Antalya on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
la, Attalensis
grc, Ἀτταλειώτης , postal_code_type =
, name = , population_density_metro_km2 = 122 , blank_name_sec1 =
Turkish Statistical Institute (Büyükşehir belediyeleri ve bağlı belediyelerin nüfusları) – 2011 The city that is now Antalya was first settled around 200 BC by the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon, which was soon subdued by the Romans. Roman rule saw Antalya thrive, including the construction of several new monuments, such as Hadrian's Gate, and the proliferation of neighboring cities. The city has changed hands several times, including to the



 King Attalus II of Pergamon is looked on as founder of the city in about 150 BC, during the
King Attalus II of Pergamon is looked on as founder of the city in about 150 BC, during the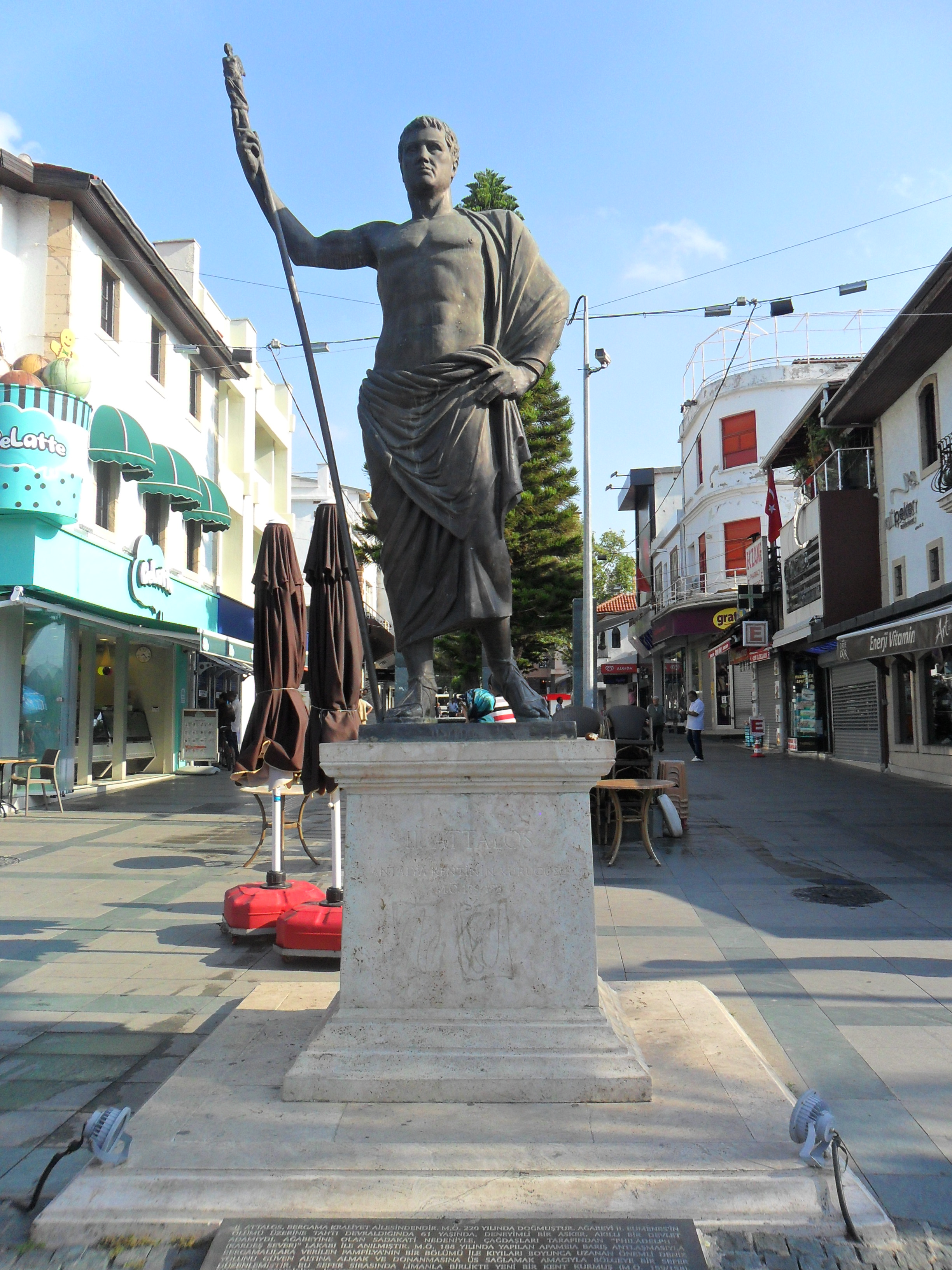  Attalea became part of the
Attalea became part of the  In the 19th century, in common with most of Anatolia, its sovereign was a "dere bey" (landlord or landowner). The family of Tekke Oğlu, domiciled near
In the 19th century, in common with most of Anatolia, its sovereign was a "dere bey" (landlord or landowner). The family of Tekke Oğlu, domiciled near  As of 1920, Antalya was reported as having a population of approximately 30,000. The harbor was described as small, and unsafe for vessels to visit in the winter. Antalya was exporting wheat, flour, sesame seeds, livestock, timber and charcoal. The latter two were often exported to
As of 1920, Antalya was reported as having a population of approximately 30,000. The harbor was described as small, and unsafe for vessels to visit in the winter. Antalya was exporting wheat, flour, sesame seeds, livestock, timber and charcoal. The latter two were often exported to


 Agricultural production includes citrus fruits, cotton, cut flowers, olives, olive oil and bananas. Antalya Metropolitan Municipality's covered wholesale food market complex meets 65% of the fresh fruit and vegetable demand of the province.
Since 2000, shipyards have been opened in Antalya Free Zone, specialized in building pleasure yachts. Some of these yards have advanced in composites boat building technology.
Corendon Airlines and SunExpress are headquartered in Antalya.
Agricultural production includes citrus fruits, cotton, cut flowers, olives, olive oil and bananas. Antalya Metropolitan Municipality's covered wholesale food market complex meets 65% of the fresh fruit and vegetable demand of the province.
Since 2000, shipyards have been opened in Antalya Free Zone, specialized in building pleasure yachts. Some of these yards have advanced in composites boat building technology.
Corendon Airlines and SunExpress are headquartered in Antalya.
