimes used in a broader sense to define landrace animals of a common phenotype located within a l ...
best known for its colorful spotted coat pattern. There is a wide range of body types within the breed, stemming from the influence of multiple breeds of horses throughout its history. Each horse's color pattern is genetically the result of various spotting patterns overlaid on top of one of several recognized base coat colors. The color pattern of the Appaloosa is of interest to those who study equine coat color genetics, as it and several other physical characteristics are linked to the leopard complex mutation (LP). Appaloosas are prone to develop equine recurrent uveitis
Equine recurrent uveitis (ERU) – also known as moon blindness, recurrent iridocyclitis, or periodic ophthalmia – is an acute, nongranulomatous inflammation of the uveal tract of the eye, occurring commonly in horses of all breeds ...
and congenital stationary night blindness; the latter has been linked to the leopard complex.
Artwork depicting prehistoric horses with leopard spotting exists in prehistoric cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s in Europe. Images of domesticated horses with leopard spotting patterns appeared in artwork from Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
and Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
China through the early modern period. In North America, the Nez Perce people of what today is the United States Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
developed the original American breed. Settlers
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
once referred to these spotted horses as the "Palouse horse", possibly after the Palouse River, which ran through the heart of Nez Perce country. Gradually, the name evolved into ''Appaloosa''.
The Nez Perce lost most of their horses after the Nez Perce War in 1877, and the breed fell into decline for several decades. A small number of dedicated breeders preserved the Appaloosa as a distinct breed until the Appaloosa Horse Club The Appaloosa Horse Club, located in Moscow, Idaho, is dedicated to preserving and promoting the Appaloosa breed. The state of Idaho adopted the Appaloosa as its state horse in 1975. More than 630,000 Appaloosas have been registered with the Appal ...
(ApHC) was formed as the breed registry
A breed registry, also known as a herdbook, studbook or register, in animal husbandry and the hobby of animal fancy, is an official list of animals within a specific breed whose parents are known. Animals are usually registered by their breeder ...
in 1938. The modern breed maintains bloodlines tracing to the foundation bloodstock
Foundation bloodstock or foundation stock refers to animals that are the progenitors, or foundation, of a breed or of a given bloodline within such. Many modern breeds can be traced to specific, named foundation animals, but a group of animals ma ...
of the registry; its partially open stud book allows the addition of some Thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thoroughbred breed. Thoroughbreds are ...
, American Quarter Horse
The American Quarter Horse, or Quarter Horse, is an American breed of horse that excels at sprinting short distances. Its name is derived from its ability to outrun other horse breeds in races of a quarter mile or less; some have been clocked at ...
and Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
blood.
Today, the Appaloosa is one of the most popular breeds in the United States; it was named the official state horse of Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
in 1975. It is best known as a stock horse used in a number of western riding disciplines, but is also a versatile breed with representatives seen in many other types of equestrian
The word equestrian is a reference to equestrianism, or horseback riding, derived from Latin ' and ', "horse".
Horseback riding (or Riding in British English)
Examples of this are:
*Equestrian sports
*Equestrian order, one of the upper classes in ...
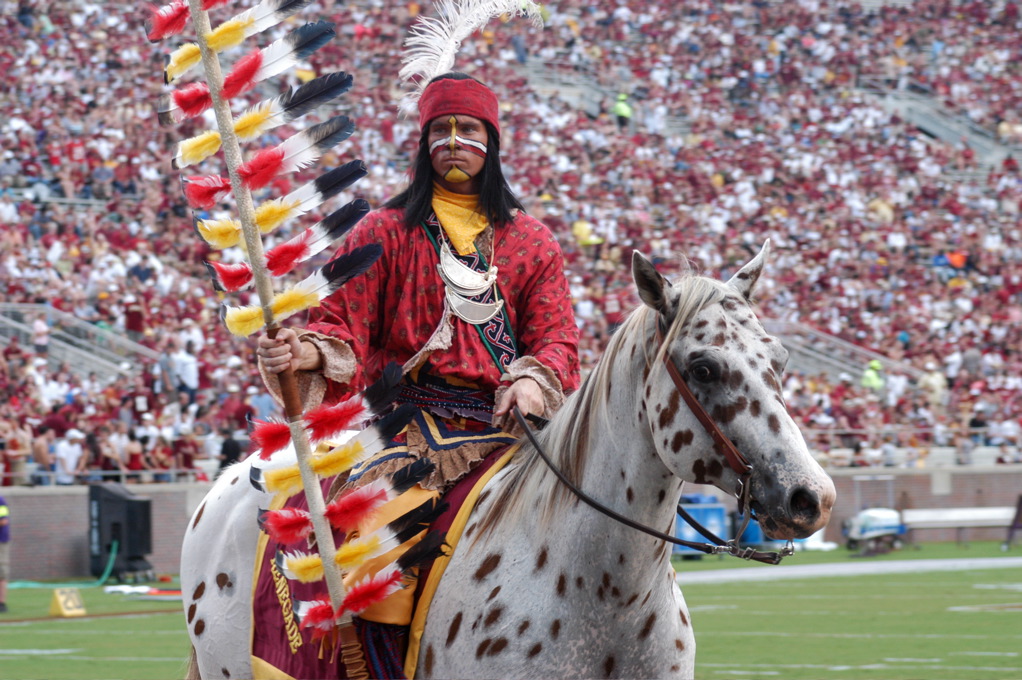
activity. Appaloosas have been used in many movies; an Appaloosa is the mascot for the Florida State Seminoles
The Florida State Seminoles are the athletic teams representing Florida State University located in Tallahassee, Florida. They compete as a member of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I level ( Football Bowl Subdivi ...
