Ancient history of Cyprus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ancient history of Cyprus shows a precocious sophistication in the  Alexander's conquests only served to accelerate an already clear drift towards Hellenisation in Cyprus. His premature death in 323 BC led to a period of turmoil as
Alexander's conquests only served to accelerate an already clear drift towards Hellenisation in Cyprus. His premature death in 323 BC led to a period of turmoil as
 Cyprus gained independence after 627 BC following the death of
Cyprus gained independence after 627 BC following the death of
 In 525 BCE, the Persian
In 525 BCE, the Persian
Ancient History of Cyprus, by the Cypriot government
History of Cyprus, Lonely Planet Travel Information
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient History of Cyprus
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
era visible in settlements such as at Choirokoitia dating from the 9th millennium BC, and at Kalavassos from about 7500 BC.
Periods of Cyprus's ancient history from 1050 BC have been named according to styles of pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
as follows:
* Cypro-Geometric I: 1050–950 BC
* Cypro-Geometric II: 950–850 BC
* Cypro-Geometric III: 850–700 BC
* Cypro-Archaic I: 700–600 BC
* Cypro-Archaic II: 600–475 BC
* Cypro-Classical I: 475–400 BC
* Cypro-Classical II: 400–323 BC
The documented history of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
begins in the 8th century BC. The town of Kition
Kition ( Egyptian: ; Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque closest to the excavation pit of the Kathari site (as of ...
, now Larnaka, recorded part of the ancient history of Cyprus on a stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek language, Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ...
that commemorated a victory by Sargon II
Sargon II ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is gener ...
(722–705 BC) of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
there in 709 BC. Assyrian domination of Cyprus (known as ''Iatnanna'' by the Assyrians) appears to have begun earlier than this, during the reign of Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "my trust belongs to the son of Ešarra"), was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 745 BC to his death in 727. One of the most prominent and historically significant Assyrian kings, T ...
(744–727 BC), and ended with the fall of the Neo Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
in 609 BC, whereupon the city-kingdoms of Cyprus gained independence once more. Following a brief period of Egyptian domination in the sixth century BC, Cyprus fell under Persian rule. The Persians did not interfere in the internal affairs of Cyprus, leaving the city-kingdoms to continue striking their own coins and waging war amongst one another, until the late-fourth century BC saw the overthrow of the Persian Empire by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.
 Alexander's conquests only served to accelerate an already clear drift towards Hellenisation in Cyprus. His premature death in 323 BC led to a period of turmoil as
Alexander's conquests only served to accelerate an already clear drift towards Hellenisation in Cyprus. His premature death in 323 BC led to a period of turmoil as Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedo ...
and Demetrius I of Macedon fought together for supremacy in that region, but by 294 BC, the Ptolemaic kingdom had regained control and Cyprus remained under Ptolemaic rule until 58 BC, when it became a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
. During this period, Phoenician and native Cypriot traits disappeared, together with the old Cypriot syllabic script, and Cyprus became thoroughly Hellenised. Cyprus figures prominently in the early history of Christianity, being the first province of Rome to be ruled by a Christian governor, in the first century, and providing a backdrop for events in the New Testament
Early history
Mycenaean settlement
The Ancient Greek historianHerodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
(5th century BC) claims that the city of Kourion, near present-day Limassol
Limassol (; el, Λεμεσός, Lemesós ; tr, Limasol or ) is a city on the southern coast of Cyprus and capital of the district with the same name. Limassol is the second largest urban area in Cyprus after Nicosia, with an urban populatio ...
, was founded by Achaean settlers from Argos. This is further supported by the discovery of a Late Bronze Age settlement lying several kilometres from the site of the remains of the Hellenic city of Kourion, whose pottery and architecture indicate that Mycenaean settlers did indeed arrive and augment an existing population in this part of Cyprus in the twelfth century BC.Christou, Demos, 1986. ''Kourion: A Complete Guide to Its Monuments and Local Museum''. Filokipros Publishing Co. Ltd., Nicosia. Introduction, p 7. The kingdom of Kourion in Cyprus is recorded on an inscription dating to the period of the Pharaoh Ramses III (1186–1155 BC) in Egypt.
Assyrian conquest
An early written source of Cypriot history mentions the nation underAssyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n rule as stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek language, Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ...
found in 1845 in the city formerly named Kition
Kition ( Egyptian: ; Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque closest to the excavation pit of the Kathari site (as of ...
, near present-day Larnaka, commemorates the victory of King Sargon II
Sargon II ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is gener ...
(721–05 BC) in 709 BC over seven kings in the land of Ia', in the district of Iadnana or Atnana. The land of Ia' is assumed to be the Assyrian name for Cyprus, and some scholars suggest that the latter may mean 'the islands of the Danaans
The Achaeans (; grc, Ἀχαιοί ''Akhaioí,'' "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively.
The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and t ...
', or Greece. There are other inscriptions referring to the land of Ia' in Sargon's palace at Khorsabad.