File:Hadrians_Gate.jpg, Hadrian's Gate
File:Yivli_Minare_Mosque_02.jpg, Yivli Minare
Hıdırlık_Tower_01.jpg, Hıdırlık Tower
File:Antalya Karatay Medrese 5763.jpg, Antalya Karatay Medrese
File:Antalya_-_Kesik_Minare_1.jpg, Kesik Minare
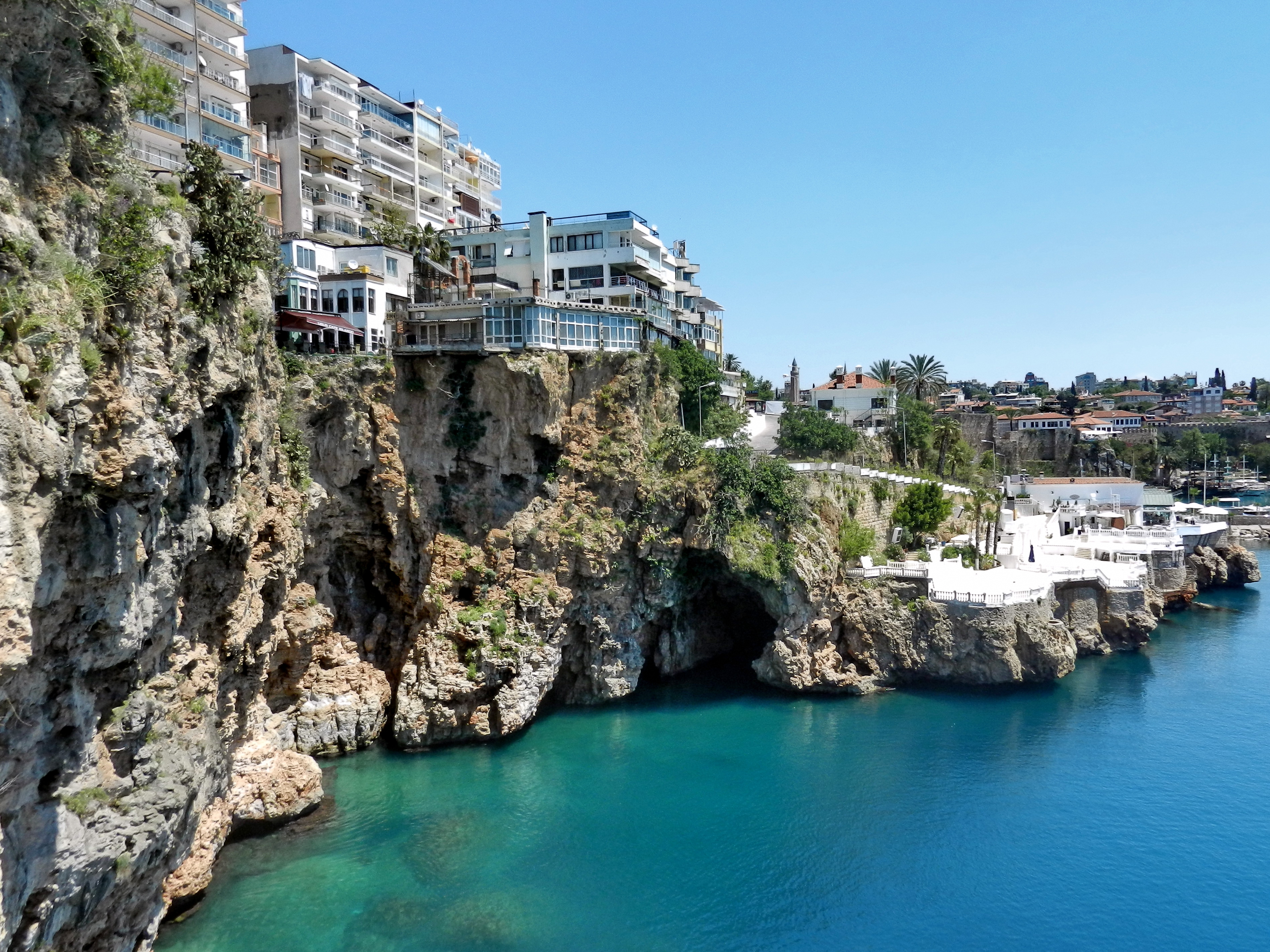


 There are urban parks and protected natural areas located outside the cities, allowing the people to have fun, rest and get closer to nature. Some of them are green areas around lake, pond and dam lakes, and some are highland and forest areas.
The prime urban green areas include Antalya City Forest, Atatürk Park, Kepez City Forest.
The largest amusement park in Antalya is the Aktur Park. Other modern recreational areas include 3 aquaparks in the city, Konyaaltı, Lara beaches, Beachpark especially for summer holidays, while Saklıkent also has facilities for skiing in the winter months.
The preserved nature areas include Güllük Mountain National Park in Antalya-Korkuteli highway, Mount Olympus National Park in Kemer and Düden and Kurşunlu Waterfalls. Other protected areas include the Damlataş and the Karain Cave and the Guver Cliff.
It offers picnic and recreation facilities in various parts of the city. Picnic areas, rafting facilities in Köprülü Kanyon in Manavgat. The part of Korkuteli-Antalya border in western part of Antalya is covered with forests. In these areas, picnic areas, playground, restaurant and similar facilities are provided. There are lake and forest views on the promenade at Feslikan Plateau to the west of the city center where visitors can also enjoy nature sports and nature walks. The oil wrestling competition festival organized in summer, what accompanied with concerts. The pond in Doyran town, located to the west of city is very suitable for picnic and fishing.
In addition to the open air recreation areas, the number of shopping centers, which have increased rapidly in recent years, can also be classified as a rest area with the facilities they offer. The shopping centers in the city are gathered in the center. Among the leading shopping centers in the city are Antalya 5M Migros, Antalya Kipa, Terra City, Deepo, Agora, and Mall of Antalya.
There are urban parks and protected natural areas located outside the cities, allowing the people to have fun, rest and get closer to nature. Some of them are green areas around lake, pond and dam lakes, and some are highland and forest areas.
The prime urban green areas include Antalya City Forest, Atatürk Park, Kepez City Forest.
The largest amusement park in Antalya is the Aktur Park. Other modern recreational areas include 3 aquaparks in the city, Konyaaltı, Lara beaches, Beachpark especially for summer holidays, while Saklıkent also has facilities for skiing in the winter months.
The preserved nature areas include Güllük Mountain National Park in Antalya-Korkuteli highway, Mount Olympus National Park in Kemer and Düden and Kurşunlu Waterfalls. Other protected areas include the Damlataş and the Karain Cave and the Guver Cliff.
