Analytic Hierarchy Process on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the theory of
In the theory of
SAP Experts
* Integrated evaluation of a community's sustanaibility in terms of environment, economy, society, institution, and culture. *
 As can be seen in the material that follows, using the AHP involves the mathematical synthesis of numerous judgments about the decision problem at hand. It is not uncommon for these judgments to number in the dozens or even the hundreds. While the math can be done by hand or with a calculator, it is far more common to use one of several computerized methods for entering and synthesizing the judgments. The simplest of these involve standard spreadsheet software, while the most complex use custom software, often augmented by special devices for acquiring the judgments of decision makers gathered in a meeting room.
The procedure for using the AHP can be summarized as:
#Model the problem as a hierarchy containing the decision goal, the alternatives for reaching it, and the criteria for evaluating the alternatives.
#Establish priorities among the elements of the hierarchy by making a series of judgments based on pairwise comparisons of the elements. For example, when comparing potential purchases of commercial real estate, the investors might say they prefer location over price and price over timing.
#Synthesize these judgments to yield a set of overall priorities for the hierarchy. This would combine the investors' judgments about location, price and timing for properties A, B, C, and D into overall priorities for each property.
#Check the consistency of the judgments.
#Come to a final decision based on the results of this process.
These steps are more fully described below.
As can be seen in the material that follows, using the AHP involves the mathematical synthesis of numerous judgments about the decision problem at hand. It is not uncommon for these judgments to number in the dozens or even the hundreds. While the math can be done by hand or with a calculator, it is far more common to use one of several computerized methods for entering and synthesizing the judgments. The simplest of these involve standard spreadsheet software, while the most complex use custom software, often augmented by special devices for acquiring the judgments of decision makers gathered in a meeting room.
The procedure for using the AHP can be summarized as:
#Model the problem as a hierarchy containing the decision goal, the alternatives for reaching it, and the criteria for evaluating the alternatives.
#Establish priorities among the elements of the hierarchy by making a series of judgments based on pairwise comparisons of the elements. For example, when comparing potential purchases of commercial real estate, the investors might say they prefer location over price and price over timing.
#Synthesize these judgments to yield a set of overall priorities for the hierarchy. This would combine the investors' judgments about location, price and timing for properties A, B, C, and D into overall priorities for each property.
#Check the consistency of the judgments.
#Come to a final decision based on the results of this process.
These steps are more fully described below.
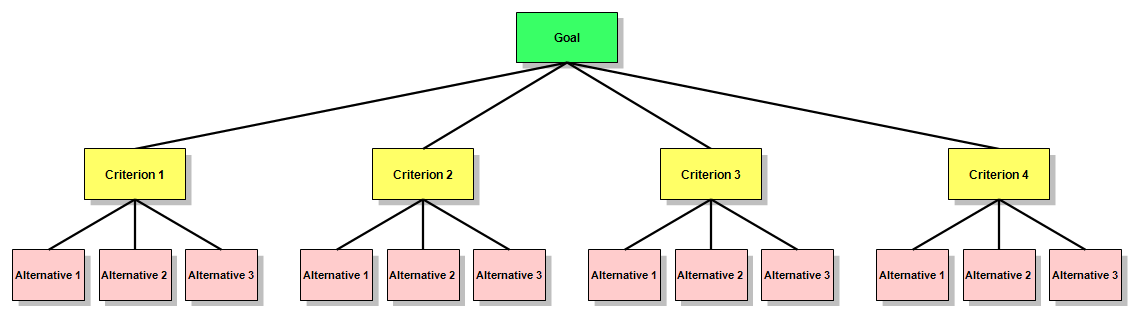 To reduce the size of the drawing required, it is common to represent AHP hierarchies as shown in the diagram below, with only one node for each alternative, and with multiple lines connecting the alternatives and the criteria that apply to them. To avoid clutter, these lines are sometimes omitted or reduced in number. Regardless of any such simplifications in the diagram, in the actual hierarchy each criterion is individually connected to the alternatives. The lines may be thought of as being directed downward from the parent in one level to its children in the level below.
To reduce the size of the drawing required, it is common to represent AHP hierarchies as shown in the diagram below, with only one node for each alternative, and with multiple lines connecting the alternatives and the criteria that apply to them. To avoid clutter, these lines are sometimes omitted or reduced in number. Regardless of any such simplifications in the diagram, in the actual hierarchy each criterion is individually connected to the alternatives. The lines may be thought of as being directed downward from the parent in one level to its children in the level below.

 Observe that the priorities on each level of the example—the goal, the criteria, and the alternatives—all add up to 1.000.
The priorities shown are those that exist before any information has been entered about weights of the criteria or alternatives, so the priorities within each level are all equal. They are called the hierarchy's default priorities. If a fifth Criterion were added to this hierarchy, the default priority for each Criterion would be .200. If there were only two Alternatives, each would have a default priority of .500.
Two additional concepts apply when a hierarchy has more than one level of criteria: local priorities and global priorities. Consider the hierarchy shown below, which has several Subcriteria under each Criterion.
Observe that the priorities on each level of the example—the goal, the criteria, and the alternatives—all add up to 1.000.