The ten kingdoms
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concu ...
listed on the prism of Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
in 673–2 BC have been identified as Soloi
Soli or Soloi ( el, Σόλοι) is an ancient Greek city on the island of Cyprus, located next to the town of Karavostasi, southwest of Morphou (Guzelyurt), and on the coast in the gulf of Morphou. Since 1974 the site has been within the territ ...
, Salamis, Paphos
Paphos ( el, Πάφος ; tr, Baf) is a coastal city in southwest Cyprus and the capital of Paphos District. In classical antiquity, two locations were called Paphos: Old Paphos, today known as Kouklia, and New Paphos.
The current city of P ...
, Kourion, Amathus and Kition on the coast, and Tamassos
Tamassos ( Greek: Ταμασσός) or Tamasos (Greek: Τἀμασος) – names Latinized as Tamassus or Tamasus – was a city-kingdom in ancient Cyprus, one of the ten kingdoms of Cyprus. It was situated in the great central plain of the is ...
, Ledrai, Idalion
Idalion or Idalium ( el, Ιδάλιον, ''Idalion'') was an ancient city in Cyprus, in modern Dali, Nicosia District. The city was founded on the copper trade in the 3rd millennium BC. Its name in the 8th century BC was "Ed-di-al" as it appears ...
and Chytroi
Chytri (or Khytri, el, Χύτροι) was one of the ten city-kingdoms of Cyprus in antiquity. It was located in the centre of the island, in the territory of Chytraea, west of Mesaoria. Today the modern town of Kythrea (Kyrka) has preserved the ...
in the interior of the island. Later inscriptions add Marion, Lapithos
Lapithos or Lapethos ( el, Λάπηθος; tr, Lapta) is a town in Cyprus. ''De facto'', it is under the control of Northern Cyprus.
Archeologists claim that Lapithos was founded by the Achean brothers Praxandros and Cepheus.
According to Stra ...
and Kerynia (Kyrenia
Kyrenia ( el, Κερύνεια ; tr, Girne ) is a city on the northern coast of Cyprus, noted for its historic harbour and castle. It is under the ''de facto'' control of Northern Cyprus.
While there is evidence showing that the wider region ...
).
Independent city-kingdoms
Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
, the last great Assyrian king. Cemeteries from this period are chiefly rock-cut tombs. They have been found, among other locations, at Tamassos
Tamassos ( Greek: Ταμασσός) or Tamasos (Greek: Τἀμασος) – names Latinized as Tamassus or Tamasus – was a city-kingdom in ancient Cyprus, one of the ten kingdoms of Cyprus. It was situated in the great central plain of the is ...
, Soloi, Patriki and Trachonas. The rock-cut 'Royal' tombs at Tamassos
Tamassos ( Greek: Ταμασσός) or Tamasos (Greek: Τἀμασος) – names Latinized as Tamassus or Tamasus – was a city-kingdom in ancient Cyprus, one of the ten kingdoms of Cyprus. It was situated in the great central plain of the is ...
, built in about 600 BC, imitate wooden houses. The pillars show Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n influence. Some graves contain the remains of horses and chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
s.
The main deity of ancient Cyprus was the Great Goddess, the Assyro-Babylonian
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language t ...
Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
, and Phoenician Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess Ashtart or Athtart ( Northwest Semitic), a deity closely related to Ishtar ( East Semitic), who was worshipped from the Bronze Age through classical antiquity. The name ...
, later known by the Greek name Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols incl ...
. She was called "the Cypriote" by Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
. Paphian inscriptions call her "the Queen". Pictures of Aphrodite appear on the coins of Salamis as well, demonstrating that her cult had a larger regional influence. In addition, the King of Paphos was the High Priest of Aphrodite. Other Gods venerated include the Phoenician Anat, Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied t ...
, Eshmun, Reshef, Mikal and Melkart and the Egyptian Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
, Thoth
Thoth (; from grc-koi, Θώθ ''Thṓth'', borrowed from cop, Ⲑⲱⲟⲩⲧ ''Thōout'', Egyptian: ', the reflex of " eis like the Ibis") is an ancient Egyptian deity. In art, he was often depicted as a man with the head of an ibis or ...
, Bes BES or Bes may refer to:
* Bes, Egyptian deity
* Bes (coin), Roman coin denomination
* Bes (Marvel Comics), fictional character loosely based on the Egyptian deity
Abbreviations
* Bachelor of Environmental Studies, a degree
* Banco Espírito ...
and Ptah
Ptah ( egy, ptḥ, reconstructed ; grc, Φθά; cop, ⲡⲧⲁϩ; Phoenician: 𐤐𐤕𐤇, romanized: ptḥ) is an ancient Egyptian deity, a creator god and patron deity of craftsmen and architects. In the triad of Memphis, he is the hu ...
, as attested by amulets. Animal sacrifices are attested to on terracotta-votives. The Sanctuary of Ayia Irini contained over 2,000 figurines.
Egyptian period
In 570 BCE, Cyprus was conquered byEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
under Amasis II
Amasis II ( grc, Ἄμασις ; phn, 𐤇𐤌𐤎 ''ḤMS'') or Ahmose II was a pharaoh (reigned 570526 BCE) of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the successor of Apries at Sais. He was the last great ruler of Egypt before the Persian conque ...