It offers picnic and recreation facilities in various parts of the city. Picnic areas, rafting facilities in Köprülü Kanyon in Manavgat. The part of Korkuteli-Antalya border in western part of Antalya is covered with forests. In these areas, picnic areas, playground, restaurant and similar facilities are provided. There are lake and forest views on the promenade at Feslikan Plateau to the west of the city center where visitors can also enjoy nature sports and nature walks. The oil wrestling competition festival organized in summer, what accompanied with concerts. The pond in Doyran town, located to the west of city is very suitable for picnic and fishing.
In addition to the open air recreation areas, the number of shopping centers, which have increased rapidly in recent years, can also be classified as a rest area with the facilities they offer. The shopping centers in the city are gathered in the center. Among the leading shopping centers in the city are Antalya 5M Migros, Antalya Kipa, Terra City, Deepo, Agora, and Mall of Antalya.

 The mayor of the Antalya Metropolitan Municipality is Muhittin Böcek of the CHP, in office since 2019. For general elections, Antalya elects 18 Members of Parliament to the Turkish Grand National Assembly.
The mayor of the Antalya Metropolitan Municipality is Muhittin Böcek of the CHP, in office since 2019. For general elections, Antalya elects 18 Members of Parliament to the Turkish Grand National Assembly.
 The football club of Antalya, Antalyaspor plays in the
The football club of Antalya, Antalyaspor plays in the

 Antalya's signature cuisine includes
Antalya's signature cuisine includes
 The main transportation to the city is by air and land. Sea routes are still under development.
In 2007, the airport added a new terminal.
The city has a main port at the south of the Konyaaltı.
The main transportation to the city is by air and land. Sea routes are still under development.
In 2007, the airport added a new terminal.
The city has a main port at the south of the Konyaaltı.

 A
A
la, Attalensis
grc, Ἀτταλειώτης , postal_code_type =
Postal code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal ...
, postal_code = 07xxx
, area_code = (+90) 242
, registration_plate = 07
, blank_name = Licence plate
, timezone = TRT
The Turkish Radio and Television Corporation (TRT; Turkish : ) is the national public broadcaster of Turkey, founded in 1964. TRT was for many years the only television and radio provider in Turkey. Before the introduction of commercial radio i ...
, utc_offset = +3
, website = , name = , population_density_metro_km2 = 122 , blank_name_sec1 =
Patron deity
A tutelary () (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety an ...
, blank_info_sec1 = Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of v ...
Antalya () is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
as well as the capital of Antalya Province. Located on Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
's southwest coast bordered by the Taurus Mountains, Antalya is the largest Turkish city on the Mediterranean coast outside the Aegean region with over one million people in its metropolitan area.2011 CensusTurkish Statistical Institute (Büyükşehir belediyeleri ve bağlı belediyelerin nüfusları) – 2011 The city that is now Antalya was first settled around 200 BC by the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon, which was soon subdued by the Romans. Roman rule saw Antalya thrive, including the construction of several new monuments, such as Hadrian's Gate, and the proliferation of neighboring cities. The city has changed hands several times, including to the
Seljuk Sultanate
The Great Seljuk Empire, or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval, culturally Turko-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, founded and ruled by the Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. It spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to ...
in 1207 and an expanding Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in 1391. Ottoman rule brought relative peace and stability for the next five hundred years. The city was occupied by Italy for three years in the aftermath of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, but was recaptured by a newly independent Turkey in the War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of ...
.
Antalya is Turkey's biggest international sea resort, located on the Turkish Riviera
The Turkish Riviera ( tr, Türk Rivierası), also known popularly as the Turquoise Coast, is an area of southwest Turkey encompassing the provinces of Antalya and Muğla, and to a lesser extent Aydın, southern İzmir and western Mersin. Th ...
. Large-scale development and governmental funding has promoted tourism. A record 13.6 million tourists passed through the city in 2019.
Etymology
The city was founded as "Attaleia" ( grc, Ἀττάλεια), named after its founderAttalos II
Attalus II Philadelphus ( Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antal ...
, king of Pergamon. This name, still in use in Greek, was later evolved in Turkish as Adalia and then Antalya. Attaleia was also the name of a festival at Delphi and Attalis (Greek: Ἀτταλίς) was the name of an old Greek tribe at Athens. Despite the close similarity, there is no connection with the name Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
History



 King Attalus II of Pergamon is looked on as founder of the city in about 150 BC, during the
King Attalus II of Pergamon is looked on as founder of the city in about 150 BC, during the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. It was named Attaleia or Attalia ( grc, Ἀττάλεια) in his honour. The city served as a naval base for Attalus's powerful fleet. Excavations in 2008, in the Doğu Garajı plot, uncovered remains dating to the 3rd century BC, suggesting that Attalea was a rebuilding and expansion of an earlier town.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
in 133 BC when Attalus III, a nephew of Attalus II, bequeathed his kingdom to Rome at his death in 133 BC. The city grew and prospered during the Ancient Roman period and was part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Pamphylia Secunda, whose capital was Perga
Perga or Perge ( Hittite: ''Parha'', el, Πέργη ''Perge'', tr, Perge) was originally an ancient Lycian settlement that later became a Greek city in Pamphylia. It was the capital of the Roman province of Pamphylia Secunda, now located i ...
.
Christianity started to spread to the region even in the 1st century: Attalea was visited by Paul of Tarsus
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
and Barnabas, as recorded in the Acts of the Apostles: "Then they passed through Pisidia and came to Pamphylia. And when they had spoken the word in Perga
Perga or Perge ( Hittite: ''Parha'', el, Πέργη ''Perge'', tr, Perge) was originally an ancient Lycian settlement that later became a Greek city in Pamphylia. It was the capital of the Roman province of Pamphylia Secunda, now located i ...
, they went down to Attalea, and from there they sailed to Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
". Some of the bishops attributed to the episcopal see of Attalea in Pamphylia may instead have been bishops of Attalea in Lydia
Attalea or Attaleia ( grc, Ἀττάλεια) was a Roman city of ancient Lydia, former diocese and is presently a Latin Catholic titular bishopric.
Its modern location is Yanantepe in Asian Turkey.
History
Attalea was originally named Agroe ...
(Yanantepe), since Le Quien lists them under both sees. No longer a residential bishopric, Attalea in Pamphylia is today listed by the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
as a titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbi ...
.