The priorities shown are those that exist before any information has been entered about weights of the criteria or alternatives, so the priorities within each level are all equal. They are called the hierarchy's default priorities. If a fifth Criterion were added to this hierarchy, the default priority for each Criterion would be .200. If there were only two Alternatives, each would have a default priority of .500.
Two additional concepts apply when a hierarchy has more than one level of criteria: local priorities and global priorities. Consider the hierarchy shown below, which has several Subcriteria under each Criterion.
 The local priorities, shown in gray, represent the relative weights of the nodes within a group of siblings with respect to their parent. The local priorities of each group of Criteria and their sibling Subcriteria add up to 1.000. The global priorities, shown in black, are obtained by multiplying the local priorities of the siblings by their parent's global priority. The global priorities for all the subcriteria in the level add up to 1.000.
The rule is this: Within a hierarchy, the global priorities of child nodes always add up to the global priority of their parent. Within a group of children, the local priorities add up to 1.000.
So far, we have looked only at default priorities. As the Analytical Hierarchy Process moves forward, the priorities will change from their default values as the decision makers input information about the importance of the various nodes. They do this by making a series of pairwise comparisons.
The local priorities, shown in gray, represent the relative weights of the nodes within a group of siblings with respect to their parent. The local priorities of each group of Criteria and their sibling Subcriteria add up to 1.000. The global priorities, shown in black, are obtained by multiplying the local priorities of the siblings by their parent's global priority. The global priorities for all the subcriteria in the level add up to 1.000.
The rule is this: Within a hierarchy, the global priorities of child nodes always add up to the global priority of their parent. Within a group of children, the local priorities add up to 1.000.
So far, we have looked only at default priorities. As the Analytical Hierarchy Process moves forward, the priorities will change from their default values as the decision makers input information about the importance of the various nodes. They do this by making a series of pairwise comparisons.
Über Preisverteilung bei Spielturnieren
''. ''Zeitschrift für Mathematik und Physik'', 63 band (1914), p. 192 that the principal right eigenvector method is not monotonic. This behaviour can also be demonstrated for reciprocal n x n matrices, where n > 3. Alternative approaches are discussed elsewhere.Zermelo, E. (1928).
Die Berechnung der Turnier-Ergebnisse als ein Maximumproblem der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung
', ''Mathematische Zeitschrift'' 29, 1929, S. 436–460 Salavati, A., Haghshenas, H., Ghadirifaraz, B., Laghaei, J., & Eftekhari, G. (2016). Applying AHP and Clustering Approaches for Public Transportation Decisionmaking: A Case Study of Isfahan City. Journal of Public Transportation, 19(4), 3.
''Analytic Hierarchy Process Tutorial''
(2012). Revoledu. *Kearns, Kevin P.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Analytical Planning: The Organization of Systems'' (1985). Oxford: Pergamon Press. . Republished 1991 by RWS, . *with Joyce Alexander. ''Conflict Resolution: The Analytic Hierarchy Process'' (1989). New York: Praeger. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Prediction, Projection and Forecasting: Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process in Economics, Finance, Politics, Games and Sports'' (1991). Boston: Kluwer Academic. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Decision Making in Economic, Social and Technological Environments'' (1994). Pittsburgh: RWS. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Models, Methods, Concepts & Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process'' (2001). Boston: Kluwer Academic. * Peniwati, Kirti; Vargas, Luis L. ''Group Decision Making: Drawing Out and Reconciling Differences'' (2007). Pittsburgh: RWS.
''International Journal of the Analytic Hierarchy Process''
An online journal about
easyAHP Online tool to make collaborative decisions using AHP
easyAHP is a free online tool to make decisions in a collaborative or individual way. easy AHP uses AHP methodology: Analytic hierarchy process.
AHP video. (9:17 YouTube clip)
Very thorough exposition of AHP by Dr. Klaus Göpel
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Example with Simulations using Matlab
– Waqqas Farooq – AHP example for college selection using matlab.
An illustrated guide (pdf)
– Dr. Oliver Meixner University of Wien – "Analytic Hierarchy Process", a very easy to understand summary of the mathematical theory
AHP example with Matlab implementation
– AHP explanation with an example and matlab code.
R ahp package
– An AHP open source package.
AHPy
- An open source Python implementation of AHP with an optimal solver for missing pairwise comparisons
Introductory Mathematics of the Analytic Hierarchy Process
– An introduction to the mathematics of the Analytic Hierarchy Process. {{commons category, Analytic Hierarchy Process
How to use AHP for Project Prioritization by Dr. James Brown (webinar)
Guide to use AHP in Excel
A guide to using AHP in Excel by Dr. Richard Hodgett
Use the AHP Methodology to More Effectively Define and Evaluate Your SAP Implementation Approach
by Jeetendra Kumar Group decision-making Multiple-criteria decision analysis Industrial engineering Project management techniques
 In the theory of
In the theory of decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
, the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), also analytical hierarchy process, is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisions, based on mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
and psychology
Psychology is the science, scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immens ...