. This brief period of Egyptian domination left its influence mainly in the arts, especially sculpture, where the rigidity and the dress of the Egyptian style can be observed. Cypriot artists later discarded this Egyptian style in favour of Greek prototypes.
Statues in stone often show a mixture of Egyptian and Greek influence. In particular, ceramics recovered on Cyprus show influence from ancient Crete. Men often wore Egyptian wigs and Assyrian-style beards. Armour and dress showed western Asiatic elements as well.
Persian period
 In 525 BCE, the Persian
In 525 BCE, the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
conquered Cyprus. Under the Persians, the Kings of Cyprus retained their independence but had to pay tribute to their overlord. The city-kingdoms began to strike their own coins in the late-sixth century BCE, using the Persian weight system. Coins minted by the kings were required to have the overlord's portrait on them. King Evelthon of Salamis (560–25 BCE) was probably the first to cast silver or bronze coins in Cyprus; the coins were designed with a ram on the obverse and an ankh (Egyptian symbol of good luck) on the reverse.
Royal palaces have been excavated in Palaepaphos and in Vouni in the territory of Marion on the North coast. They closely follow Persian examples like Persepolis
, native_name_lang =
, alternate_name =
, image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.
, map =
, map_type ...
. Vouni, on a hill overlooking Morphou Bay, was built around 520 BCE and destroyed in 380 BCE. It contained Royal audience chambers (liwan
Liwan ( ar, ليوان, , from Persian ) is a long narrow-fronted hall or vaulted portal in ancient and modern Levantine homes that is often open to the outside.Abercrombie, 1910, p. 266.Davey, 1993, p. 29. An Arabic loanword to English, it is ...
), open courtyards, bathhouses and stores.
Towns in Cyprus during this period were fortified with mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also been ...
walls on stone foundations and rectangular bastions. The houses were constructed of mud-bricks as well, whereas public buildings were faced with ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruv ...
. The Phoenician town of Carpasia, near Rizokarpasso ( tr, Dipkarpaz), had houses built of rubble masonry with square stone blocks forming the corners. Temples and sanctuaries were built mainly in a Phoenician style. Soloi
Soli or Soloi ( el, Σόλοι) is an ancient Greek city on the island of Cyprus, located next to the town of Karavostasi, southwest of Morphou (Guzelyurt), and on the coast in the gulf of Morphou. Since 1974 the site has been within the territ ...
had a small temple with a Greek plan.
A definite influence from Greece was responsible for the production of some very important sculptures. The archaic Greek art with its attractive smile on the face of the statue is found on many Cypriot pieces dating between 525–475 BCE; that is, the closing years of the Archaic period in Greece. During the Persian rule, Ionian influence on the sculptures intensified; copies of Greek korai appear, as well as statues of men in Greek dress. Naked kouroi
kouros ( grc, κοῦρος, , plural kouroi) is the modern term given to free-standing Ancient Greek sculptures that depict nude male youths. They first appear in the Archaic period in Greece and are prominent in Attica and Boeotia, with a less ...
, however, although common in Greece, are extremely rare in Cyprus, while women (Korai) are always presented dressed with rich folds in their garments. The pottery in Cyprus retained its local influences, although some Greek pottery was imported.
The most important obligation of the kings of Cyprus to the Shah of Persia
Iranian monarchism is the advocacy of restoring the monarchy in Iran, which was abolished after the 1979 Revolution.
Historical background
Iran first became a constitutional monarchy in 1906, but underwent a period of autocracy during the year ...
was the payment of tribute and the supply of armies and ships for his foreign campaigns. Thus, when Xerxes in 480 BC invaded Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, Cyprus contributed 150 ships to the Persian military expedition.
Ionian revolt
Except for the royal city of Amathus, the Kingdoms of Cyprus took part in theIonian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
in 499 BC. The revolt on Cyprus was led by Onesilos of Salamis, brother of the King of Salamis, whom he dethroned for not wanting to fight for independence. The Persians crushed the Cypriot armies and laid siege to the fortified towns in 498 BCE. Soloi surrendered after a five-month siege.
Around 450 BCE, Kition annexed Idalion with Persian help. The importance of Kition increased again when it acquired the Tamassos copper-mines.
Evagoras I of Salamis
Evagoras I
Evagoras or Euagoras ( grc, Εὐαγόρας) was the king of Salamis (411–374 BC) in Cyprus, known especially from the work of Isocrates, who presents him as a model ruler.
History
He claimed descent from Teucer, the son of Telamon and half ...
of Salamis (435–374 BCE) dominated Cypriot politics for almost forty years until his death in 374 BCE. He had favoured Athens during the closing years of the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of ...
, elicited Persian support for the Athenians against Sparta and urged Greeks from the Aegean to settle in Cyprus, assisting the Athenians in so many ways that they honoured him by erecting his statue in the Stoa (portico) Basileios in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
. At the beginning of the 4th century BC, he took control of the whole island of Cyprus and within a few years was attempting to gain independence from Persia with Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
help.