. Appaloosa bloodlines have influenced other horse breeds, including the Pony of the Americas, the Nez Perce Horse, and several gaited horse breeds.
Breed characteristics
 The Appaloosa is best known for its distinctive, leopard complex-spotted coat, which is preferred in the breed. Spotting occurs in several overlay patterns on one of several recognized base coat colors. There are three other distinctive, "core" characteristics: mottled skin, striped hooves, and eyes with a white
The Appaloosa is best known for its distinctive, leopard complex-spotted coat, which is preferred in the breed. Spotting occurs in several overlay patterns on one of several recognized base coat colors. There are three other distinctive, "core" characteristics: mottled skin, striped hooves, and eyes with a white sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber. In humans, and so ...
.
Skin mottling is usually seen around the muzzle, eyes, anus, and genitalia. Striped hooves are a common trait, quite noticeable on Appaloosas, but not unique to the breed. The sclera is the part of the eye surrounding the iris; although all horses show white around the eye if the eye is rolled back, to have a readily visible white sclera with the eye in a normal position is a distinctive characteristic seen more often in Appaloosas than in other breeds. Because the occasional individual is born with little or no visible spotting pattern, the ApHC allows "regular" registration of horses with mottled skin plus at least one of the other core characteristics. Horses with two ApHC parents but no "identifiable Appaloosa characteristics" are registered as "non-characteristic," a limited special registration status.
There is a wide range of body types in the Appaloosa, in part because the leopard complex characteristics are its primary identifying factors, and also because several different horse breeds influenced its development. The weight range varies from , and heights from . However, the ApHC does not allow pony
A pony is a type of small horse ('' Equus ferus caballus''). Depending on the context, a pony may be a horse that is under an approximate or exact height at the withers, or a small horse with a specific conformation and temperament. Compared ...
or draft breeding.
The original "old time" or "old type" Appaloosa was a tall, narrow-bodied, rangy horse. The body style reflected a mix that started with the traditional Spanish horses already common on the plains of America before 1700. Then, 18th-century European bloodlines were added, particularly those of the "pied" horses popular in that period and shipped ''en masse'' to the Americas once the color had become unfashionable in Europe. These horses were similar to a tall, slim Thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thoroughbred breed. Thoroughbreds are ...
- Andalusian type of horse popular in Bourbon-era Spain. The original Appaloosa tended to have a convex facial profile that resembled that of the warmblood
Warmbloods are a group of middle-weight horse types and breeds primarily originating in Europe and registered with organizations that are characterized by open studbook policy, studbook selection, and the aim of breeding for equestrian spor ...
- Jennet crosses first developed in the 16th century during the reign of Charles V.
The old-type Appaloosa was later modified by the addition of draft horse blood after the 1877 defeat of the Nez Perce, when U.S. Government policy forced the Native Americans to become farmers and provided them with draft horse mares to breed to existing stallions. The original Appaloosas frequently had a sparse mane and tail
The tail is the section at the rear end of certain kinds of animals’ bodies; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage to the torso. It is the part of the body that corresponds roughly to the sacrum and coccyx in mammal ...
, but that was not a primary characteristic, as many early Appaloosas did have full manes and tails. There is a possible genetic link between the leopard complex and sparse mane and tail growth, although the precise relationship is unknown.
After the formation of the Appaloosa Horse Club in 1938, a more modern type of horse was developed after the addition of American Quarter Horse
The American Quarter Horse, or Quarter Horse, is an American breed of horse that excels at sprinting short distances. Its name is derived from its ability to outrun other horse breeds in races of a quarter mile or less; some have been clocked at ...
and Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
bloodlines. The addition of Quarter Horse lines produced Appaloosas that performed better in sprint racing and in halter competition. Many cutting and reining horses resulted from old-type Appaloosas crossed on Arabian bloodlines, particularly via the Appaloosa foundation stallion
Foundation bloodstock or foundation stock refers to animals that are the progenitors, or foundation, of a breed or of a given bloodline within such. Many modern breeds can be traced to specific, named foundation animals, but a group of animals ma ...
Red Eagle. An infusion of Thoroughbred blood was added during the 1970s to produce horses more suited for racing. Many current breeders also attempt to breed away from the sparse, "rat tail" trait, and therefore modern Appaloosas have fuller manes and tails.