The 13th-century Seljuk mosque at Attalea, now in ruins, had been a Christian Byzantine basilica from the 7th century. The Great Mosque had also been a Christian basilica and the Kesik Minare Mosque had been the 5th-century Christian Church of the Panaghia or Virgin and was decorated with finely carved marble. The archaeological museum at Attalea houses some sarcophagi and mosaics from nearby Perga and a casket of bones reputed to be those of St. Nicholas, the bishop of Myra, further down the Turquoise coast. The area of Antalya was subject to naval attacks by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
.
Attalea was a major city in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. It was the capital of the Byzantine Theme of the Cibyrrhaeots
The Cibyrrhaeot Theme, more properly the Theme of the Cibyrrhaeots ( gr, θέμα Κιβυρραιωτῶν, thema Kibyrrhaiōtōn), was a Byzantine theme encompassing the southern coast of Asia Minor from the early 8th to the late 12th centuries. ...
, which occupied the southern coasts of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. According to the research of Speros Vryonis, it was the major naval station on the southern Anatolian coast, a major commercial center, and the most convenient harbor between the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi ( Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
and Cyprus and points further east. Besides the local merchants, "one could expect to see Armenians, Saracens, Jews, and Italians."
At the time of the accession of John II Comnenus in 1118, Attalea was an isolated outpost surrounded by Turkish beyliks, accessible only by sea. Following the fall of Constantinople in 1204, Niketas Choniates records that one Aldebrandus, "an Italian by birth who was strictly raised according to Roman tradition" controlled Attalea as his own fief. When Kaykhusraw, sultan of the Seljuk Turks attempted to capture the city in 1206, Aldebrandus sent to Cyprus for help and received 200 Latin infantry who defeated the attackers after a siege of less than 16 days. Kaykhusraw would take Attalea the following year and build its first mosque. Christians rebelled and captured Attalea with aid of Walter of Montbéliard in 1212. Briefly restored Byzantine rule in Attalea was ended by Kaykaus I
Kaykaus I or Izz ad-Din Kaykaus ibn Kayhkusraw ( 1ca, كَیکاوس, fa, عز الدين كيكاوس پور كيخسرو ''ʿIzz ad-Dīn Kaykāwūs pour Kaykhusraw'') was the Sultan of Rum from 1211 until his death in 1220. He was the eldest ...
in 1216.
The city and the surrounding region were conquered by the Seljuk Turks in the early 13th century. Attalea was the capital of the Turkish beylik of Teke (1321–1423) until its conquest by the Ottomans, except for a period of Cypriot rule between 1361 and 1373. The Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
traveller Ibn Battuta, who visited the city in 1335–1340, noted:
In the second half of the 17th century Evliya Çelebi wrote of a city of narrow streets containing 3,000 houses in 20 Turkish and four Greek neighborhoods. The town had grown beyond the city walls and the port was reported to hold up to 200 boats. In the 19th century, in common with most of Anatolia, its sovereign was a "dere bey" (landlord or landowner). The family of Tekke Oğlu, domiciled near
In the 19th century, in common with most of Anatolia, its sovereign was a "dere bey" (landlord or landowner). The family of Tekke Oğlu, domiciled near Perge
Perga or Perge ( Hittite: ''Parha'', el, Πέργη ''Perge'', tr, Perge) was originally an ancient Lycian settlement that later became a Greek city in Pamphylia. It was the capital of the Roman province of Pamphylia Secunda, now located i ...
had been reduced to submission in 1812 by Mahmud II
Mahmud II ( ota, محمود ثانى, Maḥmûd-u s̠ânî, tr, II. Mahmud; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the 30th Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839.
His reign is recognized for the extensive administrative, ...
, but continued to be a rival power to the Ottoman governor until the early 20th century, surviving by many years the fall of the other great beys of Anatolia. The records of the Levant (Turkey) Company, which maintained an agency in Antalya until 1825, documented the local dere beys.
In the early 20th century, Antalya had two factories spinning and weaving cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
. As of 1920, the factories had 15,000 spindles and over 200 looms. A German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-owned mill baled cotton. There were gin mill
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); ...
s.
In the 20th century, the population of Antalya increased as Turks from the Caucasus and the Balkans moved into Anatolia. The economy was centered on its port that served the inland areas, particularly Konya. Antalya (then Adalia) was picturesque rather than modern. The chief attraction for visitors was the city wall, and outside a promenade, a portion of which survives. The government offices and the houses of the higher classes were outside the walls.
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
and other goods to Italy or other Greek islands, who received mainly flour. In 1920, the city had seven flour mills. Wheat was imported, and then processed in town before exportation. Antalya imported manufactured items, mainly from the United Kingdom. The city had a Greek minority that made up 1/3 of the population until the population exchange. Antalya also had a tiny Armenian population which had a church on the street of "Hamam çikmazi" named Hovhannes Surp Garabed, which was later on demolished. Antalya also had a Jewish community which had a tiny Synagogue in the neighborhood of Balbey and a Talmud Torah. The Synagogue was closed in 1948 and its exact location is not known, and the Synagogue might not exist anymore. The Jewish community had 2 graveyards and one was located across "Donerciler carsisi"and was demolished when the area was opened to construction, but one marble tombstone belonging to a Jew named Raphael Moshe was transferred to the Antalya Museum
The Antalya Museum or Antalya Archeological Museum ( tr, Antalya Müzesi) is one of Turkey's largest museums, located in Konyaaltı, Antalya. It includes 13 exhibition halls and an open air gallery. It covers an area of and 5000 works of art ...
where it can be seen in the museum garden.
The city was occupied by Italy for three years (1919-22) in the aftermath of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, but was recaptured by a newly independent Turkey in the War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of ...
. Large-scale development beginning in the 1970s transformed Antalya from a pastoral town into one of Turkey's largest metropolitan areas. Much of this has been due to tourism, which expanded in the 21st century. In the 1985 singing diva Dalida held her last concert in Antalya.
Antalya was the host city for the 2015 G-20 summit and the EXPO 2016
Expo 2016 was an international horticultural exposition held in Antalya, Turkey. Under the aegis of the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE) Expo 2016 Antalya was the first International Horticultural Exhibition to be held in Turkey.
As ...
. Five countries have their consular missions in Antalya including Germany, Great Britain, Russia, Belgium and Serbia.
Geography
Climate
Antalya has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen: ''Csa'') or a 'humid' dry-summer subtropical climate (Trewartha
Trewartha and Andrewartha are Cornish family names (and placename, Dexter). There are places called Trewartha in the parishes of Merther, St Agnes, St Neot and Veryan.