Following resistance from the kings of Kition
Kition ( Egyptian: ; Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque closest to the excavation pit of the Kathari site (as of ...
, Amathus and Soli, who fled to the great king of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
in 390 BC to request support, Evagoras received less help from the Athenians than he had hoped for and in about 380 BCE, a Persian force besieged Salamis and Evagoras was forced to surrender. In the end, he remained king of Salamis until he was murdered in 374 BCE, but only by accepting his role as a vassal of Persia.
Evagoras I of Salamis introduced the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as ...
to Cyprus. In other parts of the island, the Phoenician script
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician alpha ...
(Kition) or the Cypriot syllabic alphabet were still used. Together with Egypt and Phoenicia, Cyprus rebelled against Persian rule again in 350 BCE, but the uprising was crushed by Artaxerxes III
Ochus ( grc-gre, Ὦχος ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
in 344 BCE.
Hellenistic period

Alexander the Great
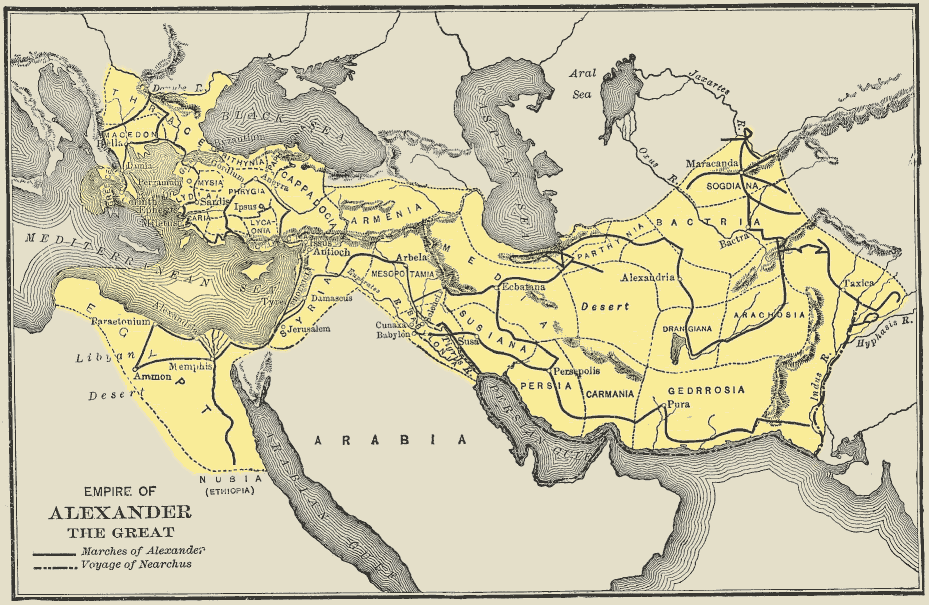
Long and sustained efforts to overthrow Persian rule proved unsuccessful and Cyprus remained a vassal of the Persian Empire until the Persian's defeat by Alexander the Great. Alexander the Great (Alexander of Macedon and Alexander III of Macedon), was born in Pella in 356 BCE and died in Babylon in 323 BCE. Son of King Philip II and Olympias, he succeeded his father to the throne of Macedonia in 336 BCE at the age of 20. He was perhaps the greatest commander in history and led his army in a series of victorious battles, creating a vast empire that stretched from Greece toEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
in Africa and to the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. The various kingdoms of Cyprus became allies of Alexander following his victorious campaigns at Granicus (334 BCE), Issus (333 BCE) and on the coast of Asia Minor, Syria and Phoenicia, where Persian naval bases were situated.
The Cypriot kings, learning of the victory of Alexander at Issus, and knowing that sooner or later, Alexander would be the new ruler of the island, since the occupation of Cyprus was necessary (along with that of Phoenicia) to open lines of communication to Egypt and Asia, rose up against their Persian overlords and made available to the fleet of Alexander the ships formerly in the service of Persia. There was a mutuality of interests: Alexander the Great increased the capacity of his fleet, and the Cypriot kings achieved political independence.
Siege of Tyre
From the area of Phoenicia, only Tyre resisted Alexander's control, and so he undertook a siege. The Cypriot fleet, together with Cypriot engineers, contributed much to the capture of this highly fortified city. Indeed, king Pnytagoras of Salamis, Androcles of Amathus, and Pasikratis ofSoloi
Soli or Soloi ( el, Σόλοι) is an ancient Greek city on the island of Cyprus, located next to the town of Karavostasi, southwest of Morphou (Guzelyurt), and on the coast in the gulf of Morphou. Since 1974 the site has been within the territ ...
, took a personal part in the siege of Tyre.