Color and spotting patterns
 The coat color of an Appaloosa is a combination of a base color with an overlaid spotting pattern. The base colors recognized by the Appaloosa Horse Club include
The coat color of an Appaloosa is a combination of a base color with an overlaid spotting pattern. The base colors recognized by the Appaloosa Horse Club include bay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a na ...
, black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
, chestnut
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce.
The unrel ...
, palomino
Palomino is a genetic color in horses, consisting of a gold coat and white mane and tail; the degree of whiteness can vary from bright white to yellow. Genetically, the palomino color is created by a single allele of a dilution gene called t ...
, buckskin, cremello or perlino, roan, gray
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be compose ...
, dun and grulla. Appaloosa markings have several pattern variations. It is this unique group of spotting patterns, collectively called the "leopard complex", that most people associate with the Appaloosa horse. Spots overlay darker skin, and are often surrounded by a "halo", where the skin next to the spot is also dark but the overlying hair coat is white.
It is not always easy to predict a grown Appaloosa's color at birth. Foals of any breed tend to be born with coats that darken when they shed their baby hair. In addition, Appaloosa foals do not always show classic leopard complex characteristics. Patterns sometimes change over the course of the horse's life although some, such as the blanket and leopard patterns, tend to be stable. Horses with the varnish roan and snowflake patterns are especially prone to show very little color pattern at birth, developing more visible spotting as they get older.
The ApHC also recognizes the concept of a "solid" horse, which has a base color "but no contrasting color in the form of an Appaloosa coat pattern". Solid horses can be registered if they have mottled skin and one other leopard complex characteristic.
Base colors are overlain by various spotting patterns, which are variable and often do not fit neatly into a specific category. These patterns are described as follows:
Color genetics
 Any horse that shows Appaloosa core characteristics of coat pattern, mottled skin, striped hooves, and a visible white sclera, carries at least one
Any horse that shows Appaloosa core characteristics of coat pattern, mottled skin, striped hooves, and a visible white sclera, carries at least one allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
of the dominant "leopard complex" (LP) gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. The use of the word "complex" is used to refer to the large group of visible patterns that may occur when LP is present. LP is an autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosom ...
incomplete dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
in the TRPM1 gene located at horse chromosome 1 (ECA 1). All horses with at least one copy of LP show leopard characteristics, and it is hypothesized that LP acts together with other patterning genes (PATN) that have not yet been identified to produce the different coat patterns. Horses that are heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
...
for LP tend to be darker than homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
horses, but this is not consistent.
Three single-nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently ...
s (SNPs) in the TRPM1 gene have been identified as closely associated with the LP mutation, although the mechanism by which the pattern is produced remains unclear. A commercially available DNA based test is likely to be developed in the near future, which breeders can use to determine if LP is present in horses that do not have visible Appaloosa characteristics.
Not every Appaloosa exhibits visible coat spotting, but even apparently solid-colored horses that carry at least one dominant LP allele will exhibit characteristics such as vertically striped hooves, white sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber. In humans, and so ...
of the eye, and mottled skin around the eyes, lips, and genitalia. Appaloosas may also exhibit sabino or pinto
Pinto is a Portuguese, Spanish, Jewish (Sephardic), and Italian surname. It is a high-frequency surname in all Portuguese-speaking countries and is also widely present in Spanish-speaking countries, Italy, India especially in Mangalore, Karnatak ...
type markings, but because pinto genes may cover-up or obscure Appaloosa patterns, pinto breeding is discouraged by the ApHC, which will deny registration to horses with excessive white markings. The genes that create these different patterns can all be present in the same horse. The Appaloosa Project, a genetic study group, has researched the interactions of Appaloosa and pinto genes and how they affect each other.
History
Recent research has suggested that Eurasian prehistoric cave paintings depicting leopard-spotted horses may have accurately reflected aphenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, developmental proc ...
of ancient wild horse. Domesticated horses with leopard complex spotting patterns have been depicted in art dating as far back as Ancient Greece, Ancient Persia, and the Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
in China; later depictions appeared in 11th-century France and 12th-century England. French paintings from the 16th and 17th centuries show horses with spotted coats being used as riding horses, and other records indicate they were also used as coach horses at the court of Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of ...
. In mid-18th-century Europe, there was a great demand for horses with the leopard complex spotting pattern among the nobility and royalty. These horses were used in the schools of horsemanship, for parade use, and other forms of display. Modern horse breeds in Europe today that have leopard complex spotting include the Knabstrupper and the Pinzgau, or Noriker horse.
The Spanish probably obtained spotted horses through trade with southern Austria and Hungary, where the color pattern was known to exist. The Conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, ...
s and Spanish settlers then brought some vividly marked horses to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
when they first arrived in the early 16th century. One horse with snowflake patterning was listed with the 16 horses brought to Mexico by Cortez, and additional spotted horses were mentioned by Spanish writers by 1604. Others arrived in the western hemisphere when spotted horses went out of style in late 18th-century Europe, and were shipped to Mexico, California and Oregon.