According to the ''Handbook of Cornish Names'' by G. Pawley White, "Tre ...
: ''Cf'' or ''Demographics
In 2010, the Address-Based Birth Recording System showed a metropolitan population of 1,001,318 (502,491 male; 498,827 female). Source for 1530–1889. According to the TÜİK Institute of Statistics, as of October 2022, 120,000 foreigners live in the city.

Economy
Cityscape
Despite having architectural heritage dating back up to Hellenistic times, most historical architecture in Antalya date to the medieval Seljuk period, with a number ofmosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s, madrasahs, masjids, caravanserais, Turkish baths and tombs giving the city a Turkish-Islamic character. Historical architecture is concentrated in the walled city, Kaleiçi; ancient structures are not well-preserved in the rest of the city of Antalya as the modern city was built on the ancient city. Kaleiçi, with its narrow cobbled streets of historic Ottoman era houses, is the old center of Antalya. With its hotels, bars, clubs, restaurants, and shopping, it has been restored to retain much of its historical character. It is surrounded by two walls in the shape of a horsenail, one of which is along the seafront, built in a continuous process from Hellenistic to Ottoman times. The historical harbour is located in this part of the city; narrow streets extend from the harbour and branch off into the old city, surrounded by wooden historical houses. Cumhuriyet Square, the main square of the city and a spot very popular for tourists and locals, is surrounded by shopping and business centres and public buildings. There are sites with traces of Hellenistic, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
, Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, and Seljuk architecture and cultures. There are also examples of the local Greek architecture in the city, with five Greek Orthodox churches in the old city.
The walled city is surrounded by a large metropolitan area. With high rates of immigration since the 1970s, this area contains large gecekondu
Gecekondu (Turkish for ''put up overnight'', plural gecekondular) is a Turkish word meaning a house put up quickly without proper permissions, a squatter's house, and by extension, a shanty or shack. Gecekondu bölgesi is a neighborhood made of ...
neighborhoods that are not well-integrated into the fabric of the city and suffer from poor economic conditions and insufficient education. Gecekondu areas are concentrated in the Kepez district, where an estimated 70% of the houses were gecekondus in 2008. In 2011, it was estimated that there were 50–60,000 gecekondus in Antalya, housing around 250,000 people.
Antalya has beaches including Konyaaltı
Konyaaltı is a district in the Antalya Province, Turkey. The name "Konyaaltı" (pronounced ), originates from the expression of "koy altı", which in the Turkish language means "the bay under the cliffs" .
The district is situated beneath the cli ...
, Lara, Karpuzkaldıran and Patara. Beydağları and Saklikent are used for winter sports.
Historic sites in the city center
* Ancient monuments include the City Walls, Hıdırlık Tower, Hadrian's Gate (also known as Triple Gate), and the Clock Tower. * Hadrian's Gate: constructed in the 2nd century by the Romans in honor of the Emperor Hadrian. * İskele Mosque: A 19th-century Mosque near the marina. *Karatay Medrese
Karatay Madrasa is a madrasa (a school with a frequently but not absolutely religious focus) built in Konya, Turkey, in 1251 by the Emir of the city Celaleddin Karatay, serving the Seljuk sultan.
History
Since 1955, the place serves as a mus ...
: A Medrese (Islamic theological seminary) built in 1250 by Emir Celaleddin Karatay.
* Kesik Minare (Broken Minaret) Mosque: Once a Roman temple then converted to a Byzantine Panayia church and finally into a mosque.
* Tekeli Mehmet Paşa Mosque: An 18th-century Mosque built in honor of Tekeli Mehmet Paşa.
* Yat Limanı: the harbour dating to Roman era.
* Yivli Minare (Fluted Minaret) Mosque: Built by the Seljuks and decorated with dark blue and turquoise tiles. This minaret eventually became the symbol of the city.
* Murat Pasha Mosque: A historic Ottoman mosque located in the city center.
* Aya Yorgi Church (Saint George Church): A historic church built by the Greeks of Antalya which is currently used as a museum housing exhibitions of historical artifacts.
* Saint Alypius Church: A tiny historic Greek Orthodox church which is still currently a functioning Orthodox Church.
* Sultan Aladdin Mosque: A historic building built as a Greek Orthodox church in 1834 and converted into a mosque in the 1950s and currently used as a Mosque.
* Ahi Yusuf Mosque: A historic mosque built in the year of 1249 and is possibly one of the oldest mosques in Antalya or even the oldest.
* Ahi Kizi Masjid: Historic masjid located in the old town.
* Kara Molla Masjid: Tiny historic masjid built in the 14th century.
* Balibey Mosque: A historic mosque built by the vizier Bali Pasha.
* Müsellim Mosque: A small historic mosque built by Hacı Osmanoğlu Mehmed Ağa in 1796.
* Antalya Synagogue: A historic Synagogue used as house currently in the Balbey neighborhood between Kavakli Masjid and the Balbey Kesik Minaret Mosque.
* Mevlevihane (Dervish lodge museum): A former Dervish lodge housing a museum about Dervishes and Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality ...
.

Main sights
* Akdeniz Kent Parkı *Antalya Aquarium
Antalya () is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey as well as the capital of Antalya Province. Located on Anatolia's southwest coast bordered by the Taurus Mountains, Antalya is the largest Turkish city on the Mediterranean coast outside the ...
* Arapsu Bridge
The Arapsu Bridge is a Roman bridge in Antalya, Turkey. The well-preserved footbridge lies in the Arapsuyu district, 5–6 km west to the city center, at the foot of an ancient mound which is associated with the Greek colony of Olbia.
Partly ...
* Atatürk Culture Park (formerly named after Hasan Subaşı)
* Düden Waterfalls
* Heart of Antalya
* Karaalioglu Park
* Konyaaltı Beach
* Tünektepe
Green areas, recreation places

 There are urban parks and protected natural areas located outside the cities, allowing the people to have fun, rest and get closer to nature. Some of them are green areas around lake, pond and dam lakes, and some are highland and forest areas.
The prime urban green areas include Antalya City Forest, Atatürk Park, Kepez City Forest.
The largest amusement park in Antalya is the Aktur Park. Other modern recreational areas include 3 aquaparks in the city, Konyaaltı, Lara beaches, Beachpark especially for summer holidays, while Saklıkent also has facilities for skiing in the winter months.