Tyre, then the most important Phoenician city, was built on a small island that was 700 metres from the shore and had two harbors, the Egyptian to the south and Sidonian to the north. The Cypriot kings, in command of 120 ships, each with a very experienced crew, provided substantial assistance to Alexander in the siege of this city, which lasted for seven months. During the final attack, the Cypriots managed to occupy the Sidonian harbour and the northern part of Tyre, while the Phoenicians loyal to Alexander occupied the Egyptian harbour. Alexander also attacked the city with siege engines by constructing a "mole", a strip of soil from the coast opposite Tyre, to the island where the city was built. In this operation, Alexander was helped by many Cypriot and Phoenician engineers who built earthworks on his behalf. Many siege engines battered the city from the "mole" and from "ippagoga" ships.
Although they lost many quinquereme
From the 4th century BC on, new types of oared warships appeared in the Mediterranean Sea, superseding the trireme and transforming naval warfare. Ships became increasingly large and heavy, including some of the largest wooden ships hitherto con ...
s, the Cypriots managed to help capture the city for Alexander. His gratitude was shown, for example, by the help he gave to Pnytagora, who seems to have been the main driver of this initiative to support Alexander, to incorporate the territory of the Cypriot kingdom of Tamassos into that of Salamis. The kingdom of Tamassos was then ruled by King Poumiaton of Kition who had purchased it for 50 talents from king Pasikypro.
In 331 BCE, while Alexander was returning from Egypt, he stayed for a while in Tyre, where the Cypriot kings, wishing to reaffirm their trust and support for him, put on a great show of honour.
Help to Amphoterus
Cypriot ships were also sent to help the admiral of Alexander the Great,Amphoterus (admiral)
Amphoterus (Greek: ) the brother of Craterus, was appointed by Alexander the Great commander of the fleet in the Hellespont in 333 BC. Amphoterus' appointment recognized his successful attempts to subdue the islands between Greece and Asia which ha ...
.
Alexander in Asia
Cyprus was an experienced seafaring nation and Alexander used the Cypriot fleet during his campaign into India; because the country had many navigable rivers, he included a significant number of shipbuilders and rowers from Cyprus, Egypt, Phoenicia and Caria in his military expedition. Cypriot forces were led by Cypriot princes such as Nikoklis, son of King Pasikrati of Solon, and Nifothona, son of King Pnytagora of Salamis. As Alexander took over control of the administrative region that had been the Persian Empire, he promoted Cypriots to high office and great responsibility; in particular, Stasanor of Soli was appointedsatrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
of the Supreme Court and Drangon in 329 BCE and Stasander Stasander ( grc, Στάσανδρος; lived 4th century B.C.) was a Soloian general in the service of Alexander the Great. Upon Alexander's death he became the satrap of Aria and Drangiana. He lost control of his satrapies after being defeated by ...
who was also from Soli appointed satrap of Aria
In music, an aria ( Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompa ...
and Drangiana.
The hope of full independence for Cyprus following the fall of the Persian Empire, however, was slow to be realized. The mints of Salamis, Kition and Paphos began to stamp coins on Alexander's behalf rather than in the name of the local kings.
The policy of Alexander the Great on Cyprus and its kings soon became clear: to free them from Persian rule but to put them under his own authority. Away from the coast of Cyprus, the interior kingdoms were left largely independent and the kings maintained their autonomy, although not in issues such as mining rights. Alexander sought to make clear that he considered himself the master of the island, and abolished the currencies of the Cypriot kingdoms, replacing them by the minting of his own coins.
Death of Alexander
The death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, while still in his early thirties, put an end to Greek aspirations for global domination. The empire he had created was divided between his generals and successors, who immediately started fighting one another. The death of Alexander the Great marks the beginning of the Hellenistic period of Cypriot history. After the death of Alexander the Great, Cyprus passed on to the Ptolemaic rule. Still under Greek influence, Cyprus gained full access to the Greek culture and thus became fully hellenised.Egypt and Syria
The wars of Alexander's successors inevitably began to involve Cyprus, and focused on two claimants,Antigonus Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( grc-gre, Ἀντίγονος Μονόφθαλμος , 'the One-Eyed'; 382 – 301 BC), son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian Greek nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he serve ...
in Syria (assisted by his son Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I (; grc, Δημήτριος; 337–283 BC), also called Poliorcetes (; el, Πολιορκητής, "The Besieger"), was a Macedonian nobleman, military leader, and king of Macedon (294–288 BC). He belonged to the Antigonid dynasty ...
) and Ptolemy Lagus
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedo ...
in Egypt.
The Cypriot kings who, so far, had managed largely to maintain their kingdoms' independence, found themselves in a new and difficult position. This was because, as Cyprus became the focus of discord between Ptolemy and Antigonus, the kings of the island now had to make new choices and alliances. Some Cypriot kingdoms chose alliance with Ptolemy, others sided with the Antigonus, yet others tried to remain neutral, leading to inevitable controversy and confrontation. The largest city and kingdom of Cyprus then appears to have been Salamis, whose king was Nicocreon. Nicocreon strongly supported Ptolemy. According to Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period.
''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ...
, he had the support of Pasikratis of Solon, Nikoklis of Paphos and Androcles of Amathus. Other kings of Cyprus, however, including Praxippos of Lapithos and Kyrenia, the Poumiaton (Pygmalion) of Kition and Stasioikos of Marion, allied themselves with Antigonus.