Nez Perce people
 The
The Nez Perce people
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames ...
lived in what today is eastern Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, and north central Idaho, where they engaged in agriculture as well as horse breeding
Horse breeding is reproduction in horses, and particularly the human-directed process of selective breeding of animals, particularly purebred horses of a given breed. Planned matings can be used to produce specifically desired characteristics in ...
. The Nez Perce first obtained horses from the Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easte ...
around 1730. They took advantage of the fact that they lived in excellent horse-breeding country, relatively safe from the raids of other tribes, and developed strict breeding selection practices for their animals, establishing breeding herds by 1750. They were one of the few tribes that actively used the practice of gelding
A gelding is a castrated male horse or other equine, such as a pony, donkey or a mule. Castration, as well as the elimination of hormonally driven behavior associated with a stallion, allows a male equine to be calmer and better-behaved, mak ...
inferior male horses and trading away poorer stock to remove unsuitable animals from the gene pool, and thus were notable as horse breeders by the early 19th century.
Early Nez Perce horses were considered to be of high quality. Meriwether Lewis
Meriwether Lewis (August 18, 1774 – October 11, 1809) was an American explorer, soldier, politician, and public administrator, best known for his role as the leader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery, wit ...
of the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gr ...
wrote in his February 15, 1806, journal entry: "Their horses appear to be of an excellent race; they are lofty, eligantly formed, active and durable: in short many of them look like fine English coarsers and would make a figure in any country." Lewis did note spotting patterns, saying, "... some of these horses are pided iedwith large spots of white irregularly scattered and intermixed with the black brown bey or some other dark colour". By "pied", Lewis may have been referring to leopard-spotted patterns seen in the modern Appaloosa, though Lewis also noted that "much the larger portion are of a uniform colour". The Appaloosa Horse Club The Appaloosa Horse Club, located in Moscow, Idaho, is dedicated to preserving and promoting the Appaloosa breed. The state of Idaho adopted the Appaloosa as its state horse in 1975. More than 630,000 Appaloosas have been registered with the Appal ...
estimates that only about ten percent of the horses owned by the Nez Perce at the time were spotted. While the Nez Perce originally had many solid-colored horses and only began to emphasize color in their breeding some time after the visit of Lewis and Clark, by the late 19th century they had many spotted horses. As white settlers moved into traditional Nez Perce lands, a successful trade in horses enriched the Nez Perce, who in 1861 bred horses described as "elegant chargers, fit to mount a prince." At a time when ordinary horses could be purchased for $15, non-Indians who had purchased Appaloosa horses from the Nez Perce turned down offers of as much as $600.
Nez Perce War
Peace with the United States dated back to an alliance arranged by Lewis and Clark, but the encroachment of gold miners in the 1860s and settlers in the 1870s put pressure on the Nez Perce. Although a treaty of 1855 originally allowed them to keep most of their traditional land, another in 1863 reduced the land allotted to them by 90 percent. The Nez Perce who refused to give up their land under the 1863 treaty included a band living in the Wallowa Valley of Oregon, led by Heinmot Tooyalakekt, widely known as Chief Joseph. Tensions rose, and in May 1877, General Oliver Otis Howard called a council and ordered the non-treaty bands to move to the reservation. Chief Joseph considered military resistance futile, and by June 14, 1877, had gathered about 600 people at a site near present-dayGrangeville, Idaho
Grangeville is the largest city in and the county seat of Idaho County, Idaho, United States, in the north central part of the state. Its population was 3,141 at the 2010 census, down from 3,228 in 2000.
Geography
According to the United Sta ...
. But on that day a small group of warriors staged an attack on nearby white settlers, which led to the Nez Perce War. After several small battles in Idaho, more than 800 Nez Perce, mostly non-warriors, took 2000 head of various livestock including horses and fled into Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
, then traveled southeast, dipping into Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
. A small number of Nez Perce fighters, probably fewer than 200, successfully held off larger forces of the U.S. Army in several skirmishes, including the two-day Battle of the Big Hole
The Battle of the Big Hole was fought in Montana Territory, August 9–10, 1877, between the United States Army and the Nez Perce tribe of Native Americans during the Nez Perce War. Both sides suffered heavy casualties. The Nez Perce wit ...
in southwestern Montana. They then moved northeast and attempted to seek refuge with the Crow Nation
The Crow, whose autonym is Apsáalooke (), also spelled Absaroka, are Native Americans living primarily in southern Montana. Today, the Crow people have a federally recognized tribe, the Crow Tribe of Montana, with an Indian reservation loc ...
; rebuffed, they headed for safety in Canada.
Throughout this journey of about the Nez Perce relied heavily on their fast, agile and hardy Appaloosa horses. The journey came to an end when they stopped to rest near the Bears Paw Mountains
The Bears Paw Mountains (Bear Paw Mountains, Bear's Paw Mountains or Bearpaw Mountains) are an insular-montane island range in the Central Montana Alkalic Province in north-central Montana, United States, located approximately 10 miles south of ...
in Montana, from the Canada–US border. Unbeknownst to the Nez Perce, Colonel Nelson A. Miles had led an infantry-cavalry column from Fort Keogh in pursuit. On October 5, 1877, after a five-day fight, Joseph surrendered. The battle—and the war—was over. With most of the war chiefs dead, and the noncombatants cold and starving, Joseph declared that he would "fight no more forever".