. It was developed by Thomas L. Saaty
Thomas L. Saaty (July 18, 1926 – August 14, 2017) was a Distinguished University Professor at the University of Pittsburgh, where he taught in the Joseph M. Katz School of Business, Joseph M. Katz Graduate School of Business. He is the inventor, ...
in the 1970s; Saaty partnered with Ernest Forman to develop '' Expert Choice'' software in 1983, and AHP has been extensively studied and refined since then. It represents an accurate approach to quantifying the weights of decision criteria. Individual expert
An expert is somebody who has a broad and deep understanding and competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized as a reliable so ...
s’ experiences are utilized to estimate the relative magnitudes of factors through pair-wise comparisons. Each of the respondents compares the relative importance each pair of items using a specially designed questionnaire.
Uses and applications
AHP has particular application ingroup decision making Group decision-making (also known as collaborative decision-making or collective decision-making) is a situation faced when individuals collectively make a choice from the alternatives before them. The decision is then no longer attributable to any ...
, and is used around the world in a wide variety of decision situations, in fields such as government, business, industry, healthcare and education.
Rather than prescribing a "correct" decision, the AHP helps decision makers find one that best suits their goal and their understanding of the problem. It provides a comprehensive and rational framework for structuring a decision problem, for representing and quantifying its elements, for relating those elements to overall goals, and for evaluating alternative solutions.
Users of the AHP first decompose their decision problem into a hierarchy of more easily comprehended sub-problems, each of which can be analyzed independently. The elements of the hierarchy can relate to any aspect of the decision problem—tangible or intangible, carefully measured or roughly estimated, well or poorly understood—anything at all that applies to the decision at hand.
Once the hierarchy is built, the decision makers systematically evaluate its various elements by comparing them to each other two at a time, with respect to their impact on an element above them in the hierarchy. In making the comparisons, the decision makers can use concrete data about the elements, but they typically use their judgments about the elements' relative meaning and importance. It is the essence of the AHP that human judgments, and not just the underlying information, can be used in performing the evaluations.
The AHP converts these evaluations to numerical values that can be processed and compared over the entire range of the problem. A numerical weight or priority is derived for each element of the hierarchy, allowing diverse and often incommensurable elements to be compared to one another in a rational and consistent way. This capability distinguishes the AHP from other decision making techniques.
In the final step of the process, numerical priorities are calculated for each of the decision alternatives. These numbers represent the alternatives' relative ability to achieve the decision goal, so they allow a straightforward consideration of the various courses of action.
Several firms supply computer software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consist ...
to assist in using the process.
While it can be used by individuals working on straightforward decisions, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is most useful where teams of people are working on complex problems, especially those with high stakes, involving human perceptions and judgments, whose resolutions have long-term repercussions.
It has unique advantages when important elements of the decision are difficult to quantify or compare, or where communication among team members is impeded by their different specializations, terminologies, or perspectives.
Decision situations to which the AHP can be applied include:
* Choice – The selection of one alternative from a given set of alternatives, usually where there are multiple decision criteria involved.
* Ranking
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than" or "ranked equal to" the second.
In mathematics, this is known as a weak order or total preorder of o ...
– Putting a set of alternatives in order from most to least desirable.
* Prioritization – Determining the relative merit of members of a set of alternatives, as opposed to selecting a single one or merely ranking them
* Resource allocation
In economics, resource allocation is the assignment of available resources to various uses. In the context of an entire economy, resources can be allocated by various means, such as markets, or planning.
In project management, resource allocatio ...
– Apportioning resources among a set of alternatives
* Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Dimensions typically measured are quality, time and cost.
Benchmarking is used to measure performanc ...
– Comparing the processes in one's own organization with those of other best-of-breed organizations
* Quality management
Quality management ensures that an organization, product or service consistently functions well. It has four main components: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control and quality improvement. Quality management is focused not on ...
– Dealing with the multidimensional aspects of quality and quality improvement
* Conflict resolution
Conflict resolution is conceptualized as the methods and processes involved in facilitating the peaceful ending of conflict and retribution. Committed group members attempt to resolve group conflicts by actively communicating information abo ...
– Settling disputes between parties with apparently incompatible goals or positions
The applications of AHP to complex decision situations have numbered in the thousands, and have produced extensive results in problems involving planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. The evolution of forethought, the capacity to think ahead, is c ...
, resource allocation
In economics, resource allocation is the assignment of available resources to various uses. In the context of an entire economy, resources can be allocated by various means, such as markets, or planning.
In project management, resource allocatio ...
, priority setting, and selection among alternatives. Other areas have included forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual ...
, total quality management, business process reengineering
Business process re-engineering (BPR) is a business management strategy originally pioneered in the early 1990s, focusing on the analysis and design of workflows and business processes within an organization. BPR aims to help organizations fundam ...
, quality function deployment, and the balanced scorecard
A balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool – a well structured report, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from ...
. Many AHP applications are never reported to the world at large, because they take place at high levels of large organizations where security and privacy considerations prohibit their disclosure. But some uses of AHP are discussed in the literature. Recently these have included:
*Deciding how best to reduce the impact of global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
(''Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei'')
* Quantifying the overall quality of software system
A software system is a system of intercommunicating components based on software forming part of a computer system (a combination of hardware and software). It "consists of a number of separate programs, configuration files, which are used to se ...
s (''Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washingt ...