Against these, Nicocreon and other pro-Ptolemaic kings conducted military operations. Ptolemy sent military support to his allies, providing troops under the command of Seleucus and Menelaus. Lapithos-Kyrenia was occupied after a siege and Marion capitulated. Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
tells us that Amathus was forced to provide hostages, while Kition was laid siege to in about 315 BCE.
Ptolemy to Cyprus
Ptolemy entered Cyprus with further military forces in 312 BCE, captured and killed the king of Kition and arrested the pro-Antigonid kings of Marion and Lapithos-Kyrenia. He destroyed the city of Marion and annulled most of the former kingdoms of Cyprus. This crucial and decisive intervention by Ptolemy in 312 BCE gave more power to the kings of Solon and Paphos, and particularly to Nicocreon of Salamis, whom Ptolemy seems to have appreciated and trusted completelyand who won the cities and the wealth of expelled kings. Salamis extended its authority throughout eastern, central and northern Cyprus, since Kition and Lapithos were absorbed into it and Tamassos already belonged. Furthermore, Nicocreon of Salamis took office as chief general in Cyprus with the blessing of Ptolemy, effectively making him master of the whole island. But the situation was fluid and the rulers of Solon and Paphos had been kept in power. Soon, King Nikoklis of Paphos was considered suspect; he was besieged and forced to suicide, and his entire family put to death (312 BCE). The following year (311 BCE) Nicocreon of Salamis died.Demetrius
After the intervention of Ptolemy in Cyprus, which subjugated the island, Antigonus and his son Demetrius reacted against the besiegers and Demetrius led a large military operation in Cyprus. Demetrius was born in 336 BC and initially fought under the command of his father in 317 BCE against Eumenes, where he particularly distinguished himself. In 307 BCE he liberated Athens, restoring democracy there and in 306 BCE, led the war against the Ptolemies. Wishing to use Cyprus as a base for attacks against Western Asia, he sailed from Cilicia to Cyprus with a large infantry force, cavalry and naval ships. Meeting no resistance, he landed in theKarpasia peninsula
The Karpas Peninsula ( el, Καρπασία; tr, Karpaz), also known as the Karpass, Karpaz or Karpasia, is a long, finger-like peninsula that is one of the most prominent geographical features of the island of Cyprus. Its farthest extent is ...
and occupied the cities Urania and Karpasia. Meanwhile, Menelaus, brother of Ptolemy I Soter, the new general of the island, gathered his forces at Salamis. Ptolemy arrived to aid his brother, but was decisively defeated at the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
, after which Cyprus came under Antigonid control.
Demetrius's father Antigonus Monophthalmus was killed in the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his ...
in 301 BC and Demetrius, having reorganized the army, was proclaimed King of Macedon, but was evicted by Lysimachus and Pyrrhus. Cyprus came once again under Ptolemaic control in 294 BC and remained under Ptolemaic rule until 58 BC, when it became a Roman province. It was ruled by a series of governors sent from Egypt and sometimes formed a minor Ptolemaic kingdom during the power struggles of the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. During this time, Cyprus forged strong commercial relationships with Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
and Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, two of the most important commercial centres of antiquity.
Full Hellenisation of Cyprus took place under Ptolemaic rule. During this period, the Eteocypriot and Phoenician languages disappeared, together with the old Cypriot syllabic script, which was replaced by the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as ...
. A number of cities were founded during this time. For example, Arsinoe was founded between old and new Paphos
Paphos ( el, Πάφος ; tr, Baf) is a coastal city in southwest Cyprus and the capital of Paphos District. In classical antiquity, two locations were called Paphos: Old Paphos, today known as Kouklia, and New Paphos.
The current city of P ...
by Ptolemy II
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gold ...
. Ptolemaic rule was rigid and exploited the island's resources to the utmost, particularly timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
.
A great contemporary figure of Cypriot letters was the philosopher Zeno of Citium
Zeno of Citium (; grc-x-koine, Ζήνων ὁ Κιτιεύς, ; c. 334 – c. 262 BC) was a Hellenistic philosopher from Citium (, ), Cyprus. Zeno was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy, which he taught in Athens from about 300 B ...
who was born at Kition about 336 BCE and founded the famous Stoic School of Philosophy at Athens, where he died about 263 BCE.
Roman period
Cyprus became aRoman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
in 58 BCE. This came about, according to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, because Publius Clodius Pulcher held a grudge against Ptolemy of Cyprus
Ptolemy of Cyprus was the king of Cyprus c. 80-58 BC. He was the younger brother of Ptolemy XII Auletes, king of Egypt, and, like him, an illegitimate son of Ptolemy IX Lathyros. He was also the uncle of Cleopatra VII.
Reign over Cyprus
He appea ...