Aftermath of the Nez Perce War
When the U.S. 7th Cavalry accepted the surrender of Chief Joseph and the remaining Nez Perce, they immediately took more than 1,000 of the tribe's horses, sold what they could and shot many of the rest. But a significant population of horses had been left behind in the Wallowa valley when the Nez Perce began their retreat, and additional animals escaped or were abandoned along the way. The Nez Perce were ultimately settled on reservation lands in north central Idaho, were allowed few horses, and were required by the Army tocrossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
to draft horse
A draft horse (US), draught horse (UK) or dray horse (from the Old English ''dragan'' meaning "to draw or haul"; compare Dutch ''dragen'' and German ''tragen'' meaning "to carry" and Danish ''drage'' meaning "to draw" or "to fare"), less oft ...
s in an attempt to create farm horses. The Nez Perce tribe never regained its former position as breeders of Appaloosas. In the late 20th century, they began a program to develop a new horse breed, the Nez Perce horse, with the intent to resurrect their horse culture, tradition of selective breeding, and horsemanship.
Although a remnant population of Appaloosa horses remained after 1877, they were virtually forgotten as a distinct breed for almost 60 years. A few quality horses continued to be bred, mostly those captured or purchased by settlers and used as working ranch
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most ofte ...
horses. Others were used in circuses and related forms of entertainment, such as Buffalo Bill's Wild West Show. The horses were originally called "Palouse horses" by settlers, a reference to the Palouse River that ran through the heart of what was once Nez Perce country. Gradually, the name evolved into "Apalouse", and then "Appaloosa". Other early variations of the name included "Appalucy", "Apalousey" and "Appaloosie". In one 1948 book, the breed was called the "Opelousa horse", described as a "hardy tough breed of Indian and Spanish horse" used by backwoodsmen of the late 18th century to transport goods to New Orleans for sale. By the 1950s, "Appaloosa" was regarded as the correct spelling.
Revitalization
The Appaloosa came to the attention of the general public in January 1937 in '' Western Horseman'' magazine when Francis D. Haines, a history professor fromLewiston, Idaho
Lewiston is a city and the county seat of Nez Perce County, Idaho, United States, in the state's north central region. It is the second-largest city in the northern Idaho region, behind Coeur d'Alene, and ninth-largest in the state. Lewiston is ...
, published an article describing the breed's history and urging its preservation. Haines had performed extensive research, traveling with a friend and Appaloosa aficionado named George Hatley, visiting numerous Nez Perce villages, collecting history, and taking photographs. The article generated strong interest in the horse breed, and led to the founding of the Appaloosa Horse Club The Appaloosa Horse Club, located in Moscow, Idaho, is dedicated to preserving and promoting the Appaloosa breed. The state of Idaho adopted the Appaloosa as its state horse in 1975. More than 630,000 Appaloosas have been registered with the Appal ...
(ApHC) by Claude Thompson and a small group of other dedicated breeders in 1938. The registry was originally housed in Moro, Oregon; but in 1947 the organization moved to Moscow, Idaho
Moscow ( ) is a city in North Central Idaho, United States. Located along the state border with Washington, it had a population of 25,435 at the 2020 census. The county seat and largest city of Latah County, Moscow is the home of the Universit ...
, under the leadership of George Hatley. The Appaloosa Museum foundation was formed in 1975 to preserve the history of the Appaloosa horse. The ''Western Horseman'' magazine, and particularly its longtime publisher, Dick Spencer, continued to support and promote the breed through many subsequent articles.
A significant crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
ing influence used to revitalize the Appaloosa was the Arabian horse
The Arabian or Arab horse ( ar, الحصان العربي , DMG ''ḥiṣān ʿarabī'') is a breed of horse that originated on the Arabian Peninsula. With a distinctive head shape and high tail carriage, the Arabian is one of the most easily ...
, as evidenced by early registration lists that show Arabian-Appaloosa crossbreeds as ten of the first fifteen horses registered with the ApHC. For example, one of Claude Thompson's major herd sires was Ferras, an Arabian stallion bred by W.K. Kellogg
William Keith Kellogg (April 7, 1860 – October 6, 1951), generally referred to as W.K. Kellogg, was an American industrialist in food manufacturing, best known as the founder of the Kellogg Company, which produces a wide variety of popular br ...
from horses imported from the Crabbet Arabian Stud of England. Ferras sired Red Eagle, a prominent Appaloosa stallion added to the Appaloosa Hall of Fame in 1988. Later, Thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thoroughbred breed. Thoroughbreds are ...
and Quarter Horse
The American Quarter Horse, or Quarter Horse, is an American breed of horse that excels at sprinting short distances. Its name is derived from its ability to outrun other horse breeds in races of a quarter mile or less; some have been clocked at ...
lines were added, as well as crosses from other breeds, including Morgans and Standardbreds. In 1983 the ApHC reduced the number of allowable outcrosses to three main breeds: the Arabian horse, the American Quarter Horse and the Thoroughbred.