The preserved nature areas include Güllük Mountain National Park in Antalya-Korkuteli highway, Mount Olympus National Park in Kemer and Düden and Kurşunlu Waterfalls. Other protected areas include the Damlataş and the Karain Cave and the Guver Cliff.
It offers picnic and recreation facilities in various parts of the city. Picnic areas, rafting facilities in Köprülü Kanyon in Manavgat. The part of Korkuteli-Antalya border in western part of Antalya is covered with forests. In these areas, picnic areas, playground, restaurant and similar facilities are provided. There are lake and forest views on the promenade at Feslikan Plateau to the west of the city center where visitors can also enjoy nature sports and nature walks. The oil wrestling competition festival organized in summer, what accompanied with concerts. The pond in Doyran town, located to the west of city is very suitable for picnic and fishing.
In addition to the open air recreation areas, the number of shopping centers, which have increased rapidly in recent years, can also be classified as a rest area with the facilities they offer. The shopping centers in the city are gathered in the center. Among the leading shopping centers in the city are Antalya 5M Migros, Antalya Kipa, Terra City, Deepo, Agora, and Mall of Antalya.
There are urban parks and protected natural areas located outside the cities, allowing the people to have fun, rest and get closer to nature. Some of them are green areas around lake, pond and dam lakes, and some are highland and forest areas.
The prime urban green areas include Antalya City Forest, Atatürk Park, Kepez City Forest.
The largest amusement park in Antalya is the Aktur Park. Other modern recreational areas include 3 aquaparks in the city, Konyaaltı, Lara beaches, Beachpark especially for summer holidays, while Saklıkent also has facilities for skiing in the winter months.
The preserved nature areas include Güllük Mountain National Park in Antalya-Korkuteli highway, Mount Olympus National Park in Kemer and Düden and Kurşunlu Waterfalls. Other protected areas include the Damlataş and the Karain Cave and the Guver Cliff.
It offers picnic and recreation facilities in various parts of the city. Picnic areas, rafting facilities in Köprülü Kanyon in Manavgat. The part of Korkuteli-Antalya border in western part of Antalya is covered with forests. In these areas, picnic areas, playground, restaurant and similar facilities are provided. There are lake and forest views on the promenade at Feslikan Plateau to the west of the city center where visitors can also enjoy nature sports and nature walks. The oil wrestling competition festival organized in summer, what accompanied with concerts. The pond in Doyran town, located to the west of city is very suitable for picnic and fishing.
In addition to the open air recreation areas, the number of shopping centers, which have increased rapidly in recent years, can also be classified as a rest area with the facilities they offer. The shopping centers in the city are gathered in the center. Among the leading shopping centers in the city are Antalya 5M Migros, Antalya Kipa, Terra City, Deepo, Agora, and Mall of Antalya.
Government

 The mayor of the Antalya Metropolitan Municipality is Muhittin Böcek of the CHP, in office since 2019. For general elections, Antalya elects 18 Members of Parliament to the Turkish Grand National Assembly.
The mayor of the Antalya Metropolitan Municipality is Muhittin Böcek of the CHP, in office since 2019. For general elections, Antalya elects 18 Members of Parliament to the Turkish Grand National Assembly.
Elections
Antalya has traditionally been seen as a stronghold for theKemalist
Kemalism ( tr, Kemalizm, also archaically ''Kamâlizm''), also known as Atatürkism ( tr, Atatürkçülük, Atatürkçü düşünce), or The Six Arrows ( tr, Altı Ok), is the founding official ideology of the Republic of Turkey.Eric J. Zurcher ...
centre-left party Republican People's Party (CHP). Being the capital of the fifth most populous province in Turkey, Antalya is politically strategic and has been a target for the governing right-wing Justice and Development Party (AKP). The AKP unexpectedly won control of the Antalya Metropolitan Municipality in the 2004 local election. The AKP won a plurality in Antalya in the 2007 general election, symbolising the city's political transformation from a CHP stronghold to a CHP-AKP marginal battleground in the 21st century. The loss of Antalya was a major political setback for the CHP not only because of its significance as a centre for tourism, but also because the CHP's former leader Deniz Baykal is a Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
for the province. The province is divided into 19 districts.
The CHP regained control of the Metropolitan Municipality in the 2009 local elections, though the AKP won a plurality in the 2011 general election. The Nationalist Movement Party (MHP) also have a strong political base in Antalya, winning approximately between 15 and 25% of the vote in elections since 2007. The city voted in favour of the AKP government's proposed constitutional reforms in the 2007 referendum, but voted against the reforms proposed in 2010.
In the 2014 local elections, Antalya once again voted for the AKP, with the MHP taking support away from the CHP by winning a record 24.3% of the vote. The CHP subsequently accused the AKP of systematic electoral fraud, and the presence of government minister Mevlüt Çavuşoğlu at one of the vote counting centres drew strong condemnation. In the 2014 presidential election, the CHP and MHP's joint candidate Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu won 53.08% of the vote. The AKP's candidate Recep Tayyip Erdoğan won 41.63% of the vote, and the HDP democratic socialist candidate Selahattin Demirtaş won 5.30% of the vote. Antalya was a hotspot for the 2013–14 anti-government protests against the AKP.
The secular main opposition, CHP, regained control of the Metropolitan Municipality in the 2019 local elections.
Sports
Süper Lig
The Süper Lig (, ''Super League''), officially known as Spor Toto Süper Lig for sponsorship reasons, is a Turkish professional league for association football clubs. It is the top-flight of the Turkish football league system and is run by the ...
. The team's home venue is Antalya Stadium
The Antalya Stadium, officially branded as Corendon Airlines Park for sponsorship reasons, is a multi-purpose stadium in Antalya, Turkey. It is used mostly for football matches, hosting Turkish Süper Lig club Antalyaspor home matches. It ha ...
, with a capacity of 33,000, which was opened in 2015. Another football venue in the city is Antalya Atatürk Stadium
Antalya Atatürk Stadium ( tr, Antalya Atatürk Stadyumu) was a multi-purpose stadium in Antalya, Turkey. It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the home games of Antalyaspor
Antalyaspor Kulübü is a Turkish professio ...
.
The city hosts a number of international sports competitions due to its longer lasting warm weather condition. Since 2006, one of the four stages of Archery World Cup
The Archery World Cup is a competition, started in 2006, organized by the World Archery Federation, where the archers compete in four stages in four countries and the best eight archers of each category (from 2010, four archers during 2006-09) ad ...
events are held at the Antalya Centennial Archery Field. It also hosted European Weightlifting Championship in 2012, European Beach Volleyball Championship in 2003, European Triathlon Championship in 2013 and World Kickboxing Championships in 2013.