'')
*Selecting university faculty (''Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania
Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania (Bloomsburg, BU or Bloom) is a campus of Commonwealth University of Pennsylvania and it is located in Bloomsburg, Pennsylvania. It is part of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE). The ...
'')
*Deciding where to locate offshore manufacturing plants (''University of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
'')
*Assessing risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environm ...
in operating cross-country petroleum pipelines (''American Society of Civil Engineers
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
'')
*Deciding how best to manage U.S. watersheds ('' U.S. Department of Agriculture'')
*More Effectively Define and Evaluate SAP Implementation ApproachesSAP Experts
* Integrated evaluation of a community's sustanaibility in terms of environment, economy, society, institution, and culture. *
Accelerated Bridge Construction
Rapid bridge replacement or accelerated bridge construction (ABC) is a technique that allows bridges to be replaced with minimum disruption to traffic. The replacement bridge is constructed on a site near the bridge to be replaced. When it is comp ...
Decision Making Tool to assist in determining the viability of accelerated bridge construction (ABC) over traditional construction methods and in selecting appropriate construction and contracting strategies on a case-by-case basis.
AHP is sometimes used in designing highly specific procedures for particular situations, such as the rating of buildings by historical significance. It was recently applied to a project that uses video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) sy ...
footage to assess the condition of highways in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
. Highway engineers first used it to determine the optimum scope of the project
A project is any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular goal.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of even ...
, and then to justify its budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environme ...
to lawmaker
A legislator (also known as a deputy or lawmaker) is a person who writes and passes laws, especially someone who is a member of a legislature. Legislators are often elected by the people of the state. Legislatures may be supra-national (for e ...
s.
The weights of the AHP judgement matrix may be corrected with the ones calculated through the Entropy Method. This variant of the AHP method is called AHP-EM.
Education and scholarly research
Though using the analytic hierarchy process requires no specialized academic training, it is considered an important subject in many institutions of higher learning, including schools of engineering and graduate schools of business. It is a particularly important subject in the quality field, and is taught in many specialized courses including Six Sigma, Lean Six Sigma, and QFD. The value of the AHP is recognized in developed and developing countries around the world. China is an example—nearly a hundred Chinese universities offer courses in AHP, and manydoctoral
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism '' l ...
students choose AHP as the subject of their research and dissertations. Over 900 papers have been published on the subject in China, and there is at least one Chinese scholarly journal devoted exclusively to AHP.
The International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process (ISAHP) holds biennial meetings of academics and practitioners interested in the field. A wide range of topics is covered. Those in 2005 ranged from "Establishing Payment Standards for Surgical Specialists", to "Strategic Technology Roadmapping", to "Infrastructure Reconstruction in Devastated Countries".
At the 2007 meeting in Valparaíso, Chile, over 90 papers were presented from 19 countries, including the US, Germany, Japan, Chile, Malaysia, and Nepal. A similar number of papers were presented at the 2009 symposium in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, when 28 countries were represented. Subjects of the papers included ''Economic Stabilization in Latvia'', ''Portfolio Selection in the Banking Sector'', ''Wildfire Management to Help Mitigate Global Warming'', and ''Rural Microprojects in Nepal''.
Use
 As can be seen in the material that follows, using the AHP involves the mathematical synthesis of numerous judgments about the decision problem at hand. It is not uncommon for these judgments to number in the dozens or even the hundreds. While the math can be done by hand or with a calculator, it is far more common to use one of several computerized methods for entering and synthesizing the judgments. The simplest of these involve standard spreadsheet software, while the most complex use custom software, often augmented by special devices for acquiring the judgments of decision makers gathered in a meeting room.
The procedure for using the AHP can be summarized as:
#Model the problem as a hierarchy containing the decision goal, the alternatives for reaching it, and the criteria for evaluating the alternatives.
#Establish priorities among the elements of the hierarchy by making a series of judgments based on pairwise comparisons of the elements. For example, when comparing potential purchases of commercial real estate, the investors might say they prefer location over price and price over timing.
#Synthesize these judgments to yield a set of overall priorities for the hierarchy. This would combine the investors' judgments about location, price and timing for properties A, B, C, and D into overall priorities for each property.
#Check the consistency of the judgments.
#Come to a final decision based on the results of this process.
These steps are more fully described below.
As can be seen in the material that follows, using the AHP involves the mathematical synthesis of numerous judgments about the decision problem at hand. It is not uncommon for these judgments to number in the dozens or even the hundreds. While the math can be done by hand or with a calculator, it is far more common to use one of several computerized methods for entering and synthesizing the judgments. The simplest of these involve standard spreadsheet software, while the most complex use custom software, often augmented by special devices for acquiring the judgments of decision makers gathered in a meeting room.
The procedure for using the AHP can be summarized as:
#Model the problem as a hierarchy containing the decision goal, the alternatives for reaching it, and the criteria for evaluating the alternatives.
#Establish priorities among the elements of the hierarchy by making a series of judgments based on pairwise comparisons of the elements. For example, when comparing potential purchases of commercial real estate, the investors might say they prefer location over price and price over timing.