By 1978 the ApHC was the third largest horse registry for light horse breeds. From 1938 to 2007 more than 670,000 Appaloosas were registered by the ApHC. The state of Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
adopted the Appaloosa as its official state horse on March 25, 1975, when Idaho Governor Cecil Andrus signed the enabling legislation. Idaho also offers a custom license plate featuring an Appaloosa, the first state to offer a plate featuring a state horse.
Registration
Moscow, Idaho
Moscow ( ) is a city in North Central Idaho, United States. Located along the state border with Washington, it had a population of 25,435 at the 2020 census. The county seat and largest city of Latah County, Moscow is the home of the Universit ...
, the ApHC is the principal body for the promotion and preservation of the Appaloosa breed and is an international organization. Affiliate Appaloosa organizations exist in many South American and European countries, as well as South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Mexico and Israel. The Appaloosa Horse Club has 33,000 members as of 2010, circulation of the ''Appaloosa Journal'', which is included with most types of membership, was at 32,000 in 2008. The American Appaloosa Association was founded in 1983 by members opposed to the registration of plain-colored horses, as a result of the color rule controversy. Based in Missouri, it has a membership of more than 2,000 as of 2008. Other "Appaloosa" registries have been founded for horses with leopard complex genetics that are not affiliated with the ApHC. These registries tend to have different foundation breeding and histories than the North American Appaloosa. The ApHC is by far the largest Appaloosa horse registry, and it hosts one of the world's largest breed shows.
The Appaloosa is "a breed defined by ApHC bloodline requirements and preferred characteristics, including coat pattern". In other words, the Appaloosa is a distinct breed from limited bloodlines with distinct physical traits and a desired color, referred to as a "color preference". Appaloosas are not strictly a " color breed". All ApHC-registered Appaloosas must be the offspring of two registered Appaloosa parents or a registered Appaloosa and a horse from an approved breed registry, which includes Arabian horses, Quarter Horses, and Thoroughbreds. In all cases, one parent must always be a regular registered Appaloosa. The only exception to the bloodline requirements is in the case of Appaloosa-colored geldings or spayed mares with unknown pedigrees; owners may apply for "hardship registration" for these non-breeding horses. The ApHC does not accept horses with draft, pony, Pinto, or Paint breeding, and requires mature Appaloosas to stand, unshod, at least . If a horse has excessive white markings not associated with the Appaloosa pattern (such as those characteristic of a pinto) it cannot be registered unless it is verified through DNA testing that both parents have ApHC registration.
Certain other characteristics are used to determine if a horse receives "regular" registration: striped hooves, white sclera visible when the eye is in a normal position, and mottled (spotted) skin around the eyes, lips, and genitalia. As the Appaloosa is one of the few horse breeds to exhibit skin mottling, this characteristic "...is a very basic and decisive indication of an Appaloosa." Appaloosas born with visible coat pattern, or mottled skin and at least one other characteristic, are registered with "regular" papers and have full show and breeding privileges. A horse that meets bloodline requirements but is born without the recognized color pattern and characteristics can still be registered with the ApHC as a "non-characteristic" Appaloosa. These solid-colored, "non-characteristic" Appaloosas may not be shown at ApHC events unless the owner verifies the parentage through DNA testing and pays a supplementary fee to enter the horse into the ApHC's Performance Permit Program (PPP). Solid-colored Appaloosas are restricted in breeding.
Color rule controversy
 During the 1940s and 1950s, when both the Appaloosa Horse Club (ApHC) and the
During the 1940s and 1950s, when both the Appaloosa Horse Club (ApHC) and the American Quarter Horse Association
The American Quarter Horse Association (AQHA), based in Amarillo, Texas, is an international organization dedicated to the preservation, improvement and record-keeping of the American Quarter Horse. The association sanctions many competitive eve ...
(AQHA) were in their formative years, minimally marked or roan Appaloosas were sometimes used in Quarter Horse breeding programs. At the same time, it was noted that two solid-colored registered Quarter Horse parents would sometimes produce what Quarter Horse aficionados call a " cropout", a foal with white coloration similar to that of an Appaloosa or Pinto
Pinto is a Portuguese, Spanish, Jewish (Sephardic), and Italian surname. It is a high-frequency surname in all Portuguese-speaking countries and is also widely present in Spanish-speaking countries, Italy, India especially in Mangalore, Karnatak ...
. For a considerable time, until DNA testing could verify parentage, the AQHA refused to register such horses. The ApHC did accept cropout horses that exhibited proper Appaloosa traits, while cropout pintos became the core of the American Paint Horse Association. Famous Appaloosas who were cropouts included Colida, Joker B, Bright Eyes Brother and Wapiti.