Since 2010, an international multiday trail running ultramarathon, called Lycian Way Ultramarathon, is held on the historical Lycian Way. The event runs eastward on a route of around from Ölüdeniz in Fethiye
Fethiye () is a city and district of Muğla Province in the Aegean Region of Turkey. It is one of the prominent tourist destinations in the Turkish Riviera. In 2019 its population was 162,686.
History
Fethiye was formerly known as Makri ...
district of Muğla Province
Muğla Province ( tr, , ) is a province of Turkey, at the country's south-western corner, on the Aegean Sea. Its seat is Muğla, about inland, while some of Turkey's largest holiday resorts, such as Bodrum, Ölüdeniz, Marmaris and Fethiye, ...
to Antalya in six days.
Education
Akdeniz University enrolls over 60,000 students and 4,000 academic and administrative staff.Culture
Cuisine

 Antalya's signature cuisine includes
Antalya's signature cuisine includes piyaz
Piyaz ( tr, piyaz, Persian: پیاز, Kurdish: pivaz, piyaz for "onion" or salad) is a kind of Turkish cuisine, Turkish cuisine and Persian salad or meze that is made from any kind of dry beans with onion, parsley and sumac. The name of Pi ...
(made with tahini, garlic, walnuts, and boiled beans), şiş köfte (spicy meatball which is cooked around a stick) spicy hibeş with mixed cumin and tahini, , and various cold Mediterranean dishes with olive oil. One local speciality is , boiled seeds of the lupin, eaten as a snack. "Grida" (also known as Lagos or Mediterranean white grouper) is a fish common in local dishes.
Festivals and events
* Antalya Golden Orange Film Festival: national film festival usually held in September / October. * Kaleiçi Old Town Festival, organized by Muratpaşa municipality, held in October. *Sandland
Sandland ( sme, Sáttomohgáddi) is a village in Loppa Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The village is located on the mainland part of Loppa, along the Sandlands fjorden, across from the uninhabited island of Silda. The nea ...
, sand art festival at Lara Beach
Museums
* Antalya Ethnographic Museum: Located in Kaleici housing artifacts of Antalya's culture, Regional dress, and architectural examples. *Antalya Museum
The Antalya Museum or Antalya Archeological Museum ( tr, Antalya Müzesi) is one of Turkey's largest museums, located in Konyaaltı, Antalya. It includes 13 exhibition halls and an open air gallery. It covers an area of and 5000 works of art ...
* Antalya Toy Museum. The Antalya Metropolitan Municipality opened the exhibition facility in 2011.
* Atatürk's House Museum
* Bir Zamanlar Antalya Müzesi: Located in Dokumapark, Kepez. Serving artifacts and documents about contemporary urban history of Antalya.
* Kaleiçi Museum: Opened in 2007 by the Mediterranean Civilizations Research Center (Akdeniz Medeniyetleri Araştırma Merkezi)
* Kepez Araba Müzesi: Located in Dokumapark, serving historical vehicles in contemporary history.
* Kepez Open Air Museum: Serving scale models of various structures of Turkey. The models were located in Minicity park in Konyaaltı
Konyaaltı is a district in the Antalya Province, Turkey. The name "Konyaaltı" (pronounced ), originates from the expression of "koy altı", which in the Turkish language means "the bay under the cliffs" .
The district is situated beneath the cli ...
before the demolition of park in late 2010's and moving to current location in Dokumapark.
* Mevlevihane Museum: Former dervish lodge with Sufi and Islamic cultural artifacts.
* Suna & İnan Kıraç Kaleiçi Museum : An ethnographic museum run by the Suna and İnan Kıraç Foundation.
Transportation
Buses
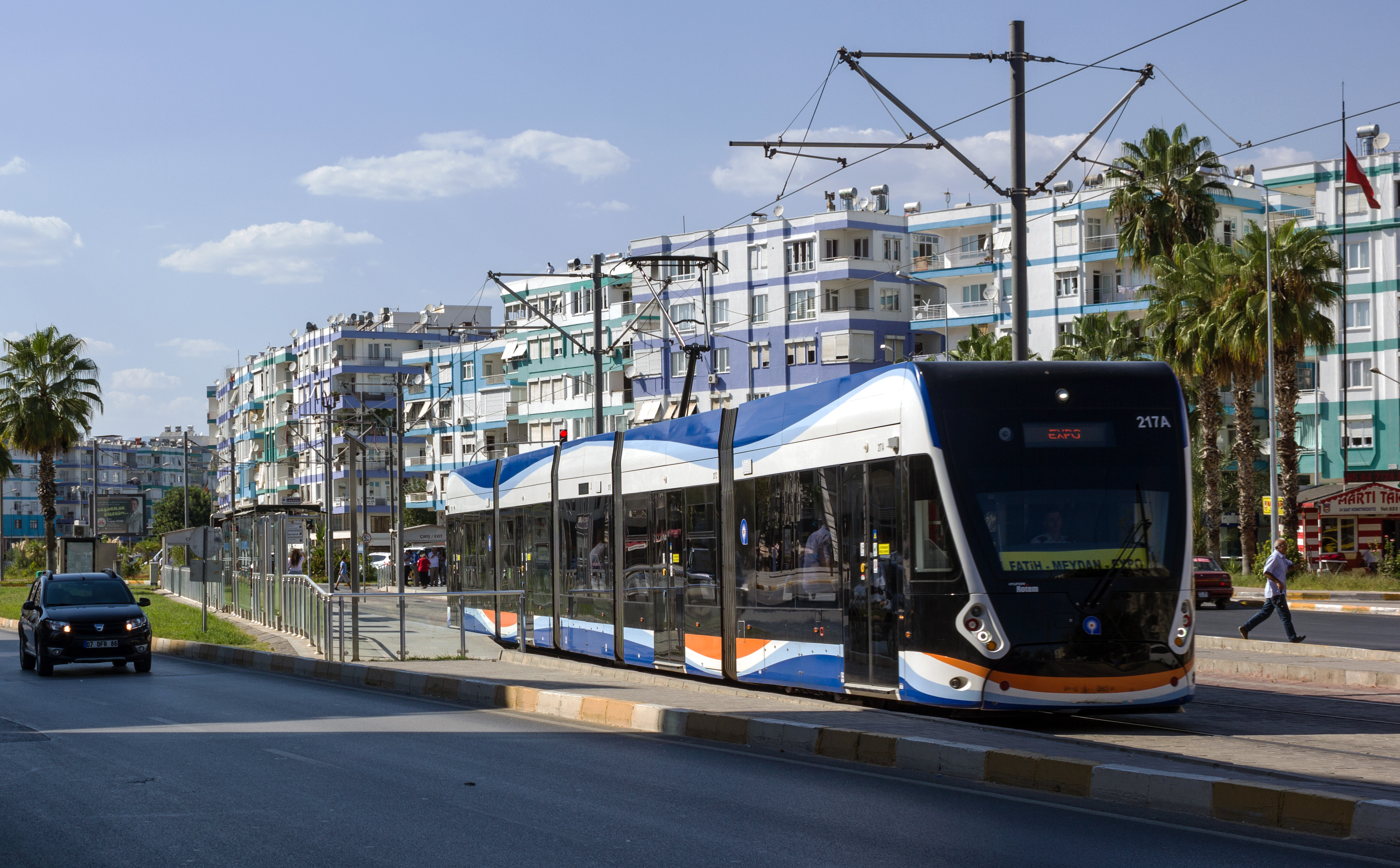
There is a network of look-alike Dolmuşes that are privately owned and operated minibuses, under municipal government control. Antalya Ulaşım, a municipally-owned corporation, runs the public bus system. The corporation owns Antobus and Antray. Antobus was started in September 2010. In 2010, the city planned to increase from 40 to 140 more buses. Payment for public transportation was made in cash until the launch of a public transportation card, ''Antkart'', in late 2007. The card system met with criticism and was subsequently canceled in June 2009, returning to a cash system. ''Halkkart'' has been used for the transportation system since the summer of 2010. ''Halkkart'' is managed by A-Kent Smart City Technologies under the control of Antalya Metropolitan Municipal government. Passengers can use identified cards to take buses or trams.Light Rail

tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
system, opened in 1999, runs from Antalya Museum, and the Sheraton Voyager and Falez hotels, along the main boulevard through the city center at Kalekapisi, Hadrian's Gate, Karaalioglu Park, and ending at Talya Oteli. Trams depart on the hour and half-hour from the terminal (east and west), and reach Kalekapisi between 10 and 15 minutes later.