#Synthesize these judgments to yield a set of overall priorities for the hierarchy. This would combine the investors' judgments about location, price and timing for properties A, B, C, and D into overall priorities for each property.
#Check the consistency of the judgments.
#Come to a final decision based on the results of this process.
These steps are more fully described below.
Model the problem as a hierarchy
The first step in the analytic hierarchy process is to model the problem as a hierarchy. In doing this, participants explore the aspects of the problem at levels from general to detailed, then express it in the multileveled way that the AHP requires. As they work to build the hierarchy, they increase their understanding of the problem, of its context, and of each other's thoughts and feelings about both. (This book is the primary source for the sections in which it is cited.)Hierarchies defined
A hierarchy is a stratified system of ranking and organizing people, things, ideas, etc., where each element of the system, except for the top one, is subordinate to one or more other elements. Though the concept of hierarchy is easily grasped intuitively, it can also be described mathematically. Diagrams of hierarchies are often shaped roughly like pyramids, but other than having a single element at the top, there is nothing necessarily pyramid-shaped about a hierarchy. Human organizations are often structured as hierarchies, where the hierarchical system is used for assigning responsibilities, exercising leadership, and facilitating communication. Familiar hierarchies of "things" include a desktop computer's tower unit at the "top", with its subordinate monitor, keyboard, and mouse "below." In the world of ideas, we use hierarchies to help us acquire detailed knowledge of complex reality: we structure the reality into its constituent parts, and these in turn into their own constituent parts, proceeding down the hierarchy as many levels as we care to. At each step, we focus on understanding a single component of the whole, temporarily disregarding the other components at this and all other levels. As we go through this process, we increase our global understanding of whatever complex reality we are studying. Think of the hierarchy that medical students use while learning anatomy—they separately consider the musculoskeletal system (including parts and subparts like the hand and its constituent muscles and bones), the circulatory system (and its many levels and branches), the nervous system (and its numerous components and subsystems), etc., until they've covered all the systems and the important subdivisions of each. Advanced students continue the subdivision all the way to the level of the cell or molecule. In the end, the students understand the "big picture" and a considerable number of its details. Not only that, but they understand the relation of the individual parts to the whole. By working hierarchically, they've gained a comprehensive understanding of anatomy. Similarly, when we approach a complex decision problem, we can use a hierarchy to integrate large amounts of information into our understanding of the situation. As we build this information structure, we form a better and better picture of the problem as a whole.Hierarchies in the AHP
An AHP hierarchy is a structured means of modeling the decision at hand. It consists of an overall goal, a group of options or alternatives for reaching the goal, and a group of factors or criteria that relate the alternatives to the goal. The criteria can be further broken down into subcriteria, sub-subcriteria, and so on, in as many levels as the problem requires. A criterion may not apply uniformly, but may have graded differences like a little sweetness is enjoyable but too much sweetness can be harmful. In that case, the criterion is divided into subcriteria indicating different intensities of the criterion, like: little, medium, high and these intensities are prioritized through comparisons under the parent criterion, sweetness. Published descriptions of AHP applications often include diagrams and descriptions of their hierarchies; some simple ones are shown throughout this article. More complex AHP hierarchies have been collected and reprinted in at least one book. 496 pages, spiral bound. Each entry includes a description and diagram of an AHP model; the models are grouped in categories: educational, government/public policy, government public/strategy, health military, non-profit, personal, planning, political, etc. More complex hierarchies can be found on a special talk page for this article. The design of any AHP hierarchy will depend not only on the nature of the problem at hand, but also on the knowledge, judgments, values, opinions, needs, wants, etc. of the participants in the decision-making process. Constructing a hierarchy typically involves significant discussion, research, and discovery by those involved. Even after its initial construction, it can be changed to accommodate newly-thought-of criteria or criteria not originally considered to be important; alternatives can also be added, deleted, or changed. To better understand AHP hierarchies, consider a decision problem with a goal to be reached, three alternative ways of reaching the goal, and four criteria against which the alternatives need to be measured. Such a hierarchy can be visualized as a diagram like the one immediately below, with the goal at the top, the three alternatives at the bottom, and the four criteria in between. There are useful terms for describing the parts of such diagrams: Each box is called a node. A node that is connected to one or more nodes in a level below it is called a parent node. The nodes to which it is so connected are called its children. Applying these definitions to the diagram below, the goal is the parent of the four criteria, and the four criteria are children of the goal. Each criterion is a parent of the three Alternatives. Note that there are only three Alternatives, but in the diagram, each of them is repeated under each of its parents. To reduce the size of the drawing required, it is common to represent AHP hierarchies as shown in the diagram below, with only one node for each alternative, and with multiple lines connecting the alternatives and the criteria that apply to them. To avoid clutter, these lines are sometimes omitted or reduced in number. Regardless of any such simplifications in the diagram, in the actual hierarchy each criterion is individually connected to the alternatives. The lines may be thought of as being directed downward from the parent in one level to its children in the level below.