In the late 1970s, the color controversy went in the opposite direction within the Appaloosa registry. The ApHC's decision in 1982 to allow solid-colored or "non-characteristic" Appaloosas to be registered resulted in substantial debate within the Appaloosa breeding community. Until then, a foal of Appaloosa parents that had insufficient color was often denied registration, although non-characteristic Appaloosas were allowed into the registry. But breeder experience had shown that some solid Appaloosas could throw a spotted foal in a subsequent generation, at least when bred to a spotted Appaloosa. In addition, many horses with a solid coat exhibited secondary characteristics such as skin mottling, the white sclera, and striped hooves. The controversy stirred by the ApHC's decision was intense. In 1983 a number of Appaloosa breeders opposed to the registration of solid-colored horses formed the American Appaloosa Association, a breakaway organization.
Uses
 Appaloosas are used extensively for both Western and English riding. Western competitions include cutting,
Appaloosas are used extensively for both Western and English riding. Western competitions include cutting, reining
Reining is a western riding competition for horses where the riders guide the horses through a precise pattern of circles, spins, and stops. All work is done at the lope (a version of the horse gait more commonly known worldwide as the canter), ...
, roping
Team roping also known as heading and heeling is a rodeo event that features a steer (typically a Corriente) and two mounted riders. The first roper is referred to as the "header", the person who ropes the front of the steer, usually around t ...
and O-Mok-See sports such as barrel racing
Barrel racing is a rodeo event in which a horse and rider attempt to run a cloverleaf pattern around preset barrels in the fastest time. In collegiate and professional ranks, it is usually a women's event, though both sexes compete at amateur and ...
(known as the Camas Prairie Stump Race in Appaloosa-only competition) and pole bending (called the Nez Percé Stake Race at breed shows). English disciplines they are used in include eventing
Eventing (also known as three day eventing or horse trials) is an equestrian event where a single horse and rider combine and compete against other competitors across the three disciplines of dressage, cross-country, and show jumping. This ...
, show jumping
Show jumping is a part of a group of English riding equestrian events that also includes dressage, eventing, hunters, and equitation. Jumping classes are commonly seen at horse shows throughout the world, including the Olympics. Sometimes ...
, and fox hunting
Fox hunting is an activity involving the tracking, chase and, if caught, the killing of a fox, traditionally a red fox, by trained foxhounds or other scent hounds. A group of unarmed followers, led by a "master of foxhounds" (or "master of ho ...
. They are common in endurance riding
Endurance riding is an equestrian sport based on controlled long-distance races. It is one of the international competitions recognized by the FEI. There are endurance rides worldwide. Endurance rides can be any distance, though they are rare ...
competitions, as well as in casual trail riding. Appaloosas are also bred for horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic pr ...
, with an active breed racing association promoting the sport. They are generally used for middle-distance racing at distances between and ; an Appaloosa holds the all-breed record for the distance, set in 1989.
Appaloosas are often used in Western movie
The Western is a genre set in the American frontier and commonly associated with folk tales of the Western United States, particularly the Southwestern United States, as well as Northern Mexico and Western Canada. It is commonly referred ...
s and television series. Examples include "Cojo Rojo" in the Marlon Brando
Marlon Brando Jr. (April 3, 1924 – July 1, 2004) was an American actor. Considered one of the most influential actors of the 20th century, he received numerous accolades throughout his career, which spanned six decades, including two Academ ...
film '' The Appaloosa'', "Zip Cochise" ridden by John Wayne
Marion Robert Morrison (May 26, 1907 – June 11, 1979), known professionally as John Wayne and nicknamed The Duke or Duke Wayne, was an American actor who became a popular icon through his starring roles in films made during Hollywood's Go ...
in the 1966 film ''El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king ...
'' and "Cowboy", the mount of Matt Damon
Matthew Paige Damon (; born October 8, 1970) is an American actor, film producer, and screenwriter. Ranked among ''Forbes'' most bankable stars, the films in which he has appeared have collectively earned over $3.88 billion at the North Ameri ...
in ''True Grit
True Grit may refer to:
Fiction
* True Grit (novel), ''True Grit'' (novel), a 1968 novel by Charles Portis
** True Grit (1969 film), ''True Grit'' (1969 film), a film adaptation by Henry Hathaway, starring John Wayne
** True Grit (2010 film), ''Tr ...
''. An Appaloosa horse is part of the controversial mascot team for the Florida State Seminoles, Chief Osceola and Renegade
Osceola and Renegade are the official mascots of the Florida State University Seminoles. Osceola, representing the historical Seminole leader Osceola, and his Appaloosa horse Renegade introduce home football games by riding to midfield with a bur ...
; even though the Seminole people were not directly associated with Appaloosa horses.