In December 2009, an light rail line Antray was opened from one of the main city public bus hubs northwest to beyond suburban areas and the zoo. An extension to Airport, Aksu and Expo 2016
Expo 2016 was an international horticultural exposition held in Antalya, Turkey. Under the aegis of the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE) Expo 2016 Antalya was the first International Horticultural Exhibition to be held in Turkey.
As ...
site was completed in 2016.
Major routes
Antalya is the southern terminus of European route E87, which connects toKorkuteli
Korkuteli is a district of Antalya Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey, north-west of the city of Antalya. It was previously called Istanoz or Stenez
Etymology
Its modern name comes from Korkut, an Ottoman prince, who was murdered by ...
, Denizli, İzmir, Çanakkale, Edirne in Turkey, along with Varna in Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Constanta in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
and Odessa in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
. Antalya is also the terminus of Turkish Highway D650, which connects Burdur
Burdur is a city in southwestern Turkey. The seat of Burdur Province, it is located on the shore of Lake Burdur. Its estimated 2010 population is 78,389.
History
Ancient history
Whilst there is evidence of habitation in the province dating ...
, Afyon, Kütahya, and Sakarya.
D400 connects with D650 in Antalya, while D650 alternative D685 connects to Isparta and provincial road 07-50 connects to Kumluca by Altınyaka, an alternative to D400.
Airports
Antalya Airport has two international terminals and one domestic terminal. In 2020, its number of passengers on international flights surpassed the total number at Istanbul Airport and Sabiha Gökçen International Airport for the first time, officially earning the title of "the capital of Turkish tourism".Antalya Public Transportation Statistics
The average amount of time people spend commuting with public transit in Antalya, for example to and from work, on a weekday is 63 min. 14.% of public transit riders, ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average amount of time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 23 min, while 50% of riders wait for over 20 minutes on average every day. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is , while 13% travel for over in a single direction.International relations
Antalya is twinned with: * Austin, United States * Bat Yam, Israel * Famagusta, Northern Cyprus * Haikou, China * Jeonju, South Korea *Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzan is the capital city, capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and t ...
, Russia
* Kunming, China
* Liwan (Guangzhou), China
* Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
, United States
* Mostar, Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
, Germany
* Omsk, Russia
* Qingdao, China
* Rostov-on-Don, Russia
* Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
, Spain
* Suncheon
Suncheon () (''Suncheon-si'') is a city in South Jeolla Province, South Korea. It is a scenic agricultural and industrial city of around 250,000 people near Suncheon Bay. It is located in the southeastern corner of Jeollanam-do, just over an hou ...
, South Korea
* Taldykorgan, Kazakhstan
* Ürümqi, China
* Vladimir, Russia
* Xining, China
* Yalta, Ukraine
Notable people
*Tarık Akıltopu
Tarık Akıltopu (born 18 March 1918 in Antalya; died 2004) was Antalya's first architect of the 20th century. He was also a poet and a writer and known as a "Antalya lover". He wrote many books and poems about the city and its history. He died i ...
, architect, historian, poet, writer
* Cafercan Aksu, football player
* Athenaeus of Attalia, physician and founder of the Pneumatist School of Medicine, 1st century AD
* Michael Attaliates Byzantine lawyer of the 11th century
* Attalus II Philadelphus King of Pergamon and the founder of Attalia
* Deniz Baykal, former leader of Republican People's Party
* Yağmur Sarıgül, musician, composer of maNga
* Ahmet Sonuç, video game streamer known as Jahrein
* Musa Uzunlar, actor
* Burak Yılmaz, football player
* Levent Yüksel
Levent Uğur Yüksel (born October 21, 1964) is a Turkish pop singer and multi instrumentalist. He has been active in live music industry since 1993.
Life
Yüksel's interest in arts and music started in an early age. He started to play violin at ...
, musician, composer
References
{{Authority control 150 BC establishments Hellenistic colonies in Anatolia Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Archaeological sites in Antalya Province Attalid colonies Mediterranean port cities and towns in Turkey New Testament places Populated coastal places in Turkey Populated places established in the 2nd century BC Populated places in Antalya Province Turkish Riviera Cities in Turkey 150s BC establishments