. The renowned Stoic and strict constitutionalist Cato the Younger
Marcus Porcius Cato "Uticensis" ("of Utica"; ; 95 BC – April 46 BC), also known as Cato the Younger ( la, Cato Minor), was an influential conservative Roman senator during the late Republic. His conservative principles were focused on the ...
was sent to annex Cyprus and organize it under Roman law. Cato was relentless in protecting Cyprus against the rapacious tax farmers that normally plagued the provinces of the Republican period. After the civil wars that ended the Roman Republic, Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
gave the island to Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
of Egypt and their daughter Cleopatra Selene, but it became a Roman province again after his defeat at the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ...
in 31 BCE. From 22 BCE onwards, Cyprus was a senatorial province
A senatorial province ( la, provincia populi Romani, province of the Roman people) was a Roman province during the Principate where the Roman Senate had the right to appoint the governor ( proconsul). These provinces were away from the outer ...
"divided into four districts centred around Paphus, Salamis, Amathus and Lapethus."Talbert, Richard J A (Ed), 1985. ''Atlas of Classical History''. Routledge. Roman Cyprus, pp 156–7. After the reforms of Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
it was placed under the Diocese of Oriens
The Diocese of the East ( la, Dioecesis Orientis; el, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of the majo ...
.
The ''Pax Romana
The Pax Romana (Latin for 'Roman peace') is a roughly 200-year-long timespan of Roman history which is identified as a period and as a golden age of increased as well as sustained Roman imperialism, relative peace and order, prosperous stabilit ...
'' (Roman peace) was only twice disturbed in Cyprus in three centuries of Roman occupation. The first serious interruption occurred in 115–16, when a revolt by Jews inspired by Messianic hopes broke out. Their leader was Artemion, a Jew with a Hellenised name, as was the practice of the time. The island suffered great losses in this war; it is believed that 240,000 Greek and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
civilians were killed. Although this number may be exaggerated, there were few or no Roman troops stationed on the island to suppress the insurrection as the rebels wreaked havoc. After forces were sent to Cyprus and the uprising was put down, a law was passed that no Jews were permitted to land on Cyprian soil, even in cases of shipwreck.
Turmoil sprang up two centuries later in 333–4, when a local official Calocaerus revolted against Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
. This rebellion ended with the arrival of troops led by Flavius Dalmatius and the death of Calocaerus.
Olive oil trade in the late Roman period
Olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: ...
was a very important part of daily life in the Mediterranean in the Roman Period. It was used for food, as a fuel for lamps, and as a basic ingredient in things like medicinal ointment, bath oils, skin oils, soaps, perfumes and cosmetics. Even before the Roman Period, Cyprus was known for its olive oil, as indicated by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
when he said that "in fertility Cyprus is not inferior to any one of the islands, for it produces both good wine and good oil".Papacostas, T., 2001, ''The Economy of Late Antique Cyprus.'' In: ''Economy and Exchange in the East Mediterranean during Late Antiquity''. Proceedings of a conference at Somerville College, Oxford, 29 May 1999, edited by S. Kingsley and M. Decker, 107–28. Oxford: Oxbow Books.
There is evidence for both a local trade of Cypriot oil and for a larger trading network that may have reached as far as the Aegean, although most Cypriot oil was probably limited to the Eastern Mediterranean. Many olive oil presses have been found on Cyprus, and not just in rural areas, where they might be expected for personal, local use. They have been found in some of the larger coastal cities as well, including Paphos, Curium and Amathus. In Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Egypt, there is a large presence of a type of amphora
An amphora (; grc, ἀμφορεύς, ''amphoreús''; English plural: amphorae or amphoras) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storag ...
made in Cyprus known as Late Roman 1 or LR1 that was used to carry oil. This indicates that a lot of Cypriot oil was being imported into Egypt. There is also evidence for Cypriot trade with Cilicia and Syria.
Olive oil was also traded locally, around the island. Amphorae found at Alaminos-Latourou Chiftlik and Dreamer's Bay, indicate that the oil produced in these areas was mostly used locally or shipped to nearby towns. The amphora found on a contemporary shipwreck at Cape Zevgari indicate that the vessel, a typical small merchant ship, was carrying oil and there is evidence from the location of the wreck and the ship itself that it was traveling only a short distance, probably west around the island.Leidwanger, J. 2007, ''Two Late Roman Wrecks from Southern Cyprus.'' IJNA 36: 308–16.
Christianity
Roman Cyprus was visited by the Apostles Paul,Barnabas
Barnabas (; arc, ܒܪܢܒܐ; grc, Βαρνάβας), born Joseph () or Joses (), was according to tradition an early Christian, one of the prominent Christian disciples in Jerusalem. According to Acts 4:36, Barnabas was a Cypriot Jew. Name ...
and St. Mark
Mark the Evangelist ( la, Marcus; grc-gre, Μᾶρκος, Mârkos; arc, ܡܪܩܘܣ, translit=Marqōs; Ge'ez: ማርቆስ; ), also known as Saint Mark, is the person who is traditionally ascribed to be the author of the Gospel of Mark. Accor ...
, who came to the island at the beginning of their first missionary journey in 45 AD, according to Christian tradition, converting the people of Cyprus to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
and founding the Church of Cyprus
The Church of Cyprus ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Κύπρου, translit=Ekklisia tis Kyprou; tr, Kıbrıs Kilisesi) is one of the autocephalous Greek Orthodox churches that together with other Eastern Orthodox churches form the communion ...