Influence
There are several American horse breeds with leopard coloring and Appaloosa ancestry. These include the Pony of the Americas and the Colorado Ranger. Appaloosas arecrossbred
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
with gaited horse breeds in an attempt to create a leopard-spotted ambling
An ambling gait or amble is any of several four-beat intermediate horse gaits, all of which are faster than a walk but usually slower than a canter and always slower than a gallop. Horses that amble are sometimes referred to as " gaited", partic ...
horse. Because such crossbred offspring are not eligible for ApHC registration, their owners have formed breed registries for horses with leopard complex patterns and gaited ability. In 1995 the Nez Perce tribe began a program to develop a new and distinct horse breed, the Nez Perce Horse, based on crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
ing the Appaloosa with the Akhal-Teke breed from Central Asia. Appaloosa stallions have been exported to Denmark, to add new blood to the Knabstrupper breed.
Health issues
Genetically linked vision issues
Two genetically-linked conditions are linked to blindness in Appaloosas, both associated with the Leopard complex color pattern. Appaloosas have an eightfold greater risk of developingEquine Recurrent Uveitis
Equine recurrent uveitis (ERU) – also known as moon blindness, recurrent iridocyclitis, or periodic ophthalmia – is an acute, nongranulomatous inflammation of the uveal tract of the eye, occurring commonly in horses of all breeds ...
(ERU) than all other breeds combined. Up to 25 percent of all horses with ERU may be Appaloosas. Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and in ...
in horses has many causes, including eye trauma, disease, and bacterial, parasitic and viral infections, but ERU is characterized by recurring episodes of uveitis, rather than a single incident. If not treated, ERU can lead to blindness. Eighty percent of all uveitis cases are found in Appaloosas with physical characteristics including roan or light-colored coat patterns, little pigment around the eyelids and sparse hair in the mane and tail denoting the most at-risk individuals. Researchers may have identified a gene region containing an allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
that makes the breed more susceptible to the disease.
Appaloosas that are homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
for the leopard complex (LP) gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
are also at risk for congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB). This form of night blindness
Nyctalopia (; ), also called night-blindness, is a condition making it difficult or impossible to see in relatively low light. It is a symptom of several eye diseases. Night blindness may exist from birth, or be caused by injury or malnutrition ...
has been linked with the leopard complex since the 1970s, and in 2007 a "significant association" between LP and CSNB was identified. CSNB is a disorder that causes an affected animal to lack night vision, although day vision is normal. It is an inherited disorder, present from birth, and does not progress over time. Studies in 2008 and 2010 indicate that both CSNB and leopard complex spotting patterns are linked to TRPM1.
Drug rules
In 2007 the ApHC implemented new drug rules allowing Appaloosas to show with the drugsfurosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mo ...
, known by the trade name of Lasix, and acetazolamide. Furosemide is used to prevent horses who bleed from the nose when subjected to strenuous work from having bleeding episodes when in competition, and is widely used in horse racing. Acetazolamide ("Acet") is used for treating horses with the genetic disease hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP), and prevents affected animals from having seizures. Acet is only allowed for horses that test positive for HYPP and have HYPP status noted on their registration papers. The ApHC recommends that Appaloosas that trace to certain American Quarter Horse
The American Quarter Horse, or Quarter Horse, is an American breed of horse that excels at sprinting short distances. Its name is derived from its ability to outrun other horse breeds in races of a quarter mile or less; some have been clocked at ...
bloodlines be tested for HYPP, and owners have the option to choose to place HYPP testing results on registration papers. Foals of AQHA-registered stallions and mares born on or after January 1, 2007 that carry HYPP will be required to be HYPP tested and have their HYPP status designated on their registration papers.
Both drugs are controversial, in part because they are considered drug maskers and diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
s that can make it difficult to detect the presence of other drugs in the horse's system. On one side, it is argued that the United States Equestrian Federation
The United States Equestrian Federation (USEF or US Equestrian) is the national governing body for most equestrian sports in the United States. It began on January 20, 1917, as the Association of American Horse Shows, later changed to the Amer ...
(USEF), which sponsors show competition for many different horse breeds, and the International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI), which governs international and Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece bet ...
equestrian competition, ban the use of furosemide. On the other side of the controversy, several major stock horse registries that sanction their own shows, including the American Quarter Horse Association
The American Quarter Horse Association (AQHA), based in Amarillo, Texas, is an international organization dedicated to the preservation, improvement and record-keeping of the American Quarter Horse. The association sanctions many competitive eve ...
, American Paint Horse Association, and the Palomino
Palomino is a genetic color in horses, consisting of a gold coat and white mane and tail; the degree of whiteness can vary from bright white to yellow. Genetically, the palomino color is created by a single allele of a dilution gene called t ...
Horse Breeders of America, The PHBA does not allow Lasix within 24 hours of show and only allows Acetazolamide for HYPP horses. allow acetazolamide and furosemide to be used within 24 hours of showing under certain circumstances.
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
The Appaloosa Horse Club
American Appaloosa Association
Appaloosa Horse Club of Canada
Appaloosa Horse Club of Denmark
Appaloosa Horse Club of Germany
American Appaloosa Horse Club Holland
Appaloosa Horse Association of New Zealand
Appaloosa Horse Club of the United Kingdom
{{subject bar , portal1=Horses, commons=y Horse breeds Horse breeds originating in the United States Horse coat colors Native American culture Horse breeds originating from Indigenous Americans