To reduce the size of the drawing required, it is common to represent AHP hierarchies as shown in the diagram below, with only one node for each alternative, and with multiple lines connecting the alternatives and the criteria that apply to them. To avoid clutter, these lines are sometimes omitted or reduced in number. Regardless of any such simplifications in the diagram, in the actual hierarchy each criterion is individually connected to the alternatives. The lines may be thought of as being directed downward from the parent in one level to its children in the level below.

Evaluate the hierarchy
Once the hierarchy has been constructed, the participants analyze it through a series of pairwise comparisons that derive numerical scales of measurement for the nodes. The criteria are pairwise compared against the goal for importance. The alternatives are pairwise compared against each of the criteria for preference. The comparisons are processed mathematically, and priorities are derived for each node. Consider the "Choose a Leader" example above. An important task of the decision makers is to determine the weight to be given each criterion in making the choice of a leader. Another important task is to determine the weight to be given to each candidate with regard to each of the criteria. The AHP not only lets them do that, but it lets them put a meaningful and objective numerical value on each of the four criteria. Unlike most surveys which adopt the five pointLikert scale
A Likert scale ( , commonly mispronounced as ) is a psychometric scale commonly involved in research that employs questionnaires. It is the most widely used approach to scaling responses in survey research, such that the term (or more fully the ...
, AHP's questionnaire is 9 to 1 to 9.
Establish priorities
This section explains priorities, shows how they are established, and provides a simple example.Priorities defined and explained
Priorities are numbers associated with the nodes of an AHP hierarchy. They represent the relative weights of the nodes in any group. Like probabilities, priorities are absolute numbers between zero and one, without units or dimensions. A node with priority .200 has twice the weight in reaching the goal as one with priority .100, ten times the weight of one with priority .020, and so forth. Depending on the problem at hand, "weight" can refer to importance, or preference, or likelihood, or whatever factor is being considered by the decision makers. Priorities are distributed over a hierarchy according to its architecture, and their values depend on the information entered by users of the process. Priorities of the Goal, the Criteria, and the Alternatives are intimately related, but need to be considered separately. By definition, the priority of the Goal is 1.000. The priorities of the alternatives always add up to 1.000. Things can become complicated with multiple levels of Criteria, but if there is only one level, their priorities also add to 1.000. All this is illustrated by the priorities in the example below. Observe that the priorities on each level of the example—the goal, the criteria, and the alternatives—all add up to 1.000.
The priorities shown are those that exist before any information has been entered about weights of the criteria or alternatives, so the priorities within each level are all equal. They are called the hierarchy's default priorities. If a fifth Criterion were added to this hierarchy, the default priority for each Criterion would be .200. If there were only two Alternatives, each would have a default priority of .500.
Two additional concepts apply when a hierarchy has more than one level of criteria: local priorities and global priorities. Consider the hierarchy shown below, which has several Subcriteria under each Criterion.
Observe that the priorities on each level of the example—the goal, the criteria, and the alternatives—all add up to 1.000.
The priorities shown are those that exist before any information has been entered about weights of the criteria or alternatives, so the priorities within each level are all equal. They are called the hierarchy's default priorities. If a fifth Criterion were added to this hierarchy, the default priority for each Criterion would be .200. If there were only two Alternatives, each would have a default priority of .500.
Two additional concepts apply when a hierarchy has more than one level of criteria: local priorities and global priorities. Consider the hierarchy shown below, which has several Subcriteria under each Criterion.
 The local priorities, shown in gray, represent the relative weights of the nodes within a group of siblings with respect to their parent. The local priorities of each group of Criteria and their sibling Subcriteria add up to 1.000. The global priorities, shown in black, are obtained by multiplying the local priorities of the siblings by their parent's global priority. The global priorities for all the subcriteria in the level add up to 1.000.
The rule is this: Within a hierarchy, the global priorities of child nodes always add up to the global priority of their parent. Within a group of children, the local priorities add up to 1.000.
So far, we have looked only at default priorities. As the Analytical Hierarchy Process moves forward, the priorities will change from their default values as the decision makers input information about the importance of the various nodes. They do this by making a series of pairwise comparisons.
The local priorities, shown in gray, represent the relative weights of the nodes within a group of siblings with respect to their parent. The local priorities of each group of Criteria and their sibling Subcriteria add up to 1.000. The global priorities, shown in black, are obtained by multiplying the local priorities of the siblings by their parent's global priority. The global priorities for all the subcriteria in the level add up to 1.000.
The rule is this: Within a hierarchy, the global priorities of child nodes always add up to the global priority of their parent. Within a group of children, the local priorities add up to 1.000.
So far, we have looked only at default priorities. As the Analytical Hierarchy Process moves forward, the priorities will change from their default values as the decision makers input information about the importance of the various nodes. They do this by making a series of pairwise comparisons.
Practical examples
Experienced practitioners know that the best way to understand the AHP is to work through cases and examples. Two detailedcase studies
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular f ...
, specifically designed as in-depth teaching examples, are provided as appendices to this article:
* Simple step-by-step example with four Criteria and three Alternatives: Choosing a leader for an organization.
* More complex step-by-step example with ten Criteria/Subcriteria and six Alternatives: Buying a family car and Machinery Selection Example.