, After their arrival in Salamis, they proceeded to Paphos where they converted the Roman governor Sergius Paulus to Christ. In the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
book of Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its messag ...
, author St. Luke
Luke the Evangelist (Latin: '' Lucas''; grc, Λουκᾶς, '' Loukâs''; he, לוקאס, ''Lūqās''; arc, /ܠܘܩܐ לוקא, ''Lūqā’; Ge'ez: ሉቃስ'') is one of the Four Evangelists—the four traditionally ascribed authors of t ...
describes how a Jewish magician named Bar-Jesus (Elymas) was obstructing the Apostles in their preaching of the Gospel. Paul rebuked him, announcing that he would temporarily become blind due to God's judgment. Paul's prediction immediately came true. As a result of this, Sergius Paulus
Lucius Sergius Paulus or Paullus was a Proconsul of Cyprus under Claudius (1st century AD). He appears in Acts 13:6-12, where in Paphos, Paul, accompanied by Barnabas and John Mark, overcame the attempts of Bar-Jesus (Elymas) "to turn the pro ...
became a believer, being astonished at the teaching of the Lord. In this way, Cyprus became the first country in the world to be governed by a Christian ruler.
Paul is credited with underpinning claims for ecclesiastical independence from Antioch. At least three Cypriot bishops (the sees of Salamis, Tremithus, and Paphos) took part in the First Council of Nicaea in 325, and twelve Cypriot bishops were present at the Council of Sardica in 344. Early Cypriot Saints include: St. Heracleidius, St. Spiridon, St. Hilarion and St. Epiphanius.
Several earthquakes led to the destruction of Salamis at the beginning of the 4th century, at the same time drought and famine hit the island.
In 431 AD, the Church of Cyprus achieved its independence from the Patriarch of Antioch
Patriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the bishop of Antioch (modern-day Antakya, Turkey). As the traditional "overseer" (ἐπίσκοπος, ''episkopos'', from which the word ''bishop'' is derived) of the first gentile Christian c ...
at the First Council of Ephesus. Emperor Zeno
Zeno ( grc, Ζήνων) may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 BC), ...
granted the archbishop of Cyprus the right to carry a sceptre instead of a pastoral staff.
See also
*List of earthquakes in Cyprus
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
* Pottery of ancient Cyprus
* Ancient Cypriot art
Notes
Further reading
* Cobham, C D, 1908. ''Excerpta Cypria, materials for a history of Cyprus''. Cambridge. Includes the Classical Sources. * * Hunt, D, 1990. ''Footprints in Cyprus''. London, Trigraph. * Leidwanger, J, 2007, ''Two Late Roman Wrecks from Southern Cyprus.'' IJNA 36: pp 308–16. * Leonard, J. and Demesticha, S, 2004. ''Fundamental Links in the Economic Chain: Local Ports and International trade in Roman and Early Christian Cyprus.'' In: ''Transport Amphorae and Trade in the Eastern Mediterranean'', Acts of the International Colloquium at the Danish Institute at Athens, September 26–9, 2002, edited by J. Eiring and J. Lund, Aarhus, Aarhus University Press: pp 189–202. * Papacostas, T, 2001, ''The Economy of Late Antique Cyprus.'' In: ''Economy and Exchange in the East Mediterranean during Late Antiquity''. Proceedings of a conference at Somerville College, Oxford, 29 May 1999, edited by S. Kingsley and M. Decker, Oxford, Oxbow Books: pp 107–28. * Şevketoğlu, M. 2015, ”Akanthou- Arkosykos, a ninth Millenium BC coastal settlement in Cyprus” in Environmental Archaeology, Association for Environmental Archaeology * Tatton-Brown, Veronica, 1979. ''Cyprus BC, 7000 years of history''. London, British Museum Publications. * Tyree, E L, 1996. * Winbladh, M.-L., Cypriote Antiquities in the Medelhavsmuseet, Stockholm 1977. * Winbladh, M-L., 'Adventuring with Cyprus. A Chronicle of the Swedish Cyprus Expedition 1927 – 1931' in The Northern Face of Cyprus. New Studies in Cypriot Archaeology and Art History, eds. Hazar Kaba & Summerer, Latife, Istanbul 2016 * Winbladh, M.-L., Kıbrıs Macerası – The Cyprus Adventure – Περιπετεια στην Κυπρο (1927–1931), Galeri Kültür Kitabevi, Lefkoşa 2013 * Winbladh, M.-L., The Origins of The Cypriots. With Scientific Data of Archaeology and Genetics, Galeri Kultur Publishing, Lefkoşa 2020 * Winbladh, M.-L., Adventures of an archaeologist. Memoirs of a museum curator, AKAKIA Publications, London 2020 * Voskos, I. & Knapp A.B. 2008, ”Cyprus at the End of the Late Bronze Age: Crisis and Colonization or Continuity and Hybridization?” American Journal of Archaeology 112External links
Ancient History of Cyprus, by the Cypriot government
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient History of Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
Phoenician colonies