Some of the books on AHP contain practical examples of its use, though they are not typically intended to be step-by-step learning aids. One of them contains a handful of expanded examples, plus about 400 AHP hierarchies briefly described and illustrated with figures. Many examples are discussed, mostly for professional audiences, in papers published by the International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process.
Criticisms
The AHP is included in mostoperations research
Operations research ( en-GB, operational research) (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a discipline that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve decis ...
and management science textbooks, and is taught in numerous universities; it is used extensively in organizations that have carefully investigated its theoretical underpinnings. While the general consensus is that it is both technically valid and practically useful, the method does have its critics.
In the early 1990s a series of debates between critics and proponents of AHP was published in ''Management Science'' and ''The Journal of the Operational Research Society,'' two prestigious journals where Saaty and his colleagues had considerable influence. These debates seem to have been settled in favor of AHP:
*An in-depth paper discussing and rebutting the academic criticisms of AHP was published in ''Operations Research'' in 2001.
*A 2008 ''Management Science'' paper reviewing 15 years of progress in all areas of Multicriteria Decision Making showed that AHP publications have far outnumbered those in any other area, characterizing their growth as "enormous."
*Also in 2008, the major society for operations research, the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences formally recognized AHP's broad impact on its fields.
Occasional criticisms still appear. A 1997 paper examined possible flaws in the verbal (vs. numerical) scale often used in AHP pairwise comparisons. Another from the same year claimed that innocuous changes to the AHP model can introduce order where no order exists. A 2006 paper found that the addition of criteria for which all alternatives perform equally can alter the priorities of alternatives.
In 2021, the first comprehensive evaluation of the AHP was published in a book authored by two academics from Technical University of Valencia
The Technical University of Valencia ( ca-valencia, Universitat Politècnica de València, UPV; , es, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia) is a Spanish university located in Valencia, with a focus on science, technology, and arts. It was founded ...
and Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena, and published by Springer Nature
Springer Nature or the Springer Nature Group is a German-British academic publishing company created by the May 2015 merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and M ...
. Based on an empirical investigation and objective testimonies by 101 researchers, the study found at least 30 flaws in the AHP and found it unsuitable for complex problems, and in certain situations even for small problems.
Rank reversal
Decision making involves ranking alternatives in terms of criteria or attributes of those alternatives. It is an axiom of some decision theories that when new alternatives are added to a decision problem, the ranking of the old alternatives must not change — that " rank reversal" must not occur. There are two schools of thought about rank reversal. One maintains that new alternatives that introduce no additional attributes should not cause rank reversal under any circumstances. The other maintains that there are some situations in which rank reversal can reasonably be expected. The original formulation of AHP allowed rank reversals. In 1993, Forman introduced a second AHP synthesis mode, called the ideal synthesis mode, to address choice situations in which the addition or removal of an 'irrelevant' alternative should not and will not cause a change in the ranks of existing alternatives. The current version of the AHP can accommodate both these schools—its ideal mode preserves rank, while its distributive mode allows the ranks to change. Either mode is selected according to the problem at hand. Rank reversal and AHP are extensively discussed in a 2001 paper in ''Operations Research'', as well as a chapter entitled ''Rank Preservation and Reversal'', in the current basic book on AHP. The latter presents published examples of rank reversal due to adding copies and near copies of an alternative, due to intransitivity of decision rules, due to adding phantom and decoy alternatives, and due to the switching phenomenon in utility functions. It also discusses the Distributive and Ideal Modes of AHP. A new form of rank reversal of AHP was found in 2014 in which AHP produces rank order reversal when eliminating irrelevant data, this is data that do not differentiate alternatives. There are different types of rank reversals. Also, other methods besides the AHP may exhibit such rank reversals. More discussion on rank reversals with the AHP and other MCDM methods is provided in therank reversals in decision-making
In decision-making, a rank reversal is a change in the rank ordering of the preferability of alternative possible decisions when, for example, the method of choosing changes or the set of other available alternatives changes. The issue of rank re ...
page.
Non-monotonicity of some weight extraction methods
Within a comparison matrix one may replace a judgement with a less favorable judgment and then check to see if the indication of the new priority becomes less favorable than the original priority. In the context of tournament matrices, it has been proven byOskar Perron
Oskar Perron (7 May 1880 – 22 February 1975) was a German mathematician.
He was a professor at the University of Heidelberg from 1914 to 1922 and at the University of Munich from 1922 to 1951. He made numerous contributions to differential ...
Landau, E. (1914). Über Preisverteilung bei Spielturnieren
''. ''Zeitschrift für Mathematik und Physik'', 63 band (1914), p. 192 that the principal right eigenvector method is not monotonic. This behaviour can also be demonstrated for reciprocal n x n matrices, where n > 3. Alternative approaches are discussed elsewhere.Zermelo, E. (1928).
Die Berechnung der Turnier-Ergebnisse als ein Maximumproblem der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung
', ''Mathematische Zeitschrift'' 29, 1929, S. 436–460 Salavati, A., Haghshenas, H., Ghadirifaraz, B., Laghaei, J., & Eftekhari, G. (2016). Applying AHP and Clustering Approaches for Public Transportation Decisionmaking: A Case Study of Isfahan City. Journal of Public Transportation, 19(4), 3.
See also
* Analytic hierarchy process – car example * Analytic hierarchy process – leader example * Analytic network process *Arrow's impossibility theorem
Arrow's impossibility theorem, the general possibility theorem or Arrow's paradox is an impossibility theorem in social choice theory that states that when voters have three or more distinct alternatives (options), no ranked voting electoral syst ...
* Decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
* Decision-making paradox
* Decision-making software Decision-making software (DM software) is software for computer applications that help individuals and organisations make choices and take decisions, typically by ranking, prioritizing or choosing from a number of options.
An early example of DM s ...
* Hierarchical decision process
* L. L. Thurstone
* Law of comparative judgment
* Multi-criteria decision analysis
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings ...
* Pairwise comparison
Pairwise comparison generally is any process of comparing entities in pairs to judge which of each entity is preferred, or has a greater amount of some quantitative property, or whether or not the two entities are identical. The method of pairwi ...
* Preference
In psychology, economics and philosophy, preference is a technical term usually used in relation to choosing between alternatives. For example, someone prefers A over B if they would rather choose A than B. Preferences are central to decision th ...
* Principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and ...
* Rank reversals in decision-making
In decision-making, a rank reversal is a change in the rank ordering of the preferability of alternative possible decisions when, for example, the method of choosing changes or the set of other available alternatives changes. The issue of rank re ...
References
Further reading
*Saaty, Thomas L. ''Decision Making for Leaders: The Analytical Hierarchy Process for Decisions in a Complex World'' (1982). Belmont, California: Wadsworth. ; Paperback, Pittsburgh: RWS. . ''"Focuses on practical application of the AHP; briefly covers theory."'' *Saaty, Thomas L. ''Fundamentals of Decision Making and Priority Theory with the Analytic Hierarchy Process'' (1994). Pittsburgh: RWS. . ''"A thorough exposition of the theoretical aspects of AHP."'' *Saaty, Thomas L. ''Mathematical Principles of Decision Making (Principia Mathematica Decernendi)'' (2009). Pittsburgh: RWS. . ''"Comprehensive coverage of the AHP, its successor the ANP, and further developments of their underlying concepts."'' *Saaty, Thomas L., with Ernest H. Forman. ''The Hierarchon: A Dictionary of Hierarchies''. (1992) Pittsburgh: RWS. . ''"Dozens of illustrations and examples of AHP hierarchies. A beginning classification of ideas relating to planning, conflict resolution, and decision making."'' *Saaty, Thomas L., with Luis G. Vargas ''The Logic of Priorities: Applications in Business, Energy, Health, and Transportation'' (1982). Boston: Kluwer-Nijhoff. (Hardcover) (Paperback). Republished 1991 by RWS, . * Kardi Teknomo''Analytic Hierarchy Process Tutorial''
(2012). Revoledu. *Kearns, Kevin P.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Analytical Planning: The Organization of Systems'' (1985). Oxford: Pergamon Press. . Republished 1991 by RWS, . *with Joyce Alexander. ''Conflict Resolution: The Analytic Hierarchy Process'' (1989). New York: Praeger. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Prediction, Projection and Forecasting: Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process in Economics, Finance, Politics, Games and Sports'' (1991). Boston: Kluwer Academic. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Decision Making in Economic, Social and Technological Environments'' (1994). Pittsburgh: RWS. *Vargas, Luis L.; Saaty, Thomas L. ''Models, Methods, Concepts & Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process'' (2001). Boston: Kluwer Academic. * Peniwati, Kirti; Vargas, Luis L. ''Group Decision Making: Drawing Out and Reconciling Differences'' (2007). Pittsburgh: RWS.
External links
''International Journal of the Analytic Hierarchy Process''
An online journal about
multi-criteria decision making
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings s ...
using the AHP.
easyAHP Online tool to make collaborative decisions using AHP
easyAHP is a free online tool to make decisions in a collaborative or individual way. easy AHP uses AHP methodology: Analytic hierarchy process.
AHP video. (9:17 YouTube clip)
Very thorough exposition of AHP by Dr. Klaus Göpel
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Example with Simulations using Matlab
– Waqqas Farooq – AHP example for college selection using matlab.
An illustrated guide (pdf)
– Dr. Oliver Meixner University of Wien – "Analytic Hierarchy Process", a very easy to understand summary of the mathematical theory
AHP example with Matlab implementation
– AHP explanation with an example and matlab code.
R ahp package
– An AHP open source package.
AHPy
- An open source Python implementation of AHP with an optimal solver for missing pairwise comparisons
Introductory Mathematics of the Analytic Hierarchy Process
– An introduction to the mathematics of the Analytic Hierarchy Process. {{commons category, Analytic Hierarchy Process
How to use AHP for Project Prioritization by Dr. James Brown (webinar)
Guide to use AHP in Excel
A guide to using AHP in Excel by Dr. Richard Hodgett
Use the AHP Methodology to More Effectively Define and Evaluate Your SAP Implementation Approach
by Jeetendra Kumar Group decision-making Multiple-criteria decision analysis Industrial engineering Project management techniques